Simple Summary
New risks to plant health are constantly emerging. Such is the case of the rice root knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola, adapted to flooded conditions and representing a risk to all types of rice agro-systems. It has been recently detected in Italy and added to the European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO) Alert List. The presence of this nematode in Europe poses a threat to rice production, as there is a high probability to spread, due to trade activities and climate changes. In view of its importance, an extensive updated review was carried out.
Abstract
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is one of the main cultivated crops worldwide and represents a staple food for more than half of the world population. Root-knot nematodes (RKNs), Meloidogyne spp., and particularly M. graminicola, are serious pests of rice, being, probably, the most economically important plant-parasitic nematode in this crop. M. graminicola is an obligate sedentary endoparasite adapted to flooded conditions. Until recently, M. graminicola was present mainly in irrigated rice fields in Asia, parts of the Americas, and South Africa. However, in July 2016, it was found in northern Italy in the Piedmont region and in May 2018 in the Lombardy region in the province of Pavia. Following the first detection in the EPPO region, this pest was included in the EPPO Alert List as its wide host range and ability to survive during long periods in environments with low oxygen content, represent a threat for rice production in the European Union. Considering the impact of this nematode on agriculture, a literature review focusing on M. graminicola distribution, biology, identification, and management was conducted.
1. Introduction
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is the third most important cereal crop in the world, just behind wheat and maize, playing a strategic role in solving food security issues. New risks to plant health are constantly emerging. Many nematodes in rice have been detected and described, but only a few have harmful effects on rice production, such is the case of the rice root-knot nematode (RKN) Meloidogyne graminicola Golden and Birchfield, 1965 (Mg) [1], recently detected in Italy and added to the European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO) Alert List [2]. Mg is considered a major threat to rice production, particularly in Asia. Projections by the Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change indicate that there will be an increase in mean annual temperature and rainfall in South Asia, West Africa, and Europe. The elevated temperature and moisture may result in an increasing rate of infection, development, and reproduction, causing shifts in Mg abundance and geographic distribution. Such effects may have a detrimental impact on rice in temperate regions. Furthermore, Mg is a clear example of how alterations in rice production (shortage of water due to socioeconomic pressure and climate change) contributed to changes in its status as the major plant-parasitic nematode (PPN) in rice. An effort has been made to gather all the information regarding several aspects of Mg to present it as a comprehensive review on rice RKN.
2. Meloidogyne graminicola—Origin and Distribution
The rice RKN, Mg, was first isolated in India by Israel et al. [3], but it was only described in 1965 when it was found on the roots of barnyard grass (Echinochloa colonum) in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, USA [4]. Since then, this nematode has been reported from the USA on rice and weeds in Louisiana, on grass in Georgia and Mississippi, and on sandbur (Cenchrus spp.) in Florida [5,6,7,8]. Its occurrence has been widely accounted in rice fields in several Asian countries [9,10,11] and also in South Africa, Colombia, Brazil, and Italy [12,13,14].
Mg has been reported to parasitize primarily in irrigated and rainfed rice in South and Southeast Asian countries, such as China, India, the Philippines, Burma (Myanmar), Bangladesh, Pakistan, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, and Nepal [15,16,17]. In China, it was first found on Allium tistulosum in the Hainan province by Zhao et al. [18]. More than a decade later, it was detected associated with rice and other hosts including weeds in the provinces of Anhui, Fujian, Hainan, Hunan, Hubei, Zhejiang, Jiangxi, and Sichuan, causing a severe incidence in the Hunan province [19,20,21,22].
In India, this nematode was first isolated in the county of Orissa from upland rice soils by Israel et al. [3]. Since then, it has been found infecting rice in the provinces of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Assam, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmi, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Manipur, Orissa, Tamil Nadu, Tripura, and West Bengal [23,24]. In 1971, its presence was referred in Thailand, causing typical root galls in entire rice-growing areas and in nursery seedbeds [25], and in Bangladesh, where it has been often associated with deepwater and pre-monsoon upland rice systems [26,27,28]. Minor infestations were reported in lowland rainfed rice areas [28]. Nonetheless, in the northwest of Bangladesh, where the dominant cropping system is lowland rainfed alternated with wheat, severe infestations of Mg were observed [29].
Later, in the 1990s, Mg was reported infesting rice fields in Sri Lanka, where it is now dispersed into major rice-growing areas of the country [30,31,32]. In a study performed in Vietnam, in 1992, to determine the PPN in deepwater rice systems, Mg was identified for the first time as one of the main causes of high yield losses of rice [33]. In Pakistan, during a survey in rice fields of Sheikhupura (Punjab), Munir and Bridge [34] reported its presence for the first time in the country and in 2007, Mg was detected in Nepal [35].
The occurrence of Mg in Africa was recorded on grass roots of Paspalum sp. in the South East region of Antsirabe, and its identification was based on morphological traits [36]. Later, in 2014, during a survey carried out in 14 sites distributed along a NW/SE axis between the towns of Marovovay and Manakara, Mg was found [37].
The first report of Mg in South America was by Monteiro et al. [38] in cyperaceas collected in Presidente Prudente, São Paulo, Brazil. However, only in 1991, Sperandio and Monteiro [39] first reported and described the species in the municipality of Palmares do Sul (Rio Grande do Sul) and, in 1994, Sperandio and Amaral [40] found Mg in other municipalities in the south of Rio Grande do Sul. The latest reports confirm the presence of the rice RKN in the region [41,42].
In Ecuador, Mg was first identified in 1987, in the “Sausalito” village located in the corner of Puerto Inca, province of Guayas, in a field planted with the cultivar Oryzica 1. In surveys conducted in the Provinces of Manabí, Guayas, and Los Ríos, Mg was not found in any other field planted with rice. Nevertheless, by 2000, it had already been disseminated to all rice fields of the Province of Guayas and, in 2002, it was present in the Province of Los Ríos [43]. In a new survey conducted in 2015 in the provinces of Guayas and Los Ríos, the rice RKN was found to be the most widespread, occurring in both rainfed lowland and irrigated areas in high densities [13].
In Colombia, Goméz et al. [44] reported the presence of galls in the roots of rice plants in the county of Tolima, Ibague. Thirteen years later, in a survey programme established by the Colombian rice federation “FEDEARROZ”, Bastidas and Montealegre [45] described the symptoms of a new rice disease denominated as “Entorchamiento” and concluded that it was caused by nematodes of the Meloidogyne genus. The species Mg was later identified, on the basis of morphological and biometrical characters, in other counties and its presence confirmed in other rice production zones, corroborating its spread throughout the country [46,47].
In Europe, Mg was detected, in July 2016, in several rice fields of northern Italy in the Piedmont region, being the first report of its presence in the EPPO region [14]. Due to this detection, the EPPO decided to include Mg in the Alert List A2 in 2017. Following the first report, it was detected in the Lombardy region, province of Pavia [2].
This Meloidogyne species is present almost in every continent (Table 1. Figure 1). Such occurrence and increase detection draws attention to its potential to affect temperate rice agro-systems adversely.

Table 1.
Distribution of Meloidogyne graminicola in Africa, America, Asia, and Europe.
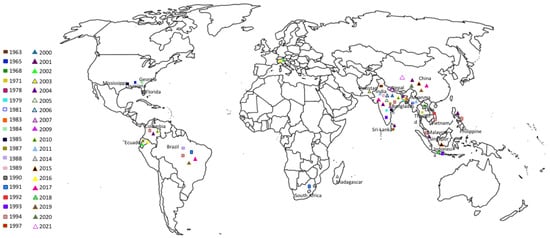
Figure 1.
Geographical distribution of Meloidogyne graminicola.
3. Life Cycle and Symptoms
Mg is a facultative meiotic parthenogenetic species with the probability of occurring amphimixis being very low [79,80]. The infective second-stage juvenile (J2) move through the soil to find a suitable host and penetrate the root near the tip. They migrate intercellularly towards the region of cell differentiation, close to the root meristem, inducing a permanent feeding site in the stele [81,82]. Once established in the roots, J2 become sedentary and flask-shaped and undergoes three molts to become third (J3) and fourth stages (J4) and adult stage. Hyperplasy and hypertrophy of surrounding cells cause the formation of macroscopically visible galls on the root system [1,83,84]. These galls with a characteristic hook shape are located mostly at the root tips, affecting root development and physiology, and a profuse proliferation of very slender and fluffy roots that lead to substantial yield losses [12,85,86]. Females remain within the galled roots, and eggs are deposited in a gelatinous matrix (egg mass) inside the root cortex. The first-stage juveniles (J1) develop inside the egg and molt to become J2. After hatching, the J2 can be released into the soil or remain within the gall to migrate and establish new feeding sites, inducing the formation of new galls [27,87,88,89]. This unusual way of laying eggs is an advantage as it allows Mg to complete its life cycle without leaving the host. Up to 50 egg-laying females can be found in a single gall, indicating that infection can be extremely high [12]. As Mg is unable to penetrate rice roots in flooded soils, it has been reported that under continuously flooded conditions, egg masses remain viable for as long as 14 months and J2 for at least five months, resuming their activity by attacking the root tips when fields are drained [27,90].
The most common underground symptom is the characteristic hook shape of the galls, as referred before. Additionally to the consumption of cytoplasmic content of giant cells by the nematode, the galling produced by Mg provokes an alteration of the root vascular system by disrupting water and nutrient transport from the roots to the aboveground parts, resulting in loss of plant vigor, poor growth, and yield reduction [91]. To maintain a compatible host–parasite relationship, Mg meddles and manipulates the defense mechanism of the plant, making it unable to prevent the nematode penetration and development [80]. Infestations of Mg cause a reduction in phenols and changes in plant immunity gene expression in the shoots and roots, causing greater susceptibility to the rice blast pathogen, Pyricularia oryzae, and fungus from soil, such as Fusarium moniliforme [3,92,93].
Aboveground symptoms due to Mg infection include patches in rice fields, stunted appearance, chlorotic leaves, early flowering and maturation, and few chaffy grains on the panicles on heavily affected root systems [80,94,95]. These symptoms are similar to that attributed to nutritional and water-associated disorders or to secondary diseases. The degree of symptom manifestation differs with time of infection, age of the plants, and climatic conditions [17]. A reduction in chlorophyll content and changes in photosynthetic rates were also reported by Swain and Prasad [96,97]. Losses in flooded rice fields occur when infected seedlings fail to develop, leaving patches of open water in the fields [27]. Overall, symptoms observed in infested upland and lowland rice fields from different geographical locations reported by several researchers match among them. For instance, in Italy, the fields showed patches, with plants exhibiting poor growth and stunting and roots having galls of different shapes and sizes [14]. In India, surveys carried out in rice fields, from different districts, a loss of vigor, reduced tillering, poor growth, and galls were detected [24,98,99].
Khan et al. [100] observed that in some species of weeds, the egg masses were found within the galls, while others had small galls with egg masses on the root surface or heavy root galling and large egg masses. In Bangladesh, Mg was associated with yellowing and stunting of deep-water rice and drowning of plants when they remain submerged and die after rapid and deep flooding [50,101]. In China, the symptoms included chlorotic leaves on heavily affected root systems, while root tips become swollen and hooked [102,103]. In South America, newly emerged leaves appear distorted and crinkled along the margins and roots show the characteristic hook-like galls [41,42,46,104].
Mg reproduces relatively fast on rice, depending on temperature and climatic conditions, when compared with other RKN species. Several authors reported that the Mg life cycle varies considerably, ranging from a very short life cycle of only 15 days at 27–37 °C [105,106] to a rather long life cycle of up to 51 days in some regions of India [107,108]. On average, Mg can complete its life cycle within 19 to 27 days during the early summer, but the period can extend by 5 to 12 days [27,105,108,109,110]. For instance, isolates from Bangladesh had a very short life cycle on rice of <19 days at temperatures of 22–29 °C [27] and an isolate from the USA completed its life cycle in 23–27 days at 26 °C [105]. Due to the short life cycle, the presence of even a small number of Mg J2 at planting can lead to an increase of the population density during a single crop cycle [111].
4. Damage/Crop Losses in Rice
Mg is the most prevalent PPN on rice and considered a major threat to rice as yield losses can reach up to 70% [12,94,112]. Mg densities of 120, 250, and 600 eggs/plant in seedlings 10, 30, and 60 days after planting were reported by Rao et al. [110], causing 10% losses. In a later study, Cuc and Prot [78] stated that a density of 100 J2/g root could be considered as high infestation. Most recently, Win et al. [74] found that population densities could exceed 1000 J2/g root with 12–16 galls/plant, contributing to a 65% yield reduction. It has also been found that there is a decline in yield when more than 75% of the roots are affected by nematodes [32]. Additionally, the water regime is an important environmental factor that influences the development and population dynamics of Mg, and the damage and yield loss that it can cause to rice. Soriano et al. [91] showed that rice cultivar tolerance to Mg varies with the water regime and that yield losses may be prevented or minimized when the rice crop is flooded early and maintain inundated until harvesting. For example, losses in lowland rainfed rice in Bangladesh can range between 16 and 20%, while in India, losses range between 16 and 32% under irrigated conditions and between 11 and 73% under flooded conditions [102,113]. In China, the highest incidence of the disease is in the Hunan provinces, exceeding 85% in infested paddy fields [19]. Furthermore, reports of Mg infestations in rice–wheat agroecosystem of India, Nepal, and Pakistan suggest that the damage caused by the rice RKN may be responsible for the poor productivity in this cropping system [10,11,35,114].
Changes in agricultural policy and adoption of new rice production technologies in South East Asian countries have influenced the status of the rice RKN problem [75]. For instance, in the Philippines, Mg became a major constrain due to the intensification of rice cropping and shortage of water supply. This situation forced the farmers to grow direct wet seeding, and intermittent irrigation, providing favorable conditions for Mg infestation and increasing the economic losses [9,75]. In India, the system of rice cultivation shifted to the so-called “system of rice intensification practice”, where a new ecological condition is being developed through modification of rice cultivation practices that includes planting younger and tender seedlings, the creation of greater aeration in soil, and regulation in irrigation. All these conditions provide a suitable environment to increase the infestation levels of the rice RKN [112,114,115].
Spatio-temporal studies have also demonstrated that densities of Mg J2 in the soil fluctuate throughout the year [116]. Moreover, Mg’s ability to survive and reproduce in off-seasons on weeds and forage crops contributes to increase the population levels in the soil, and rice infection in the next season [35]. Besides alternative hosts and irrigation, the soil type influenced the tolerance of plants to Mg and showed differences in the multiplication of the nematode [91]. Studies have also revealed that infestation levels depend on the rice cultivar [117,118], and the aggressiveness differs between populations, suggesting intraspecific variability [35,119]. It was also found that Mg consists of more than one race. In fact, populations from Florida have shown less aggressiveness and difference on the host infection and reproduction patterns than the Asian populations, and populations from Vietnam are not able to reproduce on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), soy (Glycyne max), or green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris), despite these species being reported as a host of Mg [16,119,120].
5. Host Plants
In addition to the main host, rice, Mg has a wide range of alternative hosts, including cereals and grasses, as well as dicotyledonous plants [15,120,121] (Table 2). Forty-six weeds commonly growing in or around rice fields were assessed for host suitability and were found to be moderate to good hosts of Mg [122]. Khan et al. [100] reported 17 weed species and, in 2009, Rich et al. [15} reported 24, which supported the survival and multiplication of Mg in the field, acting as a reservoir of nematodes when rice is not present during crop rotations [15] (Table 3). Furthermore, it was believed that Mg caused yield losses only in rice; however, a reduction of the root length of onion (Allium cepa) was observed, with yield losses of 16–35% in the Philippines [76]. In Nepal, India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, it is considered a threat to wheat crops and to vegetables, such as aubergine (S. melongena), tomato, and okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) [10,122,123,124,125].

Table 2.
Cultivated hosts of Meloidogyne graminicola.

Table 3.
Weeds hosts of Meloidogyne graminicola.
6. Identification Approaches: From Classical to Molecular Methods
The identification of Mg is complex and crucial to understand the host–parasite relationships and to implement appropriate management strategies. Similar to the identification of other Meloidogyne species, the classical methods are based on the symptoms (root galls), morphology, biometrics, and differential host range tests [139,140,141,142,143]. The Meloidogyne ‘graminis-group’, the most defined group within the genus, with some species being morphologically extremely similar, including M. graminicola, M. graminis, M. hainanensis, M. lini, M. oryzae, M. salasi, and M. triticoryzae [48,144]. In studies performed by Pokharel et al. [16] and Luo et al. [103], morphometrics among and within populations did not correlate with the geographic origin. Pokharel et al. [35] mentioned that J2 from Bangladesh and the United States were significantly longer and smaller than the Nepalese, and presented minor variability among them. These morphometrical differences might be due to different geographical origin and intraspecific variability, or phenotypic plasticity commonly exhibited by nematodes [16,69,145]. Morphological features, such as the female’s perineal patterns, female excretory pore position in comparison to stylet length, the position of hemizonid and tail shape in J2, as well as body, stylet, and tail measurements, are considered valuable tools for Mg identification due to their low cost, but they need specialized technicians to identify and measure these characters.
Other identification methods include enzymatic studies [146]. Isozyme phenotyping has demonstrated that the major species of Meloidogyne (M. incognita, M. javanica, M. arenaria, and M. hapla) can be differentiated by species-specific enzyme phenotypes, esterases (EST), malate dehydrogenase (MDH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT), which can be revealed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and a specific staining technique [147]. Esterase activity has demonstrated to be highly polymorphic and the most useful in the identification of the species. Furthermore, progresses in electrophoretic procedures have made possible and practical the detection of different EST phenotypes of a single female [148]. The main drawback of this method is that it requires adult females at a specific developmental stage for accurate diagnosis, which hinders its use in routine examination of soil samples that often contain only J2 or males.
Esbenshade and Triantaphyllou [146] described, in 1985, in one population of M. oryzae, an esterase phenotype designated as VS1 (very slow with one band), as having a large drawn-out band of high enzymatic activity. The same phenotype with a slightly slower band (Est VS1) was also detected in a population of Mg and two undescribed populations isolated from rice, which were later described as M. salasi. Since the VS1 phenotype did not characterize a single species, it remained the EST phenotype of these species. This fact shows the inaccuracy of this technique when identifying closely related species with similar phenotypes, such as M. salasi, M. graminicola, and M. graminis. Populations of M. oryzae showed a pattern O1 in an integrative taxonomy study performed by Mattos et al. [149]. Other studies have shown a high variability on Mg populations [48,149,150], which poses a risk of misidentification. Moreover, MDH enzymatic phenotype N1 is shared among Meloidogyne species, i.e., M. chitwoodi and M. salasi [48,146].
In order to assist Mg identification, the application of molecular methods has been used with partial success; in particular, sequences of nuclear ribosomal (rDNA) and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) as molecular markers for sequence comparison [16,35,151,152]. In 2017, Salalia et al. [69] and Fanelli et al. [14] found high variability within isolates of Mg from India and Italy, the USA, and China and, based on cytochrome oxidase subunit II and 16S ribosomal RNA (COXII-16S rRNA) genetic analysis, considered the existence of two groups of Mg: group A, which clusters the populations from the USA and Italy, and group B with those from China. According to Pokharel et al. [35], the analysis of internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences as genetic markers allowed the detection of two groups in Mg Nepalese populations: group I, clustering with M. trifoliophila, and group II with Mg from the USA. A new race of Mg from Florida, USA, which did not parasitize rice was also identified by Pokharel et al. [16], based on the ITS region and morphological and morphometric characters that are not species specific. Furthermore, Bellafiore et al. [119] and Salalia et al. [69] detected great morphological variability among populations of Mg from India and Vietnam, and using an ITS marker, concluded that all the isolates belonged to Mg. Salalia et al. [69] even suggested the presence of cryptic species among Indian populations. On the other hand, Htay et al. [152], when analyzing ITS-rDNA sequences, from the same individual or from different nematodes from the same sample noted that there was nucleotide variability. These differences could be attributed to variations among copies of the ITS within an individual, or to errors arising through PCR amplification, cloning, or sequencing [35].
Several molecular methods have been developed to detect Mg: (1) ITS-PCR-RFLP [14]; and (2) diagnostic SCAR marker [119,149,152] for rapid and reproducible identification of Mg. However, Negretti et al. [48] and Soares et al. [150] showed inespecificity associated with M. oryzae and M. ottersoni; (3) real-time PCR primers for the quantification of Mg in soil [153,154], with the drawback that some primers amplifying DNA of the closest non-target species (M. incognita and M. hapla) or not widely tested against other species; and (4) mediated isothermal amplification [154].
7. Genomic and Transcriptomics
The mitochondrial genome of three Mg isolates from the Philippines, China, and India has been sequenced [155,156,157]. Somvanshi et al. [157] included the first genome draft from India, but, recently, Phan et al. [158] generated a highly contiguous reference genome (283 scaffolds with an N50 length of 294 kb, totaling 41.5 Mb), with the highest completeness scores currently published for Meloidogyne genomes. This genome assembly constitutes a great improvement and represents a valuable molecular resource for future phylogenomic studies and evolutionary history reconstruction. Somvanshi et al. [159] improved the genome assembly of the Indian isolate IARI using long-read sequencing. Comparison of both genomes displayed a high correlation between them, 35.9 Mb of 36.86 Mb assembly in the IARI isolate anchored onto the 41.5 Mb of the Mg VN18 assembly [159]. However, there are important differences in the protein-coding genes between both genome assemblies (14,602 (IARI) vs. 10,284 (VN18)), suggesting that the different sequencing platforms used in both assemblies have captured unique features of the Mg genome.
Genomic tools have been developed to help understand the molecular responses of plants to nematode infection. Therefore, transcriptome analyses have become a useful tool to profile the expression of several key genes throughout the infection process in the feeding site, and systemically in the plant and nematode [82]. Previous research evidenced that plant–nematode interactions affect the expression of genes associated with plant immune response [80,89]. Differential expression of plant defense genes and other related changes in host plants are mainly modulated by phytohormones, such as salicylic acid, jasmonic acid, and ethylene. Research demonstrated that RKN represses the jasmonic acid pathway and a few phenylpropanoid pathway genes during the establishment in the rice plants [160,161,162].
PPN can secrete effector T-proteins into the host tissue to facilitate their infection by reprograming the host metabolism, or by preventing the plant defense responses. These effectors also have a role on nematode migration inside the plant roots and are required to initiate and maintain the feeding sites [163,164]. Haegeman et al. [165] and Petitot et al. [166] analyzed the transcriptome of Mg J2 to identify genes and its pattern of expression during infection of rice plants, leading to the identification of new candidate effector genes: Mg40980 gene encoding a metallothionein; Mg12322 and Mg28330, encoding Cys-rich proteins; and Mg11937 gene, encoding a venom allergen-like protein, among others. Over the past years, novel Mg effectors playing a role in nematode parasitism were functionally characterized, including pioneer genes [167,168], a C-type lectin [169], and a protein disulfide isomerase [170]. In 2020, Petitot et al. [171] analyzed mRNA-seq data derived from nematode-infected rice tissue to identify nematode transcripts specifically expressed when the nematode resides inside the plant, through a comprehensive transcriptome analyses of J2 and rice infected tissues until the development of young adult females. Dash et al. [172] delivered a transcriptome comparison of nematode-resistant and -susceptible rice plants in the same genetic background. Through RNA-seq, the molecular mechanisms that confer resistance to Mg during early infection were identified. These findings provide a global view of the genes expressed in the rice–Mg interaction, highlighting that Mg adapts its gene expression depending on the plant genotype. It may also suggest that the initial resistance to nematode infection is mediated by nematode recognition followed by the expression of plant defense genes and secondary metabolites.
Nevertheless, additional efforts are required to identify the underlying pathways and mechanisms responsible for the resistance of rice to Mg, as well as important genes for successful infection of the plant by Mg.
8. Management
The best strategy for management of Mg is to prevent the movement of plant and soil that in some cases may adhere to machinery or tools. In a recent pest risk analysis for Mg in Italy, it was concluded that the main ways of dispersion of this nematode are likely to be through the movement of infected plants and infested soil, non-host plants that may have grown near areas infested with Mg, and floating roots or plant material in the water [121]. Migrant waterbirds, machinery, and travelers were considered a secondary source of entrance. On the other hand, changes in the water regime (intermittent irrigation or water shortages) in many parts of the world are also contributing to the spread and infectivity of the nematode.
To minimize the losses resulting from Mg, management strategies are of extreme importance, and studies have shown that a combination of methods is the best approach to control this nematode in rice fields. The methods that have been applied to control Mg include the use of synthetic nematicides, known as the most efficient strategy, cultural methods, biological agents, and natural nematicides.
Some synthetic nematicides were, recently, strictly regulated or banned from the market, due to the adverse impacts on the environment and human health, reducing the alternatives for RKN control. Cultural methods (fallowing, soil solarization, crop diversification and rotation, etc.) also appeared to have some efficacy. For instance, crop rotation studies with non-host crops, like sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas), cowpea (Vigna unguiculata), sesame (Sesamum indicum), castor (Ricinus communis), sunflower (Helianthus annuus), soybean (Glycine max), turnip (Brassica rapa subsp. rapa), and cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis), showed to prevent Mg development [110,132,173]. Nonetheless, none of these practices have gained importance among farmers, because of the high cost and unsatisfactory results. Furthermore, as many weeds found in rice fields are hosts for Mg, serving as nematode reservoirs for the next crops, a weed management programme must be implemented to maintain a low nematode population in infested fields.
Alternative strategies, such as the “rice field flooding technique”, used by the Italian National Plant Protection Organization (Ministerial Decree of 6 July 2017) to control Mg, had some effect on the nematode population densities. Mg can still propagate under flooding conditions, but the damage induced by this nematode is lower than in shallow intermittently flooded fields [80,174]. Nevertheless, this method of control also has some limitations, as there are areas where this practice is not applicable due to the soil structure, characterized by a low water retention capacity, or restriction in water use. Another approach explored by Sacchi et al. [174] was the use of rice plants as trap crops. Preliminary results indicate that trap cropping for the management of the rice RKN is efficient in most rice-growing areas, especially those with water shortages. However, additional studies are required to establish the most effective number of trap crop cycles that are necessary to reduce Mg population density. Additionally, this technique, in our opinion, could be highly influenced by climate in northern latitudes in order to sow rice in advance and the cost of machinery and water.
The use of biological control agents, such as the fungi Paecilomyces lilacinus, Trichoderma harzianum, T. viride, and other Trichoderma spp.; the bacteria Bacillus subtilis; and the rhizobacterium Pseudomonas fluorescence, have shown promising results against Mg [175,176,177,178]. Studies by Amarasinghe and Hemachandra [178], in Sri Lanka, revealed that T. viride reduces gall formation and production of egg masses, which represents a potential strategy to be included in integrated pest management programs.
Similarly, the use of essential oils (EOs) has been explored to control RKN, as an alternative to the synthetic nematicides. The nematicidal effects of EO from spices and medicinal plants on RKN have been widely reported. The high effect of Cymbopogon spp. EO (C. martini motia, C. flexuosusand, and C. winterianus) on J2 mortality has been described [179,180,181]. Chavan et al. [182] stated that basil (Ocimum basilicum), peppermint (Mentha×piperita), and lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) EOs have nematicidal properties against Mg. In order to confirm the efficacy of these EOs, the in vitro tests must be complemented by in vivo soil-based experiments.
Host plant resistance is an environmentally friendly and cost-effective strategy to mitigate damage caused by Mg. A promising alternative for the control of Mg is the screening of germplasm for genotypes that are resistant/tolerant and the development of resistant/tolerant cultivars [80,108,183]. Resistance sources against Mg have been identified in African wild accessions of rice (O. glaberrima and O. longistaminata and O. rufipogon) [184], and variability to a certain extent has been perceived [162]. Wild accessions that are partially or fully resistant to Mg can therefore act as resistant donors for interspecific crosses with Asian cultivars of rice [184,185]. Introgression of O. glaberrima into O. sativa has led, for example, to the new rice for Africa, NERICA cultivars [186], but the introgression has not been very successful [187]. Therefore, natural resistance in O. sativa cultivars is potentially very important. In Asian rice, using the Bala and Azucena mapping population, chromosomes 1, 2, 6, 7, 9, and 11 have been reported as having quantitative trait loci (QTL) for partial resistance to Mg [111]. Mapping of Mg resistance on chromosome 10 in Asian rice (cv. Abhishek), using bulk segregant analysis, was reported by Mhatre et al. [188]. A hypersensitivity-like reaction to Mg infection found in the Asian rice cv. Zhonghua 11 suggests that resistance to Mg was qualitative rather than quantitative, involving (a) major gene(s) [189]. Galeng-Lawilao et al. [190] reported the main effect QTL for field resistance in Asian rice on chromosomes 4, 7, and 9 plus two epistatic interactions (between loci on chromosome 3 and 11, and between 4 and 8).
Few studies have used genome-wide association studies (GWASs) as a viable strategy to identify novel QTLs for PPN resistance or susceptibility in different plants [191,192]. For example, Dimkpa et al. [191] confirmed the robustness of GWAS to screen for rice–nematode interactions and identified two resistant accessions (Khao Pahk Maw and LD 24). Studies carried out, in India, by Hada et al. [193] allowed the identification of 40 highly resistant accessions. Alternatively, the profiling of the defense response of 36 rice cultivars to Mg infection revealed a variation in the expression of plant defense genes [194]. Among all the selected plant defense genes, the expression of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK20), isochorismate synthase genes (ICS1), nonexpressor of pathogenicity expression genes1 (NPR1), phytoalexin-deficient 4 (PAD4), allene oxidase synthase (AOS2), jasmonic acid-inducible rice myb gene (JAMYB), and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase (ACO7) was upregulated, possibly providing resistance against Mg. This observation matches the insignificant expression in the susceptible genotypes. These outcomes are significant and can be exploited for breeding purposes.
9. Conclusions
Climate changes and the trade activity are supporting the northerly movement of pests, which means temperate agro-systems are likely to be affected. Higher temperatures and moisture may result in an increasing rate of infection, development, and reproduction, causing shifts in abundance and geographic distribution. Such is the case of Mg that has recently been detected in Italy, posing a threat to EU rice production and other economically important crops. Its adaptability to flooded conditions means that Mg can be found in both upland (rainfed) and lowland (irrigated) rice, and in deep-water ecosystems. This rice RKN is capable of completing several generations within a single growing rice season, promoting the rapid build-up of damaging population densities and infection of more than 150 plants. Besides, there are no effective and sustainable management strategies available. Therefore, future research should be focused on the Mg distribution, biology, and on new approaches for the identification and management of this RKN species, which can be considered a threat to rice production.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.R., C.M., I.A. and M.L.I.; methodology, L.R., C.M., I.A. and M.L.I.; validation, C.M., M.L.I., I.A. and J.E.P.-R.; formal analysis, L.R., C.M. and M.L.I.; investigation, L.R.; resources, L.R., C.M. and M.L.I.; data curation, C.M., I.A., M.L.I. and J.E.P.-R.; writing—original draft preparation, L.R.; writing—review and editing, L.R., C.M., I.A., J.E.P.-R. and M.L.I.; supervision, C.M. and M.L.I.; project administration, L.R., C.M. and M.L.I.; funding acquisition, C.M. and M.L.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by CIEPQPF, Department of Chemical Engineering, UC, and CFE, Department of Life Sciences, UC, and FEDER funds through the Portugal 2020 (PT 2020) “Programa Operacional Factores de Competitividade 2020” (COMPETE2020) and by “Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia” (FCT, Portugal), under contracts UIDB/00102/2020, and UIDB/04004/2020 and by “Instituto do Ambiente, Tecnologia e Vida”; and by FCT and the European Social Funds, through “Programa Operacional Regional Centro”, under the PhD fellowship 2020.05541.BD.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data generated during this study are included in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the staff at the Laboratory of Nematology at INIAV—Nema-INIAV and the Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Kyndt, T.; Fernandez, D.; Gheysen, G. Plant-parasitic nematode infections in rice: Molecular and cellular insights. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPPO. 2018—Reporting Service (2018/196): Mg Found in 2018 in 4 Rice Fields in Lombardia Region (Province of Pavia). Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/reporting/article-6390 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Israel, P.; Rao, Y.S.; Rao, Y.R.V.J. Investigations on nematodes in rice and rice soils. Oryza 1963, 1, 125–127. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, A.M.; Birchfield, W. Meloidogyne graminicola (Heteroderidae) a new species of root-knot nematode from grass. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1965, 32, 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Birchfield, W. Host parasite relations and host range studies of a new Meloidogyne species in southern USA. Phytopathology 1965, 55, 1359–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Minton, N.A.; Tucker, E.T.; Golden, A.M. First report of Meloidogyne graminicola in Georgia. Plant Dis. 1987, 71, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windham, G.L.; Golden, A.M. First report of Meloidogyne graminicola in Mississippi. Plant Dis. 1990, 74, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handoo, Z.A.; Klassen, W.; Abdul-Baki, A.; Bryan, H.H.; Wang, Q. First record of rice root-nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) in Florida. J. Nematol. 2003, 35, 342. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano, I.R.; Reversat, G. Management of Meloidogyne graminicola and yield of upland rice in South-Luzon, Philippines. Nematology 2003, 5, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgham, J.L.; Abawi, G.S.; Duxbury, J.M.; Mazid, M.A. Impact of wheat on Meloidogyne graminicola populations in the rice–wheat system of Bangladesh. Nematropica 2004, 34, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Padgham, J.L.; Duxbury, J.M.; Mazid, A.M.; Abawi, G.S.; Hossain, M. Yield loss caused by Meloidogyne graminicola on lowland rainfed rice in Bangladesh. J. Nematol. 2004, 36, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bridge, J.; Plowright, R.A.; Peng, D. Nematodes Parasites of Rice. In Plant Parasitic Nematodes in Subtropical and Tropical Agriculture, 2nd ed.; Luc, M., Sikora, R.A., Bridge, J., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2005; pp. 87–130. [Google Scholar]
- Triviño, C.G.; Santillán, D.N.; Velasco, L.V. Plant-Parasitic nematodes associated with rice in Ecuador. Nematropica 2016, 46, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Fanelli, E.; Cotroneo, A.; Carisio, L.; Troccoli, A.; Grosso, S.; Boero, C.; De Luca, F. Detection and molecular characterization of the rice root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola in Italy. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 149, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, J.R.; Brito, J.A.; Kaur, R.; Ferrell, J.A. Weed species as hosts of Meloidogyne: A review. Nematropica 2009, 39, 157–185. [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, R.R.; Abawi, G.S.; Duxbury, J.M.; Smat, C.D.; Wang, X.; Brito, J.A. Variability and the recognition of two races in Meloidogyne graminicola. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2010, 39, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, V.; Bhardwaj, N.; Neelam, R.; Sajeesh, P.K. Meloidogyne graminicola (Golden and Birchfield) Threat to Rice Production. Res. J. Agric. For. Sci. 2014, 2, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.H.; Liu, W.Z.; Liang, C.; Duan, X.Y. Meloidogyne graminicola, a new record species from China. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2001, 5, 184–189. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.Q.; Zhang, D.Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, F.X. First report of Meloidogyne graminicola on rice (Oryza sativa) in Hunan Province, China. Plant Dis. 2017, 12, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.L.; Xu, X.; Yang, F.; Xue, Q.; Peng, Y.L.; Ji, H.L. First report of root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola, on rice in Sichuan province, Southwest China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Wu, X.; Tan, G.; Peng, D.; Xu, J.; Qiu, K.; Wu, H. First report of Meloidogyne graminicola on rice in Anhui province, China. Plant Dis. 2020, 105, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, W.; Peng, D. First Report of Meloidogyne graminicola on Rice in Henan Province, China. Plant Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabur, A.S.; Taya, A.S.; Bajaj, H.K. Life cycle of Meloidogyne graminicola on paddy and its host range studies. Indian J. Nematol. 2004, 34, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamad, F.; Khan, M.R. Status and yield loss assessment of rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola infestation in Siddharthnagar District, Uttar Pradesh. Ann. Plant Prot. Sci.-Indian J. 2018, 26, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buangsuwon, D.; Tonboonek, P.; Rujirachoon, G.; Braun, A.J.; Taylor, A.L. Nematodes. In Rice Diseases and Pests of Thailand; Rice Protection Research Centre, Rice Department, Ministry of Agriculture: Bangkok, Thailand, 1971; pp. 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.O.; Talukdar, M.J. A new disease of rice caused by the nematode Meloidogyne sp. In Proceedings of the Pakistan Science Conference, Peshawar, Pakistan, 27–30 September 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Bridge, J.; Page, S.L.J. The rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola, on deep water rice (Oryza sativa subsp. indica). Rev. Nematol. 1982, 5, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Miah, S.A.; Shahjahan, A.K.M.; Hossain, M.A.; Sharma, N.R. A survey of rice disease in Bangladesh. Trop. Pest. Manag. 1985, 31, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgham, J.L. Impact of The Rice Root-Knot Nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) on Lowland Rainfed Rice in Northern Western Bangladesh. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ekanayake, H.M.R.K.; Toida, Y. Nematode parasites of agricultural crops and their distribution in Sri Lanka. Jpn. Agric. Res 1997, 4, 23–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ekanayake, H.M.R.K. Histopathological changes caused by Meloidogyne graminicola in rice roots. Ann. Sri Lanka Dep. Agric. 2001, 3, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Nugaliyadde, L.; Dissanayake, D.M.N.; Herath, H.M.D.N.; Dharmasena, C.M.D.; Jayasundara, D.M. Outbreak of rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola (Golden & Birchfield) in Nikewaratiya, Kurunegala in Maha 2000/2001. (Short Communication). Ann. Sri Lanka Dep. Agric. 2001, 3, 373–374. [Google Scholar]
- Cuc, N.T.T.; Prot, J. Root-parasitic nematodes of deep-water rice in the Mekong delta of Vietnam. Fundam. Appl. Nematol. 1992, 15, 575–577. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, A.; Bridge, J. Rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola Golden and Birchfield, 1965 from rice in Pakistan. Pak. J. Nematol. 2003, 21, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, R.R.; Abawi, G.S.; Zhang, N.; Duxbury, J.M.; Smart, C.D. Characterization of isolates of Meloidogyne from rice–wheat production fields in Nepal. J. Nematol. 2007, 39, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Kleynhans, K.P. The Root-Knot Nematodes of South Africa; No. 231:61; Technical Communication, Department of Agricultural Development: Pretoria, South Africa, 1991; p. 136.
- Chapuis, E.; Besnard, G.; Andrianasetra, S.; Rakotomalala, M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Bellafiore, S. First report of the root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) in Madagascar rice fields. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2016, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteiro, A.R.; Ferraz, L.C.C.B. Encontro de Meloidogyne graminicola e primeiro ensaio de hospedabilidade no Brasil. Nematol. Bras 1988, 12, 149–150. [Google Scholar]
- Sperandio, C.A.; Monteiro, A.R. Ocorrência de Meloidogyne graminicola em arroz irrigado no Rio Grande do Sul. Nematol. Bras. 1991, 15, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Sperandio, C.A.; Amaral, A.S. Ocorrência de Meloidogyne graminicola causador da falsa bicheira do arroz irrigado no Rio Grande do Sul. Rev. Lavoura Arrozeira 1994, 47, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bellé, C.; Balardin, R.R.; Dalla Nora, D.; Schmitt, J.; Gabriel, M.; Ramos, R.F.; Antoniolli, Z.I. First Report of Meloidogyne graminicola (Nematoda: Meloidogynidae) on barley (Hordeum vulgare) in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellé, C.; Ramos, R.F.; Balardin, R.R.; Kaspary, T.E.; Brida, A.L. Reaction of rice cultivars to Meloidogyne graminicola as a function of irrigation management. Commun. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triviño, C.G.; Velasco, L.V. Problemas que Afectan la Producción de Arroz; EC, 8, 17; Revista Informativa; INIAP (Instituto Nacional Autónomo de Investigación Agropecuarias): Quito, Ecuador, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, J.; Puerta, F.; Gómez, R. Nematodos fitoparásitos asociados a las siembras de arroz en la terraza de Ibagué, Tolima-Colombia. Rev. Arroz 1981, 30, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bastidas, H.; Montealegre, S.F.A. Aspectos generales de la nueva enfermedad del arroz llamada entorchamiento. Arroz 1994, 43, 392–416. [Google Scholar]
- Jaraba-Navas, J.; Lozano, Z.; Pérez, C.R. Identificación del nematodo del nudo radical del arroz en los departamentos de Cesar y Guajira. Fitopatol. Colomb. 2001, 25, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos, L.M.; Moya, J.G. Nematodes associated with rice crops in Huila and Tolima. Agron. Colomb. 2010, 28, 577–579. [Google Scholar]
- Negretti, R.R.R.D.; Mattos, V.S.; Manica-Berto, R.; Gomes, C.B.; Carneiro, R.M.D.G.; Somavilla, L.; Castagnone-Sereno, P.; Regina, M.D.G. Characterisation of Meloidogyne species complex parasitising rice in southern Brazil. Nematology 2017, 19, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, S.L.; Bridge, J.; CABI. Plant nematodes on deep-water rice in Bangladesh. (ODM Report on visit to Bangladesh, 19 June–9 August, 1978). Available online: https://www.cabi.org/isc/abstract/19810881735 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Page, S.L.J.; Bridge, J.; Cox, P.; Rahman, L. Root and soil parasitic nematodes of deep water rice areas in Bangladesh. Int. Rice Res. Notes 1979, 4, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.L.; Taylor, B. Nematode pests associated with deep water rice in Bangladesh. Int. Rice Res. Notes 1983, 8, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.L.; Evans, A.A.F.; Miah, S.A. Plant damage and yield loss caused by the rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola in deepwater rice in Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Bot. 1990, 19, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, G.K.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, S. First report of Meloidogyne graminicola infecting banana in China. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netscher, C.; Erlan, S. A root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola, parasitic on rice in Indonesia. Afro-Asian J. Nematol. 1993, 3, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Nurjayadi, M.Y.; Munif, A.; Suastika, G. Identification of the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola, on rice plants in West. Java. J. Phytopathol. Indones. 2015, 11, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Mirsam, H.; Kurniawati, F. First report in South Sulawesi: Morphological and molecular characters of root-knot nematodes associated with rice roots in Wajo District, South Sulawesi. Indones. J. Plant Prot. 2018, 22, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, K.S.K.; Krishnappa, K.; Rao, Y.S. Response of some improved rice varieties to the development and reproduction of Meloidogyne graminicola Golden and Birchfield, 1965. Mysore J. Agric. Sci. 1979, 13, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, J.S.; Panwar, M.S.; Rao, Y.S. Occurrence of root knot-nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola in semideepwater rice. Curr. Sci. 1985, 54, 387–388. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, J.S.; Panwar, M.S.; Rao, Y.S. Nematode problems of rice in India. Trop. Pest Manag. 1987, 33, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, V.K.; Chhabra, H.K. A new record of Meloidogyne graminicola on Echinochloa crus-galli in Punjab. Indian J. Nematol. 1989, 19, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, H.S.; Khan, E.; Sehgal, M. Occurrence of two species of root-knot nematodes infecting rice, wheat and monocot weeds in northern India. Ann. Plant Prot. Sci. 1993, 1, 41–142. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, R.C.; Mukherjee, B.; Dasgupta, M.K.; Siddiqi, M.R. Prevalence and distribution of plant parasitic nematodes in rice fields of Tripura, India. Afro-Asian J. Nematol. 1994, 4, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Baqri, Q.H.; Ahmad, N. Qualitative and quantitative studies of plant and soil inhabiting nematodes associated with rice crop in Sikkim, India. Rec. Zool. Surv. India 2000, 98, 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- Sheela, M.S.; Jiji, T.; Nisha, M.S.; Rajkumar, J. A new record of Meloidogyne graminicola on rice, Oryza sativa L in Kerala. Indian J. Nematol. 2005, 35, 218. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, J.S.; Vishakanta, L.; Gubbaiah, V. Outbreak of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) disease in rice and farmers perceptions. Indian J. Nematol. 2006, 36, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.K.; Kalia, C.S.; Kaul, V. New record of root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola infecting rice in Jammu. Indian J. Nematol. 2007, 37, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, J.S.; Somasekhar, N.; Varaprasad, K.S. Nematode infestation in paddy. In Nematode Infestations; Part I: Food Crop; Khan, M.R., Jairajpuri, M.S., Eds.; Indian Academy of Sciences: Bengaluru, India, 2010; pp. 17–71. [Google Scholar]
- Pankaj, A.S.; Jain, R.K.; Singh, K. Incidence of Meloidogyne graminicola on rice in Andaman Islands. Ann. Plant Prot. Sci. 2011, 19, 259–260. [Google Scholar]
- Salalia, R.; Walia, R.K.; Somvanshi, V.S.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, A. Morphological, morphometric, and molecular characterization of intraspecifc variations within Indian populations of Meloidogyne graminicola. J. Nematol. 2017, 49, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manser, P.D. Meloidogyne graminicola a cause of root-knot of rice. FAO Plant Prot. Bull. 1968, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Manser, P.D. Notes on the rice root-knot nematode in Laos. FAO Plant Prot. Bull. 1971, 19, 138–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zainal-Abidin, A.A.; Monen-Abdullah, M.A.; Azawiyah, A.H. Meloidogyne graminicola: A new threat to rice cultivation in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Plant Protection in the Tropics, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 28–31 March 1994; pp. 246–247. [Google Scholar]
- Myint, Y.Y. Country report on root-knot nematode in Burma. In Proceedings of the 3rd Research Planning Conference on Root-knot Nematodes, Meloidogyne spp., Region VI, Raleigh, NC, USA, 20–24 July 1981; North Carolina State University: Jakarta, Indonesia; pp. 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Win, P.P.; Kyi, P.P.; DeWaele, D. Effect of agro-ecosystem on the occurrence of the rice root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola on rice in Myanmar. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2011, 40, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prot, J.C.; Soriano, I.R.S.; Matias, D. Major root-parasitic nematodes associated with irrigated rice in the Philippines. Fundam. Appl. Nematol. 1994, 17, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Gergon, E.B.; Miller, S.A.; Halbrendt, J.M.; Davide, R.G. Effect of rice root-knot nematode on growth and yield of Yellow Granex scallion. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AVA. Diagnostic Records of the Plant Health Diagnostic Services; Plant Health Centre, Agri-Food & Veterinary Authority: Singapore, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cuc, T.T.; Prot, J.C. Nematode parasites of deepwater and irrigated rice in the Mekong River Delta. In Proceedings of the conference held by Vietnam and IRRI: A Partnership in Rice Research, Hanoi, Vietnam, 4–7 May 1994; pp. 51–260. [Google Scholar]
- Triantaphyllou, A.C. Gametogenesis and the chromosomes of two root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne graminicola and M. naasi. J. Nematol. 1969, 1, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mantelin, S.; Bellafiore, S.; Kyndt, T. Meloidogyne graminicola: A major threat to rice agriculture. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williamson, V.M. Root-knot nematode resistance genes in tomato and their potential for future use. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 1998, 36, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheysen, G.; Mitchum, M.G. How nematodes manipulate plant development pathways for infection. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, R.N.; Rao, Y.S. Root-knot nematode resistance in rice. In Proceedings of the Second General Congress Breeding researches in Asia and Oceana SABRAO, New Delhi, India, 22–28 February 1973; pp. 1080–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, D.C.; Niblack, T.L. Biology and ecology of nematodes. In Manual of Agricultural Nematology; Nickle, W.R., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 47–71. [Google Scholar]
- Win, P.P.; Kyi, P.P.; Maung, Z.T.Z.; Myint, Y.Y.; DeWaele, D. Comparison of the damage potential and yield loss of the rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola, on lowland and upland rice varieties from Myanmar. Russ. J. Nematol. 2015, 23, 53–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Azeem, F.; Li, H.; Bohlmann, H. Smart parasitic nematodes use multifaceted strategies to parasitize plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulk, M.M. Meloidogyne graminicola. In CIH Descriptions of Plant-parasitic Nematodes; Set 6, No. 87; Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux: Farnham Royal, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Jena, R.N.; Rao, Y.S. Nature of resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) to the root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) II. In Histopathology of nematode infection in rice varieties. Proc. Natl. Indian Acad. Sci.-Sect. B 1977, 86, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyndt, T.; Denil, S.; Haegeman, A.; Trooskens, G.; Bauters, L.; Van Criekinge, W.; De Meyer, T.; Gheysen, G. Transcriptional reprogramming by root-knot and migratory nematode infection in rice. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.K. Survival of Meloidogyne graminicola eggs under different moisture conditions in vitro. Nematol. Mediterr. 1982, 10, 221–222. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano, I.R.S.; Prot, J.C.; Matias, D.M. Expression of tolerance for Meloidogyne graminicola in rice cultivars as affected by soil type and flooding. J. Nematol. 2000, 32, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hazarika, B.P. Meloidogyne graminicola and Sclerotium rolfsii interaction in rice. Int. Rice Res. Notes 2001, 26, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Kyndt, T.; Zemene, H.Y.; Haeck, A.; Singh, R.; Vleesschauwer, D.D.; Denil, S.; De Meyer, T.; Höfte, M.; Demeestere, K.; Gheysen, G. Below-ground attack by the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola predisposes rice to blast disease. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plowright, R.; Bridge, J. Effect of Meloidogyne graminicola (Nematoda) on the establishment, growth and yield of rice cv.IR36. Nematology 1990, 36, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, J.; Luc, M.; Plowright, R.A. Nematode Parasites of Rice. In Plant Parasitic Nematodes in Subtropical and Tropical Agriculture; Luc, M., Ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1990; pp. 69–108. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, B.N.; Prasad, J.S. Chlorophyll content in rice as influenced by the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola infection. Curr. Sci. 1988, 57, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, B.; Prasad, J.S. Photosynthetic rate in rice as influenced by the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola, infection. Rev. Nematol. 1989, 12, 431–432. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindra, H.; Sehgal, M.; Narasimhamurthy, H.B.; Khan, I.; Shruthi, S.A. Evaluation of rice landraces against rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhamurthy, H.B.; Ravindra, H.; Mukesh, S.; Rani, N.; Suresha, D.; Ekabote, S.D.; Ganapathi, G. Biology and life cycle of rice root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 477–479. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.R.; Ghosh, S.; Bhattacharya, S.P. Weed hosts of rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola from West Bengal. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 22, 583–584. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbar, A.; Javed, N.; Munir, A.; Abbas, H.; Khan, S.A.; Moosa, A.; Ali, M.A. Occurrence and molecular characterization of Meloidogyne graminicola on rice in Central Punjab, Pakistan. J. Nematol. 2020, 52, e2020–e2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.L.; Maria, M.; Barsalote, E.M.; Castillo, P.; Zheng, J.W. Morphological and molecular characterization of the rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola, Golden and Birchfield, 1965 occurring in Zhejiang, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2724–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Li, B.X.; Wu, H.Y. Incidence of the rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola, in Guangxi, China. Plant Pathol. J. 2020, 3, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.B.; Fontana, E.M.; Carneiro, R.M.G.; Almeida, M.R.A. Ocurrence of Meloidogyne graminicola em Santa Maria, RS. Cienc. Rural 1997, 27, 501–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yik, C.P.; Birchfield, W. Host studies and reactions of cultivars to Meloidogyne graminicola. Phytopathology 1979, 69, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.K.; Singh, K.P. A technique for studying the life cycle of Meloidogyne graminicola in rice roots. Pest Sci. Manag. Int. Rice Res. Notes 2010, 35, 4185. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.S.; Israel, P. Life history and bionomics of Meloidogyne graminicola, the rice root-knot nematode. Indian Phytopathol. 1973, 26, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, T.K.; Ganguly, A.K.; Gaur, H.S. Global status of rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 6016–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, N.C. Pathogenicity of Meloidogyne graminicola (Golden and Birchfield, 1965) in rice. In Proceedings of the All India Nematology Symposium, New Delhi, India, 21–22 August 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.S.; Prasad, J.S.; Yadava, C.P.; Padalia, C.R. Influence of rotation crops in rice soils on the dynamics of parasitic nematodes. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 1984, 2, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Uzzo, F.; Wilson, M.J.; Price, A.H. Physiological and genetic mapping study of tolerance to root-knot nematode in rice. New Phytol. 2007, 3, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Jain, R.K.; Ghule, T.M.; Pal, S. Root-knot Nematodes in India-A Comprehensive Monograph. In All India Coordinated Research Project on Plant Parasitic Nematodes with Integrated Approach for their Control; Indian Agricultural Research Institute: New Delhi, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, J.S.; Panwar, M.S.; Rao, Y.S. Screening of some rice cultivars against the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola. Indian J. Nematol. 1986, 16, 112–113. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.K.; Khan, M.R.; Kumar, V. Rice root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) infestation in rice. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2012, 45, 635–645. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, Z.; Khan, M.R.; Ahamad, F. Relative antagonistic potential of some rhizosphere biocontrol agents for the management of rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola. Biol. Control 2018, 126, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, P.P.; Kyi, P.P.; Maung, Z.T.Z.; De Waele, D. Population dynamics of Meloidogyne graminicola and Hirschmanniella oryzae in a double rice-cropping sequence in the lowlands of Myanmar. Nematology 2013, 15, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, L.D.; Kariyapperuma, K.A.D.P.S.; Pathirana, H.N.I. Study on approaches to integrated control of Meloidogyne graminicola in rice. J. Sci. Univ. Kelaniya 2007, 3, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amarasinghe, L.D. An integrated approached to the management of rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola in Sri Lanka. J. Sci. Univ. Kelaniya 2011, 6, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellafiore, S.; Jougla, C.; Chapuis, E.; Besnard, G.; Suong, M.; Vu, P.N.; De Waele, D.; Gantet, P.; Thi, X.N. Intraspecific variability of the facultative meiotic parthenogenetic root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) from rice fields in Vietnam. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2015, 338, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, J.B.; Langdon, K.R. Host of the rice root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola. In Nematology Circular, No. 172; Florida Department of Agriculture: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Torrini, G.; Roversi, P.F.; Cesaroni, C.F.; Marianelli, L. Pest risk analysis of rice root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) for the Italian territory. EPPO Bull. 2020, 50, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.K. Host suitability of some crops to Meloidogyne graminicola. Indian J. Nematol. 1977, 30, 483–485. [Google Scholar]
- Soomro, M.H.; Hauge, N.G.M. Relationship between inoculum density of Meloidogyne graminicola, growth of rice seedling and development of the nematode. Pak. J. Nematol. 1992, 11, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Duxbury, J.M. Sustainability of Post-Green Revolution Agriculture: The Rice-Wheat Cropping System of South Asia; Annual Report; Soil Management CRSP Management Entity, University of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, R.R.; Abawi, G.S.; Duxbury, J.M.; Smart, C. Characterization of root-knot nematodes recovered from rice-wheat fields in Nepal. J. Nematol. 2004, 36, 341–342. [Google Scholar]
- Usha, D.; Khetarpal, R.K.; Agarwal, P.C.; Ijun Lal, A.; Manju, L.K.; Gupta, K.; Parak, D.B. Potential Quarantine Pests for India: Cereals; NBPGR: New Delhi, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Reversat, G.; Soriano, I. The potential role of bananas in spreading rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola. Int. Rice Res. Notes 2002, 27, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- EPPO 2016–Reporting Service (2016/211): First report of Meloidogyne graminicola in Italy. Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/reporting/article-5956 (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Chen, J.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Ning, X.L.; Shi, C.H.; Cheng, X.; Xiao, S.; Liu, G.K. First report of Meloidogyne graminicola infecting Chinese chive in China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.S.; Israel, P.; Biswas, H. Weed and rotation crop plants as hosts for the rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola (Golden and Birchfield). Oryza 1970, 7, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, J.A.; Kaur, R.; Cetintas, R.; Stanley, J.D.; Mendes, M.L.; McAvoy, E.J.; Powers, T.O.; Dickson, D.W. Identification and isozyme characterization of Meloidogyne spp. infecting horticultural and agronomic crops, and weed plants in Florida. Nematology 2008, 10, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, H.; Sehgal, M.; Narasimhamurthy, H.B.; Jayalakshmi, K.; Khan, I. Rice root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) an emerging problem. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 3143–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belair, G.; Benoit, D.L. Host susceptibility of 32 common weeds to Meloidogyne hapla in organic soils of southwestern Quebec. J. Nematol. 1996, 28, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Mulyadi, M.; Triman, B. Study on host plant of root-knot nematode of rice. Indonesian J. Plant Prot. 1995, 1, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, H.K.; Dabur, K.R. Cyperus deformis, a new host record of rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola. Indian J. Nematol. 2000, 30, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Mani, A.; Hinai, M.A. Host range and distribution of Meloidogyne incognita and M. javanica in the Sultanate of Oman. Nematropica 1996, 26, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Bellé, C.; dos Santos, P.S.; Kaspary, T.E. First report of rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola, infecting Juncus microcephalus in Brazil. J. Nematol. 2021, 53, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, D.N.; Kurdikeri, C.B.; Gowda, C.K. Weeds as hosts of root-knot nematodes. Indian J. Nematol. 1995, 25, 215–216. [Google Scholar]
- Chitwood, B.G. Root-knot nematode. Part I. A review of the genus Meloidogyne Golden, 1887. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1949, 16, 90–104. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenback, J.B.; Hirschmann, H.; Sasser, J.N.; Trintaphyllou, A.C. A Guide to the Four most Common Species of Root-Knot Nematode (Meloidogyne spp.), with a Pictorial Key; Department of Plant Pathology, North Carolina State University/USAID: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Beek, J.G.; Vereijken, P.F.G.; Poleij, L.M.; Van Silfhout, C.H. Isolate-by-cultivar interaction in root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne hapla, M. chitwoodi, and M. fallax on potato. Can. J. Bot 1998, 76, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, M.; Perry, R.; Starr, J. Meloidogyne species-a diverse group of novel and important plant parasites. In Root-Knot Nematodes, 1st ed.; Perry, R.N., Moens, M., Starr, J.L., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, Oxfordshire, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sasser, J.N.; Triantaphyllou, A.C. Identification of Meloidogyne species and races. J. Nematol. 1977, 9, 283. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, S.B. Identification of Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne Species); CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, D.A.S.; Decraemer, W.; Moens, T.; dos Santos, G.A.P.; Derycke, S. Low genetic but high morphological variation over more than 1000 km coastline refutes omnipresence of cryptic diversity in marine nematodes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esbenshade, P.R.; Triantaphyllou, A.C. Use of enzyme phenotypes for identification of Meloidogyne species (Nematoda: Tylenchida). J. Nematol. 1985, 17, 6–20. [Google Scholar]
- Esbenshade, P.R.; Triantaphyllou, A.C. Isozyme phenotypes for the identification of Meloidogyne species. J. Nematol. 1990, 22, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, R.M.; Almeida, M.R.A.; Quénéhervé, P. Enzyme phenotypes of Meloidogyne spp. populations. Nematology 2000, 2, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, V.S.; Mulet, K.; Cares, J.H.; Gomes, C.B.; Fernandez, D.; de Sá, M.F.G.; Castagnone-Sereno, P. Development of diagnostic SCAR markers for M. graminicola, M. oryzae and M. salasi associated to irrigated rice fields in Americas. Plant Dis. 2018, 103, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soares, M.R.C.; Mattos, V.S.; Leite, R.R.; Gomes, A.C.M.M.; Gomes, C.B.; Castagnone-Sereno, P.; Carneiro, R.M.D.G. Integrative taxonomy of Meloidogyne graminicola populations with different esterase phenotypes parasitising rice in Brazil. Nematology 2020, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.A.; Nischwitz, C.; Skantar, A.M.; Schmitt, M.E.; Subbotin, S.A. Root-knot nematodes in golf course greens of the western United States. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Htay, C.C.; Peng, H.; Huang, W.; Kong, L.; He, W.; Holgado, R.; Peng, D.L. The development and molecular characterization of a rapid detection method for rice root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola). Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 146, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuta, A.; Toyota, K.; Min, Y.Y.; Maung, T.T. Development of real-time PCR primers for the quantification of Meloidogyne graminicola, Hirschmanniella oryzae and Heterodera cajani, pests of the major crops in Myanmar. Nematology 2016, 18, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, D.; Tang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, F. Rapid and sensitive detection of Meloidogyne graminicola in soil using conventional PCR, Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification, and Real-Time PCR methods. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, G.; Jühling, F.; Chapuis, É.; Zedane, L.; Lhuillier, É.; Mateille, T.; Bellafiore, S. Fast assembly of the mitochondrial genome of a plant parasitic nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) using next generation sequencing. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2014, 337, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhuo, K.; Lin, B.; Wang, H.; Liao, J. The complete mitochondrial genome of Meloidogyne graminicola (Tylenchina): A unique gene arrangement and its phylogenetic implications. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somvanshi, V.S.; Tathode, M.; Shukla, R.N.; Rao, U. Nematode Genome Announcement: A Draft Genome for Rice Root-Knot Nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola. J. Nematol. 2018, 50, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phan, N.T.; Orjuela, J.; Danchin, E.; Klopp, C.; Perfus-Barbeoch, L.; Kozlowski, D.K.; Bellafiore, S. Genome structure and content of the rice root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola). Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 11006–11021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somvanshi, V.S.; Dash, M.; Bhat, C.G.; Budhwar, R.; Godwin, J.; Shukla, R.N.; Patrignani, A.; Schlapbach, R.; Rao, U. An improved draft genome assembly of Meloidogyne graminicola IARI strain using long-read sequencing. Gene 2021, 793, 145748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Gheysen, G.; Denil, S.; Lindsey, K.; Topping, J.F.; Nahar, K.; Haegeman, A.; De Vos, W.H.; Kyndt, T. Transcriptional analysis through RNA sequencing of giant cells induced by Meloidogyne graminicola in rice roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3885–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, H.; Gheysen, G.; Ullah, C.; Verbeek, R.; Shang, C.; De Vleesschauwer, D.; Hofte, M.; Kyndt, T. The role of thionins in rice defence against root pathogens. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, C.; Dutta, T.K.; Banakar, P.; Rao, U. Comparing the defence-related gene expression changes upon root-knot nematode attack in susceptible versus resistant cultivars of rice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haegeman, A.; Mantelin, S.; Jones, J.T.; Gheysen, G. Functional role of effectors of plant-parasitic nematodes. Gene 2012, 492, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewezi, T.; Baum, T.J. Manipulation of plant cells by cyst and root-knot nematode effectors. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2013, 26, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haegeman, A.; Bauters, L.; Kyndt, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Gheysen, G. Identification of candidate effector genes in the transcriptome of the rice root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitot, A.-S.; Dereeper, A.; Agbessi, M.; Da Silva, C.; Guy, J.; Ardisson, M.; Fernandez, D. Dual RNA-seq reveals Meloidogyne graminicola transcriptome and candidate effectors during the interaction with rice plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.W.; Lin, B.; Huang, Q.; Hu, L.; Zhuo, K.; Liao, J. A novel Meloidogyne graminicola effector, MgGPP, is secreted into host cells and undergoes glycosylation in concert with proteolysis to suppress plant defences and promote parasitism. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naalden, D.; Haegeman, A.; de Almeida-Engler, J.; Birhane Eshetu, F.; Bauters, L.; Gheysen, G. The Meloidogyne graminicola effector Mg16820 is secreted in the apoplast and cytoplasm to suppress plant host defense responses. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 2416–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhuo, K.; Naalden, D.; Nowak, S.; Xuan Huy, N.; Bauters, L.; Gheysen, G. A Meloidogyne graminicola C-type lectin, Mg01965, is secreted into the host apoplast to suppress plant defence and promote parasitism. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Z.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Maria, M.; Qu, N.; Zheng, J.W. Meloidogyne graminicola protein disulfide isomerase may be a nematode effector and is involved in protection against oxidative damage. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitot, A.-S.; Dereeper, A.; Da Silva, C.; Guy, J.; Fernandez, D. Analyses of the root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) transcriptome during host infection highlight specific gene expression profiling in resistant rice plants. Pathogens 2020, 9, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, M.; Somvanshi, V.S.; Budhwar, R.; Godwin, J.; Shukla, R.N.; Rao, U. A rice root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola resistant mutant rice line shows early expression of plant-defence genes. Planta 2021, 253, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.S. Research on rice nematodes. In Rice in India; Padmanabhan, S.Y., Ed.; ICAR Monograph: New Delhi, India, 1985; pp. 591–615. [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi, S.; Torrini, G.; Marianelli, L.; Mazza, G.; Fumagalli, A.; Cavagna, B.; Ciampitti, M.; Roversi, P.F. Control of Meloidogyne graminicola a root-knot nematode using rice plants as trap crops: Preliminary results. Agriculture 2021, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, T.T.L.; Padgham, J.L.; Sikora, R.A. Biological control of the rice root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola on rice, using endophytic and rhizosphere fungi. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2009, 55, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhamurthy, H.B.; Ravindra, H.; Mukesh, S.; Ekabote, S.D.; Ganapathi, G. Bio-management of rice root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Seenivasan, N.; David, P.M.M.; Vivekanandan, P.; Samiappan, R. Biological control of rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola, through mixture of Pseudomonas fluorescens strains. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2021, 22, 611–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, L.D.; Hemachandra, K.H.D.J.K. Meloidogyne graminicola infestation in selected Sri Lankan rice varieties, Oryza sativa L. and nemato-toxic effect of Trichoderma viride to reduce infectivity. J. Sci. Univ. Kelaniya 2020, 13, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, N.K.; Verma, K.K.; Verma, B.S.; Malik, M.S.; Dhindsa, K.S. Nematicidal activity of EOs of Cymbopogon grasses. Nematologica 1985, 31, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, D.B.; Goswami, B.K.; Tomar, S.S. Nematicidal activity of some EOs against Meloidogyne incogn. Indian Perfum. 1987, 31, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Oka, Y.; Nacar, S.; Putievsky, E.; Ravid, U.; Yaniv, Z.; Spiegel, Y. Nematicidal activity of EOs and their components against the root-knot nematode. Phytopathology 2000, 90, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chavan, S.N.; Somasekhar, N.; Rani, J. Nematicidal activity of essential oils against rice root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola. Indian J. Nematol. 2019, 49, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, R.R.; Duxbury, J.M.; Abawai, G. Evaluation of Protocol for Assessing the Reaction of Rice and Wheat Germplasm to Infection by Meloidogyne graminicola. J. Nematol. 2012, 44, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soriano, I.; Schmit, V.; Brar, D.; Prot, J.C.; Reversat, G. Resistance to rice root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola identified in Oryza longistaminata and O. glaberrima. Nematology 1999, 1, 95–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plowright, R.; Coyne, D.L.; Nash, P.; Jones, M.P. Resistance to the rice nematodes Heterodera sacchari, Meloidogyne graminicola and M. incognita in Oryza glaberrima and O. glaberrima x O. sativa interspecies hybrids. Nematology 1999, 1, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibba, L.; Zeller, M.; Diagne, A. The impact of new Rice for Africa (NERICA) adoption on household food security and health in the Gambia. Food Secur. 2017, 9, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabasan, M.T.N.; Kumar, A.; De Waele, D. Evaluation of resistance and tolerance of rice genotypes from crosses of Oryza glaberrima and O. sativa to the rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2017, 43, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhatre, P.H.; Pankaj, A.S.; Singh, A.K.; Ellur, R.K.; Kumar, P. Molecular mapping of rice root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne graminicola) resistance gene in Asian rice (Oryza sativa L.) using STMS markers. Indian J. Genet. 2017, 77, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.T.; De Waele, D.; Lorieux, M.; Xiong, L.; Bellafiore, S. A hypersensitivity-like response to Meloidogyne graminicola in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Phytopathology 2018, 108, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galeng-Lawilao, J.; Kumar, A.; De Waele, D. QTL mapping for resistance to and tolerance for the rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola. BMC Genet. 2018, 19, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimkpa, S.O.N.; Lahari, Z.; Shrestha, R.; Douglas, A.; Gheysen, G.; Price, A.H. A genome-wide association study of a global rice panel reveals resistance in Oryza sativa to root-knot nematodes. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warmerdam, S.; Sterken, M.G.; Van Schaik, C.; Oortwijn, M.E.; Sukarta, O.C.; Lozano-Torres, J.L.; Smant, G. Genome-wide association mapping of the architecture of susceptibility to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita in Arabidiopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hada, A.; Dutta, T.K.; Singh, N.; Singh, B.; Rai, V.; Singh, N.K.; Rao, U. A genome-wide association study in Indian wild rice accessions for resistance to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzade, B.; Singh, D.; Phani, V.; Kumbhar, S.; Rao, U. Profiling of defence responsive pathway regulatory genes in Asian rice (Oryza sativa L.) against infection of Meloidogyne graminicola (Nematoda: Meloidogynidae). 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).