High Prevalence and Diversity of Cephalosporin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Including Extraintestinal Pathogenic E. coli CC648 Lineage in Rural and Urban Dogs in Northwest Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
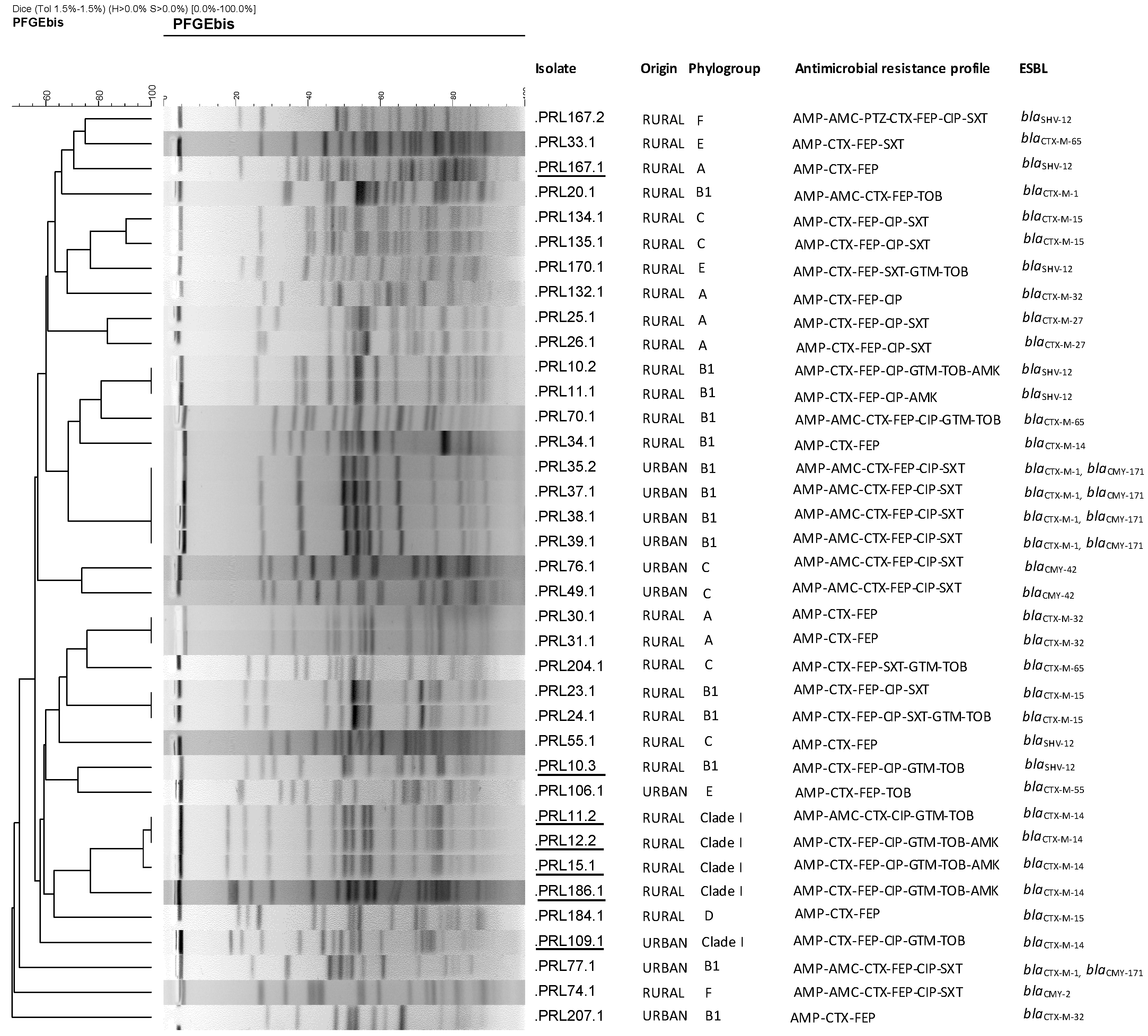
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection, Culture, and Bacterial Identification
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance-Encoding Genes
4.3. Characterization of E. coli Isolates: Virulence Traits, Phylogroups, STs and Clonotypes, Serotyping, and PFGE
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, M.B.; Kidd, J.T.; Harris, N.A.P.; Schembri, A.M.; Beatson, A.S.; Paterson, L.D.; Walker, J.M. Antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, M. Antibiotic-Resistant Priority Pathogens List. Available online: https://www.who.int/ (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadi, V.A.; Hariharan, H.; Amadi, A.O.; Matthew-Belmar, V.; Nicholas-Thomas, R.; Lanza Perea, M.; Carter, K.; Eugene, R.; Kalasi, K.; Alhassan, A.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of commensal Escherichia coli isolated from feces of non-diarrheic dogs in Grenada, West Indies. Vet. World 2019, 12, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, C.D.; Dobrindt, U. What defines extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli? Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manges, A.R.; Geum, H.M.; Guo, A.; Edens, T.J.; Fibke, C.D.; Pitout, J.D. Global extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (Expec) lineages. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, D.H. Reservoirs of antimicrobial resistance in pet animals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, S148–S152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argudín, M.A.; Deplano, A.; Meghraoui, A.; Dodémont, M.; Heinrichs, A.; Denis, O.; Nonhoff, C.; Roisin, S. Bacteria from animals as a pool of antimicrobial resistance genes. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halsby, K.D.; Walsh, A.L.; Campbell, C.; Hewitt, K.; Morgan, D. Healthy animals, healthy people: Zoonosis risk from animal contact in pet shops, a systematic review of the literature. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomba, C.; Rantala, M.; Greko, C.; Edward Baptiste, K.; Catry, B.; van Duijkeren, E.; Mateus, A.; Moreno, A.M.; Pyörälä, S.; Ružauskas, M.; et al. Public health risk of antimicrobial resistance transfer from companion animals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bunt, G.; Fluit, A.C.; Spaninks, M.P.; Timmerman, A.J.; Geurts, Y.; Kant, A.; Scharringa, J.; Mevius, D.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Bonten, M.J.M.; et al. Faecal carriage, risk factors, acquisition and persistence of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae in dogs and cats and co-carriage with humans belonging to the same household. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baede, V.O.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Broens, E.M.; Duim, B.; Dohmen, W.; Nijsse, R.; Timmerman, A.J.; Hordijk, J. Longitudinal study of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-and AmpC-producing enterobacteriaceae in household dogs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 3117–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Torralba, J.; Oteo, A.; Asenjo, V.; Bautista, E.F.; Alós, J.I. Survey of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in companion dogs in Madrid, Spain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2499–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köck, R.; Daniels-Haardt, I.; Becker, K.; Mellmann, A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Mevius, D.; Schwarz, S.; Jurke, A. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in wildlife, food-producing, and companion animals: A systematic review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovejero, C.M.; Escudero, J.A.; Thomas-Lopez, D.; Hoefer, A.; Moyano, G.; Montero, N.; Martin-Espada, C.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B. Highly tigecycline-resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae sequence TYPE 11 (ST11) & ST147 isolates from companion animals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungquist, O.; Ljungquist, D.; Myrenås, M.; Rydén, C.; Finn, M.; Bengtsson, B. Evidence of household transfer of ESBL-/pAmpC-producing Enterobacteriaceae between humans and dogs–a pilot study. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2016, 6, 31514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, K.; Hase, A.; Matsuo, M.; Horimoto, T.; Ogasawara, J. Prevalence and genetic characterization of cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae among dogs and cats in an animal shelter. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Tripartite Guide to Addressing Zoonotic Diseases in Countries Taking a Multisectoral, One Health Approach. Published in 2019 by The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, The World Organisation for Animal Health and The World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.oie.int/ (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- CDC. Prioritizing Zoonotic Diseases for Multisectoral, One Health Collaboration in the United States; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019; pp. 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, P.; Ceccarelli, D.; Odent, E.; Sarrazin, S.; Graveland, H.; Van Gompel, L.; Battisti, A.; Caprioli, A.; Franco, A.; Wagenaar, J.A.; et al. Antimicrobial usage and resistance in companion animals: A cross-sectional study in three european countries. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary use (CVMP) 3 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) 2019. Available online: www.ema.europa.eu/contact (accessed on 29 June 2020).
- Gómez-Poveda, B.; Moreno, M.A. Antimicrobial prescriptions for dogs in the capital of Spain. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolun, V.; Küçükbasmaci, Ö.; Törümküney-Akbulut, D.; Çatal, Ç.; Anǧ-Küçüker, M.; Anǧ, Ö. Relationship between ciprofloxacin resistance and extended-spectrum β-lactamase production in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae strains. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupouy, V.; Abdelli, M.; Moyano, G.; Arpaillange, N.; Bibbal, D.; Cadiergues, M.C.; Lopez-Pulin, D.; Sayah-Jeanne, S.; De Gunzburg, J.; Saint-Lu, N.; et al. Prevalence of beta-lactam and quinolone/fluoroquinolone resistance in enterobacteriaceae from dogs in France and Spain—characterization of ESBL/pAmpC isolates, genes, and conjugative plasmids. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Gracia, R.C.; Cortés-Cortés, G.; Lozano-Zarain, P.; Bello, F.; Martínez-Laguna, Y.; Torres, C. Faecal Escherichia coli isolates from healthy dogs harbour CTX-M-15 and CMY-2 β-lactamases. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: Improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, D.; Overesch, G.; Endimiani, A.; Collaud, A.; Thomann, A.; Perreten, V. Occurrence and genetic characteristics of third-generation cephalosporin-resistant Escherichia coli in Swiss retail meat. Microb. Drug Resistance 2014, 20, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierikx, C.; van der Goot, J.; Fabri, T.; van Essen-Zandbergen, A.; Smith, H.; Mevius, D. Extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-and AmpC-β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in Dutch broilers and broiler farmers. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; Cantón, R.; Garcillán-Barcia, M.P.; Novais, Â.; Galán, J.C.; Alvarado, A.; De La Cruz, F.; Baquero, F.; Coque, T.M. Spread of blaCTX-M-14 is driven mainly by IncK plasmids disseminated among Escherichia coli phylogroups A, B1, and D in Spain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5204–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumi, M.V.; Mas, J.; Elena, A.; Cerdeira, L.; Muñoz, M.E.; Lincopan, N.; Gentilini, É.R.; Di Conza, J.; Gutkind, G. Co-occurrence of clinically relevant β-lactamases and MCR-1 encoding genes in Escherichia coli from companion animals in Argentina. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 230, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamborova, I.; Dolejska, M.; Vojtech, J.; Guenther, S.; Uricariu, R.; Drozdowska, J.; Papousek, I.; Pasekova, K.; Meissner, W.; Hordowski, J.; et al. Plasmid-mediated resistance to cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones in various Escherichia coli sequence types isolated from rooks wintering in Europe. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börjesson, S.; Egervärn, M.; Lindblad, M.; Englunda, S. Frequent occurrence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase- and transferable AMPC beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli on domestic chicken meat in Sweden. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2463–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Jiménez, D.; García-Meniño, I.; Fernández, J.; García, V.; Mora, A. Chicken and turkey meat: Consumer exposure to multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae including mcr-carriers, uropathogenic E. coli and high-risk lineages such as ST131. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 331, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, L.W. Extraintestinal foodborne pathogens. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Jiménez, D.; García-Meniño, I.; Herrera, A.; García, V.; López-Beceiro, A.; Alonso, M.P.; Blanco, J.; Mora, A. Genomic characterization of Escherichia coli isolates belonging to a new hybrid aepec/expec pathotype o153:H10-a-st10 eae-beta1 occurred in meat, poultry, wildlife and human diarrheagenic samples. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flament-Simon, S.C.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; García, V.; Duprilot, M.; Mayer, N.; Alonso, M.P.; García-Meniño, I.; Blanco, J.E.; Blanco, M.; Blanco, J. Clonal structure, virulence factor-encoding genes and antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli, causing urinary tract infections and other extraintestinal infections in humans in spain and france during 2016. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flament-Simon, S.C.; García, V.; Duprilot, M.; Mayer, N.; Alonso, M.P.; García-Meniño, I.; Blanco, J.E.; Blanco, M.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; Blanco, J. High prevalence of ST131 subclades C2-H30Rx and C1-M27 among extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli causing human extraintestinal infections in patients from two hospitals of Spain and France during 2015. Front. Cell. Inf. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.C.; Penha Filho, R.A.C.; Andrade, L.N.; Berchieri, A.; Darini, A.L.C. Detection of chromosomal blaCTX-M-2 in diverse Escherichia coli isolates from healthy broiler chickens. Clin. Microbiol. Inf. 2014, 20, O623–O626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, X.-Y.; Xia, Y.-B.; Guo, Z.-W.; Ma, Z.-B.; Yi, M.-Y.; Lv, L.-C.; Lu, P.-L.; Yan, J.-C.; Huang, J.-W.; et al. Clonal spread of Escherichia coli ST93 carrying mcr-1-Harboring IncN1-IncHI2/ST3 plasmid among companion animals, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Bai, X.; Ma, J.; Dang, R.; Xiong, Y.; Fanning, S.; Bai, L.; Yang, Z. Characterization of five Escherichia coli isolates co-expressing ESBL and mcr-1 resistance mechanisms from different origins in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa-Ezdra, R.; Grill Diaz, F.; Vieytes, M.; García-Fulgueiras, V.; Caiata, L.; Ávila, P.; Brasesco, M.; Christophersen, I.; Cordeiro, N.F.; Algorta, G.; et al. First three Escherichia coli isolates harbouring mcr-1 in Uruguay. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resistance 2020, 20, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohmen, W.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Bos, M.E.H.; van Marm, S.; Scharringa, J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Heederik, D.J.J. Carriage of extended-spectrum β-lactamases in pig farmers is associated with occurrence in pigs. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, W.; Tanaka, H.; Taniguchi, Y.; Iimura, M.; Soga, E.; Kubo, R.; Matsuo, N.; Kawamura, K.; Arakawa, Y.; Nagano, Y.; et al. Acquisition of mcr-1 and Cocarriage of Virulence Genes in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolates from Municipal Wastewater Influents in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Johnston, B.D.; Gordon, D.M. Rapid and specific detection of the Escherichia coli sequence type 648 complex within phylogroup F. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, K.E.; Wertheim, H.; Zadoks, R.N.; Baker, S.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Dance, D.; Jenney, A.; Connor, T.R.; Hsu, L.Y.; Severin, J.; et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3574–E3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludden, C.; Moradigaravand, D.; Jamrozy, D.; Gouliouris, T.; Blane, B.; Naydenova, P.; Hernandez-Garcia, J.; Wood, P.; Hadjirin, N.; Radakovic, M. A one health study of the genetic relatedness of Klebsiella pneumoniae and their mobile elements in the east of England. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domokos, J.; Damjanova, I.; Kristof, K.; Ligeti, B.; Kocsis, B.; Szabo, D. Multiple benefits of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants in Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 high-risk clone and recently emerging ST307 clone. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, L.; Feudi, C.; Fortini, D.; Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Bonura, C.; Endimiani, A.; Mammina, C.; Ocampo, A.M.; Jimenez, J.N.; et al. Diversity, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance of the KPCproducing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 clone. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.; Alonso, C.A.; Silva, V.; Pimenta, P.; Cunha, R.; Martins, C.; Igrejas, G.; Torres, C.; Poeta, P. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from healthy and sick dogs in Portugal. Microb. Drug Resistance 2019, 26, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 10.0, valid from 2020-01-01. European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Available online: http://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/ (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- García-Meniño, I.; García, V.; Mora, A.; Díaz-Jiménez, D.; Flament-Simon, S.C.; Alonso, M.P.; Blanco, J.E.; Blanco, M.; Blanco, J. Swine enteric colibacillosis in Spain: Pathogenic potential of mcr-1 ST10 and ST131 E. Coli Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Porter, S.; Johnston, B.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Spurbeck, R.R.; Mobley, H.L.T.; Williamson, D.A. Host Characteristics and Bacterial Traits Predict Experimental Virulence for Escherichia coli Bloodstream Isolates from Patients with Urosepsis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurbeck, R.R.; Dinh, P.C.; Walk, S.T.; Stapleton, A.E.; Hooton, T.M.; Nolan, L.K.; Kim, K.S.; Johnson, J.R.; Mobley, H.L.T. Escherichia coli isolates that carry vat, fyua, chua, and yfcv efficiently colonize the urinary tract. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 4115–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinée, P.A.; Jansen, W.H.; Maas, H.M.; le Minor, L.; Beaud, R. An unusual H antigen (Z66) in strains of Salmonella typhi. Ann. Microbiol. 1981, 132, 331–334. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7294611 (accessed on 7 June 2020).
- Weissman, S.J.; Johnson, J.R.; Tchesnokova, V.; Billig, M.; Dykhuizen, D.; Riddell, K.; Rogers, P.; Qin, X.; Butler-Wu, S.; Cookson, B.T.; et al. High-resolution two-locus clonal typing of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, T.; Falush, D.; Lan, R.; Colles, F.; Mensa, P.; Wieler, L.H.; Karch, H.; Reeves, P.R.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Ochman, H.; et al. Sex and virulence in Escherichia coli: An evolutionary perspective. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 1136–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Verhoef, J.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Brisse, S. Multilocus sequence typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J. Clinc. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Isolate | Serotype | PG | ST (CC) | 1 CH | ESBL | 2 Antimicrobial Resistance | 3 Virulence-Gene Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRL11.2 | O1:H45 | clade I | 770 (None) | 116-552 | CTX-M-14 | AMP-AMC-CTX-CIP-GTM-TOB | fimH552 iucD iutA kpsM II-K5 traT malX chuA |
| PRL12.2 | O1:H45 | clade I | 770 (None) | 116-552 | CTX-M-14 | AMP-CTX-FEP-CIP-GTM-TOB-AMK | fimH552 hlyF iucD iutA kpsM II-K5 traT malX chuA |
| PRL15.1 | O1:H45 | clade I | 770 (None) | 116-552 | CTX-M-14 | AMP-CTX-FEP-CIP-GTM-TOB-AMK | fimH552 hlyF iucD iutA kpsM II-K5 traT malX chuA |
| PRL109.1 | O1:H45 | clade I | 770 (None) | 116-552 | CTX-M-14 | AMP-CTX-FEP-CIP-GTM-TOB | fimH552 hlyF iucD iutA kpsM II-K5 traT malX chuA |
| PRL186.1 | O1:H45 | clade I | 770 (None) | 116-552 | CTX-M-14 | AMP-CTX-FEP-CIP-GTM-TOB-AMK | fimH552 hlyF iucD iutA kpsM II-K5 traT malX chuA |
| PRL167.1 | O18:H11 | A | 93 (168) | 11-neg | SHV-12 | AMP-CTX-FEP | hlyF iucD iutA kpsM II-K5 |
| PRL10.3 | O23:H16 | B1 | 453 (86) | 6-31 | SHV-12 | AMP-CTX-FEP-CIP-GTM-TOB | fimH31 hlyF iucD iutA iron kpsM II-K5 cvaC traT iss fyuA |
| PRL10.1 | O83:H42 | F | 1485 (648) | 231-58 | SHV-12 | AMP-CTX-FEP-CIP- SXT | fimH48 hlyF iucD iutA iron kpsM II-K5 cvaC traT malX tsh ompT iss chuA vat fyuA yfcV |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abreu-Salinas, F.; Díaz-Jiménez, D.; García-Meniño, I.; Lumbreras, P.; López-Beceiro, A.M.; Fidalgo, L.E.; Rodicio, M.R.; Mora, A.; Fernández, J. High Prevalence and Diversity of Cephalosporin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Including Extraintestinal Pathogenic E. coli CC648 Lineage in Rural and Urban Dogs in Northwest Spain. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080468
Abreu-Salinas F, Díaz-Jiménez D, García-Meniño I, Lumbreras P, López-Beceiro AM, Fidalgo LE, Rodicio MR, Mora A, Fernández J. High Prevalence and Diversity of Cephalosporin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Including Extraintestinal Pathogenic E. coli CC648 Lineage in Rural and Urban Dogs in Northwest Spain. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(8):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080468
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbreu-Salinas, Fátima, Dafne Díaz-Jiménez, Isidro García-Meniño, Pilar Lumbreras, Ana María López-Beceiro, Luis Eusebio Fidalgo, María Rosario Rodicio, Azucena Mora, and Javier Fernández. 2020. "High Prevalence and Diversity of Cephalosporin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Including Extraintestinal Pathogenic E. coli CC648 Lineage in Rural and Urban Dogs in Northwest Spain" Antibiotics 9, no. 8: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080468
APA StyleAbreu-Salinas, F., Díaz-Jiménez, D., García-Meniño, I., Lumbreras, P., López-Beceiro, A. M., Fidalgo, L. E., Rodicio, M. R., Mora, A., & Fernández, J. (2020). High Prevalence and Diversity of Cephalosporin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Including Extraintestinal Pathogenic E. coli CC648 Lineage in Rural and Urban Dogs in Northwest Spain. Antibiotics, 9(8), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080468








