Abstract
The Space Solar Power Station/Satellite (SSPS) is a large-scale space-borne facility intended for the direct collection and conversion of solar energy in the extra-stratospheric region. The optimization of its light collection and conversion (LCC) structures, analysis of dynamic characteristics, and design of attitude control systems represent core technical bottlenecks impeding the advancement of SSPS. To address these issues, this study investigates a novel conceptual line-focusing SSPS. Firstly, a multi-objective collaborative optimization model is developed to optimize the structural parameters of the concentrator and photovoltaic (PV) array. Subsequently, based on the optimized parameters, a coupled multi-body dynamic model is formulated, incorporating gravity-gradient torque and other space-borne disturbance factors. Finally, a distributed Proportional–Integral–Derivative (PID) controller is proposed to achieve three-axis attitude stabilization of the SSPS. Simulation results demonstrate that the light collection efficiency achieves 81.9% with a power density of 4792.24 W/m2; concurrently, a balance between the geometric parameters of the LCC system and the aforementioned key performance indicators is attained, and the proposed controller possesses favorable anti-disturbance performance.
1. Introduction
The Space Solar Power Station/Satellite (SSPS) is an ultra-large-scale energy solution that directly collects and converts sunlight in space, and then transmits it to receiving targets via wireless energy carriers [1]. On one hand, solar irradiance in space reaches up to 1367 W/m2—ten times that of terrestrial solar energy—and remains unaffected by factors such as day-night cycles and weather conditions, making it a promising candidate for providing foundational energy to Earth [2]. On the other hand, utilizing SSPS could revolutionize the economical and convenient provision of energy for future space equipment, e.g., delivering continuous power support to satellite platforms and mobile space objects [3,4,5].
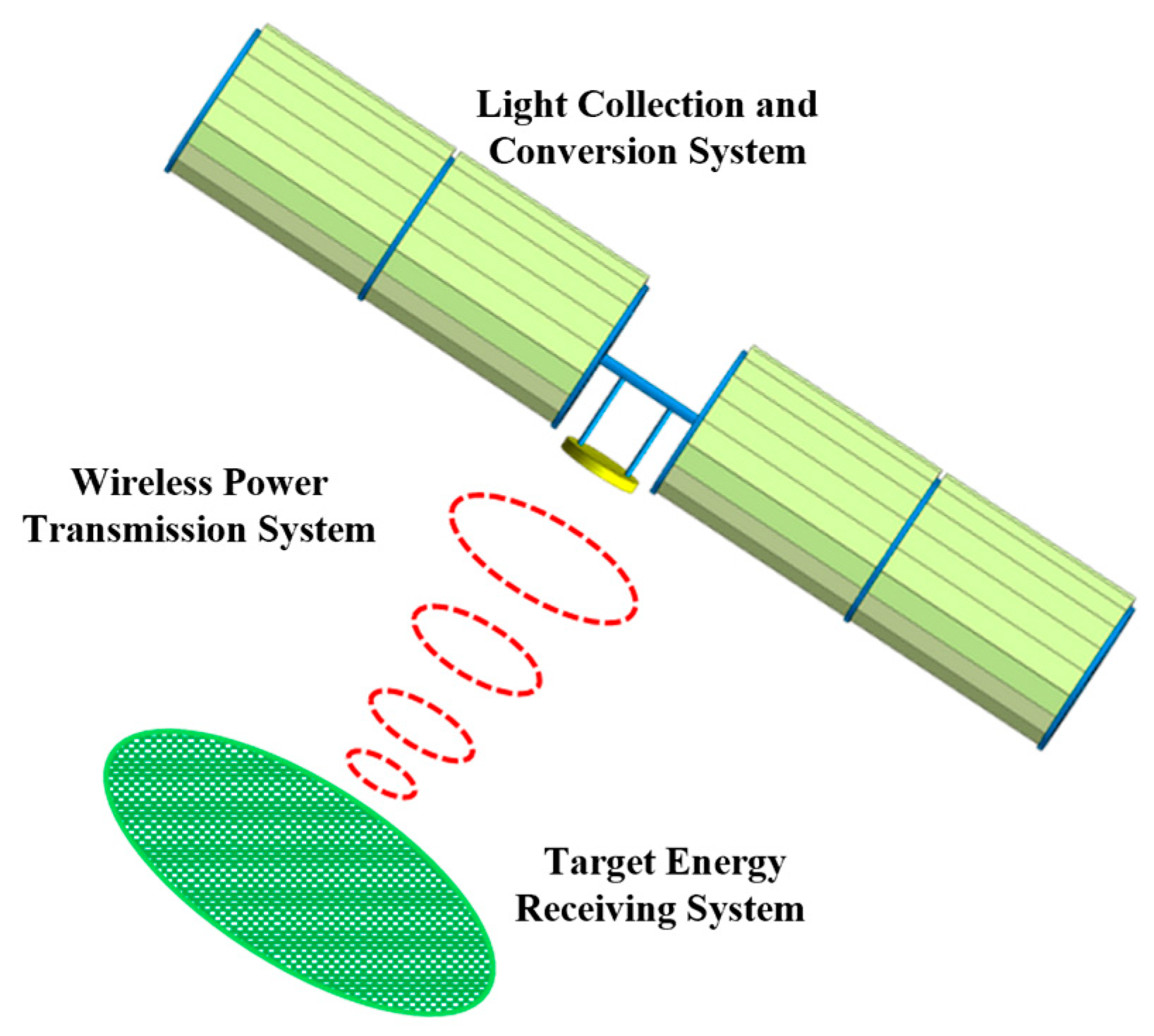
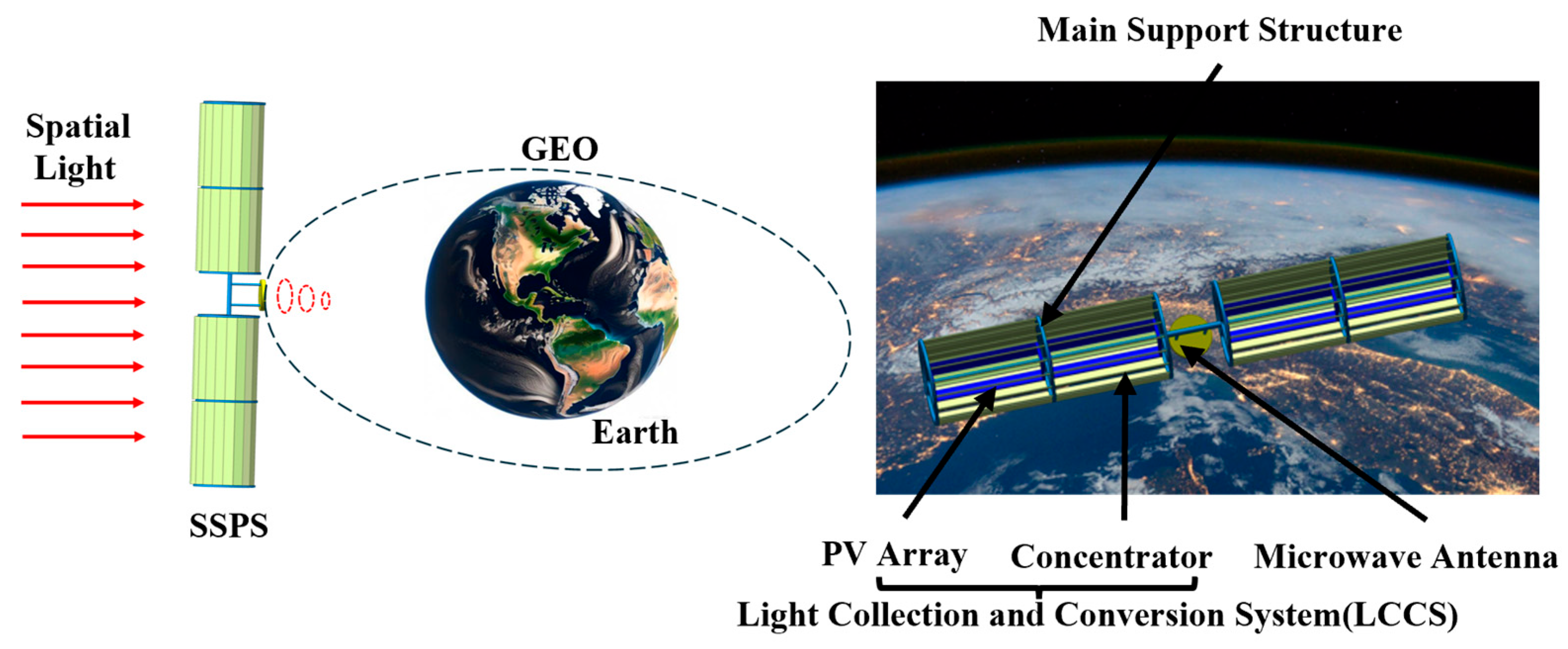
As shown in Figure 1, an SSPS comprises three subsystems: the Light Collection and Conversion (LCC) system, Microwave Power Transmission (MPT) system, and Target Energy Receiving (TER) system. As the front-end subsystem, the LCC system can achieve gigawatt-level power output and kilometer-scale dimensions (far exceeding those of current spacecraft), and it directly determines the energy transmission efficiency and scale of the SSPS. SSPS can be categorized into concentrating and non-concentrating types [6]. The concentrating type has become the current research focus due to its smaller photovoltaic (PV) array area and higher energy conversion efficiency. Since Glaser proposed the SSPS concept in 1968 [7], various configurations have been developed, including concentrating ones such as the Integrated Symmetrical Concentrator (ISC) proposed by NASA, the Solar Tower scheme, and the ALPHA system designed by the Artemis team [8,9,10]. However, some of these configurations are limited by complex tracking mechanisms, excessive mass, and low conversion efficiency. In recent years, Chinese schemes—such as the Orb-shape Membrane Energy Gathering Array (OMEGA) SSPS [11] and the Multi-Rotary Joint SSPS (MR-SSPS) [12]—have achieved breakthroughs in control degrees of freedom and system reliability. Nevertheless, optimizing collection efficiency and lightweight design at the gigawatt scale still requires further research [13]. Yang et al. [14,15] noted that the collaborative optimization of concentrators and PV arrays is key to overcoming efficiency limitations, but most existing studies focus on a single optimization objective. Additionally, the sun-tracking requirement for the LCC system and Earth-pointing requirement for the antenna increase the complexity of configuration optimization and dynamic analysis.
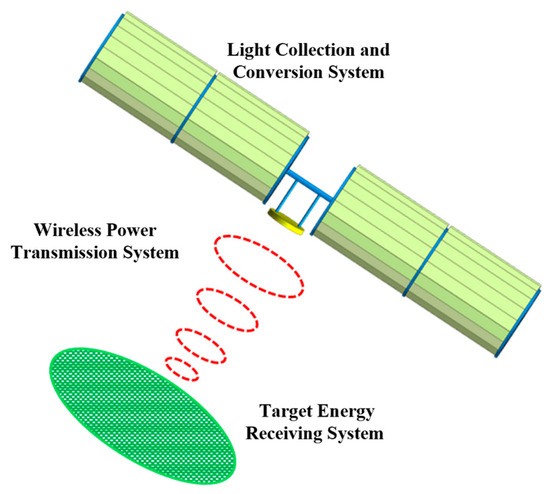
Figure 1.
SSPS Structure and energy transmission link.
The large scale of the SSPS gives rise to distinct dynamic challenges, especially in multi-body and rigid-flexible coupling scenarios [16]. In terms of multi-body coupling, the MR-SSPS—featuring a hundred-meter central truss and multiple large solar sub-arrays [17]—experiences significant attitude coupling effects due to relative subsystem motions, while the time-varying characteristics of gravity-gradient torques and solar radiation pressure further exacerbate control difficulties [18]. In the OMEGA system [19,20], large-scale rotation of PV arrays induces residual gravity-gradient torques in the pitch direction, leading to periodic attitude oscillations within ±0.018°. In rigid-flexible coupling research, Li et al. [21] pointed out that vibrations of large flexible appendages notably alter system dynamic responses, which traditional simplified models cannot accurately capture. To address this issue, Li and his team studied large sun-facing beam structures, exploring gravity-gradient-induced steady deformations and vibrations with geometric nonlinearity considered [22]. The modeling techniques for flexible space structures have evolved into a relatively mature system. Core methodologies include: (1) the Finite Element Method (FEM), which supports procedural modeling and integration with commercial software but faces computational bottlenecks when analyzing ultra-large-scale structures [23,24]; (2) the Absolute Nodal Coordinate Formulation (ANCF), which excels at describing large deformations and rigid-flexible coupling, yet suffers from reduced computational efficiency due to the strong nonlinearity of its stiffness matrices [25,26]; (3) the Floating Frame of Reference Formulation (FFRF), which couples absolute coordinates with local deformation coordinates to balance accuracy and efficiency, and has been applied to the multibody dynamic modeling of megawatt-class SSPS [27,28]; and (4) Structure-Preserving Methods, based on Hamiltonian mechanics to retain the intrinsic properties of the system, though they present greater difficulty in handling complex boundary conditions [29,30].
Given the ultra-large-scale flexible structural characteristics of SSPS, the coupling problems induced by appendage vibrations during attitude maneuvers are particularly pronounced. Transient dynamic excitations generated during attitude adjustments can trigger sustained vibrations in flexible components such as concentrator membranes and photovoltaic array substrates. This not only degrades the pointing accuracy of the light collection and conversion system and induces fatigue damage at structural joints but may also interfere with the stability of microwave power transmission. Within the field of vibration suppression for large flexible space structures, typical mitigation strategies are available. Passive control achieves energy dissipation through material constitutive properties or structural design, exemplified by damping solutions combining piezoelectric stacks with shunt circuits [31] and multi-layered viscous laminated structures based on superelastic shape memory alloys (SMA) [32]. Active control, in contrast, realizes vibration cancelation through a sensor-actuator closed loop, with typical techniques including filtered PID control and Positive Position Feedback (PPF) control [33]. Regarding control methodologies, beyond the aforementioned passive and active vibration suppression techniques, other approaches include centralized adaptive control, sliding mode control, and distributed control. Centralized adaptive control offers strong robustness but involves high computational complexity; sliding mode control provides fast response but is plagued by chattering issues; and distributed control can reduce communication burdens but has often been focused on single control objectives [34].
To achieve high collection efficiency and high-precision attitude control, this paper focuses on a novel linear-focusing SSPS configuration. Firstly, by collaboratively optimizing the geometric parameters of concentrators and PV arrays, both light collection efficiency and structural lightweighting are improved. Secondly, a multi-body dynamics model is constructed, with emphasis on deriving the time-varying expression of the gravitational gradient torque. Finally, the design of a distributed PID control strategy has achieved both the three-axis stability of the SSPS and the high-precision coordinated control of the LCC system (for solar tracking) and the microwave antenna (for ground-pointing).
2. Structural Characteristic of the LCC System
This section first establishes the geometric models of the concentrator and PV array. A collaborative optimization model is then constructed, with the objectives of maximizing light collection efficiency and power–area ratio. The Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm is used to solve the model, yielding the optimal number of concentrator segments and control point coordinates of the PV array. Based on the optimization results, the dynamic parameters of the concentrator are calculated. Finally, an overall gigawatt (GW)-scale SSPS scheme is established, and the corresponding dynamic parameters are derived.
2.1. Geometric Configuration
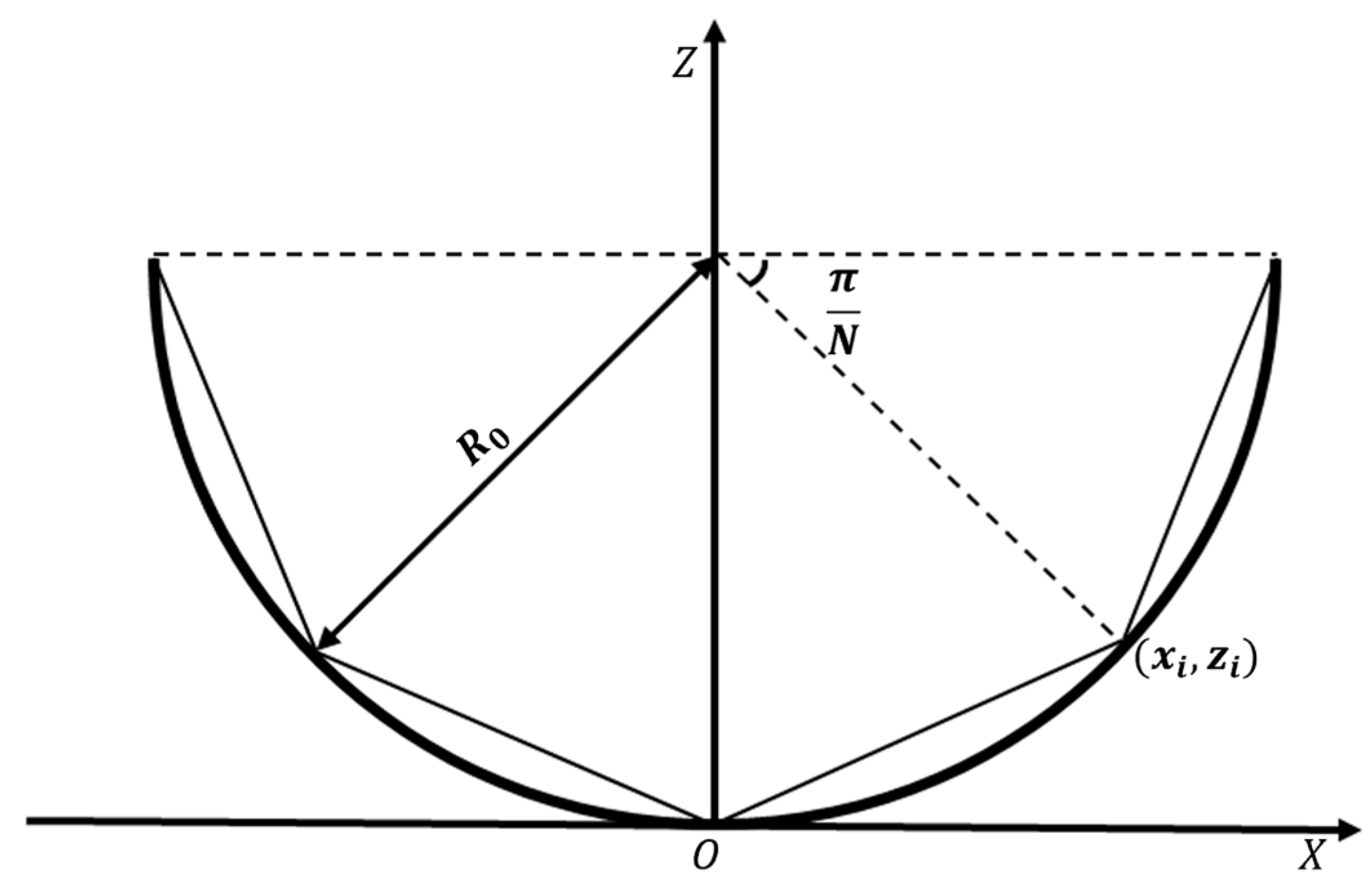
As shown in Figure 2, the generatrix of a line-focusing concentrator can be described by the following equation:
where denotes the cross-sectional radius of the concentrator, which is calculated as:
where W represents the optical power irradiated onto the PV array by the concentrator, denotes the reflectivity of the concentrator, is the solar energy density in space, with I0 = 1367 W/m2, is the collection efficiency; and L indicates the axial length of the concentrator along the Y-axis.
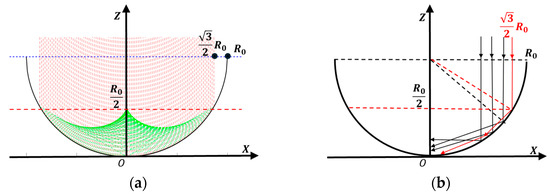
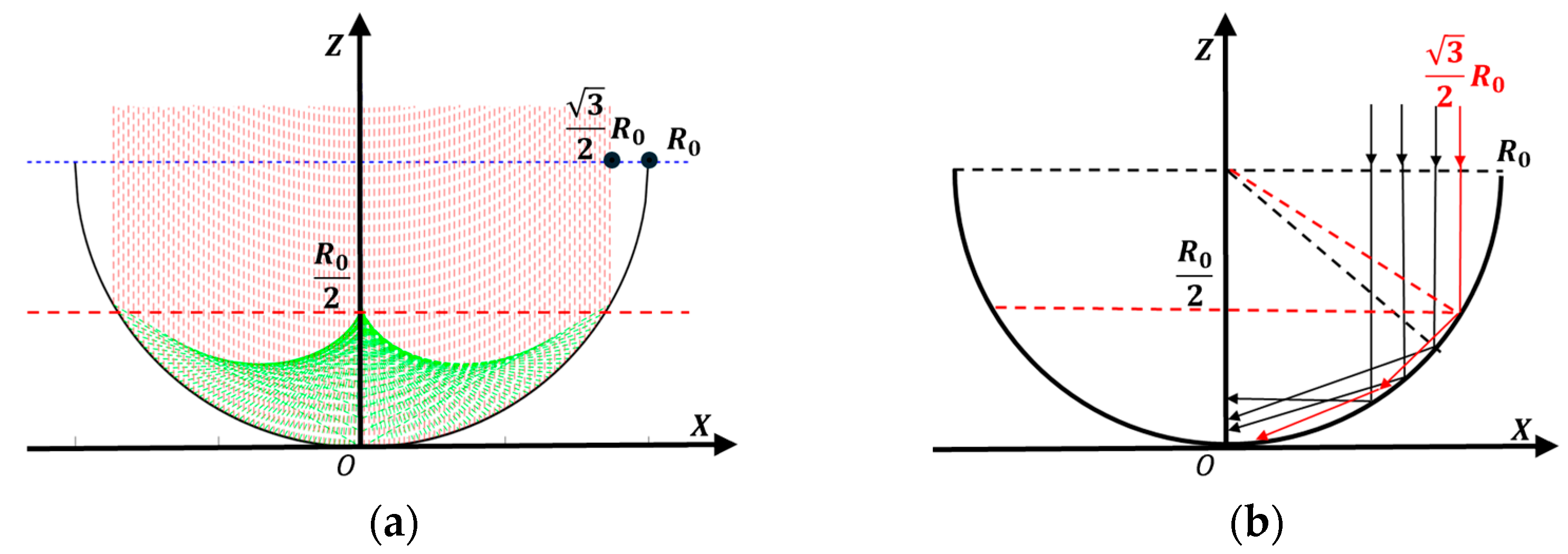
Figure 2.
Shape of the generator line of the concentrator: (a) energy distribution; (b) light reflection.
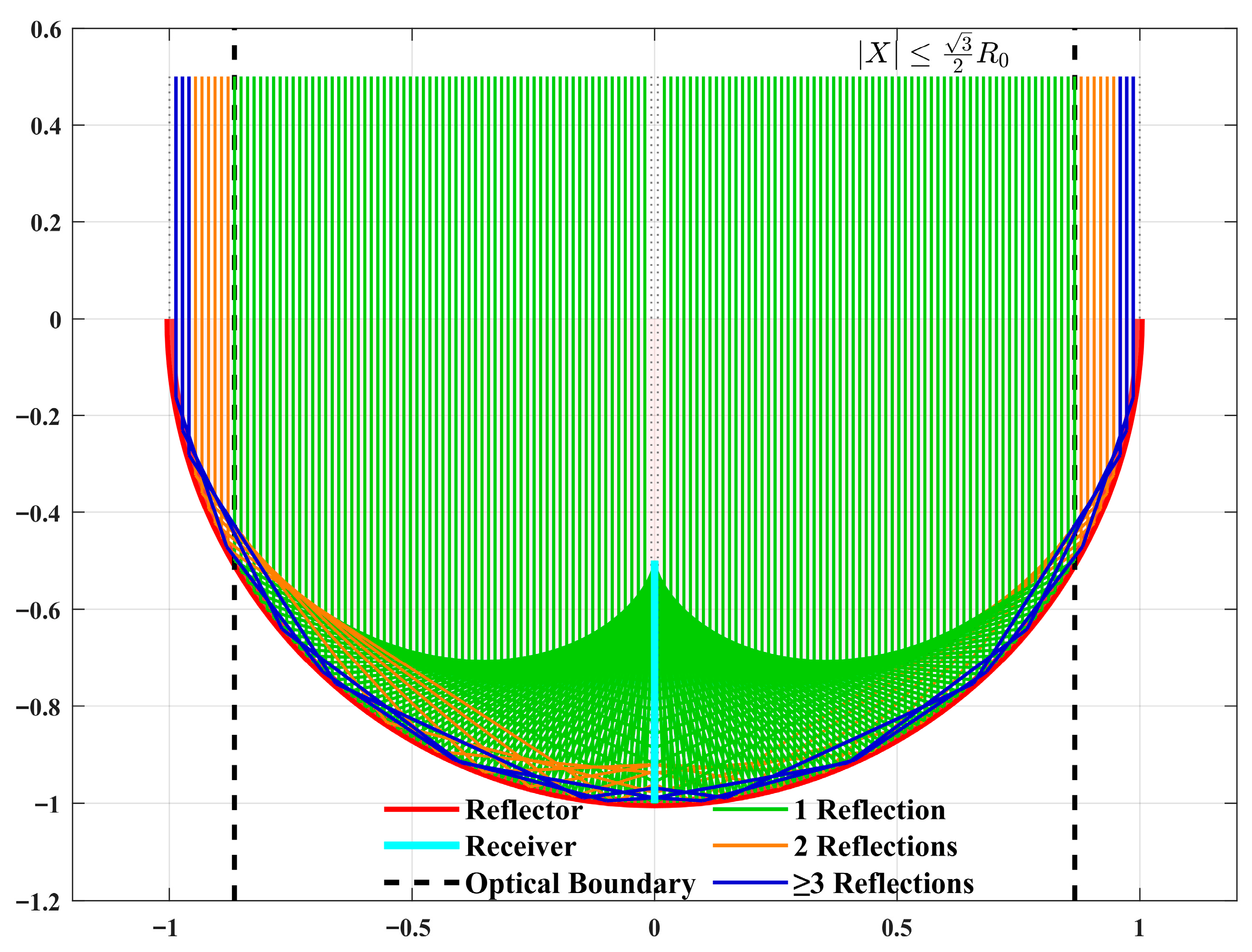
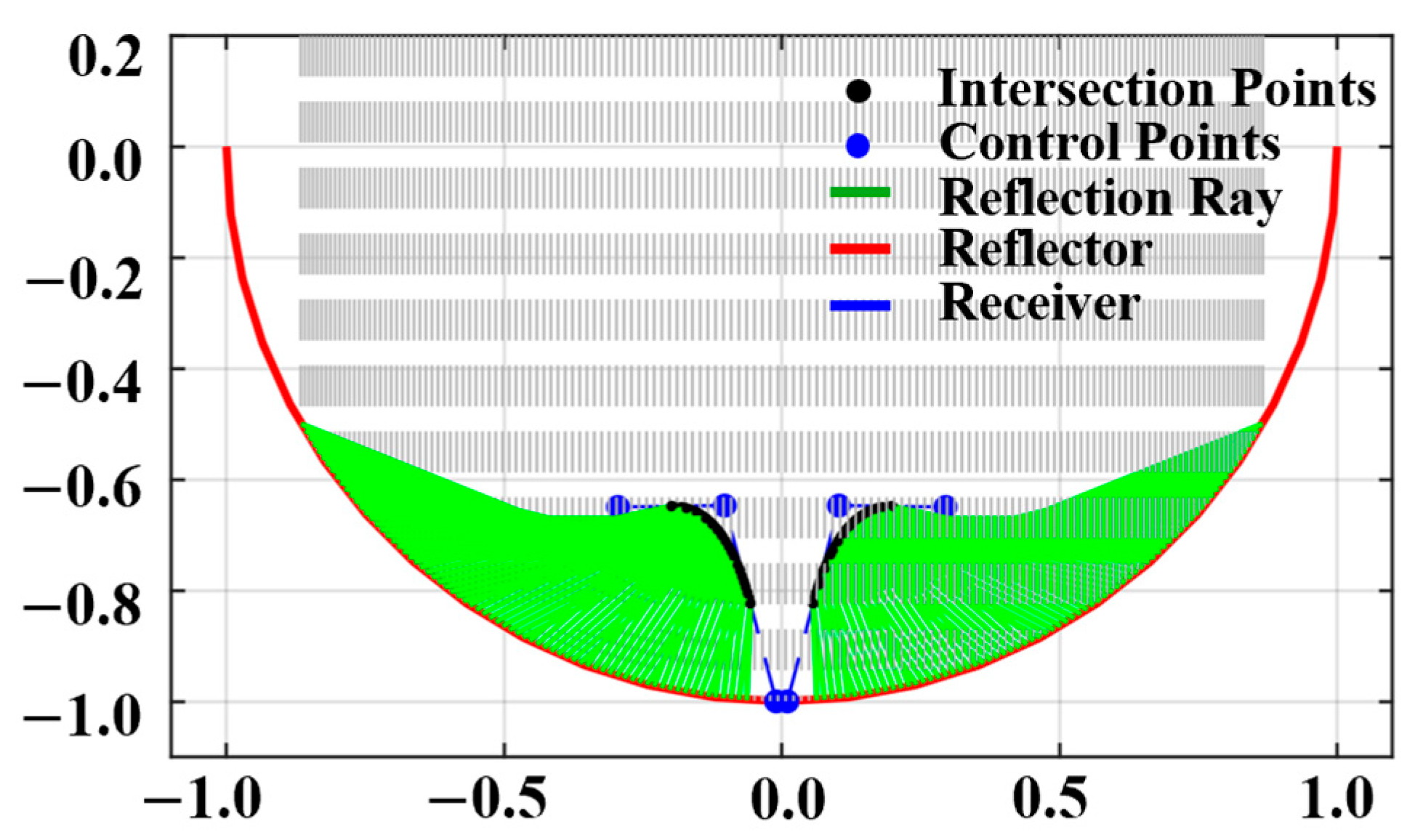
As shown in Figure 3, for the normalized calculation, the reflecting surface is an ideal circle. With X = 0 as the receiving surface, the PV array spans from Y = −1 (starting point) to Y = −0.5 (ending point). The light ray distribution is illustrated in Figure 1. According to the law of light ray distribution, this receiving surface can capture nearly 100% of the incident light rays.
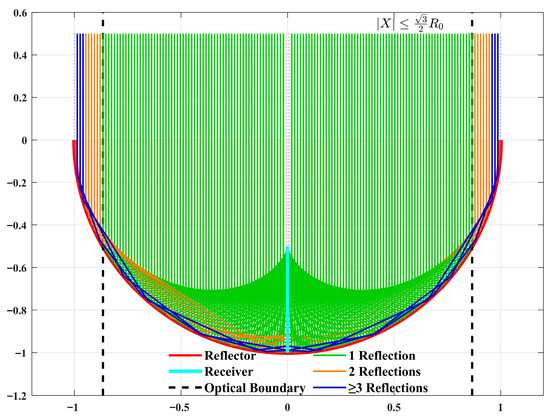
Figure 3.
Line-Focused light distribution reflection region diagram.
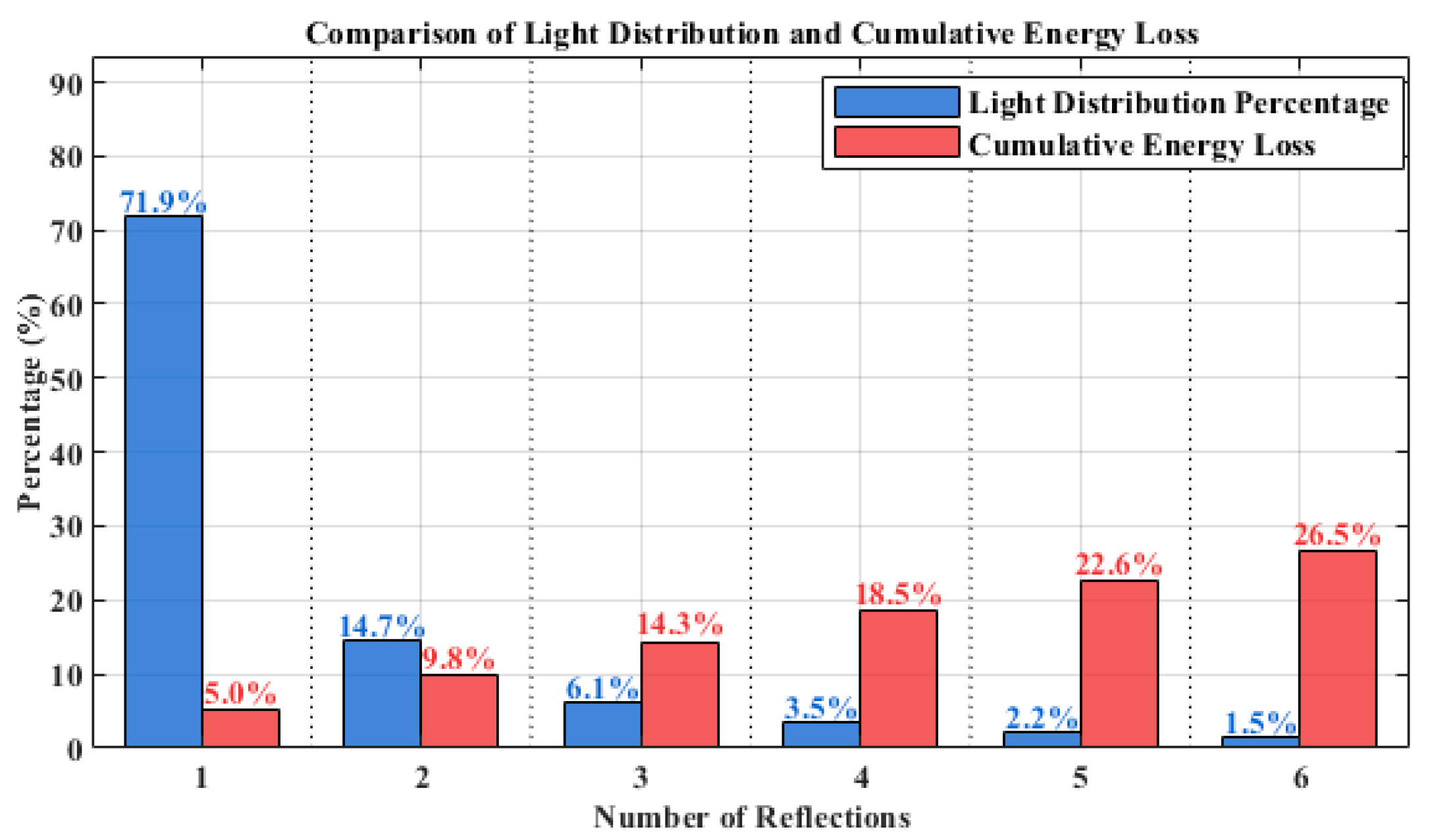
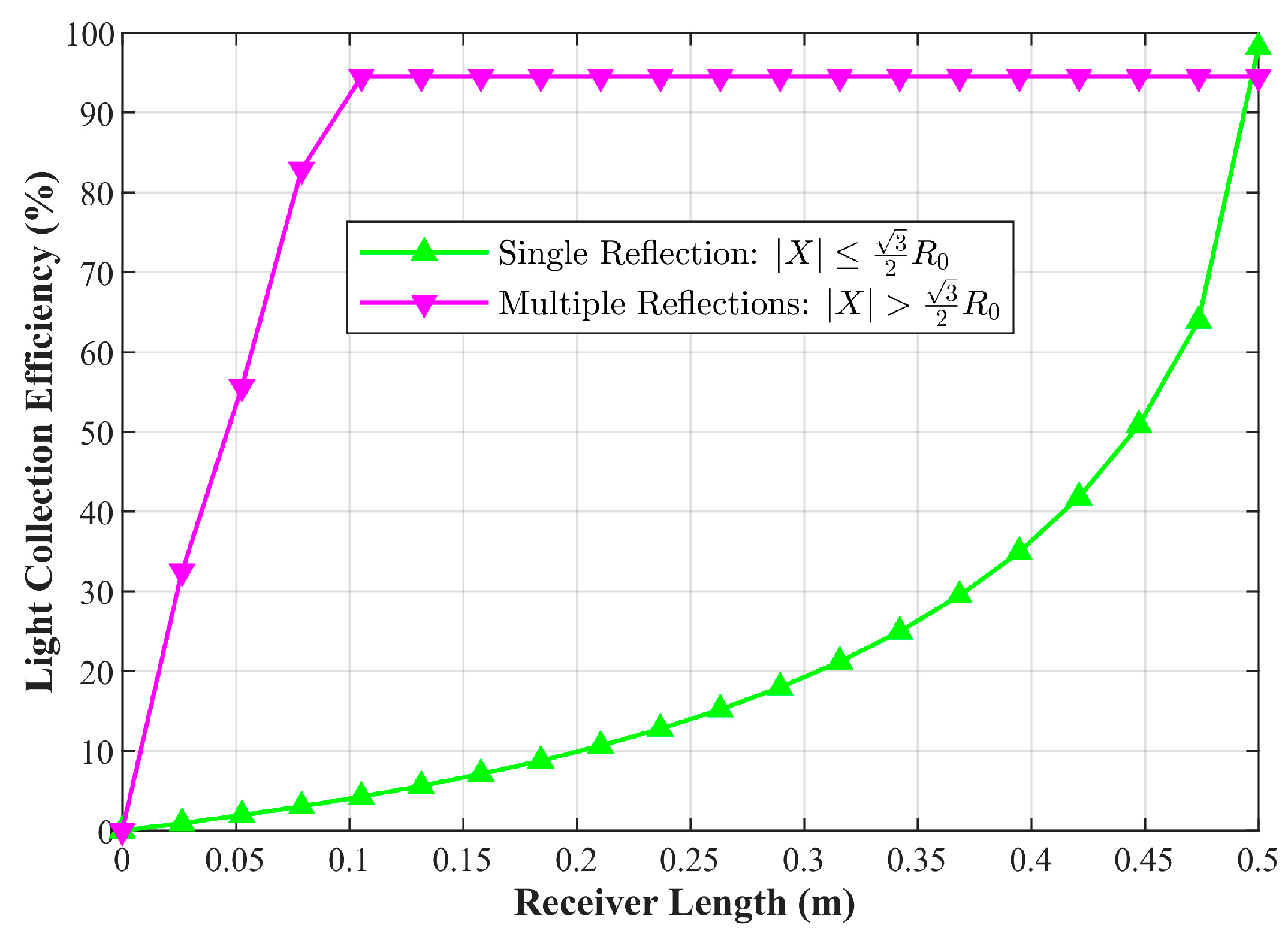
After classifying these light rays and assuming a 5% energy loss per reflection, the statistical law shown in Figure 4 was obtained. Among the rays, 72.2% undergo one reflection (with the boundary of single reflection defined as ), while the proportions of light rays undergoing two, three, four, five, and six reflections are 14.5%, 6.1%, 3.5%, 2.2%, and 1.5%, respectively. The corresponding energy attenuation degrees are 5.0%, 9.8%, 14.3%, 18.5%, 22.6%, and 26.5%. The length of the solar cell array and the arc length of the concentrating mirror corresponding to each reflection region are presented in Table 1. From the perspectives of light ray proportion, energy attenuation degree, and the dimensional parameters of the concentrating mirror and solar cell array, the single-reflection region plays a dominant role.
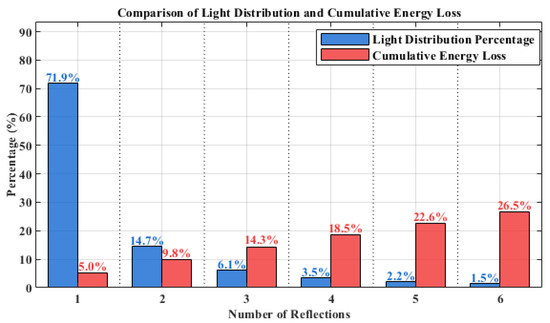
Figure 4.
Comparison of light distribution and cumulative energy loss.

Table 1.
Dimensions of the PV array and concentrator corresponding to different reflection zones.
As shown in Figure 5, with a fixed number of incident rays, the solar array gradually increases in length at a constant step size starting from an initial length of 0, and the proportion of reflected rays captured is simultaneously statistics. It is found that in the multiple reflection zone (i.e., the zone satisfying ), the light capture efficiency of the solar array saturates rapidly with increasing length. This is because the propagation paths of reflected rays in this zone are concentrated, and most rays can be efficiently captured by a relatively short receiving surface. Thus, its incremental contribution to the subsequently constructed objective function f(P) (Equation (5)) is very limited. In contrast, in the single reflection zone (), the light capture efficiency exhibits a significant linear growth relationship with the length of the solar array, serving as the core incremental source driving the improvement of the objective function f(P).
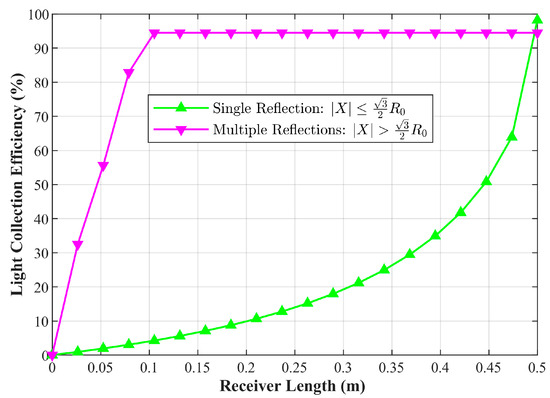
Figure 5.
Light Collection Efficiency of Single and Multiple Reflection Zones.
Based on the above characteristics, the optimal design of the solar array’s geometric shape within the single reflection zone substantially enhances computational efficiency by avoiding reduced numerical simulation efficiency from complex ray tracing in multi-reflection scenarios and lowering the computational complexity and convergence difficulty of the optimization algorithm. It improves engineering feasibility through clear ray propagation paths, simplified solar array-concentrator matching, reduced requirements for structural processing accuracy, manufacturing costs and assembly errors, while eliminating potential local thermal concentration in multi-reflection zones to simplify thermal management system design and enhance long-term operational reliability. The compact geometric layout reduces volume and mass constraints during space deployment, making it more suitable for the on-orbit operation requirements of the SSPS.
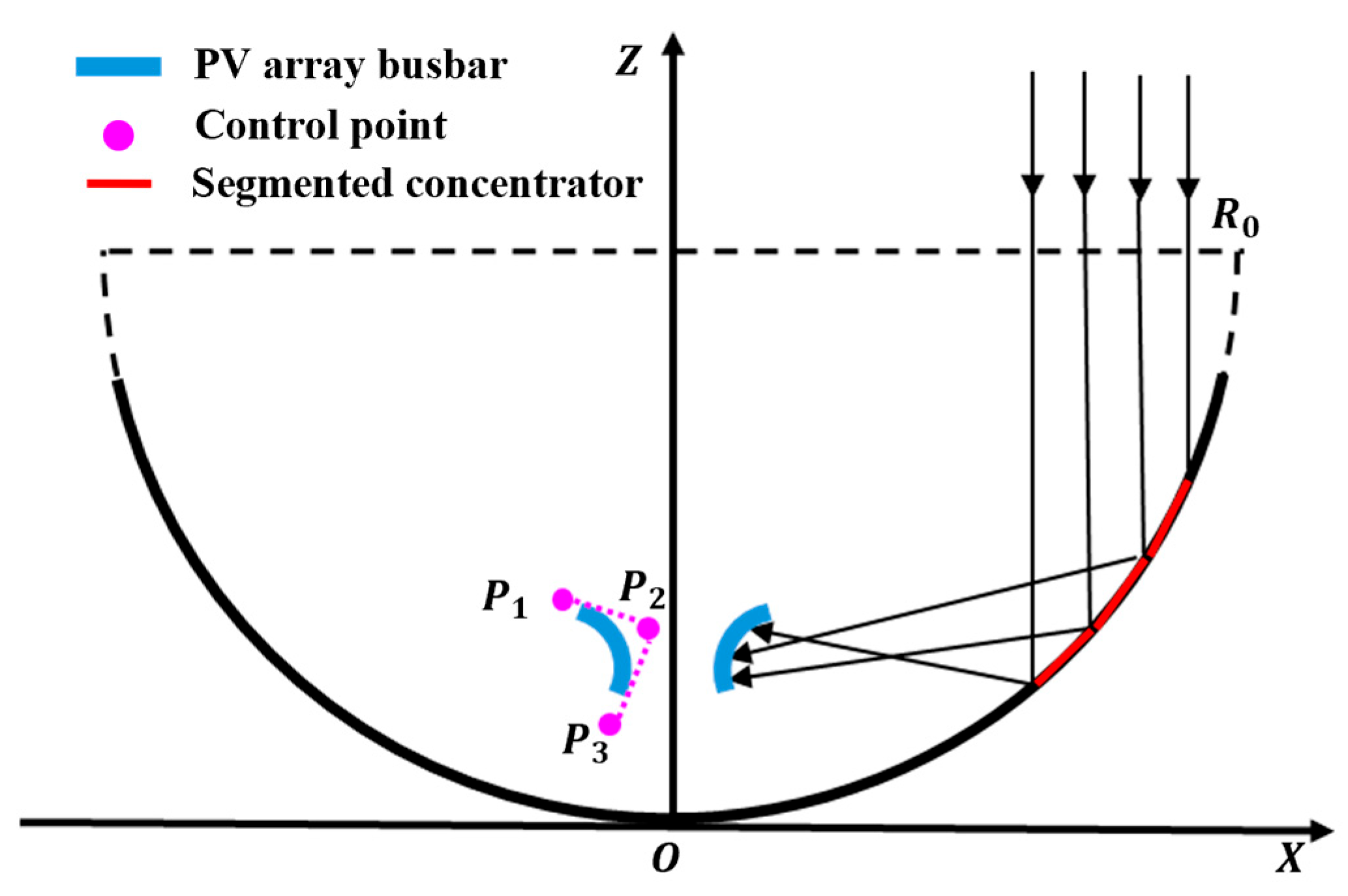
Due to the large scale and high power of the SSPS, a modular configuration is required to reduce the difficulty of manufacturing and launching. In this paper, the generatrix of the concentrator is approximated by line segments, and the concentrator is divided into multiple planar segments.
In the cross-section shown in Figure 6, the vertex coordinates can be expressed as:
where i denotes the index of the polygon vertex, and N represents the number of segments.
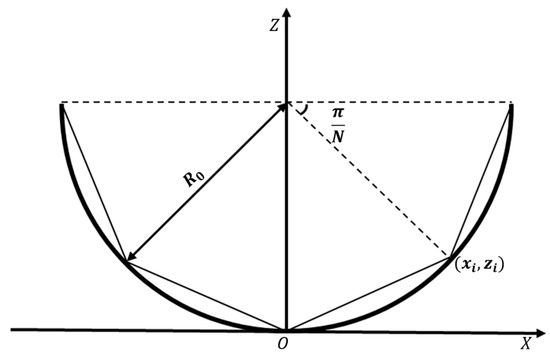
Figure 6.
Two-dimensional splicing diagram of the concentrator.
As illustrated in Figure 7 the geometry of the PV array is described by B-spline curves. Because the B-spline curves exhibit continuity across all points and have the ability to assume any form of curve morphology through the adjustment of the coordinates of the control points [35], this paper employs B-spline curves to depict the shape of the PV array. Subsequently, the desired light power density distribution is achieved by modifying the control points.
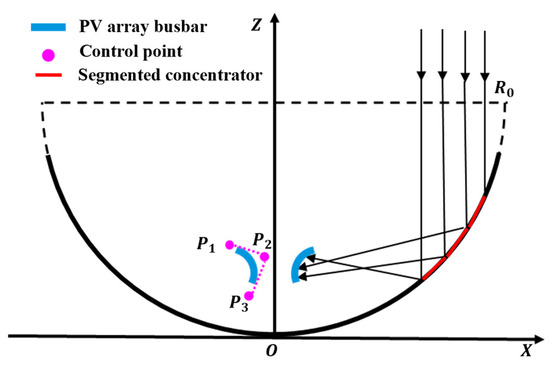
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of the receiving surface morphology.
The functional form of the B-spline curve is expressed as:
where denotes a point on the curve, n is the number of control points, p is the order of the curve, represents the B-spline basis function, and is the coordinate of each control point.
2.2. Structural Optimization
To improve the light distribution characteristics of the PV array, an optimization model is established:
where denotes the maximum uniformity of the concentration distribution; is the optical concentration ratio, i represents the number of statistical segments of the PV array; and represent the lower and upper bounds of the optical concentration ratio, respectively; U is the feasible domain of the control point coordinates; denotes the normalized power–area ratio; represents the normalized collection efficiency; and are weighting coefficients, with .
The ray-tracing algorithm is employed to simulate the optical behavior of the LCC system, with the number of incident rays set to . Owing to its advantages of fast convergence, strong global search capability, and ease of integration with other algorithms, the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm is utilized for numerical simulation [36].
To balance computational efficiency and optimization accuracy, the PSO parameters are configured as follows: a population size of 50, maximum iterations of 200, an initial inertia weight of 0.90, an inertia decay rate of 0.98, and a stagnation tolerance of 100 consecutive generations (i.e., the optimization terminates early if no improvement in the optimal fitness value is observed for 100 successive generations). The parameter selection is justified by practical optimization demands: (1) a population size of 50 strikes a trade-off between escaping local optima and minimizing computational overhead; (2) 200 iterations serve as the upper limit to ensure stable convergence, while the 100-generation stagnation tolerance enables early termination when the solution stabilizes, avoiding redundant calculations and significantly improving computational efficiency; (3) the initial inertia weight (0.90) and decay rate (0.98) balance global exploration and local exploitation during the optimization process.
Within the multi-objective optimization framework targeting maximum collection efficiency and power-to-area ratio, we first constructed a continuous weight coefficient sequence (0 to 1, step size = 0.05) covering all potential trade-offs between the two objectives. For each weight value, the aforementioned PSO algorithm was run to calculate objective function values and generate candidate solutions. Subsequently, the Pareto weighting method was applied to assess non-dominated solutions: it assigns weights to objectives based on their relative importance, synthesizes their weighted performance to quantify objective trade-offs, and thereby determines an optimal point reference.
As depicted in Figure 8, are the two-dimensional light distribution, morphology, and corresponding parameters of the optimized LLC system.
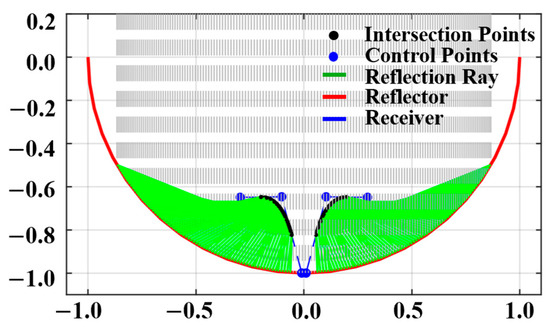
Figure 8.
Optimized two-dimensional cross-sectional diagram of the LCC system.
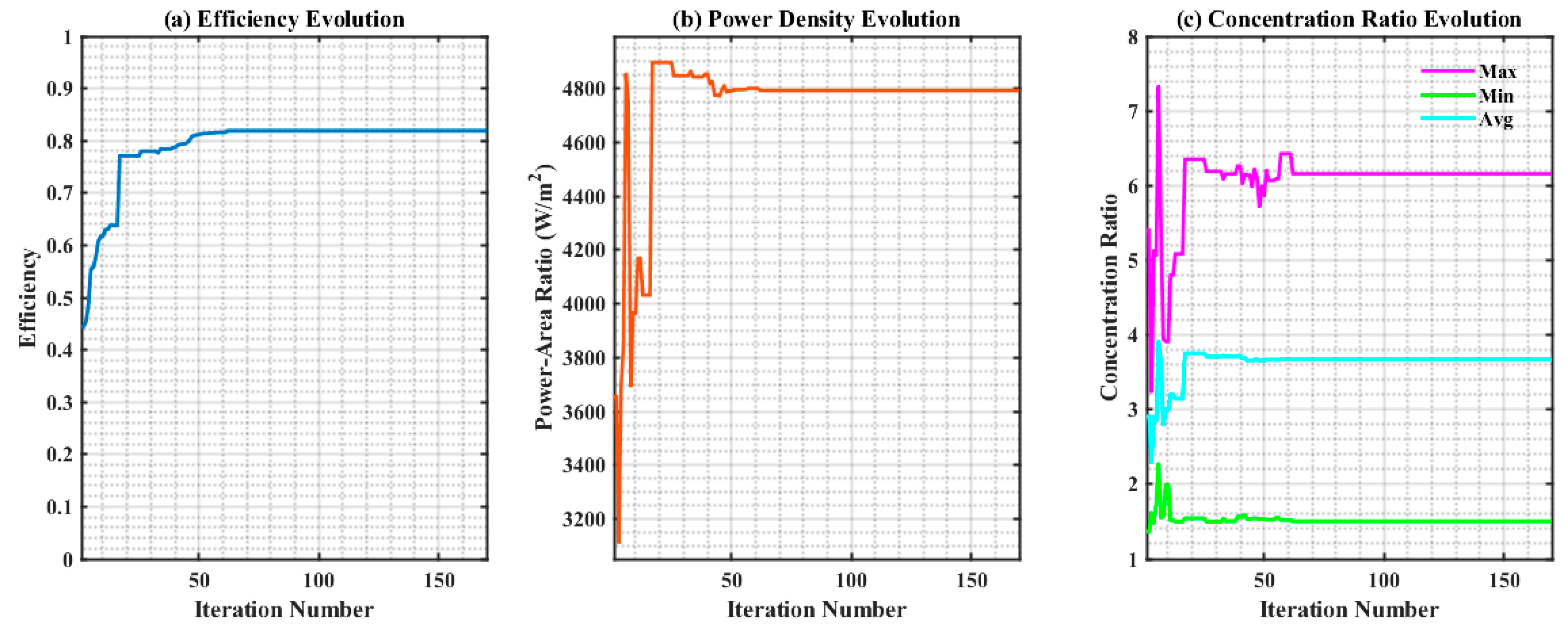
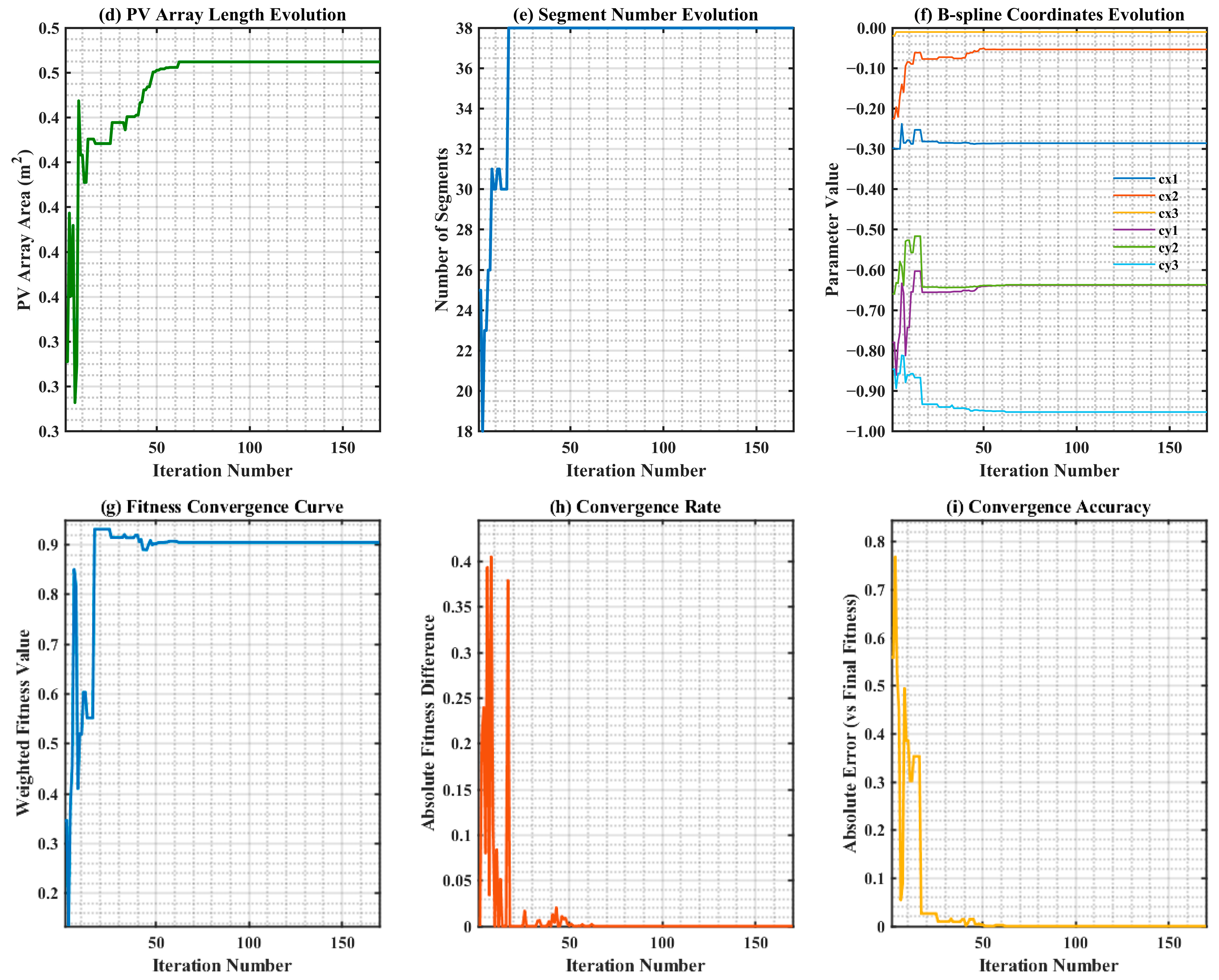
Figure 9 illustrates the dynamic variation in normalized light distribution parameters for the optimization process (corresponding to weight coefficient ) selected from the Pareto front of optimal solutions. It encompasses evolution curves of nine core indicators: Efficiency, Power–Area ratio, Concentration ratio, PV array area, Number of segments, B-spline parameters and Fitness convergence, and so on.
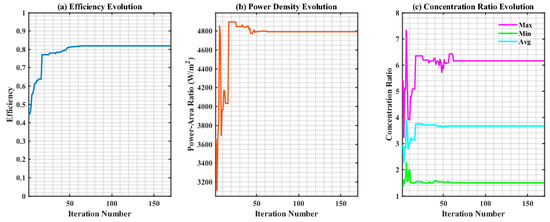
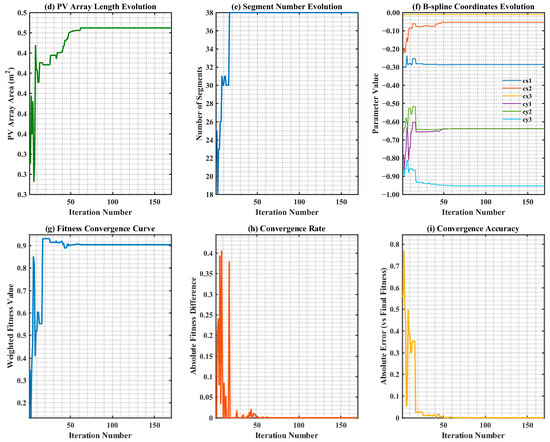
Figure 9.
The graph of normalized light distribution parameters: (a) Efficiency; (b) Power–Area ratio; (c) Concentration ratio; (d) PV array area; (e) Number of segments; (f) B-spline parameters value; (g) Fitness convergence curve; (h) Convergence rate; (i) Convergence accuracy.
Among the 21 weight-corresponding system schemes, 7 Pareto non-dominated solutions are screened out—and these are exactly the 7 sets of optimized parameters presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The parameters corresponding to the weights under the non-dominated solutions.
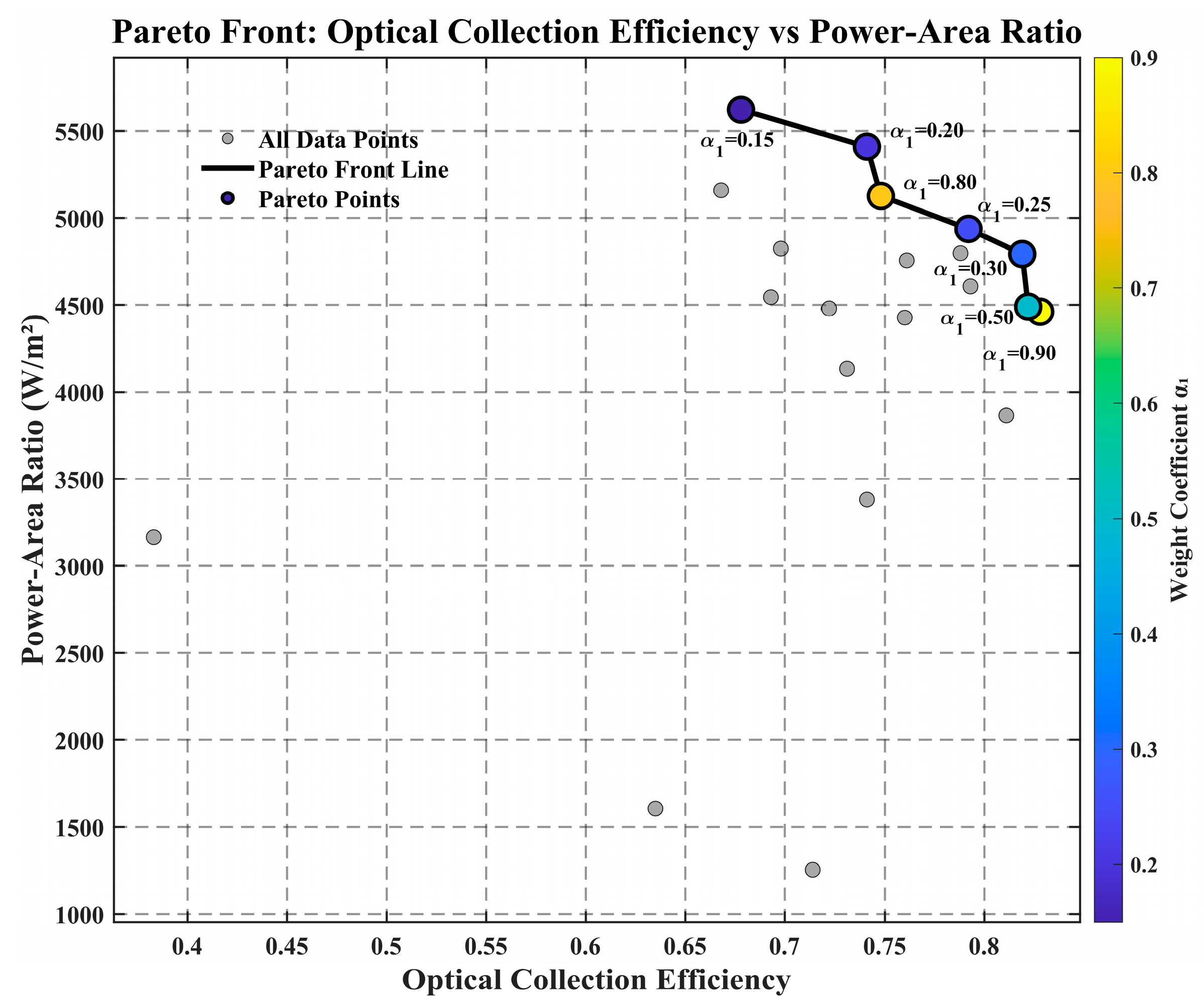
The Pareto front in Figure 10 clearly demonstrates the trade-off between these two objectives. Figure 10 reveals that when α1 = 0.9 (prioritizing efficiency), the system attains a peak efficiency of 0.828, albeit with a moderate power density of 4460.53 W/m2; conversely, when α1 = 0.15 (prioritizing power density), the power density peaks at 5621.90 W/m2, while the efficiency drops to 0.678.
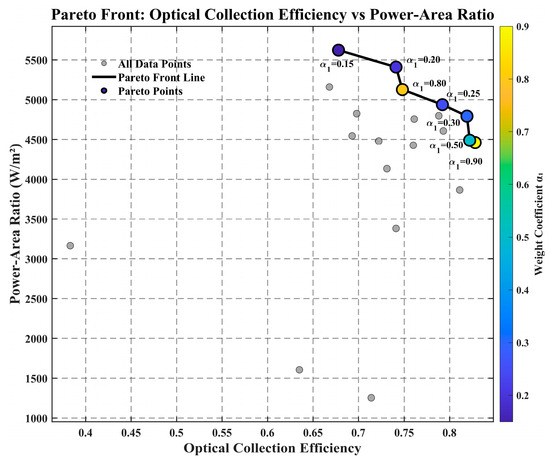
Figure 10.
Weight and its impact on Efficiency and Power–Area Ratio.
The Pareto node corresponding to α1 = 0.3 serves as an optimal option for balanced application scenarios. As shown in Table 2, this node sustains a high efficiency of 0.819 alongside a competitive power density of 4792.24 W/m2. Its associated parameters—including a 0.46 m2 PV area, an average concentration ratio of 3.67, and 38 segments—strike a well-rounded balance between performance and practical implementability.
2.3. Optimized-Based Subsystem Inertial Parameter Calculation
To support the accurate solution of kinematic equations, inertial parameters of subsystems serve as essential foundational inputs, and their reliability directly affects the precision of subsequent dynamic analysis and system performance evaluation. Building on the preliminary optimization work of the line-focusing SSPS system presented earlier, this section focuses specifically on the calculation of inertial parameters for key subsystems.
Since the concentrator and the PV array are rigidly connected coaxially and rotate about the , the position of the combined center of mass is determined by the mass distribution of these two components, calculated as:
where and denote the position vectors of the centers of mass of the concentrator and the PV array, respectively. The total mass of the concentrator is given by , and the total mass of the PV array is , where is the optimized area of the PV array. The area of a segment, , can be determined from the chord length corresponding to the arc length and the concentrator length, approximately as . and represent the densities of the concentrator and the PV array, respectively.
and are calculated as:
where A is PV array area, the definitions of and are the same as those in Equation (3), m represents the number of partitions in the PV array, and are the coordinate points of single partition of the PV array.
The inertia calculations for the concentrator and the PV array are as follows:
where is obtained by summing the contributions of each mirror segment, is the mass of a single concentrator segment, is the inertia of the segment in its local coordinate system, is the vector from the centroid of the k-th segment to the system centroid, and is the rotation matrix from the local coordinate system of the segment to the concentrator’s centroid coordinate system. The parameters in Equation (10) are similar to those in Equation (9).
The inertia of the concentrator and the PV array is converted to the total inertia in the combined centroid coordinate system. The vector from the centroid of the concentrator to the combined centroid is , and the displacement vector from the PV array centroid to the combined centroid is .
According to the parallel axis theorem, the total inertia of the concentrator and PV array is:
2.4. Configuration of a Line-Focusing SSPS
As illustrated in Figure 11, a line-focusing SSPS is designed to operate in GEO, with its structure primarily consisting of a main supporting structure, modular concentrators, PV arrays, and a microwave antenna. The concentrators reflect sunlight onto the PV array in a line-focusing mode for photoelectric conversion. When the relative position between the LCC system and the sun changes, the LCC system performs single-degree-of-freedom rotation via a rotation mechanism, ensuring that the central normal of the LCC system remains parallel to the direction vector of the incident sunlight.
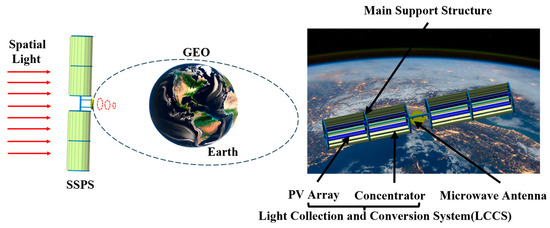
Figure 11.
Schematic diagram of the overall configuration of the SSPS.
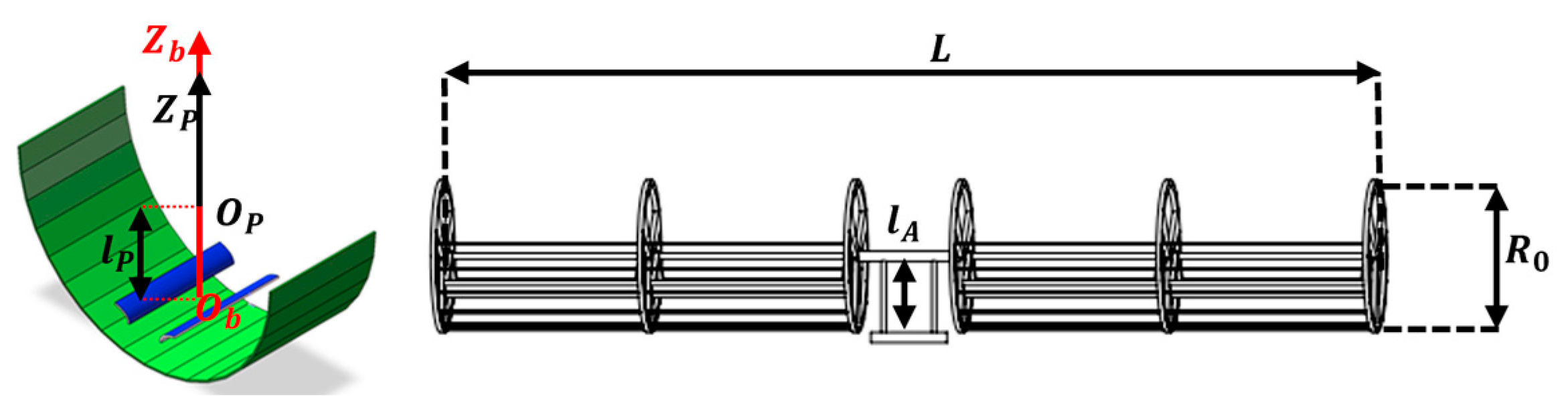
Based on the previous optimization, Table 3 and Figure 12 present the fundamental parameters of the line-focusing SSPS, including mass, inertia, and dimension.

Table 3.
Fundamental parameters related to the dynamics of a GW-Class SSPS.
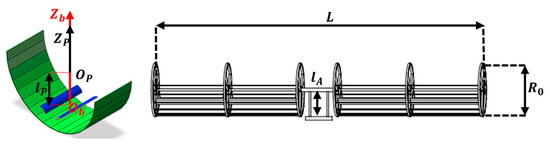
Figure 12.
Diagram of characteristic dimensions.
3. Kinematic and Dynamic Modeling
This section establishes the attitude dynamics model of the SSPS, providing theoretical support for subsequent controller design. First, fundamental coordinate systems are defined to specify the spatial reference positions of each component. Second, the kinematic transformation relationships among subsystems are derived to quantify relative motion and attitude coupling characteristics. With Lagrangian approach and appropriate assumptions, a multi-body coupled dynamics model is constructed and attitude motion is discussed. Finally, the expression of gravity-gradient torque is derived while the time-varying coupling relationship with attitude angles is analyzed.
3.1. Coordinate Systems
Based on the structural characteristics of the line-focusing SSPS, the coordinate systems illustrated in Figure 13 are established as follows:
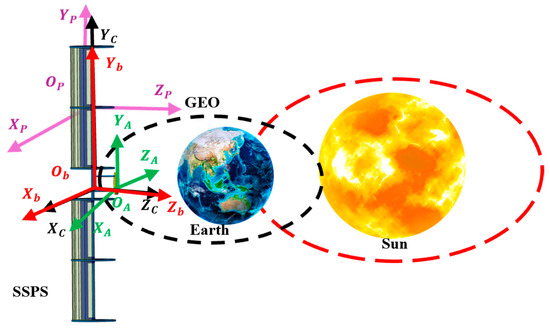
Figure 13.
Diagram of coordinate system description.
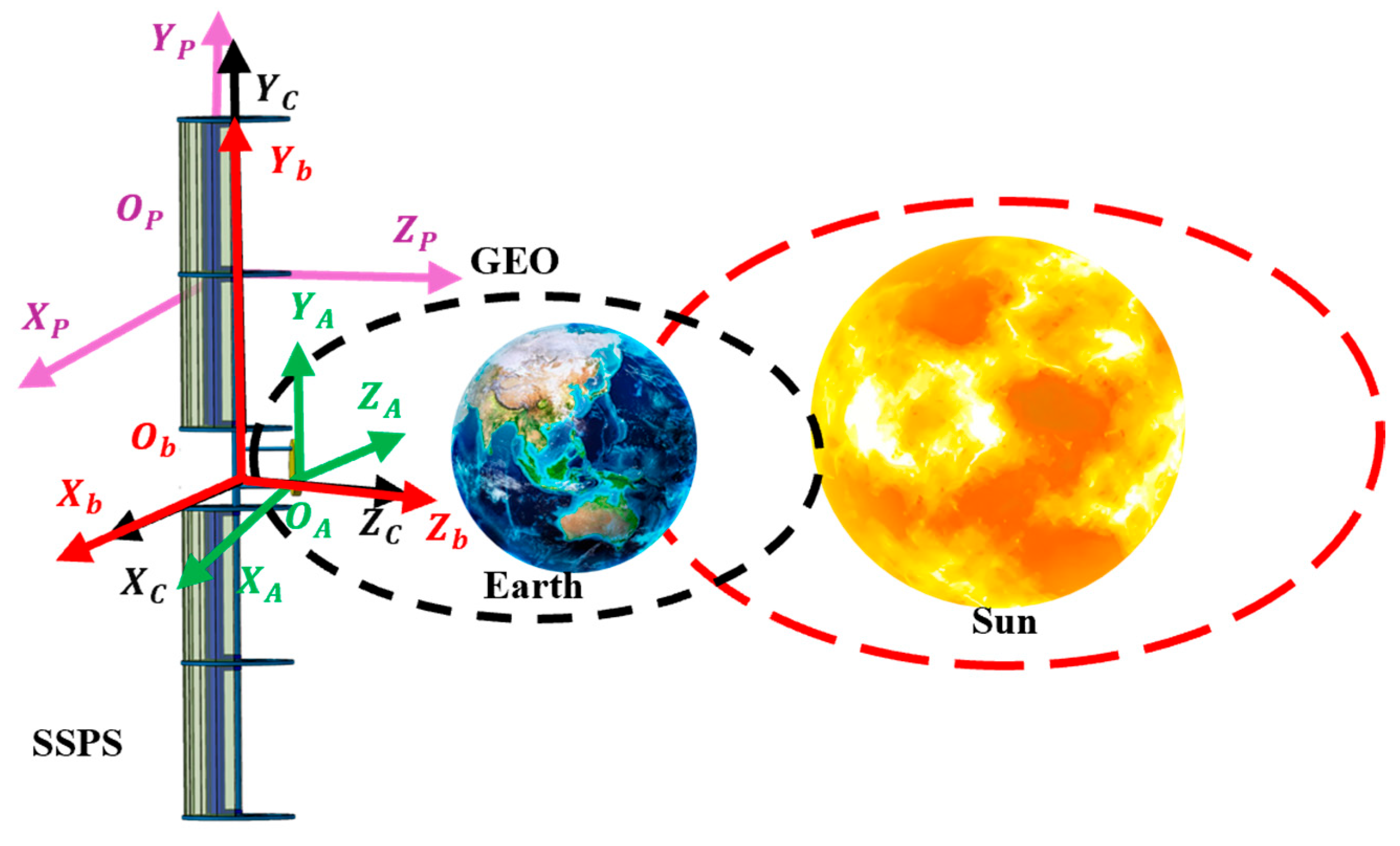
Body coordinate system (Ob-XbYbZb): Its origin Ob coincides with the center of mass of the main supporting structure. Zb is defined as the yaw axis pointing toward the Earth’s center; Xb is the roll axis aligned with the SSPS’s orbital direction; Yb is determined by the right-hand rule. The coordinate system of the main supporting structure (OC-XCYCZC) is coincident with the body coordinate system.
Antenna coordinate system (OA-XAYAZA): Its origin OA coincides with the center of mass of the transmitting antenna. ZA is perpendicular to the antenna plane; XA points in the tangential direction of the antenna motion and lies in the antenna’s central plane; YA follows the right-hand rule.
LCC system coordinate system (OP-XPYPZP): Its origin OP is located at the center of mass of the LCC system. ZP points toward the Sun; XP is defined as the direction opposite to the displacement of the body coordinate system’s Yb axis relative to the LCC system; YP follows the right-hand rule.
3.2. Description of the Kinematic Relationships
When the LCC system rotates about the Yb-axis of the body coordinate system, the transformation matrix from the LCC system coordinate system to the body coordinate system can be expressed as:
where represents the rotation angle of the LCC system about the Yb-axis.
The microwave transmitting antenna possesses only rotational degrees of freedom about the XA-axis and YA-axis. Accordingly, the transformation matrix from the antenna coordinate system to the body coordinate system can be expressed as:
where and denote, respectively, the roll and pitch angles of the microwave transmitting antenna.
The stabilized attitude of the SSPS is represented using Euler angles in the Z-Y-X rotation sequence. The transformation matrix from the orbital coordinate system to the body coordinate system is expressed as:
where , and correspond to the yaw, pitch, and roll angles, respectively.
Since the SSPS attitude angles are sufficiently small, linearization of Equation (14) yields the following result:
The vector of the LCC system coordinate system relative to the body coordinate system can be expressed as:
where represents the rotation radius of the LCC system.
The vector of the antenna coordinate system relative to the body coordinate system can be expressed as:
where denotes the distance from the centroid to the body coordinate system when the microwave antenna is fixed.
The angular velocity of the SSPS body in the inertial frame can be expressed as:
where denotes the angular velocity of the orbital coordinate system relative to the inertial coordinate system, while represents the angular velocity of the body coordinate system relative to the orbital coordinate system.
The rotational angular velocity of the LCC system relative to the body coordinate system can be expressed as:
The rotational angular velocity of the microwave transmitting antenna relative to the body coordinate system can be expressed as:
By assuming that the attitude angles of the microwave transmitting antenna are small, the linearized form of Equation (20) can be expressed as:
3.3. Dynamic Modeling
In this section, the Lagrangian method is employed to establish the attitude dynamics model, with the following basic assumptions introduced: the acceleration of the SSPS main body is negligible, while the rotations of the LCC system and antenna, the system’s centroid displacement, and the angular velocities of the SSPS main body, LCC system and antenna are all small quantities, whose combinations are higher-order infinitesimals and thus can be neglected.
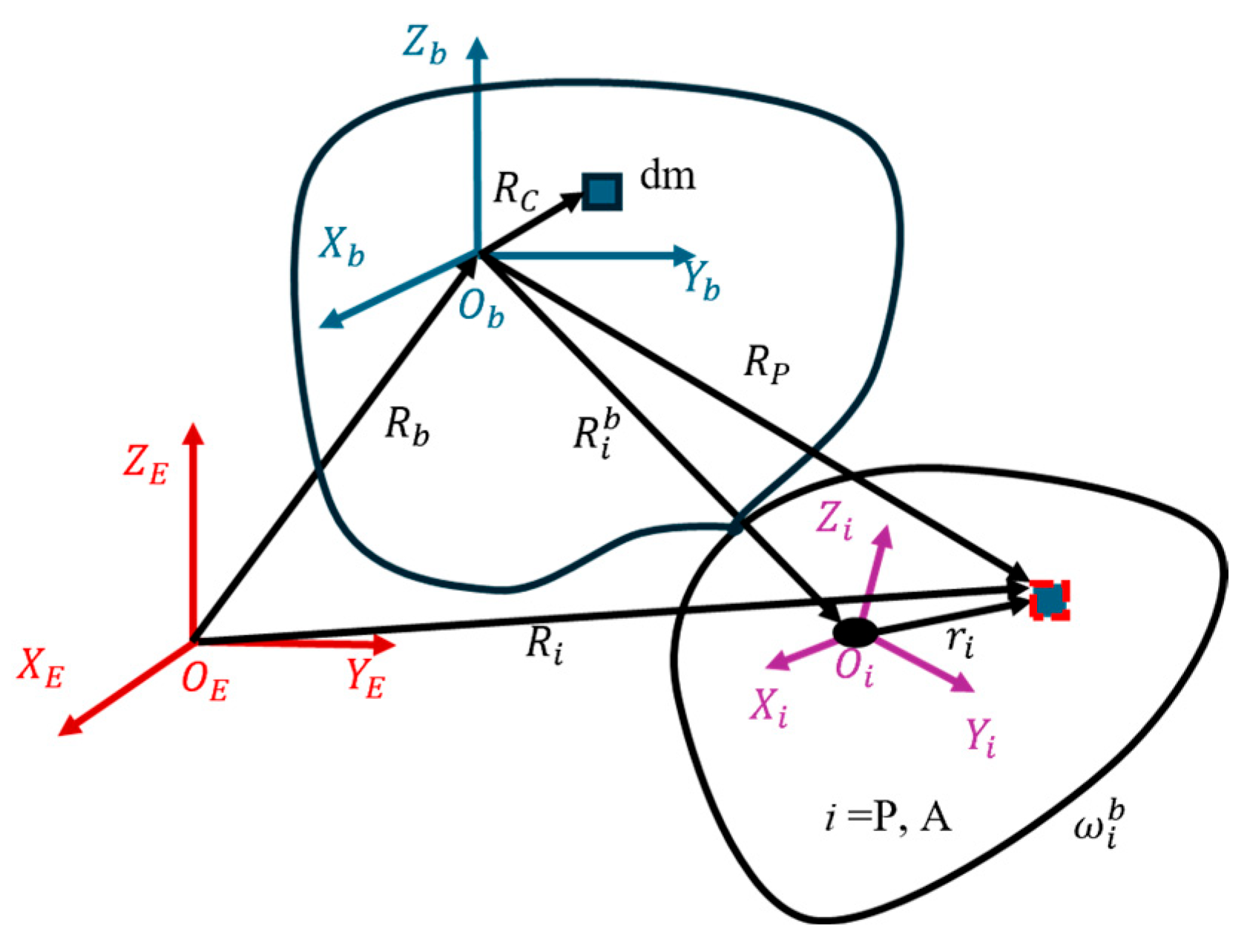
As shown in Figure 14, the position vector and velocity of an arbitrary point on the LCC system or microwave transmitting antenna can be expressed as:
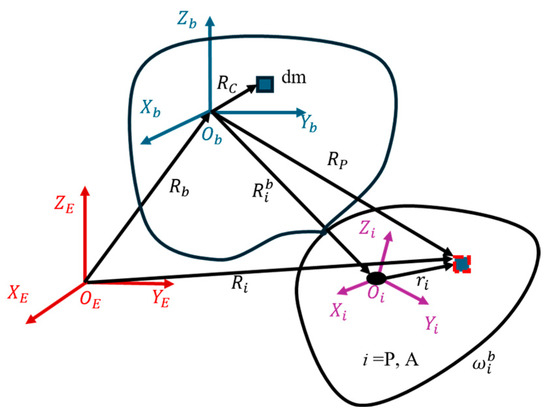
Figure 14.
Vector diagram of each coordinate system.
The kinetic energy of the main supporting structure is expressed as:
Furthermore, the kinetic energy of LCC system or microwave transmitting antenna is expressed as:
Using (by defining the center of mass, the first-order moment equals 0), the terms involving can be simplified. After integration, the cross terms vanish, leaving only those terms independent of . Thus, Equation (25) can be simplified as:
where denotes the mass of the main supporting structure, the mass of the LCC system or the microwave transmitting antenna, is the inertia of LCC system or the microwave antenna, , represents the angular velocity of the SSPS, is the angular velocity of the LCC system or microwave antenna relative to the body coordinate system, is the vector of the LCC system or microwave antenna coordinate system with respect to the body coordinate system, and is the vector of the SSPS with respect to the body coordinate system in the inertia coordinate system.
By combining Equation (24) with Equation (26), the total kinetic energy of the system can be expressed as:
The matrix is defined as a generalized coordinate. The Lagrangian is L = T (gravitational potential energy is neglected, i.e., V is ignored). For each generalized coordinate of , the corresponding Lagrange equation is:
By differentiating with the six generalized coordinates and neglecting higher-order small terms and ignoring translational coupling, the following dynamic equations can be obtained:
where , all elements in the matrix are measured relative to the body coordinate system. is the input of the controller. is the inertia of the LCC system or microwave transmitting antenna relative to its own center of mass coordinate system, and is the inertia matrix of the LCC system or microwave transmitting antenna relative to the body coordinate system, expressed as:
3.4. Space Disturbance Analysis
3.4.1. Derivation of the Gravity Gradient Torque
During operation, the LCC system must track the sun, and the antenna needs to point toward the Earth. The system’s attitude accuracy significantly impacts the energy collection efficiency. Variations in the mass distribution relative to the orientation of the gravitational field generate a gravity gradient torque that can influence attitude control performance. Existing general theories of gravity gradient torque in spacecraft dynamics are often difficult to apply directly to the specific rotational constraints and mass distribution characteristics of these composite systems. Therefore, this paper derives a tailored expression for the gravity gradient torque specifically for such composite systems, providing a dynamic foundation for achieving high-precision attitude control. The expression for the gravity gradient torque used in practical engineering applications is given by:
where G is the universal gravitational constant, M is the mass of the Earth, denotes the vector from the center of mass of the LCC system or the microwave antenna to the Earth. , , is the orbital altitude; is the unit vector pointing from the Earth’s center to the spacecraft’s center of mass, , is the inertia of the spacecraft relative to the body coordinate system.
When the SSPS operates in a circular orbit, the following relation holds: , where is the orbital angular velocity. Thus, Equation (31) can be rewritten as:
For the main supporting structure, its coordinate system coincides with the body-fixed frame. In this case, , and the gravity gradient torque matrix, calculated from Equation (31) with higher-order small terms neglected, is:
The vector of the antenna’s center of mass relative to the body coordinate system is , from which can be derived. Define the attitude angle vector of the antenna system as , which fully describes the attitude coupling between the main body and the antenna. By adopting the small-angle assumption, neglecting high-order coupling terms, and substituting the above vectors into Equation (31), the following result is obtained:
where is the attitude angle-torque coefficient matrix, representing the weighting relationship between the attitude angles and the gravity gradient torque. is a constant vector determined by the asymmetry of the system inertia tensor, independent of the attitude angles.
For the LCC system, . Since the inertia of the LCC system relative to the body coordinate system is time-varying, the gravity gradient torque involves nonlinear time-varying terms with and , rendering the system nonlinear and time—varying. Given that the desired operational principle of the LCC system dictates , substituting this constraint allows for a variable transformation that reduces the system to a linear time—varying form.
Therefore, the gravity gradient torque matrix of the LCC system can be expressed as a function of and :
where , , and are time-varying coefficient functions, defined as:
The gravity gradient torque components in the X and Z directions are only related to φ, with their coefficients being periodic functions of time. In contrast, the gravity gradient torque component in the Y direction contains both time-varying terms associated with θ and time-invariant constant terms independent of the attitude angles, reflecting the coupling between the inertia tensor asymmetry and orbital motion. Simultaneously, it can be observed that when the SSPS attitude angles are sufficiently small, the gravity gradient torque in the X and Z directions vanishes, whereas in the Y direction, a residual time-varying gravity gradient torque term persists.
3.4.2. Earth Shape Perturbation in GEO
Traditional spacecraft attitude dynamics typically assumes the Earth is a uniformly mass-distributed sphere, whose gravitational potential only includes the central gravitational term. However, the Earth is actually oblate-spheroidal, with the equatorial radius being approximately 21.3 km longer than the polar radius [37]. This non-spherical characteristic introduces high-order terms in the spherical harmonic expansion of the Earth’s gravitational potential; among these, the second-order zonal harmonic term (J2 term) has the most significant impact, accounting for over 90% of the Earth’s non-spherical gravitational perturbation. The spherical harmonic expansion of the Earth’s gravitational potential (up to the J2 term) can be expressed as [38]:
where denotes the distance from the spatial point to the Earth’s center; is the geocentric latitude (the angle between the position vector and the Earth’s equatorial plane); is the second-order Legendre polynomial, which describes the correction of the Earth’s equatorial bulge to the gravitational potential.
Gravitational acceleration corresponds to the gradient of the gravitational potential, . In the spherical coordinate system, the components of acceleration are:
In the orbital coordinate system, the geocentric direction is ; convert this to the body coordinate system: .
For each subsystem, the perturbing torque consists of two components: one is the torque arising from the difference between the gravitational force acting on the subsystem (due to its centroid offset) and that at the system’s centroid; the other is the gradient torque generated by the coupling between the subsystem’s own inertia tensor and the gravitational gradient. The expression for the perturbing torque is:
where is the inertia tensor of the subsystem in the body frame; is the position vector of the subsystem’s centroid in the body frame; is acceleration at the system’s centroid (in the geocentric inertial frame); is GEO radius.
- At the system’s centroid: , thus:
For the main support structure, the offset torque is zero, and the torque is:
For the LCC system and the antenna, the torque is the sum of two components: the gradient torque generated by the coupling between the inertia tensor and the gravitational gradient , and the offset torque caused by the difference between the gravitational acceleration at this point and that at the system’s centroid (due to centroid offset). Its expression is:
4. Attitude Controller Design
This section focuses on the design of the SSPS attitude controller. First, based on the dynamic model established in the previous section, the attitude control objectives for the main supporting structure, LCC system, and antenna are defined. The pointing accuracy requirements for the subsystems are quantified, and the attitude error bounds are specified. Building on this, the control input terms in the dynamic equation are determined, and a composite control strategy combining PID feedback is proposed. Finally, the performance of the designed attitude controller is validated and analyzed via simulation results.
4.1. Control Objectives and Error Definition
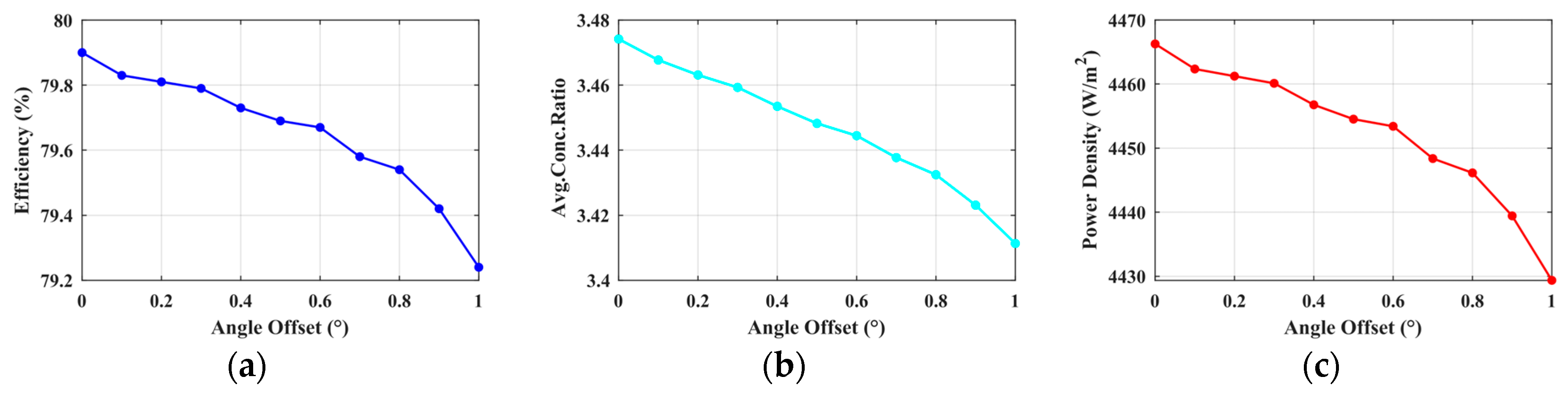
Based on the operational characteristics of the SSPS in geostationary Earth orbit (GEO), the core tasks of the system include: (1) achieving three-axis stabilization of the main support structure; (2) maintaining Sun-pointing for the LCC system; (3) ensuring Earth-pointing for the microwave transmitting antenna. As shown in Figure 15, taking the LCC system as an example: when its attitude angle deviates by 1 degree along the Z-axis, the light collection efficiency decreases by 0.65%, the average concentration ratio decreases by 0.05, and the power–area ratio decreases by 30 W/m2. Combined with the system dynamics model, the attitude control objective is defined as follows: the steady-state errors of the attitude angles of the main structure, LCC system, and antenna—relative to their desired attitudes —must not exceed 1 degree.
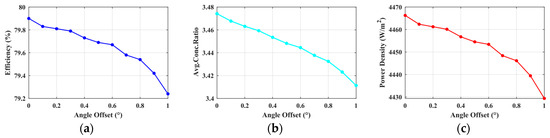
Figure 15.
The relationship between the offset angle of the LCC system and the collection performance; (a) Collection efficiency; (b) Average concentration ratio; (c) Power density.
The attitude error is defined as:
4.2. Controller Design
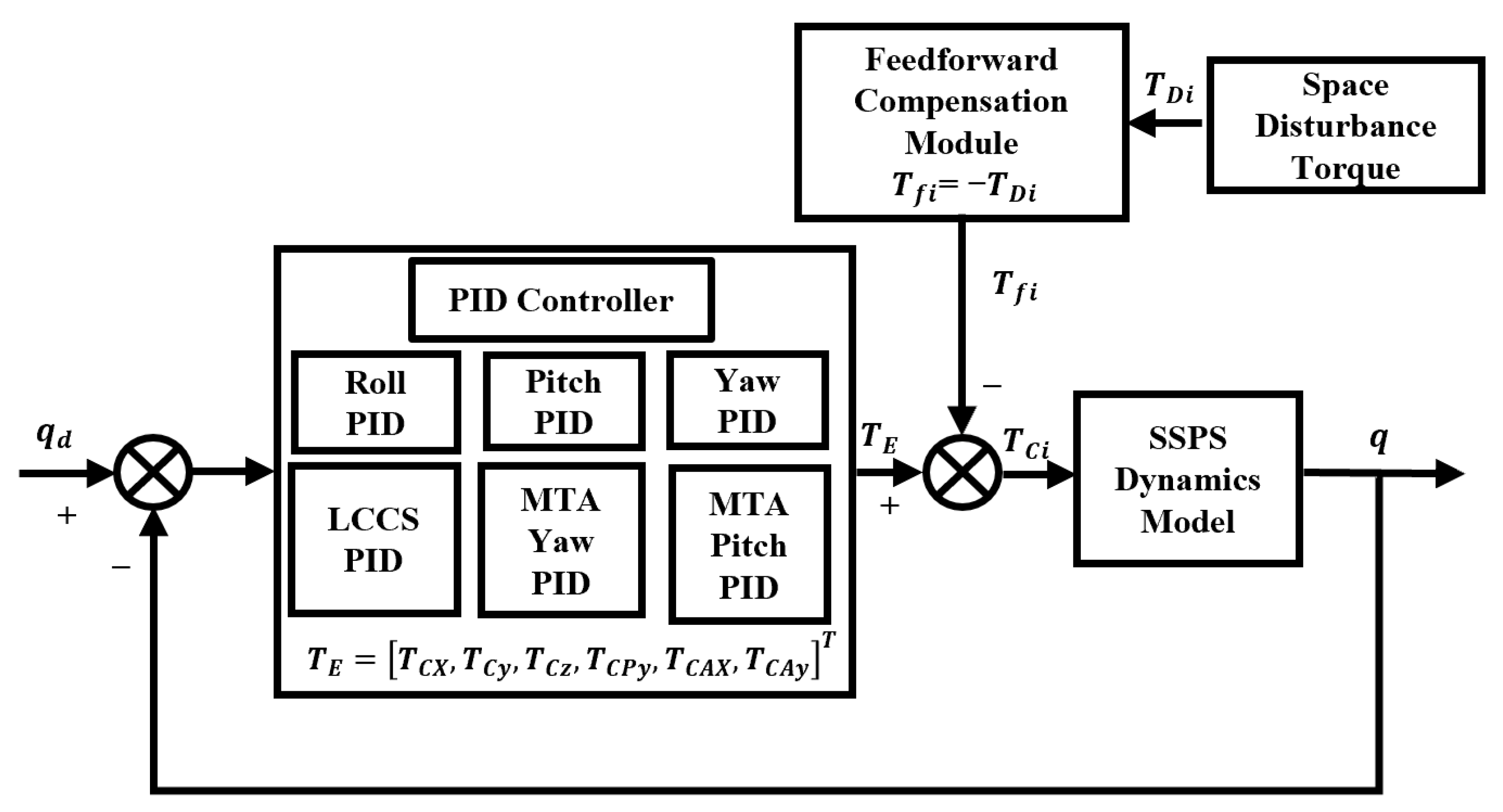
A composite control law combining PID feedback and disturbance feedforward compensation, is designed to offset known disturbances and correct attitude errors, as illustrated in Figure 16. The general form of the PID control law can be expressed as:
where are the proportional, integral, and derivative gain matrices, respectively, and is the feedforward compensation term used to cancel known disturbances such as the gravity gradient torque.
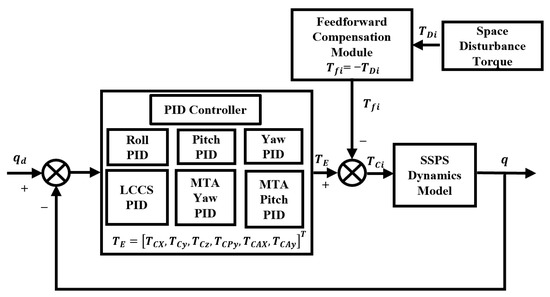
Figure 16.
Controller logic diagram.
The gravity gradient torque and Earth oblateness-induced gravitational torque constitute the dominant disturbance sources for the SSPS. As illustrated in Figure 16, the attitude error is fed into a distributed PID control architecture, where decentralized nodes govern the three-axis channels of the SSPS, the LCC system, and the antenna to achieve three-axis stabilization. These nodes synergistically synthesize the composite control torque () injected into the SSPS dynamics model, the distributed topology achieves robust disturbance attenuation.
4.3. Simulation Results
To verify the performance of the designed attitude controller, the initial generalized coordinates, desired generalized coordinates, and desired generalized angular velocities are set as follows:
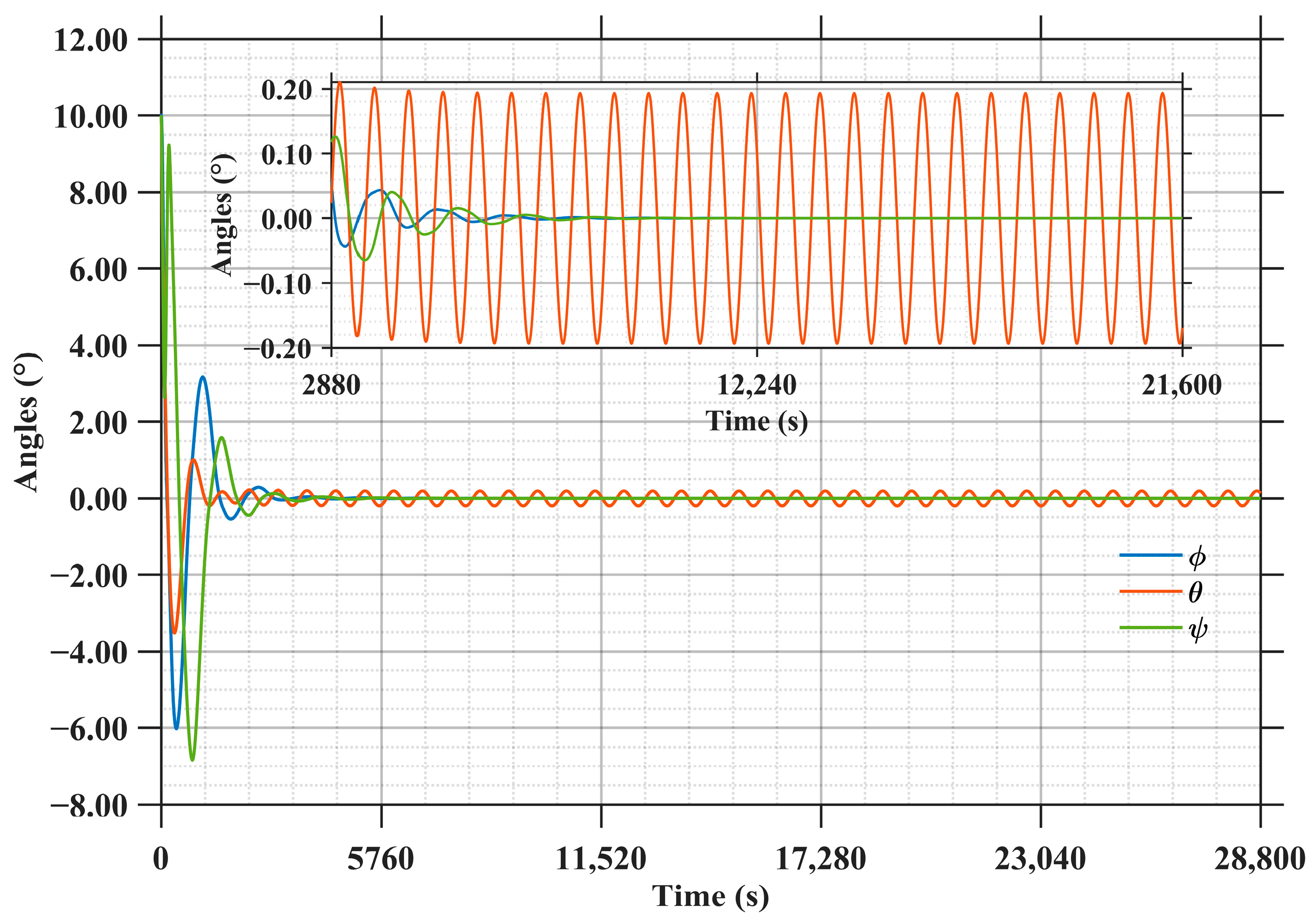
As shown in Figure 17, the results indicate that the roll angle (φ), pitch angle (θ), and yaw angle (ψ) of the main structure all exhibit a damped oscillatory convergence trend. Among these three angles, the pitch angle (θ) converges the fastest, stabilizing within ±0.2° at approximately 2500 s. In contrast, the roll angle (φ) and yaw angle (ψ) gradually converge to within ±0.2 degree at 4000, respectively. Beyond 6000, the roll and yaw angle errors converge to within ±0.05 degree, achieving ultra-high steady-state accuracy. However, the pitch angle error exhibits periodic variations with an amplitude of approximately 0.2 degree.
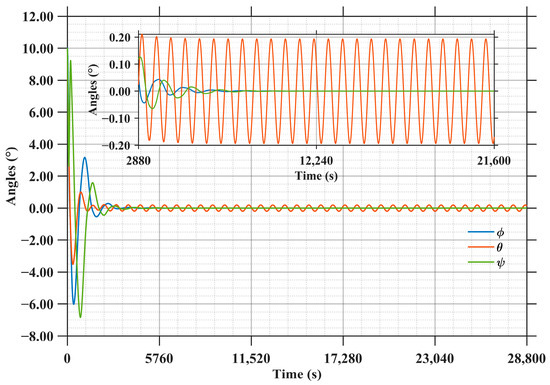
Figure 17.
Attitude angle error of SSPS.
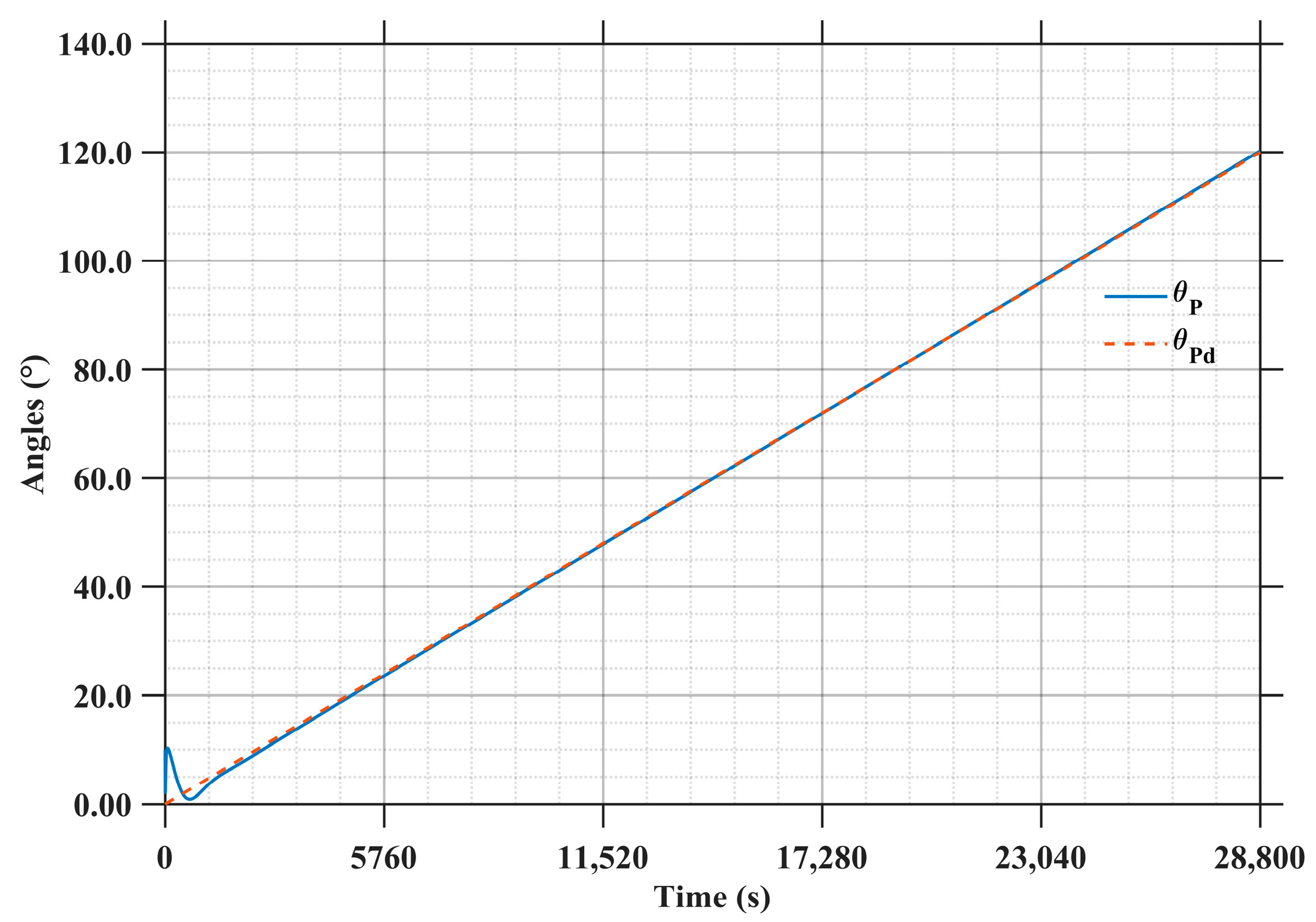
As shown in Figure 18, the LCC system needs to track sunlight based on the desired rotation principle . The initial deviation of 1.00 degree is completely eliminated after 2500 s. Then, the system reaches a steady rotational state, with the tracking error stabilized within ±0.30 degree.
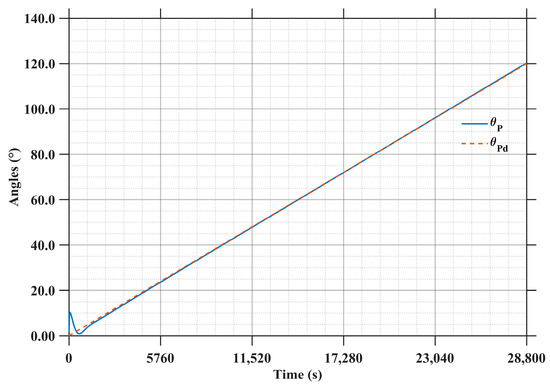
Figure 18.
Attitude Angle Error of the LCC system.
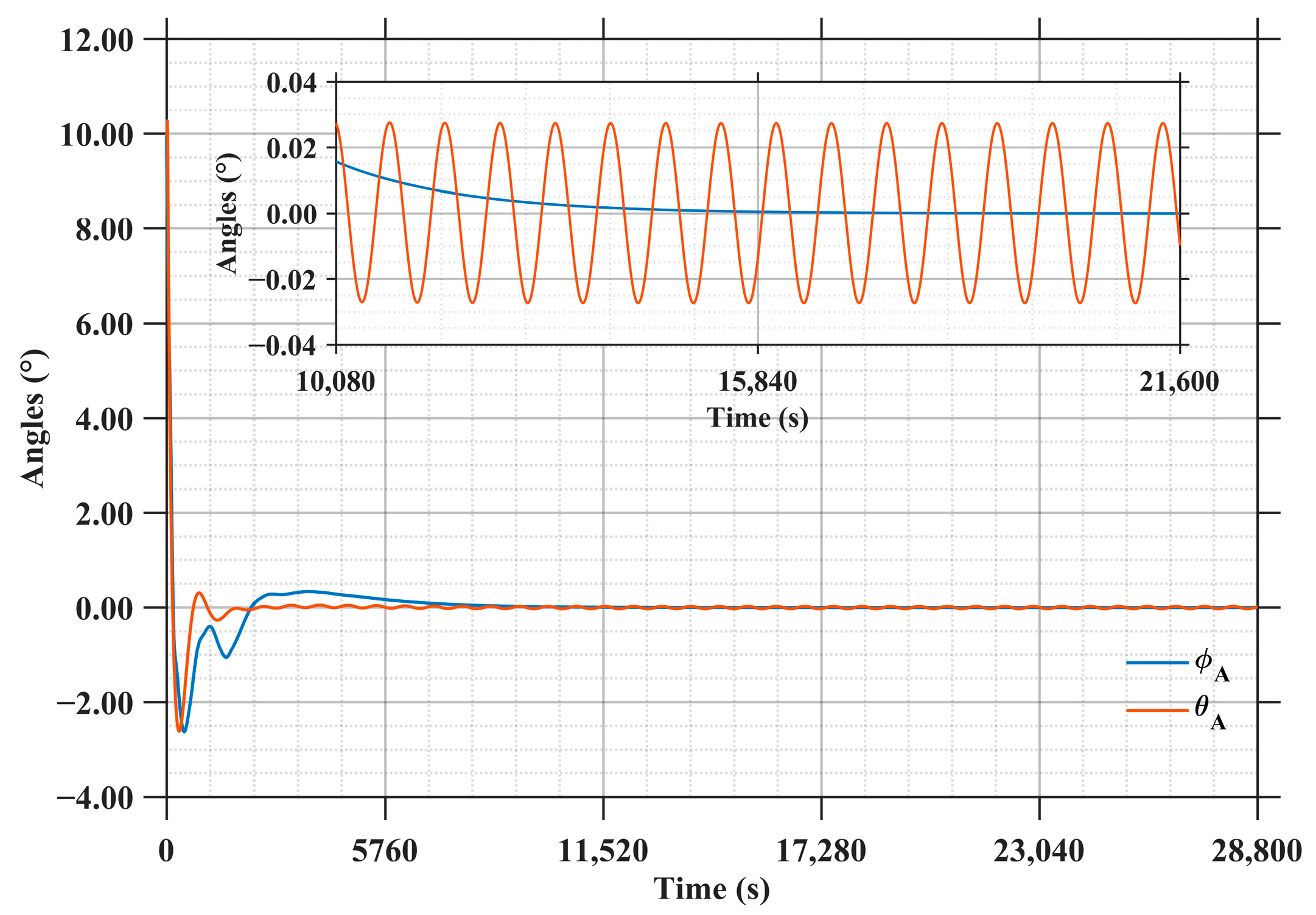
Figure 19 illustrates the attitude error evolution of the antenna’s roll angle and pitch angle. It can be seen that both angles exhibit a rapid convergence trend. Specifically, within 2000 s, the errors of roll and pitch angle are adjusted and begin to stabilize. Beyond 10,000 s, they further converge to within degree, achieving ultra-high pointing accuracy. In particular, the pitch angle exhibits periodic oscillations within the range of ±0.02 degrees during the steady phase.
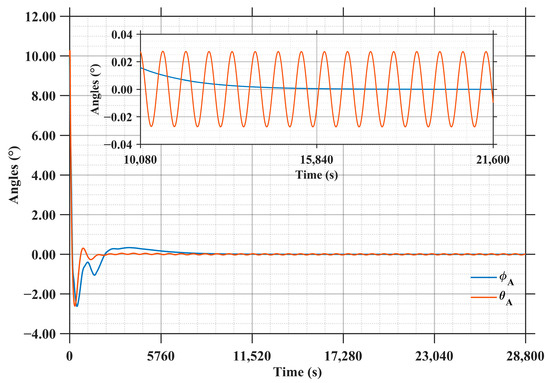
Figure 19.
Attitude angle error of the microwave transmitting antenna.
Practical systems commonly exhibit model parameter errors, non-ideal actuator characteristics, and time delays [32]. To this end, we design the following comparative models to sequentially investigate the impacts of inertia estimation errors, actuator noise, and time delays on the performance of the control system.
To simulate inertia parameter identification errors or inertia variations induced by load fluctuations, there exists a deviation between the nominal inertia used in the controller and the actual inertia in the simulation model. Considering the drive noise of actuators (e.g., motors), a white noise is superimposed on the control command . Considering computational, communication, and actuator response delays, a fixed time delay is introduced into the control loop. The corresponding uncertainty model is described as follows:
where takes values within the interval corresponding to a maximum possible deviation of ±30% relative to the nominal inertia. , and the noise standard deviation is set to 5% of the maximum control torque to simulate typical actuator disturbances. represents a typical control system cycle.
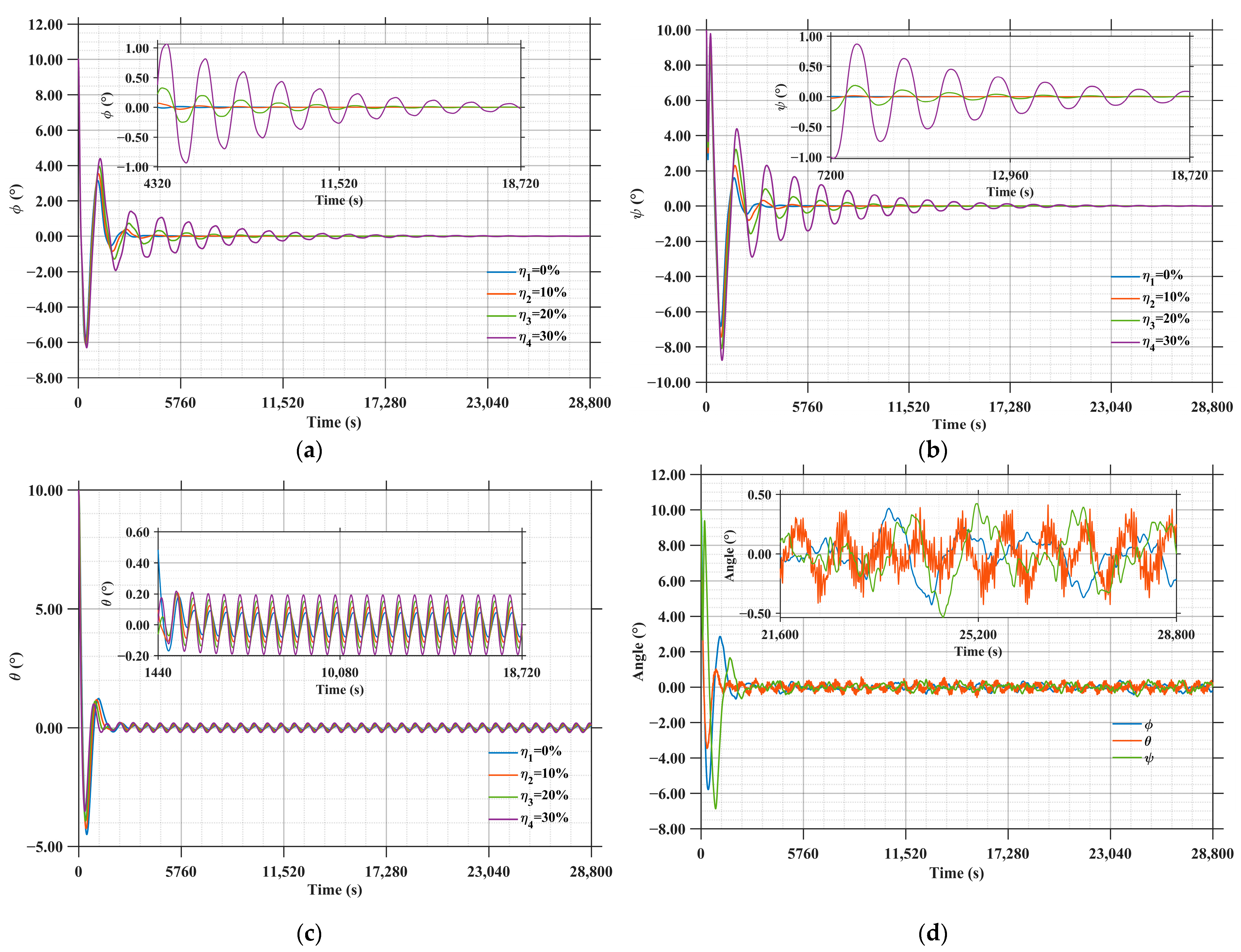
As shown in Figure 20a,b, the error angles in the φ(roll) and ψ(yaw) directions exhibit periodic oscillatory decay. A larger inertia error η corresponds to a greater oscillation amplitude: specifically, the error angle in the φ direction stabilizes within ±0.5° around 7000 s, while that in the φ direction achieves stabilization within ±0.5° at approximately 10,000 s.
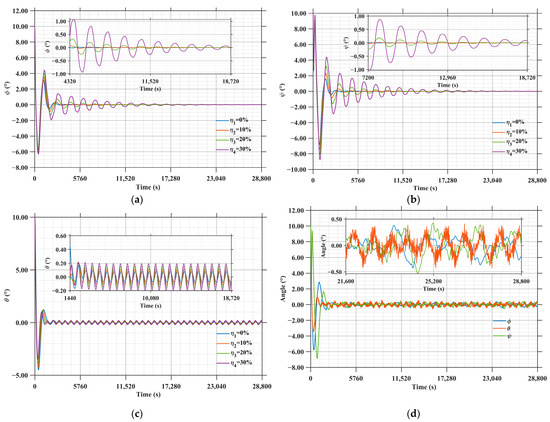
Figure 20.
Sensitivity of SSPS attitude error to inertia estimation error, time delay and actuator noise disturbances: (a) The influence of inertia error on the roll direction of SSPS; (b) The influence of inertia error on the yaw direction of SSPS; (c) The influence of inertia error on the pitch direction of SSPS; (d) Sensitivity of SSPS attitude error to time delay and actuator noise disturbances.
As shown in Figure 20c, the error angle in the θ (pitch) direction displays periodic oscillations without attenuation. Similarly, a larger inertia error η leads to a larger oscillation amplitude, and the attitude angle error stabilizes roughly within ±0.2°. This small-angle periodic oscillation persists, which is attributed to the real-time sun-tracking requirement of the LCC system—periodic variations are induced by the residual gravity gradient torque.
As shown in Figure 20d, under the combined disturbances of time delay and actuator noise, after 2500 s, the fluctuation amplitudes of the SSPS attitude errors (across roll, yaw, and pitch directions) all stabilize around ±0.5°; additionally, the error curves for each direction exhibit sustained oscillations with a period of approximately 1500 s.
In summary, inertia estimation error, time delay, and actuator noise all significantly degrade the attitude control performance of the SSPS. An increase in inertia estimation error amplifies the oscillation amplitude of attitude errors, while time delay and actuator noise induce sustained fluctuations in attitude errors.
5. Conclusions
This study systematically investigates the issues of attitude stabilization and pointing control for SSPS through theoretical modeling, characteristic analysis, and simulation validation. The main conclusions are as:
Based on the line-focusing mode and PSO algorithm, a multi-objective collaborative optimization was implemented for the LCC system. Accordingly, the light collection efficiency reached 81.9%, with a power density of 4792.24 W/m2; simultaneously, a balance between the geometric parameters of the LCC system and the aforementioned key performance indicators was achieved. This optimization result not only verifies the effectiveness of the proposed multi-objective strategy but also demonstrates its engineering applicability and practical value for SSPS light collection and conversion system design. A complete rigid-body attitude dynamics model has been preliminarily established, which fully accounts for the coupling effects between the motion of large appendages and the primary structure attitude. The expression of gravity gradient torque has been derived, revealing the time-varying characteristics of the LCC system’s gravity gradient torque, and its linear time-varying formulation has been presented. A PID configuration scheme was proposed to improve attitude control accuracy. The designed controller effectively stabilizes the primary body attitude with a steady-state error not exceeding ±0.2°, drives the LCC system to accurately track the Sun with a tracking error within ±0.3°, maintains the microwave antenna’s Earth-pointing accuracy within ±0.1°, and exhibits robust anti-disturbance capability against external disturbances.
In future work, the key directions are as follows: (1) Regarding light distribution optimization, further expand the optimization objective system (including uniformity, thermal load, and manufacturability constraints, among others) to align with the practical operational requirements of space solar power stations (SSPS); (2) Extend the current rigid-body dynamics model to a rigid-flexible coupled framework, with a focus on quantifying the impacts of elastic vibrations and structural deformations of ultra-large flexible appendages on the attitude stability and control accuracy of SSPS.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M. and Y.Y.; methodology, W.L.; software, W.W.; validation, H.Z., Y.D., X.J. and G.F.; formal analysis, J.M.; investigation, W.L.; resources, G.F.; data curation, W.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.Y.; visualization, Y.D.; supervision, Y.Y.; project administration, X.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers 52105275, 52405288, and 52405274; the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China, grant number 2025JC-YBMS-544; and the Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number ZR2023QE100.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to [unpublished SSPS engineering design parameters and proprietary data protected by intellectual property agreements].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SSPS | Space Solar Power Station/Satellite |
| MPT | Microwave Power Transmission |
| TER | Target Energy Receiving |
| LCC | Light Collection and Conversion |
| LCCS | Light Collection and Conversion System |
| PID | Proportional–Integral–Derivative |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
References
- Rodgers, E.; Sotudeh, J.; Mullins, C.; Hernandez, A.; Gertsen, E.; Joseph, N.; Le, H.; Smith, P. Space Based Solar Power. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum and Ascend 2024, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 29 July–2 August 2024; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- A Concept Geo-SPS and Airship Multi-Megawatt Power Relay System. In Proceedings of the 55th International Astronautical Congress of the International Astronautical Federation, the International Academy of Astronautics, and the International Institute of Space Law, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4 October 2004; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2024.
- Duan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Z.; Mi, J.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Li, X. On the Innovation, Design, Construction, and Experiments of OMEGA-Based SSPS Prototype: The Sun-Chasing Project. Engineering 2024, 36, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankins, J.C. A Fresh Look at Space Solar Power: New Architectures, Concepts and Technologies. Acta Astronaut. 1997, 41, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, N. The Wireless Power Transmission: Inductive Coupling, Radio Wave, and Resonance Coupling. WIREs Energy Environ. 2012, 1, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Duan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ji, X.; Li, X. Secondary Concentrator Design of an Updated Space Solar Power Satellite with a Spherical Concentrator. Sol. Energy 2021, 214, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Fthenakis, V. Power from the Sun: Its Future (Revisited). Energy Syst. 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, C.; Fikes, J.; Gerry, M.; Perkinson, D.; Feingold, H.; Olds, J. The Abacus/Reflector and Integrated Symmetrical Concentrator—Concepts for Space Solar Power Collection and Transmission. In Proceedings of the 35th Intersociety Energy Conversion Engineering Conference and Exhibit, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24–28 July 2000; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Seboldt, W.; Klimke, M.; Leipold, M.; Hanowski, N. European Sail Tower SPS Concept. Acta Astronaut. 2001, 48, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Tanaka, K.; Higuchi, K.; Okuizumi, N.; Kawasaki, S.; Shinohara, N.; Senda, K.; Ishimura, K. A New Concept of Solar Power Satellite: Tethered-SPS. Acta Astronaut. 2007, 60, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, B.; Wang, D.; Li, X. A Novel Design Project for Space Solar Power Station (SSPS-OMEGA). Acta Astronaut. 2016, 121, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z. High-Voltage and High-Power Electricity Generation, Transmission and Management of MR-SPS. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, G.; Ji, X.; Pei, M. Modular Line-Focused Space Solar Power Satellite. Aerospace 2021, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, G.; Wang, D.; Li, X. Energy Distribution Design on the Photovoltaic Cell Array of the SSPS-OMEGA Concept. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 134, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, G.; Li, M. Solar Ray Collection Rate Fluctuation Analysis with Monte Carlo Ray Tracing Method for Space Solar Power Satellite. Sol. Energy 2019, 185, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, J.; Ding, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, J. Research Progress of Multi-Agent Attitude Coordinated Control of Space Solar Power Station Energy Transmission System. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. C 2022, 103, 1031–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, C. Modular Multirotary Joints SPS Concept—Challenges and Design Considerations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2025, 61, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Wu, Z. Multibody Dynamics and Robust Attitude Control of a MW-Level Solar Power Satellite. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 106575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Duan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, G.; Li, M.; Yang, Y. Effect of Operational Condition of Rotational Subsystem on Attitude Control for Space Solar Power Station. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, G.; Li, M.; Li, X. Attitude Control of Space Solar Power Satellite with Large Range of Relative Motion among Subsystems. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Deng, Z.; Ouyang, H.; Wei, Y. A Simple Orbit-Attitude Coupled Modelling Method for Large Solar Power Satellites. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 145, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, T.; Li, J.; Deng, Z. Gravity-Gradient-Induced Transverse Deformations and Vibrations of a Sun-Facing Beam. AIAA J. 2019, 57, 5491–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleghani, B.; Sleight, D.; Muheim, D.; Belvin, K.; Wang, J. Assessment of Analysis Approaches for Solar Sail Structural Response. In Proceedings of the 39th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Huntsville, AL, USA, 20–23 July 2003; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Wang, H.; Gao, F.; Yao, W.; Sun, G.; Shao, X. Rigid–Flexible Coupling Dynamics Modeling and Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control for Large Space Solar Power Stations. Acta Astronaut. 2025, 232, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S. Dynamics of Multibody Systems—Third Edition A.A. Shabana Cambridge University Press, The Edinburgh Building, Shaftesbury Road, Cambridge, CB2 2RU, UK. 2005. 374pp, Illustrated. £45. ISBN 0-521-85011-8. Aeronaut. J. 2006, 110, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tian, Q.; Hu, H.-Y. Deployment Dynamics of a Simplified Spinning IKAROS Solar Sail via Absolute Coordinate Based Method. Acta Mech. Sin. 2013, 29, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Veubeke, B.F. The Dynamics of Flexible Bodies. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1976, 14, 895–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Z.; Feng, C.; Chen, X. Reanalysis-Based Fast Solution Algorithm for Flexible Multi-Body System Dynamic Analysis with Floating Frame of Reference Formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2020, 49, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cao, D.; He, G.; Liu, L. Thermal Alternation Induced Vibration Analysis of Spacecraft with Lateral Solar Arrays in Orbit. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 86, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Xu, M.; Song, J.; Gao, Q.; Deng, Z. Coupling Dynamic Behaviors of Flexible Stretching Hub-Beam System. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 151, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindigni, C.R.; Esposito, A.; Orlando, C.; Alaimo, A. Comparison of Piezoelectric Stack-Based Passive and Active Vibration Suppression Systems for Satellite Solar Panels. Vibration 2025, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, G.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Park, S.-W.; Oh, H.-U. Development of a Passive Vibration Damping Structure for Large Solar Arrays Using a Superelastic Shape Memory Alloy with Multi-Layered Viscous Lamination. Aerospace 2025, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Deng, Z. A Review of Dynamic Analysis on Space Solar Power Station. Astrodynamics 2023, 7, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermoldina, G.T.; Suimenbayev, B.T.; Sysoev, V.K.; Suimenbayeva, Z.B. Features of Space Solar Power Station Control System. Acta Astronaut. 2019, 158, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piegl, L.A.; Rajab, K.; Smarodzinana, V. Curve Interpolation with Directional Constraints for Engineering Design. Eng. Comput. 2008, 24, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevris, V.; Papadrakakis, M. A Hybrid Particle Swarm-Gradient Algorithm for Global Structural Optimization. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2010, 26, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamill, P. Astronautics: The Physics of Space Flight, 2nd ed. Am. J. Phys. 2012, 80, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, R.G. Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 1998, 21, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.