Abstract
Food quality assessment is a critical aspect of food production and safety, ensuring that products meet both regulatory and consumer standards. Traditional methods such as sensory evaluation, chromatography, and spectrophotometry are widely used but often suffer from limitations, including subjectivity, high costs, and time-consuming procedures. In recent years, the development of electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) technologies has provided rapid, objective, and reliable alternatives for food quality monitoring. These bio-inspired sensing systems mimic human olfactory and gustatory functions through sensor arrays and advanced data processing techniques, including artificial intelligence and pattern recognition algorithms. The e-nose is primarily used for detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in food, making it effective for freshness evaluation, spoilage detection, aroma profiling, and adulteration identification. Meanwhile, the e-tongue analyzes liquid-phase components and is widely applied in taste assessment, beverage authentication, fermentation monitoring, and contaminant detection. Both technologies are extensively used in the quality control of dairy products, meat, seafood, fruits, beverages, and processed foods. Their ability to provide real-time, non-destructive, and high-throughput analysis makes them valuable tools in the food industry. This review explores the principles, advantages, and applications of e-nose and e-tongue systems in food quality assessment. Additionally, it discusses emerging trends, including IoT-based smart sensing, advances in nanotechnology, and AI-driven data analysis, which are expected to further enhance their efficiency and accuracy. With continuous innovation, these technologies are poised to revolutionize food safety and quality control, ensuring consumer satisfaction and compliance with global standards.
1. Introduction
In the past several years, numerous review articles have addressed the applications of electronic nose and electronic tongue technologies in food analysis and quality control [1,2]. These reviews have primarily focused on the general principles of sensor systems, traditional sensing mechanisms, and early-stage applications in food quality monitoring. Others have explored developments in sensor fabrication, pattern recognition techniques, and the role of electronic tongues in evaluating taste attributes. While these studies have significantly contributed to the understanding of these technologies, most are limited in scope with respect to recent innovations [3]. Notably, few reviews have comprehensively addressed the integration of advanced artificial intelligence algorithms, the combination of e-nose and e-tongue systems, and their emerging applications in real-time monitoring, food safety, and authentication. Therefore, the present review aims to complement and extend the existing literature by focusing on the latest advancements from 2022 to 2025, with particular attention to sensor improvements, machine learning-based data interpretation, and dual-technology applications in food quality assessment [4,5,6]. Food quality and safety are essential considerations in modern food production, distribution, and consumption. Ensuring that food meets high standards in terms of freshness, taste, and chemical composition is crucial for both consumers and regulatory authorities [3]. Traditional methods for evaluating food quality, such as sensory analysis and chemical testing, rely on human perception and laboratory-based techniques [5]. However, these approaches can be subjective, time-consuming, and expensive. In recent years, advancements in sensor technology and artificial intelligence have led to the development of electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) systems, which offer rapid, objective, and reliable means of assessing food quality [6,7,8].
E-nose and e-tongue technologies are inspired by the human olfactory and gustatory systems, respectively, and aim to mimic their functions using sensor arrays and machine learning algorithms [9,10,11]. The ability of these systems to detect, analyze, and classify complex mixtures of volatile compounds (in the case of e-nose) and liquid-phase analytes (in the case of e-tongue) has made them valuable tools in food quality monitoring [12,13]. Their applications span multiple domains, including freshness evaluation, contamination detection, authentication of food products, and process control in food industries [14,15]. With growing concerns over food fraud, adulteration, and safety hazards, the use of intelligent sensing technologies is becoming increasingly important [16,17]. The integration of e-nose and e-tongue systems with modern analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and artificial intelligence-based pattern recognition, further enhances their precision and applicability. This review aims to explore the role of e-nose and e-tongue systems in food quality assessment, highlighting their working principles, recent advancements, and real-world applications in the food industry.
2. Fundamentals of E-Nose and E-Tongue Technologies
The electronic nose (e-nose) is a bio-inspired analytical device developed to detect and evaluate volatile compounds by simulating the human olfactory system [14,18,19]. It comprises an array of broadly responsive gas sensors that interact with odor molecules, generating a characteristic signal pattern or “fingerprint” for each sample. These complex signals are analyzed using machine learning algorithms, such as principal component analysis (PCA) and artificial neural networks (ANNs), enabling accurate classification and interpretation of odor profiles [18,19]. The sensor array may comprise metal oxide semiconductors (MOS) [20], conducting polymers, quartz crystal microbalances (QCM) [21], or surface acoustic wave (SAW) sensors [22]. These sensors change their electrical properties when exposed to volatile compounds. The signal processing unit converts sensor responses into digital signals. The pattern recognition system uses AI algorithms to identify and classify odor profiles. The data storage and display unit provides an interface for analyzing and visualizing results. E-nose technology has been applied extensively in food freshness assessment [18], aroma profiling [21], spoilage detection [22], adulteration monitoring [23], and in medical [11] and military applications [16]. The electronic tongue (e-tongue) is designed to analyze liquid-based food components by mimicking the human gustatory system (Figure 1b). Unlike the e-nose, which focuses on volatile compounds, the e-tongue detects dissolved substances such as salts, sugars, acids, and bitter compounds. The sensor array is made up of electrochemical sensors such as potentiometric, voltammetric, or impedance sensors that interact with liquid samples. The transduction mechanism converts chemical interactions into electrical signals. The data processing unit uses multivariate analysis and pattern recognition methods (e.g., PCA, linear discriminant analysis (LDA), and support vector machines (SVM)) to classify taste profiles. E-tongue systems have been widely used in beverage authentication, taste evaluation, contamination detection, and monitoring of fermentation processes [24,25].
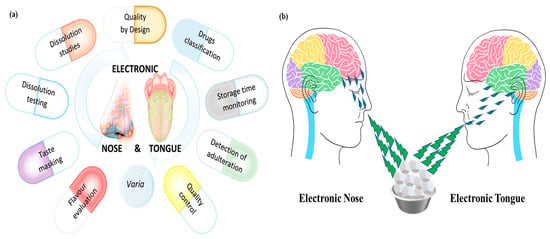
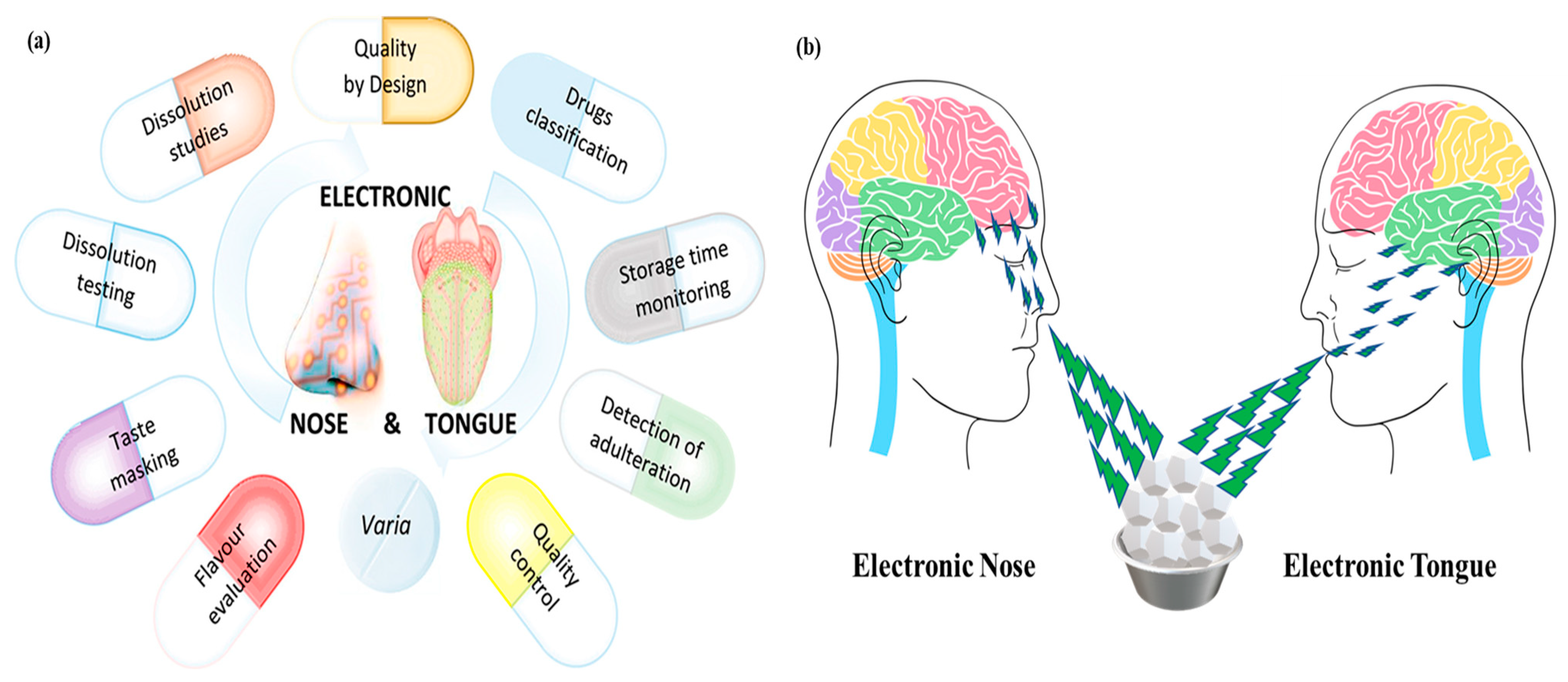
Figure 1.
Versatile applications and working principles of e-nose and e-tongue systems. (a) Various applications of electronic noses (e-noses) and electronic tongues (e-tongues) in food quality assessment, safety monitoring, and industrial applications [26]. (b) Schematic representation of the working principles of e-noses and e-tongues, illustrating how these bio-inspired sensors mimic human sensory perception.
3. Necessity of E-Nose and E-Tongue in Food Quality Analysis
Traditional food quality assessment methods rely on human sensory panels, chromatography, spectrophotometry, and microbiological tests (Figure 1a) [26]. While these techniques are well-established, they have several limitations: laboratory-based methods often require sample preparation and lengthy analysis. Sensory evaluation is influenced by human perception and fatigue. The equipment for chromatographic and spectroscopic analysis is expensive and requires skilled operators. Moreover, many conventional methods are not suitable for rapid, on-site analysis [27]. To overcome these challenges, e-nose and e-tongue technologies provide automated, objective, and rapid assessment, making them highly suitable for food quality control [28,29]. A major advantage of e-nose and e-tongue systems is that they do not require altering or destroying the sample, unlike some chemical methods. They show high sensitivity and specificity, as they are capable of detecting subtle differences in food composition (Figure 1b). Automation and rapid detection provide results in real time, improving efficiency. Multivariate data analysis uses machine learning to enhance classification accuracy. This method can be easily applied to various food matrices, including dairy, meat, seafood, and beverages [30,31].
4. Applications of E-Nose and E-Tongue in Food Quality Assessment
One of the most critical applications of e-nose and e-tongue technologies is the evaluation of food freshness and spoilage [20,25,27]. Spoiled food releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and undergoes chemical changes that can be detected by these technologies. The e-nose can detect changes in volatile compounds such as ammonia and trimethylamine in meat and seafood, which indicate spoilage. Coffee is one of the most widely consumed beverages globally and represents a significant sector in the international commodity market, ranking second only to crude oil in economic value. Given its complex aroma profile, the use of electronic nose (e-nose) systems in coffee quality evaluation has gained considerable attention. E-nose technology enables rapid, non-destructive detection and classification of volatile aromatic compounds associated with different coffee varieties, processing methods, and roasting levels. Recent research has demonstrated the utility of e-nose systems in monitoring bioactive and aromatic compound changes during roasting, providing insights into how varying roast degrees influence coffee flavor development and compound stability [20,21,22]. Furthermore, advanced analytical approaches combining gas chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC-TOFMS), gas chromatography–ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS), and e-nose technologies have been used to discriminate between Arabica coffee beans from different geographic origins based on their volatile profiles [23,24,25]. These integrated sensor and chromatography systems enhance the accuracy and resolution of aroma profiling, supporting both quality control and origin authentication in the coffee industry. The e-tongue helps in monitoring pH changes and rancidity in milk and cheese. Food adulteration is a major global issue, with economic and health implications. The e-nose and e-tongue have been used to detect adulterants in food products. These methods can differentiate pure honey [30] and olive oil [31] from products mixed with cheaper substitutes. Such techniques also ensure authenticity in wine and other beverages by detecting variations in taste and aroma profiles. Fermentation is a complex process that influences the flavor and texture of food. The e-nose and e-tongue can monitor fermentation by detecting changes in chemical composition. They have been used to track fermentation stages and detect off-flavors in beer [28] and wine production [29]. They also help ensure optimal microbial activity for consistent quality in yogurt [19] and cheese-based products [20]. Food contamination by bacteria, mycotoxins, and chemical residues poses health risks. E-nose and e-tongue systems provide an early warning mechanism for detecting such contaminants. These methods readily identify residual pesticide chemicals in fruits and vegetables. They also detect volatile markers associated with bacterial growth and pathogenic contamination in meat. Understanding consumer preferences is crucial for food manufacturers. The e-tongue is used in flavor profiling and taste standardization, helping companies optimize product formulations based on target markets.
This review highlights how the integration of e-nose and e-tongue technologies in food quality assessment represents a significant advancement in the food industry. We explain in detail how these devices offer rapid, reliable, and cost-effective solutions for evaluating freshness, authenticity, contamination, and sensory attributes. With continuous improvements in sensor technology and artificial intelligence, e-nose and e-tongue systems are expected to play an increasingly important role in ensuring food safety and meeting consumer expectations. Their applications are likely to expand further with advancements in nanotechnology, artificial intelligence, and IoT-based smart sensing, making food quality monitoring more efficient and accessible.
5. Emerging Research and Applications of E-Nose in Food Quality Measurement
The e-nose emulates both the structural and functional aspects of the human and mammalian olfactory systems through a bionic approach. Its mechanism of gas recognition closely mirrors the biological olfactory process, as illustrated in Figure 2a,b [32,33]. Ensuring food quality and safety has become a priority in the food industry due to increasing consumer demand for fresh, unadulterated, and high-quality food products. Traditional methods of food quality assessment, such as sensory evaluation and laboratory-based chemical analysis, are effective but often time-consuming, costly, and sometimes subjective. As a result, electronic nose (e-nose) technology has emerged as a reliable alternative for food quality measurement. The electronic nose (e-nose) is a biomimetic sensing system that replicates the function of the human olfactory system to detect and evaluate volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released from food items. By employing cross-reactive sensor arrays and intelligent signal processing, the e-nose can identify characteristic odor profiles associated with food spoilage, contamination, adulteration, and freshness. Innovations in nanomaterials, machine learning algorithms, and IoT integration have significantly enhanced the sensitivity, selectivity, and real-time capabilities of e-nose systems in food quality monitoring [32,33]. This article explores the emerging research and novel applications of e-nose technology in food quality measurement. It highlights the role of e-nose systems in freshness detection, spoilage monitoring, food authentication, contamination assessment, and smart packaging. Furthermore, current trends and future prospects are discussed, particularly focusing on AI integration, miniaturization, and real-time monitoring [34,35].
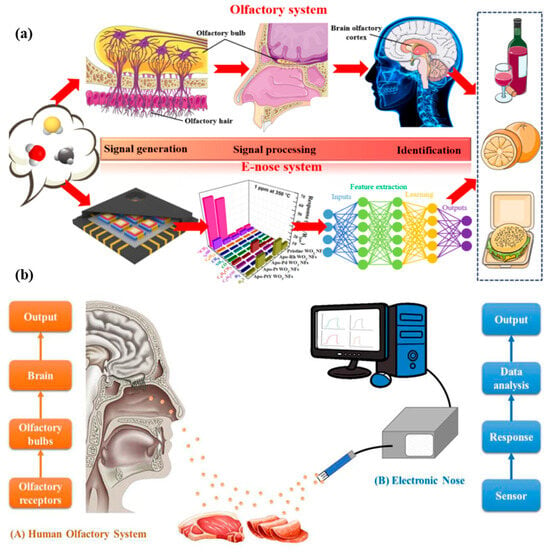
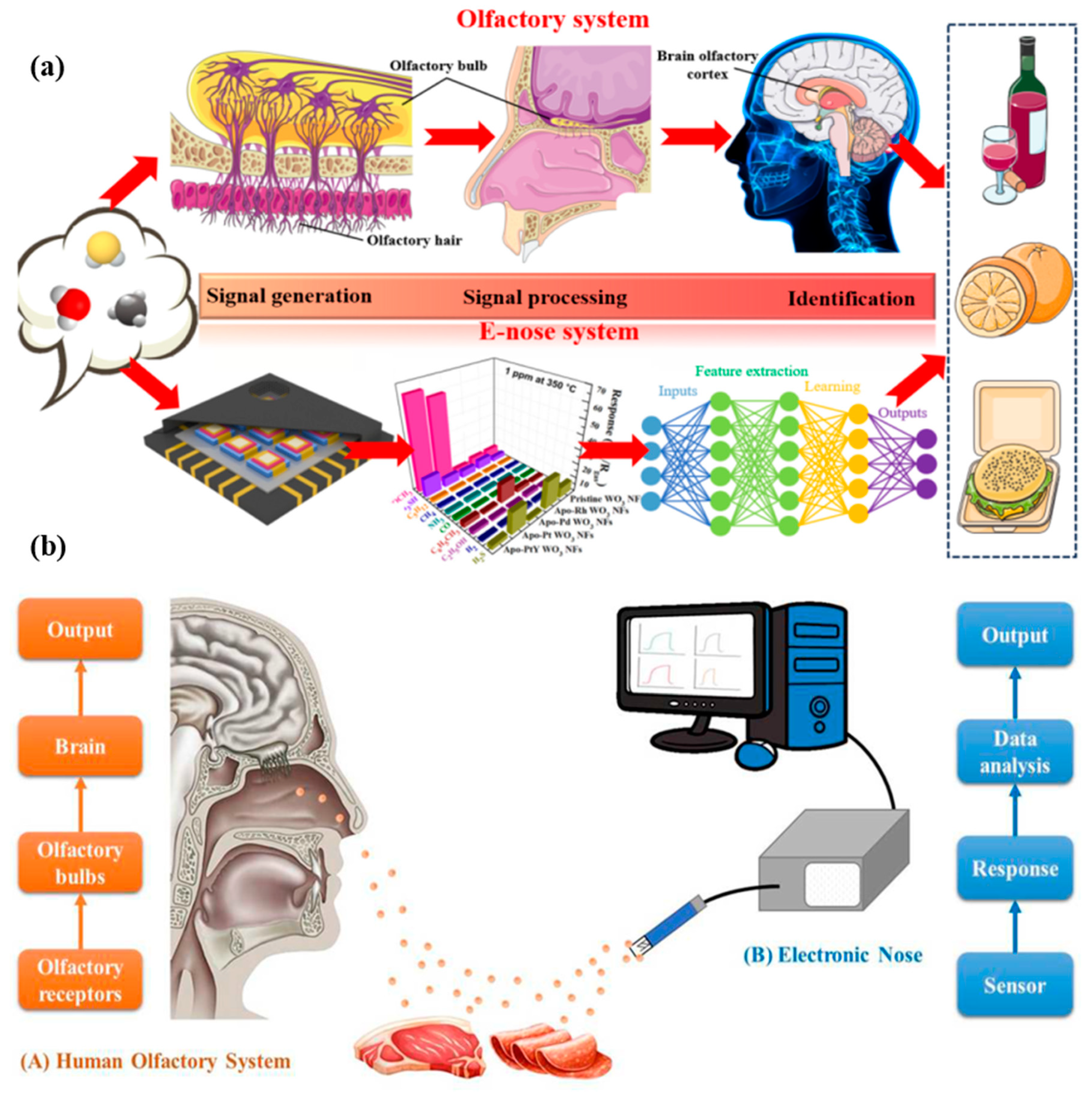
Figure 2.
E-nose system and its comparison with the biological olfactory system. (a) Graphical representation of an e-nose system integrated with computer technology for automated data analysis and odor recognition [32]. (b) Comparative schematic of the biological olfactory system and e-nose technology, highlighting similarities in odor detection and signal processing [33].
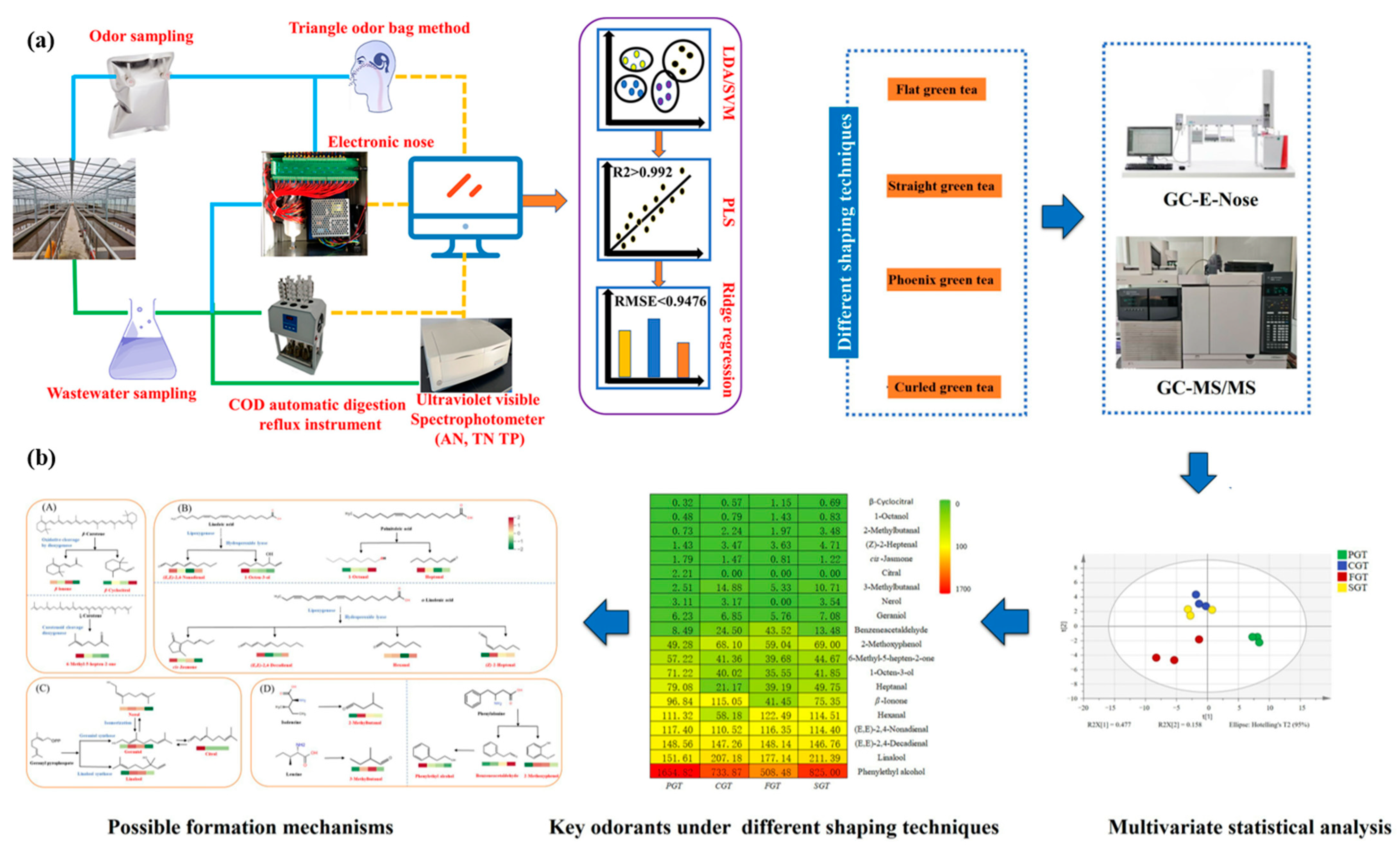
Ensuring that wastewater discharged from treatment plants complies with regulatory limits is crucial for protecting public health. This challenge can be effectively addressed by enhancing the accuracy and speed of water quality parameter assessment and odor concentration measurement [36]. A novel approach for the precise analysis of wastewater quality parameters and odor concentration using an electronic nose device is depicted in Figure 3a. The study was conducted in three key steps: (1) qualitatively identifying wastewater samples from various sampling points, (2) examining the correlation between electronic nose response signals and both water quality parameters and odor concentration, and (3) quantitatively predicting odor concentration and water quality parameters. To classify wastewater samples from different sampling points, various feature extraction methods were combined with support vector machine (SVM) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA), achieving a maximum recognition accuracy of 98.83%. In the second step, partial least squares regression (PLSR) was employed to analyze the correlation, yielding an R² value of 0.992. For the final step, ridge regression was utilized to predict water quality parameters and odor concentration, achieving a root mean square error (RMSE) of less than 0.9476. These findings demonstrate that electronic nose technology can effectively assess water quality parameters and odor concentrations in wastewater effluents, offering a reliable method for monitoring compliance with environmental regulations.
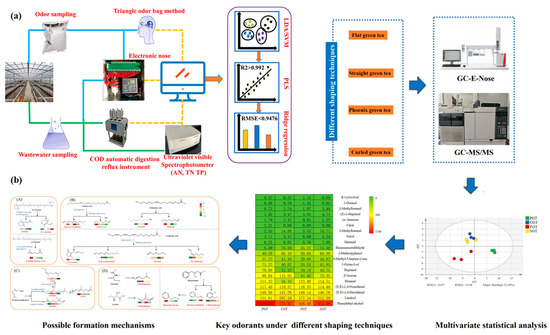
Figure 3.
E-nose-based odor analysis in wastewater treatment. (a) Schematic representation of the triangular odor bag method for wastewater odor analysis using the e-nose technique [36]. (b) Integration of gas chromatography (GC) technology with the e-nose system, illustrating how GC-imprinted e-nose technology enhances odor detection accuracy [37].
The shaping process plays a vital role in green tea manufacturing; however, its impact on aroma quality remains insufficiently understood (Figure 3b). This study explored the effects of four shaping techniques—flat green tea (FGT), straight green tea (SGT), phoenix green tea (PGT), and curled green tea (CGT)—on the aroma quality and volatile metabolites of green tea using gas chromatography–electronic nose (GC-E-Nose) and gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS). The results revealed that different shaping methods significantly influenced the development of aroma profiles and volatile compounds in green tea. Among these methods, PGT processing was found to enhance aroma quality most effectively.
A total of 60 volatile components were identified using GC-MS/MS, with 54 consistently detected across all shaping techniques [37]. Notably, PGT processing led to higher concentrations of alcohols, esters, and ketones, contributing to an improved aromatic profile. Additionally, 20 key odorants were identified, with (E,E)-2,4-decadienal, (E,E)-2,4-nonadienal, phenylethyl alcohol, and benzene acetaldehyde playing significant roles in defining the overall aroma of green tea. These compounds primarily originated from lipid degradation and the Maillard reaction. GC-E-nose provided a valuable complement to sensory evaluation, enabling rapid differentiation of green tea samples processed with different shaping techniques. These findings offer both theoretical insights and practical guidance for developing novel green tea products with distinct shapes and enhanced aromatic characteristics.
6. Advancements in E-Nose Technology for Food Quality Assessment
The accuracy and sensitivity of e-nose devices depend largely on the type of sensors used. Recent research has led to the development of advanced sensor technologies that enhance the detection capabilities of e-nose systems [38,39]. Metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) sensors are widely used in e-nose devices due to their high sensitivity to VOCs. Recent advancements in nanostructured MOS sensors have improved selectivity, making them effective for food quality control applications such as detecting spoilage in dairy, meat, and seafood products [2,11,27]. The conducting polymers have gained attention due to their ability to respond rapidly to changes in VOC concentrations. Researchers have been working on multi-layered conducting polymer sensors, which allow for better differentiation between food aroma profiles. Surface acoustic wave (SAW) sensors have been increasingly used in food analysis due to their ability to detect low-concentration VOCs. Recent studies have explored their application in detecting pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables, helping to ensure food safety.
The integration of biological elements such as enzymes and antibodies with e-nose sensors has led to the development of biosensor-based e-nose devices. These have been effectively used for detecting pathogens, toxins, and allergens in food products [21]. One of the primary uses of e-nose technology is in detecting food freshness and spoilage. As food deteriorates, it emits characteristic volatile compounds that can be identified by e-nose systems. Freshness is a major concern in perishable products such as meat and seafood. The e-nose has been successfully used to monitor the degradation of fish and meat by detecting ammonia, trimethylamine, and sulfur compounds, which are indicative of spoilage. A recent study demonstrated that MOS-based e-nose systems can classify beef samples based on freshness levels with an accuracy of over 95%.
In seafood quality assessment, e-nose devices have been employed to differentiate between fresh fish, refrigerated fish, and spoiled fish based on VOC profiles. Dairy products are highly perishable, and their shelf life depends on factors such as microbial contamination and oxidation [11,14,17]. The e-nose has been used to detect rancidity in milk and cheese by identifying changes in VOC composition. Research on yogurt fermentation has shown that e-nose combined with AI algorithms can effectively track lactic acid bacteria activity, helping to optimize fermentation conditions. Food fraud, including adulteration and mislabeling, is a major global concern. E-nose technology has been increasingly utilized to ensure food authenticity. Honey is often adulterated with sugar syrups, making it challenging to authenticate using conventional methods. The e-nose has been used to detect adulteration by analyzing VOC differences between pure and adulterated honey samples. A study using a SAW-based e-nose demonstrated 98% accuracy in differentiating pure honey from adulterated samples. The quality of olive oil and wine is influenced by processing techniques, storage conditions, and geographical origin. The e-nose has been applied to distinguish between extra virgin olive oil and lower-grade oils, to identify wine varietals, and to detect off-flavors caused by contamination. These applications have led to quality assurance improvements in the wine and olive oil industries, reducing economic losses due to fraud. Food contamination can arise from pathogenic bacteria, mycotoxins, and chemical residues. E-nose devices have been used to provide rapid, real-time detection of foodborne contaminants [40]. For example, the e-nose has been employed in detecting Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria contamination in food products by analyzing the VOCs produced through bacterial metabolism. Researchers have demonstrated that e-nose systems can differentiate between contaminated and non-contaminated poultry samples within minutes, offering a significant advantage over traditional microbial tests. Molds that produce mycotoxins, such as aflatoxins and ochratoxins, pose serious health risks. The e-nose has been used in the detection of mold contamination in grains and nuts. Studies have shown that the e-nose can identify fungal infections in stored grains before visible signs of spoilage appear, helping in early intervention and loss prevention. Recent research has also explored the use of e-nose technology for detecting pesticide residues in fresh produce, providing a non-invasive and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional chemical analysis methods. The integration of e-nose technology with smart packaging systems represents an emerging trend in food quality control. Smart packaging equipped with e-nose sensors can continuously monitor food freshness and alert consumers or manufacturers when spoilage occurs [41,42].
7. Emerging Research and Applications of E-Tongue in Food Quality Measurement
Maintaining high standards of food quality and safety is a top priority in the food industry, as consumers demand products that are fresh, nutritious, and free from contamination [7,9,15]. Conventional food quality evaluation techniques, including sensory analysis and chemical testing, are widely used but often involve lengthy procedures, require skilled personnel, and may be affected by subjective perception. To address these limitations, the electronic tongue (e-tongue) has been developed as an advanced analytical tool capable of detecting and identifying complex liquid-based food components with precision. Inspired by the human gustatory system, the e-tongue uses an array of sensors to analyze the chemical composition of food and beverages. These sensors respond to taste-related compounds such as acids, sugars, salts, and bitter compounds, generating unique electrical signals that can be processed through computational models [15,16,17]. Recent innovations in nanomaterial-based sensors, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing have significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of e-tongue applications. This article explores the emerging research and expanding applications of e-tongue technology in food quality assessment. It highlights advancements in sensor design, taste profiling, contamination detection, product authentication, and fermentation monitoring. Additionally, future directions, such as real-time analysis, integration with smart systems, and miniaturization, are discussed to provide insights into the evolving role of e-tongue technology in the food sector [43,44,45].
8. Advancements in E-Tongue Technology for Food Quality Assessment
The performance of e-tongue technology relies heavily on its sensor arrays, which respond to chemical interactions in food samples. Ongoing research has focused on developing highly selective and durable sensors to enhance the sensitivity and reproducibility of e-tongue measurements [8,9,14]. Potentiometric sensors operate based on ion-selective electrodes (ISEs) that measure voltage changes caused by interactions with food compounds. Recent developments have led to multi-electrode potentiometric sensors, enabling the simultaneous detection of multiple taste elements in beverages such as juices, milk, and alcoholic drinks [3,25]. Voltammetric sensors detect food components based on their electrochemical properties. Recent studies have explored the use of graphene-based voltammetric sensors, which exhibit high conductivity and enhanced stability, making them well-suited for identifying subtle differences in taste profiles. Impedance-based sensors assess the electrical conductivity of liquid samples to determine food composition. Researchers have been integrating bio-functionalized nanomaterials into impedance sensors to improve their selectivity for specific food contaminants, such as heavy metals and toxins [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. Biomimetic sensors, inspired by biological mechanisms, are a key innovation in this area. Biosensor-based e-tongue systems incorporate taste receptor proteins or synthetic recognition elements to enhance sensitivity. These systems have shown promising results in differentiating between natural and artificial sweeteners, providing valuable insights for food formulation and product development [46,47].
The ability of e-tongue devices to accurately assess taste properties has made them valuable tools for food product development, flavor enhancement, and quality control. E-tongue systems have been widely adopted for assessing the sweetness, bitterness, and acidity of beverages, ensuring flavor consistency across different production batches. In wine evaluation, e-tongue technology has been used to classify different wine varieties based on acidity, tannin levels, and alcohol content [22,23,24]. Research in coffee quality assessment has demonstrated that the e-tongue can distinguish between different coffee bean origins and roasting levels by analyzing caffeine and polyphenol concentrations. Dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese contain complex chemical compositions that influence both taste and texture. The e-tongue has been utilized to monitor fermentation progression in yogurt production by detecting changes in lactic acid concentration and to evaluate cheese ripening stages, providing insights into flavor development over time. Food adulteration and mislabeling are growing concerns, affecting consumer trust and product integrity [18,19,20]. E-tongue technology has emerged as a powerful tool for detecting substituted, diluted, or falsely labeled food products. Similar to the e-nose, e-tongue technology has been applied to differentiate between pure and sugar-syrup-adulterated honey. The device successfully identified variations in sugar composition, allowing for rapid authentication without complex chemical tests. The e-tongue has been used to assess the authenticity of extra virgin olive oil, distinguishing between high-quality oils and lower-grade mixtures. Similar research has been conducted in the detection of synthetic additives in milk, ensuring compliance with food safety regulations [22,23,24]. Food contamination poses serious health risks, and early detection of hazardous compounds is crucial. E-tongue devices have been developed to monitor contamination by detecting changes in the chemical composition of food and beverages [5,6,7]. Certain heavy metals, such as lead, cadmium, and mercury, are toxic and can accumulate in food sources. E-tongue systems have been designed to detect metal ions in drinking water, fruit juices, and alcoholic beverages, providing a cost-effective alternative to traditional laboratory testing. Spoiled food often exhibits changes in acidity and other chemical properties. E-tongue technology has been used to identify microbial spoilage in meat and poultry products, where bacterial growth alters the taste profile. It has also been applied to pasteurized milk, where spoilage detection helps improve storage and distribution practices. Fermentation plays a crucial role in food production, affecting taste, texture, and nutritional value. The use of e-tongue technology for real-time fermentation monitoring has led to improvements in production efficiency and quality control. In beer brewing, e-tongue devices have been used to analyze changes in bitterness and alcohol content, ensuring product consistency. In soy sauce fermentation, researchers have utilized e-tongue technology to optimize fermentation parameters, leading to enhanced flavor development [48,49,50].
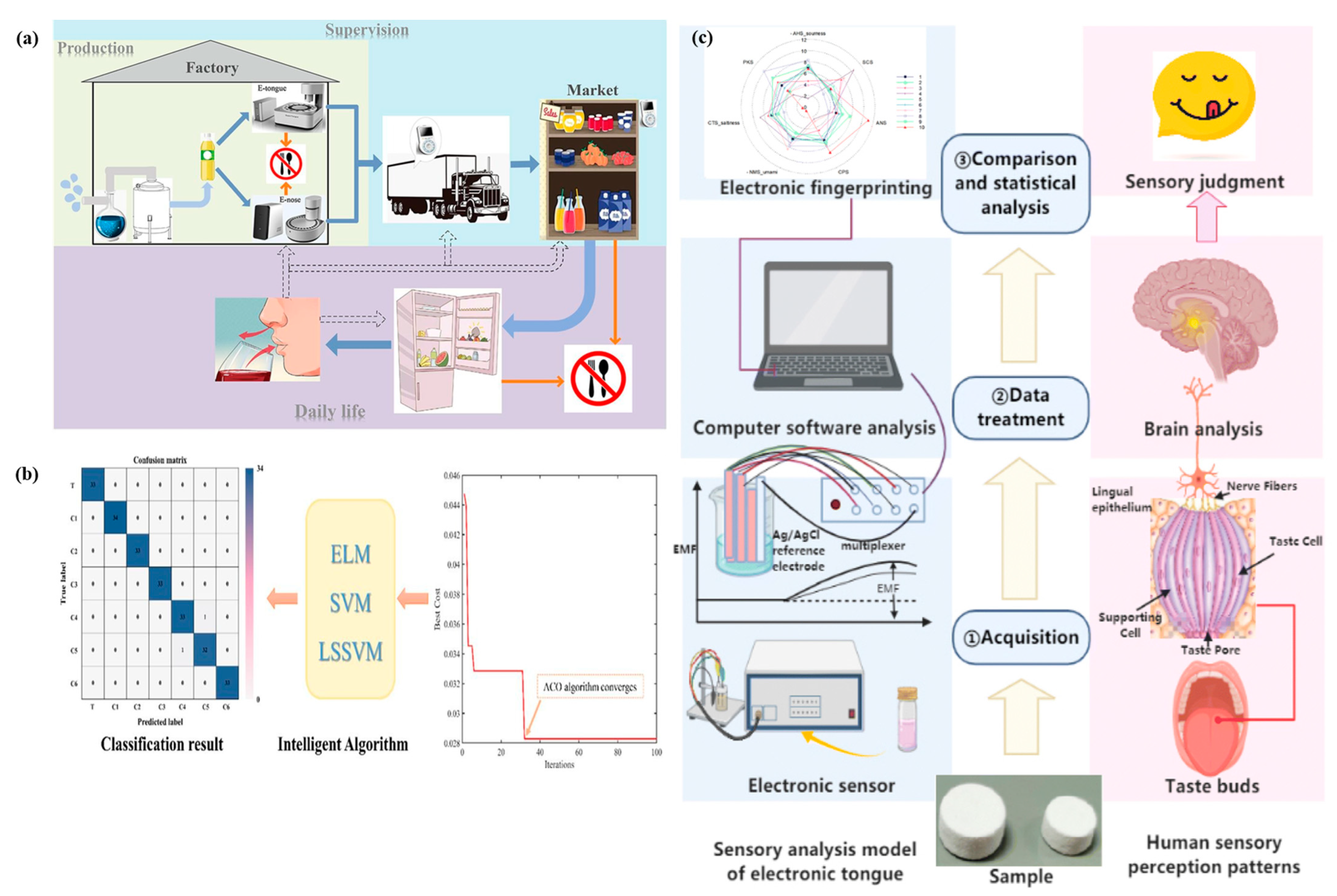
To meet the needs of both food producers and consumers, electronic tongue (e-tongue) and electronic nose (e-nose) technologies play vital roles in ensuring food quality and safety across food production, regulatory supervision, and daily-life applications [51]. This study provides a comprehensive overview of the principles, advancements, and applications of these technologies (Figure 4a). The core components of e-tongue and e-nose systems were analyzed, including sensor arrays as the primary hardware and intelligent sensory algorithms as the core software for data processing. The findings indicated that food quality control and monitoring during production represent the most significant areas of application for both technologies. Notably, e-tongue and e-nose systems, with prediction accuracies ranging from 80% to 96%, dominate food analysis applications, demonstrating their reliability in assessing freshness, authenticity, and contamination. A major trend in recent research is the increasing use of multiple intelligent sensory algorithms, where the combination of two or more data processing methods has become standard practice. Furthermore, the integration of e-nose and e-tongue technologies has gained attention due to its enhanced accuracy. Studies have revealed that combining both technologies resulted in an 8–25% improvement in food category recognition and quality prediction compared to using either technology individually. Lastly, the challenges and future directions of e-nose and e-tongue systems were discussed, emphasizing the need for improved sensor stability, enhanced data standardization, and broader commercial adoption to further advance their applications in food quality assurance.
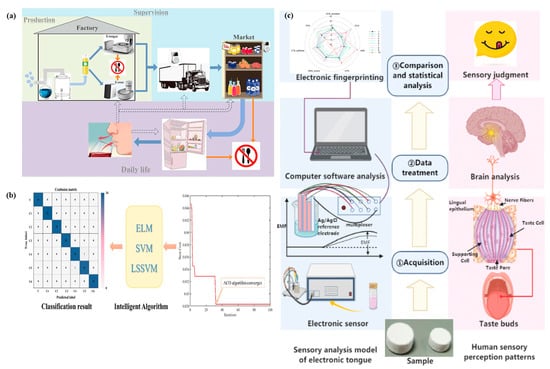
Figure 4.
Applications of e-tongue and e-nose in food safety and quality control. (a) Comprehensive application of electronic tongue and nose technologies in food production, supervision, and daily life, covering the entire food supply chain from manufacturing to consumption [51]. (b) Graphical representation of e-tongue technology combined with multivariate analysis for advanced data interpretation and quality assessment [52]. (c) Comparative analysis of the human sensory system and the taste evaluation mechanism of the electronic tongue [53].
The taste profile is a key determinant in evaluating the quality and classification of black tea, playing a crucial role in preventing fraud and economic losses [52]. This study presents an innovative approach to assessing the quality of Congou black tea by integrating an electronic tongue (e-tongue) system with the ant colony optimization (ACO) algorithm and stoichiometric analysis (Figure 4b). The electronic tongue system effectively captured the taste characteristics of black tea, generating potential signals from 700 samples across seven quality grades. These signals were transformed into nine relative taste characteristic values, providing a comprehensive representation of taste quality. To refine the dataset, the ACO method was applied to optimize taste indicators derived from artificial lipid membrane sensors, ensuring that the most relevant features were selected for further analysis. Subsequently, discriminant models were developed using extreme learning machine (ELM), support vector machine (SVM), partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA), and least squares-support vector machine (LS-SVM) to classify black tea quality based on the optimized taste features. The results demonstrated that the LS-SVM model, built on five key taste features, exhibited superior predictive performance, achieving a 99.14% correct discriminant rate in the prediction set. These findings highlight the potential of electronic tongue technology as a reliable and efficient tool for quality assessment in Congou black tea production, offering significant prospects for application in tea authentication, grading, and industrial quality control.
In the development of new drugs and dosage forms, bitterness masking is a crucial strategy for improving patient compliance and ensuring better treatment adherence. In this study, binder jetting 3D printing (BJ-3DP) was successfully employed to fabricate immediate-dissolving tablets (IDTs) that dispersed within seconds (Figure 4c) [53]. The palatability of these IDTs was quantitatively assessed using the ASTREE electronic tongue (e-tongue) [53]. The results demonstrated that the cross-inductance sensors of the e-tongue system effectively evaluated the taste-masking efficiency of the 3D-printed IDTs. Principal component analysis (PCA), in combination with design of experiments (DoE) modeling, was used to analyze the response signals and assess the impact of sucralose and spearmint flavoring on bitterness masking. The findings confirmed that the two additives had a synergistic effect on palatability, and their optimal concentrations were successfully determined. The adaptability of BJ-3DP enables the customization of drug formulations, including variations in dosage strength and flavor profiles, particularly where traditional oral taste testing is impractical. Ethical considerations and logistical challenges often limit human-based palatability assessments in pharmaceutical formulation development. This study highlights the potential of e-tongue technology as an objective, reproducible, and non-invasive tool for taste evaluation in drug development, eliminating the need for human sensory panels. By integrating 3D printing and electronic tongue analysis, pharmaceutical formulations can be tailored to individual palatability preferences, improving drug acceptance and compliance [51,52,53]. This approach represents a significant advancement in personalized medicine, allowing for precise formulation adjustments to enhance the sensory attributes of 3D-printed oral drug delivery systems.
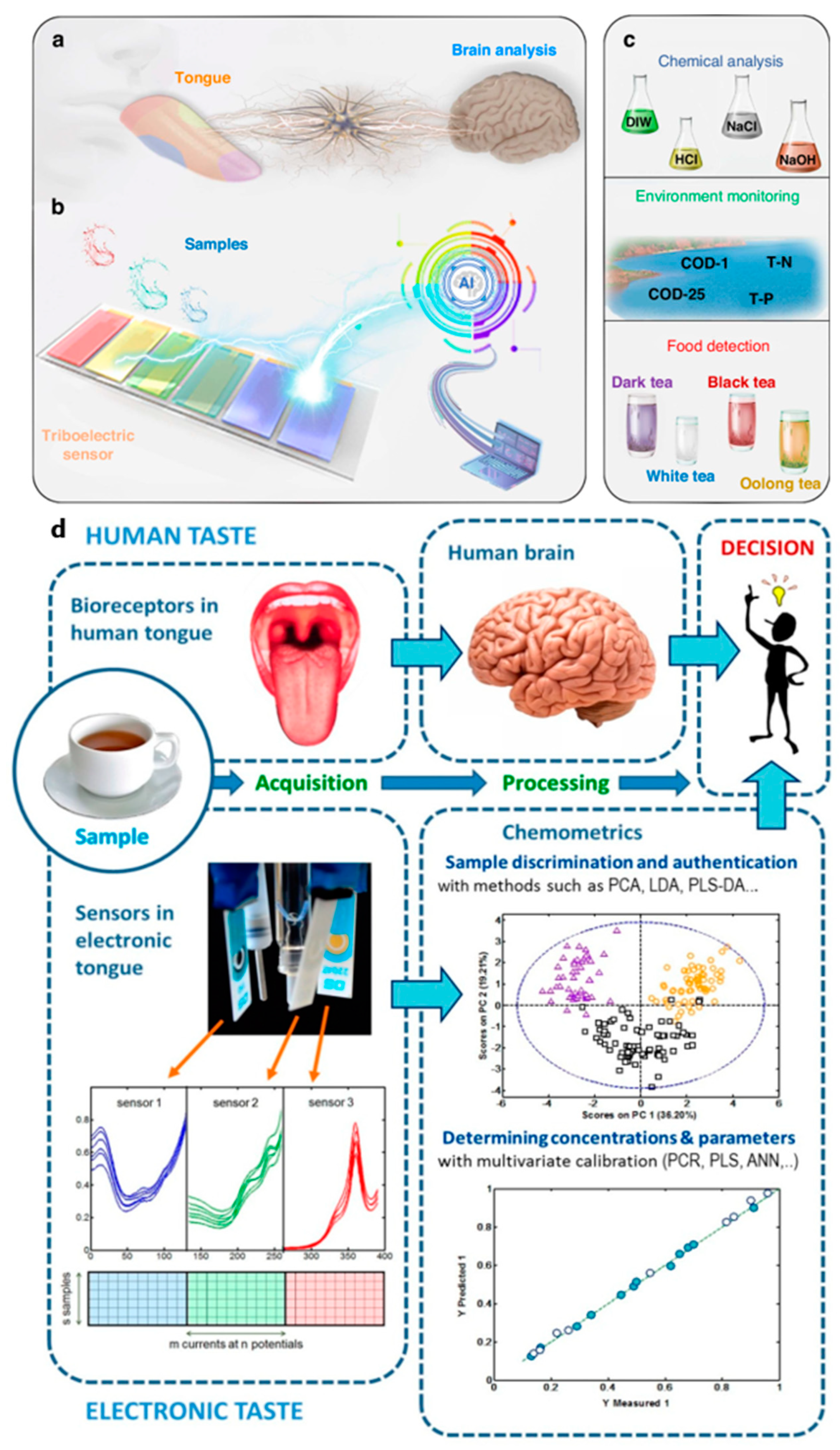
The electronic tongue (e-tongue) is a sophisticated sensing technology that imitates human taste perception. It utilizes an array of cross-sensitive sensors coupled with artificial intelligence (AI)-driven data processing techniques to enable accurate analysis, classification, and recognition of liquid-based taste compounds [35,36,37]. Conventional e-tongues, which rely on electrochemical detection methods, often face challenges such as large size, high sample volume requirements, and reliance on external power sources, limiting their application in in vivo medical diagnostics and analytical chemistry. Inspired by the biological mechanisms of the human tongue, triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG)-based components have been integrated into e-tongue platforms to enhance sensitivity, reduce power consumption, and enable miniaturization [25,26]. In this study, a multichannel triboelectric bioinspired e-tongue (TBIET) system was developed on a single glass slide chip, significantly improving taste classification accuracy through the integration of multiple sensory signals [43,44,45]. The performance of the TBIET was validated using diverse test samples, including representative biological fluids, environmental substances, and beverages. The system demonstrated exceptional classification accuracy, achieving 100% identification for chemical solutions, 98.3% accuracy for environmental samples, and 97.0% accuracy for four distinct tea varieties. Additionally, the classification accuracy for NaCl solutions of varying concentrations reached 96.9%, highlighting the device’s high sensitivity in distinguishing subtle differences in liquid compositions. The TBIET platform represents a major breakthrough in e-tongue technology, offering ultrahigh sensitivity to the electrical properties of liquid samples, rapid analysis, and excellent reliability. The development of a self-powered, portable triboelectric e-tongue prototype marks a significant advancement in the field, enhancing the feasibility of real-time, on-site liquid sample analysis for applications in food quality monitoring, medical diagnostics, and environmental assessment [48,49,50].
In the field of food quality control, voltammetric electronic tongues have emerged as a valuable complement to the more widely used potentiometric electronic tongues and electronic noses, particularly in complex analytical scenarios that require a higher level of information processing [54], the summary of the e-nose and e-tongue in recent research in food quality assessment are listed in Table 1. For datasets that exhibit near-linearity, traditional chemometric techniques such as principal component analysis (PCA), linear discriminant analysis (LDA), partial least squares (PLS), and PLS-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) can be effectively used to differentiate samples based on origin, freshness, and key food quality indicators. However, in cases where data exhibits strong non-linearity, more advanced chemometric approaches, such as artificial neural networks (ANNs) and support vector machines (SVMs), are necessary for improved model performance. Despite their advantages, these non-linear modeling techniques pose challenges. For example, the architecture of ANNs requires meticulous design, often determined through trial-and-error approaches, making model development highly situation-dependent. Consequently, many models remain inaccessible as supplementary materials in research publications, contributing to a “black box” perception that hampers the widespread adoption of ANN- and SVM-based voltammetric tongue data analysis, unlike more interpretable techniques such as PCA or PLS. In recent years, the design and application of voltammetric electronic tongues have diversified, particularly with the increasing use of screen-printed electrodes. The initial strategy of using pulse activation signals and metallic electrodes has gradually been replaced by conventional voltammetric scans (primarily cyclic voltammetry, CV) and chemically modified electrodes, which improve cross-selectivity and enable more effective discrimination between food samples (Figure 5a–c). This trend is seen as a positive evolution, as chemically modified electrodes enhance the interaction between sensors and sample components, leading to more precise differentiation of food products [54].
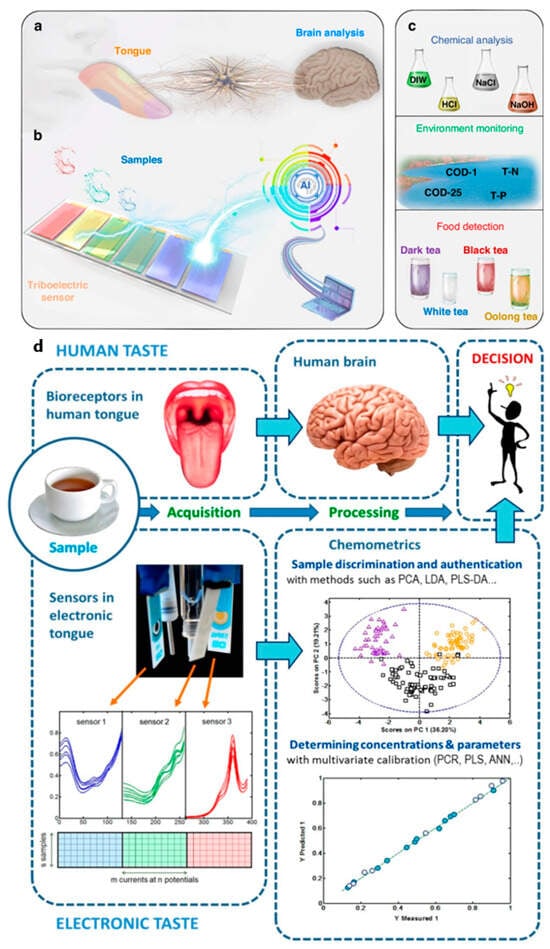
Figure 5.
Structural and functional aspects of bioinspired e-tongue technology. (a) Functional bionics of human taste perception, illustrating how e-tongue technology replicates gustatory sensing. (b) Structural diagram of an artificial taste system utilizing a triboelectric sensor array for enhanced sensitivity. (c) Diverse applications of the triboelectric bioinspired electronic tongue (TBIET) in food quality evaluation and medical diagnostics [54]. (d) General schematic of voltammetric electronic tongues, depicting key components and signal processing mechanisms used in taste analysis [55].
However, to maximize the practicality and efficiency of voltammetric e-tongue systems, it is essential to simplify and optimize both electrode selection and data processing strategies (Figure 5d) [55]. Statistical methods should be employed to validate the necessity of each sensor in an array, ensuring that redundant or excessive sensors are minimized (e.g., using eight sensors for predicting a single parameter may be unnecessary). Furthermore, powerful data compression techniques, such as discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and fast Fourier transform (FFT), should be more widely adopted to reduce computational time, maintaining the efficiency advantage of voltammetric e-tongues over traditional chromatographic methods. Additionally, efforts should focus on enhancing calibration models to address matrix effects and signal drift, ensuring the long-term reliability of e-tongue performance under real-world conditions. Implementing multivariate adaptations of established univariate methodologies, such as the standard addition method and internal standard approach, would be highly beneficial in this regard. Ultimately, for voltammetric electronic tongues to transition from proof-of-concept research to widespread commercial adoption in food quality and provenance assessment, they must be built on robust, reproducible, and cost-effective electrode arrays. Additionally, data processing tools must be seamlessly integrated into commercially available software, making these systems more accessible to industry professionals. Only through these advancements can voltammetric e-tongues achieve reliable, scalable, and practical applications in the food industry [55].

Table 1.
Summary of recent studies on electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) applications in food quality assessment.
Table 1.
Summary of recent studies on electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) applications in food quality assessment.
| No. | Sensor Type | Sensor Array Material | Analytes Detected | Sample Matrix | Detection Limit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | E-nose | MOS | VOCs | Beef | 0.1 ppm | [56] |
| 2 | E-tongue | Lipid Membrane | Caffeine, Catechins | Tea | — | [57] |
| 3 | E-nose | QCM | Sulfur Compounds | Fish | 0.05 ppm | [58] |
| 4 | E-tongue | Potentiometric | Sugars, Acids | Fruit Juice | — | [59] |
| 5 | E-nose | Conducting Polymer | Ammonia, VOCs | Chicken | 0.2 ppm | [60] |
| 6 | E-tongue | Voltammetric | Sodium, Potassium | Tomato Sauce | — | [61] |
| 7 | E-nose | MOS | Esters, Aldehydes | Olive Oil | 0.1 ppm | [62] |
| 8 | E-tongue | Impedance | Bitterness, Umami | Beer | — | [63] |
| 9 | E-nose | SAW | Ethanol, VOCs | Wine | 0.3 ppm | [64] |
| 10 | E-tongue | Biosensor | Sucralose, Bitterness | Pharmaceuticals | — | [65] |
| 11 | E-nose | Hybrid (MOS + QCM) | Methane, Ethanol, VOCs | Milk | 0.05 ppm | [66] |
| 12 | E-tongue | Lipid Membranes | Taste Profile | Dairy | — | [67] |
| 13 | E-nose | Metal Oxide | Ammonia, Trimethylamine | Shrimp | 0.1 ppm | [68] |
| 14 | E-tongue | Voltammetric | Polyphenols | Red Wine | — | [69] |
| 15 | E-nose | Colorimetric Sensor Array | VOCs | Mango | — | [70] |
| 16 | E-tongue | Potentiometric Array | Chloride, Organic Acids | Pickled Vegetables | — | [71] |
| 17 | E-nose | Optical Fiber Sensors | Aldehydes, Acids | Dairy | — | [72] |
| 18 | E-tongue | Impedance | Taste compounds | Soy Sauce | — | [73] |
| 19 | E-nose | MOS | VOCs | Sausages | 0.2 ppm | [74] |
| 20 | E-tongue | Electrochemical | Organic Acids | Fruit Juices | — | [75] |
| 21 | E-nose | Polymer Nanocomposite | Alcohols, VOCs | Beer | 0.05 ppm | [76] |
| 22 | E-tongue | Enzyme-Modified Electrodes | Sweeteners | Soft Drinks | — | [77] |
| 23 | E-nose | MOS | VOCs | Mushrooms | — | [78] |
| 24 | E-tongue | ChemFET | Salts, Acids | Sauces | — | [79] |
| 25 | E-nose | Paper-Based Sensor Array | Aroma Profile | Chocolate | — | [80] |
| 26 | E-tongue | Impedance | Taste Profile | Milk | — | [81] |
| 27 | E-nose | Gas Sensor Network | VOCs | Stored Fruits | — | [82] |
| 28 | E-tongue | Potentiometric | Tannins, Bitterness | Black Tea | — | [83] |
| 29 | E-nose | MOS | VOC Fingerprinting | Yogurt | 0.1 ppm | [84] |
| 30 | E-tongue | Voltammetric | Organic Compounds | Fruit Purees | — | [85] |
| 31 | E-nose | QCM | Alcohols, Esters | Cheese | — | [86] |
| 32 | E-tongue | Hybrid Sensor | Saltiness, Acidity | Snacks | — | [87] |
| 33 | E-nose | CNT-Based Sensor | Ethanol, VOCs | Kombucha | 0.1 ppm | [88] |
| 34 | E-tongue | Electrochemical | Amino Acids | Tofu | — | [89] |
| 35 | E-nose | Biopolymer Sensor | Aromatics | Spices | — | [90] |
| 36 | E-tongue | Voltammetric | Acids, Esters | Vinegar | — | [91] |
| 37 | E-nose | Colorimetric Array | VOC Fingerprints | Green Tea | — | [92] |
| 38 | E-tongue | Impedance | Mineral Content | Mineral Water | — | [93] |
| 39 | E-nose | SAW | Aromatics | Nuts | — | [94] |
| 40 | E-tongue | Lipid Membrane | Taste Profile | Ice Cream | — | [95] |
| 41 | E-nose | Optical Sensor Array | VOCs | Dried Herbs | — | [96] |
| 42 | E-tongue | Potentiometric | Sourness, Bitterness | Sauces | — | [97] |
| 43 | E-nose | Hybrid (MOS + Optical) | Spoilage VOCs | Fish | 0.05 ppm | [98] |
| 44 | E-tongue | Conductometric | Taste Compounds | Packaged Foods | — | [99] |
| 45 | E-nose | CNT-Film Sensor | Aromatics | Roasted Coffee | — | [100] |
| 46 | E-tongue | Voltammetric | Sugar Content | Juices | — | [101] |
| 47 | E-nose | Electrochemical Array | Aldehydes | Meat | 0.1 ppm | [102] |
| 48 | E-tongue | Enzyme-Modified Electrodes | Bitterness, Artificial Sweeteners | Diet Sodas | — | [103] |
| 49 | E-nose | Flexible Gas Sensor Array | VOCs | Packaged Fish | — | [104] |
| 50 | E-tongue | Hybrid Array | Salts, Organic Acids | Soups | — | [105] |
9. Challenges Facing E-Nose and E-Tongue Technologies
Despite their promising capabilities, the widespread commercialization of e-nose and e-tongue technologies faces multiple challenges, including technical limitations, economic constraints, and regulatory hurdles [56,57,58]. A key issue lies in achieving consistent long-term sensor stability and reproducibility across different operating conditions. One of the critical challenges in the development and application of both e-nose and e-tongue technologies lies in the area of signal analysis [59,60,61]. Accurate interpretation of sensor responses often captured as sensograms requires robust algorithms capable of extracting detailed and meaningful profile information from a single measurement. Ideally, each reading should yield a comprehensive chemical or sensory fingerprint, reducing the need for repeated tests and improving efficiency [62,63,64]. However, limitations such as baseline drift, signal instability, sensor saturation, and overlapping responses can complicate this process. Baseline stability is especially important for ensuring reproducibility over time and across different batches or environmental conditions [65,66,67]. Additionally, noise reduction, signal normalization, and feature extraction techniques must be carefully optimized to enhance the reliability and interpretability of the data. Future progress in this area will likely rely on the integration of more advanced data processing methods, such as deep learning, time-series modeling, and sensor fusion strategies, to improve pattern recognition and quantification from complex datasets [68,69,70]. Over time, sensor arrays may degrade, leading to decreased sensor performance due to environmental factors such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and prolonged exposure to VOCs. Current e-nose and e-tongue devices require regular recalibration to maintain accuracy, which adds to operational costs. Ongoing research is focused on the development of self-calibrating sensors that automatically adjust to environmental conditions [106,107,108], as well as the use of nano-engineered sensor coatings that enhance durability and resistance to contamination. One of the major hurdles in the adoption of e-nose and e-tongue technologies is the lack of standardized data formats and analysis protocols [71,72,73]. Since different manufacturers use varying sensor technologies and algorithms, data collected from different devices is often incompatible. To address this, there are ongoing efforts to establish global data-sharing platforms where researchers and food manufacturers can access standardized aroma and taste datasets [74,75,76]. Additionally, there is the development of open-source AI models that can interpret e-nose and e-tongue data across multiple industries [109,110]. The high cost of sensor materials and manufacturing is a major barrier to the widespread adoption of e-nose and e-tongue devices [111]. Advanced biomimetic sensors and nanomaterials significantly increase production costs [77,78,79]. As a result, small-scale food producers may find it financially unfeasible to invest in e-nose and e-tongue technology [112]. Potential solutions include the introduction of government incentives for small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to adopt food quality monitoring technologies [80,81,82]. Despite their potential, e-nose and e-tongue devices face regulatory hurdles in terms of food safety compliance and consumer acceptance. Many food regulatory agencies, such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), require extensive validation before allowing e-nose and e-tongue devices to be used in official food quality assessments. Some consumers may be hesitant to rely on AI-driven food assessments, preferring traditional laboratory tests [83,84,85]. To address this, collaboration between research institutions, industry leaders, and regulatory agencies is essential to develop clear guidelines for e-nose and e-tongue validation, along with public awareness campaigns highlighting the reliability and benefits of these technologies in ensuring food safety [86,87,88].
The future of e-nose and e-tongue technology in food quality assessment is highly promising, with advancements in AI, miniaturization, IoT connectivity, and blockchain integration opening new avenues for innovation [89,90,91]. However, challenges such as sensor stability, data standardization, cost barriers, and regulatory approvals must be addressed to facilitate widespread adoption [113,114,115]. With ongoing research and collaboration between scientists, food industries, and regulatory bodies, e-nose and e-tongue technologies have the potential to revolutionize food safety, authentication, and sensory evaluation, ensuring higher-quality products for consumers worldwide [92,116].
10. Future Aspects and Challenges of E-Nose and E-Tongue
The rapid advancement of sensor technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics has significantly enhanced the potential of electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) systems in food quality assessment [117]. These biomimetic sensing platforms have significantly advanced food safety, freshness monitoring, adulteration detection, and product authentication by providing rapid, objective, and non-destructive analysis [93,94,95]. However, their full-scale deployment in the food industry remains limited due to persisting technical, economic, and regulatory challenges. This section explores the future prospects and challenges of e-nose and e-tongue technologies, focusing on emerging innovations, real-world applications, integration with smart systems, and barriers to commercialization [118,119,120]. One of the most promising advancements in e-nose and e-tongue technology is their integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). AI-driven algorithms can significantly improve the accuracy, sensitivity, and reliability of these devices by refining their pattern recognition capabilities. Traditional pattern recognition techniques, such as principal component analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA), are increasingly being replaced by deep learning models, which enable better classification of complex aroma and taste profiles [96,97,98]. AI-powered e-nose and e-tongue devices have the potential to evolve into self-learning sensors that improve their accuracy over time by continuously updating their databases with new samples. Machine learning models can be used to predict shelf life, detect early signs of spoilage, and monitor fermentation processes based on historical VOC and taste data.
The future of e-nose and e-tongue technology lies in the development of miniaturized, portable, and wearable sensor devices. Advances in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), nanotechnology, and flexible electronics are leading to the development of compact and handheld versions of these systems [98,99,100]. Miniature e-nose and e-tongue devices could be used by food inspectors, manufacturers, and consumers to perform on-site quality analysis in grocery stores, production plants, and restaurants. In addition, future developments may include wearable sensors for taste and smell analysis, such as e-nose sensors embedded in smartwatches or mobile devices, allowing users to assess food freshness prior to consumption. The integration of e-nose and e-tongue technology with IoT platforms is expected to revolutionize food quality monitoring by enabling real-time data collection, cloud storage, and remote analysis [99,100]. IoT-enabled e-nose and e-tongue sensors can be embedded in food packaging to monitor freshness and send alerts to consumers via smartphone applications when spoilage is detected. In the future, food processing plants may use AI-driven cloud platforms to continuously monitor e-nose and e-tongue readings across supply chains, thereby reducing waste and minimizing contamination risks [101,102,103]. E-nose and e-tongue devices could play a crucial role in the development of personalized nutrition by helping consumers tailor their diets based on their sensory preferences and health conditions. E-tongue technology could analyze an individual’s salty, bitter, or sweet taste preferences and recommend dietary choices that align with both their taste perception and nutritional needs [104,105,106]. Advanced e-tongue sensors may also be capable of detecting allergens and toxins in food, providing real-time alerts to individuals with dietary restrictions or allergies. Meanwhile, blockchain technology is increasingly being used to enhance food traceability and transparency. The integration of e-nose, e-tongue, and blockchain technologies could enable manufacturers and regulatory authorities to track food authenticity, freshness, and safety throughout the supply chain [121,122]. E-nose and e-tongue readings could be uploaded to a secure blockchain ledger, ensuring that food authenticity data remain tamper-proof. QR codes linked to blockchain records could allow consumers to verify food quality and origin by scanning packaging labels with their smartphones.
11. Conclusions
The electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) have emerged as innovative technologies for food quality assessment, offering rapid, objective, and non-destructive evaluation of food aroma, taste, freshness, and safety. Inspired by the human olfactory and gustatory systems, these biomimetic devices utilize advanced sensor arrays and data processing techniques to detect volatile and non-volatile compounds, making them valuable tools in the food industry. Both the e-nose and e-tongue have found widespread applications in spoilage detection, adulteration analysis, authenticity verification, and fermentation monitoring across various food and beverage products. With advancements in sensor technology, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and miniaturization, these devices have improved in sensitivity, accuracy, and portability. Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) systems and cloud-based data analytics has further enhanced their potential for real-time food monitoring and quality control. Despite these advantages, challenges such as sensor drift, data standardization, high manufacturing costs, and regulatory acceptance remain obstacles to broader implementation. Ongoing research focuses on addressing these limitations by developing self-calibrating sensors, cost-effective materials, and AI-driven analytical models to improve performance and scalability. With continuous technological advancements, the integration of e-nose and e-tongue systems presents a powerful approach to multi-dimensional food quality assessment. These intelligent sensing technologies are poised to revolutionize food safety, quality assurance, and consumer trust, ensuring a more efficient and reliable food industry in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.V. and B.I.; methodology, G.M.; validation, I.S.K., S.-C.K. and G.M.; resources, B.I.; data curation, G.M.; writing—original draft preparation, R.V.; writing—review and editing, S.-C.K.; visualization, G.M.; supervision, S.-C.K.; project administration, I.S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This project was carried out with the support of the “2024 System Semiconductor Technology Development Support Project” of Chungbuk Technopark.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wilson, A.D. Electronic-Nose Applications in Forensic Science and for Analysis of Food, Beverage, and Environmental Samples. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. Progress in Electronic-Nose Technologies for Environmental Monitoring and Food Safety: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riul, A.; Dantas, C.A.R.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Oliveira, O.N. Recent Advances in Electronic Tongues. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. The Role of Electronic-Nose Technology in Food and Beverage Analysis. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, Y.; Toko, K. Recent Advances in Electronic Tongue Technology for Food Quality and Safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 132, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, D.; Aquino, A.; Effting, L.; Mantovani, A.C.G.; Bona, E.; Conte-Junior, C.A. E-sensing and nanoscale-sensing devices associated with data processing algorithms applied to food quality control: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 6605–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Y. Advances in E-Nose and E-Tongue Sensors for Food Quality Assessment. Sensors 2022, 22, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, M.; Escuder-Gilabert, L. A 21st Century Technique for Food Control: Electronic Noses. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 638, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, F.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Electronic Nose: Current Status and Future Trends. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutfi, A.; Coradeschi, S.; Mani, G.K.; Shankar, P.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Electronic Noses for Food Quality: A Review. J. Food Eng. 2015, 144, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwińska, M.; Wiśniewska, P.; Dymerski, T.; Wardencki, W.; Namieśnik, J. Advances in Electronic Noses and Tongues for Food Authenticity Testing. Adv. Food Authent. Test. 2015, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Development of a Graphene-Based Electronic Tongue for Food Authentication. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Qi, X.; Zhang, X. A Portable Multi-Channel E-Nose for the Detection of Food Spoilage. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.B.; Tudu, B.; Shaw, L.; Jana, A.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Bandyopadhyay, R. Instrumental testing of tea by combining the responses of electronic nose and tongue. J. Food Eng. 2012, 110, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, C.D.; Paolesse, R.; Martinelli, E.; Capuano, R. Solid-State Gas Sensors for Artificial Olfaction. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2506–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Du, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H. Application of an Electronic Tongue in Food Analysis. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L. The qualitative and quantitative assessment of tea quality based on E-nose, E-tongue and E-eye combined with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddi, Z.; Mabrouk, S.; Bougrini, M.; Tahri, K.; Sghaier, K.; Barhoumi, H.; El Bari, N.; Maaref, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Bouchikhi, B. E-Nose and e-Tongue combination for improved recognition of fruit juice samples. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonacci, A.; Scafile, A.; Billeci, L.; Sansone, F. Electronic Nose and Tongue for Assessing Human Microbiota. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zang, M.; Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Li, D.; Li, X. Effect of two types of thermal processing methods on the aroma and taste profiles of three commercial plant-based beef analogues and beef by GC-MS, E-nose, E-tongue, and sensory evaluation. Food Control. 2023, 146, 109551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wan, H.; Zhang, X.; Ha, D.; Wang, P. Electronic Nose and Electronic Tongue. In Bioinspired Smell and Taste Sensors; Wang, P., Liu, Q., Wu, C., Hsia, K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J. Determination of Tea Quality by Electronic Nose. J. Food Eng. 2007, 82, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Niu, M.; Niu, Y. Comparative Study on Volatile Compounds and Taste Components of Different Durian Cultivars Based on GC-MS, UHPLC, HPAEC-PAD, E-Tongue and E-Nose. Molecules 2021, 27, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, D.; Aheto, J.H.; Feng, F.; Duan, T. Integration of a low-cost electronic nose and a voltammetric electronic tongue for red wines identification. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4330–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Mao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, G.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, F.; et al. Characterization of prepared soft-shelled turtle dishes of different pretreatment combined with irradiation based on flavor profiles using E-nose, E-tongue and HS-SPME-GC–MS. Food Chem. X 2025, 27, 102352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, T.; Migoń, D.; Gębicki, J.; Kamysz, W. Critical review of electronic nose and tongue instruments prospects in pharmaceutical analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1077, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L.; De Saja, J.A.; González-Antón, R.; García-Hernández, C.; Medina-Plaza, C.; García-Cabezón, C.; Martín-Pedrosa, F. Electronic Noses and Tongues in Wine Industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 212083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, L. Qualification and quantisation of processed strawberry juice based on electronic nose and tongue. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 60, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Cai, Y.; Wu, X.; Gai, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, D. Characterization of selected commercially available grilled lamb shashliks based on flavor profiles using GC-MS, GC × GC-TOF-MS, GC-IMS, E-nose and E-tongue combined with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, H.; Lin, L.; Du, X.; Tang, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, H. The qualitative and quantitative assessment of xiaochaihu granules based on e-eye, e-nose, e-tongue and chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 205, 114298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.Y.; Kwak, H.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, O.; Kim, S.S. Comparison of a descriptive analysis and instrumental measurements (electronic nose and electronic tongue) for the sensory profiling of Korean fermented soybean paste (doenjang). J. Sens. Stud. 2017, 32, e12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; Wu, H. Electronic Noses: From Gas-Sensitive Components and Practical Applications to Data Processing. Sensors 2023, 24, 4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munekata, P.E.; Finardi, S.; De Souza, C.K.; Meinert, C.; Pateiro, M.; Hoffmann, T.G.; Domínguez, R.; Bertoli, S.L.; Kumar, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Applications of Electronic Nose, Electronic Eye and Electronic Tongue in Quality, Safety and Shelf Life of Meat and Meat Products: A Review. Sensors 2022, 23, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, Z. Variations in volatile organic compounds in Zhenyuan Daocai samples at different storage durations evaluated using E-nose, E-tongue, gas chromatography, and spectrometry. LWT 2022, 173, 114186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvova, L.; Jahatspanian, I.; Mattoso, L.H.; Correa, D.S.; Oleneva, E.; Legin, A.; Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R. Potentiometric E-Tongue System for Geosmin/Isoborneol Presence Monitoring in Drinkable Water. Sensors 2019, 20, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Weng, X.; Chang, Z. Development of an electronic nose to characterize water quality parameters and odor concentration of wastewater emitted from different phases in a wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Hu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Influence of Different Shaping Techniques on the Aroma Quality and Volatile Metabolites of Green Tea Revealed by Gas Chromatography Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2024, 14, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Han, L.; Zhou, X. Sensor Fusion in E-Nose and E-Tongue Systems for Enhanced Accuracy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 381, 133289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibaduiza, D.; Anaya, M.; Gómez, J.; Sarmiento, J.; Perez, M.; Lara, C.; Ruiz, J.; Osorio, N.; Rodriguez, K.; Hernandez, I. Electronic Tongues and Noses: A General Overview. Biosensors 2024, 14, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, S.; Benedetti, S.; Scampicchio, M.; Pangerod, E. Characterization and classification of Italian Barbera wines by using an electronic nose and an amperometric electronic tongue. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 525, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D.; Baietto, M. Applications of E-Nose Technology in Food Industry. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 76, 103067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, S.; Buratti, S.; Spinardi, A.; Mannino, S.; Mignani, I. Electronic nose as a non-destructive tool to characterise peach cultivars and to monitor their ripening stage during shelf-life. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2008, 47, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti, M.; Apetrei, C.; Lozano, J.; Anyogu, A. Electronic Noses and Tongues: Beyond Human Senses. Biosensors 2019, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Ali, M.; Hashim, N.; Abd Aziz, S.; Lasekan, O. Principles and recent advances in electronic nose for quality inspection of agricultural and food products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. Application of Electronic-Nose Technologies and VOC-Biomarkers for the Noninvasive Early Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Sensors 2018, 18, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti, M.; Apetrei, C.; Lozano, J.; Anyogu, A. Potential use of electronic noses, electronic tongues and biosensors as multisensor systems for spoilage examination in foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; González, A.; Díaz, C. Development of a Miniaturized E-Nose for Real-Time Food Spoilage Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 382, 133315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrieli, G.; Muszynski, M.; Ruch, P. Electronic noses and tongues: Current trends and future needs. Digit. Sens. Sci. 2022, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrini, M.; Tahri, K.; Haddi, Z.; El Bari, N.; Llobet, E.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Bouchikhi, B. Aging time and brand determination of pasteurized milk using a multisensor e-nose combined with a voltammetric e-tongue. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 45, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yang, L.; Peng, W.; Liu, J.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. A Novel Method for the Discrimination of Semen Arecae and Its Processed Products by Using Computer Vision, Electronic Nose, and Electronic Tongue. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2015, 753942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Hu, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, D.; Tian, S. Electronic tongue and electronic nose for food quality and safety. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Li, T.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhang, Z. Estimation of Congou black tea quality by an electronic tongue technology combined with multivariate analysis. Microchem. J. 2021, 163, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Hong, X.; Han, X.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Liu, N.; Gao, X.; et al. Taste Masking Study Based on an Electronic Tongue: The Formulation Design of 3D Printed Levetiracetam Instant-Dissolving Tablets. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qian, J.; Adil, M.; Bi, Y.; Wu, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W. Bioinspired integrated triboelectric electronic tongue. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2024, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, N.; Ariño, C.; Esteban, M.; Manuel, J. Voltammetric Electronic Tongues in Food Analysis. Sensors 2018, 19, 4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binson, V.A.; George, M.M.; Sibichan, M.A.; Raj, M.; Prasad, K. Freshness Evaluation of Beef using MOS Based E-Nose. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things (IDCIoT), Bengaluru, India, 5–7 January 2023; pp. 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yu, W.; Liu, P. Electronic Tongue for Tea Quality and Flavor Evaluation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, R.; Li, M. Evaluation of Freshness in Fish Using an E-Nose System. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Artificial Intelligence for Food Quality Assessment: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, J.; Kvaal, K. Electronic nose and artificial neural network. Meat Sci. 1997, 49, S273–S286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, Y.; Toko, K. Electronic Tongues—A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3001–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, T.; Caro, I.; García-González, D.L. Identification of Olive Oil Authenticity Using an E-Nose System. Foods 2023, 12, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Monitoring the Fermentation Process of Beer with an Electronic Tongue. J. Inst. Brew. 2013, 119, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, P.; Palacios, O.; Marín, L. Next-Generation E-Nose and E-Tongue Technologies for Food Authentication. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, R.; Lu, Z. Portable E-Nose for Dairy Quality Monitoring: A Comparative Study with GC-MS. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J. Hybrid Sensor Arrays for Multi-Component Analysis in Food E-Nose Applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 368, 132037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winquist, F.; Bjorklund, R.; Krantz-Rülcker, C.; Lundström, I.; Östergren, K.; Skoglund, T. An electronic tongue in the dairy industry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 111–112, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, P.; Robinson, J.; Geevaretnam, J.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Development of electronic nose (Shrimp-Nose) for the determination of perishable quality and shelf-life of cultured Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus Vannamei). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 317, 128192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Cho, H. Development of an Electronic Tongue System for the Evaluation of Korean Fermented Sauces. Sensors 2023, 23, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagin, M.; Winquist, F. Electronic noses and tongues in food safety assurance. High Throughput Screen. Food Saf. Assess. 2014, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrei, C. Voltammetric Electronic Tongue for the Detection of Adulterated Olive Oils. Sensors 2023, 23, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balivo, A.; Cipolletta, S.; Tudisco, R.; Iommelli, P.; Sacchi, R.; Genovese, A. Electronic Nose Analysis to Detect Milk Obtained from Pasture-Raised Goats. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Verma, A.; Sharma, S. Smart Nanosensor Arrays for Beer Freshness Detection Using Electronic Nose. Food Chem. 2022, 381, 132356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Benedetti, S.; Magnani, L.; Pianezzola, A.; Buratti, S. Seafood freshness: E-nose data for classification purposes. Food Control 2022, 138, 108994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J. A Paper-Based Electronic Nose for On-Site Spoilage Detection in Fruit. Sensors 2023, 23, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Haque, F.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.J.; Seo, J.H.; Mativenga, M.; Walker, B. Practical organic electronic noses using semi-permeable polymer membranes. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 37, 102137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wu, H. Real-Time Quality Monitoring of Fresh Meat Using an AI-Assisted E-Nose. Food Control 2022, 141, 109206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, P.; Suárez, J.I.; Lozano, J. Triangular Test of Amanita Mushrooms by Using Electronic Nose and Sensory Panel. Foods 2019, 8, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, M.A.; García, P.; Pérez, F. Enhancing Food Authentication with Sensor Fusion: Integration of E-Nose and E-Tongue Systems. Foods 2023, 12, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Ma, R.; Zhang, W. Machine Learning for Odor Recognition Using an E-Nose. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Hu, Y. Electrochemical Tongue Based on Enzyme-Modified Electrodes for Beverage Authentication. Food Chem. 2023, 396, 133877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrei, C.; Apetrei, I.M. Voltammetric Electronic Tongue for the Detection of Milk Adulteration. Sensors 2022, 22, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yin, X.; Huo, X.; Zhao, X.; Wu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J. Development of a colorimetric sensor array with weighted RGB strategy for quality differentiation of Anji white tea. J. Food Eng. 2025, 391, 112458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H. Wireless Sensor Network-Based E-Nose for Real-Time Fruit Ripeness Detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, L.F.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Chocolate Classification by an Electronic Nose with Pressure Controlled Generated Stimulation. Sensors 2016, 16, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, L. E-Nose Coupled with Chemometrics for Cheese Aroma Profiling. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, J. Hybrid Electronic Tongue for Snack Food Flavor Analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seesaard, T.; Wongchoosuk, C. Recent Progress in Electronic Noses for Fermented Foods and Beverages Applications. Fermentation 2022, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, L.; He, W.; Cao, C.; Song, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Su, G. Aggregates from the concentration process for soybean protein isolate hydrolysates: Impacts, characteristics and preventive strategies. LWT 2023, 186, 115129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.J. Nanotechnology mediated intelligent and improved food packaging. Int. Nano Lett. 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Q. Voltammetric Electronic Tongue for Acidity Estimation in Vinegar. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Sun, X.; Lin, W. Colorimetric Sensor Array-Based E-Nose for Green Tea Quality Discrimination. Sensors 2023, 23, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagin, M.Y.; Eriksson, M.; Winquist, F. Drinking Water Analysis Using Electronic Tongues. Electron. Noses Tongues Food Sci. 2015, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrei, C.; De Saja, J.A. SAW Sensor-Based Electronic Nose for Nut Classification. Sensors 2023, 23, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tahara, Y.; Yatabe, R.; Toko, K. Taste Sensor: Electronic Tongue with Lipid Membranes. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, P.; Yang, M. Optical Electronic Nose for Detecting Herbal Tea Volatiles. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Hai, N.; Guo, P.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, H.; Ding, L. Characteristics of Umami Taste of Soy Sauce Using Electronic Tongue, Amino Acid Analyzer, and MALDI−TOF MS. Foods 2023, 13, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, L. Multi-Sensor E-Nose for Fish Freshness Evaluation with Hybrid Algorithms. Sensors 2023, 23, 3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bett-Garber, K.L.; Watson, M.A.; Lea, J.M.; Bai, J.; Baldwin, E.; Raithore, S. Efficacy of Monitoring the Sensory Taste Characteristics in Pomegranate Juice with Electronic Tongue and Chemical Measurements. J. Food Qual. 2014, 37, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Riemenschneider, L.; Panes-Ruiz, L.A.; Ibarlucea, B.; Cuniberti, G. Discrimination of Complex Mixtures Using Carbon Nanotubes-based Multichannel Electronic Nose: Coffee Aromas. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Nanotechnology Materials and Devices Conference (NMDC), Paestum, Italy, 22–25 October 2023; pp. 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L. Sugar Quantification in Juices Using Voltammetric Electronic Tongue. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnaghi, L.R.; Capone, F.; Zanoni, C.; Alberti, G.; Quadrelli, P.; Biesuz, R. Colorimetric Sensor Array for Monitoring, Modelling and Comparing Spoilage Processes of Different Meat and Fish Foods. Foods 2020, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podrażka, M.; Bączyńska, E.; Kundys, M.; Jeleń, P.S.; Witkowska Nery, E. Electronic Tongue—A Tool for All Tastes? Biosensors 2018, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Huang, H. Flexible Gas Sensor Array for VOC Detection in Packaged Fish. Sensors 2023, 23, 6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, C.W.; Park, S.; Choi, S.; Park, S.H.; Nam, G.B.; Ryu, J.; Eom, T.H.; Kim, B.; Kim, C.; et al. MXene-based high performance microfluidic pH sensors for electronic tongue. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 409, 135636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Yadav, B.K. Electronic nose for detection of food adulteration: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 846–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y. Electronic nose and its application in the food industry: A review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2024, 250, 21–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, M.; Adhikari, B. Advances of electronic nose and its application in fresh foods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2700–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliszczyńska-Świgło, A.; Chmielewski, J. Electronic Nose as a Tool for Monitoring the Authenticity of Food. A Review. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1800–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, A.R.; Leone, F.; Cheli, F.; Chiofalo, V. Fusion of electronic nose, electronic tongue and computer vision for animal source food authentication and quality assessment—A review. J. Food Eng. 2017, 210, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Adhikari, B. Application of electronic tongue for fresh foods quality evaluation: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 746–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Xu, J. Applications of electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) in food quality-related properties determination: A review. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2019, 4, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvini, R.; Pigani, L. Toward the Development of Combined Artificial Sensing Systems for Food Quality Evaluation: A Review on the Application of Data Fusion of Electronic Noses, Electronic Tongues and Electronic Eyes. Sensors 2021, 22, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaraj, R.; Arumugam, B.; Mayakrishnan, G.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, S.C. A Review on Electrospun Nanofiber Composites for an Efficient Electrochemical Sensor Applications. Sensors 2022, 23, 6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, V.; Kamachiyappan, P.; Manjunath, R.; Balamurugan, S.; Ashokkumar, A.; Ashraf Ali, M.; Kim, S. Simple chalcone-based chemosensor for colorimetric naked-eye detection of Al3+ and Cu2+ ions. Opt. Mater. 2021, 123, 111881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaraj, R.; Periyannan, J.; Mayakrishnan, G.; Kim, S.C.; Muniyandi, M. Surface modified and advanced magnetoelastic sensors for biomedical application. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 48, 104247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, B.; Bo, T.; Zhang, J.; Fan, S.; Yang, Y. Comparative analysis of flavor characteristics of two rounds of Qingxiangxing Baijiu by GC×GC-TOFMS, HS-GC-IMS, GC-E-nose and E-tongue. Food Biosci. 2024, 63, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayinbate, B.; Yang, L.; Badar, I.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Xu, B. Characterization of flavor profile of beef jerky from different regions of China using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, electronic tongue, and electronic nose. Food Chem. X 2024, 25, 102245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kh, A.A.; Mi, S.; Tian, H.; Xu, X.; Abdo, A.A.A.; Aleryani, H.; Wang, X. Evaluation of flavor characteristics in Chinese wheat flour paste using electronic-nose, electronic-tongue, and headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry at different fermentation stages. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 2454–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, M.; Rudy, M.; Stanisławczyk, R. Electronic Sensing Technologies in Food Quality Assessment: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 15, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Sun, L.; Li, M.; Zhu, Y.; Deng, W.; Yu, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, Z. Investigating flavor and quality characteristics in Chinese bacon from different regions using integrated GC-IMS, electronic sensory assessment, and sensory analysis. Meat Sci. 2025, 220, 109709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, A.; Lei, Y.; Pan, G. Data augmentation of flavor information for electronic nose and electronic tongue: An olfactory-taste synesthesia model combined with multiblock reconstruction method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 272, 126810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).