Abstract
Diabetes mellitus is a pathology with increasing frequency in society, being one of the main causes of death worldwide. For this reason, new therapeutic targets have been studied over the years. 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11β-HSD1) is an enzyme responsible for reducing cortisone to its active form cortisol, which can lead to metabolic changes such as insulin resistance and hyperglycemia. Therefore, 11β-HSD1 inhibition may offer a new therapeutic approach for type 2 diabetes mellitus. This work intends to systematically review the available scientific evidence on this subject. For this, a search was conducted in three databases and 15 clinical and in vivo preclinical studies were included in this review. Despite the high inhibitory and selectivity levels achieved with several molecules and the demonstrated clinical efficacy in diabetes treatment, no phase III clinical trials have yet been conducted. This is important because the long-term effects of 11β-HSD1 inhibitors including the consequences in hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis must be evaluated. However, this enzyme remains a promising target for drug development, including due to its effectiveness in controlling various factors that constitute the metabolic syndrome and its potential for multiple indications in patients with diabetes, including wound healing and weight loss.
1. Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a common chronic disease characterized by increased blood glucose levels, called hyperglycemia, and its prevalence increases with age, affecting both sexes and all age groups [1]. In T2DM occurs a progressive loss of adequate pancreatic β-cell insulin secretion frequently associated to insulin resistance [2]. The long-term effects of uncontrolled diabetes include the development of microvascular (lesions of small blood vessels) and macrovascular (lesions of large blood vessels) complications, which develop silently and are often already installed when they are detected [1]. Of the microvascular complications, it is worth highlighting retinopathy (the main cause of blindness in adults), neuropathy (which, in combination with macrovascular dysfunction leads to the appearance of diabetic foot ulcers and, in extreme situations, amputation), and nephropathy (which, in more advanced cases, can cause renal failure) [3]. The most common macrovascular complications are atherosclerosis (which can lead to the development of coronary artery disease or angina pectoris and, in more serious conditions, acute myocardial infarction) and arteriosclerosis (which increases blood pressure, among other problems) [3].
Several criteria may be independently used to establish the diagnosis of T2DM: A 75 g oral glucose tolerance test with a 2 h value of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher; a random plasma glucose of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or more with typical symptoms of hyperglycemia; a fasting plasma glucose of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher on more than one occasion; or a glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) value of 6.5% (48 mmol/mol) or more [2].
Currently, there are several pharmacological approaches that can be used for T2DM, such as the use of biguanides, sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, acarbose, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, and insulin [4]. However, other pharmacological classes have also been studied for future use in T2DM treatment, namely 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11β-HSD1) inhibitors [5].
11β-HSD1 is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-dependent enzyme mainly expressed in liver and fat tissues and is responsible for the reduction of cortisone to its active form cortisol [6,7,8,9], important glucocorticoids (GC) for homeostasis regulation. Among other activities, GC oppose the insulin action [10]. In fact, one of the relevant functions of cortisol is to promote key gluconeogenesis enzymes in the liver, by inducing both phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) gene expression, which is responsible to phosphorylate oxaloacetate and form phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP) [11], and glucose 6-phosphatase (G6Pase) [12], which hydrolyses glucose 6-phosphate, resulting in the formation of free glucose, the final step in gluconeogenesis. This process can contribute to hyperglycemia.
The activation of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA) begins in stress situations in the hypothalamus with the secretion of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH). This process stimulates the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) by the anterior pituitary gland, which in turn circulates through the bloodstream to adrenal cortex and stimulates adrenal gland to produce cortisol [10]. Although the circulation of cortisol is centrally controlled by HPA axis, the GC action in tissues is mainly regulated by two 11β-HSD isoforms, type 1 and type 2, which catalyze the inter-conversion of active steroids (cortisol) and inactive metabolites (cortisone) [13]. 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (11β-HSD2) is a NAD+ dependent enzyme mainly present in the kidney, which oxidizes cortisol to the inactive metabolite cortisone and reverts the 11β-HSD1 action [6,9].
In the liver, these hormones are converted into their metabolites, which are rapidly excreted in the urine [14]. Cortisol is reduced to allo-tetrahydrocortisol (allo-THF) and tetrahydrocortisol (THF) by 5α- and 5β-reductases, respectively, and cortisone is reduced to tetrahydrocortisone (THE) by 5β-reductases [15]. These metabolites generally account for more than 50% of total GC in urine [15]. The ratio of these cortisol metabolites (allo-THF + THF) to the cortisone metabolite (THE) is approximately the same ratio of liver cortisol and cortisone values [15]. For this reason, this ratio is often used as an indirect measure of the total 11β-HSD1 activity [8].
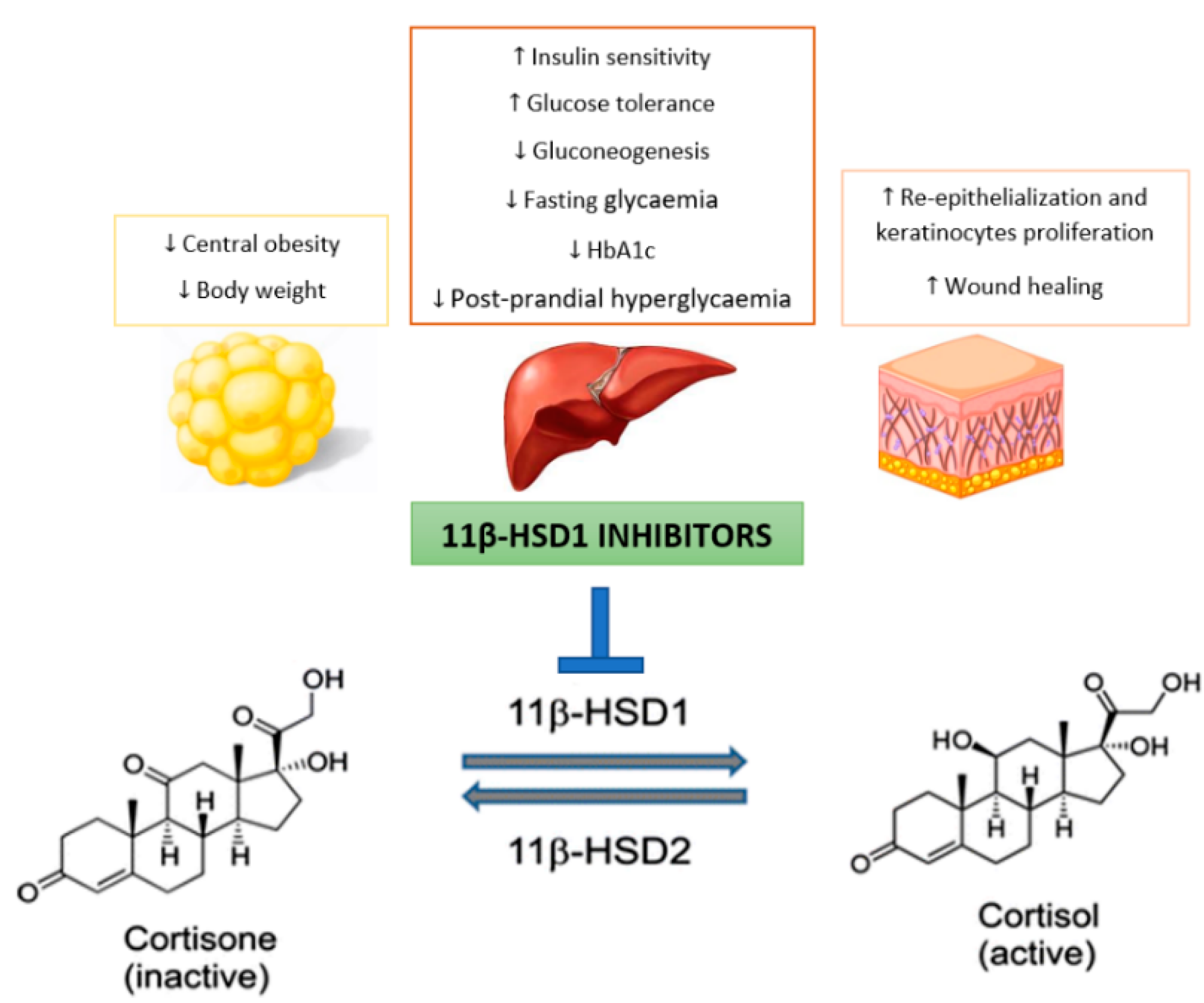
Since GC metabolism is regulated by 11β-HSD1, an increased tissue activity of this enzyme may contribute to elevated intracellular cortisol levels and thus lead to metabolic changes such as insulin resistance and hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and redistribution in adipose tissue [9]. Thus, intracellular cortisol production mediated by 11β-HSD1 may play a pathogenic role in T2DM and its comorbidities [9]. For this reason, this enzyme has become a new therapeutic target for the development of antidiabetic drugs (Figure 1) [16].
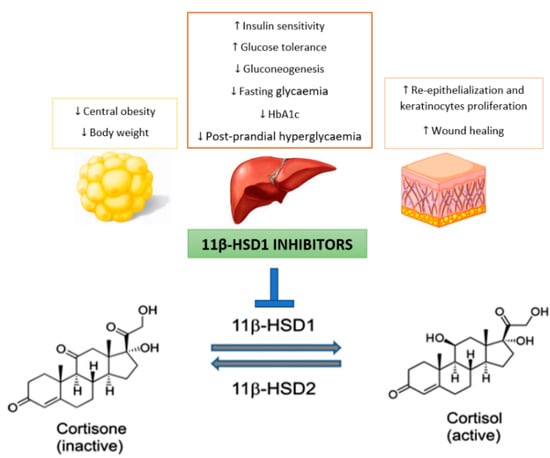
Figure 1.
Potential benefits of selectively targeting 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11β-HSD1) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Although this enzyme is not directly involved in cortisol biosynthesis by adrenal glands, prolonged inhibition of cortisol production mediated by 11β-HSD1 leads to HPA axis activation to ensure homeostasis [9]. In this context, reducing the intracellular GC concentration in liver and adipose tissues without changing the plasma concentration of these hormones will be probably a very effective T2DM treatment [17]. Therefore, it is important that these inhibitors do not significantly affect 11β-HSD2 activity, in order to avoid undesirable events such as sodium retention, hypokalemia (low levels of potassium in the blood) and hypertension [6]. This has led the industry to develop selective 11β-HSD1 inhibitors.
Diabetic foot is one of T2DM complications. In this context, continuous exposure to GC, such as cortisol, can affect normal skin healing by inhibiting the proliferation and migration of keratinocytes, in addition to causing a more slowly reepithelization [18]. Thus, it is not surprising that preclinical studies evidenced that 11β-HSD1 inhibition improves skin function and accelerates wound healing [18]. This has not yet been demonstrated in humans, nevertheless there is a study that aims to investigate the effects of inhibiting GC activation on skin function in T2DM patients [19]. Although it is already possible to access the details of this study, there are still no published results [19].
Therefore it is expected that continued selective 11β-HSD1 inhibition will be effective in diabetes treatment, with beneficial effects on obesity, hypertension and dyslipidemia as well as in wound healing [20,21].
The aim of this review is to update the existing information on the development of 11β-HSD1 inhibitors for future use in diabetes treatment, particularly focusing on clinical and in vivo preclinical studies. As the last most extensive review was published in August 2013 [21], we will cover the literature since 2013. With this work, we intend to gather the most relevant data on the effectiveness and safety of these investigational drugs in order to understand the potential for a possible future commercialization.
2. Materials and Methods
A review of the literature existing between 1 January 2013 and 14 January 2020 was performed by searching articles in PubMed, Cochrane, and Scopus databases using combinations of the following keywords: “11β-HSD1 inhibitors”, “11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitors”, “type 2 diabetes mellitus”, “hyperglycemia”, and “metabolic syndrome”. The search and selection of articles was performed by 2 independent individuals/researchers. The search strategy used in the individual databases is described in Appendix A.
Table 1 show the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Only clinical and in vivo preclinical studies were included to assess the efficacy and safety of 11β-HSD1 inhibitors that could be used in the future for T2DM treatment. All publications that fell under one or more exclusion criteria were excluded. Abstracts published in recognized peer-reviewed scientific journals were also included.

Table 1.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
The selection of articles was based on PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses), consisting of a checklist of 27 items and a 4-level flow chart [22].
3. Results
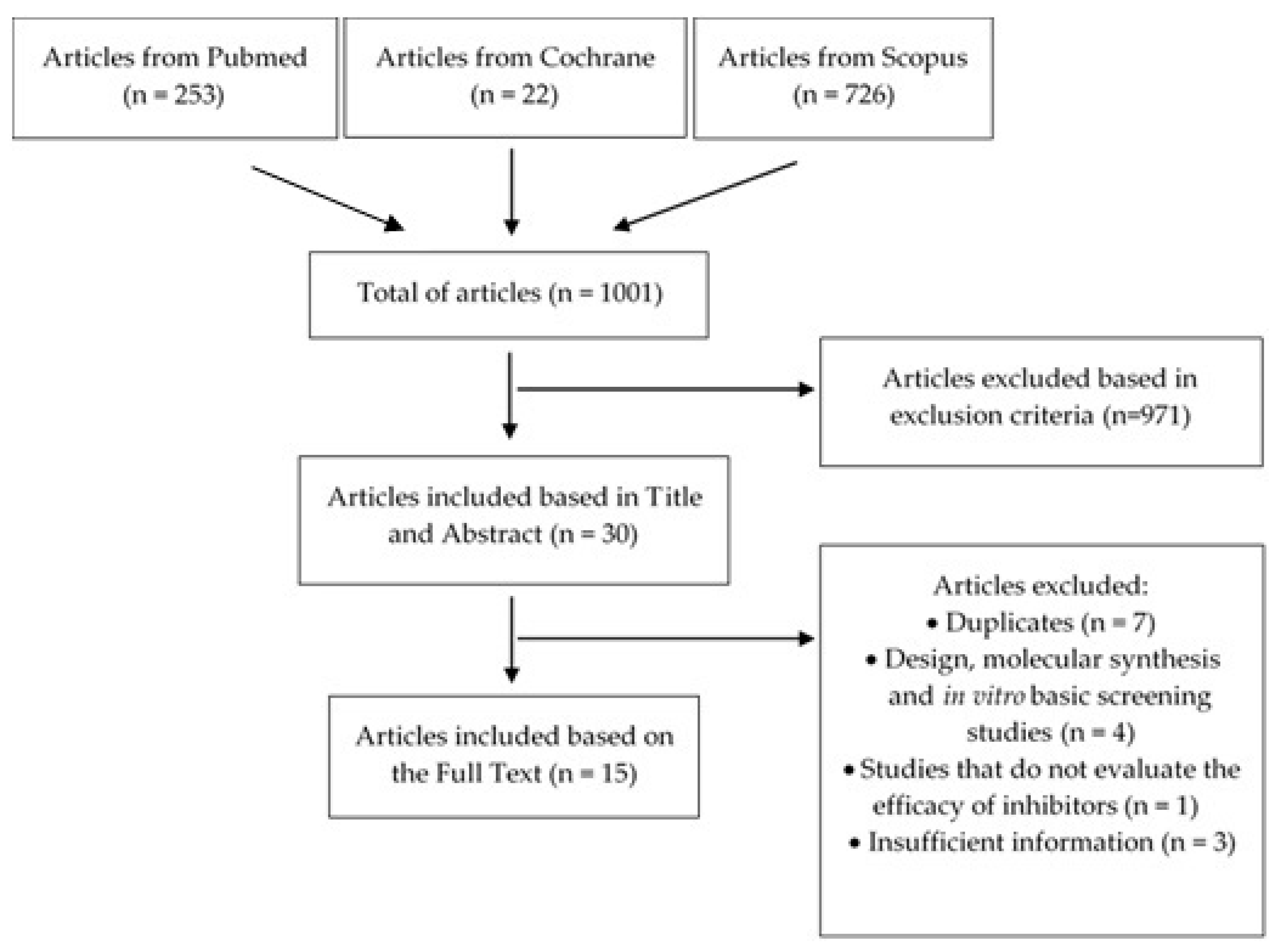
The search in the three referred databases resulted in a total of 1001 articles (Figure 2), of which 971 were excluded because they covered requirements defined by exclusion criteria (Table 1). Thus, 30 articles were evaluated in this phase, based in title and abstract. Of these, 7 corresponded to duplicates, 4 concerned design, molecular synthesis and in vitro basic screening, 1 did not evaluate the efficacy of 11β-HSD1 inhibitors and 3 have insufficient information (specifically, the information about the efficacy is not enough) (Figure 2). These reasons led to their exclusion. Therefore, a total of 15 articles were included and deeply analyzed for this literature review.
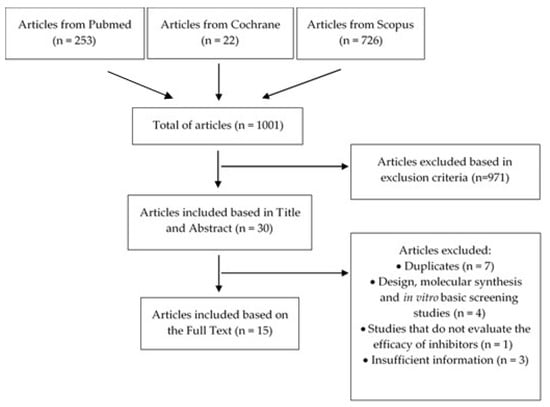
Figure 2.
Flowchart regarding the article selection process.
3.1. Clinical Trials
The main data existing in the published clinical studies evaluating the effects of 11β-HSD1 inhibitors are summarized in Table 2 and can be complemented with the information included in the text of this section.

Table 2.
Results of clinical trials (phase I-II studies) with selective 11β-HSD1 inhibitors.
The study presented by Wu et al. showed that compound BI 187004 had a strong inhibitory effect on 11β-HSD1 activity in adipose tissue (equal to or higher than 90% over 24 h in doses above 160 mg/day) and also globally, mainly in the liver (the ratio cortisol/cortisone decreased 95% and the ratio (allo-THF + THF)/THE decreased 75%). Oral administration of BI 187004 was safe and well tolerated in both populations [23]. Freude et al. also observed that the same experimental molecule inhibited 11β-HSD1, given the fact that the ratio of urinary metabolites THF and THE decreased by about 75% [24]. In addition, this compound was well tolerated in T2DM patients. However, no improvement in fasting plasma glucose or weighted mean glucose after treatment, when compared to baseline and placebo in both groups, was observed. Furthermore, the incidence of treatment-related adverse events (AE) was 19–33% in placebo patients and up to 31% in BI 187004-treated patients [24]. Another study developed by the same research group suggested that BI 135585 was well tolerated in both populations and lead to a significant 11β-HSD1 liver inhibition in patients with T2DM, since the ratio (allo-THF + THF)/THE decreased about 75% in the lowest tested dose [8]. In adipose tissue, 90% inhibition occurred in healthy subjects, whereas in patients with T2DM the enzyme was not sufficiently inhibited [8]. In a single-dose study, there were no notable findings with respect to AE. On the other hand, in a multiple-dose study, the most frequent AE were gastrointestinal disorders (18.1%), followed by nervous system disorders (13.9%) and infections (11.1%). However, no serious AE were reported [8].
Heise et al. concluded that, despite the short treatment duration, both RO-151 and RO-838 led to improvements in HbA1c levels. The difference in HbA1c values versus placebo approached the statistical significance for the lowest RO-151 dose, with a mean difference of 0.37% [25]. Improvements in insulin sensitivity parameters were observed for the high dose groups with relative increases by 38% for RO-838 and 26% for RO-151. Based on urinary THF and THE concentrations, the results showed a dose-dependent 11β-HSD1 inhibition, especially with RO-151 (the maximum inhibition observed on day 27 was 86–88% in low doses and 92% in high doses). In this case, the inhibition was sustained for the whole day at both doses. In the other hand, RO-838 originated a less pronounced inhibition (54–55% in low doses and 62–69% in high doses). The AE incidence was similar in both groups. In the treated population 33–45% AE were reported and in the control group the occurrence of AE was 38%. Again, no serious AE were observed, and the majority were solved without leaving any sequelae [25].
Treatments with ABT-384 at 1–100 mg once daily during 7 days and with 10–100 mg of the same molecule once daily during 21 days led to an almost complete liver 11β-HSD1 inhibition, being observed a reduction of the ratio (allo-THF + THF)/THE in 87–97% [14]. In adults treated with ABT-384, some of the AEs observed were headache and dizziness. However, the only AE that might be related to the experimental drug was rash. Diarrhea, headache, dyspepsia, and drowsiness have been reported in the older population. ABT-384 showed similar safety profiles between elderly and adult subjects and the results of these two clinical studies support future research on its therapeutic potential [14].
The results achieved by Wright et al. are from two phase I clinical trials. The first study was an initial investigation which primarily evaluated the safety in subjects given single oral doses of 0.4–100 mg of MK-0916. In the second study, in which subjects received 0.2–225 mg of MK-0916 followed by daily doses of 0.2–100 mg for 13 days, a primary goal was to evaluate the hepatic 11β-HSD1 inhibition [26]. In subjects receiving 6 mg of MK-0916 once daily was observed an 84% liver inhibition of cortisone-cortisol conversion. In addition, doses equal to or higher than 1.58 mg/day caused a 31–42% reduction in allo-THF + THF ratio /THE [26]. Oral MK-0916 administration appeared to be well tolerated and no serious AE was reported. In addition, the referred AE were mild to moderate in intensity. These included drowsiness and fatigue, reported in a subject administered placebo, and disorientation and hypogeusia, nightmares and abdominal pain in a subject administered MK-0916 [26].
3.2. In Vivo Preclinical Trials
In Table 3 is presented the most relevant information on the in vivo preclinical studies collected through the application of this search strategy. This data can be complemented with the information included in the text of this section.

Table 3.
Results of in vivo preclinical studies with selective 11β-HSD1 inhibitors.
In diet-induced obesity (DIO) mice (fed with a high-fat diet) (DIO-C57B6/J), oral administration of CNX-010-49 at the single 30 mg/kg dose inhibited the hepatic 11β-HSD1 activity by 58% and 24% at 1 h and 7 h, respectively [27]. In adipose tissue the highest inhibition was 41% at 1 h and continued to be similar till 7 h. The enzyme inhibition significantly reduced the liver glucose release by near 45% and the fasting glucose levels were reduced by 15% after 5 weeks. In the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), a 13% decrease in glucose levels was observed when the animals were treated with CNX-010-49, indicating that this molecule also has the potential to reduce the post-prandial hyperglycemia. Moreover, insulin sensitivity was significantly improved in CNX-010-49 treated animals [27].
In non-diabetic lean C57BL/6J mice, it was observed by Byun et al. a significant 11β-HSD1 activity inhibition (88.8% in liver and 40.6% in adipose tissue) 2 h after oral administration of 45 mg/Kg of UI-1499. The inhibition was maintained 6 h after dosing in both liver and adipose tissue (37.2% and 28.0%, respectively), although at reduced levels [5]. Fasting glycemia reductions of 40.1% and 30.6% were also observed in type 2 diabetic KKAy mice treated with 10 and 30 mg/Kg of the same compound, respectively. The administration of 30 mg/Kg reduced HbA1c concentration by 1.4% and confirmed the anti-hyperglycemic effect of compound IU-1499 [5].
The study conducted by Hong et al. included several animal species, and therefore some relevant results were obtained [17]. In fact, 2 h after oral 45 mg/Kg administration of INU-101 in C57BL/6J mice it was observed a significant inhibition of the hepatic activity of 11β-HSD1 by 56.8% and 38.3% in adipose tissue. The inhibition was maintained 6 h after dosing in both liver and adipose tissue (40.3% and 23.9%, respectively), although the levels were reduced. In Cynomolgus monkeys this inhibition was 41.7% in liver and 49.4% in adipose tissue. In type 2 diabetic KKAy mice, fasting glycemia decreased 26.7% and 41.3% after administration of 10 and 30 mg/Kg, respectively. These studied doses also reduced HbA1c by 8.0% and 14.1%, respectively, which confirmed the INU-101 hyperglycemic effect. Concerning liver 11β-HSD1 inhibition in KKAy mice, no effect was observed with 10 mg/Kg of INU-101, whereas 36% inhibition was observed when administered at 30 mg/Kg. In this same dosage, the inhibition in adipose tissue was near 65%. No effect was observed in ob/ob-mice (obese mice which develop T2DM) at the lowest dose, but administration of 30 mg/Kg of INU-101 reduced glycemia by 31.1% and HbA1c levels by 12.2%. A dose-dependent glycemia decrease was observed in Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats (11.4% to 60 mg/Kg and 32.7% to 120 mg/Kg). Thus, globally, these results indicate that compound INU-101 may represent a new therapeutic approach for T2DM treatment [17].
In DIO-C57BL/6 mice, compound SKI2852 led to a strong inhibition of cortisone-cortisol conversion by 80% in both liver and adipose tissue [28]. In ob/ob mice a 34% decrease in postprandial glycemia values and a 21% decrease in HbA1c values were observed. These results suggest that the selective and potent 11βHSD1 inhibition originated by compound SKI2852 may improve the metabolic syndrome symptoms, such as insulin resistance. Besides, SKI2852 treatment led to a dose-dependent suppression of both PEPCK and G6Pase expression levels, compared with vehicle treatment. These data suggest that 11βHSD1 inhibition by SKI2852 may improve the whole body and hepatic insulin sensitivities and reverse diabetic symptoms by, at least in part, suppression of these gluconeogenic enzyme expression levels in DIO mice [28].
Compound KR-67105 also led to a concentration-dependent 11β-HSD1 inhibition [29]. In non-obese C57BL/6 mice the treatment with 60 mg/Kg originated the maximum inhibition in liver (between 65–70%), followed by the treatment with 40 mg/Kg, with inhibition below 50%. These results were observed 2 h after KR-67105 administration. On the other hand, the 11β-HSD1 inhibition in adipose tissue was higher with the treatment with 40 mg/Kg (between 75–80%) than 60 mg/Kg (between 60–65%). In DIO-C57BL/6 mice, the liver enzyme inhibition was between 55–60% while in adipose tissue was between 40–45%. In this case, the results suggested that this experimental drug may improve glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity by inhibiting 11β-HSD1 activity. Besides, KR-67105 also shows anti-diabetic action by the suppression of diabetes related gene expressions such as G6Pase and PEPCK in the liver after 100 mg/kg administration to DIO-C57BL/6 mice [29].
In the study carried out by Park et al. in 2014, the most relevant result was an 11β-HSD1 inhibition between 80–90% in liver and 80% in adipose tissue after KR-67500 (50 mg/Kg) administration to DIO-C57BL/6 mice. The administration of 10 mg/Kg to C57BL/6 mice led to an inhibition between 85–90% in liver and between 90–95% in adipose tissue, observed 2 h post-dose [30].
Treatment of lean SHR-cp rats with Compound 11 significantly reduced 11β-HSD1 activity by 96% in liver and 92% in adipose tissue when compared with rats receiving vehicles [31]. In SHR-cp obese rats (rat model of metabolic syndrome) this reduction was 90% and 97%, respectively. At the end of treatment, Compound 11 significantly improved glucose tolerance and reduced insulin resistance in obese rats [31].
The total body cortisol production by 11β-HSD1 activity was reduced by 2/3 after treatment with HSD1-I, while liver production of this hormone was completely eliminated [32]. In this study, it was also determined the effect of prolonged 11β-HSD1 inhibition on hormone-stimulated glucose metabolism in fasted conscious dogs. In this 4-h metabolic challenge, it was increased the concentration of glucagon and epinephrine (two counter-insulin hormones), and insulin (to replicate the hyperinsulinemia associated with the hyperglycemia which occurs in insulin-resistant individuals or when glucagon and epinephrine levels are elevated). In response to the metabolic challenge, hepatic glucose production was stimulated in placebo group, resulting in hyperglycemia. On the other hand, endogenous glucose production decreased due to the reduction in glycogenolysis (breakdown of glycogen present in the liver into glucose molecules) and glucose utilization was increased, both caused by the inhibition of 11β-HSD1. These data suggest that 11β-HSD1 inhibitors may be of therapeutic interest in the control of diseases characterized by excessive hepatic glucose production and insulin resistance. However, neither PEPCK or G6Pase liver levels differed between groups at the end of the study [32].
The research involving compound H8, developed by Yuan et al., led to the conclusion that the higher dose evaluated (10 mg/Kg) showed the most relevant inhibitory effects. In db/db mice (a model of phase 1 to 3 T2DM and obesity), this inhibition was about 70% in the liver and between 60–70% in adipose tissue. The lower dose (5 mg/Kg) reduced the 11β-HSD1 activity by 50% in the liver and between 50–60% in adipose tissue. In addition, the PEPCK and G6Pase expression in liver was significantly reduced after H8 administration. These results show that this compound ameliorated glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity [33].
4. Discussion
GC are essential endocrine hormones which regulate almost all important physiological functions of our body [10,34]. The 11β-HSD1 enzyme boosts the levels of these hormones by regenerating cortisol, especially in liver and adipose tissues [35]. Since GC promote gluconeogenesis and antagonize the hypoglycemic insulin actions, increasing its concentration has negative effects on individuals with T2DM. Therefore, selective 11β-HSD1 inhibition could become a new therapy against hyperglycemia. In this context, carbenoxolone, a glycyrrhetinic acid derivative, was the first 11β-HSD1 inhibitor tested in humans. Although it is not selective, it has shown the ability to increase the sensitivity to hepatic insulin and to decrease glucose production, which is a clear evidence of the potential metabolic benefits of inhibiting 11β-HSD1 in T2DM control [36].
Given the clear relevance of T2DM for the society and the potential of this therapeutic strategy, this systematic review aimed to update the existing information on the development of 11β-HSD1 inhibitors, focusing on clinical (Table 2) and in vivo preclinical (Table 3) studies.
As with T1DM, rodents are the most thoroughly used animals to study human T2DM [37]. In this case, both obese, reflecting the human condition where obesity is closely linked to T2DM development, and non-obese animal models, with varying degrees of insulin resistance and pancreatic beta cell failure have been used [38]. In addition to the general advantages of using rodents as disease models (e.g., small size, easy accessibility, possibility of using many animals at the same time, easy genetic manipulation), the diabetic rodents category includes a variety of models that can spontaneously develop diabetes similar to human T2DM [37]. Furthermore, these animal models also allow the study of molecular mechanisms leading to diabetes and all the stages of this disease, from its onset and development to the beginning of the complications [37]. Old-world non-human primates can also develop T2DM, which has similarities to the human condition and thus can also be useful as a model [38]. However, there are some limitations in the use of animal T2DM models. Firstly, in most models (including rodents) diabetes develops because of the inability to increase pancreatic β-cells mass in response to obesity-induced insulin resistance. In addition, animals (except monkeys) usually develop diabetes without displaying the same islet pathology identified in humans [37]. Furthermore, when testing therapies in animal diabetes models, the most common endpoint of measurement is blood glucose concentration. It should be pointed out that different species tend to have different blood glucose concentrations than the observed in humans, and thus, definitions for diabetes in humans should not necessarily be applied to animals [38].
In almost all in vivo pre-clinical studies included in this review (Table 3), the duration and level of 11β-HSD1 activity inhibition in different tissues (liver and adipose) were evaluated by an ex-vivo 11β-HSD1 inhibition assay [5,17,27,28,29,30,33]. In addition, despite the multiple results achieved, no preclinical trial refers to safety in vivo.
Pharmacological 11β-HSD1 inhibition with CNX-010-49, KR-67105, Compound 11 and H8 have normalized most of metabolic dysregulations in rodents, including hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance and insulin resistance [27,29,31,33] and therefore may be useful as new therapeutic compounds for T2DM prevention and treatment. The selective and potent enzyme inhibition achieved with SKI2852 makes it a compound with great potential and an important drug candidate for diabetes treatment [28]. KR-67105 and other compounds also show anti-diabetic action by the suppression of diabetes-related gene expressions, such as G6Pase and PEPCK in mice, and therefore may provide a new therapeutic window in T2DM prevention and treatment [29].
Over the years, many new chemical compounds have been identified and evaluated in preclinical studies for T2DM treatment, but very few reach the clinical evaluation. Of these, only a few drugs or drug candidates have enough efficacy and safety to proceed for phase III clinical studies. In addition, despite some of the new compounds have robust antidiabetic properties, the underlying mechanism of action is still unclear namely due to uncertain target pathways [39]. Therefore, the need to continue developing new clinically effective and safer drugs to treat T2DM is clear. In this point, the interest in new, selective and potent 11β-HSD1 inhibitors has been maintained over the years. This literature review demonstrates that some experimental drugs clinically studied over the recent years have high inhibitory levels in liver and adipose tissue (Table 2) and have been shown to be safe and well tolerated in both healthy individuals and patients with T2DM [8,14,23,24,25,26]. In all clinical trials, the majority of AE was of mild intensity, transient in nature and resolved without sequelae. There were no serious AE, no deaths and no withdrawals due to an AE. However, to date, there are no phase III clinical trials on this context and therefore the studies published so far are of short duration.
GC levels in target tissues depend on circulating steroid concentrations (tightly controlled by the HPA axis) as well as on 11β-HSD1 activities, which control the amount of cortisol at a cellular level. Regarding clinical trials, for ex vivo 11β-HSD1 activity measurement, subcutaneous adipose tissue sample collection was carried out via incision biopsy [8,25]. All subjects underwent a mandatory wash-out period of their oral antidiabetic medication [8] other than metformin [25]. Safety assessments included electrocardiogram, vital signs assessments, blood pressure monitoring and HPA function [8,14,25,26].
Despite the interesting results observed in the several clinical trials selected by this systematic review (Table 2), some differences between the studied compounds could be detected. In addition, generally, studies of longer duration should be performed to obtain more clear data. In fact, the pharmacodynamics assessment demonstrated a relevant BI 187004 effect on 11β-HSD1 inhibition. Despite this evidence, this compound did not improve glycemic control after 4 weeks of treatment, evidencing a low therapeutic potential in T2DM [24]. In addition, there is a significant and sustained 11β-HSD1 inhibition in the liver after BI 135585 treatment. However, future studies are required to clarify its therapeutic potential in view of its effects on enzyme inhibition in adipose tissue [8]. Concerning RO-151 and RO-838, both demonstrated slight metabolic improvements, particularly with RO-151 in high dose. However, the observed changes often did not reach statistical significance and were not clearly dose dependent. Therefore, longer duration studies are needed to further investigate their potential for diabetes treatment [25]. Furthermore, compound ABT-384 demonstrated favorable safety and pharmacodynamics profiles in the dose range tested in phase 1 studies, which support future research on its therapeutic potential [14]. Finally, daily oral dosage of MK-0916 afforded substantial 11β-HSD1 inhibition in liver. Such treatment is also generally well tolerated. It remains to be seen whether such inhibition, either by MK-0916 or by other agents, will turn out to be clinically useful [26].
Since diabetes is a chronic disease, long treatments are needed to keep blood sugar levels under control. In this context, Gutierrez et al. have shown that continuous 11β-HSD1 inhibition in adipose tissue in humans can lead to tachyphylaxis [40]. It is generally assumed that the inhibition achieved at the end of acute administration is maintained after repeated dosing. However, the study conducted by these authors showed that the 11β-HSD1 inhibition in human adipose tissue was lost after repeated doses of AZD8329, a known inhibitor of this enzyme, when compared with acute administration [40].
In response to 11β-HSD1 inhibition, serum cortisol levels tend to decrease, but due to negative feedback in HPA axis, compensatory increases in ACTH levels occur, resulting in cortisol biosynthesis by the adrenal gland to restore cortisol homeostasis in the bloodstream [8,14]. However, due to the increased ACTH production, the maintained cortisol level is at the expense of hyperandrogenism, as a major consequence, and adrenal hypertrophy [41]. Besides, in some studies included in this review, the HPA axis was mildly activated since concentrations of ACTH and adrenal androgen precursors were slightly increased [8,14,23,25]. Therefore, the future development of these compounds also will require an assessment of the consequences of the HPA axis activation in long-term treatments [25]. Some of the studies presented here have tested the efficacy of 11β-HSD1 inhibitors in combination with metformin, which is currently the first-line T2DM treatment [4]. Since insulin has a capacity to suppress 11β-HSD1 liver activity, in patients with T2DM the insulin resistance may lead to a lack of this suppression [42]. The initial hypothesis put forward by Anderson et al. was that metformin, by increasing insulin sensitivity and reducing liver 11β-HSD1 activity could limit the effectiveness of these inhibitors. However, the results revealed that this drug enhances cortisol regeneration throughout the body and also in liver by increasing the activity of the enzyme, both in obese men without T2DM and in obese men with T2DM. Therefore, concomitant administration of metformin with 11β-HSD1 inhibitors could even maximize their metabolic benefits. Thus, this does not appear to be a reason for the relatively limited efficacy of the selective 11β-HSD1 inhibitors [42].
Apparently, GC can stimulate or inhibit the inflammation, namely depending on their concentration [10]. Thus, excessive GC levels, caused by stress situations or pharmacological therapies, can adversely affect the skin integrity, compromising the wound healing [43]. Consequently, inflammation is more prolonged, keratinocyte proliferation and migration are inhibited, and reepithelization occurs more slowly. In this context, a study by Tiganescu et al. evidenced a faster re-epithelialization and healing in mice topically treated with the experimental drug RO-151, a 11β-HSD1 inhibitor [44]. In fact, 14 days after the appearance of the wound, the neoepidermal area was 23% in mice receiving vehicles, but increased to 50% after 11β-HSD1 inhibition [44]. In addition, while vehicle-treated mice needed 18 days to achieve 40% re-epithelialization, the enzyme blockade reduced this time by more than one week [44]. It should also be noted that in older mice a faster epidermis proliferation was observed when compared to the litter of the same species, with a reduction in wound area of about 50% after 4 days [44]. It can thus be predicted that topical application of 11β-HSD1 inhibitors may suppress inflammation and accelerate wound healing. In this ambit, a study by Terao et al. showed that topical enzyme inhibition promotes keratinocyte proliferation and accelerates skin regeneration, suggesting that intracellular cortisol activation may negatively regulate the proliferation of these cells [43]. These authors suggested that the reduction in 11β-HSD1 expression in keratinocytes around the wound may be a normal physiological mechanism that promotes the proliferation of these cells during wound healing [43]. Therefore, and although there are no clinical studies demonstrating this, topical application of 11β-HSD1 inhibitors may be potentially effective in the treatment of chronic wounds in diabetic patients [43].
Finally, it was suggested that an increased 11β-HSD1 activity can contribute to the development of central obesity and associated comorbidities such as diabetes, due to the enzyme effect on cortisol levels [45]. In this context, Anderson et al. found that the body 11β-HSD1 activity was higher in obese men with T2DM [42]. In the study published by Heise et al., the lower dose and the higher dose of RO-838 in diabetic patients caused a reduction in body weight of 0.86 and 1.08 kg, respectively, after four weeks of treatment [25]. In addition, the lower dose and the higher dose of RO-151 led to a reduction in body weight of 1.11 and 1.67 kg, respectively [25]. These results shows that these two inhibitors tend to improve some parameters that characterize the metabolic syndrome, in particular obesity and hyperglycemia [25]. Therefore, a major advantage that 11β-HSD1 inhibitors could have over many current antidiabetic drugs would be weight loss.
5. Conclusions
The prevalence of T2DM has steadily increased over the last decades and became one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Although currently there are several therapies with proven efficacy for diabetes treatment, new substances have been developed. Clinically tested 11β-HSD1 inhibitors appear to be relatively effective and safe, and the majority showed a strong inhibitory effect on liver and adipose tissues, in addition to reducing fasting glycemia, post-prandial hyperglycemia and HbA1c. However, no phase III clinical trials have yet been conducted and there are several challenges to be addressed. For example, for this class of compounds, efficacy assessments are difficult in early-phase clinical studies as it is unclear after which treatment duration 11β-HSD1 inhibitors start to lead to a consistent blood glucose-lowering effect and how long it takes to achieve maximum glucose-lowering efficacy. In addition, prolonged inhibition of this enzyme might lead to interference in HPA axis and therefore it is important to determine if this might be a problem for treatment strategies. Nevertheless, 11β-HSD1 remains a promising target for drug development and future studies can be expected in this field. In T2DM context, these inhibitors can lead to a gluconeogenesis reduction, promoted by high levels of cortisol, and an improvement in insulin sensitivity, beyond the additional benefits it can have in these patients, such as weight loss and wound healing.
Author Contributions
C.A., C.M., and S.S. performed the systematic review. C.A. organized and analyzed the results. C.A. and C.M. wrote the first draft. All authors wrote the final draft and performed corrections. All authors made substantial contributions. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge National Funds by FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology (UID/Multi/00709/2019), and FEDER funds through the POCI—COMPETE 2020—Operational Programme Competitiveness and Internationalization in Axis I—Strengthening research, technological development and innovation (Project POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007491).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Research strategy.
Table A1.
Research strategy.
| PUBMED (Research Date: 18 November 2019) |
|
| COCHRANE (Research Date: 18 November 2019) |
|
| SCOPUS (Research Date: 14 January 2020) |
|
References
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association, A.D. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S14–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S.; Habtemariam, S. Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes complications. Med. Foods Potential Ther. Type 2 Diabetes Assoc. Dis. 2019, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, B.T.; Davies, M. Glycaemic management of type 2 diabetes. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 47, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.Y.; Shin, Y.J.; Nam, K.Y.; Hong, S.P.; Ahn, S.K. A novel highly potent and selective 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor, UI-1499. Life Sci. 2015, 120, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Li, H.; Bai, H.; Su, Z.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chu, Y.; et al. Synthesis of novel curcumin analogues for inhibition of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 with anti-diabetic properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 77, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.-Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Wu, S.; Yoon, D.S.; Wang, H.; Hong, Z.; O’Connor, S.P.; Li, J.; Li, J.J.; Kennedy, L.J.; et al. Discovery of Clinical Candidate 2-((2S,6S)-2-Phenyl-6-hydroxyadamantan-2-yl)-1-(3′-hydroxyazetidin-1-yl)ethanone [BMS-816336], an Orally Active Novel Selective 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4932–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freude, S.; Heise, T.; Woerle, H.-J.; Jungnik, A.; Rauch, T.; Hamilton, B.; Schölch, C.; Huang, F.; Graefe-Mody, U. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of BI 135585, a selective 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1 (HSD1) inhibitor in humans: Liver and adipose tissue 11β-HSD1 inhibition after acute and multiple administrations over 2 weeks. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollis, G.; Huber, R. 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibition in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.C.I.; Epel, E.S.; White, M.L.; Standen, E.C.; Seckl, J.R.; Tomiyama, A.J. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation and cortisol activity in obesity: A systematic review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 62, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chourpiliadis, C.; Mohiuddin, S.S. Biochemistry, Gluconeogenesis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.; Han, H.; Kim, M.; Koo, S. CREB and FoxO1: Two transcription factors for the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. BMB Rep. 2013, 46, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M. Inhibitors of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in antidiabetic therapy. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 203, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Katz, D.A.; Locke, C.; Daszkowski, D.J.; Wang, Y.; Rieser, M.J.; Awni, W.M.; Marek, G.J.; Dutta, S. Clinical safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor ABT-384 in healthy volunteers and elderly adults. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2013, 2, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshiro, M.; Ohno, Y.; Masaki, H.; Iwase, H.; Aoki, N. Comprehensive study of urinary cortisol metabolites in hyperthyroid and hypothyroid patients. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2006, 64, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Espinosa, J.J.; García-Jiménez, S.; Ríos, M.Y.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; López-Vallejo, F.; Webster, S.P.; Binnie, M.; Ibarra-Barajas, M.; Ortiz-Andrade, R.; Estrada-Soto, S. Antihyperglycemic and sub-chronic antidiabetic actions of morolic and moronic acids, in vitro and in silico inhibition of 11β-HSD 1. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.P.; Han, D.; Chang, K.H.; Ahn, S.K. A novel highly potent and selective 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor, INU-101. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 835, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.T.; Zmijewski, M.A. Glucocorticoids Inhibit Wound Healing: Novel Mechanism of Action. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1012–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCT03313297. Glucocorticoids and Skin Healing in Diabetes (GC-SHealD). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/nct03313297 (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Hamilton, B.S.; Himmelsbach, F.; Nar, H.; Schuler-Metz, A.; Krosky, P.; Guo, J.; Guo, R.; Meng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lala, D.S.; et al. Pharmacological characterization of the selective 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 inhibitor, BI 135585, a clinical candidate for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 746, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.; Walker, B.R. 11β-HSD1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Drugs 2013, 73, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2016 Annual Meeting of the American College of Clinical Pharmacology, September 25-27, 2016, Bethesda, MD. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2016, 5, 3–56. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical Diabetes/Therapeutics. Diabetes. 65 (Suppl. 1), pp. A221–A360. Available online: http://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/lookup/doi/10.2337/db16-861-1374 (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Heise, T.; Morrow, L.; Hompesch, M.; Häring, H.-U.; Kapitza, C.; Abt, M.; Ramsauer, M.; Magnone, M.-C.; Fuerst-Recktenwald, S. Safety, efficacy and weight effect of two 11β-HSD1 inhibitors in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, D.H.; Stone, J.A.; Crumley, T.M.; Wenning, L.; Zheng, W.; Yan, K.; Yang, A.Y.; Sun, L.; Cilissen, C.; Ramael, S.; et al. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic studies of the 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor MK-0916 in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anil, T.M.; Dandu, A.; Harsha, K.; Singh, J.; Shree, N.; Kumar, V.S.; Lakshmi, M.N.; Sunil, V.; Harish, C.; Balamurali, G.V.; et al. A novel 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type1 inhibitor CNX-010-49 improves hyperglycemia, lipid profile and reduces body weight in diet induced obese C57B6/J mice with a potential to provide cardio protective benefits. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Jeong, K.-H.; Han, H.Y.; Son, H.J.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.; Sa, J.H.; Jun, H.-S.; Ryu, J.H.; et al. A potent and selective 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor, SKI2852, ameliorates metabolic syndrome in diabetic mice models. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 768, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Jung, W.H.; Kang, N.S.; Park, J.S.; Bae, G.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Rhee, S.D.; Kang, S.K.; Ahn, J.H.; Jeong, H.G.; et al. Anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effect of a novel selective 11β-HSD1 inhibitor in the diet-induced obese mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 721, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Bae, S.J.; Choi, S.; Son, Y.H.; Park, S.B.; Rhee, S.D.; Kim, H.Y.; Jung, W.H.; Kang, S.K.; Ahn, J.H.; et al. A novel 11β-HSD1 inhibitor improves diabesity and osteoblast differentiation. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 52, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnackenberg, C.G.; Costell, M.H.; Krosky, D.J.; Cui, J.; Wu, C.W.; Hong, V.S.; Harpel, M.R.; Willette, R.N.; Yue, T.-L. Chronic Inhibition of 11 β -Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Activity Decreases Hypertension, Insulin Resistance, and Hypertriglyceridemia in Metabolic Syndrome. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 427640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnick, J.J.; Ramnanan, C.J.; Saraswathi, V.; Roop, J.; Scott, M.; Jacobson, P.; Jung, P.; Basu, R.; Cherrington, A.D.; Edgerton, D.S. Effects of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1 inhibition on hepatic glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E747–E756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Li, H.; Bai, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. The 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor protects against the insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in db/db mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 788, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Chen, L.; Fan, Z.; Teng, F.; Zhao, Y.; Guan, F.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y. Interplay between H6PDH and 11β-HSD1 implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4107–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stimson, R.H.; Walker, B.R. The role and regulation of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2013, 15, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, R.C.; Rooyackers, O.; Walker, B.R. Effects of the 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitor carbenoxolone on insulin sensitivity in men with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Halapas, A.; Kalafatakis, K.; Kamper, E. The Use of Animal Models in the Study of Diabetes Mellitus. In Vivo 2009, 23, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- King, A.J.F. The use of animal models in diabetes research. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 877–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J.; Day, C. The future of new drugs for diabetes management. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 155, 107785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, P.M.; Gyte, A.; Deschoolmeester, J.; Ceuppens, P.; Swales, J.; Stacey, C.; Eriksson, J.W.; Sjostrand, M.; Nilsson, C.; Leighton, B. Continuous inhibition of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type i in adipose tissue leads to tachyphylaxis in humans and rats but not in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4806–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.S.; Stewart, P.M. 11Β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 and Its Role in the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis, Metabolic Syndrome, and Inflammation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4645–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.J.; Andrew, R.; Homer, N.Z.; Jones, G.C.; Smith, K.; Livingstone, D.E.; Walker, B.R.; Stimson, R.H. Metformin Increases Cortisol Regeneration by 11βHSD1 in Obese Men With and Without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, M.; Murota, H.; Kimura, A.; Kato, A.; Ishikawa, A.; Igawa, K.; Miyoshi, E.; Katayama, I. 11Β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase-1 Is a Novel Regulator of Skin Homeostasis and a Candidate Target for Promoting Tissue Repair. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiganescu, A.; Tahrani, A.; Morgan, S.A.; Otranto, M.; Desmoulière, A.; Abrahams, L.; Hassan-Smith, Z.; Walker, E.A.; Rabbitt, E.H.; Cooper, M.S.; et al. 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase blockade prevents age-induced skin structure and function defects. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3051–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, Q.; Shao, S. 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 in Obese Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 354, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).