Whole-Genome Sequence of Multidrug-Resistant Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Carrying Biofilm-Associated Genes and a Unique Composite of SCCmec
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Susceptibility Testing of S. epidermidis
2.2. Phenotypic Detection of Biofilm
2.3. Characterization and Typing of Bacterial Genomes
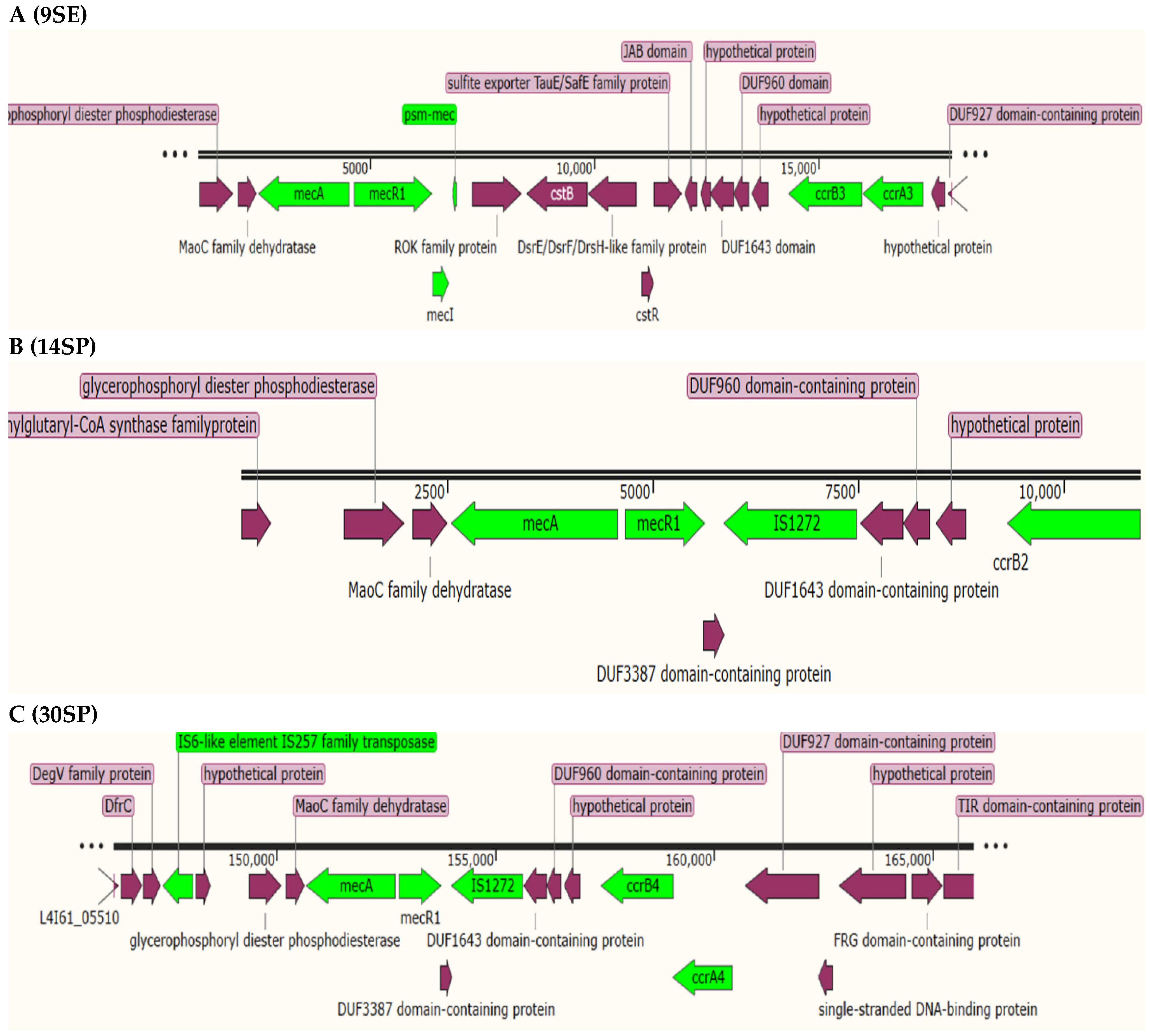
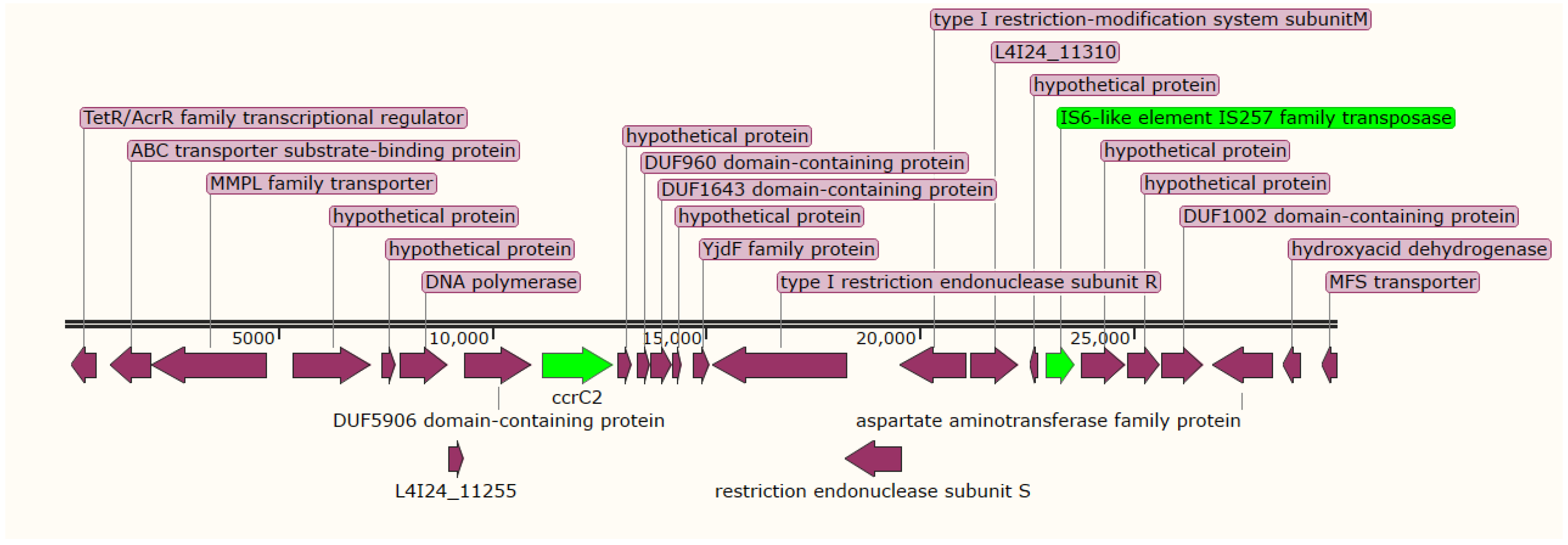
2.4. Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome (SCC) Detection and Typing
2.5. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes, Mobile Genetic Elements, and Virulence Factors
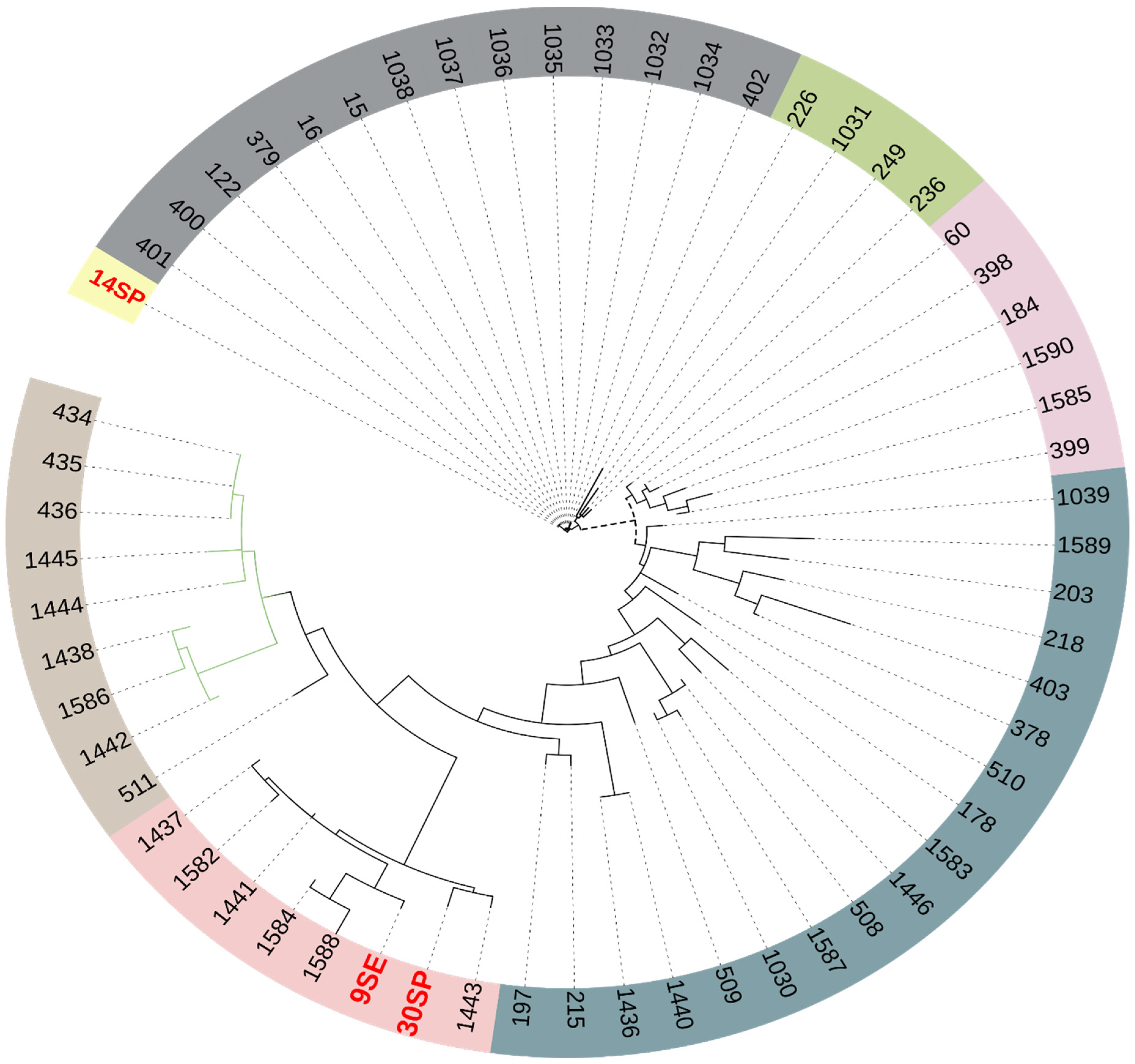
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolates
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Phenotypic Detection of Biofilm Production
4.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS) and Data Analysis
4.5. Prediction of Resistome and Mobilome
4.6. Pan-Genome Analysis and Phylogenetic Tree
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, H.; Tong, Y.; Cheng, J.; Abbas, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Si, D.; Zhang, R. Biofilm and Small Colony Variants An Update on Staphylococcus aureus Strategies toward Drug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, I.A.; Otto, M.; Strunk, T.; Currie, A.J. Look Who’s Talking: Host and Pathogen Drivers of Staphylococcus epidermidis Virulence in Neonatal Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgueiro, V.C.; Iorio, N.L.P.; Ferreira, M.C.; Chamon, R.C.; Dos Santos, K.R.N. Methicillin resistance and virulence genes in invasive and nasal Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates from neonates. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, L.M.; Conlon, B.P.; Kidd, S.P. Antibiotic tolerance and the alternative lifestyles of Staphylococcus aureus. Essays Biochem. 2017, 61, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Holden, M.T.; Feil, E.J.; Lindsay, J.A.; Peacock, S.J.; Day, N.P.; Enright, M.C.; Foster, T.J.; Moore, C.E.; Hurst, L.; Atkin, R. Complete genomes of two clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains: Evidence for the rapid evolution of virulence and drug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9786–9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.; Dadashi, M.; Pormohammad, A.; Khoramrooz, S.S.; Mirzaii, M.; Gholipour, A.; Darban-Sarokhalil, D. Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis in Iran: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 13, e58410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, L.V.; Calduch, P.B.; Rodríguez, L.F.; Ortega, D.N.; Samper, A.M.D.; Rodríguez, J.C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis infectious keratitis: Clinical and microbiological profile. Rev. Española Quimioter. 2022, 35, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlet, C.P.; Brown, M.M.; Horswill, A.R. Commensal staphylococci influence Staphylococcus aureus skin colonization and disease. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Neyestanaki, D.; Mansouri, S.; Tadjrobehkar, O.; Pardakhty, A.; Tabatabaeifar, F.; Morones-Ramírez, J.R.; Jamali, Z.; Isaei, E. High prevalence of multi-drug resistant and different SCCmec types among coagulase-negative Staphylococci spp. collected from clinical samples and skin of healthcare workers in Kerman, Southeast Iran. Gene Rep. 2022, 26, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekoe, S.O.; Hane-Weijman, S.; Trads, S.L.; Orman, E.; Opintan, J.; Hansen, M.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Styrishave, B. Reservoir of Antibiotic Residues and Resistant Coagulase Negative Staphylococci in a Healthy Population in the Greater Accra Region, Ghana. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, R.; Last, K.; Becker, S.L.; Papan, C. Update on coagulase-negative Staphylococci—What the clinician should know. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalik, M.; Samet, A.; Podbielska-Kubera, A.; Savini, V.; Międzobrodzki, J.; Kosecka-Strojek, M. Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) as a significant etiological factor of laryngological infections: A review. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilmann, C.; Ziebuhr, W.; Becker, K. Are coagulase-negative staphylococci virulent? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro-Hubinger, L.; Moraes Riboli, D.F.; Abraão, L.M.; Pereira Franchi, E.P.L.; da Cunha, R.D.S.; de Lourdes, M. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Clones Are Widely Distributed in the Hospital and Community. Pathogens 2021, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Peters, B.M.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Xu, Z.; Shirliff, M.E. Staphylococcal chromosomal cassettes mec (SCCmec): A mobile genetic element in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 101, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, Y. Current Status of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec (SCCmec). Antibiotics 2022, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.; Hellmark, B.; Söderquist, B. Characterization of SCCmec elements in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from blood cultures from neonates during three decades. Apmis 2011, 119, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkaraddi, U.; Nandihal, N.W. Clinico-bacteriological profile and antibiogram of Staphylococcus epidermidis with special emphasis on Methicillin resistance and hospital acquired infections in a tertiary care center south India. Indian J. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 9, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wayne, P. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Thirtieth Informational Supplement. Inform. Suppl. 2020, 31, 100–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Chao, X.; Fei, M.; Dai, Y.; Liu, B. Analysis of S. Epidermidis icaA and icaD genes by polymerase chain reaction and slime production: A case control study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ibrahem, S.; Salmenlinna, S.; Lyytikäinen, O.; Vaara, M.; Vuopio-Varkila, J. Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strains from bacteraemic patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argemi, X.; Hansmann, Y.; Prola, K.; Prévost, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci pathogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Molecular basis of Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. In Seminars in Immunopathology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.Y.; Monk, I.R.; Gonçalves da Silva, A.; Seemann, T.; Chua, K.Y.; Kearns, A.; Hill, R.; Woodford, N.; Bartels, M.D.; Strommenger, B. Global spread of three multidrug-resistant lineages of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Rao, L.; Lin, C. The Dissemination of Fusidic Acid Resistance Among Staphylococcus epidermidis Clinical Isolates in Wenzhou, China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Satorius, A.E.; Raff, M.R.; Rivera, A.; Newton, D.W.; Younger, J.G. Multilocus sequence typing for interpreting blood isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2014, 2014, 787458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, A.; Ghebremedhin, B. Genetic determinants and biofilm formation of clinical Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates from blood cultures and indwelling devises. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 3, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson, E.; Johannesen, T.B.; Nilsdotter-Augustinsson, Å.; Söderquist, B.; Stegger, M. Comparative genomics of Staphylococcus epidermidis from prosthetic-joint infections and nares highlights genetic traits associated with antimicrobial resistance, not virulence. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Vale, B.C.M.; Nogueira, A.G.; Cidral, T.A.; Lopes, M.C.S.; de Melo, M.C.N. Decreased susceptibility to chlorhexidine and distribution of qacA/B genes among coagulase-negative Staphylococcus clinical samples. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.Ş.; Aslantaş, Ö. Antimicrobial resistance and underlying mechanisms in Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawi, H.S.; Elhag, K.; Mahgoub, E.; Altayb, H.N.; Hamid, M.M.A. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Carbapenem Resistance Gram Negative Bacilli among Hospitalized Patients in Khartoum State. 2019. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4748/latest.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Kwong, S.M.; Ramsay, J.P.; Jensen, S.O.; Firth, N. Replication of staphylococcal resistance plasmids. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, M.A.; Tonthat, N.K.; Kwong, S.M.; babu Chinnam, N.; Liu, M.A.; Skurray, R.A.; Firth, N. Mechanism of staphylococcal multiresistance plasmid replication origin assembly by the RepA protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9121–9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udo, E.E.; Boswihi, S.S.; Mathew, B.; Noronha, B.; Verghese, T. Resurgence of chloramphenicol resistance in methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus due to the acquisition of a variant florfenicol exporter (Fexav)-mediated chloramphenicol resistance in Kuwait hospitals. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaledi, A.; Esmaeili, D.; Jamehdar, S.A.; Esmaeili, S.-A.; Neshani, A.; Bahador, A. Expression of MFS efflux pumps among multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. Der Pharm. Lett. 2016, 8, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Conlan, S.; Mijares, L.A.; Becker, J.; Blakesley, R.W.; Bouffard, G.G.; Brooks, S.; Coleman, H.; Gupta, J.; Gurson, N.; Park, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis pan-genome sequence analysis reveals diversity of skin commensal and hospital infection-associated isolates. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, C.; Chen, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, M.; Chu, Z.; Wang, Y. Staphylococcus aureus phenol-soluble modulins α1–α3 act as novel toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 antagonists to inhibit HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, J.; Hetsa, B.A.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.K.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. Genomic Analysis of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolates From Clinical Sources in the Kwazulu-Natal Province, South Africa. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 656306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Both, A.; Weißelberg, S.; Heilmann, C.; Rohde, H. Emergence of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord, M.; Ardebili, A.; Jamalan, M.; Jahanbakhsh, R.; Behnampour, N.; Ghaemi, E.A. Evaluation of biofilm formation and presence of ica genes in Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical isolates. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2018, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauters, G.; Vaneechoutte, M. Approaches to the identification of aerobic Gram-negative bacteria. In Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 11th ed.; Jorgensen, J.H., Pfaller, M.A., Carroll, K.C., Funke, G., Landry, M.L., Richter, S.S., Warnock, D.W., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 613–634. [Google Scholar]
- Mogana, R.; Adhikari, A.; Tzar, M.; Ramliza, R.; Wiart, C. Antibacterial activities of the extracts, fractions and isolated compounds from Canarium patentinervium Miq. against bacterial clinical isolates. BMC Complementary Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouidhi, B.; Zmantar, T.; Jrah, H.; Souiden, Y.; Chaieb, K.; Mahdouani, K.; Bakhrouf, A. Antibacterial and resistance-modifying activities of thymoquinone against oral pathogens. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2011, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaieb, K.; Chehab, O.; Zmantar, T.; Rouabhia, M.; Mahdouani, K.; Bakhrouf, A. In vitro effect of pH and ethanol on biofilm formation by clinicalica-positiveStaphylococcus epidermidis strains. Ann. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, R.; Sawicki, R.; Juda, M.; Stankevic, M.; Rybojad, P.; Sawicki, M.; Malm, A.; Ginalska, G. A comparative analysis of phenotypic and genotypic methods for the determination of the biofilm-forming abilities of Staphylococcus epidermidis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 310, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sabeel, S.; Salih, M.A.; Ali, M.; El-Zaki, S.-E.; Abuzeid, N.; Elgadi, Z.A.M.; Altayb, H.N.; Elegail, A.; Ibrahim, N.Y.; Elamin, B.K. Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Sudanese patients. Tuberc. Res. Treat. 2017, 2017, 8340746. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST. org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.; Hasman, H.; Larsen, J.; Stegger, M.; Johannesen, T.B.; Allesøe, R.L.; Lemvigh, C.K.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O.; Larsen, A.R. SCC mec Finder, a web-based tool for typing of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec in Staphylococcus aureus using whole-genome sequence data. Msphere 2018, 3, e00612–e00617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antipov, D.; Hartwick, N.; Shen, M.; Raiko, M.; Lapidus, A.; Pevzner, P.A. plasmidSPAdes: Assembling plasmids from whole genome sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3380–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Jin, Q.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2019: A comparative pathogenomic platform with an interactive web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D687–D692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raue, S.; Fan, S.-H.; Rosenstein, R.; Zabel, S.; Luqman, A.; Nieselt, K.; Götz, F. The genome of Staphylococcus epidermidis O47. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Antibiotic | Staphylococcus epidermidis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9SE | 14SP | 30SP | ||||
| MIC (μg/mL) | Disk Diffusion Susceptibility a | MIC (μg/mL) | Disk Diffusion Susceptibility a | MIC (μg/mL) | Disk Diffusion Susceptibility a | |
| Ciprofloxacin | ≤2 | S | 256 | R | 256 | R |
| Tetracycline | 32 | R | ≤2 | S | 32 | R |
| Cefoxitin | - | R | - | R | - | R |
| Erythromycin | - | S | - | R | - | S |
| Clindamycin | - | R | - | S | - | S |
| Trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole | - | S | - | R | - | R |
| Gentamicin | ≤2 | S | ≤2 | S | ≥1024 | R |
| Chloramphenicol | 512 | R | 256 | R | 512 | R |
| Ampicillin | 256 | R | ≥1024 | R | 4 | R |
| Strains | Proteins | Clusters | Singletons |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. epidermidis 9SE | 2285 | 2184 | 96 |
| S. epidermidis 14SP | 2321 | 2212 | 99 |
| S. epidermidis 30SP | 2230 | 2150 | 73 |
| S. epidermidis 949_S8 | 2119 | 2094 | 23 |
| S. epidermidis BPH0662 | 2654 | 2412 | 182 |
| S. epidermidis RP62A | 2401 | 2304 | 60 |
| S. epidermidis ATCC_12228 | 10,252 | 2583 | 2766 |
| S. epidermidis ID | Acetyltransferase | CcrA | CcrB | Fdh | IcaA | IcaB | IcaC | IcaD | IcaR | IS256-like | mecA | mecC | PSM-b1 | PSM-mec | QacA | Tn554 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC12228 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| RP62A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 949_S8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BPH0662 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 9SE | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 14SP | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 30SP | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ID | SCCmec Genes | Type/Temp Coverage | Contig | Identity | Position in Contig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9SE | ccrC2-allele-1:1:KR187111 | III(3A)/63.85% XIII(9A) | 20 | 96.44 | 11,178..12,863 |
| ccrB3:1:852082:AB037671 | 21 | 100.00 | 14,339..15,967 | ||
| ccrA3:1:852082:AB037671 | 21 | 100.00 | 15,988..17,334 | ||
| mecA:12:AB505628 | 21 | 100.00 | 2522..4531 | ||
| mecR1:1:D86934 | 21 | 100.00 | 4638..6395 | ||
| mecI:1:D86934 | 21 | 100.00 | 6395..6766 | ||
| 14SP | mecA:12:AB505628 | IV(2B&5)/74.73% | 25 | 100.00 | 2560..4569 |
| dmecR1:1:AB033763 | 25 | 100.00 | 4666..5652 | ||
| IS1272:3:AM292304 | 25 | 100.00 | 5641..7483 | ||
| ccrB4:2:BK20781:FJ670542 | 15 | 92.20 | 7117..8745 | ||
| ccrC1-allele-7:1:EF190468 | 11 | 100.00 | 74,999..76,675 | ||
| subtype-IVc(2B):3:81108:AB096217 | 11 | 100.00 | 85,144..86,298 | ||
| ccrA2:7:81108:AB096217 | 11 | 100.00 | 90,315..91,664 | ||
| ccrB2:7:81108:AB096217 | 25 | 100.00 | 9325..10,914 | ||
| 30SP | mecA:12:AB505628 | VI(4B)/87.47% | 3 | 100.00 | 150,689..152,698 |
| dmecR1:1:AB033763 | 3 | 100.00 | 152,795..153,781 | ||
| IS1272:3:AM292304 | 3 | 100.00 | 153,770..155,612 | ||
| ccrB4:2:BK20781:FJ670542 | 3 | 94.05 | 157,433..159,061 | ||
| ccrA4:1:HDE288:AF411935 | 3 | 99.85 | 159,058..160,419 | ||
| IS1272:2:AB033763 | 1 | 91.12 | 213,133..214,709 |
| S. epidermidis | Contig | ARGs | Position | Coverage | Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9SE | 5 | fosB | 78015-78443 | 100% | 99.5% |
| 35 | fusB | 1634-993 | 100% | 100% | |
| 21 | mecA | 2522-4528 | 100% | 100% | |
| 36 | aac(6′)-aph(2″) | 1519-80 | 100% | 99.9% | |
| 22 | fosD | 78015-78443 | 100% | 99.5% | |
| qacA | 12368-13912 | 100% | 100% | ||
| 31 | mupA | 158-3232 | 100% | 99.96% | |
| 14SP | 28 | aadD | 191-952 | 100% | 100% |
| 11 | msr(A) | 1716-250 | 100% | 99.7 % | |
| 7 | fosB | 71675-72103 | 100% | 96.5% | |
| blaZ | 130038-130883 | 100% | 100% | ||
| 6 | dfrG | 58760-59257 | 100% | 100% | |
| 18 | fusB | 45606-46247 | 100% | 100% | |
| 25 | mecA | 2560-4566 | 100% | 100% | |
| 34 | aac(6′)-aph(2″) | 1839-400 | 100% | 100% | |
| 30SP | 2 | fosB | 225233-225661 | 100% | 96.27% |
| 15 | msr(A) | 13445-14911 | 100% | 99.72% | |
| blaZ | 8566-9411 | 100% | 99.88% | ||
| 3 | mecA | 150689-152695 | 100% | 100% | |
| fusC | 167439-168077 | 100% | 99.21% | ||
| 18 | tet(K) | 1122-2501 | 100% | 100% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altayb, H.N.; Elbadawi, H.S.; Baothman, O.; Kazmi, I.; Alzahrani, F.A.; Nadeem, M.S.; Hosawi, S.; Chaieb, K. Whole-Genome Sequence of Multidrug-Resistant Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Carrying Biofilm-Associated Genes and a Unique Composite of SCCmec. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070861
Altayb HN, Elbadawi HS, Baothman O, Kazmi I, Alzahrani FA, Nadeem MS, Hosawi S, Chaieb K. Whole-Genome Sequence of Multidrug-Resistant Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Carrying Biofilm-Associated Genes and a Unique Composite of SCCmec. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(7):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070861
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltayb, Hisham N., Hana S. Elbadawi, Othman Baothman, Imran Kazmi, Faisal A. Alzahrani, Muhammad Shahid Nadeem, Salman Hosawi, and Kamel Chaieb. 2022. "Whole-Genome Sequence of Multidrug-Resistant Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Carrying Biofilm-Associated Genes and a Unique Composite of SCCmec" Antibiotics 11, no. 7: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070861
APA StyleAltayb, H. N., Elbadawi, H. S., Baothman, O., Kazmi, I., Alzahrani, F. A., Nadeem, M. S., Hosawi, S., & Chaieb, K. (2022). Whole-Genome Sequence of Multidrug-Resistant Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Carrying Biofilm-Associated Genes and a Unique Composite of SCCmec. Antibiotics, 11(7), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070861







