Abstract
Moringa oleifera leaves (MOLs) have gained significant attention due to their nutritional and biological activity. Therefore, this study aimed to examine its flavor characteristics and underlying compositions. In this study, we used ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), electronic nose, electronic tongue, and molecular docking to comprehensively investigate the chemical properties and flavor profiles of MOLs. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and GC-MS were instrumental in identifying the 20 non-volatile and 19 volatile constituents of MOLs, respectively. The electronic nose and electronic tongue systems provided an objective evaluation of the sweet, bitter, and spicy attributes and flavor characteristics of MOLs. Concurrently, molecular docking was employed to elucidate the material basis of flavor profiles. It revealed that glucosinolates and flavonoids are probably the key components for the bitter taste of MOLs. The sweet taste may be attributed to glucosinolates and flavonoids. The spicy scent appears to be linked to the presence of glucosinolates and alkaloids. The integration of these techniques confers a thorough understanding of the chemical composition and sensory properties of MOLs. These findings have significant implications for innovative applications in the food industry as well as pharmaceuticals and agriculture sectors; furthermore, they contribute towards enhancing the perception of Moringa oleifera as a valuable natural resource.
1. Introduction
Moringa oleifera, commonly known as the drumstick tree, is a expeditiously growing, drought-resistant tree species native to the Indian subcontinent [1]. Its leaves, seeds, and flowers have been traditionally used for nutritional and medicinal purposes due to their high content of bioactive compounds, such as vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytochemicals [2]. In addition, Moringa oleifera leaves (MOLs) exhibit a broad spectrum of pharmacological activities, including antioxidant potentiality, anticancer efficacy, antidiabetic properties, hepatoprotective effects against liver damage, antiobesity attributes along with antimicrobial activity against pathogens. Additionally, they possess anti-inflammatory characteristics while modulating immune responses and conferring cardioprotection [3,4].
Recent years have witnessed a growing interest in the investigation of the biological activity [5,6] and nutritional value [7,8,9] of MOLs. Flavor constitutes a distinctive sensory characteristic of food and is pivotal in assessing its nutritional value [10]. The chemical composition forms the fundamental basis for bioactivity [11]. Thus, elucidating the chemical compositions and flavor characteristics of MOLs is of great value for these studies and holds considerable relevance for potential applications in the food [12,13], pharmaceutical [14,15], agricultural [16,17], animal husbandry [18,19], and advanced material industries [20,21].
To obtain a comprehensive understanding of the chemical properties and flavor profiles of MOLs, multiple analytical techniques are often necessary [22]. The commonly employed techniques in such investigations encompass ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF/MS) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). UPLC-Q-TOF-MS facilitates the identification and quantification of a diverse array of compounds within the sample [23], while GC-MS enables the analysis of volatile constituents, which significantly contribute to the odor and taste profiles [24]. The UPLC-Q-Orbitrap-MS analysis revealed a total of 39 compounds, and the contents of acetyl-glucomoringin, caffeoylquinic acid, feruloylquinic acid, and coumarylquinic acid were high [25]. A total of 42 compounds were characterized by UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap-MS, encompassing phenolic acids, flavonoids, isothiocyanates, nucleosides, alkaloids, and additional compounds [26]. An electronic nose (E-nose) and electronic tongue (E-tongue) simulate the olfactory and gustatory senses, thereby furnishing valuable data pertaining to the odor, taste, and general quality of the sample. For example, utilizing the electronic tongue technology, a study determined the bitterness of Andrographis Herba and identified the key bitter compounds [27]. Also, a study employed an electronic nose and tongue to discern the bitterness and astringency in green tea, demonstrating that an optimized sensor array in conjunction with a backpropagation neural network model can effectively predict taste attributes, thereby providing a viable and reliable method for the rapid assessment of green tea’s flavor profile [28]. These technologies have proven to be very effective in improving the assessment of food quality compared to conventional methods [29]. Furthermore, employing molecular docking technology enables investigation into the interaction between chemical ligands and olfactory and taste receptor proteins, thereby elucidating the underlying basis of MOLs’ odor and taste [30,31,32].
In the current study, we employed a comprehensive approach combining UPLC-Q-TOF-MS, GC-MS, electronic nose, electronic tongue, and molecular docking to investigate the chemical properties and flavor profiles of MOLs (the technical roadmap, as shown in Figure S1). The results provide a thorough comprehension of flavor attributes and the material basis of MOLs, thereby representing the first objective and systematic exploration of the flavor characteristics of Moringa oleifera leaves using modern technologies. These findings offer valuable insights that can potentially contribute to the development of functional food and healthcare products in the future.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
The Indian species (YD), improved Indian species (PKM1), improved PKM1 species (PKM2), and Honghe No.1 species (HH) were purchased from Yunnan Kunbaitang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Kunming, Yunnan, China), Yunnan Tianyou Technology Development Co., Ltd. (Dehong, Yunnan, China), Yunnan Qidao Agricultural Science and Technology Development Co., Ltd. (Kunming, Yunnan, China), and Red River Valley Moringa Industry Co., Ltd. (Kunming, Yunnan, China), respectively. The medicinal material was identified as MOLs by Professor Yang Bin, Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences. The samples were stored in sealed bags after being dried and stored at −20 °C before analysis.
Thirty-seven representative medicinal materials were selected from the 2020 edition of Chinese Pharmacopoeia, including 8 kinds of sour medicinal materials (Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus, Chebulae Fructus, Portulacae Herba, Chaenomelis Fructus, Schisandrae Sphenantherae Fructus, Crataegi Fructus, Corni Fructus, Mume Fructus), 10 kinds of bitter herbs (Scutellariae Radix, Isatidis Radix, Rhei Radix et Rhizoma, Sophorae Tonkinensis Radix et Rhizoma, Magnoliae Officinalis Cortex, Isatidis Folium, Aloe, Sophorae Flavescentis Radix, Coptidis Rhizoma, Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex), 9 kinds of sweet herbs (Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma, Codonopsis Radix, Phragmitis Rhizoma, Polygonati Odorati Rhizoma, Sennae Folium, Cannabis Fructus, Stellariae Radix, Astragali Radix, Ionicerae Japonicae Flos), 5 kinds of spicy medicinal materials (Sinapis Semen, Chuanxiong Rhizoma, Angelicae Dahuricae Radix, Raphani Semen, Descurainiae Semen Lepidii Semen), and 5 kinds of salty medicinal materials (Sinapis Semen, Chuanxiong Rhizoma, Angelicae Dahuricae Radix, Raphani Semen, Descurainiae Semen Lepidii Semen). Also, 15 kinds of spicy flavor and their representative medicinal materials were selected, including 5 kinds of spicy medicinal materials (Sinapis Semen, Angelicae Dahuricae Radix, Chuanxiong Rhizoma, Asari Radix et Rhizoma, Perillae Folium), 5 kinds of bitter herbs (Descurainiae Semen Lepidii Semen, Magnoliae Officinalis Cortex, Polygalae Radix, Platycodonis Radix, Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium), and 5 kinds of spicy and sweet herbs (Raphani Semen, Angelicae Sinensis Radix, Cinnamomi Ramulus, Saposhnikoviae Radix, Puerariae Lobatae Radix).
The Corni Fructus, Sophorae Tonkinensis Radix et Rhizoma, and Magnoliae Officinalis Cortex were collected from the Chinese Medicine Resource Center of the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (Beijing, China). Sodium chloride was purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and other medicinal materials were purchased from Beijing Tongrentang Pharmacy (Beijing, China).
2.2. Reagents
Acetonitrile and methanol (HPLC grade) were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Pittsburgh, USA). Formic acid (HPLC grade) and ethyl acetate were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Anhydrous sodium sulfate was purchased from Beijing Chemical Reagent Company (Beijing, China). Reference compounds, including glucomoringin, vicenin-2, vitexin, isoquercitrin, and astragalin, were obtained by Beijing Beiterenkang Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China), Chengdu Pusi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China), Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and Chengdu Cloma Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China).
2.3. Apparatus
Heracles II fast gas phase electronic nose (Alpha M.O.S., Toulouse, France), Astree II electronic tongue (Alpha M.O.S., Toulouse, France), Xevo G2-XS Q-TOF Mass Spectrometer (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA), QP2010 Ultra gas chromatography mass spectrometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), BT-125D electronic balance (Sartorius Scientific Instruments, Goettingen, Germany), SPS 202F electronic balance (Ohaus Corporation, Parsippany, NJ, USA), Alpha-2-4-LD-plus freeze dryer (Martin Christ Osterode, Germany), and Centrifuge 5810R desktop high-speed refrigerated centrifuge (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) were used.
2.4. E-Tongue Analysis
The E-tongue Astree by Alpha MOS, Toulouse, France, was utilized to ascertain the taste of MOLs, featuring seven sensors for sourness, saltiness, umami, sweetness, bitterness, and complex taste, alongside a reference Ag/AgCl electrode. The device operated with a test voltage of −1 to 1 V, a step of 0.2 V, and a sensitivity of 10−4 mol. The waveform employed was a multi-frequency pulse voltammetry with 1 Hz, 10 Hz, and 100 Hz frequencies. Each sample was repeated 7 times. The acquisition time of the electronic tongue sensor in each sample was 120 s, and one data point was collected per second.
For the sample preparation, different medicinal materials were treated with different methods. A total of 16 grams of common medicinal materials were soaked with 200 mL (w/v) deionized water for 30 min. And the sample was boiled for 60 min. The filtrate was collected, diluted to 200 mL, and centrifuged twice at 12,000 rpm in a bench high-speed freezing centrifuge (Centrifuge 5810R, Ebbend Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) for 15 min each time. The supernatant was diluted 4 times with Wahaha purified water to obtain a diluent with a concentration of 20 mg/mL. A total of 4 grams of natrii sulfas sample were dissolved in 200 mL (w/v) boiled pure water to boil for 10 min. The filtrate was collected, diluted to 200 mL, and centrifuged twice at 12,000 rpm in a bench high-speed freezing centrifuge (Centrifuge 5810R, Ebbend Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) for 15 min each time. A total of 4 grams of sodium chloride sample and 200 mL of purified water were stirred and dissolved with a glass rod to obtain a solution with a concentration of 20 mg/mL. These solutions were filtered through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane for electronic tongue analysis.
2.5. E-Nose Analysis
The odor assessment of MOLs was executed with the Heracles II rapid GC-E-Nose system from Alpha M.O.S., Toulouse, France. A 20 mL headspace vial was filled with 1 g of powdered MOL medicine and sealed. For the separation process, two columns with different polarities were applied: the weak polar MXT-5 (20 m × 0.18 mm I.D. × 0.4 μm) (Restek, Bellefonte, PA, USA) and the medium polar MXT-1701 (dimensions identical to MXT-5), both from Restek, USA.
The parameters of the E-nose were set as follows: data acquisition time of 110 s, injection speed of 125 μL/s, injection volume of 3 mL, injection port temperature of 300 °C, injection duration of 29 s, incubation temperature of 50 °C, incubation time of 30 min, oscillator speed of 500 r/min, initial temperature of trap of 50 °C, shunt speed of trap of 10 min, capture duration of 34 s, final temperature of trap of 240 °C, initial column temperature of 50 °C, temperature programming from 2 °C/s to 250 °C, and detector temperature of 260 °C. Each sample was analyzed five times.
2.6. Molecular Docking Study
The three-dimensional structure files of bitter receptor molecules were downloaded in the pdb format from the Bitter Data Bank (http://bitterdb.agri.huji.ac.il/dbbitter.php#recpSearch, accessed on 26 November 2021). The three-dimensional structure files of spicy and sweet receptor molecules were downloaded in the pdb format from the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database (https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/, accessed on 26 November 2021). Subsequently, the Pymol and Discovery Studio 2020 (DS) software was employed to remove the primary ligand from the receptor, retaining only a singular protein chain of the polymeric protein. Finally, the AutoDock Tools (ADT) 1.5.6 software was utilized to eliminate water, hydrogenate, adjust charge, set atomic type structure, and save the file in the pdbqt format.
The three-dimensional structure file of small molecules in the SDF format was searched for in the Pubchem database and converted into the PDB format by the OpenBableGUI 3.1.1 software. The structural formula of the compounds not found in the Pubchem database were drawn with the ChemDraw 19.0 software, saved in the cdxml format, and then converted to the pdb format after Chem3D energy minimization. Then, the small molecules were hydrogenated, charged, and set to ligand, detected rotation key, and set rotation key using the Autodock tools tool, and saved in the pdbqt format.
The semi-flexible molecular docking of the pretreated receptor protein and small molecules was performed using the AutoDock Vina 1.1.2 software. Molecular docking was performed by using small-molecule compounds as ligands and corresponding olfactory taste proteins as receptors to explain the material basis of taste and odor in MOLs. The docking range covered the entire protein. The specific docking receptors, ligands, and corresponding parameters are shown in Table S1. Then, the initially constructed models were imported into the Pymol and Discovery Studio 2020 (DS) software for the visual analysis of two-dimensional interaction relationships and three-dimensional spatial distribution positions.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data obtained from electronic tongue and nose responses were preprocessed using five methods: retention of original data, normal standardization, range normalization, decentralization, and normalization. These methods were applied to mitigate diurnal variations and enhance the discriminative power of the partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA). Notably, normalization against the MOL (PKM1) reference minimized variability, underscoring its utility as a control in distinguishing between intra- and inter-group differences.
Post-normalization, eigenvalues corresponding to the stabilization period of the electronic tongue response (91–120 s, 101–120 s, 111–120 s) and the number of measurements (3–7 times, 4–7 times, 5–7 times) were extracted for the subsequent PLS-DA analysis. The analysis revealed that the 111–120 s interval and 5–7 measurements yielded optimal conditions for discerning medicinal materials, as evidenced by reduced intra-group and increased inter-group variance on the PLS-DA plot.
The data structuring was refined by excluding irrelevant herbs and sensors, taking into account the diverse sensitivities of sensors to specific tastes. Subsequently, a Fisher discriminant analysis was applied to the normalized eigenvalues obtained from the electronic tongue sensors, revealing a taste hierarchy and confirming the absence of sour and salty attributes in MOLs. Consequently, acidic and salty medicinal materials, along with their respective sensors AHS and CTS, were excluded to optimize the data structure and enhance model discriminability.
A discriminant analysis was performed using partial least squares (PLS-DA) with SMICA 14.1 and artificial neural networks (ANNs) in Matlab R2017a. The Fisher discriminant analysis, conducted using SPSS version 23, ensured a rigorous analytical approach.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Chemical Properties Based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and GC-MS
The qualitative identification of non-volatile and volatile components was conducted by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and GC-MS, respectively, according to the method in our previous article [33]. A total of 20 non-volatile and 19 volatile common components were identified in the four varieties of MOLs. The outcomes of this UPLC-Q-TOF-MS study are consistent with the results reported by Coppin et al. [34] and Kashiwada et al. [35], suggesting that the non-volatile constituents of MOLs predominantly consist of flavonoids, with quercetin and kaempferol derivatives being the primary flavonoids detected. Meanwhile, the GC-MS analysis conducted in this study is in concordance with the findings of Al-Ghanayem et al. [36] and Li et al. [37], corroborating that aldehydes and hydrocarbons constitute the majority of volatile compounds in MOLs.
3.2. Taste Analysis Based on E-Tongue by PLS-DA and ANN
The PLS-DA method, which combines partial least squares regression with classification techniques, is widely employed for discriminant analyses. This approach effectively reduces data dimensionality and facilitates the identification of distinctions among different groups [38]. Retention times from sensors of varying polarities were converted to Kovats indices using E-tongue software and matched against the AroChemBase database, establishing these identifiers as independent variables. Peak areas from gas chromatograms served as dependent variables. The outcomes obtained from the electronic tongue analysis demonstrated the presence of three predominant components, with respective contribution rates of 30.6%, 27.1%, and 26.4%. They represent the t [1], t [2], and t [3] axes in Figure 1, respectively. Collectively, these components accounted for an overall cumulative contribution rate of 84.1%, suggesting the establishment of a robust model. Figure 2 shows that the bitter medicinal materials are mainly distributed in the upper right of the figure, while the sweet medicinal materials are distributed in the sitting side of the figure. According to the PLS-DA chart, MOLs are distributed in the middle between bitter and sweet medicinal materials, indicating the taste is sweet and bitter.
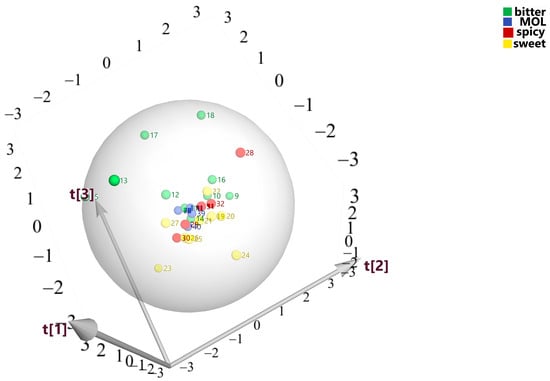
Figure 1.
PLS−DA plot of electronic tongue measurement data. Note: 9 Radix Scutellariae, 10 Radix Isatidis, 11 Radix et Rhizoma Rhei, 12 Radix Sophorae Tonkinensis, 13 Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis, 14 Folium Isatidis, 15 Aloe, 16 Radix Sophorae Flavescentis, 17 Rhizoma Coptidis, 18 Cortex Phellodendri, 19 Radix Glycyrrhizae, 20 Radix Codonopsis, 21 Radix Aloe, 22 Rhizoma Polygoni Multiflori, 23 Folium Sennae, 24 Fructus Cannabis, 25 Radix Bupleuri, 26 Radix Astragali, 27 Flos Lonicerae, 28 Semen Sinapis, 29 Rhizoma Chuanxiong, 30 Radix Angelicae Dahuricae, 31 Semen Raphani, 32 Semen Lepidii, 38 Moringa leaves (PKM1), 39 Moringa leaves (PKM2), 40 Moringa leaves (YD), 41 Moringa leaves (HH).
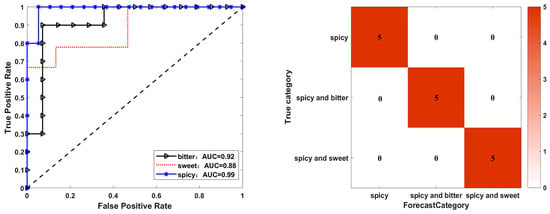
Figure 2.
ROC curve (left) and confusion matrix (right) of the artificial neural network by E-tongue.
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) emulate the brain’s neural architecture to learn from data, offering enhanced generalization and the capacity to model intricate non-linear relationships [39]. The data are imported into the Neural Pattern Recognition toolbox of the software for ANN analysis, with the sensor response value as the input variable and the grouping information as the output variable. An ANN analysis was performed using the Matlab R2017 9.2.0 software. The training set, validation set, and testing set were 70%, 15%, and 15%, respectively. In addition, training function was trainscg, and performance function was crossentropy. The number of hidden layers was three. The evaluation of the E-tongue model revealed an overall accuracy rate of 83.3% for all sets, indicating that the model was robustly established and capable of accurately predicting unknown samples. Additionally, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) values exceeded 0.5, further supporting the model’s effectiveness (see Figure 2). According to the confusion matrix diagram, the true taste of the bitter or sweet herbs was predicted to be bitter and sweet, rather than spicy. The data for MOL were the PKM1 variety (bitterness, 99.93%), PKM2 variety (sweetness, 99.98%), YD variety (sweetness, 100.00%), and HH variety (sweetness, 96.32%). These results suggest that the ANN predicted that the taste of three varieties of MOLs was sweet and the rest was bitter.
3.3. Odor Analysis Based on E-Nose by PLS-DA and ANN
The results of the E-nose show the contribution rates of principal components 1, 2, and 3 were 28.2%, 23.2%, and 23.6%, respectively, with the cumulative contribution rate reaching 75.0%. They represent the t [1], t [2], and t [3] axes in Figure 3, respectively. The results show pungent, pungent-sweet, and pungent-bitter herbs were clustered separately, and MOLs were distributed among the three types of herbs. Therefore, the PLS-DA inferred that the smell of MOLs was spicy.
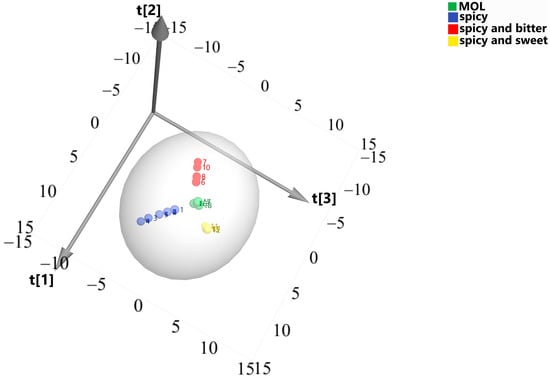
Figure 3.
PLS−DA plot of the electronic nose measurement data. Note: 1 Mustard, 2 Angelica, 3 Chuanxiong, 4 Asarum, 5 Perilla leaves, 6 Tinglizi, 7 Magnolia, 8 Polygala, 9 Platycodon grandiflorum, 10 Tangerine peel, 11 Raphani, 12 Angelica, 13 Cinnamon, 14 Saposhnikovia divaricata, 15 Pueraria, 16 Moringa leaves (PKM1), 17 Moringa leaves (PKM2), 18 Moringa leaves (YD), 19 Moringa leaves (HH).
The evaluation index of the E-nose model showed that the accuracy of all sets was 100% and the AUC was greater than or equal to 0.5, which showed that the model was well established and could predict unknown samples (Figure 4). The data of MOLs were imported as a predictor variable, and the prediction results were the PKM1 varieties (spicy, 89.69%), PKM2 varieties (spicy, 87.44%), YD varieties (spicy, 99.97%), and HH varieties (spicy, 100.00%). These results suggest that the ANN speculated that MOLs may be spicy. These results suggest that the PLS-DA and ANN of the E-tongue and E-nose data could be used for taste and odor analysis of MOLs. These outcomes contribute to a more objective and scientific understanding of the taste and odor properties of MOLs.
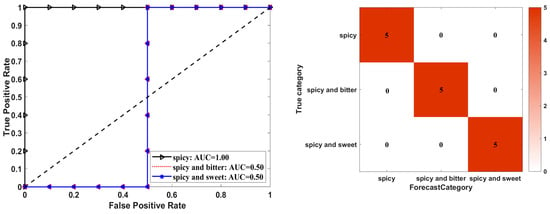
Figure 4.
ROC curve (left) and confusion matrix (right) of the artificial neural network by E-nose.
3.4. Results of Molecular Docking Study
In the docking results, the binding energy represents the affinity between the ligand and the receptor, with a smaller binding free energy indicating a more stable conformation. A binding affinity of less than −5.0 kcal·mol−1 is indicative of favorable binding activity [40]. The results show that, apart from malic acid, which had a strong binding to the T2R10 and T2R38 bitter taste receptors, the other 15 compounds also show strong binding to all three bitter taste proteins (T2R10, T2R14, and T2R38) (Tables S2–S4). This implicates a substantial affinity of these 15 compounds for the bitter taste receptors, potentially underpinning the bitter taste of MOLs. These compounds include a diverse array of alkaloids, glucosinolates, and flavonoids.
In summary, the non-volatile components of MOLs that are likely to bind to the bitter taste receptors T2R10, T2R14, and T2R38 encompass specific compounds such as 4-O-(α-L-acetylrhamnopyranosyloxy)-thioglucoside isomer III, Vicenin-2, isoquercitrin, quercetin acetylglucoside, kaempferol malonyl hexose, and kaempferol-hydroxy-methylglutaryl glucoside. This suggests that glucosinolates and flavonoids could be responsible for the bitterness of these compounds. Similarly, all compounds are found to bind mainly to the larger N-terminal region of the sweet taste protein, with binding energies below or equal to −5.0 kcal/mol. This suggests that the presence of certain substances in MOLs, such as glucosinolates, flavonoids, organic acids, and adenosine, may contribute to their sweet taste properties (Tables S5 and S6, Figure 5). The spicy taste of MOLs, on the other hand, may be due to compounds like glucosinolates, aldehydes, ketones, terpenoids, nitriles, acids, alkanes, and alkaloids (Tables S7 and S8, Figure 5).
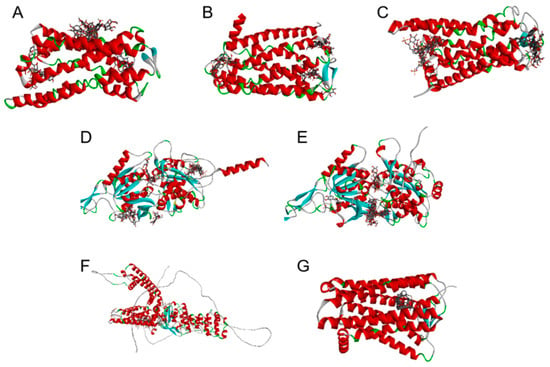
Figure 5.
Molecular docking. Bitter taste proteins: (A) T2R10, (B) T2R14, (C) T2R38. Sweet taste proteins: (D) T1R2, (E) T1R3. Spicy taste proteins: (F) TRPV1, (G) OR7D4.
4. Discussion
According to the results of the electronic nose and electronic tongue combined with chemical composition, the selection of receptor protein molecules in the molecular docking experiment was carried out. The binding of flavor substances to chemical receptors (receptor proteins or ion channels) was a prerequisite for the taste or odor perception [41,42,43]. Building upon the insights gained from electronic tongue and electronic nose analyses, it was hypothesized that MOLs possess sensory attributes encompassing sweetness, bitterness, and spiciness. Consequently, specific olfactory and taste receptors were chosen for molecular docking studies. The sweet taste receptors are known as T1R and have two subtypes, T1R2 and T1R3, which work together to detect sweetness [44]. If either subtype is eliminated, the capacity to perceive sweetness is forfeited. Hence, researchers have directed their attention towards investigating the sweet taste receptors T1R2 and T1R3. Bitter taste receptors are encompassed within the taste receptor family 2 (T2R), with 25 different subtypes. These receptors respond differently to bitter compounds [45]. Glucosinolates are unique to MOLs; so, the T2R38 receptor sensitive to the N–C = S structure was selected. The widely reported broad-spectrum bitter taste receptors T2R10 and T2R14 were also chosen. It has been found that the therapeutic properties of spicy Chinese medicine may be due to their interaction with the TRPV1 channel [46]. Olfactory receptors (OR) belong to GPCR [47], and OR7D4 is considered the target of spicy Chinese medicine. Therefore, TRPV1 and OR7D4 proteins were selected for docking analysis in this study. Prior to the docking process, both receptor and ligand molecules underwent pretreatment procedures. The results of the molecular docking analysis provide insights into the association between the flavor characteristics and chemical components of MOLs. Our findings suggest that the bitter and sweet tastes may be probably associated with various components such as alkaloids and flavonoids. Studies have shown that berberine as an alkaloid could activate the bitter taste responses of enteroendocrine STC-1 cells [48]. In addition, the high glucosinolate content in rocket leaves is associated with increased bitterness and pungency [49]. This further confirms that the bitter taste of MOLs is probably related to the glucosinolates and alkaloid components. However, there was no literature on the dose relationship between bitter or sweet taste and composition. This is worth studying in greater detail in future studies to quantify the medicinal taste of different varieties of MOLs accurately. Because the sample source is different, the composition will be different. This may be due to the variety of moringa leaf source, resulting in differences between the components. Therefore, in order to avoid these situations as much as possible, we should increase the sample collection in the future.
MOLs predominantly comprise flavonoids, polyphenols, phenylpropanoids, terpenoids, steroids, alkaloids, isothiocyanates, and a diverse array of organic acids. These compounds exhibit significant pharmacological activities, such as hypoglycemic and hypouricemic effects, antitumor properties, regulation of blood lipid levels, antioxidant activity, and hepatoprotective effects [50]. Notably, flavonoids, which exhibit an average content of 3%–6%, represent a pivotal functional constituent of MOLs. Most research studies have indicated that flavonoids in MOLs are the primary chemical components associated with its medicinal effects [51]. The molecular docking results reveal that both the sweet and bitter compounds identified in MOLs comprised flavonoids. It is noteworthy that polyphenols in MOLs primarily consist of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Furthermore, quercetin and kaempferol, which are the principal constituents of flavonoids, exhibited robust neuroprotective effects in a cellular experiment [52]. Investigations conducted by Mohamed et al. have demonstrated the potent antimicrobial and anticancer activities of phenolics, hydrocarbons, long-chain fatty acids, alcohols, and esters in MOLs through GC-MS analysis and cell experiments [53]. And in our study, palmitic acid was identified as a volatile component of MOLs through the GC-MS analysis. Additionally, the molecular docking results indicate that palmitic acid serves as the fundamental component contributing to the spicy flavor of MOLs. The findings imply a robust correlation between the flavor attributes of Chinese medicine and its chemical constituents. This discovery offers a novel approach for predicting the pharmacological properties of medicinal substances based on their flavor characteristics. Moreover, these discoveries hold significant value in guiding research on the flavor characteristics and material basis of traditional Chinese medicine.
5. Conclusions
In this research, various techniques were used to study the chemical properties and flavors of Moringa oleifera leaves. Four different varieties of Moringa oleifera were analyzed, revealing the presence of 20 non-volatile and 19 volatile components. The taste profile of Moringa oleifera was determined to be a combination of bitterness and sweetness, accompanied by a predominantly spicy aroma. The molecular analysis further elucidated the specific compounds responsible for these taste and odor characteristics. A thorough understanding of Moringa oleifera’s chemical composition can pave the way for the creation of flavor-enhanced products and the exploration of innovative therapeutic and nutritional applications. Consequently, this research provides valuable insights into the potential utilization of Moringa oleifera in fields such as food science, nutrition, and medicine.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors12090199/s1. Figure S1: Technical roadmap of the main research content; Table S1: Taste receptor protein and ligand information table of molecular docking; Table S2: Binding results of the T2R10 receptor protein with the corresponding ligands; Table S3: Binding results of the T2R14 receptor protein with the corresponding ligands; Table S4: Binding results of the T2R38 receptor protein with the corresponding ligands; Table S5: Binding results of the T1R2 receptor protein with the corresponding ligands; Table S6: Binding results of the T1R3 receptor protein with the corresponding ligands; Table S7: Binding results of the TRPV1 receptor protein with the corresponding ligands; Table S8: Binding results of the OR7D4 receptor protein with the corresponding ligands.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.L.; methodology, M.Z.; software, M.Z., Z.T. and G.W.; validation, M.Z., N.C., Z.T., J.X., L.Y. and G.W.; formal analysis, M.Z., M.G., N.C., Z.T., J.X., L.Y. and G.W.; investigation, M.Z., M.G., N.C., J.X. and L.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z. and M.G.; writing—review and editing, H.L. and B.Y.; supervision, H.L. and B.Y.; project administration, H.L. and B.Y.; funding acquisition, H.L. and B.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (CI2021A04511, CI2023E002 and CI2023E001TS), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82173964), and National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1706106).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to National Key Laboratory of Agro-products Processing, Institute of Food Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science for their instrumental and technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Stohs, S.J.; Hartman, M.J. Review of the Safety and Efficacy of Moringa oleifera. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Tiwari, P.; Sahu, P.; Kumar, S. A review of the phytochemical and pharmacological characteristics of Moringa oleifera. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2018, 10, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonewane, K.; Chouhan, S.S.; Rajan, M.; Chauhan, N.S.; Rout, O.P.; Kumar, A.; Baghel, G.S.; Gupta, P.K. Pharmacological, ethnomedicinal, and evidence-based comparative review of Moringa oleifera Lam. (Shigru) and its potential role in the management of malnutrition in Tribal Regions of India, especially Chhattisgarh. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 8, 314–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyani, W.; Murwanti, R.; Sulaiman, T.N.S.; Hertiani, T. Flavonoid from Moringa oleifera leaves revisited: A review article on in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies of antidiabetic insulin-resistant activity. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2023, 14, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Dong, J.-F.; Lin, Z.-H.; Li, W.; Liu, L.; Hu, S.-L.; Zhang, L.; Lou, W.-Y.; et al. Efficient extraction and excellent activity of flavonoid from Moringa oleifera leaves and its microencapsulation. LWT 2023, 184, 115021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzan, G.; Sacco, A.; Giovannozzi, A.M.; Portesi, C.; Schiavone, C.; Salafranca, J.; Wrona, M.; Nerín, C.; Rossi, A.M. Development of innovative antioxidant food packaging systems based on natural extracts from food industry waste and Moringa oleifera leaves. Food Chem. 2024, 432, 137088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudel, A.; Cohen, R.; Abbo, S.; Kerem, Z. Developing a nutrient-rich and functional wheat bread by incorporating Moringa oleifera leaf powder and gluten. LWT 2023, 187, 115343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsou, K.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Athanasiadis, V.; Bozinou, E.; Rumbos, C.I.; Athanassiou, C.G.; Lalas, S.I. Enhancing the Nutritional Profile of Tenebrio molitor Using the Leaves of Moringa oleifera. Foods 2023, 12, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Tao, L.; Kang, X.-R.; Wang, Z.-L.; Su, L.-Y.; Li, L.-F.; Gu, F.; Zhao, C.-C.; Sheng, J.; Tian, Y. Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves as new raw food material: A review of its nutritional composition, functional properties, and comprehensive application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, D.; Bautista-Baños, S. A review on the use of essential oils for postharvest decay control and maintenance of fruit quality during storage. Crop. Prot. 2014, 64, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Gharat, K.; Kaur, D.; Kasbe, S.; Maroo, K.; Jhangiani, A.; Parulekar, O.; Dhamapurkar, V.; Thakur, K.; Marick, A.; et al. GC-MS Analysis, Thermal Characterization and Biomedical Applications of Essential Oil from Cymbopogon martinii: In vitro Approach. Adv. Res. 2022, 23, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonik, S.K.; Tamanna, S.T.; Happy, T.A.; Haque, M.N.; Islam, S.; Faruque, M.O. Formulation and evaluation of cereal-based breads fortified with natural prebiotics from green banana, moringa leaves powder and soya powder. Appl. Food Res. 2024, 4, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, O.J.; Leitão, A.; Gaspar, M.C.; Vitorino, C.; Sousa, J.J.; de Sousa, H.C.; Braga, M.E.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M. Fortified chocolate mousse with powder and extract from Moringa oleifera leaves for nutritional value improvement. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; An, T.; Lv, B.; Tao, S.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. Moringa oleifera leaf supplementation relieves oxidative stress and regulates intestinal flora to ameliorate polycystic ovary syndrome in letrozole-induced rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 5137–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaza-Hamladji, S.; Benhabyles, N.; Toubal, S.; El Haddad, D.; Bouchenak, O.; Bellalemi, N.; Berrichi, D.; Meziani, I. Flavonoic content and antibacterial evaluation of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves grow in Algeria. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2023, 14, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ibrar, D.; Hasnain, Z.; Nawaz, M.; Rais, A.; Ullah, S.; Gul, S.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Irshad, S. Moringa Leaf Extract Mitigates the Adverse Impacts of Drought and Improves the Yield and Grain Quality of Rice through Enhanced Physiological, Biochemical, and Antioxidant Activities. Plants 2023, 12, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, S.; Saleem, S.; Iqbal, U.; Mahmood, S.; Akhter, M.S.; Akbar, N.; El-Sheikh, M.; Kaushik, P. Moringa olifera leaf extract increases physio-biochemical properties, growth and yield of Pisum sativum grown under salinity stress. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2024, 36, 103056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, M.; Najafi, A.; Sharifi, S.D.; Mohammadi-Sangcheshmeh, A.; Mehr, M.R.-A. Effects of dietary Moringa oleifera leaf extract on semen characteristics, fertility, and hatchability in aged broiler breeder roosters. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, L.; Yu, L.; He, J.; Zhu, K.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, X.; et al. Moringa oleifera leaf improves meat quality by modulating intestinal microbes in white feather broilers. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istiqomah, N.I.; Budianti, S.I.; Cuana, R.; Puspitarum, D.L.; Mahardhika, L.J.; Suharyadi, E. Magnetically separable and reusable Fe3O4/chitosan nanocomposites green synthesized utilizing Moringa oleifera extract for rapid photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, E.K.; Tumbelaka, R.M.; Ardiyanti, H.; Istiqomah, N.I.; Suharyadi, E. Green synthesis of magnetically separable and reusable Fe3O4/Cdots nanocomposites photocatalyst utilizing Moringa oleifera extract and watermelon peel for rapid dye degradation. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2023, 6, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, F.; Sui, X.; Fang, Y.; Tang, X.; Shen, X. Assessment the flavor of soybean meal hydrolyzed with Alcalase enzyme under different hydrolysis conditions by E-nose, E-tongue and HS-SPME-GC–MS. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.-J.; Cao, L.-G.; Tan, D.-P.; Qin, L.; Lu, Y.-L.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Qian, Y.; Bai, C.-J.; Yang, J.-Y.; Ling, H.; et al. UPLC-Q/TOF-MS coupled with multivariate analysis for comparative analysis of metabolomic in Dendrobium nobile from different growth altitudes. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Xie, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Characterization of volatile metabolites in Pu-erh teas with different storage years by combining GC-E-Nose, GC–MS, and GC-IMS. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, L.; Yongliang, Z. UPLC-Q-Orbitrap-MS2 analysis of Moringa oleifera leaf extract and its antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 2090–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, J.; Yu, B.; Ren, C.; Yan, T.; Jia, Y.; He, B. LC-MS/MS-based chemical profiling of water extracts of Moringa oleifera leaves and pharmacokinetics of their major constituents in rat plasma. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, H.; Yu, X.; Luo, H.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Tang, L.; Wang, Z. Determination of Bitterness of Andrographis Herba Based on Electronic Tongue Technology and Discovery of the Key Compounds of Bitter Substances. Molecules 2018, 23, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H. Detection of bitterness and astringency of green tea with different taste by electronic nose and tongue. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Xu, J. Applications of electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) in food quality-related properties determination: A review. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2020, 4, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Meng, R.; Qiao, K.; Cao, B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Electronic tongue, proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry, spectral analysis, and molecular docking characterization for determining the effect of α-amylase on flavor perception. Food Res. Int. 2024, 181, 114078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X. Identification, flavor characteristics and molecular docking of umami taste peptides of Xuanwei ham. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Dou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H. The material basis of bitter constituents in Carbonized Typhae Pollen, based on the integration strategy of constituent analysis, taste sensing system and molecular docking. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 242, 116028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.X.; Li, H.; Chen, N.; Xiang, J.J.; Lin, L.J.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, B. Mechanism of Moringa Folium in Treatment of Constipation Based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and GC-MS and Network Pharmacology. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2022, 28, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, J.P.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Pan, M.-H.; Ho, C.-T.; Juliani, R.; Simon, J.E.; Wu, Q. Determination of flavonoids by LC/MS and anti-inflammatory activity in Moringa oleifera. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1892–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwada, Y.; Ahmed, F.A.; Kurimoto, S.-I.; Kim, S.-Y.; Shibata, H.; Fujioka, T.; Takaishi, Y. New α-glucosides of caffeoyl quinic acid from the leaves of Moringa oleifera Lam. J. Nat. Med. 2011, 66, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghanayem, A.A.; Alhussaini, M.S.; Asad, M.; Joseph, B. Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract Promotes Healing of Infected Wounds in Diabetic Rats: Evidence of Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Proliferative Properties. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Lü, X. Uncovering the effect of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf addition to Fuzhuan Brick Tea on sensory properties, volatile profiles and anti-obesity activity. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 2404–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Meng, L.; Chen, X.; Yuan, L.; Cai, Q.; Shi, W.; Huang, G. Non-parametric partial least squares–discriminant analysis model based on sum of ranking difference algorithm for tea grade identification using electronic tongue data. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 311, 127924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, S.; Cevoli, C.; Fabbri, A.; Alessandrini, L.; Rosa, M.D. Evaluation of Coffee Roasting Degree by Using Electronic Nose and Artificial Neural Network for Off-line Quality Control. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C960–C965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tao, X.; Gao, Y.; Jin, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, W.; Wu, J. Study on the mechanism of Shujin Tongluo granules in treating cervical spondylosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Medicine 2023, 102, e34030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yiasmin, M.N.; Tristanto, N.A.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guan, S.; Wang, Z.; Hua, X. Computational simulations on the taste mechanism of steviol glycosides based on their interactions with receptor proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 255, 128110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Molecular mechanisms of bitterness and astringency in the oral cavity induced by soyasaponin. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Ke, Q.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, E.; Shen, T.; Sun, Z.; Xiao, Z. Unraveling the characteristic chestnut aroma compounds in MeiTanCuiYa green tea and their interaction mechanisms with broad-spectrum olfactory receptors using molecular docking. LWT 2024, 194, 115785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Qu, H.; Mao, C.; Niu, Y. Study on the sweetening mechanism of aroma compounds in yangshan peach using sensory analysis, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation techniques. LWT 2024, 191, 115562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhof, W.; Batram, C.; Kuhn, C.; Brockhoff, A.; Chudoba, E.; Bufe, B.; Appendino, G.; Behrens, M. The Molecular Receptive Ranges of Human TAS2R Bitter Taste Receptors. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaka, A.; Viswanath, V.; Patapoutian, A. Trp Ion Channels and Temperature Sensation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 29, 135–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Xie, J.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Z. How functional foods play critical roles in human health. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2012, 1, 26–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liang, J.; Gu, F.; Du, D.S.; Chen, F.X. Berberine activates bitter taste responses of enteroendocrine STC-1 cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 447, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.H.; Lee, O.N.; Park, H.Y.; Ku, K.-M. Seasonal Effects of Glucosinolate and Sugar Content Determine the Pungency of Small-Type (Altari) Radishes (Raphanus sativus L.). Plants 2022, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Hu, Q.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Moringa oleifera leaves. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2021, 52, 4422–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.L.; Xu, Y.-B.; Wu, J.-L.; Li, N.; Guo, M.-Q. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of Moringa oleifera leaves and their functional chemical constituents. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, S.; Serrano, C.; Li, L.; Sun, B. Characterization, Large-Scale HSCCC Separation and Neuroprotective Effects of Polyphenols from Moringa oleifera Leaves. Molecules 2022, 27, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, M.; Mohamed, M.F.; Elhalwagi, A.; El-Itriby, H.A.; Shawki, H.H.; Abdelhamid, I.A. Moringa peregrina Leaves Extracts Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2698570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).