Antibiotics 2022, 11(7), 907; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070907 - 7 Jul 2022
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2686
Abstract
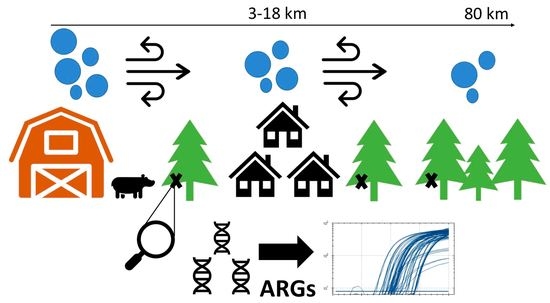
Monitoring antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) is vital to the One Health approach to tackling the antibiotic resistance crisis. It has been suggested that conifer needles can be used as passive bioaerosol samplers. Here, the use of conifer needles as biomonitors of ARGs in
[...] Read more.
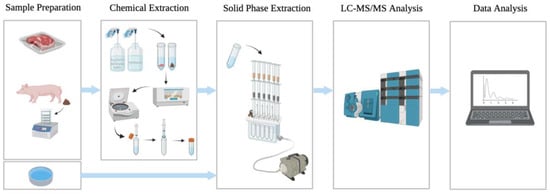
Monitoring antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) is vital to the One Health approach to tackling the antibiotic resistance crisis. It has been suggested that conifer needles can be used as passive bioaerosol samplers. Here, the use of conifer needles as biomonitors of ARGs in bioaerosols was assessed as a proof-of-concept. Needles were collected from trees surrounding pig farms, villages, and forest sites in Québec, Canada. Needles were homogenised and DNA was extracted. Results of qPCR analyses showed biomass estimates were consistent across samples. Number and quantity of ARGs was significantly lower in forest sites when compared to the farm and village, comprising a distinct resistome. Consistent with previous findings, the most common ARGs were tetracyclines and sulfonamides, which were found close to agricultural activities. Although results were limited, there is great potential for using the conifer phyllosphere as a passive bioaerosol sampler. This method represents an accessible way to promote ARG surveillance over long distances from point sources.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antimicrobial Resistance and the Environment: One Health Approach, 2nd Edition)
►
Show Figures