Simple Summary
Idiazabal is a traditional cheese produced from raw ewe milk in the Basque Country (Southwestern Europe). The sensory properties of raw milk cheeses have been attributed, among other factors, to microbial shifts that occur during the production and ripening processes. In this study, we used high-throughput sequencing technologies to investigate the microbiota of Latxa ewe raw milk and the dynamics during cheese production and ripening processes. The microbiota of raw milk was composed of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), environmental bacteria and non-desirable bacteria. Throughout the cheese making and ripening processes, the growth of LAB was promoted, whereas that of non-desirable and environmental bacteria was inhibited. Moreover, some genera not reported previously in raw ewe milk were detected and clear differences were observed in the bacterial composition of raw milk and cheese among producers, in relation to LAB and environmental or non-desirable bacteria, some of which could be attributed to the production of flavour related compounds.
Abstract
In this study, we used high-throughput sequencing technologies (sequencing of V3–V4 hypervariable regions of 16S rRNA gene) to investigate for the first time the microbiota of Latxa ewe raw milk and the bacterial shifts that occur during the production and ripening of Idiazabal cheese. Results revealed several bacterial genera not reported previously in raw ewe milk and cheese, such as Buttiauxella and Obesumbacterium. Both the cheese making and ripening processes had a significant impact on bacterial communities. Overall, the growth of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) (Lactococcus, Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc, Enterococcus, Streptococcus and Carnobacterium) was promoted, whereas that of non-desirable and environmental bacteria was inhibited (such as Pseudomonas and Clostridium). However, considerable differences were observed among producers. It is noteworthy that the starter LAB (Lactococcus) predominated up to 30 or 60 days of ripening and then, the growth of non-starter LAB (Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc, Enterococcus and Streptococcus) was promoted. Moreover, in some cases, bacteria related to the production of volatile compounds (such as Hafnia, Brevibacterium and Psychrobacter) also showed notable abundance during the first few weeks of ripening. Overall, the results of this study enhance our understanding of microbial shifts that occur during the production and ripening of a raw ewe milk-derived cheese (Idiazabal), and could indicate that the practices adopted by producers have a great impact on the microbiota and final quality of this cheese.
1. Introduction
Idiazabal cheese is a semi-hard or hard cheese made exclusively from the raw milk of Latxa and/or Carranzana sheep, with a minimum ripening time of 60 days. Its production is located in the Basque Country (Southwestern Europe) and has a Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) [1]. Most of the producers attached to the Idiazabal PDO are small family dairies that lead the whole process, from livestock management to cheese making and final sales. Although Idiazabal cheese production is a strictly regulated process, producers may use different practices that may affect the characteristics of the final product. The most considerable differences in production practices are noticed in the management and feeding of the herd, leading to differences in milk quality [2]; in the use of artisanal or commercial rennet, or in the parameters selected during cheese making and ripening, since the Idiazabal PDO specifications establish ranges [3].
Idiazabal cheese, as other cheeses prepared from raw milk, has a richer and more intense aromatic profile compared with those produced from pasteurized milk [4,5]. Such interesting sensory properties of raw milk cheeses have previously been attributed, among other factors, to the complex dynamics of microbial composition during cheese making and ripening [5,6]. The quality of raw milk, use of starters and their intrinsic characteristics, type of rennet used and ripening time are some factors that determine the cheese microbiota [5,7,8,9]. The microbiota of milk has a diverse and complex composition, but it is mainly composed of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) [5,10]. In Idiazabal cheese, the most common LAB are Lactococcus, Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc [11,12]. These bacteria metabolize the lactose present in milk, generating lactic acid and other compounds, such as acetic acid, ethanol and diacetyl. These compounds, along with others produced during ripening, determine the sensory properties of cheese [13]. Although LAB are predominant, other low-abundance microorganisms are also part of the microbial ecosystem of cheese [10,14,15], and consequently contribute to the quality of the final product [16,17].
The characteristics of LAB and other microorganisms present in Idiazabal cheese have been described and related to its sensory properties in several studies [11,12,18,19]. However, these studies were performed 20 years ago using culture-dependent methods. Nowadays, high-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies are used to monitor microbial communities in different fermented products [20,21,22], including cheese [23,24,25]. The HTS techniques allow the detection of a large number of bacteria, including those present in relatively small numbers [26,27,28,29], those present in a viable but non-cultivable state (VBNC) [30] and those not detected by other culture-dependent or independent methods [30,31,32,33,34].
The vast majority of studies on cheese focus on cheese produced from cow milk [24,35,36], and only a few studies have been carried out on cheese produced from the raw milk of ewe [37,38,39]. Moreover, little is known about the bacterial composition of raw ewe milk [40,41,42] and how it changes during cheese making and ripening processes [26,43,44].
Therefore, this study aimed to (1) characterize the bacterial communities of the raw milk of Latxa ewe; (2) analyse the effect of cheese making and ripening processes on bacterial populations; and (3) study the potential differences among producers producing the same type of cheese. To the best of our knowledge, no comprehensive metagenomic study has been conducted to date on raw ewe milk-derived cheeses. Moreover, although Idiazabal cheese has an internationally recognized PDO [1], no HTS studies have been performed to characterize its bacterial populations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Milk and Cheese Sampling
To analyse the microbiota of Latxa ewe raw milk and Idiazabal cheeses, samples were collected from four artisanal Idiazabal PDO cheese producers (identified as A, B, C and D), whose dairies were situated in different geographic locations throughout the Basque Country. Milk was kept in refrigeration tanks before cheese making. Cheeses were produced from the collected milk samples, according to specifications issued by the Idiazabal Designation of Origin Regulatory Board [3], using Choozit MM 100 LYO 50 DCU (mixture of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar. diacetylactis) (DuPont NHIB Ibérica S.L., Barcelona, Spain) as the starter. Milk was coagulated using artisanal rennet prepared from the stomachs of Latxa lambs (extracted during the first month of lactation, cleaned, dried, salted and ground, as described previously [45]) or commercial rennet NATUREN® 195 Premium (Chr. Hansen Holding A/S, Hørsholm, Denmark). Cheese ripening was carried out in chambers maintained at 8–14 °C temperature and 80–95% relative humidity. Cheeses were collected in duplicate at six time points during ripening (1, 7, 14, 30, 60 and 120 days). Therefore, a total of 4 raw milk samples and 48 cheese samples were analysed. Samples were collected and transported to the laboratory under refrigerated conditions (3 °C) for analysis.
2.2. DNA Extraction
DNA extraction was performed immediately after sample arrival, following the method described by Erkus et al. [46], with some modifications. To extract DNA from cheese samples, 10 g of each sample was suspended in 90 mL of 2% (w/v) sterile sodium citrate (pH 8.0), and homogenized in a stomacher (Masticator Basic 400; IUL Instruments, Königswinter, Germany) six times, each for 20 s ON and 10 s OFF. Then, 1.5 mL of the resulting suspension was centrifuged at 8000× g for 10 min at 4 °C, and the fat-containing supernatant was discarded. The obtained pellet was resuspended in 600 µL of sodium citrate, and centrifuged three times at 8000× g for 10 min at 4 °C. DNA was extracted with DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. To extract DNA from milk samples, 10 mL of raw milk from each sample was processed as described above, however, without the need for homogenisation in the stomacher.
2.3. Library Preparation and Sequencing
HTS analysis was performed in the Sequencing and Genotyping Unit of the Genomic Facility/SGIker (supported by UPV/EHU, MICINN, GV/EJ, FSE) of the University of the Basque Country. The 16S rRNA gene library was prepared using Nextera XT DNA Library Preparation Kit (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), according to the 16S rRNA gene metagenomics workflow of Illumina. The V3–V4 regions of the 16S rRNA gene were amplified by PCR (forward primer: 5′-TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3′; reverse primer: 5′-GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGGACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC-3′) as described by Klindworth et al. [47]. Then, 16S rRNA gene sequencing was performed on the Illumina MiSeq platform using the MiSeq Reagent Kit v3 (2 × 300 bp) (Illumina Inc.).
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
Quality filtering and trimming of raw reads were performed using the MiSeq Reporter software (Illumina), and taxonomic classification was performed using the MG-RAST web data analysis tool [48], based on the Silva SSU database [49]. Since the sequencing of most variable regions of the 16S rRNA gene is effective up to the genus level, and seldom discriminates among species adequately [50], the taxonomic classification was performed up to the genus rank. Rarefaction curves were also generated using MG-RAST.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Relative bacterial abundance (%) was calculated based on the identified sequences, and three significant figures were used to express the results. The IBM SPSS statistical package version 26.0 (IBM SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA, 2019) was used for data preparation and analysis. Mann–Whitney U test and Kruskal-Wallis analysis of variance with Bonferroni correction were performed using the SPSS package. The objective was to estimate differences in reads and operational taxonomic units (OTUs) between milk and cheese samples, and to analyse the influence of producer, cheese making and ripening time factors on bacterial phyla and genera abundance. To determine the direction and strength of correlations among the main bacterial genera, Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients were calculated using SPSS, and displayed as a heat map in RStudio version 1.3.959 and R version 3.6.3 [51] using the “gplots” package [52]. To analyse the effect of producer and ripening time factors on the abundance of the main bacterial genera, Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA) was computed in R using the “vegan” package [53]. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of the main bacterial genera was performed using their log-transformed, when necessary, and Unit Variance scaled abundance data, and plotted using the SIMCA software (version 15.0.0.4783; Umetrics AB, Umeå, Sweden). The number of principal components (PCs) was determined by eigenvalues (greater than 1.5) and cross validation. The aim was to study microbial dynamics in cheeses according to producer and ripening time factors. An Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (OPLS-DA) was performed in SIMCA to confirm whether microbial communities of samples differed according to the producer.
Alpha and beta diversity indices were calculated by taking into account the sequence abundance of all bacterial genera present in milk and cheese samples. Alpha diversity was assessed in R using different packages, depending on the objective: “tidyverse” package for data cleaning and preparation for analysis [54]; “BiodiversityR” package for calculating Shannon, Simpson, Inverse Simpson, Berger and Shannon evenness (Jevenness and Eevenness) diversity indices [55]; and “vegan” package for calculating Chao1 and ACE diversity indices. Significant differences among producers for each diversity index were analysed in SPSS using Kruskal-Wallis test. Beta diversity indices (Bray–Curtis and Jaccard dissimilarities) were calculated using the “vegan” package of R, and plotted into a Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) model using the “APE” package of R [56].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Data
A total of 10,798,992 16S rRNA gene sequences were obtained from Latxa ewe raw milk and Idiazabal cheese samples (n = 52), with an average sequence length of 348 ± 101 bp, mean GC content of 53 ± 5% and 10,388 OTUs. Altogether, 24 bacterial phyla, 209 families and 645 genera were identified. Further details of the reads, OTUs and number of identified phyla, families and/or genera are summarised in Table 1. The number of sequences obtained from cheese samples was significantly greater than those obtained from milk samples (p ≤ 0.001), although no significant differences were observed in the number of identified OTUs between the two sample types (p > 0.05). Moreover, both milk and cheese samples obtained from different producers showed significant dissimilarities in the number of reads (p ≤ 0.01) and identified OTUs (p ≤ 0.001), with producer A being clearly distinct from the other three producers. In general, the rarefaction curves showed a clear and strong stabilizing tendency (Figure S1), indicating sufficient sampling of microbial communities. Overall, this study reports a greater number of sequence reads, OTUs and taxonomic identifications in raw ewe milk and cheese than previous studies [14,38,39,44].

Table 1.
Metataxonomic data of Latxa ewe raw milk and Idiazabal cheese samples at 6 ripening times (1, 7, 14, 30, 60 and 120 days) from 4 producers (A, B, C and D) (n = 52).
3.2. In-Depth Analysis of Microbial Shifts
3.2.1. Bacterial Composition of the Raw Milk of Ewe
Milk is an important source of microorganisms in cheese [5,57]. A total of 21 bacterial phyla, 165 families and 455 genera were identified in raw milk samples. At the phylum level (Figure 1A, Table S1), Firmicutes (10.5–54.1%) and Proteobacteria (16.9–40.7%) were the most dominant, followed by Bacteroidetes (5.44–19.6%). Other phyla, with abundances higher than 1%, were detected only in milk samples obtained from some producers: Actinobacteria and Verrucomicrobia in samples obtained from producer C (3.75% and 1.33%, respectively) and D (2.97% and 2.75%, respectively), and Planctomycetes in samples from producer D (1.28%). In general, the predominance of Firmicutes and Proteobacteria in raw ewe milk is consistent with previous studies [26,40,42], although differences in the abundance of each phylum have been reported among milk samples collected from different breeds [26,40,41,42]. However, raw milk samples of Latxa ewe were characterized by the high-level abundance of Bacteroidetes and a notable presence of Verrucomicrobia and Planctomycetes in comparison with milk collected from other breeds [26,40,42]. This indicates a differential characteristic of Latxa ewe raw milk used for Idiazabal cheese production.
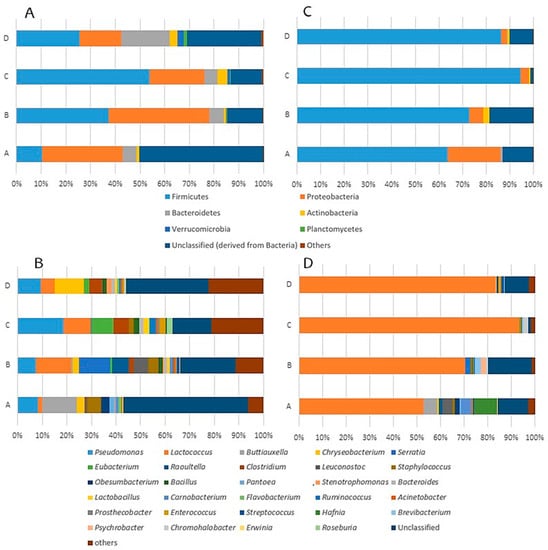
Figure 1.
Relative abundance (%) of bacterial phyla and genera of Latxa ewe raw milk ((A,B), respectively) and 1-day-old ripened Idiazabal cheese samples ((C,D), respectively) produced by four producers (A, B, C, D).
A total of 24 genera with abundance greater than 1% were identified, and 10 of these genera showed abundance higher than 5% (Figure 1B, Table S2). Lactococcus (1.64–14.5%), Eubacterium (0.0766–9.18%), Clostridium (0.183–6.09%), Leuconostoc (0–6.10%) and Staphylococcus (0.291–5.48%) were the most abundant genera within Firmicutes. Similarly, Pseudomonas (7.36–18.5%), Buttiauxella (0–14.1%), Serratia (0.0245–12.6%) and Raoultella (0–6.86%) showed the highest abundance within Proteobacteria, and Chryseobacterium (0–11.7%) within Bacteroidetes. Differences were observed among milk samples obtained from different producers (Table S2). While Pseudomonas and Lactococcus were identified as the main genera common to all analysed raw milk samples, the remaining genera were characteristic of each producer. The abundance of the rest of genera classified as “others” and unclassified sequences was remarkable (6.25–22.4% and 15.6–50.8%, respectively).
Differences observed in the microbial composition of milk samples at the phylum and genus levels among producers (Tables S1 and S2) could be caused by various factors such as differences in lactation stage, flock management and feeding, or sources of microorganisms, for instance, mammary gland diseases or microorganisms contaminating the teat surface, practices and materials employed during milking or dairy environment [5,10,15,41]. Moreover, these factors could explain the differences observed in bacterial communities between the raw milk of Latxa ewe and that of other ewe breeds [40,41,42].
The identified bacterial genera were divided into three groups: LAB, comprising genera previously classified as LAB [57]; environmental bacteria, including bacteria derived from the natural environment [58]; and non-desirable bacteria, containing genera exhibiting a pathogenic potential [59] or related to spoilage [60]. The LAB identified in this study included the genera Lactococcus, Leuconostoc, Enterococcus, Lactobacillus, Carnobacterium and Streptococcus. These gram-positive bacteria have frequently been identified in dairy products [57,61], and their presence in the raw milk of ewe breeds, other than Latxa, has been confirmed by HTS, albeit at different abundances [42,43,44].
The environmental bacterial genera identified in this study included Obesumbacterium, Roseburia and Prosthecobacter. These genera have been isolated from different natural sources, such as soil, fresh and salt water as well as animal and human gut [62,63,64]; however, to the best of our knowledge, no study has reported their presence in raw ewe milk.
The non-desirable bacterial genera identified in this study included Pseudomonas, Clostridium, Staphylococcus and Bacillus, which are widely known pathogens [59,65]. For instance, Pseudomonas is the most important psychrotrophic bacteria in raw milk, which may even predominate in refrigerated milk [10]. It comes from natural environment [66] and has been related to hygiene conditions [67,68]. Some species belonging to the genera Buttiauxella, Serratia, Chryseobacterium, Eubacterium, Raoultella, Ruminococcus, Pantoea, Stenotrophomonas, Bacteroides, Flavobacterium and Acinetobacter have also been described as opportunistic or as emerging pathogens [69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79]. Moreover, some of these genera, such as Serratia and Clostridium, are also related to milk spoilage, resulting in off-flavours [80] and to the cheese blowing defect because of CO2 production [81]. The presence of these bacteria in raw ewe milk has been reported only in a few studies [42,59,82,83]. To the best of our knowledge, the genera Buttiauxella, Serratia, Eubacterium, Raoultella, Ruminococcus and Bacteroides have not been identified in raw ewe milk so far.
3.2.2. Bacterial Shifts during the Cheese Making Process
Next, the effect of the cheese making process, which encompasses all the production stages from milk to 1-day-old ripened cheeses, on microbiota was analysed. In this way, the bacterial composition of Latxa ewe raw milk and 1-day-old ripened Idiazabal cheese was compared. In 1-day-old ripened cheese samples, bacteria belonging to 19 phyla, 160 families and 450 genera were detected; thus, the number of identified bacterial families and genera were similar between 1-day-old ripened cheese and raw milk samples, but the number of bacterial phyla identified in cheese was less than that identified in raw milk. However, the cheese making process had a great impact on the abundance of bacterial communities (Figure 1C,D, Tables S1 and S2). At the phylum rank (Figure 1C, Table S1), the relative abundance of Firmicutes increased remarkably in 1-day-old ripened Idiazabal cheese samples (63.7–94.7%), while that of Proteobacteria decreased (2.61–22.4%), although remaining as the second most important phyla. In general, the abundances of the rest of phyla decreased, although the effect of the cheese making process was not statistically significant in all cases. The abundance of sequences classified as “others” was considerably reduced (<0.01%), and unidentified sequences accounted for lower, yet remarkable, abundance (1.21–18.6%). To date, very few HTS studies have analysed the effect of the cheese making process on bacterial communities in raw ewe milk cheeses [43,44], and even fewer at the phylum rank [26]. In comparison to raw ewe milk-derived cheeses, more HTS studies have been conducted on cow milk-derived cheeses [29,84]. De Pasquale et al. [26] have reported an increase in Firmicutes abundance and a decrease in Proteobacteria abundance in Canestrato Pugliese raw ewe milk-derived cheese, but the changes were more drastic than those observed in this study. No information could be found in the literature concerning the effect of the manufacturing process on the remaining phyla.
The effect of the cheese making process on the main bacterial genera is shown in Figure 1D and Table S2. Within LAB, Lactococcus was the most abundant genus in 1-day-old ripened cheese samples collected from all producers (52.5–93.2%), although a notably lower abundance was observed for producer A. The effect of the cheese making process on the remaining genera in the LAB group varied with the producer. The abundance of Lactobacillus decreased in cheese samples collected from all producers, except producer A (<0.200% in all producers); abundances of Leuconostoc and Carnobacterium were higher in producer A samples (4.48% and 4.40%, respectively); abundances of Streptococcus and Enterococcus were slightly higher in the cheese samples of producer A (0.507% and 0.458%, respectively) and producer D (0.993% and 0.892%, respectively). The genus Lactococcus was predominant during the cheese making process because of its presence in the starter culture, confirming that bacteria comprising the starter culture grow and predominate, as has been previously observed for Pecorino Siciliano cheese [39]. The proliferation of non-starter LAB (NSLAB) has been reported previously, although there are clear differences according to the type of cheese. For instance, Lactococcus and Lactobacillus have been reported as predominant in Caciofiore della Sibilla cheese [43], whereas Lactococcus, Carnobacterium and Enterococcus predominate in Canestrato Pugliese cheese [26].
In general, the abundance of non-desirable bacteria was less than 1% after cheese making, although the abundance of some bacterial genera, namely Buttiauxella (0–5.79%), Serratia (0.00179–2.16%) and Raoultella (0.0151–1.43%), was maintained at a remarkable level or even increased in cheese obtained from some producers (Figure 1D, Table S2). The opportunistic bacteria Hafnia, Brevibacterium and Psychrobacter [85,86,87], which had low abundance in milk (<1%), also increased their abundances in the cheese of some producers (0.00282–9.62%, 0.0210–2.43% and 0.00168–2.28%, respectively). Notably, these bacterial genera exhibit lipase and/or protease activities [88,89,90], and produce interesting volatile compounds (such as 1-hexanol, 1-propanol, propyl butanoate or butyl butanoate), affecting cheese quality [91,92,93]. Overall, the abundance of environmental bacteria decreased during cheese making, although Obesumbacterium maintained a remarkable abundance in samples from producer A (1.89%). Moreover, the environmental genus Chromohalobacter [94], which showed low abundance in milk, exhibited higher abundance in cheese, especially that obtained from producer C (1.78%). The abundance of bacteria classified as “others” and of unidentified bacteria in cheese (1.31–2.74% and 1.26–18.6%, respectively) was lower than that in milk (Figure 1D, Table S2). Suppression of the growth of environmental and non-desirable bacteria, such as Pseudomonas or Staphylococcus, during cheese making has been reported previously [26,43]. Nonetheless, little has been reported about the prevalence of opportunistic or emerging pathogens and environmental bacteria after the cheese making process using raw ewe milk. De Pasquale et al. [26] have detected Raoultella in Canestrato Pugliese cheese but not in raw milk and Alegría et al. [32] have reported a prevalence of Chromohalobacter in fresh Oscypek cheese. Hafnia and Psychrobacter have been identified in other cheeses prepared from raw ewe milk [38,95], although the effect of the cheese making process on the abundance of these bacteria is unknown.
The cheese making process adds other factors that can influence the bacterial communities [9], in addition to factors that determine the milk microbiota (Section 3.2.1). Briefly, the conversion of milk to cheese decreases the pH to 4.5–5.3, which interferes with the growth of most bacteria, except LAB [9,57]. The NaCl concentration of the brine and low salt tolerance of most bacteria only facilitate the growth of LAB [57] and halophiles, such as Psychrobacter [96] and Chromohalobacter [94]. The decrease in moisture content and water activity (aw) also suppresses the proliferation of most bacteria, except LAB, because of their resistance to reduced aw values [9,57]. Moreover, variation that occurs in the redox potential during the conversion of milk to cheese only allows the growth of facultative or obligate anaerobic bacteria [57]. It is worth mentioning that artisanal rennet employed for the production of some raw ewe milk cheeses could be an important source of microorganisms, for example LAB [8]. The use of lamb rennet paste containing pregastric lipase results in higher lipolysis and the development of the characteristic flavour of Idiazabal cheese [97]. Although artisanal rennet contains high levels of a wide range of microorganisms, including aerobic mesophilic bacteria [98], no significant differences have been detected in microbial counts in Idiazabal cheeses prepared using artisanal or commercial rennet [99]; however, it would be interesting to elucidate this aspect using culture-independent methods, such as HTS. Finally, it has been observed that small differences in the environment of dairy facilities producing artisanal cheeses can lead to the development of site-specific “household” microbiota [100]. Therefore, these factors could explain the differences in bacterial composition observed among different raw ewe milk cheeses and among producers producing the same type of cheese.
3.2.3. Bacterial Shifts during the Cheese Ripening Process
Finally, the effect of the ripening process on the bacterial composition of cheese was studied. A total of 23 phyla, 197 families and 583 genera were identified throughout the cheese ripening process; thus, the number of bacterial families and genera was higher during cheese ripening than in raw milk and in cheese after the cheese making process. At the phylum level (Table S1), the abundance of Firmicutes increased (from a mean of 79.4% at 1 day of ripening to 97.7% at 120 days of ripening), while that of Proteobacteria decreased sharply (from 8.56% to 0.116%). In general, abundance of the remaining phyla not predominant during the cheese making process and that of “others” and unidentified bacteria were reduced, except Actinobacteria in the cheese of some producers; nonetheless, the change in abundance levels was not significant for all phyla. Overall, the predominance of Firmicutes and reduction in the abundance of Proteobacteria and remaining phyla have previously been reported in other raw ewe milk cheeses such as Liqvan cheese [38,44].
The cheese ripening time had a considerable impact on bacterial abundance at the genus level, resulting in large differences among producers (Figure 2, Table S2). Within LAB, Lactococcus remained the most dominant genus in Idiazabal cheese during ripening at all times and for all producers (mean abundance: 74.9% at 1 day of ripening, and 74.5% at 120 days of ripening), except producer A, which showed notably lower proportions of Lactococcus. The effect of ripening time on bacterial abundance was significant only for Lactobacillus, with an increase in its abundance for all producers (from 0.0949% to 8.96%), while the evolution of the abundance of the remaining genera varied with the producer. In cheeses from producer A, the abundance of Leuconostoc, which increased after cheese making, was unquestionably promoted by ripening time (from 4.48% to 31.0%), whereas that of Carnobacterium decreased (from 4.40% to 0.330%). In cheeses obtained from producers A and D, the abundances of Streptococcus and Enterococcus, which increased during the cheese making process, also increased during ripening (from 0.750% to 4.52% and from 0.675% to 2.12%, respectively). Overall, taking into account LAB dynamics (Table S2) and their correlations during ripening time (Figure 3), a clear pattern was observed. The abundance of Lactococcus decreased over 30 or 60 days of ripening, depending on the producer, when NSLAB (Leuconostoc, Lactobacillus, Streptococcus and Enterococcus) began to proliferate. In other words, from the first ripening month on these NSLAB begin to proliferate and become an important part of the final microbiota of the cheese.
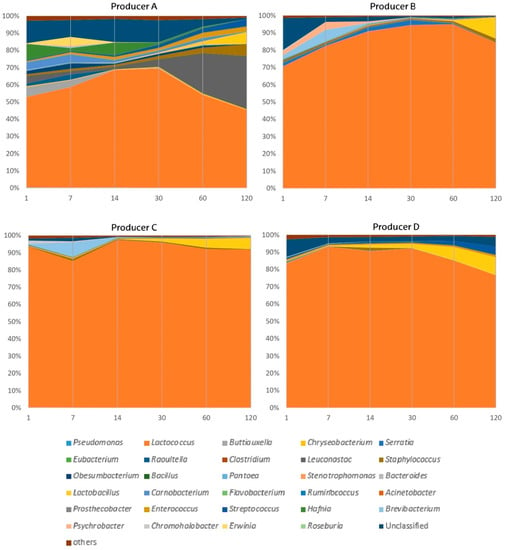
Figure 2.
Microbial shifts at genus rank during ripening time (from 1 to 120 days) of Idiazabal cheese samples from different producers (A–D).
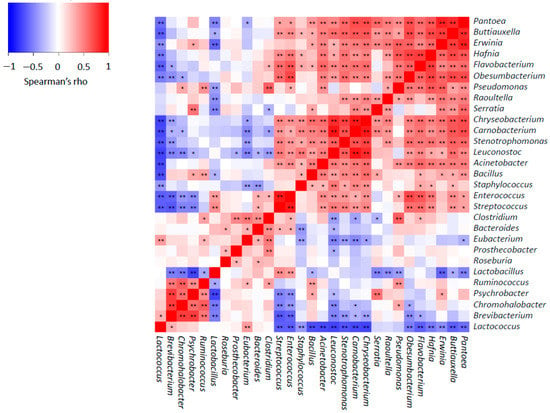
Figure 3.
Spearman’s rank correlations between main bacterial genera found in Idiazabal cheese samples. Significant correlations are represented by ** p ≤ 0.01 and * p ≤ 0.05.
The predominance of bacteria added as part of the starter culture has also been previously reported during the ripening of other raw ewe milk cheeses, such as Pecorino Siciliano cheese [38,39]. However, lactose depletion, salt concentration, and low pH and temperature decrease the viability of starter LAB, and depending on lysis rates, the NSLAB gain importance [101]. The proliferation of Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc, Streptococcus or Enterococcus has also been observed in other raw ewe milk cheeses [26,38,39,95]; however, the NSLAB composition of other types of raw ewe milk cheeses is different from that of Idiazabal cheese [38,39,43,44]. These differences are important, since NSLAB affect, among others, the proteolysis and lipolysis of cheese, and consequently, its final properties, including flavour and texture [102,103,104].
Overall, the abundance of environmental bacteria, except Obesumbacterium, decreased throughout the ripening period; Obesumbacterium showed an increase in abundance at 7 days of ripening (3.03%) in samples from producer A (Figure 2, Table S2). Among the non-desirable bacteria, Hafnia, Staphylococcus, Buttiauxella, Psychrobacter, Raoultella, Serratia and Brevibacterium remained abundant during cheese ripening (>1%), depending on the producer. Nonetheless, their dynamics differed during ripening. The abundance of Buttiauxella decreased throughout the ripening phase, while that of Staphylococcus increased until 120 days of ripening. The remaining genera showed an increase in abundance at intermediate time points (at 7, 14 or 30 days of ripening). Moreover, the emerging pathogen Erwinia [105], whose abundance was minor in milk (<1%), also showed an increase in abundance in samples from producer A (5.15% at 7 days) (Table S2). Considering that some of these genera, including Hafnia, Brevibacterium and Psychrobacter, are related to the production of volatile compounds [91,92,93], the results of this study suggest that their contribution to the sensory properties of cheese would occur at beginning of the ripening process. The abundance of bacteria classified as “others” and that of unidentified bacteria decreased (from 2.08% to 0.665% and from 10.8% to 1.69%, respectively). Most of these environmental and non-desirable genera have previously been reported in raw ewe milk cheeses [26,37,38,39,43,106,107], including the notable presence of Staphylococcus and the increase in its abundances during ripening [26,38,39]. Nonetheless, Obesumbacterium and Hafnia have only been found in Alberquilla cheese prepared from a mixture of ewe and goat milk [31]. To the best of our knowledge, information on the evolution of most of these bacteria during the ripening period is scarce.
Furthermore, we examined the correlation among the main bacterial genera during ripening (Figure 3). Spearman’s rank correlations showed some positive relationships between LAB and non-desirable or environmental genera, for example, Streptococcus–Stenotrophomonas, Enterococcus–Pseudomonas and Leuconostoc–Bacillus. However, a remarkable number of negative correlations were detected, confirming that LAB tend to predominate and limit the proliferation of non-desirable or environmental bacteria, as observed previously [44]. Moreover, this supports the idea that the growth of aroma-related bacteria (such as Hafnia, Brevibacterium and Psychrobacter) is inhibited during the first few weeks of ripening [57]. Changes in the physicochemical properties of cheese throughout the ripening process could explain LAB predominance, similar to the cheese making process. Overall, reduced aw, high NaCl concentration, refrigeration temperatures during ripening, evolution of oxidation-reduction potential to a more reduced state and the decline in pH may affect the proliferation of most bacteria, and LAB are almost the unique that could proliferate [57]. Moreover, it is well known that competitive interaction mechanisms exist between bacteria [44,108]; for example, LAB produce organic acids or bacteriocins [57,109,110]. However, different parameters, such as temperature and relative humidity, could also affect bacterial proliferation during cheese ripening [57,111] and explain the differentiation observed among the cheeses from different producers.
3.3. Overall Effect of Producer and Ripening Time Factors
To examine the effect of producer and ripening time on the main bacterial genera of Idiazabal cheese, a multivariate analysis was performed. PERMANOVA showed that producer and ripening time factors had a statistically significant effect on modulating the microbial composition of Idiazabal cheeses (p ≤ 0.001 and p ≤ 0.01, respectively) (data not shown), thus confirming the results of univariate analysis (Kruskal-Wallis test). Moreover, the F statistic indicated a higher influence of the producer than that of the ripening time (17.3 and 7.17, respectively) on cheese microbiota.
PCA of the main bacterial genera identified in cheese samples revealed five PCs (PC1–5), which accounted for 77.0% of the total variance in cheese microbiota due to the producer and ripening time. According to the scores plot (Figure 4A), PC1 (accounting for 35.5% of the explained variance) was related to the producer factor, thus leading to a clear differentiation between the samples of producer A and those of the other producers. According to the loadings plot (Figure 4B), Lactococcus, Carnobacterium, Leuconostoc, Chryseobacterium, Hafnia, Buttiauxella, Obesumbacterium, Pantoea, Erwinia, Enterococcus, Raoultella, Streptococcus, Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus were highly correlated to PC1 (Figure 4B), indicating that these genera were the most responsible for the differentiation of cheese microbiota among producers. On the other hand, PC2 (accounting for 16.9% of the explained variance) was correlated with the ripening time factor. Therefore, samples were distributed from positive (for less ripened cheeses) to negative (for more ripened cheeses) values (Figure 4A). Psychrobacter, Brevibacterium, Chromohalobacter, Bacillus and Serratia showed positive loadings in PC2, indicating their disappearance along ripening. Instead, Lactobacillus showed negative loadings, indicating that its abundance increased during the ripening phase (Figure 4B). This would confirm the results of the PERMANOVA and indicate that producer factor has a greater impact on cheese microbiota than ripening time.
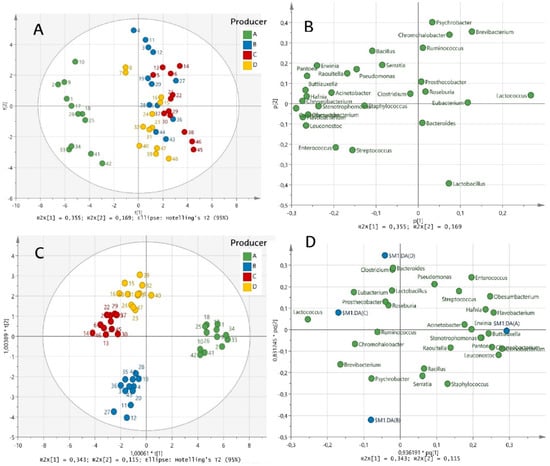
Figure 4.
Scores and loadings plots of PCA ((A,B), respectively) and OPLS-DA ((C,D), respectively) based on main bacterial genera of Idiazabal cheese samples from four producers (A, B, C and D). Samples are coloured according to the producer and labels indicate samples ID.
Compared with PC1 and PC2, the other three PCs, PC3, PC4 and PC5, explained lesser variance in cheese microbiota (11.9%, 6.84% and 5.89% respectively) (Figure S2). Nonetheless, taking together the five PCs provided by the PCA, an idea of the cheeses’ microbiota evolution during the ripening time was obtained for each producer. For producer A, the microbial composition of less ripened cheeses was characterized by Hafnia, Buttiauxella, Carnobacterium, Obesumbacterium, Raoultella, Pantoea, Chryseobacterium and Erwinia genera. As the ripening progressed, Lactococcus proliferated, and the cheese microbiota was finally characterized by high abundance of Leuconostoc, Lactobacillus, Streptococcus and Enterococcus. For producer B, less ripened cheeses were characterized by Serratia, Psychrobacter, Brevibacterium, Chromohalobacter and Bacillus, but as ripening progressed, the microbiota was simplified, with Lactococcus, Lactobacillus and Staphylococcus as the predominating genera. For producer C, less ripened cheeses were characterized by Chromohalobacter, Brevibacterium and Pseudomonas, and throughout ripening, the microbiota was simplified by the predominating genera Lactococcus and Lactobacillus. For producer D, Pseudomonas, Serratia, Bacillus and Raoultella characterized the less ripened cheeses, but the microbiota was predominated by Lactococcus, Lactobacillus, Enterococcus and Streptococcus as the ripening progressed. In general, the microbial dynamics described in Section 3.2 were confirmed by multivariate analysis.
Finally, OPLS-DA, which yielded 3 + 2 + 0 components and with the parameters and , confirmed the differentiation among producers (Figure 4C). Producer A was clearly distinguished from the other producers, as observed before. However, producer B also showed a clear differentiation from producers C and D. The loadings plot (Figure 4D) revealed the characteristic genera in the cheeses of each producer, corroborating the results of the in-depth analysis of microbial shifts and the PCA.
3.4. Alpha and Beta Diversity Analyses
To analyse alpha diversity, different indices were employed, and the evolution of bacterial richness, evenness and biodiversity was examined (Table S3). Chao1 and ACE richness estimators showed a negative trend during the transition from milk to 120-day-old ripened cheese, which was either more pronounced or less pronounced depending on the producer. This implies that a non-negligible number of bacterial genera originally present in raw ewe milk disappeared during cheese making and ripening. Overall, these results are consistent with what has been previously observed for other raw ewe milk cheeses, such as Liqvan cheese [43,44]. According to the uniformity, Shannon evenness and Berger indices showed a decreasing trend throughout the cheese making and ripening processes, indicating that the microbial population of cheese was dominated by a few genera. Nevertheless, uniformity increased after 30 or 60 days, depending on the producer, since other genera gained importance. To the best of our knowledge, there has been no report to date on the shifts in bacterial uniformity during production and ripening of raw ewe milk-derived cheeses. Finally, combining the measurement of the number of genera and their abundance, the Shannon, Simpson and Inverse Simpson biodiversity indices confirmed a downward trend from milk to 30- or 60-day-old ripened cheeses, depending on the producer. However, subsequently, biodiversity increased until 120 days of ripening. In other words, it was confirmed that up to the first or second month of ripening, a few bacterial genera predominated; however, subsequently, other bacteria proliferated and acquired importance. Ramezani et al. [44] have also reported a greater complexity of biodiversity in raw milk than in curd or cheese, and an increase in biodiversity during the conversion of curd into Liqvan cheese. However, De Pasquale et al. [26] have reported a higher biodiversity in curd after moulding than in milk or final cheese. In general, statistically significant differences were observed in alpha diversity between producer A and the others (Figure 5). Differences in alpha diversity among producers of other raw ewe milk and cheeses have rarely been studied [37].
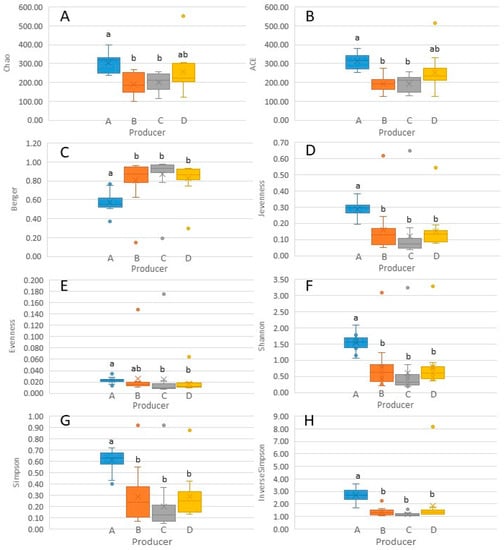
Figure 5.
Box plot representation of bacterial alpha diversity indices ((A) Chao1; (B) ACE; (C) Berger; (D) Jevenness; (E) Eevenness; (F) Shannon; (G) Simpson; (H) Inverse Simpson) of Latxa ewe raw milk and Idiazabal cheese samples obtained from four producers (A, B, C and D). For each diversity index, different letters indicate significant differences between producers at p ≤ 0.05.
Subsequently, to clarify differences in the microbial composition of cheeses among producers, beta diversity was calculated. At genus level, cheese samples were distributed into three clusters corresponding to cheeses from producer A, producer B and producers C and D, which were very similar (Figure 6). Samples from producer A were tightly clustered, indicating less microbial changes during the ripening time compared with cheeses from other producers. Samples collected from producers A and B at 120 days of ripening grouped close to those collected from producers C and D at the same time point, indicating similar bacterial composition among cheese samples of different producers at the end of ripening. In addition, milk samples were far from the general dispersion of cheese samples, indicating clear differences in bacterial composition between the two sample types. To the best of our knowledge, very few studies have been published comparing beta diversity of the same raw ewe milk and cheese among different producers [37,39,40,44]. Endres et al. [40] have reported differences in raw ewe milk samples among different dairies, and Cardinali et al. [37] have reported differences among the producers of Queijo de Azeitão cheese. Beta diversity has also been used to differentiate among the different types of ewe cheeses [95] and to analyse the effect of specific starters on cheese microbiota [39].
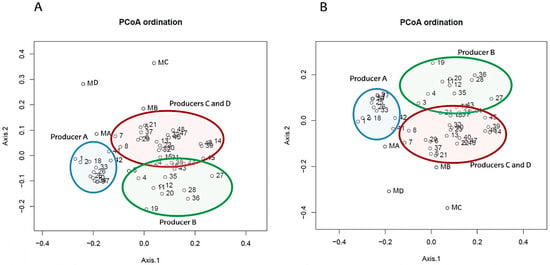
Figure 6.
PCoA of bacterial beta diversity at genus rank based on Bray-Curtis (A) and Jaccard (B) dissimilarities.
Taking together, alpha and beta diversity indices confirmed the results of the in-depth analysis of microbial shifts, univariate analysis (Kruskal-Wallis test) and multivariate analyses (PERMANOVA, PCA and OPLS-DA). The cheese making and ripening processes had an undoubted impact on the bacterial communities. Overall, bacteria from the starter culture predominated at the beginning of ripening, but after 30 or 60 days of ripening, the bacteria from raw milk, especially NSLAB, began to proliferate and become noticeable. Nonetheless, clear differences in the microbial composition of raw ewe milk and cheese samples were observed among producers, which could indicate that differences in practices, such as flock management and milking, as well as parameters selected during cheese making and ripening processes would determine the final microbiota.
4. Conclusions
This is the first HTS study carried out with the objective of characterizing the microbiota of Latxa ewe raw milk and examining the bacterial shifts that occur during the production and ripening of Idiazabal cheese. This research confirms that HTS techniques allow a better understanding of the microbial communities, which could not be achieved previously using culture-dependent techniques. Several bacterial genera were detected for the first time in raw ewe milk and cheese. Both the cheese making process and ripening time had a remarkable impact on bacterial communities, although considerable differences were observed among producers. Thus, the use of raw milk and the practices and conditions employed by each producer for flock management, milking and cheese making and ripening could determine the microbiota. The growth of LAB was promoted throughout the cheese making and ripening processes, whereas that of non-desirable and environmental bacteria was inhibited. However, LAB composition differed among producers, and the growth of NSLAB was promoted after 30 or 60 days of ripening. In addition, in some cases, bacteria related to the production of volatile compounds (such as Hafnia, Brevibacterium and Psychrobacter) showed notable abundance during the first few weeks of ripening.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology11050769/s1, Figure S1: Rarefaction curves of microbial populations of the studied samples from each producer. Each graph represents a producer (A, B, C and D) and each line is coloured according to the Sample ID; Figure S2: Scores and loadings plots of PCA based on main bacterial genera of Idiazabal cheeses from 4 producers (A, B, C and D). Samples are coloured according to the producer and labels indicate samples identification; Table S1: Mean and standard deviation of bacterial phyla of Latxa ewe raw milk and Idiazabal cheese samples at 6 ripening times (1, 7, 14, 30, 60 and 120 days) from 4 producers (A, B, C and D) (n = 52).; Table S2: Mean and standard deviation of bacterial genera of Latxa ewe raw milk and Idiazabal cheese samples at 6 ripening times (1, 7, 14, 30, 60 and 120 days) from 4 producers (A, B, C and D) (n = 52): Table S3: α-diversity indices of Latxa ewe raw milk and Idiazabal cheese samples at 6 ripening times (1, 7, 14, 30, 60 and 120 days) from 4 producers (A, B, C and D) (n = 52).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, validation, investigation and resources, G.S.-G., I.H., G.A. and M.V; formal analysis and data curation, G.S.-G., I.H. and G.A. writing—original draft preparation, G.S.-G.; writing—review and editing, G.S.-G., I.H., G.A. and M.V.; visualization, G.S.-G.; supervision, project administration and funding acquisition, M.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Basque Government, grant to Research Groups number IT944-16. G. Santamarina-García received a predoctoral grant from the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available yet as some data sets are being used for additional publications.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Idiazabal PDO cheesemakers for collaborating with this study and the technical support provided by SGIker (UPV/EHU, ERDF, EU).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Diario Oficial de las Comunidades Europeas. Reglamento (CE) N° 1107/96 de La Comisión de 12 de Junio de 1996 Relativo Al Registro de Las Indicaciones Geográficas y de Las Denominaciones de Origen Con Arreglo Al Procedimiento Establecido En El Artículo 17 Del Reglamento (CEE) No 2081/92 Del Consejo. DOCE 1996, 148, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Valdivielso, I.; Bustamante, M.A.; Aldezabal, A.; Amores, G.; Virto, M.; Ruiz De Gordoa, J.C.; De Renobales, M.; Barron, L.J.R. Case Study of a Commercial Sheep Flock under Extensive Mountain Grazing: Pasture Derived Lipid Compounds in Milk and Cheese. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boletín Oficial del Estado. Orden del 30 de noviembre por la que se aprueba el Reglamento de la Denominación de Origen «Idiazabal» y su Consejo Regulador. BOE 1993, 289, 34591–34596. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, L.J.R.; Redondo, Y.; Aramburu, M.; Gil, P.; Pérez-Elortondo, F.J.; Albisu, M.; Nájera, A.I.; de Renobales, M.; Fernández-García, E. Volatile Composition and Sensory Properties of Industrially Produced Idiazabal Cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, O.; Cotter, P.D. Microbiota of Raw Milk and Raw Milk Cheeses. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology, 4th ed.; McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Cotter, P.D., Everett, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peláez, C.; Requena, T. Exploiting the Potential of Bacteria in the Cheese Ecosystem. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, S.; Palmas, F. Hygienic Conditions and Microbial Contamination in Six Ewe’s-Milk-Processing Plants in Sardinia, Italy. J. Food Prot. 1997, 60, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciata, M.; Sannino, C.; Ercolini, D.; Scatassa, M.L.; De Filippis, F.; Mancuso, I.; La Storia, A.; Moschetti, G.; Settanni, L. Animal Rennets as Sources of Dairy Lactic Acid Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2050–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Possas, A.; Bonilla-Luque, O.M.; Valero, A. From Cheese-Making to Consumption: Exploring the Microbial Safety of Cheeses through Predictive Microbiology Models. Foods 2021, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The Complex Microbiota of Raw Milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Elortondo, F.J.; Albisu, M.; Barcina, Y. Changes in the Microflora of Idiazabal Cheese with the Addition of Commercial Lactic Starters. Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 1993, 48, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Elortondo, F.J.; Aldámiz Echobarria, P.; Albisu, M.; Barcina, Y. Indigenous Lactic Acid Bacteria in Idiazabal Ewes’ Milk Cheese. Int. Dairy J. 1998, 8, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierry, A.; Pogacic, T.; Weber, M.; Lortal, S. Production of Flavor Compounds by Lactic Acid Bacteria in Fermented Foods. In Biotechnology of Lactic Acid Bacteria: Novel Applications, 2nd ed.; Mozzi, F., Raya, R.R., Vignolo, G.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 314–340. ISBN 9781118868386. [Google Scholar]
- Kamilari, E.; Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Papademas, P.; Kamilaris, A.; Tsaltas, D. Characterizing Halloumi Cheese’s Bacterial Communities through Metagenomic Analysis. LWT 2020, 126, 109298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Ning, C.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, C.; Chen, N.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S. Impacts of Manufacture Processes and Geographical Regions on the Microbial Profile of Traditional Chinese Cheeses. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niro, S.; Fratianni, A.; Tremonte, P.; Sorrentino, E.; Tipaldi, L.; Panfili, G.; Coppola, R. Innovative Caciocavallo Cheeses Made from a Mixture of Cow Milk with Ewe or Goat Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, F.; Shi, X.; Wang, B.; Li, K.; Li, B.; Zhuge, B. Dynamic Correlations between Microbiota Succession and Flavor Development Involved in the Ripening of Kazak Artisanal Cheese. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendia, C.; Ibañez, F.C.; Torre, P.; Barcina, Y. Influence of the Season on Proteolysis and Sensory Characteristics of Idiazabal Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Elortondo, F.J.; Albisu, M.; Barcina, Y. Physicochemical Properties and Secondary Microflora Variability in the Manufacture and Ripening of Idiazabal Cheese. Lait 1999, 79, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Chen, X.-X.; Han, B.-Z. Contrasting the Microbial Community and Metabolic Profile of Three Types of Light-Flavor Daqu. Food Biosci. 2021, 144, 101395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Xie, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Q. Bacterial Community and Composition of Different Traditional Fermented Dairy Products in China, South Africa, and Sri Lanka by High-Throughput Sequencing of 16S RRNA Genes. LWT 2021, 144, 111209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, M.; Chen, X.H.; Dong, M.S. Comparative Analysis of the Bacterial Diversity of Chinese Fermented Sausages Using High-Throughput Sequencing. LWT 2021, 150, 111975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolcati, F.; Ferrocino, I.; Bottero, M.T.; Dalmasso, A. Short Communication: High-Throughput Sequencing Approach to Investigate Italian Artisanal Cheese Production. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 10015–10021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nero, L.A.; Andretta, M.; Almeida, T.T.; Ferreira, L.R.; Camargo, A.C.; Yamatogi, R.S.; Carvalho, A.F.; Call, D.R. Lactic Microbiota of the Minas Artisanal Cheese Produced in the Serro Region, Minas Gerais, Brazil. LWT 2021, 148, 111698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.K.; Carstens, C.K.; Ramachandran, P.; Shazer, A.G.; Narula, S.S.; Reed, E.; Ottesen, A.; Schill, K.M. Metagenomics of Pasteurized and Unpasteurized Gouda Cheese Using Targeted 16S RDNA Sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pasquale, I.; Calasso, M.; Mancini, L.; Ercolini, D.; La Storia, A.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Causal Relationship between Microbial Ecology Dynamics and Proteolysis during Manufacture and Ripening of Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) Cheese Canestrato Pugliese. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4085–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ercolini, D.; De Filippis, F.; La Storia, A.; Iacono, M. “Remake” by High-Throughput Sequencing of the Microbiota Involved in the Production of Water Buffalo Mozzarella Cheese. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8142–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michailidou, S.; Pavlou, E.; Pasentsis, K.; Rhoades, J.; Likotrafiti, E.; Argiriou, A. Microbial Profiles of Greek PDO Cheeses Assessed with Amplicon Metabarcoding. Food Microbiol. 2021, 99, 103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yu, P.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Shifts in Diversity and Function of Bacterial Community during Manufacture of Rushan. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 12375–12393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Lei, F.; Wang, B.; Jiang, S.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shao, Y. Bacterial Diversity in Goat Milk from the Guanzhong Area of China. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7812–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abriouel, H.; Martín-Platero, A.; Maqueda, M.; Valdivia, E.; Martínez-Bueno, M. Biodiversity of the Microbial Community in a Spanish Farmhouse Cheese as Revealed by Culture-Dependent and Culture-Independent Methods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 127, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegría, Á.; Szczesny, P.; Mayo, B.; Bardowski, J.; Kowalczyk, M. Biodiversity in Oscypek, a Traditional Polish Cheese, Determined by Culture-Dependent and -Independent Approaches. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masoud, W.; Vogensen, F.K.; Lillevang, S.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Sørensen, S.J.; Jakobsen, M. The Fate of Indigenous Microbiota, Starter Cultures, Escherichia Coli, Listeria Innocua and Staphylococcus Aureus in Danish Raw Milk and Cheeses Determined by Pyrosequencing and Quantitative Real Time (QRT)-PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 153, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarza, P.; Yilmaz, P.; Pruesse, E.; Glöckner, F.O.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H.; Whitman, W.B.; Euzéby, J.; Amann, R.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Uniting the Classification of Cultured and Uncultured Bacteria and Archaea Using 16S RRNA Gene Sequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertani, G.; Levante, A.; Lazzi, C.; Bottari, B.; Gatti, M.; Neviani, E. Dynamics of a Natural Bacterial Community under Technological and Environmental Pressures: The Case of Natural Whey Starter for Parmigiano Reggiano Cheese. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paula, A.C.L.; Medeiros, J.D.; Fernandes, G.R.; da Silva, V.L.; Diniz, C.G. Microbiome of Industrialized Minas Frescal Cheese Reveals High Prevalence of Putative Bacteria: A Concern in the One Health Context. LWT 2021, 139, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, F.; Ferrocino, I.; Milanović, V.; Belleggia, L.; Corvaglia, M.R.; Garofalo, C.; Foligni, R.; Mannozzi, C.; Mozzon, M.; Cocolin, L.; et al. Microbial Communities and Volatile Profile of Queijo de Azeitão PDO Cheese, a Traditional Mediterranean Thistle-Curdled Cheese from Portugal. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimov, S.G.; Gyurova, A.; Zagorchev, L.; Dimitrov, T.; Georgieva-Miteva, D.; Peykov, S. NGS-Based Metagenomic Study of Four Traditional Bulgarian Green Cheeses from Tcherni Vit. LWT 2021, 152, 112278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaglio, R.; Franciosi, E.; Todaro, A.; Guarcello, R.; Alfeo, V.; Randazzo, C.L.; Settanni, L.; Todaro, M. Addition of Selected Starter/Non-Starter Lactic Acid Bacterial Inoculums to Stabilise PDO Pecorino Siciliano Cheese Production. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, C.M.; Castro, Í.M.S.; Trevisol, L.D.; Severo, J.M.; Mann, M.B.; Varela, A.P.M.; Frazzon, A.P.G.; Mayer, F.Q.; Frazzon, J. Molecular Characterization of the Bacterial Communities Present in Sheep’s Milk and Cheese Produced in South Brazilian Region via 16S RRNA Gene Metabarcoding Sequencing. LWT 2021, 147, 111579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Blanco, C.; Gutiérrez-Gil, B.; Puente-Sánchez, F.; Marina, H.; Tamames, J.; Acedo, A.; Arranz, J.J. Microbiota Characterization of Sheep Milk and Its Association with Somatic Cell Count Using 16s RRNA Gene Sequencing. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2020, 137, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biçer, Y.; Telli, A.E.; Sönmez, G.; Telli, N.; Uçar, G. Comparison of Microbiota and Volatile Organic Compounds in Milk from Different Sheep Breeds. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 12303–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, F.; Osimani, A.; Taccari, M.; Milanović, V.; Garofalo, C.; Clementi, F.; Polverigiani, S.; Zitti, S.; Raffaelli, N.; Mozzon, M.; et al. Impact of Thistle Rennet from Carlina Acanthifolia All. Subsp. Acanthifolia on Bacterial Diversity and Dynamics of a Specialty Italian Raw Ewes’ Milk Cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 255, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ferrocino, I.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Cocolin, L. Molecular Investigation of Bacterial Communities during the Manufacturing and Ripening of Semi-Hard Iranian Liqvan Cheese. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bustamante, M.; Chávarri, F.; Santisteban, A.; Ceballos, G.; Hernández, I.; José Miguélez, M.; Aranburu, I.; Barrón, L.J.R.; Virto, M.; De Renobales, M. Coagulating and Lipolytic Activities of Artisanal Lamb Rennet Pastes. J. Dairy Res. 2000, 67, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkus, O.; de Jager, V.C.L.; Geene, R.T.C.M.; van Alen-Boerrigter, I.; Hazelwood, L.; van Hijum, S.A.F.T.; Kleerebezem, M.; Smid, E.J. Use of Propidium Monoazide for Selective Profiling of Viable Microbial Cells during Gouda Cheese Ripening. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 228, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of General 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene PCR Primers for Classical and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Diversity Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; D’Souza, M.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A.; et al. The Metagenomics RAST Server—A Public Resource for the Automatic Phylogenetic and Functional Analysis of Metagenomes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SILVA: A Comprehensive Online Resource for Quality Checked and Aligned Ribosomal RNA Sequence Data Compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, J.S.; Spakowicz, D.J.; Hong, B.Y.; Petersen, L.M.; Demkowicz, P.; Chen, L.; Leopold, S.R.; Hanson, B.M.; Agresta, H.O.; Gerstein, M.; et al. Evaluation of 16S RRNA Gene Sequencing for Species and Strain-Level Microbiome Analysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Warnes, G.R.; Bolker, B.; Bonebakker, L.; Gentleman, R.; Huber, W.; Liaw, A.; Lumley, T.; Maechler, M.; Magnusson, A.; Moeller, S.; et al. Package “Gplots” Title Various R Programming Tools for Plotting Data [R Package Gplots Version 3.1.1]. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=gplots (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Mcglinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Package “Vegan”. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindt, R.; Coe, R. Tree Diversity Analysis: A Manual and Software for Common Statistical Methods for Ecological and Biodiversity Studies; World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF): Nairobi, Kenya, 2005; ISBN 92 9059 179 X. [Google Scholar]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of Phylogenetics and Evolution in R Language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, P.F.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; McSweeney, P.L.H. Fundamentals of Cheese Science, 2nd ed.; Fox, P.F., Guinee, T.P., Cogan, T.M., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781489976819. [Google Scholar]
- Quintana, Á.R.; Seseña, S.; Garzón, A.; Arias, R. Factors Affecting Levels of Airborne Bacteria in Dairy Farms: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van den Brom, R.; de Jong, A.; van Engelen, E.; Heuvelink, A.; Vellema, P. Zoonotic Risks of Pathogens from Sheep and Their Milk Borne Transmission. Small Rumin. Res. 2020, 189, 106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Wang, N.S. Spoilage of Milk and Dairy Products. In The Microbiological Quality of Food: Foodborne Spoilers; Bevilacqua, A., Corbo, M.R., Sinigaglia, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2017; pp. 151–178. ISBN 9780081005033. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, M.; Shao, Z.; Hungwe, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, W. Metabolism Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Expanding Applications in Food Industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 612285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradh, A.D. Gram-Negative Spoilage Bacteria in Brewing. In Brewing Microbiology: Managing Microbes, Ensuring Quality and Valorising Waste; Hill, A.E., Ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 175–194. ISBN 9781782423492. [Google Scholar]
- Staley, J.T. The Genus Prosthecobacter. In The Prokaryotes; Starr, M.P., Stolp, H., Trüper, H.G., Balows, A., Schlegel, H.G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 477–479. ISBN 9783662131879. [Google Scholar]
- Suchodolski, J.S. Gastrointestinal Microbiota. In Canine and Feline Gastroenterology; Washabau, R.J., Day, M.J., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2012; pp. 32–41. ISBN 9781416036616. [Google Scholar]
- Vataščinová, T.; Pipová, M.; Fraqueza, M.J.R.; Maľa, P.; Dudriková, E.; Drážovská, M.; Lauková, A. Short Communication: Antimicrobial Potential of Lactobacillus plantarum Strains Isolated from Slovak Raw Sheep Milk Cheeses. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 6900–6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falardeau, J.; Keeney, K.; Trmčić, A.; Kitts, D.; Wang, S. Farm-to-Fork Profiling of Bacterial Communities Associated with an Artisan Cheese Production Facility. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellassi, P.; Rocchetti, G.; Nocetti, M.; Lucini, L.; Masoero, F.; Morelli, L. A Combined Metabolomic and Metagenomic Approach to Discriminate Raw Milk for the Production of Hard Cheese. Foods 2021, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeluri Jonnala, B.R.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; Sheehan, J.J.; Cotter, P.D. Sequencing of the Cheese Microbiome and Its Relevance to Industry. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Actor, J.K. Clinical Bacteriology. In Elsevier’s Integrated Review Immunology and Microbiology; Actor, J.K., Ed.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 105–120. ISBN 978-0-323-07447-6. [Google Scholar]
- Antonello, V.S.; Dallé, J.; Domingues, G.C.; Ferreira, J.A.S.; Fontoura, M.d.C.Q.; Knapp, F.B. Post-Cesarean Surgical Site Infection Due to Buttiauxella agrestis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 22, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergogne-Bérézin, E. Bacteria: Acinetobacter. In Encyclopedia of Food Safety; Motarjemi, Y., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 337–341. ISBN 9780123786128. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, V.; Abriouel, H.; Benomar, N.; Kabisch, J.; Chieffi, D.; Cho, G.-S.; Franz, C.M.A.P. Opportunistic Food-Borne Pathogens. In Food Safety and Preservation; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 269–306. ISBN 9780128149560. [Google Scholar]
- Guiu, A.; Buendía, B.; Llorca, L.; Gómez Punter, R.M.; Girón, R. Chryseobacterium spp., a New Opportunistic Pathogen Associated with Cystic Fibrosis? Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2014, 32, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; You, C.; Ren, J.; Chen, W.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Z. Variation in Raw Milk Microbiota throughout 12 Months and the Impact of Weather Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morin, A. Pantoea. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 1028–1032. ISBN 9780123847331. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, E.C.; Mörgelin, M.; Cooney, J.C.; Frick, I.M. Interaction of Bacteroides fragilis and Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron with the Kallikrein-Kinin System. Microbiology 2011, 157, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Titécat, M.; Wallet, F.; Vieillard, M.H.; Courcol, R.J.; Loïez, C. Ruminococcus gnavus: An Unusual Pathogen in Septic Arthritis. Anaerobe 2014, 30, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waśkiewicz, A.; Irzykowska, L. Flavobacterium spp.—Characteristics, Occurrence, and Toxicity. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 938–942. ISBN 9780123847331. [Google Scholar]
- Appel, T.M.; Quijano-Martínez, N.; De La Cadena, E.; Mojica, M.F.; Villegas, M.V. Microbiological and Clinical Aspects of Raoultella spp. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 686789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, R.; Xue, T.; Weeks, M.; Turner, M.S.; Bansal, N. Inhibition of Bacterial Growth in Sweet Cheese Whey by Carbon Dioxide as Determined by Culture-Independent Community Profiling. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 217, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morandi, S.; Battelli, G.; Silvetti, T.; Tringali, S.; Nunziata, L.; Villa, A.; Acquistapace, A.; Brasca, M. Impact of Salting and Ripening Temperatures on Late Blowing Defect in Valtellina Casera PDO Cheese. Food Control 2021, 120, 107508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotou, K.; Tzora, A.; Voidarou, C.; Alexopoulos, A.; Plessas, S.; Avgeris, I.; Bezirtzoglou, E.; Akrida-Demertzi, K.; Demertzis, P.G. Isolation of Microbial Pathogens of Subclinical Mastitis from Raw Sheep’s Milk of Epirus (Greece) and Their Role in Its Hygiene. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuka, M.M.; Engel, M.; Skelin, A.; Redžepović, S.; Schloter, M. Bacterial Communities Associated with the Production of Artisanal Istrian Cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 142, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J.M.; Delgado-Macuil, R.J.; Zelaya-Molina, L.X.; Maya-Lucas, O.; Ruesga-Gutiérrez, E.; Anaya-Esparza, L.M.; de la Mora, Z.V.; López-De la Mora, D.A.; Arteaga-Garibay, R.I. Bacterial Succession through the Artisanal Process and Seasonal Effects Defining Bacterial Communities of Raw-Milk Adobera Cheese Revealed by High Throughput Dna Sequencing. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.P. The Genus Psychrobacter. In The Prokaryotes; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 920–930. ISBN 9780387307466. [Google Scholar]
- Shweta, F.N.U.; Gurram, P.R.; O’Horo, J.C.; Khalil, S. Brevibacterium Species: An Emerging Opportunistic Cause of Bloodstream Infections. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 1093–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Yuan, C.; Du, Y.; Yang, P.; Qian, C.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.; Liu, B. Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Hafnia Genus Reveals an Explicit Evolutionary Relationship between the Species Alvei and Paralvei and Provides Insights into Pathogenicity. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anast, J.M.; Dzieciol, M.; Schultz, D.L.; Wagner, M.; Mann, E.; Schmitz-Esser, S. Brevibacterium from Austrian Hard Cheese Harbor a Putative Histamine Catabolism Pathway and a Plasmid for Adaptation to the Cheese Environment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturkoglu-Budak, S.; Wiebenga, A.; Bron, P.A.; de Vries, R.P. Protease and Lipase Activities of Fungal and Bacterial Strains Derived from an Artisanal Raw Ewe’s Milk Cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 237, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Palmer, J.; Teh, K.H.; Flint, S. Identification and Selection of Heat-Stable Protease and Lipase-Producing Psychrotrophic Bacteria from Fresh and Chilled Raw Milk during up to Five Days Storage. LWT 2020, 134, 110165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pasquale, I.; Di Cagno, R.; Buchin, S.; De Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M. Spatial Distribution of the Metabolically Active Microbiota within Italian PDO Ewes’ Milk Cheeses. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deetae, P.; Bonnarme, P.; Spinnler, H.E.; Helinck, S. Production of Volatile Aroma Compounds by Bacterial Strains Isolated from Different Surface-Ripened French Cheeses. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irlinger, F.; In Yung, S.A.Y.; Sarthou, A.S.; Delbès-Paus, C.; Montel, M.C.; Coton, E.; Coton, M.; Helinck, S. Ecological and Aromatic Impact of Two Gram-Negative Bacteria (Psychrobacter celer and Hafnia alvei) Inoculated as Part of the Whole Microbial Community of an Experimental Smear Soft Cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 153, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillaguamán, J.; Delgado, O.; Mattiasson, B.; Hatti-Kaul, R. Chromohalobacter sarecensis sp. Nov., a Psychrotolerant Moderate Halophile Isolated from the Saline Andean Region of Bolivia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuka, M.M.; Wallisch, S.; Engel, M.; Welzl, G.; Havranek, J.; Schloter, M. Dynamics of Bacterial Communities during the Ripening Process of Different Croatian Cheese Types Derived from Raw Ewe’s Milk Cheeses. PLoS ONE. 2013, 8, e80734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-López, M.L.; Santos, J.A.; Otero, A.; Rodríguez-Calleja, J.M. Psychrobacter. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 261–268. ISBN 9780123847331. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, I.; Barrón, L.J.R.; Virto, M.; Pérez-Elortondo, F.J.; Flanagan, C.; Rozas, U.; Nájera, A.I.; Albisu, M.; Vicente, M.S.; de Renobales, M. Lipolysis, Proteolysis and Sensory Properties of Ewe’s Raw Milk Cheese (Idiazabal) Made with Lipase Addition. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.F.; Conde, S.; Albisu, M.; Pérez-Elortondo, F.J.; Etayo, I.; Virto, M.; De Renobales, M. Hygienic Quality of Ewes’ Milk Cheeses Manufactured with Artisan-Produced Lamb Rennet Pastes. J. Dairy Res. 2007, 74, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etayo, I.; Pérez Elortondo, F.J.; Gil, P.F.; Albisu, M.; Virto, M.; Conde, S.; Rodriguez Barron, L.J.; Nájera, A.I.; Gómez-Hidalgo, M.E.; Delgado, C.; et al. Hygienic Quality, Lipolysis and Sensory Properties of Spanish Protected Designation of Origin Ewe’s Milk Cheeses Manufactured with Lamb Rennet Paste. Lait 2006, 86, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Mills, D.A. Facility-Specific “House” Microbiome Drives Microbial Landscapes of Artisan Cheesemaking Plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5214–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blaya, J.; Barzideh, Z.; LaPointe, G. Symposium Review: Interaction of Starter Cultures and Nonstarter Lactic Acid Bacteria in the Cheese Environment. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3611–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantzen, C.A.; Kot, W.; Pedersen, T.B.; Ardö, Y.M.; Broadbent, J.R.; Neve, H.; Hansen, L.H.; Dal Bello, F.; Østlie, H.M.; Kleppen, H.P.; et al. Genomic Characterization of Dairy Associated Leuconostoc Species and Diversity of Leuconostocs in Undefined Mixed Mesophilic Starter Cultures. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Mancini, L.; Fox, P.F. Pros and Cons for Using Non-Starter Lactic Acid Bacteria (NSLAB) as Secondary/Adjunct Starters for Cheese Ripening. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; et al. Impact of NSLAB on Kazakh Cheese Flavor. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamaden, W.I.; Zhen-fen, Z.; Hegab, I.M.; Shang-li, S. Experimental Infection in Mice with Erwinia persicina. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. High-Throughput Sequencing for Detection of Subpopulations of Bacteria Not Previously Associated with Artisanal Cheeses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5717–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sádecká, J.; Šaková, N.; Pangallo, D.; Koreňová, J.; Kolek, E.; Puškárová, A.; Bučková, M.; Valík, L.; Kuchta, T. Microbial Diversity and Volatile Odour-Active Compounds of Barrelled Ewes’ Cheese as an Intermediate Product That Determines the Quality of Winter Bryndza Cheese. LWT 2016, 70, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, D.J.; Donnelly, C.W. Growth and Survival of Microbial Pathogens in Cheese. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology, 4th ed.; McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Cotter, P.D., Everett, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 573–594. ISBN 9780122636530. [Google Scholar]
- Gontijo, M.T.P.; Silva, J.d.S.; Vidigal, P.M.P.; Martin, J.G.P. Phylogenetic Distribution of the Bacteriocin Repertoire of Lactic Acid Bacteria Species Associated with Artisanal Cheese. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.I.; Simsek, O. Characterization of Pathogen-Specific Bacteriocins from Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Application within Cocktail against Pathogens in Milk. LWT 2019, 115, 108464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, A.C.; Malcata, F.X.; Oliveira, J.C. Effect of Production Factors and Ripening Conditions on the Characteristics of Serra Cheese. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 32, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).