Abstract
This work reports the development and optimization of a rapid and low-cost pen-on-paper plotting approach for the fabrication of paper-based analytical devices (PADs) using commercial writing stationery. The desired fluidic patterns were drawn on the paper substrate with commercial marker pens using an inexpensive computer-controlled x–y plotter. For the fabrication of electrochemical PADs, electrodes were further deposited on the devices using a second x–y plotting step with commercial writing pencils. The effect of the fabrication parameters (type of paper, type of marker pen, type of pencil, plotting speed, number of passes, single- vs. double-sided plotting), the chemical resistance of the plotted devices to different solvents and the structural rigidity to multiple loading cycles were assessed. The analytical utility of these devices is demonstrated through application in optical sensing of total phenols using reflectance calorimetry and in electrochemical sensing of paracetamol and ascorbic acid. The proposed manufacturing approach is simple, low cost, flexible, rapid and fit-for-purpose and enables the fabrication of sub-“one-dollar” PADs with satisfactory mechanical and chemical resistance and good analytical performance.
1. Introduction
Although the use of paper as a platform to perform chemical assays has a long history [1,2,3,4], the birth of the modern field of paper-based analytical devices (PADs) was marked by the pioneering work by the Whitesides’ group [5] and the concept was further extended in recent years with the introduction of 3D and folding PADs incorporating additional and promising functionalities for sample manipulation, transport and detection [6,7].
The key features of paper as a substrate for the fabrication of PADs are [1,8]: (a) flexibility, which enables the formation of complex and conformable 2D and 3D structures that are not subject to tearing upon bending; (b) low thickness (typically tens or hundreds of micrometers), resulting in low (in the microliter or sub-microliter range) sample/regent volume required for analysis; (c) absorbency, which allows storage and delivery of an exact volume of samples/reagents inside the paper matrix and enrichment of the sample via multiple addition/drying steps; (d) lightness (typically around 10 mg/cm2), which enhances the scope for portability; (e) high surface-to-volume ratio, enabling the more efficient immobilization of reagents, enzymes or biomolecular probes; (f) hydrophilicity and capillary action, i.e., the ability of paper to wick fluids and allow solution movement through capillary forces dispenses with the use of pumps and permits multidirectional fluid flow in all directions; (g) chemical and biological inertness, enabling compatibility with biological samples; (h) disposability and biodegradability, since cellulose is rapidly degraded by microorganisms (~50 days) without toxic by-products and can be easily disposed of by incineration, eliminating the problem of contamination with biological material; (i) low cost and wide worldwide availability, which reduces the overall cost of the analysis.
As a result of recent advances in the field of PADs, a host of devices have been developed for application in various fields such as clinical diagnostics and point-of-care testing, environmental monitoring and food quality control [9,10,11]. The patterning of the hydrophobic barriers is a critical step in the fabrication of PADs and several approaches have been proposed in the literature; the relative advantages and drawbacks of these methods have been summarized in many relevant reviews [8,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Among them, pen-on-paper (PoP) strategies involve the use of a writing tool (i.e., suitable pen, crayon, pencil or marker) to deposit functional materials on paper substrates with the view to create either hydrophobic patterns or conductive areas (electrodes) [15]. PoP is considered as a promising do-it-yourself approach towards the fabrication of “one-dollar PADs” [16,18].
In order to create hydrophobic patterns on paper, several materials and PoP methodologies have been applied: commercial wax pencils or crayons [19,20,21]; a heated pen to dispense molten wax [22]; commercial acrylate-based plastic [23]; typo correction pens [24,25]; and 3D pens [26]. The disadvantages of these methods are the limited spatial resolution achieved and the need for post-fabrication treatment (by heating or UV irradiation). On the other hand, home-made pens or empty cartridges of commercial pens filled with various hydrophobic materials prepared in-house have been reported for the creation of hydrophobic patterns, including: trichloro perfluoroalkylsilane [27]; nail polish [28]; water-based alkyl ketene dimer [29,30]; modified commercial permanent ink [31]; and solubilized poly(methyl methacrylate) [32]. However, all these methods require a lengthy preparation step, careful optimization of the composition of the functional material to be used and heating (after the fabrication of the PADs) to eliminate residual solvents. Another promising alternative PoP strategy is the use of commercial permanent marker pens. These pens are based on permanent inks (consisting of a hydrophobic resin, a solvent and a colorant) of varying hydrophobicity; their advantages are that their composition is constant and they are low cost and widely available with different tip sizes, offer reasonable resolution and require no pre- or post-fabrication treatment. Initial PoP applications using marker pens involved hand drawing of the desired patterns using a template [33]. More recently, inexpensive computer-controlled x–y plotters were introduced that enable large-scale PoP fabrication of PADs and better device-to-device reproducibility [34,35,36]. Regarding the formation of electrodes on PADs, two main PoP fabrication routes exist. The first is based on commercial or conductive inks formulated in-house and deposited on paper via ball-point or drawing pens [22,37,38,39,40] while the second method utilizes deposition via abrasion with commercial or home-made writing pencils [34,41,42,43,44,45].
Although the use of marker pens and writing pencils has been reported before for the fabrication of PADs [31,32,33,34], surprisingly, no comparative studies exist on the type of paper, the type of writing tool and the associated operational characteristics of the resulting devices (such as their chemical resistance). Therefore, the aim of this work was the development and optimization of a high-troughput and fast PoP method for the fabrication of functional fully drawn PADs and electrochemical PADs using exclusively mechanical plotting with commercial writing stationery. In this context, a systematic study of the type of paper, writing tools and plotting conditions was undertaken to gain more insight into the fabrication procedure. In addition, the chemical resistance to common solvents and the mechanical rigidity of the PADs to multiple loading cycles were evaluated. Finally, applicability of the fully PoP-drawn PADs was demonstrated for optical and electrochemical detection. Compared to the most popular PAD fabrication methods (wax printing, inkjet printing and lithography), the proposed PoP approach exhibits the following advantages: it does not require pre- or post-fabrication treatment (heating or curing), thereby simplifying and speeding up the manufacturing process; it utilizes lower cost and commercially available writing stationary; it offers greater flexibility since the drawing process can be readily fine-tuned (in terms of single- or double-sided plotting, number of passes and plotting speed); and, more significantly, it enables the fabrication of both fluidic patterns and electrodes with the same equipment in a sequential dual-step mode by merely exchanging writing tools [15,16,18].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
All the chemicals were of analytical grade and purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). De-ionized water was used throughout.
Aqueous methylene blue solutions (100 mg L−1 and 10 mg L−1) were used for the hydrophobicity tests and the chemical resistance tests.
The types of papers and marker pens used for the fabrication of PADs are listed in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. Faber-Castell grade 3B, 5B and 7B pencils were used to draw the electrodes.

Table 1.
Types of papers, specifications and longitudinal migration properties. Specifications are reported as stated by the manufacturers (https://www.mn-net.com/media/pdf/cb/85/77/Catalog-Filtration-EN.pdf; https://d1lqgfmy9cwjff.cloudfront.net/csi/pdf/e/mk01.pdf; https://beta-static.fishersci.com/content/dam/fishersci/en_US/documents/programs/scientific/brochures-and-catalogs/brochures/ge-healthcare-whatman-filtration-products-brochure.pdf) (accessed on 12 July 2021).

Table 2.
Types of marker pens and their performance in terms of channel isolation properties (2 passes were applied to all the pens; plotting speed 2.7 cm s−1).
2.2. Instrumentation and Signal Evaluation
Fluidic patterns with the desired shape were drawn using the open-access software Inkscape version 1.0.1 (Inkscape Project, https://inkscape.org/about/ (accessed on 12 July 2021)). The AxiDraw extension for Inkscape was used for controlling an AxiDraw desktop x–y plotter (Evil Mad Science LLC, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) connected to a PC via a USB interface.
Images of the drawing lines and cross-sections obtained with the different markers were captured by a Carl Zeiss AXIO microscope (Oberkochen, Germany) connected to a DSC-S75 Sony digital camera. Processing of the images and measurement of line thickness was performed with the open-source Dscaler software and the Microsoft Photo Editor application.
Optical detection on the PADs was based on reflectance colorimetry. The PADs were scanned with a Deskjet F380 printer (Hewlett Packard, Palo Alto, CA, USA) using the HP Solution Center and the “Scan with corrected tones” option. Further processing of the digital images to convert the color intensity of the selected colored area to grayscale was performed with InkScape 1.0.1.
The contact angle measurements were performed with a GBX Model DGD-DS contact angle meter (Digidrop, Dublin, Ireland).
For electrochemical measurements, a Palmsens potentiostat, controlled by the PSTrace 5.5 software, was used (Palmsens, Houten, the Netherlands). All electrochemical data evaluation was performed with the PSTrace 5.5 software.
2.3. Fabrication of PADs
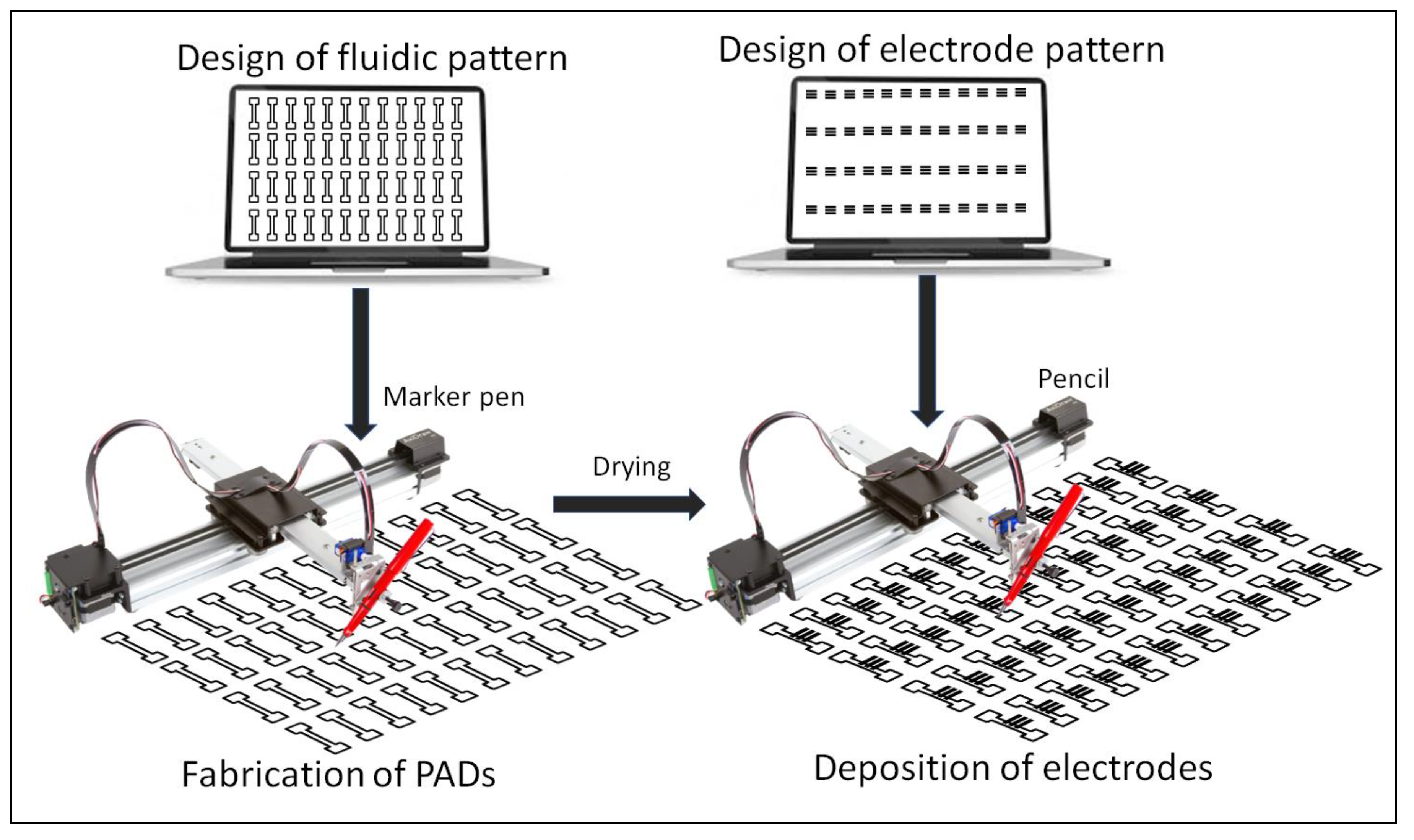
The procedure for the fabrication of PADs is schematicaly illustrated in Figure 1. The selected paper was positioned onto a flat glass surface and the selected marker pen was inserted into the holder of the plotter. Several PADs were patterned on the paper and left at room temperature for 5 min to allow the solvent to evaporate. For double-sided plotting, the pattern was repeated on the reverse side of the paper after aligning the paper with the aid of pre-set alignment marks drawn of the glass surface. In the case of electrochemical PADs, the marker pen was removed from the holder of the plotter and replaced with a writing pencil which was used to deposit the graphite electrodes. The electrode pattern was aligned with the fluidic pattern with the aid of pre-set alignment marks drawn of the glass surface. Finally, the paper was cut using scissors to obtain the individual PADs which were carefully handled using tweezers. The plotting conditions are described in the text. The nominal dimensions of the fluidic PADs designed and fabricated in this work are shown in Figure S1 (Supplementary Material). The cost of each PAD (in terms of materials) is less than USD 0.05.
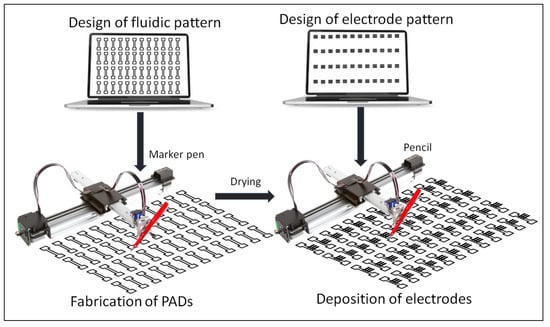
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the fabrication of the fluidic PADs used in this work.
2.4. Optical and Electrochemical Detection
The total phenolic content was determined by the Folin–Ciocalteu approach using gallic acid as a standard. White wine samples were diluted 1:1 with de-ionized water. The PADs were positioned horizontally and 5 μL of a 2.0 mol L−1 of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent was applied onto the center of the test zone. Then, a 10 μL aliquot of gallic acid standard (in the concentration range 0–3 mmol L−1 prepared in an aqueous solution containing 6% (v/v) ethanol) was placed at the center of the test zone. Finally, 10 μL of a 20.0% (w/v) Na2CO3 solution was applied to the center of the test zone (circular PADs) or the sample zone (fluidic PADs). The Na2CO3 solution spread radially within the test zone (circular PADs) or migrated to the test zone (fluidic PADs) to initiate the colorimetric reaction which produced a dark blue/gray color; the PADs were left for 15 min to allow the reaction to complete and then scanned. For comparison, a standard Folin–Ciocalteu method was employed [46].
Cyclic voltammograms (CVs) of the ferrocyanide/ferricyanide redox couple in the fluidic PADs were obtained by positioning them horizonatally and placing a deoxygenated 40 μL aliquot of a 0.002 mol L−1 potassium ferrocyanide/0.002 mol L−1 potassium ferricyanide solution in 0.01 mol L−1 KCl in the sample zone. The solution was allowed to reach the test zone and the CV was recorded with respect to the pseudo-reference graphite electrode at a scan rate of 10 mV s−1.
A gin sample was spiked with different concentrations of paracetamol and diluted 1:1 with 0.2 mol L−1 H2SO4. An orange juice sample was spiked with different concentrations of ascorbic acid, filtered and diluted 1:10 with 1 mol L−1 phosphate buffer (pH 7). For differential pulse (DP) voltammetry, the fluidic PADs were positioned horizontally, and a 40 μL aliquot of the sample was placed in the sample zone. The sample was allowed to reach the test zone and the DP voltammogram was recorded with respect to the pseudo-reference graphite electrode at a scan rate of 10 mV s−1 with pulse height 25 mV and pulse width 20 ms.
For all the electrochemical measurements, two conditioning measurements were carried out (that were discarded) followed by three analytical measurements (that were stored).
3. Results
3.1. Investigation of Type of Paper
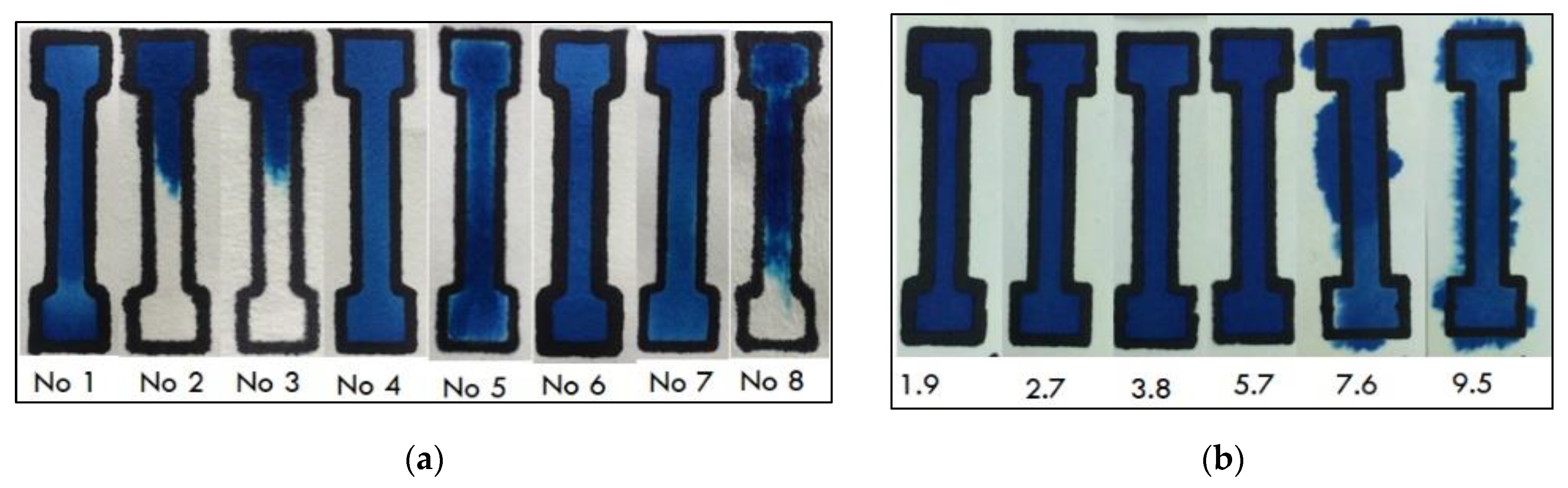
Thus far, comparative data of different paper substrates in conjunction with the PoP formation of PADs are very scarce (typically, Whatman grade 1 filter or chromatographic paper is used by default). In this context, the type of paper is critical since it affects the way the solution moves through the cellulose matrix. In this work, eight types of papers were investigated including six types of filter paper (papers No 1–4, No 6 and No 8), differing in their nominal filtration speeds, and two types of chromatographic paper (papers No 5 and No 7); the different papers used and their specifications are listed in Table 1. The solution migration properties were investigated by fabricating fluidic PADs by single-sided plotting with a BIC Marking Pro ultra-resistant permanent marker (pen No 17 in Table 2) with two passes at 2.7 cm−1, placing the PADs at a horizontal position, applying 100 μL of an aqueous solution of methylene blue to the sample zone of the fluidic device and observing the device after the solution flow stopped; photos of the devices using the eight types of paper are illustrated in Figure 2a. It was found that in filter papers No 2, 3, and 8, the solution traveled some distance along the fluidic channel but the flow stopped before the solution reached the opposite end. Conversely, in filter papers No 1, 4 and 6 and the chromatographic papers 5 and 7, the solution eventually migrated along, and reached the opposite end of, the fluidic channel, indicating better solution longitudinal migration properties. From these results and the data in Table 1, a rough inverse correlation can be established between the longitudinal migration efficiency and the nominal filtration speed of the individual filter papers. This is accounted for by the fact that two opposing migration effects are at play: axial migration (solution movement as the liquid penetrates the paper moving from one side of the paper to the opposite side) and longitudinal migration (solution movement along the fluidic channel with direction from the sample zone to the test zone). In fast-filtering papers (i.e., papers No 2, 3 and 8), axial migration predominates and the solution rapidly penetrates the paper matrix, forming droplets at the opposite side of the paper, an effect that was verified by optical inspection; as soon as droplets are formed while the paper is held in the horizontal position, the longitudinal solution movement stops. Ιn slow-filtering filter papers (i.e., papers No 1, 4, 6) and the chromatographic papers No 5 and 7, the axial migration (i.e., the paper penetration process) is much slower so that, in the timescale of the experiment, solution did not have sufficient time to penetrate and reach the opposite side of the paper. Therefore, longitudinal migration prevails and the solution moves along the entire fluidic channel through capillary forces.

Figure 2.
Photos illustrating (a) longitudinal solution transport in the 8 different types of papers (100 μL of methylene blue; pen No 17; two passes; single-sided; pen plotting speed 2.7 cm s−1), (b) the effect of the plotting speed (in cm s−1) on the isolation ability and the barrier line width (100 μL of methylene blue; pen No 17; paper No 5; single-sided plotting; 2 passes).
Therefore, the slow-filtering filter papers No 1, 4 and 6 and the chromatographic papers No 5 and 7 were found to possess satisfactory longitudinal migration properties and could be potentially used for the fabrication of the PADs.
3.2. Investigation of the Type of Marker Pen
So far, no comparative data exist on the different types of commercial marker pens for the PoP formation of PADs and only the Staedler permanent Lumocolor waterproof (pen No 1 in Table 2) has been used for this purpose (e.g., [34,36]). However, according to our initial experiments, the isolation capability of this marker pen was found to be questionable and a systematic study of 17 types of commercially available marker pens was undertaken to assess their channel isolation abilities (Table 2). The ink formulations are proprietary to the respective manufacturers and no data of their chemical composition are disclosed. However, all permanent markers utilize a coloring pigment, a hydrophobic resin and a solvent. The pressure applied during the drawing process is sufficient to force the ink to (partially or fully) penetrate the paper and the solvent quickly evaporates (in a few minutes), leaving the dry resin on paper which ultimately serves as the hydrophobic barrier. The channel isolation ability of each marker pen depends both on the composition of the ink and its ability to penetrate the paper substrate. The channel isolation ability was investigated by plotting the channels using two passes at 2.7 cm s−1, letting the ink dry for 10 min, applying 100 μL of an aqueous solution of methylene blue to the sample area of the fluidic device and visually inspecting the device after the solution flow was stopped. Using two passes, none of the pens No 1–16 achieved satisfactory isolation after plotting on one side of the paper. Plotting on both sides of the paper (two passes on each side at 2.7 cm s−1) provided satisfactory isolation ability with: the Staedtler permanent Lumocolor waterproof pen (pen No 1); the Edding 300 permanent marker water-resistant 1.5–3 mm pen (pen No 6); the Olejowy paint marker GR-25 1.8 mm (pen No 8); and the Edding 780 0.8 mm (Pen No 13). However, double-sided plotting is undesirable since it necessitates reversal of the paper, re-aligning and re-plotting. The BIC Marking Pro ultra-resistant permanent marker (pen No 17) provided satisfactory isolation ability after plotting only on one side of the paper using two passes at 2.7 cm s−1 in combination with all the paper types and was selected for further work. This was corroborated by microscopic examination of the cross-section at the barrier areas which showed that the ink completely penetrated the paper substrate with all the types of paper studied in this work (Figure S2 (Supplementary Material)).
3.3. Investigation of the PAD Fabrication Parameters
Once pen No 17 was selected, different fabrication parameters were studied. One important parameter is the actual border width which is directly related to the nominal thickness of the marker pen’s point size. The nominal thickness of the selected pen No 17 is 1.1 mm but the actual width of the borders is larger and depends on the type of paper substrate, the plotting speed and the number of passes. Table 3 summarizes the border thickness achieved using different types of papers. While papers No 1, 4, 5, 6 and 7 offer good transport properties (as discussed in Section 3.1), papers No 1 and 6 cause excessive dispersion of the ink, resulting in wider borders (as shown in Table 3 and Figure 2a). Papers 4, 5 and 7 produced statistically non-significant differences in both optical and electrochemical detection and paper 7 was used for subsequent experiments.

Table 3.
Average border line thickness and contact angles on different types of paper using pen No 17 (nominal thickness 1.1 mm) (single-sided plotting; 2 passes; pen plotting speed 1.9 cm s−1).
Another important parameter is the plotting speed. As illustrated in Figure 2b, pen plotting speeds higher than 5.7 cm s−1 did not ensure effective channel isolation. Lower pen plotting speeds yielded satisfactory channel isolation but led to wider borders and, consequently, lower spatial resolution, as shown in Figure 2b and Table S1 (Supplementary Material). In this work, pen plotting speeds in the range 1.9–3.8 cm s−1 were normally used.
The hydrophobicity of the selected pen No 17 was assessed via contact angle measurements. Contact angles were measured by first drawing a circular area on the paper substrate and then placing a drop of water on the plotted area. Contact angles recorded for different paper substrates were ≥115°, suggesting a highly hydrophobic surface in all the cases (Table 3); Figure S3 (Supplementary Material) demonstrates the hydrophobicity of the selected pen No 17 on paper No 7.
Finally, the chemical stability of the borders drawn with pen No 17 in solutions containing acids, bases and organic solvents was assessed by applying 100 μL of the respective aqueous solution containing methylene blue to the sample area of the fluidic device and recording the device after the solution flow was stopped. The results are summarized in Figure S4 (Supplementary Material), showing that the devices can be used in conjunction with aqueous solutions of common solvents (AcCN, EtOH and MeOH) in the range 20–50% (v/v) and with aqueous solutions of common acids (HCl, H2SO4, HNO3) and NaOH in the range 0.1–0.5 mol L−1.
Finally, in view of potential applications in biosensing (where successive washing and rinsing steps are envisaged), the structural rigidity and the border resistance of the PADs was tested using 20 successive cycles involving the addition of 50 μL of aqueous solution and drying in ambient conditions (the total volume of solution added was 1 mL). No leakage of the solution was observed under these conditions.
3.4. Applications in Optical and Electrochemical Detection
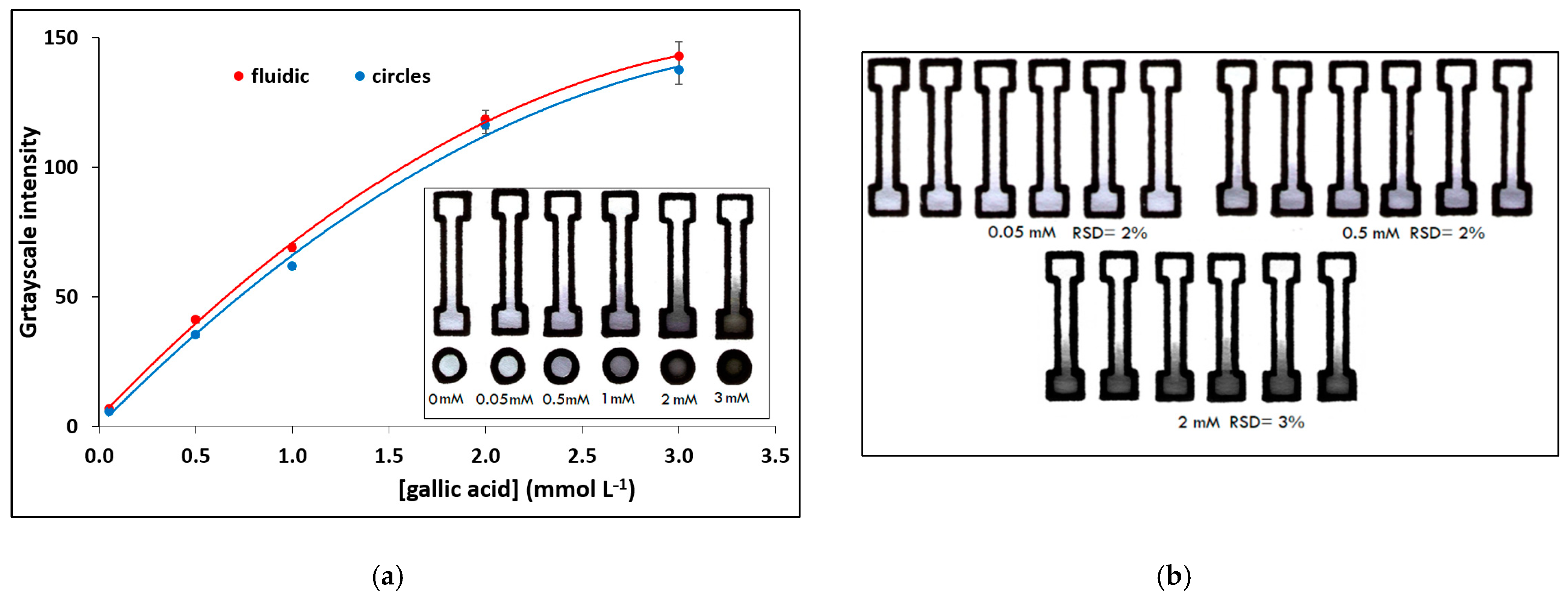
The PADs were applied in the determination of total phenolic content (using gallic acid as standard) using reflectance colorimetry. Calibration plots for the determination of gallic acid in the range 0–3 mmol L−1 of the fluidic PADs and circular PADs (for comparison) are illustrated in Figure 3a and the photos of the respective PADs for the assay are shown as an inset. The limit of detection (LOD) was 0.015 mmol L−1 and was calculated as the concentration that corresponds to a signal equal to 3.3 × sb (where sb is the blank signal). The between-device reproducibility was evaluated in different fluidic PADs for multiple determinations of gallic acid at three concentration levels (Figure 3b); the coefficients of variation ranged from 2% to 4%.
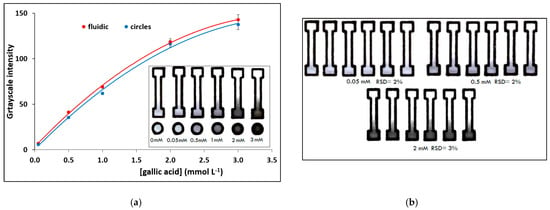
Figure 3.
Assay of total phenols using gallic acid as standard: (a) calibration plot and photos of the assay at different gallic acid concentrations of fluidic and circular PADs, (b) photos illustrating between-device reproducibility at 3 concentration levels (pen No 17; paper 7; single-sided plotting; 2 passes; pen plotting speed 2.7 cm−1).
The method was applied to the determination of the phenolic content of 10 white wines and the results were positively correlated with the standard method (Figure S5, Supplementary Material) [43]. It is worth noting that no leakage was observed despite the fact that aqueous ethanolic solutions were used.
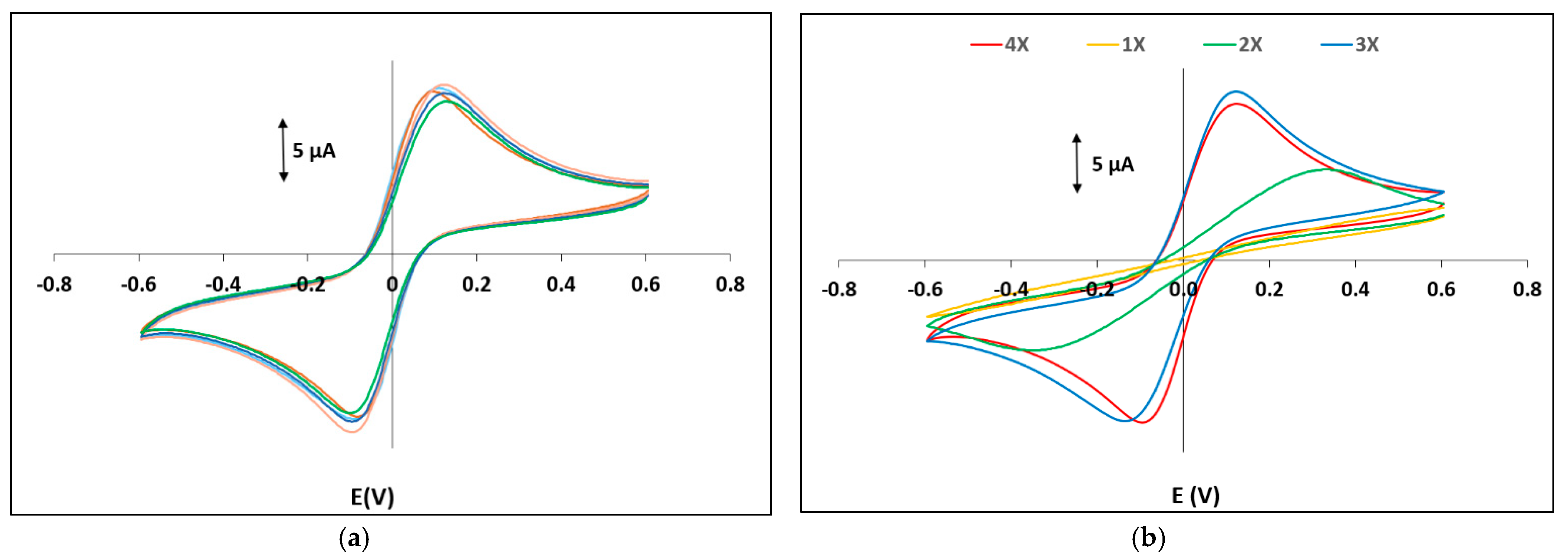
Deposition of electrodes was performed directly on the PADs using a second x–y plotting step with commercial writing pencils. The electrochemical PADs were initially characterized by CV using a ferrocyanide/ferricyanide solution as a redox probe. Figure S6 (Supplementary Material) illustrates CVs using three grades of pencil (3B, 5B and 7B) of different hardness. The medium-hardness 5B grade produced the highest redox signal and the smallest peak-to-peak separation (suggesting better charge transfer properties); the measured peak heights of the ferro/ferri couple were 78 ± 6% of the theoretically calculated peak heights. The harder pencil 3B produced the smallest redox signal (probably due to the lower carbon content of the lead which results in a smaller active surface area) and the largest peak-to-peak separation. Although the softest pencil 7B contains more graphite than the other two, it produced intermediate results between pencils 3B and 5B and this was attributed to the fact that the softer carbon material adhered poorly on the paper surface. Figure 4a illustrates CVs of five different electrochemical PADs using the grade 5B pencil; the between-device reproducibility (expressed as the coefficient of variation) in peak heights was <8% (indicating satisfactory fabrication reproducibility) and in peak potentials was <2% (indicating good stability of the graphite pseudo-reference electrode). The effect of the number of passes with the pencil was also studied (Figure 4b) and it was found that at least three passes are necessary to achieve a constant electrochemical response.
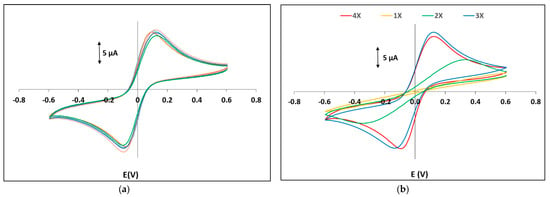
Figure 4.
CVs of a 2.0 mmol L−1 potassium ferrocyanide/ 2.0 mmol L−1 potassium fferricyanide solution in 0.01 mol L−1 KCl (a) of 5 different electrochemical PADs and (b) electrochemical PADs with 1, 2, 3 and 4 passes with the grade 5B pencil (pen No 17; paper 7; single-sided plotting; 2 passes; pen plotting speed 2.7 cm s−1; pencil plotting speed 32 cm s−1).
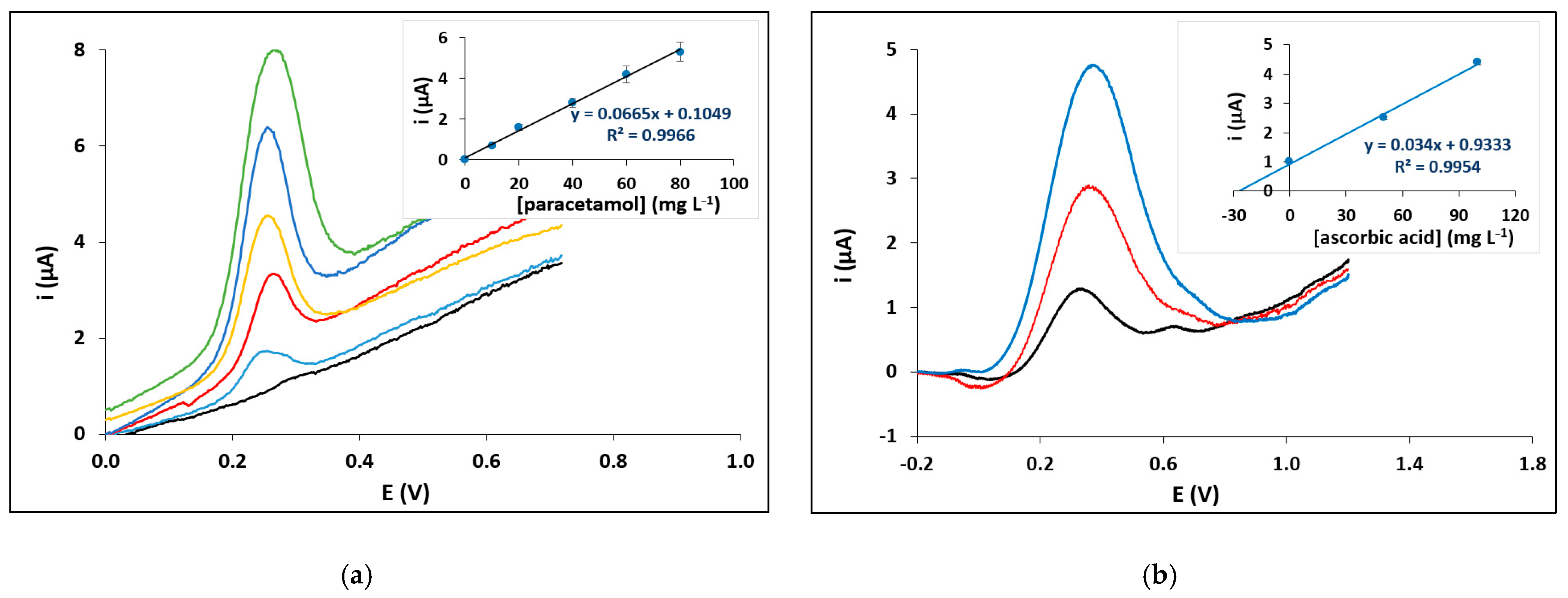
The electrochemical PADs were successfully applied to the detection of paracetamol in gin. Paracetamol is an analgesic used to adulterate low-quality alcoholic drinks to prevent hangover [41]. Figure 5a illustrates voltammograms and a calibration curve for paracetamol (as an inset) obtained in the matrix of gin. The LOD (calculated as LOD = 3.3 × si/a, where si is the standard deviation of the intercept of the calibration plot and a is the slope of the calibration plot) was 3.1 mg L−1 and the between-device relative standard deviation ranged from 7–12%; the LOD was lower than the one achieved with the only existing electrochemical PAD for paracetamol detection [41]. A second application involved the determination of ascorbic acid in an orange juice sample. The determination was carried out using the method of standard additions and representative voltammograms are illustrated in Figure 5b together with the standard addition graph as an inset. The determined concentration of ascorbic acid in the orange juice sample was 27.4 ± 5.5 mg/100 mL (n = 3), and the recovery was 95%. The LOD was 5.7 mg L−1 and it was similar or better than those obtained with other electrochemical PADs [47,48]. The chemical resistance of the PADs proved satisfactory in both samples involving ethanolic solutions, buffers and dilute acids.
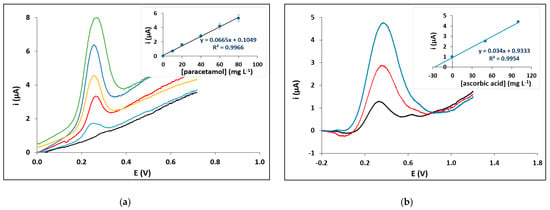
Figure 5.
Application of the electrochemical PADs. (a) Voltammograms of different concentrations of paracetamol in a gin sample (calibration curve as inset). (b) Determination of ascorbic acid in an orange juice sample (standard additions curve as inset). Pen No 17; pencil 5B; paper 7; single-sided plotting; 2 passes; pen plotting speed 2.7 cm s−1; pencil plotting speed 32 cm s−1).
4. Conclusions
A method for fabricating PADs via a PoP approach using x–y plotting with commercial stationery was developed and optimized. Among the marker pens investigated for the formation of hydrophobic barriers, the BIC Marker Pro could provide channel isolation with single-sided plotting. Regarding paper types, slow-filtering filter papers as well as chromatographic papers provided satisfactory longitudinal transport properties. Plotting speeds ≤ 5.7 cm s−1 could be used in conjunction with aqueous solutions without leakage. The PADs offered satisfactory chemical resistance to aqueous solutions of common organic solvents (in the range 20–50% (v/v)) and common acids and bases (in the range 0.1–0.5 mol L−1) and satisfactory rigidity after multiple loading cycles. A representative optical assay (determination of total phenols) with the PADs exhibited positive correlation with a standard optical method with between-device coefficient of variation ≤4%. Three-electrode electrochemical PADs were fabricated via x–y plotting with a writing pencil. The grade 5B pencil was found the more appropriate while the between-device coefficient of variation (using the peak heights of the ferri/ferro redox probe) was <8%. The electrochemical PADs were successfully applied to detect paracetamol in gin and ascorbic acid in orange juice. The proposed methodology to fabricate PADs is fit-for-purpose, rapid, simple, low cost and flexible.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors9070178/s1, Figure S1. Nominal (as designed) dimensions of the PADs and the electrochemical PADs fabricated in this work, Figure S2. Cross-section profiles of the channels drawn with pen No 17 using single-sided plotting on the 8 paper types studied in this work, Figure S3. Demonstration of hydrophobicity of pen No 17 on paper No 7, Table S1. Effect of the drawing speed on the barrier line width, Figure S4. Chemical resistance of devices plotted with pen No 17 on paper No 7, Figure S5. Correlation of the phenolic content (in gallic acid equivalents, GAE) measured with the PADs and the standard method, Figure S6. CVs of a 2.0 mmol L−1 potassium ferrocyanide/2.0 mmol L−1 potassium ferricyanide solution in 0.01 mol L−1 KCl on PADs with electrodes drawn with pencils of grade 3B, 5B and 7B.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.E., V.P.; methodology, V.P., E.S., D.S.; validation, V.P., E.S., D.S.; writing—original draft preparation, V.P., D.S.; writing—review and editing, A.E.; supervision, A.E.; project administration, A.E.; funding acquisition, A.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Social Fund-ESF) through the Operational Programme “Human Resources Development, Education and Lifelong Learning 2014–2020” in the context of the project “Development of paper-based integrated fluidic electrochemical biosensors using nanomaterial labels” (MIS 5047930). The publication of the article is financed by the Special Account of Research Grants of the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and supplementary material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Nery, E.W.; Kubota, L.T. Sensing approaches on paper-based devices: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 7573–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Shibata, H.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. Toward practical application of paper-based microfluidics for medical diagnostics: State-of-the-art and challenges. Lab. Chip 2017, 17, 1206–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemal Yetisen, A.; Safwan Akram, M.; Lowe, C.R. Paper-based microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab. Chip 2013, 13, 2210–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Marzo, A.M.; Merkoçi, A. Paper-based sensors and assays: A success of the engineering design and the convergence of knowledge areas. Lab. Chip 2016, 16, 3150–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low volume, portable bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunningham, J.C.; DeGregory, P.R.; Crooks, R.M. New Functionalities for Paper-Based Sensors Lead to Simplified User Operation, Lower Limits of Detection, and New Applications. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 9, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boobphahom, S.; Nguyet Ly, M.; Soum, V.; Pyun, N.; Kwon, O.S.; Rodthongkum, N.; Shin, K. Recent Advances in Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices toward High-Throughput Screening. Molecules 2020, 25, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribhuwan Singh, A.; Lantigua, D.; Meka, A.; Taing, S.; Pandher, M.; Camci-Unal, G. Paper-Based Sensors: Emerging Themes and Applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suntornsuk, W.; Suntornsuk, L. Recent applications of paper-based point-of-care devices for biomarker detection. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, C.T.; Hou, C.Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Fu, L.M. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for environmental analysis of soil, air, ecology and river water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 126855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.M.; Wang, Y.N. Detection methods and applications of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 107, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Turab Jafry, A.; Lee, J. Fabrication, Flow Control, and Applications of Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Molecules 2019, 24, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozer, T.; McMahon, C.; Henry, C.S. Advances in Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 13, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akyazi, T.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Benito-Lopez, F. Review on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices towards commercialization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1001, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; He, X.; Xu, F.; Li, F. Pen-on-paper strategies for point-of-care testing of human health. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishat, S.; Jafry, A.T.; Martinez, A.W.; Awan, F.R. Paper-based microfluidics: Simplified fabrication and assay methods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 336, 129681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hugh Fan, Z. Fabrication and Operation of Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 9, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh Singhal, H.; Prabhu, A.; Nandagopal, M.S.G.; Dheivasigamani, D.; Kumar Mani, N. One-dollar microfluidic paper-based analytical devices: Do-It-Yourself approaches. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, W.; Jiang, L.; Qin, J.; Lin, B. Rapid prototyping of paper-based microfluidics with wax for low-cost, portable bioassay. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kong, Q.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Bian, Z.; Zheng, X.; Ma, C.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Hand-drawn & written pen-on-paper electrochemiluminescence immunodevice powered by rechargeable battery for low-cost point-of-care testing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Abedi Ostad, M.; Hajinia, A.; Heidari, T. A novel direct and cost effective method for fabricating paper-based microfluidic device by commercial eye pencil and its application for determining simultaneous calcium and magnesium. Microchem. J. 2017, 133, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, F.; Xing, Y.; Liu, Z.; You, M.; Li, Y.; Wen, T.; Qu, Z.; Li, X.L.; Xu, F. Pen-on-paper strategy for point-of-care testing: Rapid prototyping of fully written microfluidic biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes Aguilar, L.; Marques Petroni, J.; Souza Ferreira, V.; Gabriel Lucca, B. Easy and rapid pen-on-paper protocol for fabrication of paper analytical devices using inexpensive acrylate-based plastic welding repair kit. Talanta 2020, 219, 121246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Mani, N.; Prabhu, A.; Kumar Biswas, S.; Chakraborty, S. Fabricating Paper Based Devices Using Correction Pens. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsha, V.; Aishwarya, S.; Murchana, S.; Naveen, G.; Ramya, M.; Rathinasabapathi, P. Correction pen based paper fluidic device for the detection of multiple gene targets of Leptospira using Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 174, 105962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, L.R.; Duarte, L.C.; Coltro, W.K.T. Instrument-free fabrication of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices through 3D pen drawing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 312, 128018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyola-Reynoso, S.; Heim, A.P.; Halbertsma-Black, J.; Zhao, C.; Tevis, I.D.; Çınar, S.; Cademartiri, R.; Liu, X.; Bloch, J.F.; Thuo, M.M. Draw your assay: Fabrication of low-cost paper-based diagnostic and multi-well test zones by drawing on a paper. Talanta 2015, 145, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satarpai, T.; Siripinyanond, A. Alternative Patterning Methods for Paper-based Analytical Devices Using Nail Polish as a Hydrophobic Reagen. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamidon, N.N.; Hong, Y.; Salentijn, G.I.J.; Verpoorte, E. Water-based alkyl ketene dimer ink for user-friendly patterning in paper microfluidics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1000, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Guo, P.; Guan, P.; Wang, S.; Lei, Y.; Wang, G. The fabrication of paper separation channel based SERS substrate and its recyclable separation and detection of pesticides. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 240, 118561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuchtavorn, N.; Macka, M. A novel highly flexible, simple, rapid and low-cost fabrication tool for paper-based microfluidic devices (mPADs) using technical drawing pens and in-house formulated aqueous inks. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 919, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhavamani, J.; Hamid Mujawar, L.; Soror El-Shahawi, M. Hand drawn paper-based optical assay plate for rapid and trace level determination of Ag+ in water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Low-Cost Fabrication of Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices by One-Step Plotting. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6331–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dossi, N.; Petrazzi, S.; Toniolo, R.; Tubaro, F.; Terzi, F.; Piccin, E.; Svigelj, R.; Bontempelli, G. Digitally Controlled Procedure for Assembling Fully Drawn Paper-Based Electroanalytical Platforms. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10454–10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderinezhad, F.; Amin, R.; Temirel, M.; Yenilmez, B.; Wentworth, A.; Tasoglu, S. High-throughput rapid-prototyping of low-cost paper-based microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, R.; Ghaderinezhad, F.; Li, L.; Lepowsky, E.; Yenilmez, B.; Knowlton, S.; Tasoglu, S. Continuous-Ink, Multiplexed Pen-Plotter Approach for Low-Cost, High-Throughput Fabrication of Paper-Based Microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6351–6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosale, A.; Shankar, R.; Ganesand, V.; Shrivas, K. Direct-Writing of Paper Based Conductive Track using Silver Nano-ink for Electroanalytical Application. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 209, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soum, V.; Cheong, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.; Chuong, M.; Ryeon Ryu, S.; Ki Yuen, P.; Kwon, O.S.; Shin, K. Programmable Contact Printing Using Ballpoint Pens with a Digital Plotter for Patterning Electrodes on Paper. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 16866–16873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, F.; Hu, J.; Hong Wee, W.; Long Han, Y.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Jian Lu, T.; Xu, F. Direct writing electrodes using a ball pen for paper-based point-of-care testing. Analyst 2015, 140, 5526–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukird, J.; Soum, V.; Kwon, O.S.; Shin, K.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. 3D paper-based microfluidic device: A novel dual-detection platform of bisphenol A. Analyst 2020, 145, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.A.; Cardoso, T.M.G.; Chagas, C.L.S.; Oliveira, V.X.G.; Munoz, R.A.A.; Henry, C.S.; Santana, M.H.P.; Paixa, T.R.L.C.; Coltro, W.K.T. Detection of Analgesics and Sedation Drugs in Whiskey Using Electrochemical Paper-based Analytical Devices. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2250–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes Jomma, E.; Bao, N.; Ding, S.N. A pencil drawn microelectrode on paper and its application in two-electrode electrochemical sensors. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 3513–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qian, D.; Li, Y.; Bao, N.; Gu, H.; Yu, C. Fully-drawn pencil-on-paper sensors for electroanalysis of dopamine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 769, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otávio Orzaria, L.; Aparecida de Araujo Andreottia, I.; Fernando Bergamini, M.; Humberto Marcolino Junior, L.; Campos Janegitz, B. Disposable electrode obtained by pencil drawing on corrugated substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 264, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossi, N.; Toniolo, R.; Impellizzieri, F.; Tubaro, F.; Bontempelli, G.; Terzi, F.; Piccin, E. A paper-based platform with a pencil-drawn dual amperometric detector for the rapid quantification of ortho-diphenols in extravirgin olive oil. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 950, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slinkard, K.; Singleton, V.L. Total Phenol Analysis: Automation and Comparison with Manual Methods. Am. J. Enol. Viticul. 1977, 28, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kit-Anan, W.; Olarnwanich, A.; Sriprachuabwong, C.; Karuwan, C.; Tuantranont, A.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Srituravanich, W.; Pimpin, A. Disposable paper-based electrochemical sensor utilizing inkjet-printed polyaniline-modified screen-printed carbon electrode for ascorbic acid detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 685, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez-Bajo, E.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T. Paper-based platforms with coulometric readout for ascorbic acid determination in fruit juices. Analyst 2020, 145, 3431–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).