Abstract
With the increasing penetration of renewable energy and the rising demand for power quality, the dynamic performance and accuracy of grid-voltage detection have become crucial for the control of grid-following devices such as dynamic voltage restorers (DVRs). However, the conventional moving average filter (MAF) in grid-voltage detection suffers from inherent limitations in dynamic response. To address this issue, this paper proposes a voltage-detection method, which is based on an adaptive variable-parameter filtering algorithm termed MAF-MATCH-V. First, a cascaded filter model is constructed by integrating a zero-pole matcher (MATCH) with the MAF. Frequency-domain analysis demonstrates that the MATCH compensates for the mid- and high-frequency magnitude attenuation and reduces the phase delay of the MAF, thereby accelerating the dynamic response while preserving its harmonic-rejection capability. Second, the influence of the matching coefficient on the time-domain response is investigated, and a time-varying adaptive strategy is designed to balance rapid disturbance recognition with steady-state convergence. Finally, experimental results under various non-ideal grid conditions demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior overall performance compared with conventional approaches. Specifically, MAF-MATCH-V realizes millisecond-level event recognition and zero steady-state error convergence, making it a practical solution for the real-time control of grid-following equipment in modern power systems.
1. Introduction
With the large-scale integration of renewable energy sources [1] and dynamic loads such as electric vehicle charging stations [2], along with the frequent occurrence of short-circuit faults and large motor startups [3], grid voltages are increasingly subject to disturbances including sags, swells, fluctuations, and harmonic pollution [4]. Such events not only threaten the stable operation of industrially sensitive equipment, such as adjustable-speed drives (ASDs) [5], programmable logic controllers (PLCs) [6], and data center servers [7], but also pose severe challenges to the control accuracy of grid-following devices, such as renewable energy inverters [8], dynamic voltage restorers (DVRs) [9], and uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs) [10]. The reliable operation of these devices depends critically on the real-time and accurate detection of grid voltage. Therefore, developing detection methods that can simultaneously ensure fast dynamic response and high steady-state accuracy under complex disturbance environments is of great significance for improving the control performance of grid-following equipment in modern power systems.
Over the past decades, both academia and industry have proposed a variety of voltage-detection techniques, yet each has inherent limitations. Peak detection and missing-voltage detection methods [11] can determine the occurrence of sags within half a grid cycle, but they fail to capture complete event characteristics and exhibit poor noise immunity. The root-mean-square (RMS) detection method [12] offers stronger robustness to disturbances, but suffers from slow response and weak frequency adaptability. Recursive least squares (RLS) algorithms [13] can achieve rapid detection while effectively suppressing specific harmonics; however, their accuracy degrades significantly in the presence of unmodeled high-frequency harmonics or noise. In the transform domain, wavelet transform (WT) methods [14] are highly sensitive to abrupt signal changes and can quickly identify the start and end of sags, but their performance strongly depends on the choice of wavelet basis, which limits generality [15]. Similarly, generalized discrete Fourier transform (GDFT) [16] utilizes comb filters to extract specific frequency components and improves dynamic performance by eliminating redundant zeros and poles, but its performance deteriorates under high harmonic distortion. Generalized delayed signal cancellation (GDSC) techniques [17,18] also rely on configuring zeros and poles to eliminate specific harmonics, yet their delay parameters must be retuned for different grid environments. Neural-network-based methods [19] exploit nonlinear mapping to decouple multiple disturbances and extract the fundamental voltage component from distorted signals; however, their performance depends heavily on the representativeness of training data and they are less suitable for deployment on resource-constrained microcontrollers.
Voltage detection methods based on the synchronous reference frame (SRF) [20] have been widely applied in industry due to their simple structure and strong adaptability. Researchers have integrated various filters into the SRF framework to improve performance [21,22]. The SRF-LPF method [23], for instance, employs a low-bandwidth low-pass filter to enhance robustness, but at the expense of significant detection delay. The dual second-order generalized integrator (DSOGI)-based SRF method [24] offers good frequency adaptability, yet still faces a trade-off between dynamic performance and harmonic suppression [25]. In [26], a voltage-detection method based on a selective harmonic extraction algorithm is proposed, which exhibits strong grid adaptability. However, its iterative computation is complex and, in practice, only a limited number of frequency components can be targeted. A common drawback of these methods lies in the core filtering algorithm: none of them can achieve an effective balance between dynamic response and disturbance rejection, particularly under non-ideal grid conditions involving harmonics, phase jumps, and frequency drifts [27].
The moving average filter (MAF) has attracted extensive attention in grid-voltage detection due to its simple implementation and excellent harmonic suppression capability. When combined with SRF, it is frequently employed in phase-locked loops and voltage detection schemes [28,29]. However, the inherent structure of the MAF dictates that improved filtering performance comes at the cost of increased delay [30], limiting its suitability for rapidly varying voltages. To overcome this drawback, several improved MAF-based schemes have been proposed. In [31], the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) is used to dynamically analyze the frequency characteristics of grid voltage in real time, thereby adjusting the MAF window length. In [32], the MAF is cascaded with DSOGI to reduce window width and improve response speed. Other studies have explored hybrid filtering strategies: for example, MAF combined with delayed signal cancellation (DSC) [32], MAF cascaded with double synchronous reference frame (DDSRF) [33], and MAF cascaded with linear active disturbance rejection control (LADRC) [34]. However, these hybrid approaches place higher computational demands on microcontrollers. Moreover, reference [35] proposed a phase compensation method to enhance the MAF’s dynamic response, but without discussing the negative effects of overshoot and convergence during transients.
To overcome the above challenges, this paper proposes a grid-voltage detection method based on an adaptive variable-parameter MAF-MATCH algorithm, aiming to achieve fast and accurate voltage event recognition under non-ideal grid conditions such as unbalance and harmonic distortion. The core idea is to resolve the inherent contradiction of static filtering through dynamic parameter matching. The main contributions of this work are summarized as follows:
- The zero-pole characteristics of the conventional MAF are analyzed, revealing the limitations caused by mid- and high-frequency attenuation in dynamic performance. A cascaded filter model is then constructed by integrating MAF with a zero-pole matcher (MATCH), enabling frequency-domain compensation to retain harmonic suppression capability while improving response speed.
- A time-varying trajectory for the matching coefficient is designed, allowing adaptive adjustment during disturbances. This resolves the limitations of fixed-parameter schemes, achieving a balance between rapid disturbance recognition and stable steady-state convergence.
- Comprehensive tests under various non-ideal grid conditions—including symmetrical sags/swells, phase jumps, asymmetrical sags, and harmonic distortions—are conducted. Comparisons with conventional methods such as SRF-LPF, DSOGI, and GDFT demonstrate that the proposed method delivers superior overall performance in terms of recognition speed, convergence accuracy, and disturbance immunity.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the construction of the MAF-MATCH cascaded model and analyzes its characteristics in both the time and frequency domains. Section 3 presents the design of the adaptive variable-parameter strategy, details the parameter optimization process, and develops the proposed voltage-detection method based on the variable-parameter MAF-MATCH algorithm. Section 4 shows and discusses the experimental results under various grid conditions. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper.
2. Grid-Voltage Detection Method Based on MAF-MATCH
2.1. Conventional Grid-Voltage Detection Using MAF
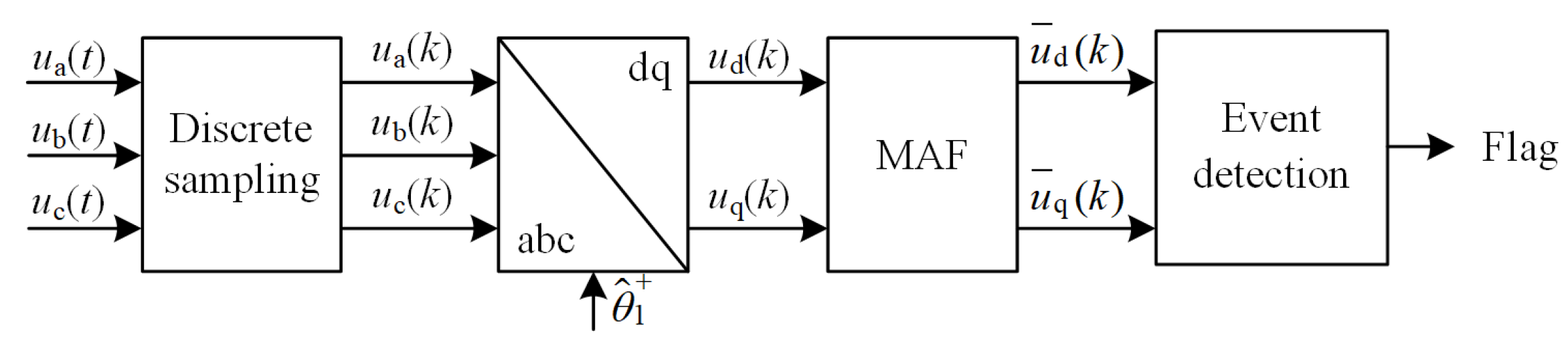
Figure 1 illustrates the conventional grid-voltage detection scheme based on the moving average filter (MAF) algorithm.
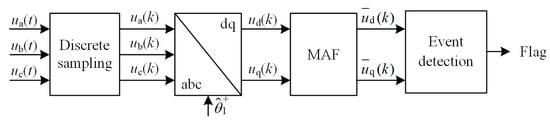
Figure 1.
Structure of the conventional grid-voltage detection method based on the MAF algorithm.
First, the three-phase grid voltage signal u(t) is discretely sampled to obtain the sequence u(k). The signal is then transformed into the synchronous rotating dq-frame using the positive-sequence Park transformation, resulting in the voltage magnitude udq(k), which can be expressed as
where denotes the estimated phase angle of the fundamental positive-sequence grid voltage. And the fundamental component of udq(k) appears in direct-current (DC) form, while the harmonic components appear in alternating-current (AC) form. By applying the MAF algorithm, the harmonics can be effectively filtered, yielding the smoothed voltage signal as follows:
where N is the window length of the MAF algorithm. A larger window provides stronger filtering but introduces more pronounced delay. The dq-axis components are then combined to form the magnitude of the detected voltage, which is compared against the thresholds, 0.9 p.u. for sag and 1.1 p.u. for swell, to estimate the real-time grid voltage. Essentially, the MAF acts as a linear filter, whose behavior can be described in the Z-domain.
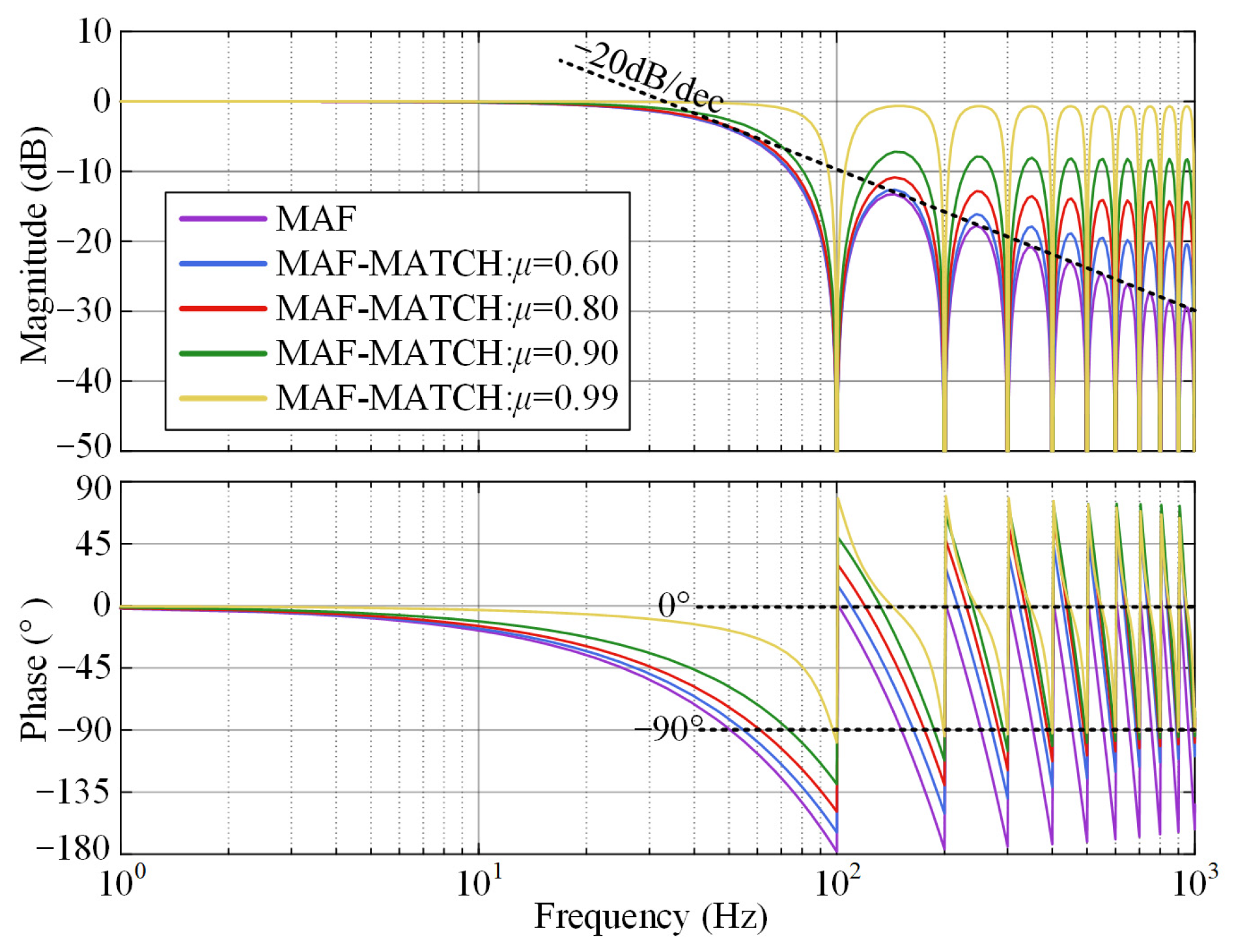
When expanded in zero-pole form, the MAF contains N zeros and a single pole. The N zeros form a comb filter that suppresses information at equally spaced frequency points, while the pole amplifies a specific frequency component. Since the pole of the MAF is located at 0 Hz, it coincides with one of its zeros. This allows the MAF to pass the DC component while simultaneously suppressing the AC components at those equally spaced frequency points. The corresponding Bode diagram of the MAF is shown in Figure 2. It can be observed that the MAF exhibits inherent harmonic rejection capability, making it suitable for non-ideal grid environments. However, its amplitude response suffers from a −20 dB per decade attenuation in the mid- and high-frequency range. In grid-voltage detection applications, this attenuation slows down the recognition of disturbances, thus limiting the dynamic performance of the MAF.
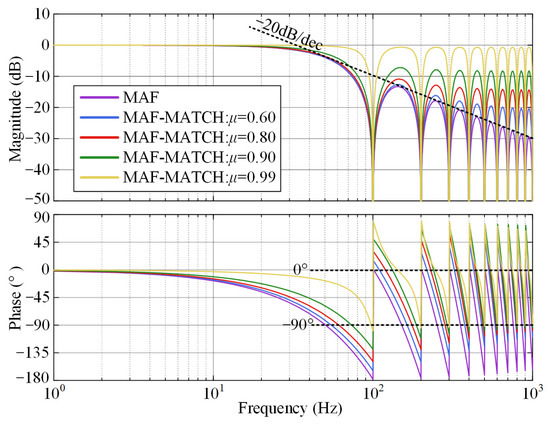
Figure 2.
Bode diagram of the MAF-MATCH filter under different matching levels.
2.2. MAF-MATCH Algorithm
To address the dynamic performance limitations of the MAF, a zero-pole matcher (MATCH) algorithm is proposed. Its transfer function in the Z-domain can be expressed as
where μ denotes the matching coefficient, ranging from 0 to 1. When expanded in zero-pole form, the expression of MATCH can be written as
It can be seen that MATCH contains one zero and N poles. By cascading the MATCH with the MAF, the combined system can be represented as
From the above expression, it can be observed that MATCH can achieve an approximate cancellation of each zero-pole pair in the MAF. The degree of cancellation depends on the value of the matching coefficient μ, which determines the overall matching level.
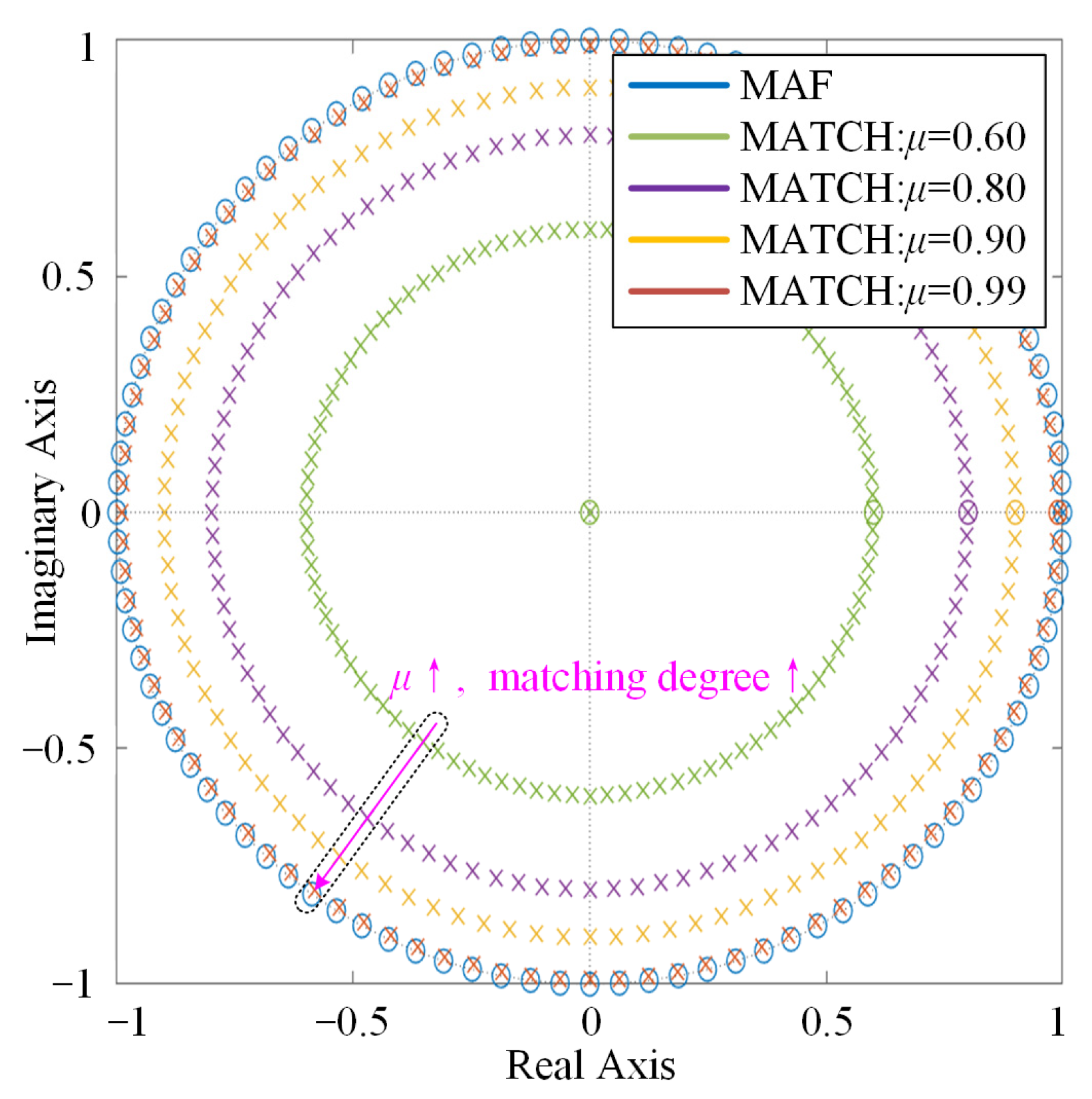
Figure 3 shows the zero-pole distributions of the cascaded MAF-MATCH filter under different matching levels. As μ increases, the poles of the MATCH gradually approach the zeros of the MAF, resulting in a higher level of zero-pole cancellation. When μ is close to 1, nearly complete cancellation can be achieved. As shown in Figure 2, with increasing μ, the amplitude response in the mid- and high-frequency ranges is partially compensated, while the average phase delay is reduced from approximately −90° to nearly 0°. Meanwhile, the notch depth at the comb frequencies remains close to that of the original MAF, only slightly weakened as μ approaches 1. This indicates that the MAF-MATCH effectively preserves the harmonic suppression capability of the MAF while improving its dynamic response.
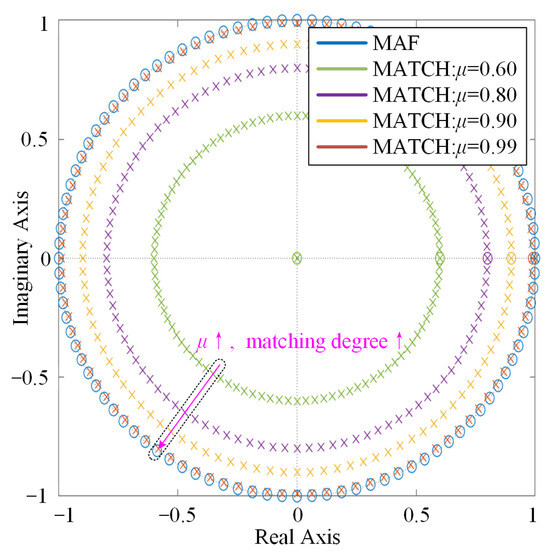
Figure 3.
Zero-pole distribution of the MAF-MATCH filter under different matching levels.
To further evaluate the dynamic performance, the time-domain behavior is analyzed using the unit-step response. First, by rearranging (6), expression can be obtained as follows:
Under a unit-step excitation, the system output in the Z-domain can be expressed as
According to the properties of the Z-domain, the expressions of the time sequences y1[n] and y2[n] can be obtained as
Therefore, the impulse sequence y[n] can be represented in the form of a time-domain convolution as
Based on the convolution property, the expression of y[n] can be obtained as
For ease of analysis, a further simplification yields the closed-form expression of y[n].
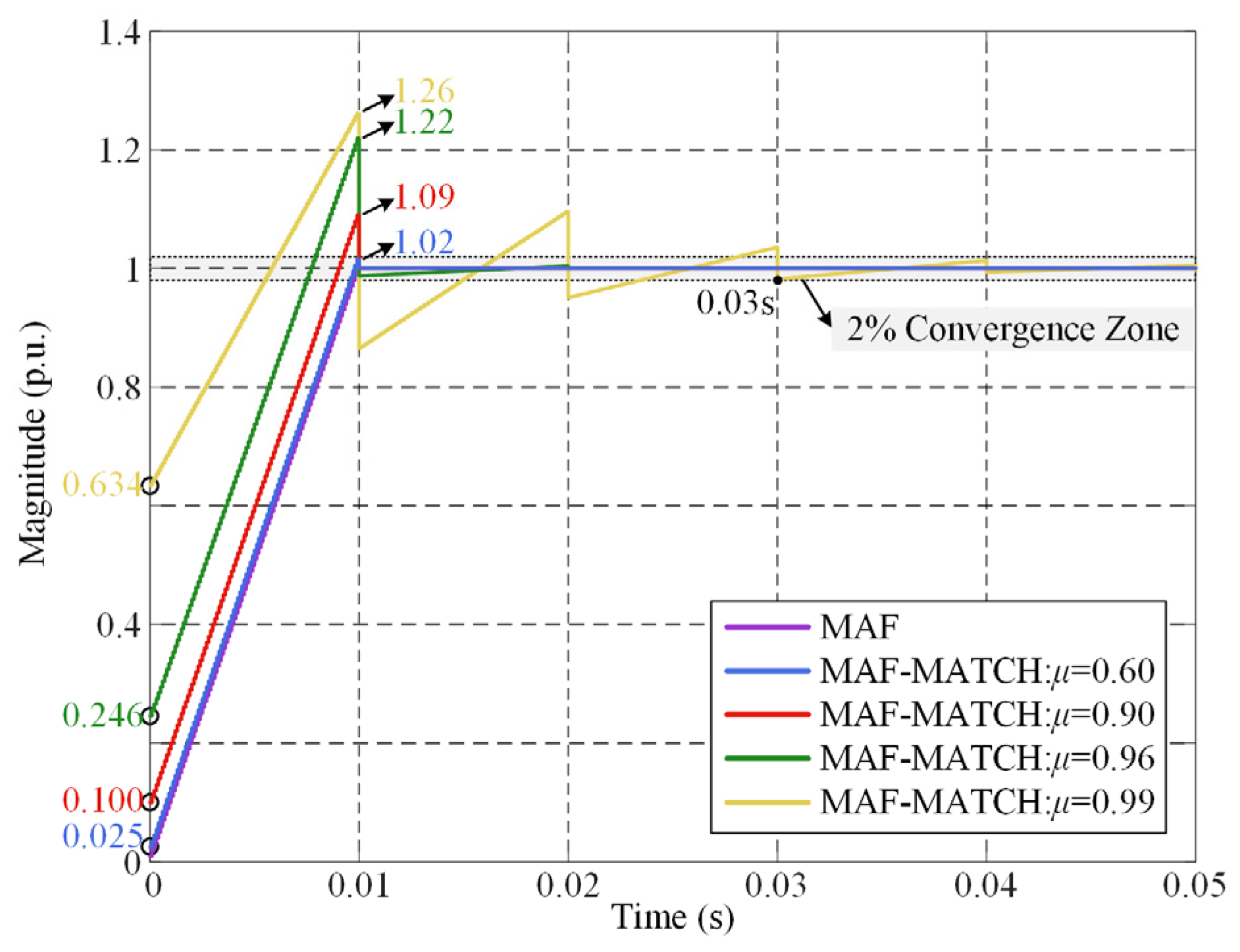
Based on the above expression, the time-domain response curves of the MAF-MATCH algorithm under different matching levels can be plotted, as shown in Figure 4. It can be observed that as the matching coefficient μ increases, the initial response value rises from 0 (for the conventional MAF without MATCH) to 0.634, which facilitates faster detection of transient voltage events. However, higher values of μ also introduce negative effects. On the one hand, the overshoot grows significantly—for instance, reaching up to 26% when μ = 0.99. On the other hand, larger μ exacerbates oscillations in the response, leading to longer settling times (e.g., 30 ms at μ = 0.99). These effects hinder accurate voltage estimation during disturbances.
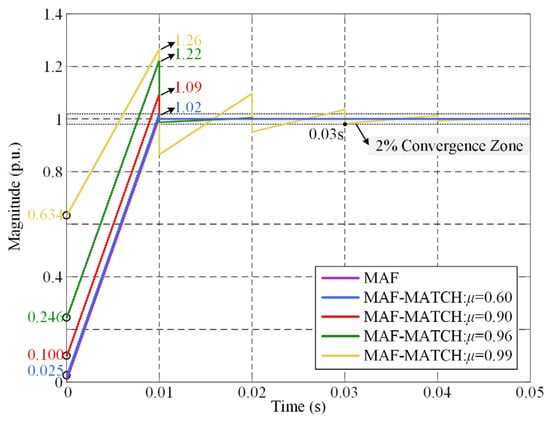
Figure 4.
Unit-step response curves of the MAF-MATCH filter under different matching levels.
3. Adaptive Variable-Parameter MAF-MATCH Algorithm
The fixed-parameter approach (denoted as MAF-MATCH-F) cannot simultaneously satisfy the dynamic performance requirements of voltage detection. Specifically, a large matching coefficient μ enables fast disturbance recognition but leads to excessive overshoot and oscillatory behavior, while a small μ ensures smooth convergence but slows down the recognition process. Therefore, a static choice of μ inevitably compromises one performance aspect for another.
To overcome this limitation, this paper introduces an adaptive variable-parameter strategy. The key idea is to adopt a larger value of μ immediately after a voltage disturbance is detected, thereby accelerating disturbance recognition, and then gradually decrease μ to a smaller value during the subsequent convergence stage to ensure stability. This transforms the MAF-MATCH algorithm from a static matching mechanism into a dynamic one, allowing a better trade-off between recognition speed and steady-state accuracy.
3.1. Adaptive Rule
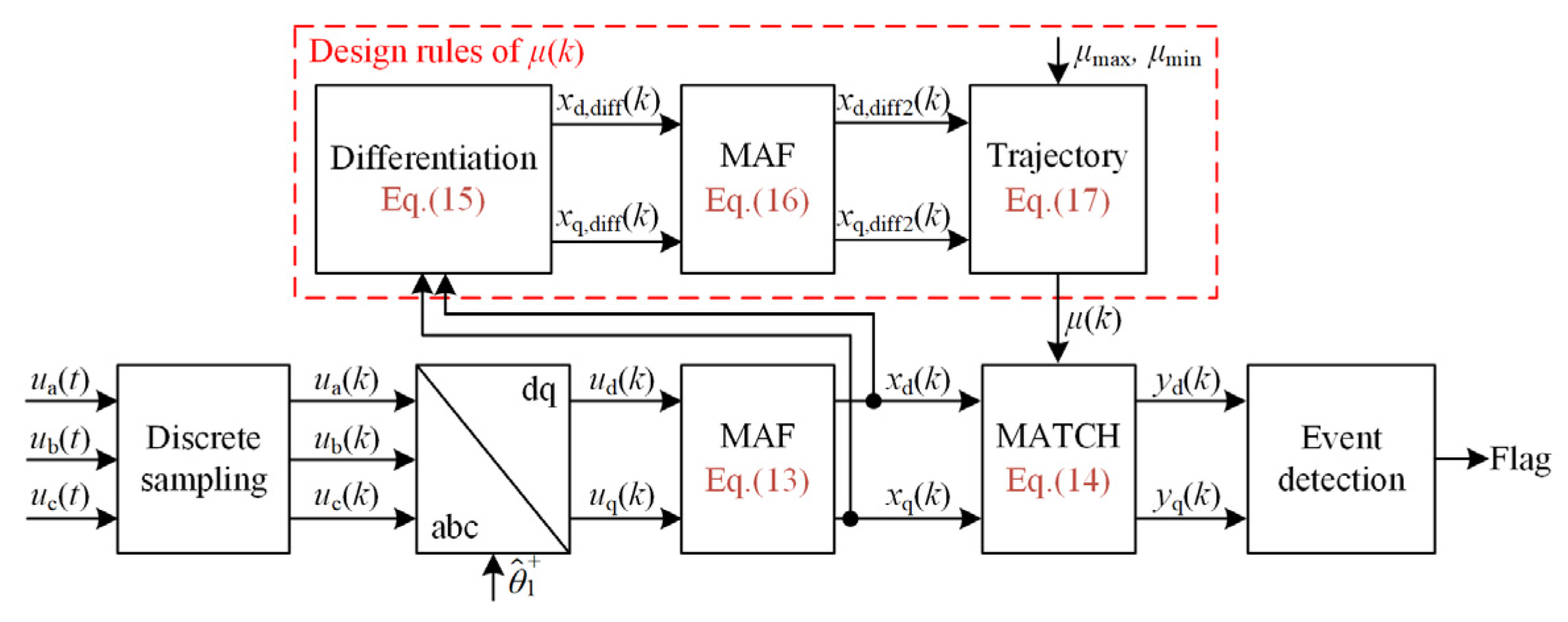
Since the system with variable parameters does not satisfy the linear time-invariant (LTI) property, it is difficult to derive a closed-form analytical expression. Instead, the adaptive process can be described using recursive relations. According to Equations (3) and (4), the discrete-time equations of the MAF and the variable-parameter MAF-MATCH (denoted as MAF-MATCH-V) can be expressed as follows:
where u(k) is the input sequence of the MAF, x(k) and y(k) represent the outputs of the MAF and MATCH, respectively. And μ(k) is the adaptive matching coefficient. To enable practical implementation, the adaptive rule for μ(k) is formulated as follows. First, the MAF output x(k) is differenced and normalized:
where δ is the differential threshold, determined by the sampling frequency. To ensure robustness, the differential sequence xdiff(k) is further smoothed using an M-point sliding window average.
It should be noted that the sliding window size M must be no smaller than the MAF window N, such that μ(k) varies smoothly during the convergence stage. Finally, the adaptive trajectory of μ(k) is designed as
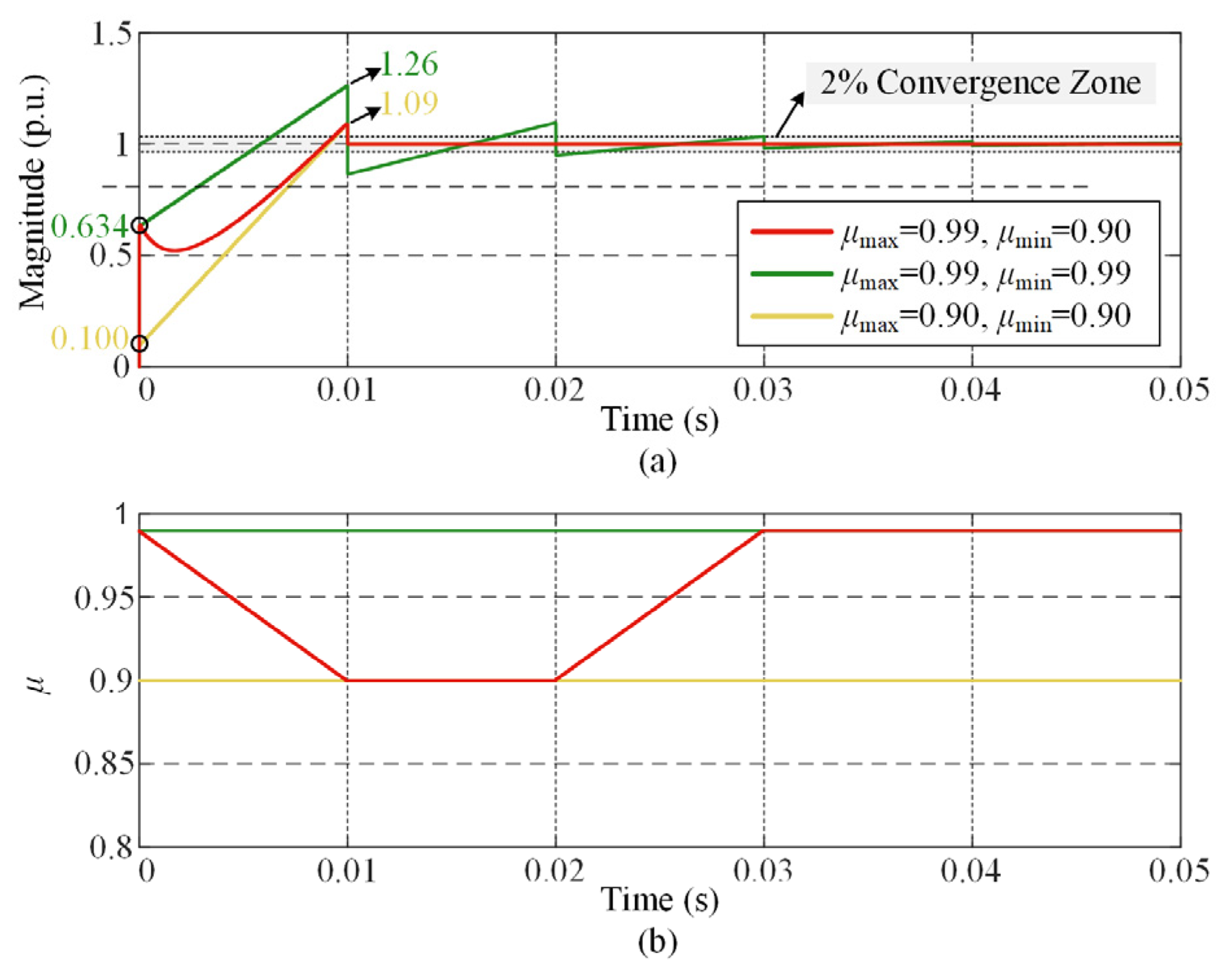
where μmax and μmin denote the upper and lower bounds of the matching coefficient, respectively. Figure 5 illustrates the unit-step responses of the MAF-MATCH-V algorithm under different combinations of (μmax, μmin). As shown, when μ(k) varies adaptively between 0.99 and 0.90, the system exhibits superior dynamic performance compared with fixed-parameter configurations, e.g., (0.99, 0.99) and (0.90, 0.90). Specifically, the adaptive rule yields a higher initial response value, a smaller overshoot, and eliminates oscillatory behavior during convergence.
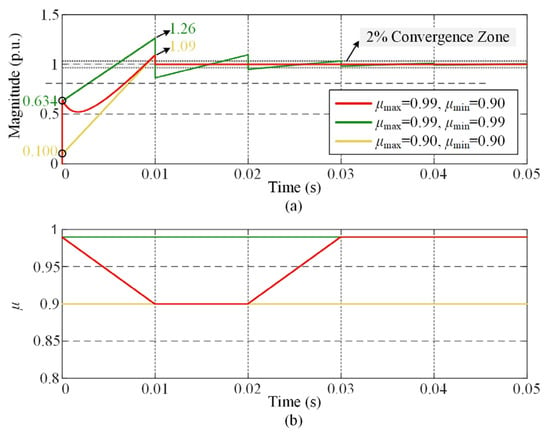
Figure 5.
Unit-step response of the MAF-MATCH-V algorithm under different (μmax, μmin): (a) Step-response results; (b) trajectory of μ.
According to the above adaptive rule, the overall control structure of the proposed voltage-detection method using the MAF-MATCH-V algorithm is depicted in Figure 6.
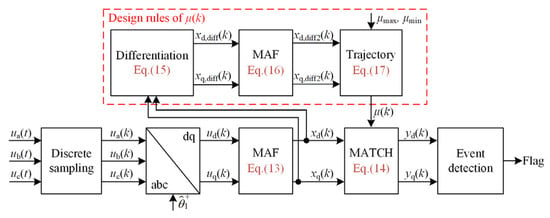
Figure 6.
Structure of the grid-voltage detection method based on the MAF-MATCH-V algorithm.
3.2. Parameter Design
In the MAF-MATCH-V algorithm, the selection of μmax and μmin directly affects the dynamic response of the system. Therefore, the parameters must be quantitatively analyzed with respect to several performance indicators, including the initial response value, overshoot, convergence time, and rise time.
3.2.1. Initial Response Value
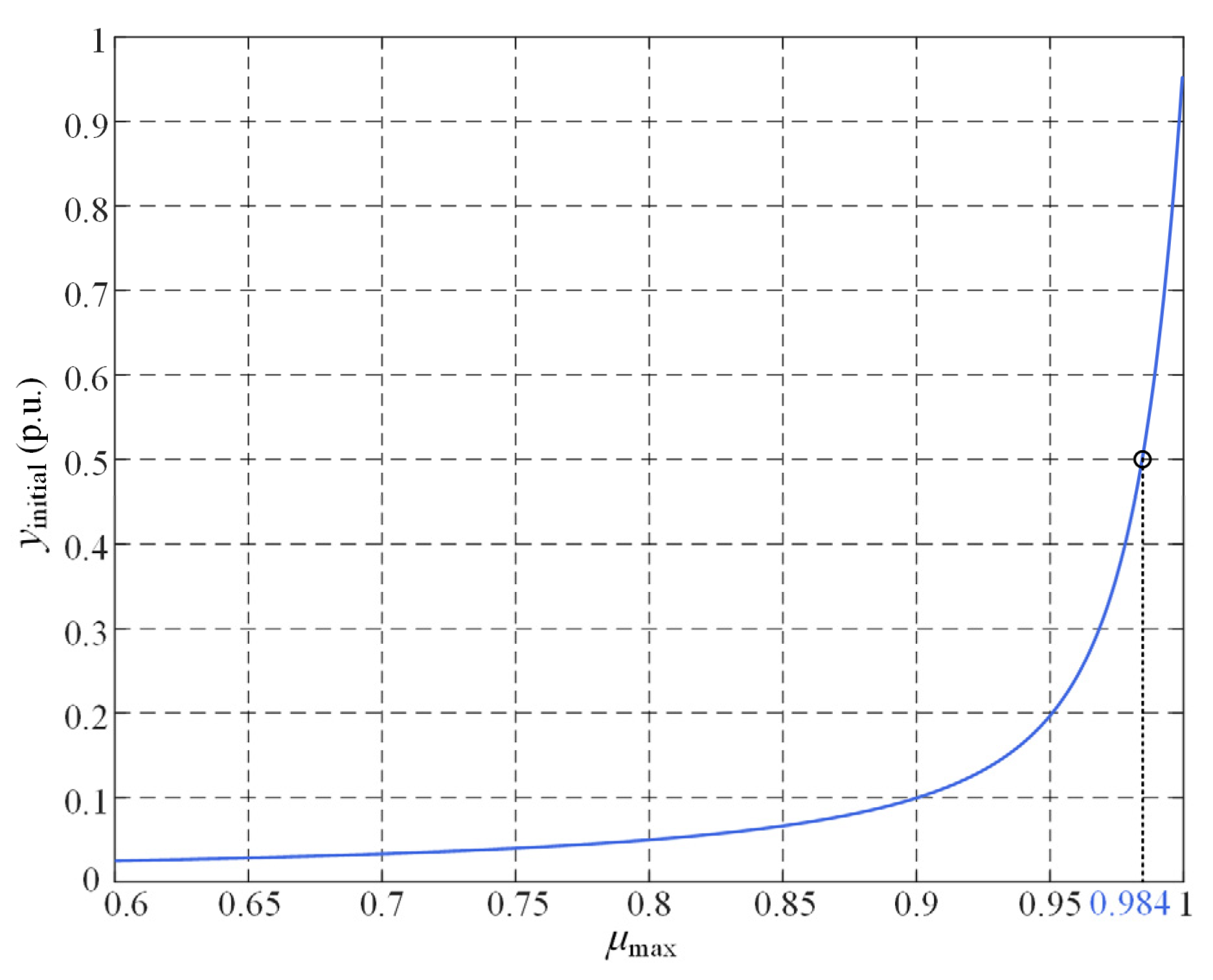
For the unit-step response, the initial response value depends solely on the instantaneous value of μ(0), e.g., μmax, and is independent of the subsequent trajectory. Based on Equations (13) and (14), the analytical expression of the initial value can be derived.
Figure 7 illustrates the relationship between the initial response value and μmax. It can be seen that the two exhibit a monotonic relationship. When μmax exceeds 0.984, the initial response value exceeds 0.5 p.u., ensuring sufficient speed for transient voltage recognition.
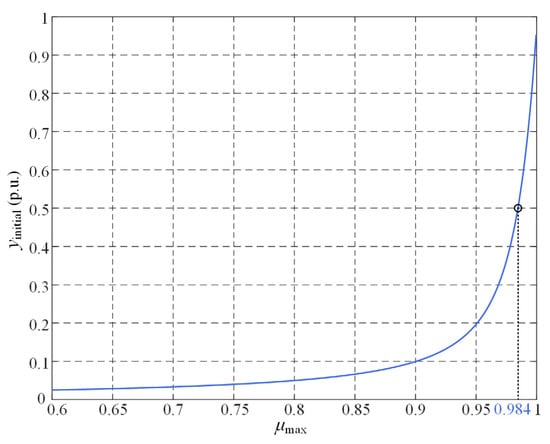
Figure 7.
Relationship curve between the initial response value and the matching parameter.
3.2.2. Overshoot and Convergence Time
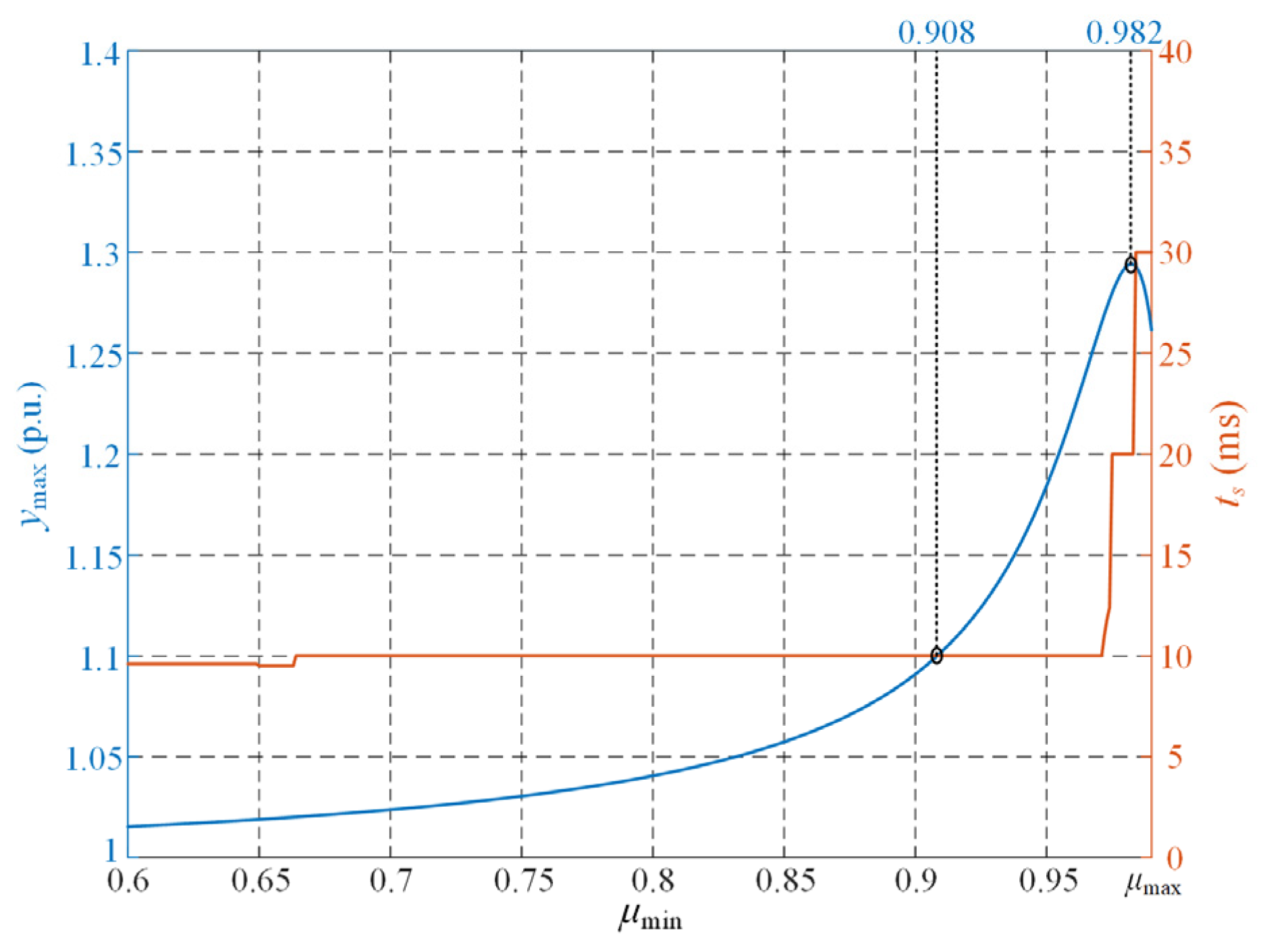
Based on Equations (13)–(17), the expression of the overshoot can be derived as
The overshoot of the system is determined mainly by μmin. Figure 8 shows the curves of overshoot and convergence time (2% criterion) with respect to μmin. The results reveal a non-monotonic behavior: when μmin < 0.982, the overshoot increases with μmin; when μmin > 0.982, the overshoot decreases as μmin increases. Meanwhile, the convergence time rises significantly when μmin approaches μmax, due to enhanced oscillatory behavior. To guarantee accurate voltage detection, μmin must be smaller than 0.908, thereby limiting the overshoot to values below 1.1 p.u. and ensuring the convergence time remains within half a grid cycle.
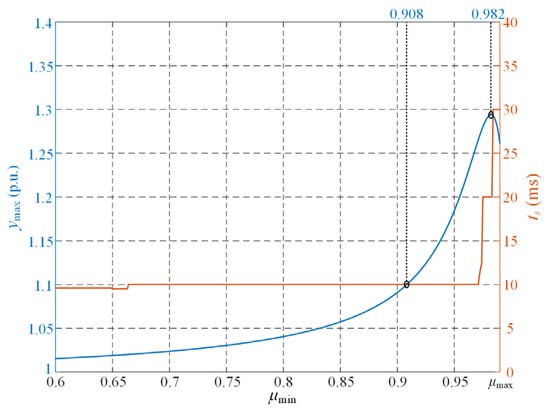
Figure 8.
Relationship curves of overshoot and convergence time versus the matching parameter.
3.2.3. Rise Time
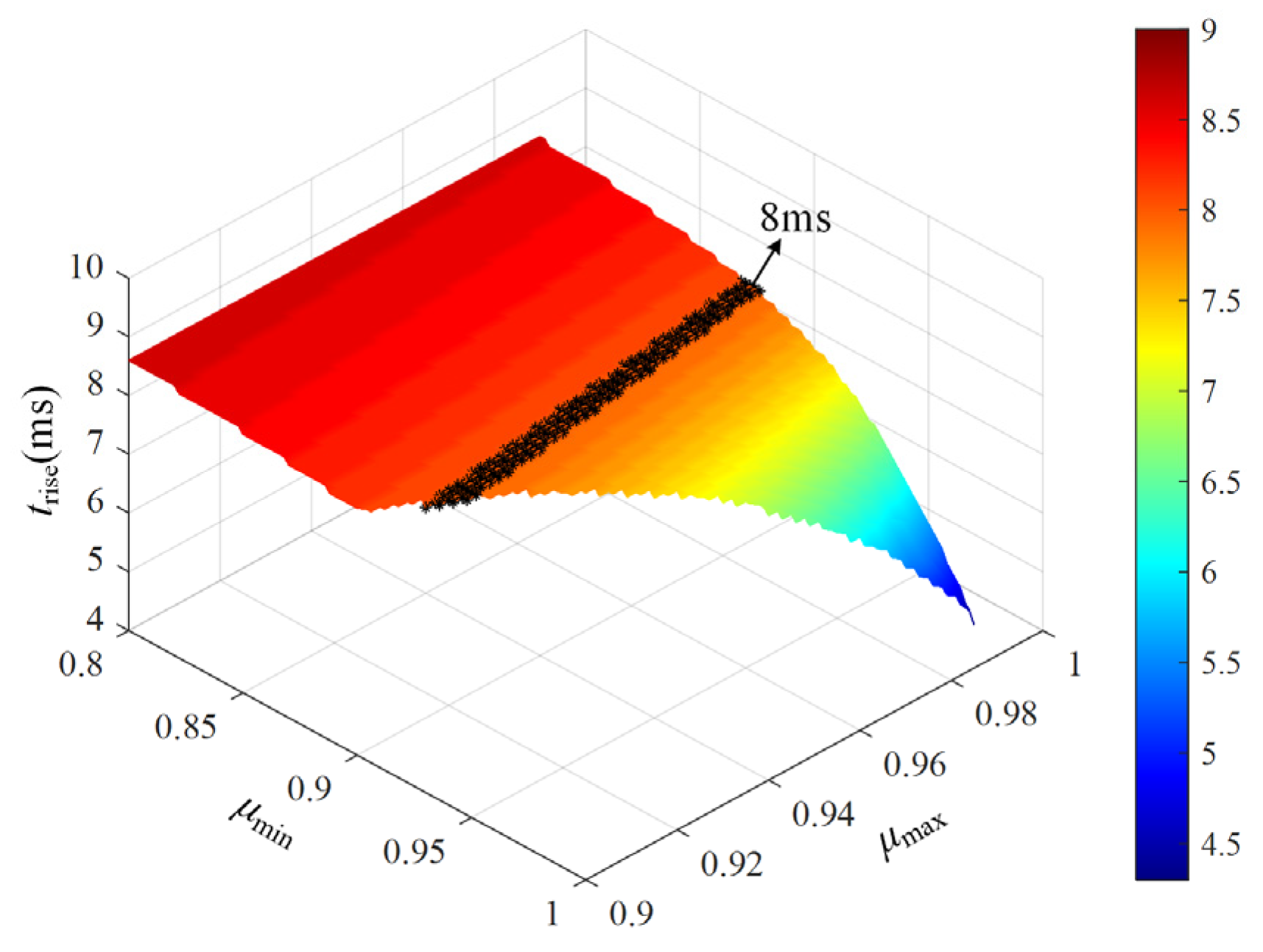
The rise time trise reflects the speed of voltage estimation and depends on both the initial response and the recursive dynamics. Figure 9 presents the three-dimensional surface of rise time with respect to μmax and μmin. It can be observed that trise decreases significantly as μmin increases, and decreases slightly with larger μmax. The contour line in Figure 9 marks a rise time of 8 ms, indicating that the parameter region to the right of the contour is preferable to guarantee fast convergence.
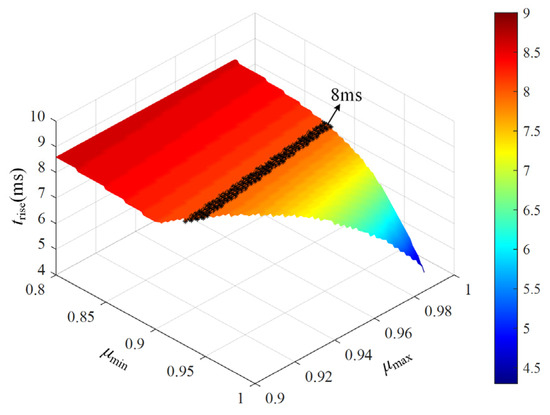
Figure 9.
Three-dimensional surface of rise time with respect to μmax and μmin.
By comprehensively considering all performance constraints, this paper selects μmax = 0.99 and μmin = 0.90. Under these settings, the unit-step response achieves an initial value of 0.634 p.u., an overshoot of 1.09 p.u., and a rise time of 8 ms, representing an effective balance between recognition speed, overshoot suppression, and convergence stability.
4. Experimental Validation
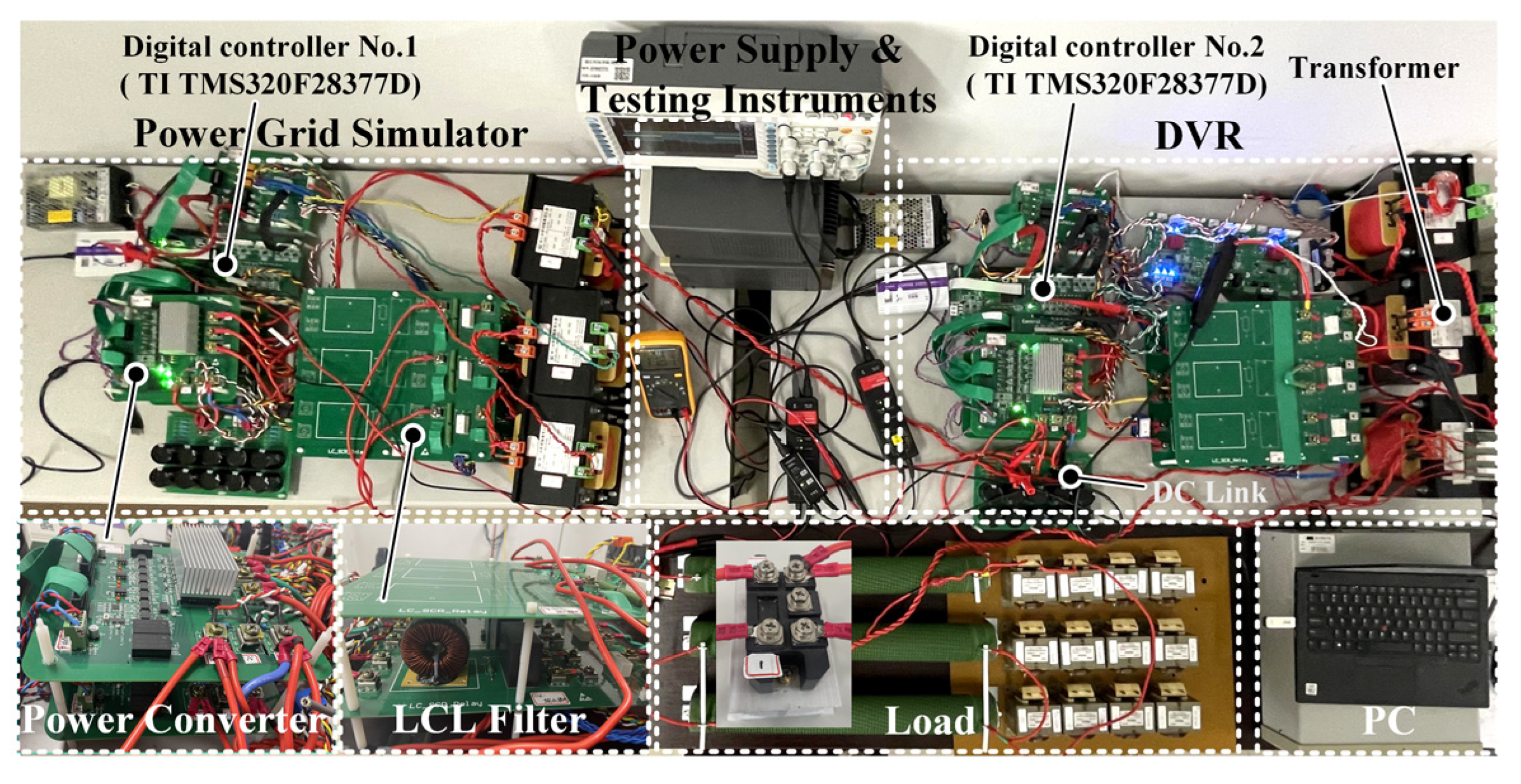
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed MAF-MATCH-V method, an experimental platform is established, consisting of a programmable Dynamic Voltage Restorer (DVR) and a programmable grid simulator, as illustrated in Figure 10. Both devices employ the Texas Instruments DSP TMS320F28377D as the main control unit. The proposed voltage detection algorithm is implemented on the DSP of the DVR. The programmable grid simulator is used to emulate various grid conditions, including symmetrical voltage sags, symmetrical swells, phase jumps, asymmetrical sags, and harmonic distortions. The main system parameters are summarized in Table 1.
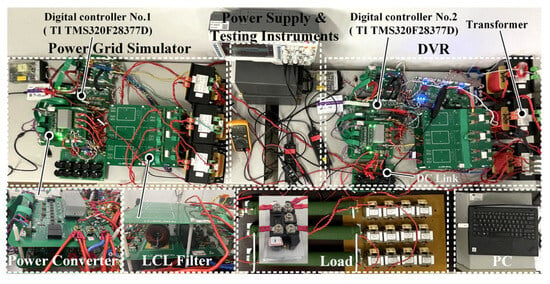
Figure 10.
The experimental platform for MAF-MATCH-V.

Table 1.
Main system parameters of the experimental setup.
The disturbances are configured to represent representative non-ideal operating conditions commonly encountered in practical power systems. In this paper, the effectiveness of the proposed approach is validated under the following typical scenarios:
- Symmetrical sag with a depth of Udepth1;
- Symmetrical swell with a depth of Udepth1;
- Asymmetrical sag with a depth of Udepth2 accompanied by a phase jump of θjump;
- Symmetrical sag with a depth of Udepth1 under background harmonic distortion, where the harmonics are specified in Table 1.
In addition to comparisons with the detection methods based on MAF and MAF-MATCH-F, the proposed method is also benchmarked against other widely used grid-voltage detection methods, including SRF-LPF, DSOGI, and GDFT. The control parameters of each method are selected according to the corresponding references: the cutoff frequency of SRF-LPF is set to 50 Hz, the control gain of DSOGI is chosen as 1.414, and the GDFT is configured to suppress the 6k ± 1-order harmonics. It should be noted that the dynamic performance of voltage-sag detection can be quantified using the recognition time trec, representing the time required to identify a disturbance, which is related to Usag,th and Uswell,th. And the settling time ts, which is defined by the 2% error criterion, reflecting the convergence speed of the voltage magnitude estimation.
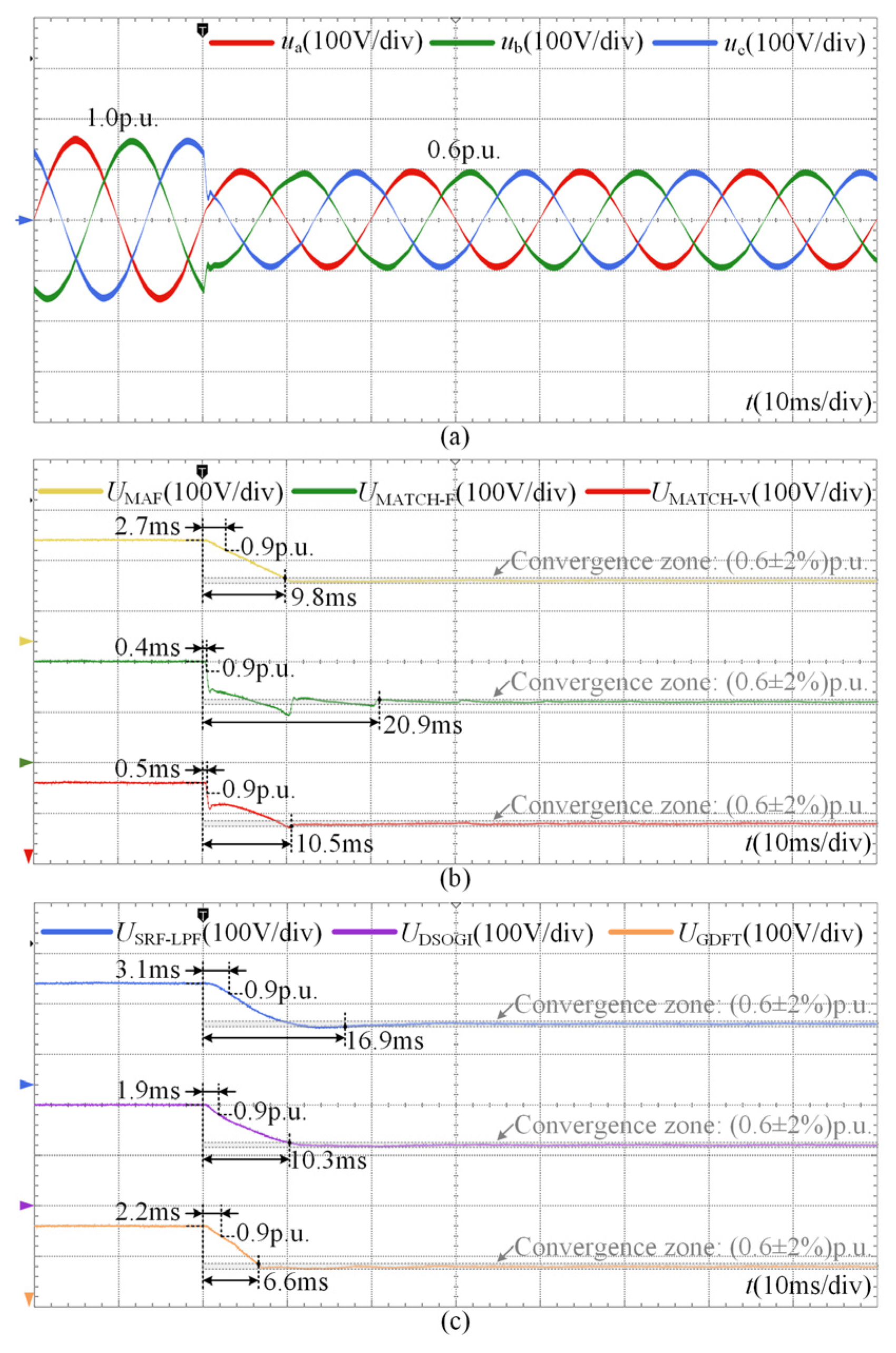
The results obtained under the symmetrical sag condition are presented in Figure 11. As shown in Figure 11b, the conventional MAF method achieves convergence within 9.8 ms, but requires 2.7 ms to recognize the disturbance. Such a recognition delay is insufficient for the timely response of high-dynamic-performance equipment, such as DVRs. The MAF-MATCH-F method, with a high matching coefficient, can identify the disturbance within 0.4 ms. However, this comes at the expense of significant overshoot and pronounced oscillations, leading to a settling time of 20.9 ms. These oscillations reduce the accuracy of compensation for DVRs and similar devices. In contrast, the proposed MAF-MATCH-V method achieves a recognition time of 0.5 ms and a settling time of 10.5 ms, thereby maintaining a balanced dynamic performance. The experimental observations are consistent with the theoretical analysis discussed in Section 3. As illustrated in Figure 11c, the SRF-LPF and DSOGI methods exhibit only moderate dynamic performance. The GDFT method, designed for selective harmonic suppression, benefits from a relatively small window length and achieves a short settling time of 6.6 ms. Nevertheless, its recognition still requires 2.2 ms, which limits its applicability in fast-response scenarios.
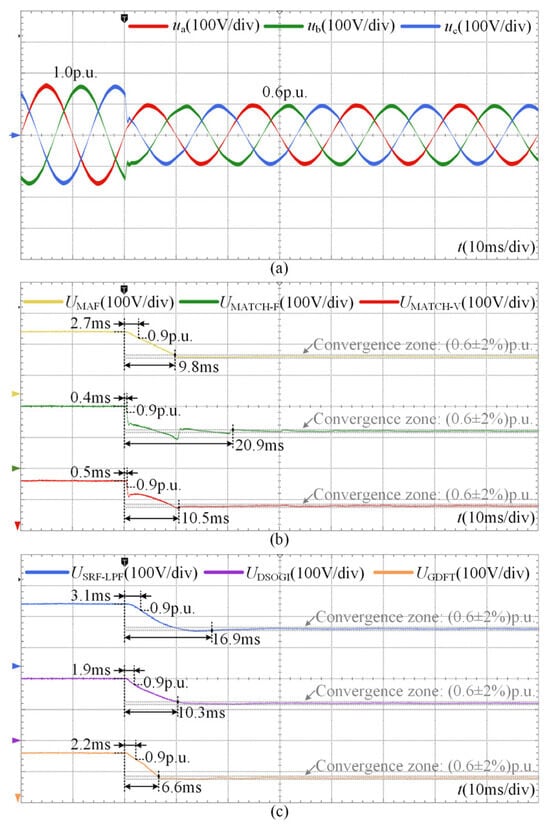
Figure 11.
Experimental results under the symmetrical sag condition: (a) three-phase grid voltages; (b) detection process of MAF, MAF-MATCH-F and MAF-MATCH-V; (c) detection process of SRF-LPF, DSOGI and GDFT.
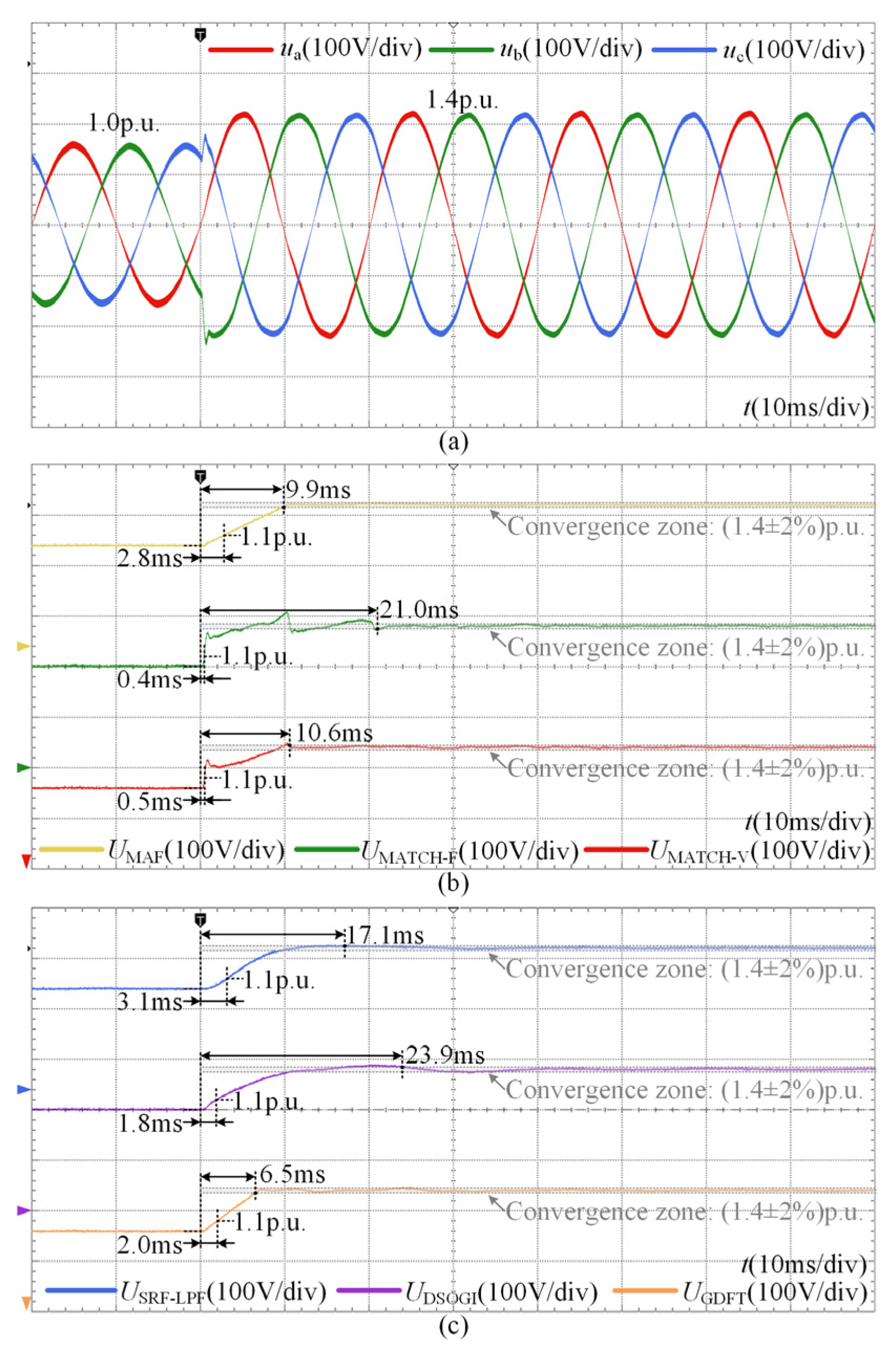
The results under the symmetrical swell condition are shown in Figure 12. The dynamic performance of the different detection methods is similar to that under the sag condition. Most methods struggle to achieve an effective balance among the various dynamic indices, whereas the proposed MAF-MATCH-V method achieves a recognition time of 0.5 ms and a settling time of 10.6 ms.
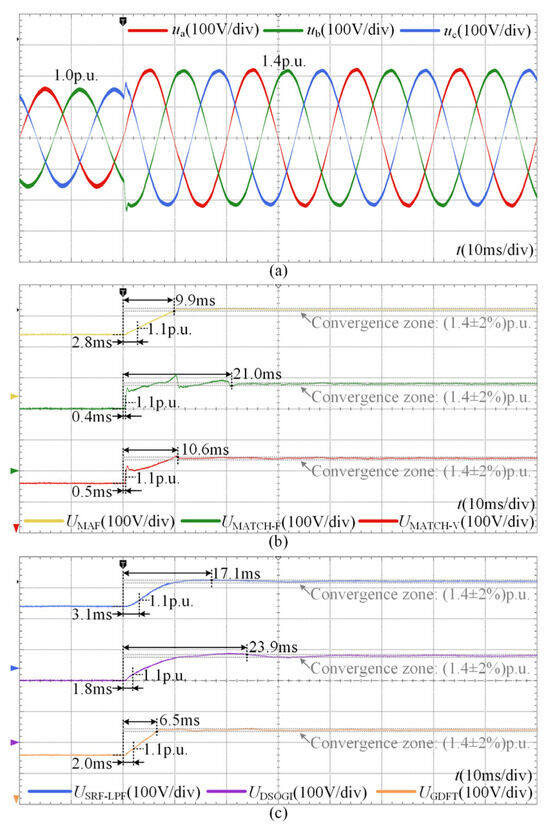
Figure 12.
Experimental results under the symmetrical swell condition: (a) three-phase grid voltages; (b) detection process of MAF, MAF-MATCH-F and MAF-MATCH-V; (c) detection process of SRF-LPF, DSOGI and GDFT.
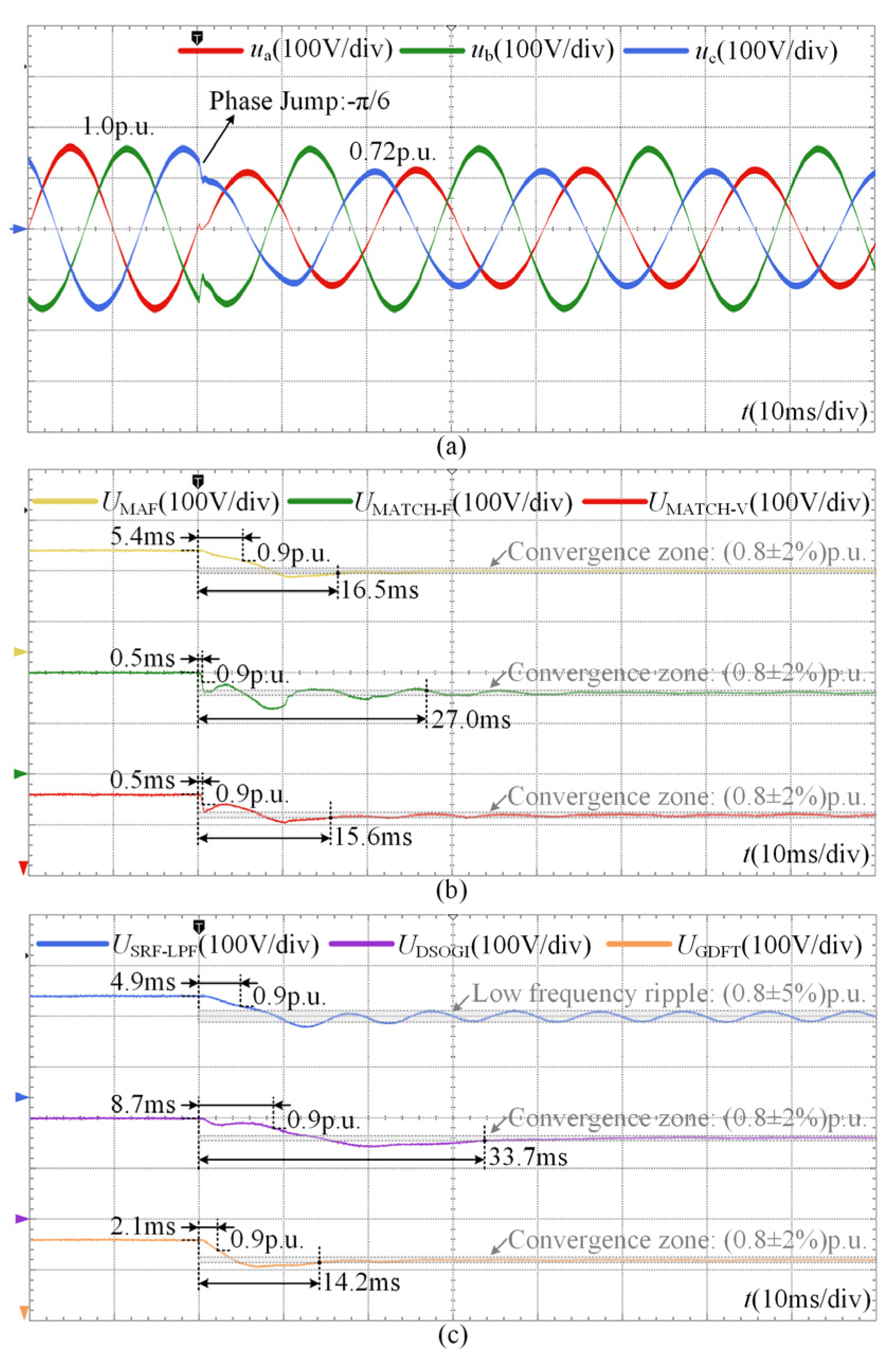
The experimental results under the asymmetrical sag condition with a phase jump are shown in Figure 13. After the voltage sag occurs, the recognition times of the MAF, SRF-LPF, DSOGI, and GDFT methods are 5.4 ms, 4.9 ms, 8.7 ms, and 2.1 ms, respectively, whereas the proposed MAF-MATCH-V method identifies the disturbance in only 0.5 ms. This demonstrates the superior sensitivity of the adaptive scheme in detecting abrupt voltage events. It should be noted that asymmetrical sags inherently introduce negative-sequence components. As a result, the SRF-LPF method, which lacks negative-sequence suppression capability, exhibits a low-frequency oscillation with an amplitude of approximately 5% even after convergence. In contrast, the other methods successfully converge within the 2% error criterion. Among these, the MAF-MATCH-F method achieves fast recognition but requires as long as 27.0 ms to reach steady-state magnitude estimation due to pronounced overshoot and oscillatory dynamics. The DSOGI method effectively suppresses the negative-sequence component; however, because of the phase jump, its settling time extends to 33.7 ms. By comparison, the proposed MAF-MATCH-V method achieves a much shorter settling time of 15.6 ms, striking a better balance between disturbance recognition and accurate steady-state estimation.
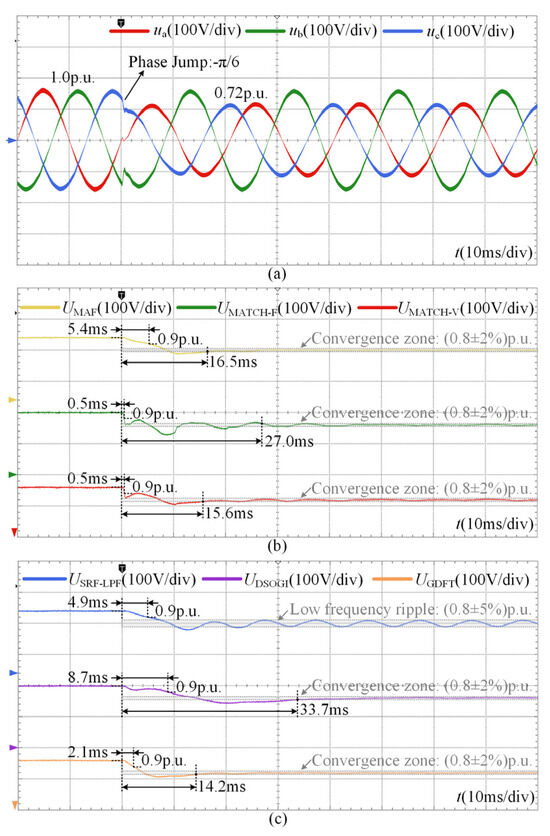
Figure 13.
Experimental results under the asymmetrical sag condition with a phase angle jump: (a) three-phase grid voltages; (b) detection process of MAF, MAF-MATCH-F and MAF-MATCH-V; (c) detection process of SRF-LPF, DSOGI and GDFT.
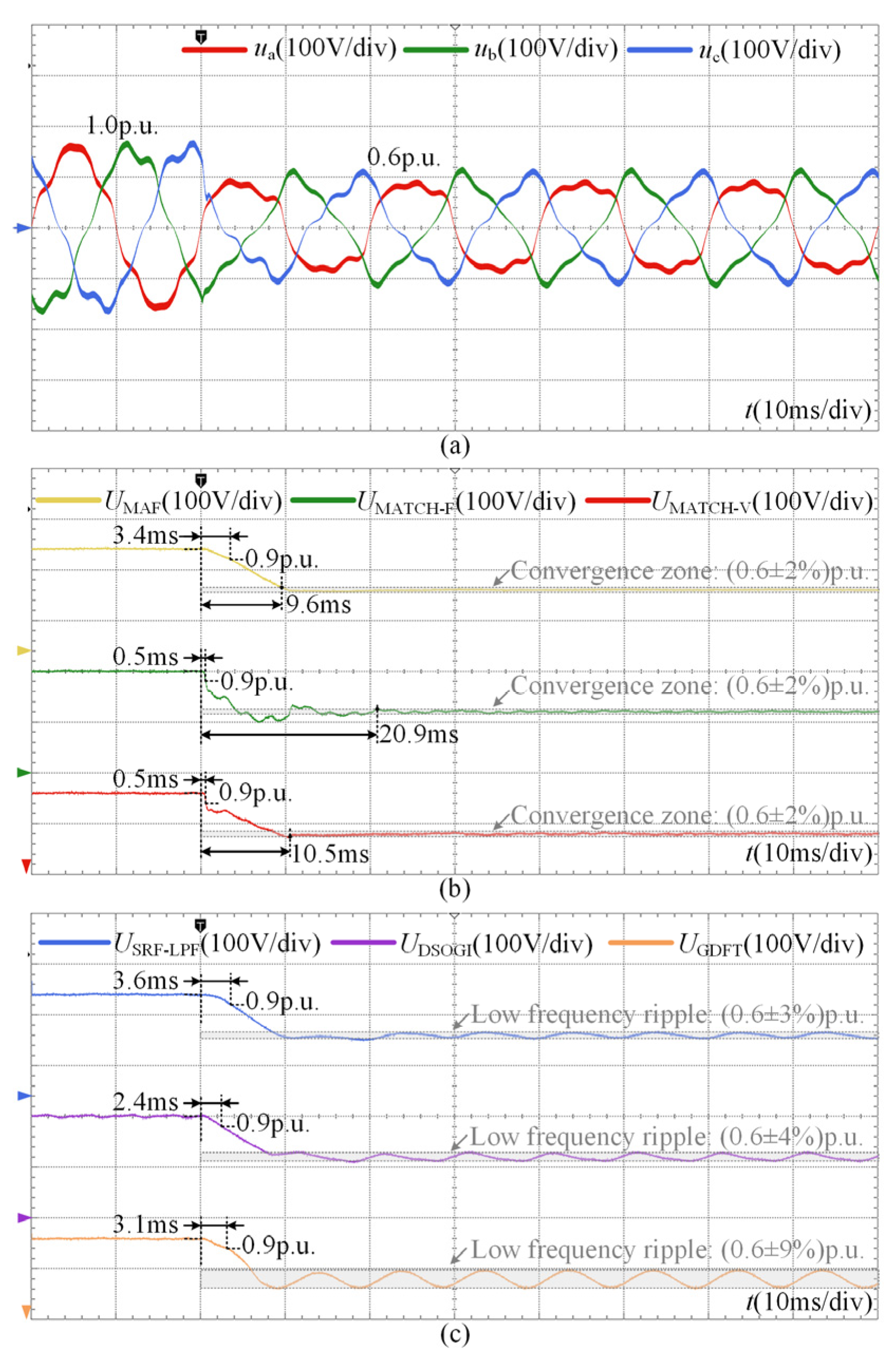
The results for the symmetrical sag condition with background harmonic distortion are presented in Figure 14. Prior to the sag event, all methods remain stable despite the presence of 5th and 7th harmonic components in the grid voltage. Once the sag occurs, the proposed MAF-MATCH-V method promptly identifies the disturbance within 0.5 ms, whereas the SRF-LPF, DSOGI, and GDFT methods require 3.6 ms, 2.4 ms, and 3.1 ms, respectively. In terms of steady-state performance, the SRF-LPF, DSOGI, and GDFT methods exhibit noticeable low-frequency ripples after convergence due to their limited harmonic attenuation capability, with ripple amplitudes of approximately 3%, 4%, and 9%, respectively. In contrast, the proposed MAF-MATCH-V method reaches zero steady-state error within 10.5 ms, thereby demonstrating strong disturbance rejection and harmonic robustness.
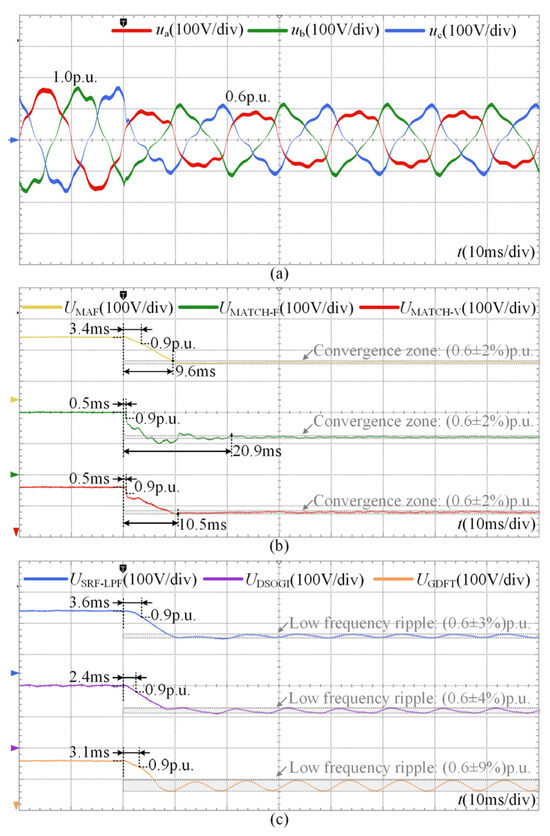
Figure 14.
Experimental results under symmetrical sag condition with harmonic distortion: (a) three-phase grid voltages; (b) detection process of MAF, MAF-MATCH-F and MAF-MATCH-V; (c) detection process of SRF-LPF, DSOGI and GDFT.
The comprehensive experimental results for various detection methods under different grid conditions are summarized in Table 2. The proposed MAF-MATCH-V method demonstrates consistently fast dynamic response and high steady-state accuracy across all test scenarios. In other words, the method achieves a favorable balance between dynamic performance and disturbance rejection capability.

Table 2.
Experimental performance of different voltage-sag detection methods.
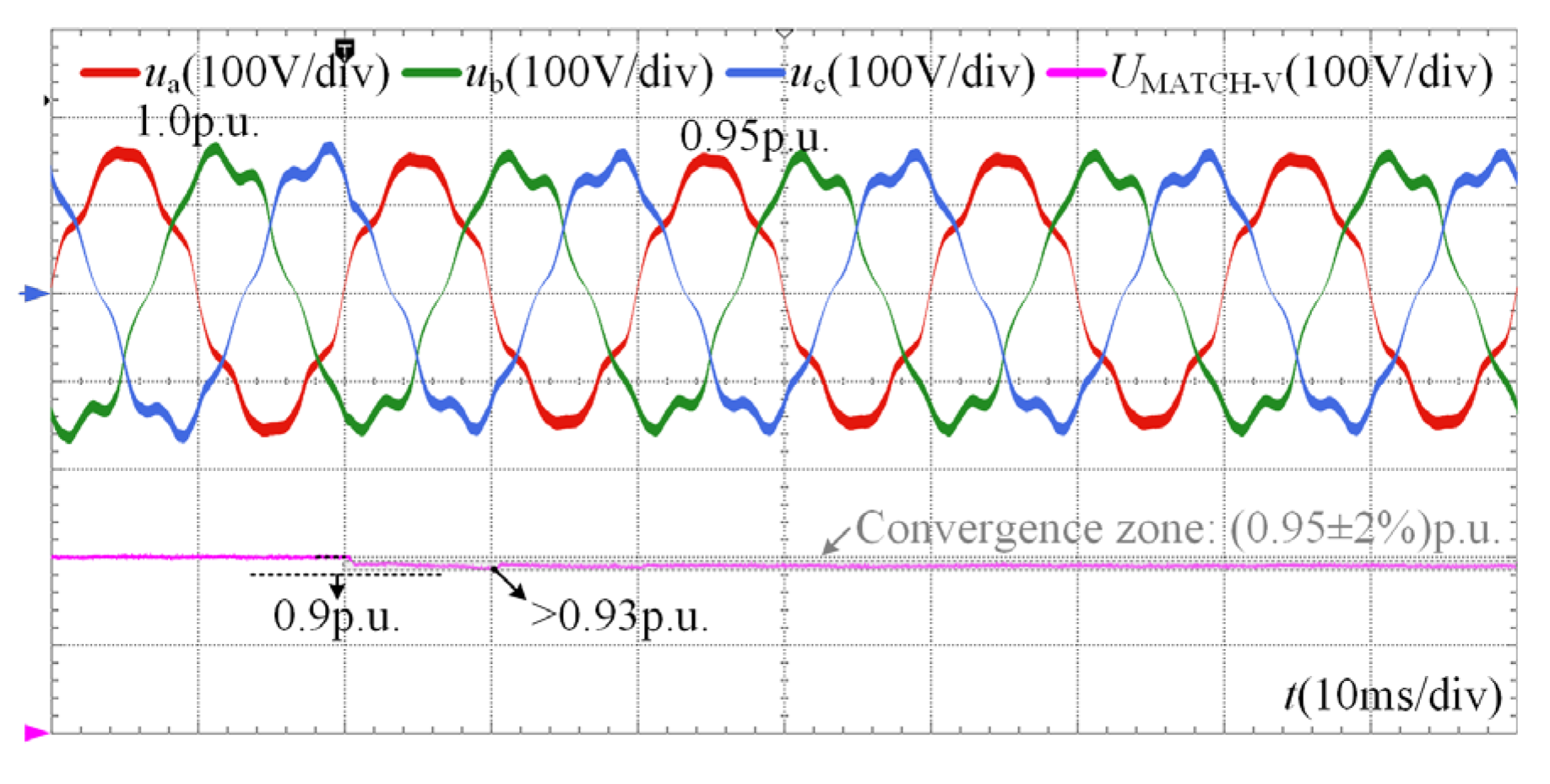
In addition to severe disturbances such as short circuits, voltage detection methods should also demonstrate robustness against small disturbances, for example, those caused by load variations on distribution lines. The performance of the proposed method under a shallow sag condition with background harmonics is illustrated in Figure 15. Following the disturbance, the grid voltage drops slightly to 0.95 p.u. Despite the small magnitude of this variation, the proposed MAF-MATCH-V method successfully estimates the fundamental voltage amplitude with high accuracy within half a fundamental cycle. Before convergence, the maximum overshoot is 0.93 p.u., which provides a sufficient detection margin and effectively prevents misjudgment.
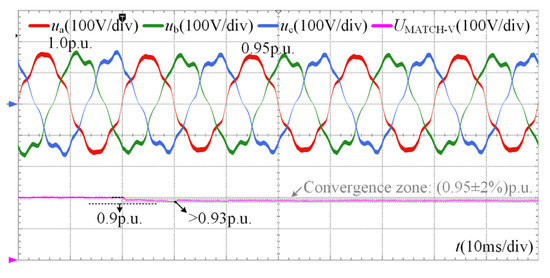
Figure 15.
Experimental results under the shallow sag condition with harmonic distortion.
5. Conclusions
This paper has proposed a novel grid-voltage detection method based on the adaptive variable-parameter MAF-MATCH-V algorithm to address the dynamic performance limitations of the conventional MAF approach. By introducing the matcher algorithm, the method effectively compensates for the mid- and high-frequency magnitude attenuation of MAF and reduces its average phase delay. Furthermore, a time-varying control strategy is designed to dynamically adjust the matching coefficient μ: adopting a larger value during the disturbance instant to ensure rapid recognition, and reducing it thereafter to guarantee stable convergence. This strategy transforms the MAF-MATCH algorithm from a static matching scheme into an adaptive dynamic one, achieving a favorable balance between transient and steady-state performance. Experimental results demonstrate that, under various grid conditions, the proposed MAF-MATCH-V method outperforms conventional approaches such as SRF-LPF, DSOGI, and GDFT. The method achieves millisecond-level disturbance recognition and zero steady-state error convergence while also exhibiting strong robustness against harmonic distortion, negative-sequence suppression, and detection margin for small disturbances. These advantages make the proposed method a practical and effective solution for the real-time control of grid-following devices such as DVRs in non-ideal grid environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.S. and Y.L.; methodology, D.C.; validation, Z.L.; formal analysis, Z.L. and B.Y.; investigation, D.C.; writing—original draft preparation, X.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.L.; funding acquisition, X.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Science and Technology Project of State Grid Fujian Electric Power Co., Ltd., under Grant No. 521330240009.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author X.S., Y.L. and B.Y. were employed by the company State Grid Fujian Electric Power Co., Ltd., Quanzhou Power Supply Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Gupta, S.; Shukla, A. Enhancing Stability of AC-DC Microgrid Cluster and Reducing Diesel Dependency With BSS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2025, 61, 4958–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, S.M.; Assessment, V.S. Detection, and Classification in Distribution Systems Embedded With Fast Charging Stations. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 89864–89880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Nair, A.R.; Bhattarai, R.; Kamalasadan, S.; Muttaqi, K.M. A coordinated optimal feedback control of distributed generators for mitigation of motor starting voltage sags in distribution networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. A Unified Framework for Adaptive and Flexible Phase Angle Regulation in Single-Phase UPQC. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 12779–12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khergade, A.; Satputaley, R.; Patro, S.K. Investigation of Voltage Sags Effects on ASD and Mitigation Using ESRF Theory-Based DVR. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2021, 36, 3752–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, S. Sensitivity of Programmable Logic Controllers to Voltage Sags. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2019, 34, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Premium Power Supply Scheme for Data Center With SMES and DG Integration. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 5701805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yao, J.; Yang, D.; Xie, H.; Zhao, L.; Jin, R. Improved LVRT Strategy for DFIG-Based Wind Turbine Considering RSC-GSC Interaction During Symmetrical Grid Faults. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2025, 40, 1674–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardhanan, S.; Mulla, M.A. Implementation of Voltage Imbalance Mitigation Using SOGI Based PV-DVR System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 7858–7868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shao, Y.; Liu, X. A Voltage Harmonic Self-Suppression Strategy of Single-Phase UPS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 15685–15693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lin, Y.; Sun, C.; Lin, L.; Yu, H.; Xue, F.; Su, W.; Luo, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. An Overview of Voltage Sag Detection Methods. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/IAS Industrial and Commercial Power System Asia (I&CPS Asia), Shanghai, China, 8–11 July 2022; pp. 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisavljević, A.M.; Katić, V.A.; Dumnić, B.P.; Popadić, B.P. Overview of voltage dips detection analysis methods. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Power Electronics (Ee), Novi Sad, Serbia, 19–21 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achlerkar, P.D.; Panigrahi, B.K. Recursive Least Squares-Based Adaptive Parameter Estimation Scheme for Signal Transformation and Grid Synchronization. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 2427–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mallick, R.K.; Nayak, P.; Ramasamy, T.N.; Panda, G. Dynamic Power Quality Disturbance Classification in Grid-Integrated PV Systems: Leveraging Clark Transformed Modal Voltage and Subspace Weighted KNN. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 116572–116586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zhang, T.; Lim, E.; López-Benítez, M.; Ma, F.; Yu, L. A Review of Wavelet Analysis and Its Applications: Challenges and Opportunities. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 58869–58903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Xing, Y. Fast and Flexible Selective Harmonic Extraction Methods Based on the Generalized Discrete Fourier Transform. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 3484–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilmiş, F.; Karaca, H.; Ahmed, H. High-Order Delayed Signal Cancellation-Based PLL Under Harmonically Distorted Grid Voltages. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 9003609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán-Pérez, J.; García-Cerrada, A.; Ochoa-Giménez, M.; Zamora-Macho, J.L. Delayed-Signal-Cancellation-Based Sag Detector for a Dynamic Voltage Restorer in Distorted Grids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2019, 10, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahoui, A.; Boukais, B.; Mesbah, K.; Otmane-Cherif, T. Neural Networks Based Frequency-Locked Loop for Grid Synchronization Under Unbalanced and Distorted Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Istanbul, Turkey, 25–27 September 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.; Jarial, R.K.; Roncero-Sánchez, P.; Ungarala, M.R.; Guerrero, J.M. An Improved Hybrid Prefiltered Open-Loop Algorithm for Three-Phase Grid Synchronization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 2480–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, P.; Amini, J.; Moallem, M. Improving performance of three-phase MAF-PLL under asymmetrical DC-offset condition. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 111200–111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestan, S.; Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Abusorrah, A.M.; Khadkikar, V.; Rodriguez, J. Control Design of Grid Synchronization Systems for Grid-Tied Power Converters Using Symmetrical Optimum Method: A Comprehensive Reference. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 13650–13673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillapawicharn, Y.; Kumsuwan, Y. Dual Low Pass Filter-Based Voltage Sag Detection for Voltage Sag Compensator under Distorted Grid Voltages. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Chonburi, Thailand, 19–21 March 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qian, H.; Hu, Y.; Bian, S.; Xie, S. Overview of SOGI-Based Single-Phase Phase-Locked Loops for Grid Synchronization Under Complex Grid Conditions. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 39275–39291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalke, D.; Gurrala, G. Design of IEC/IEEE 60255-118-1-2018 Compliant SOGI-PLL for Synchrophasor Measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 9003611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, R.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G. A Novel Voltage Sag Detection Method Based on a Selective Harmonic Extraction Algorithm for Nonideal Grid Conditions. Energies 2022, 15, 5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Feng, Z.; Wang, M.; Wu, M.; Chen, D. An Optimized LVRT Control Strategy of Cascaded Modular Medium-Voltage Inverter for Large-Scale PV Power Plant. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 7744–7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestan, S.; Ramezani, M.; Guerrero, J.M.; Freijedo, F.D.; Monfared, M. Moving average filter based phase-locked loops: Performance analysis and design guidelines. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2750–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, P.; Huang, L.; Chen, X.; He, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Performance improvement of a three-phase PLL under distorted grid conditions based on frequency adaptive hybrid pre-filtering. IET Power Electron. 2022, 15, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellouli, M.; Hamouda, M.; Slama, J.B.H.; Al-Haddad, K. A third-order MAF based QT1-PLL that is robust against harmonically distorted grid voltage with frequency deviation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 1600–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, P.; Amini, J.; Moallem, M. Variable Window Size Moving Average Filter for Phase-Locked-Loop Synchronization. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 88111–88121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smadi, I.A.; Kreashan, H.A.; Atawi, I.E. Enhancing the Filtering Capability and the Dynamic Performance of a Third-Order Phase-Locked Loop under Distorted Grid Conditions. Energies 2023, 16, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellouli, M.; Hamouda, M.; Ahmed, H.; Slama, J.B.H.; Al-Haddad, K. A Grid Synchronization PLL With Accurate Extraction Technique of Positive/Negative Sequences and DC-Offset Under Frequency Drift. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 9002611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, X.; Hoang, T.T.G.; Tian, L. An enhanced phase-locked loop for non-ideal grids combining linear active disturbance controller with moving average filter. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 149, 109021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestan, S.; Guerrero, J.M.; Abusorrah, A.M. MAF-PLL With Phase-Lead Compensator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3691–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).