Genome-Wide Analysis of Soybean Polyamine Oxidase Genes Reveals Their Roles in Flower Development and Response to Abiotic Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characterization of Soybean PAO Family Genes
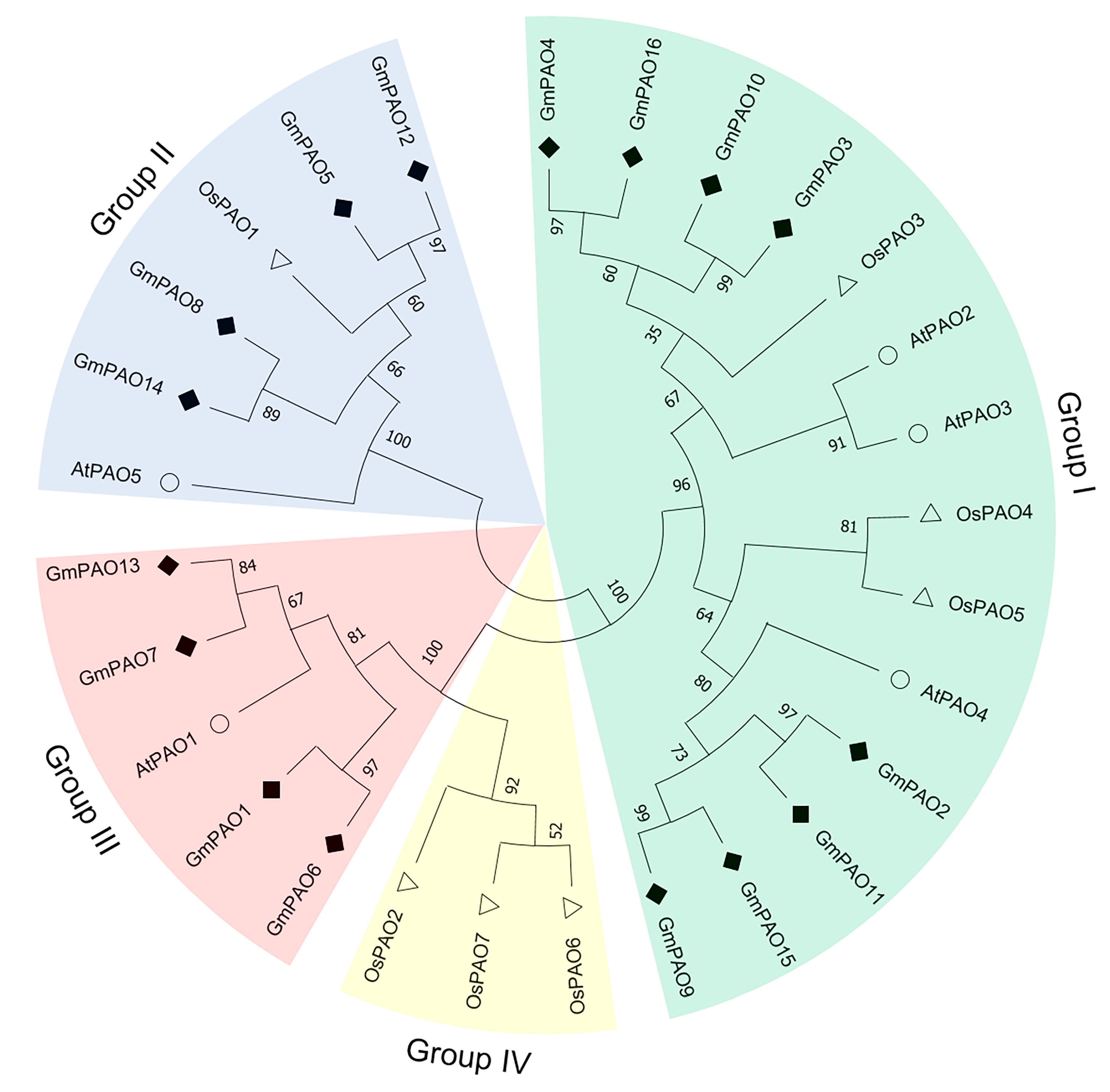
2.2. Chromosomal Mapping and Phylogenetic Analysis of GmPAOs
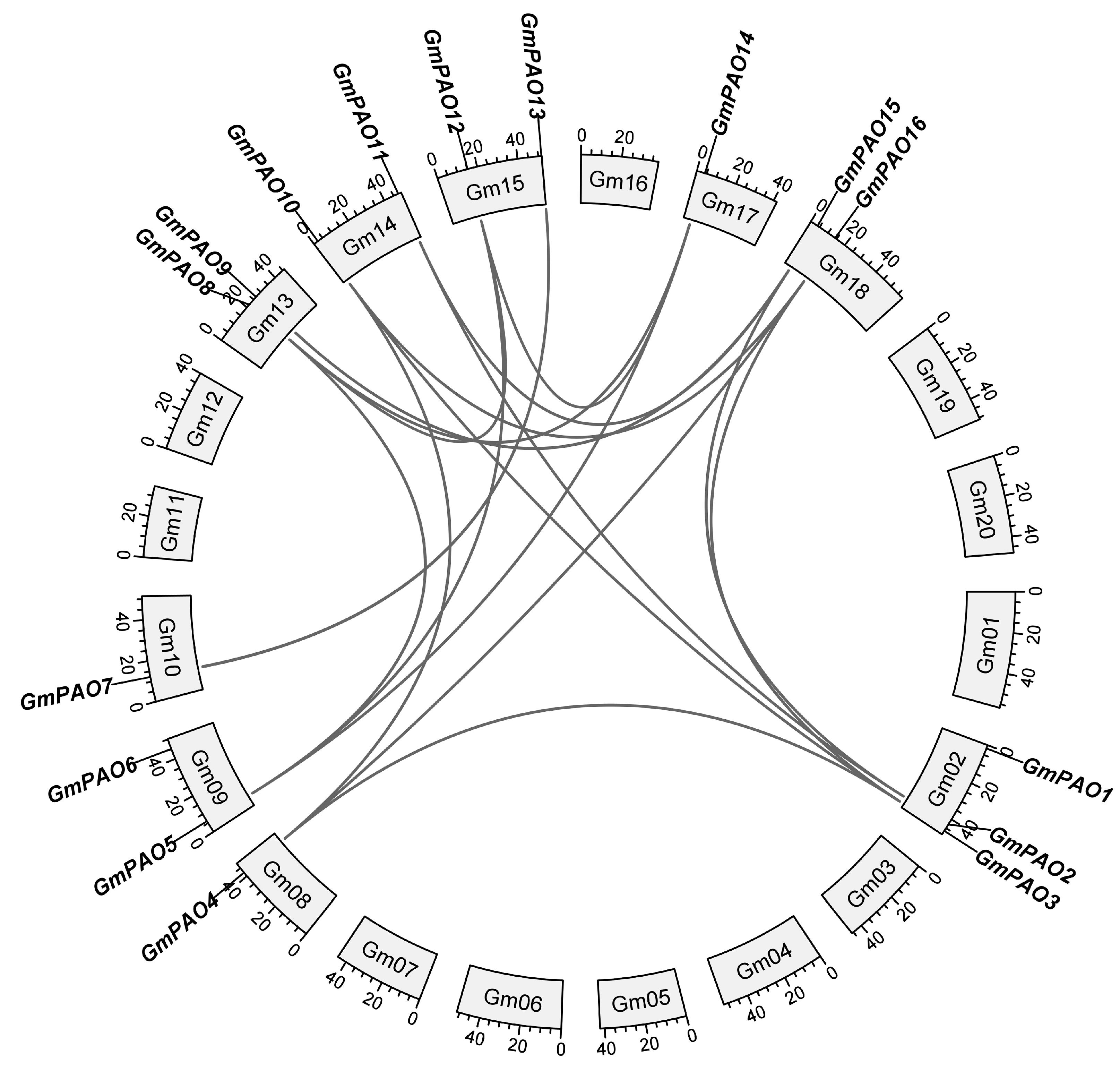
2.3. Collinearity Relationship and Evolutionary Constraint of the GmPAO Family
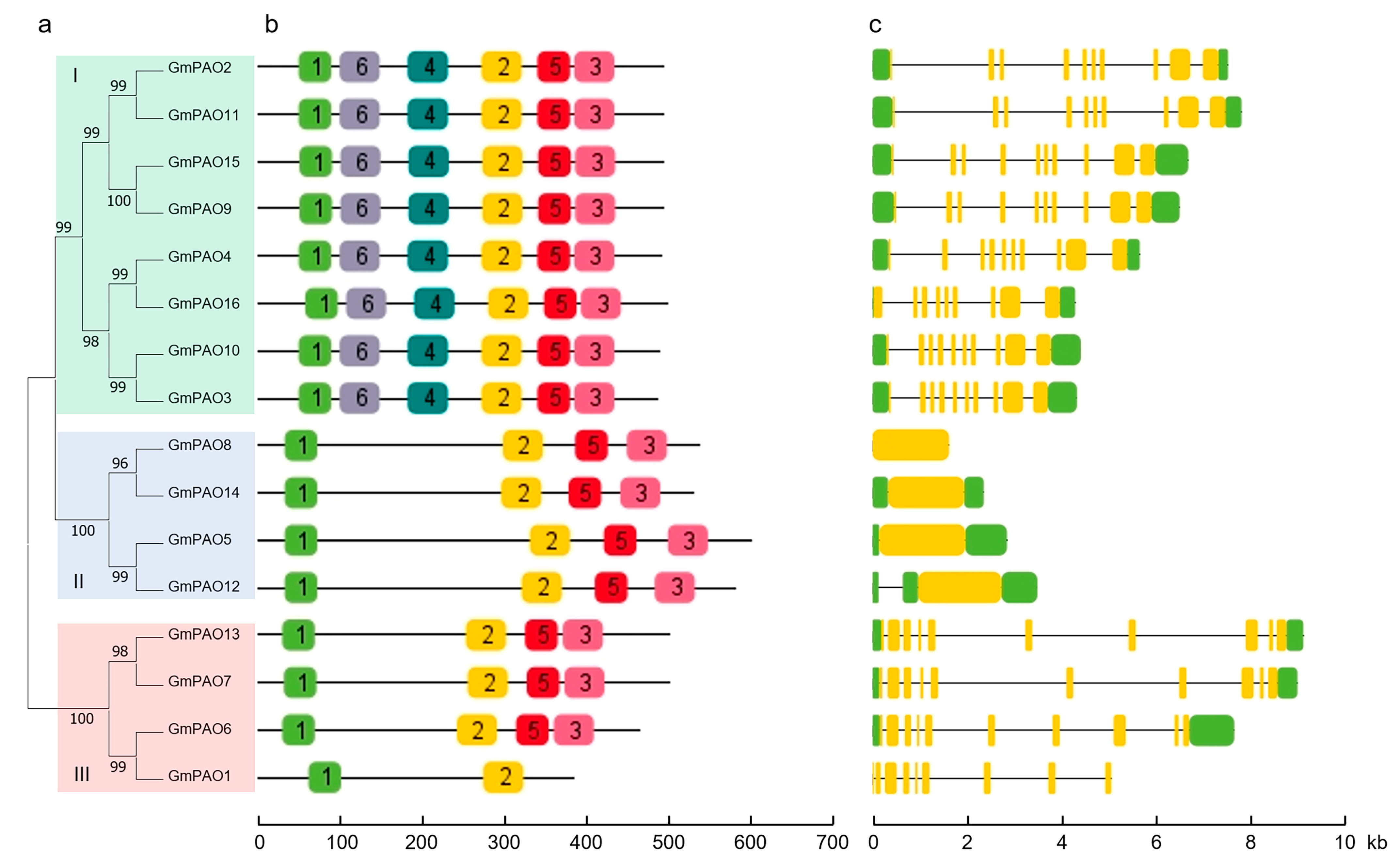
2.4. Conserved Motif and Gene Structure Analyses
2.5. Modeling of the Secondary and Tertiary Structures of GmPAOs
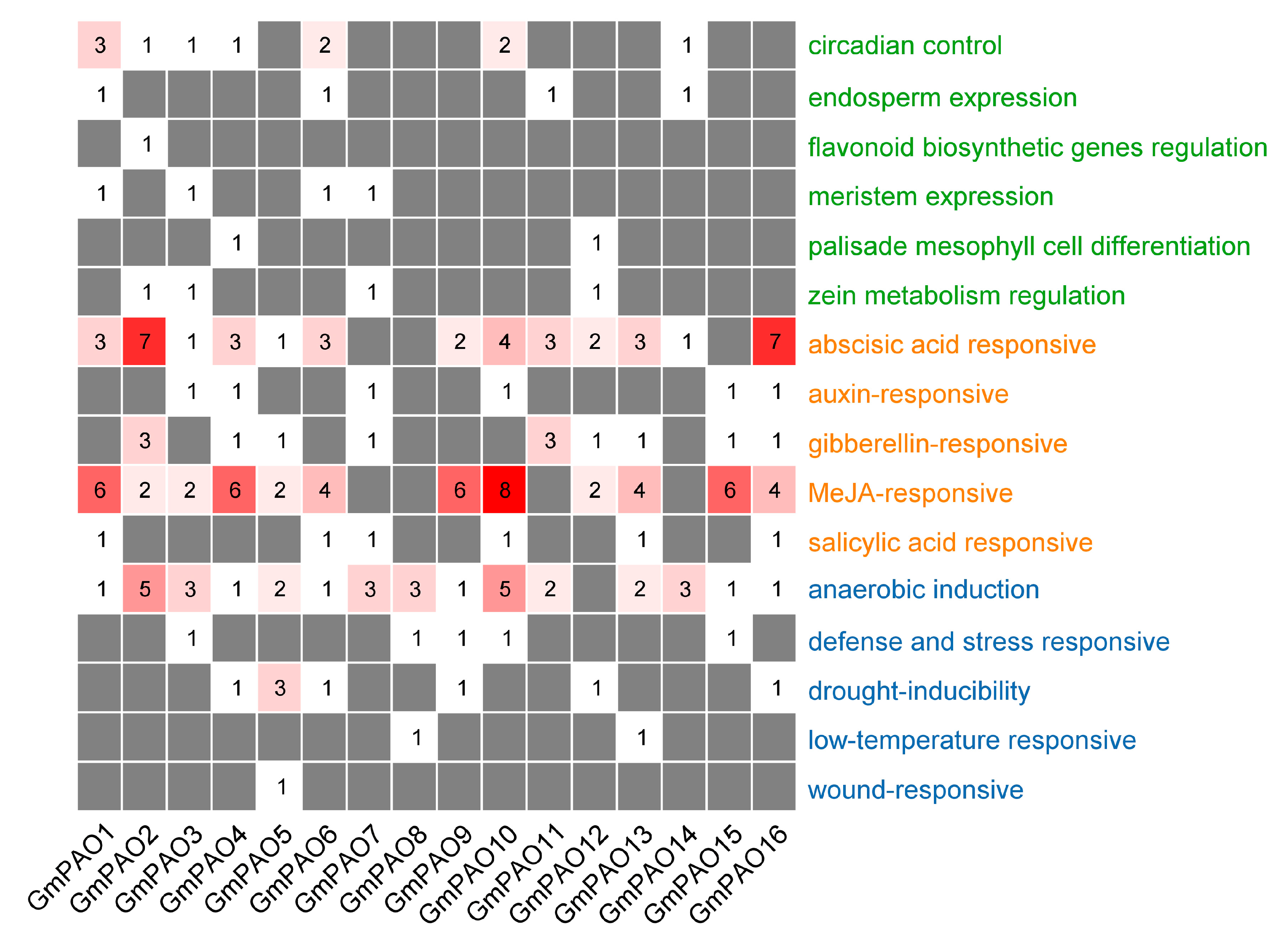
2.6. Analysis of GmPAO Promoters
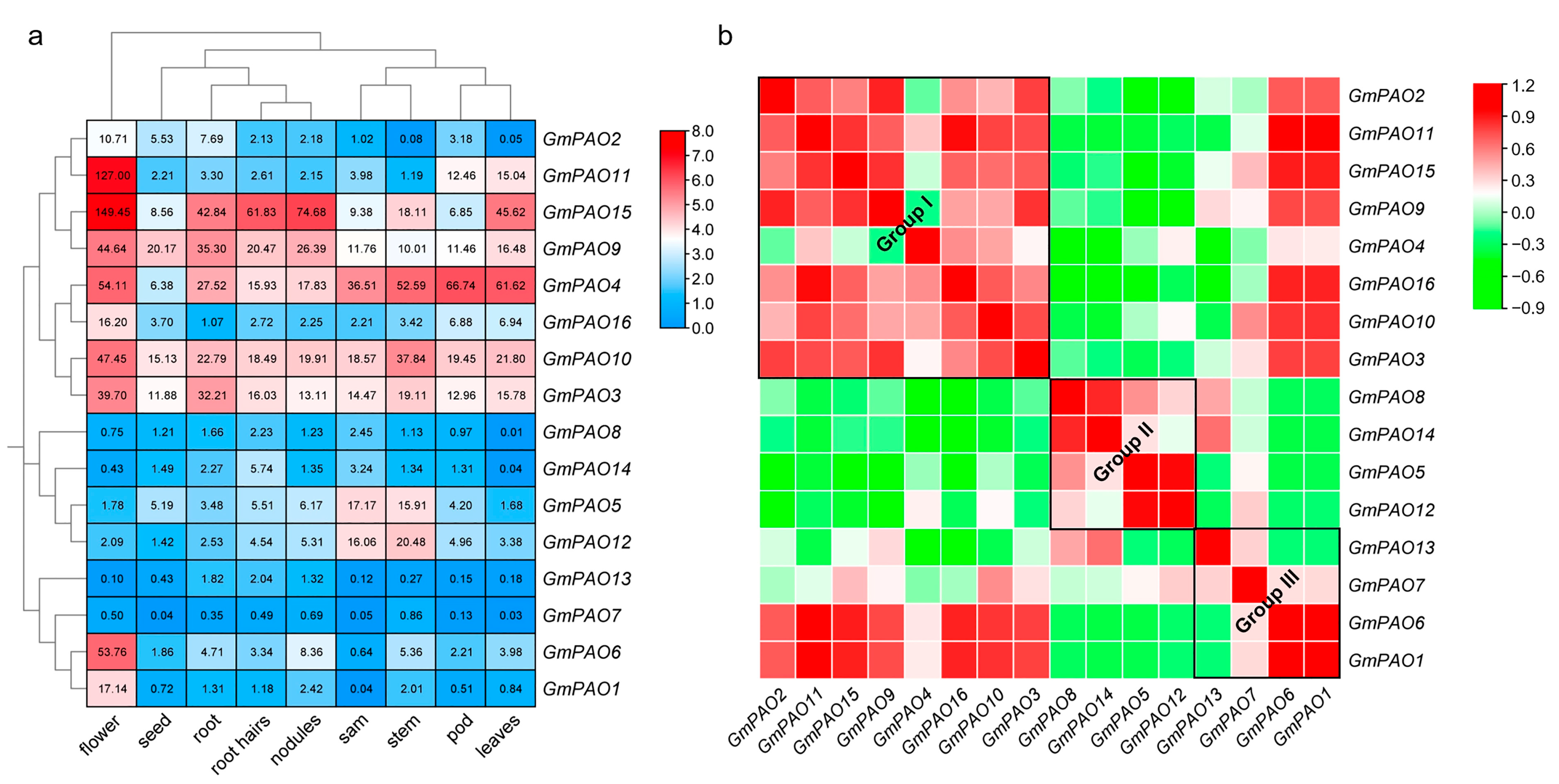
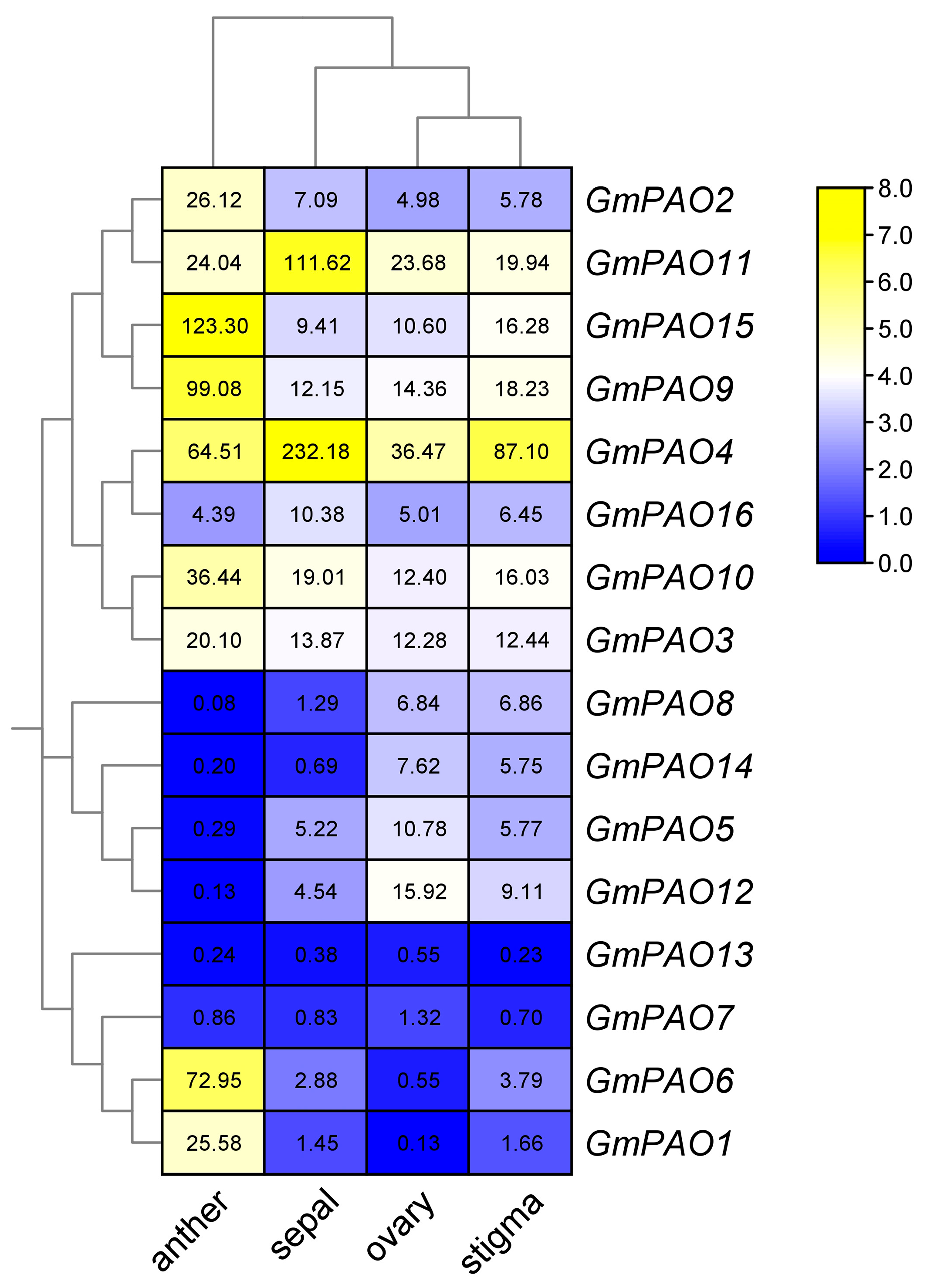
2.7. Expression Pattern of GmPAOs in Different Soybean Organs/Tissues
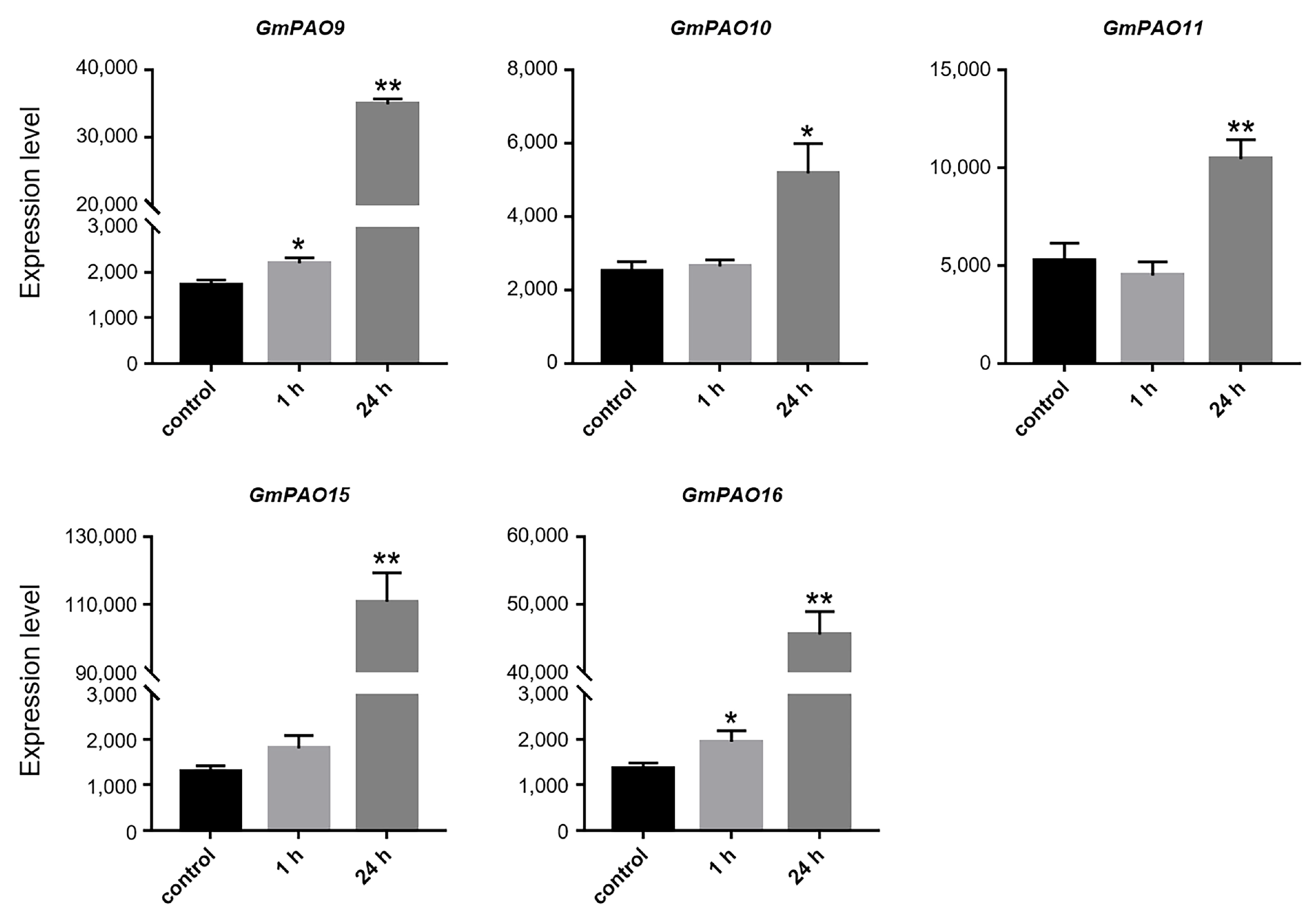
2.8. Expression Profiling of GmPAOs Under Abiotic Stress
3. Discussion
3.1. Identification and Evolution of Soybean PAO Gene Family
3.2. Role of GmPAOs in Soybean Development and Phytohormone Response
3.3. Role of GmPAOs in Response to Cold, Drought, and Submergence Stress
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of GmPAOs from Soybean Genome and Physiochemical Analysis
4.2. Chromosomal Mapping and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Analysis of Collinear Relationship and Ka/Ks Values
4.4. Analysis of Conserved Motifs, Gene Structure, Protein Structure, and Cis-Acting Elements
4.5. Expression Analysis of GmPAOs in Different Organs and Floral Tissues
4.6. Expression Profiling Under Abiotic Stress
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blázquez, M.A. Polyamines: Their role in plant development and stress. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2024, 75, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the polyamine oxidase gene family in Solanum tuberosum L. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, L.F.; Elbl, P.; Navarro, B.V.; Macedo, A.F.; Dos Santos, A.L.; Floh, E.I.; Cooke, J. Elucidation of the polyamine biosynthesis pathway during Brazilian pine (Araucaria angustifolia) seed development. Tree Physiol. 2017, 37, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, H.L.; Blomstedt, C.K.; Neale, A.D.; Gleadow, R.; DeBoer, K.D.; Hamill, J.D. Effects of down-regulating ornithine decarboxylase upon putrescine-associated metabolism and growth in Nicotiana tabacum L. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3367–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, N.K.; Nelson, T. Arabidopsis thickvein mutation affects vein thickness and organ vascularization, and resides in a provascular cell-specific spermine synthase involved in vein definition and in polar auxin transport. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rangel, D.; Chávez-Martínez, A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, A.A.; Maruri-López, I.; Urano, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Jiménez-Bremont, J.F. Simultaneous silencing of two arginine decarboxylase genes alters development in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, J.; Miao, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, D.; Gu, H.; Cui, H.; Shi, S.; et al. The spermine synthase OsSPMS1 regulates seed germination, grain size, and yield. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 1522–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini-Fracassini, D.; Di-Sandro, A.; Del-Duca, S. Spermine delays leaf senescence in Lactuca sativa and prevents the decay of chloroplast photosystems. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcázar, R.; Altabella, T.; Marco, F.; Bortolotti, C.; Reymond, M.; Koncz, C.; Carrasco, P.; Tiburcio, A.F. Polyamines: Molecules with regulatory functions in plant abiotic stress tolerance. Planta 2010, 231, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavladoraki, P.; Cona, A.; Angelini, R. Copper-containing amine oxidases and FAD-dependent polyamine oxidases are key players in plant tissue differentiation and organ development. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Kim, D.W.; Niitsu, M.; Maeda, S.; Watanabe, M.; Kamio, Y.; Berberich, T.; Kusano, T. Polyamine oxidase 7 is a terminal catabolism-type enzyme in Oryza sativa and is specifically expressed in anthers. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Qian, Y. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of polyamine oxidase genes in maize reveal essential roles in abiotic stress tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 950064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordenave, C.D.; Granados Mendoza, C.; Jiménez Bremont, J.F.; Gárriz, A.; Rodríguez, A.A. Defining novel plant polyamine oxidase subfamilies through molecular modeling and sequence analysis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavladoraki, P.; Rossi, M.N.; Saccuti, G.; Perez-Amador, M.A.; Polticelli, F.; Angelini, R.; Federico, R. Heterologous expression and biochemical characterization of a polyamine oxidase from Arabidopsis involved in polyamine back conversion. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1519–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fincato, P.; Moschou, P.N.; Spedaletti, V.; Tavazza, R.; Angelini, R.; Federico, R.; Roubelakis-Angelaki, K.A.; Tavladoraki, P. Functional diversity inside the Arabidopsis polyamine oxidase gene family. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Watanabe, K.; Murayama, C.; Izawa, S.; Niitsu, M.; Michael, A.J.; Berberich, T.; Kusano, T. Polyamine oxidase5 regulates Arabidopsis growth through thermospermine oxidase activity. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 1575–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdallah, O.; Ahou, A.; Mancuso, N.; Pompili, V.; Macone, A.; Pashkoulov, D.; Stano, P.; Cona, A.; Angelini, R.; Tavladoraki, P. The Arabidopsis polyamine oxidase/dehydrogenase 5 interferes with cytokinin and auxin signaling pathways to control xylem differentiation. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 997–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaszler, N.; Benkő, P.; Molnár, Á.; Zámbori, A.; Fehér, A.; Gémes, K. Absence of Arabidopsis polyamine oxidase 5 influences the cytokinin-induced shoot meristem formation from lateral root primordia. Plants 2023, 12, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimalasekera, R.; Schaarschmidt, F.; Angelini, R.; Cona, A.; Tavladoraki, P.; Scherer, G.F. POLYAMINE OXIDASE2 of Arabidopsis contributes to ABA mediated plant developmental processes. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 96, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Uemura, T.; Teshima, Y. Polyamine oxidase 2 is involved in regulating excess spermidine contents during seed germination and early seedling development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 516, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cona, A.; Cenci, F.; Cervelli, M.; Federico, R.; Mariottini, P.; Moreno, S.; Angelini, R. Polyamine oxidase, a hydrogen peroxide-producing enzyme, is up-regulated by light and down-regulated by auxin in the outer tissues of the maize mesocotyl. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, Y.; Kim, D.W.; Watanabe, K.; Sasaki, A.; Niitsu, M.; Berberich, T.; Kusano, T.; Takahashi, Y. Constitutively and highly expressed Oryza sativa polyamine oxidases localize in peroxisomes and catalyze polyamine back conversion. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Shao, G.; Jiao, G.; Sheng, Z.; Xie, L.; Hu, S.; Tang, S.; Wei, X.; Hu, P. Targeted mutagenesis of POLYAMINE OXIDASE 5 that negatively regulates mesocotyl elongation enables the generation of direct-seeding rice with improved grain yield. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoda, H.; Hiroi, Y.; Sano, H. Polyamine oxidase is one of the key elements for oxidative burst to induce programmed cell death in tobacco cultured cells. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschou, P.N.; Delis, I.D.; Paschalidis, K.A.; Roubelakis-Angelakis, K.A. Transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing polyamine oxidase are not able to cope with oxidative burst generated by abiotic factors. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, L.; Xiao, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xue, X.; Xu, L.; Zhou, P.; Ran, J.; Huang, Z.; et al. Genome-wide identification of polyamine oxidase (PAO) family genes: Roles of CaPAO2 and CaPAO4 in the cold tolerance of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, W.; Tian, L.; Fu, Y.; Tan, L.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, C.; Liu, F. Polyamine oxidase 3 is involved in salt tolerance at the germination stage in rice. J. Genet. Genom. 2022, 49, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarza, X.; Atanasov, K.E.; Marco, F.; Arbona, V.; Carrasco, P.; Kopka, J.; Fotopoulos, V.; Munnik, T.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Tiburcio, A.F.; et al. Polyamine oxidase 5 loss-of-function mutations in Arabidopsis thaliana trigger metabolic and transcriptional reprogramming and promote salt stress tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, J.H. CsPAO4 of Citrus sinensis functions in polyamine terminal catabolism and inhibits plant growth under salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incà, R.; Mattioli, R.; Tomasella, M.; Tavazza, R.; Macone, A.; Incocciati, A.; Martignago, D.; Polticelli, F.; Fraudentali, I.; Cona, A.; et al. A Solanum lycopersicum polyamine oxidase contributes to the control of plant growth, xylem differentiation, and drought stress tolerance. Plant J. 2024, 119, 960–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Q.; Zhu, X.F.; Tian, W.G.; Cheng, W.H.; Hakim; Sun, J.; Jin, S.X.; Zhu, H.G. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of polyamine oxidase genes in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Cell Tiss. Organ. Cult. 2017, 129, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, J.H. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the polyamine oxidase gene family in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis). Gene 2015, 555, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Tao, M.; Li, M.; Yang, H.; Xia, E.H.; Chen, Q.; Wan, X. Genome-wide identification of seven polyamine oxidase genes in Camellia sinensis (L.) and their expression patterns under various abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 544933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Yan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Peng, H.; Jing, M.F.; Dou, D.L. GmPAO-mediated polyamine catabolism enhances soybean Phytophthora resistance without growth penalty. Phytopathol. Res. 2022, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, S.J.; Zhang, H.Z.; Wang, P.W. The improvement of soybean salt tolerance by overexpressed GmPAO1. Phyton-int. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 92, 1109–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, C.D.; Springer, N.M.; Hirsch, C.N. Genomic limitations to RNA sequencing expression profiling. Plant J. 2015, 84, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.W.; Huang, B.B.; Jia, D.Y.; Mann, T.; Jiang, X.Y.; Qiu, Y.X.; Niitsu, M.; Berberich, T.; Kusano, T.; Liu, T.B. Identification of seven polyamine oxidase genes in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and their expression profiles under physiological and various stress conditions. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 228, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Tan, B.; Feng, J. Polyamine oxidase (PAO)–mediated polyamine catabolism plays potential roles in peach (Prunus persica L.) fruit development and ripening. Tree Genet. Genomes 2021, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fincato, P.; Moschou, P.N.; Ahou, A.; Angelini, R.; Roubelakis-Angelakis, K.A.; Federico, R.; Tavladoraki, P. The members of Arabidopsis thaliana PAO gene family exhibit distinct tissue- and organ-specific expression pattern during seedling growth and flower development. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagor, G.H.M.; Inoue, M.; Kusano, T.; Berberich, T. Expression profile of seven polyamine oxidase genes in rice (Oryza sativa) in response to abiotic stresses, phytohormones and polyamines. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2021, 27, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yariuchi, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Noutoshi, Y.; Takahashi, T. Responses of polyamine-metabolic genes to polyamines and plant stress hormones in Arabidopsis seedlings. Cells 2021, 10, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, H.; Zhang, J.; Bai, W.; Kuai, P.; Cheng, J.; Lu, J.; Lou, Y.; Li, R. Jasmonate-mediated polyamine oxidase 6 drives herbivore-induced polyamine catabolism in rice. Plant J. 2024, 120, 2000–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajguz, A.; Piotrowska-Niczyporuk, A. Biosynthetic pathways of hormones in plants. Metabolites 2023, 13, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.K.; Pandey, A.; Hamurcu, M.; Vyhnánek, T.; Zargar, S.M.; Kahraman, A.; Topal, A.; Gezgin, S. Exploring strigolactones for inducing abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2024, 60, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, F.M.; Maiale, S.J.; Rossi, F.R.; Marina, M.; Ruíz, O.A.; Gárriz, A. Polyamine metabolism responses to biotic and abiotic stress. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1694, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Alcázar, R.; Bueno, M.; Tiburcio, A.F. Polyamines: Small amines with large effects on plant abiotic stress tolerance. Cells 2020, 9, 2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, I.; Roy, P.C.; Das, E.; Mishra, S.; Chowdhary, G. Plant peroxisomal polyamine oxidase: A ubiquitous enzyme involved in abiotic stress tolerance. Plants 2023, 12, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagor, G.H.; Zhang, S.; Kojima, S.; Simm, S.; Berberich, T.; Kusano, T. Reducing cytoplasmic polyamine oxidase activity in Arabidopsis increases salt and drought tolerance by reducing reactive oxygen species production and increasing defense gene expression. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdel, H.; Hassani, S.B.; Ghotbi-Ravandi, A.A.; Bernard, F. Contrasting the expression pattern change of polyamine oxidase genes and photosynthetic efficiency of maize (Zea mays L.) genotypes under drought stress. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, N.; Li, D.; Hu, L. Melatonin improved waterlogging tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) by reprogramming polyamine and ethylene metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, P.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Jia, X.; An, P.; Tang, Y.; et al. Foliar application of spermidine alleviates waterlogging-induced damages to maize seedlings by enhancing antioxidative capacity, modulating polyamines and ethylene biosynthesis. Life 2022, 12, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chu, M.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Tang, S.; Ding, C.; Li, G. Exogenous spermidine alleviates oxidative damage and reduce yield loss in rice submerged at tillering stage. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Lan, C.J.; Li, C.Z.; Li, C.J.; Huang, J.Q. Exogenous spermidine and calcium alleviate waterlogging stress in cherry tomato at the seedling stage. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 307, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.J.; Lv, M.W.; Liu, Z.M.; Yang, X.; Yang, L.J.; Dong, L.L.; Lei, F.L.; Xie, A.Q.; Zhang, D.L.; Bao, M.Y.; et al. The polyamine signaling pathway in response to waterlogging stress of Paeonia lactiflora. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant. 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.Q.; Gascuel, O. An improved general amino acid replacement matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Zhang, K.; Duanmu, H.; Yu, Y. The myosin family genes in soybean: Genome-wide identification and expression analysis. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 160, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Randall, S.K. Functionality of soybean CBF/DREB1 transcription factors. Plant Sci. 2016, 246, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, B.G.; Li, S.; Rajasundaram, D.; Lamichhane, S.; Fukao, T. Overlapping and stress-specific transcriptomic and hormonal responses to flooding and drought in soybean. Plant J. 2021, 107, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Gene ID | DNA (bp) | Transcript (bp) | Peptide (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | Instability Index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GmPAO1 | Glyma.02G018800 | 5022 | 1158 | 385 | 43.29 | 5.60 | 38.08 | −0.181 |
| GmPAO2 | Glyma.02G240000 | 7474 | 2073 | 494 | 54.90 | 5.81 | 35.44 | −0.026 |
| GmPAO3 | Glyma.02G282000 | 4303 | 2434 | 487 | 54.11 | 5.68 | 37.47 | −0.062 |
| GmPAO4 | Glyma.08G303800 | 5622 | 2087 | 490 | 54.15 | 5.59 | 36.28 | −0.077 |
| GmPAO5 | Glyma.09G063000 | 2834 | 2834 | 600 | 65.91 | 5.82 | 43.26 | −0.339 |
| GmPAO6 | Glyma.09G227500 | 7608 | 2516 | 465 | 52.18 | 5.18 | 39.87 | −0.274 |
| GmPAO7 | Glyma.10G090700 | 8933 | 2086 | 500 | 56.47 | 5.00 | 44.91 | −0.267 |
| GmPAO8 | Glyma.13G104100 | 1617 | 1617 | 538 | 59.38 | 6.06 | 42.81 | −0.222 |
| GmPAO9 | Glyma.13G153100 | 6460 | 2550 | 493 | 54.44 | 5.59 | 28.01 | −0.002 |
| GmPAO10 | Glyma.14G032300 | 4385 | 2413 | 489 | 54.34 | 5.78 | 36.58 | −0.058 |
| GmPAO11 | Glyma.14G209400 | 7760 | 2268 | 494 | 54.65 | 5.60 | 37.04 | −0.031 |
| GmPAO12 | Glyma.15G169600 | 3473 | 2969 | 581 | 63.67 | 6.00 | 39.77 | −0.312 |
| GmPAO13 | Glyma.15G276500 | 9075 | 2063 | 501 | 56.17 | 5.20 | 40.19 | −0.262 |
| GmPAO14 | Glyma.17G055000 | 2346 | 2346 | 530 | 58.31 | 5.93 | 42.27 | −0.200 |
| GmPAO15 | Glyma.18G045100 | 6641 | 2597 | 493 | 54.50 | 5.79 | 28.32 | −0.049 |
| GmPAO16 | Glyma.18G116300 | 4266 | 1861 | 498 | 55.05 | 5.79 | 34.69 | 0.105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Jin, B.; Gao, M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Z.; Duan, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of Soybean Polyamine Oxidase Genes Reveals Their Roles in Flower Development and Response to Abiotic Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121867
Yu Y, Jin B, Gao M, Zhang K, Liu Z, Duan X. Genome-Wide Analysis of Soybean Polyamine Oxidase Genes Reveals Their Roles in Flower Development and Response to Abiotic Stress. Plants. 2025; 14(12):1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121867
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yang, Bohuai Jin, Meina Gao, Ke Zhang, Zhouli Liu, and Xiangbo Duan. 2025. "Genome-Wide Analysis of Soybean Polyamine Oxidase Genes Reveals Their Roles in Flower Development and Response to Abiotic Stress" Plants 14, no. 12: 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121867
APA StyleYu, Y., Jin, B., Gao, M., Zhang, K., Liu, Z., & Duan, X. (2025). Genome-Wide Analysis of Soybean Polyamine Oxidase Genes Reveals Their Roles in Flower Development and Response to Abiotic Stress. Plants, 14(12), 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121867








