Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Eruca sativa Miller Leaf Extract Exhibits Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Antibiofilm, and Anti-Metastatic Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
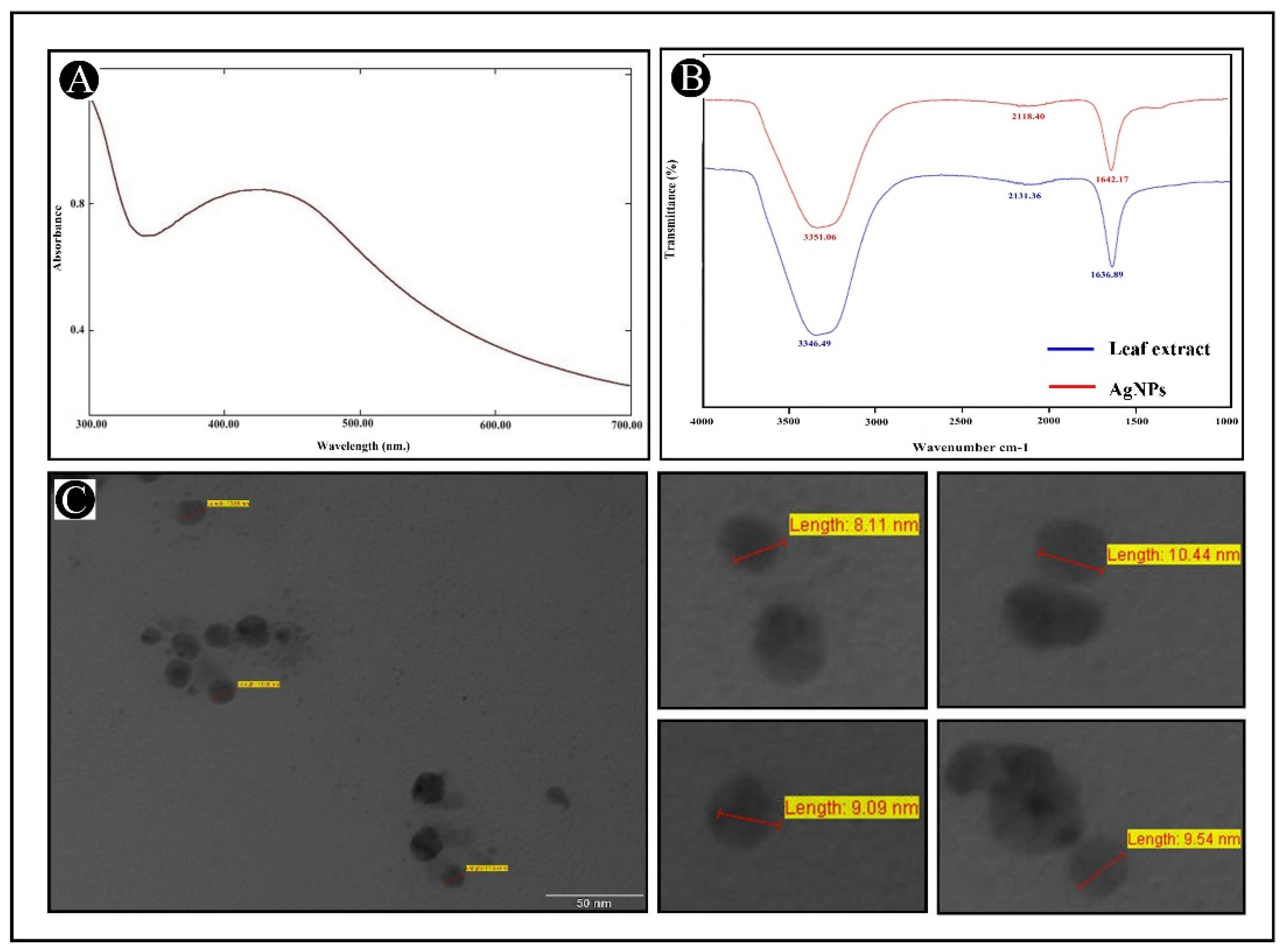
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of AgNPs
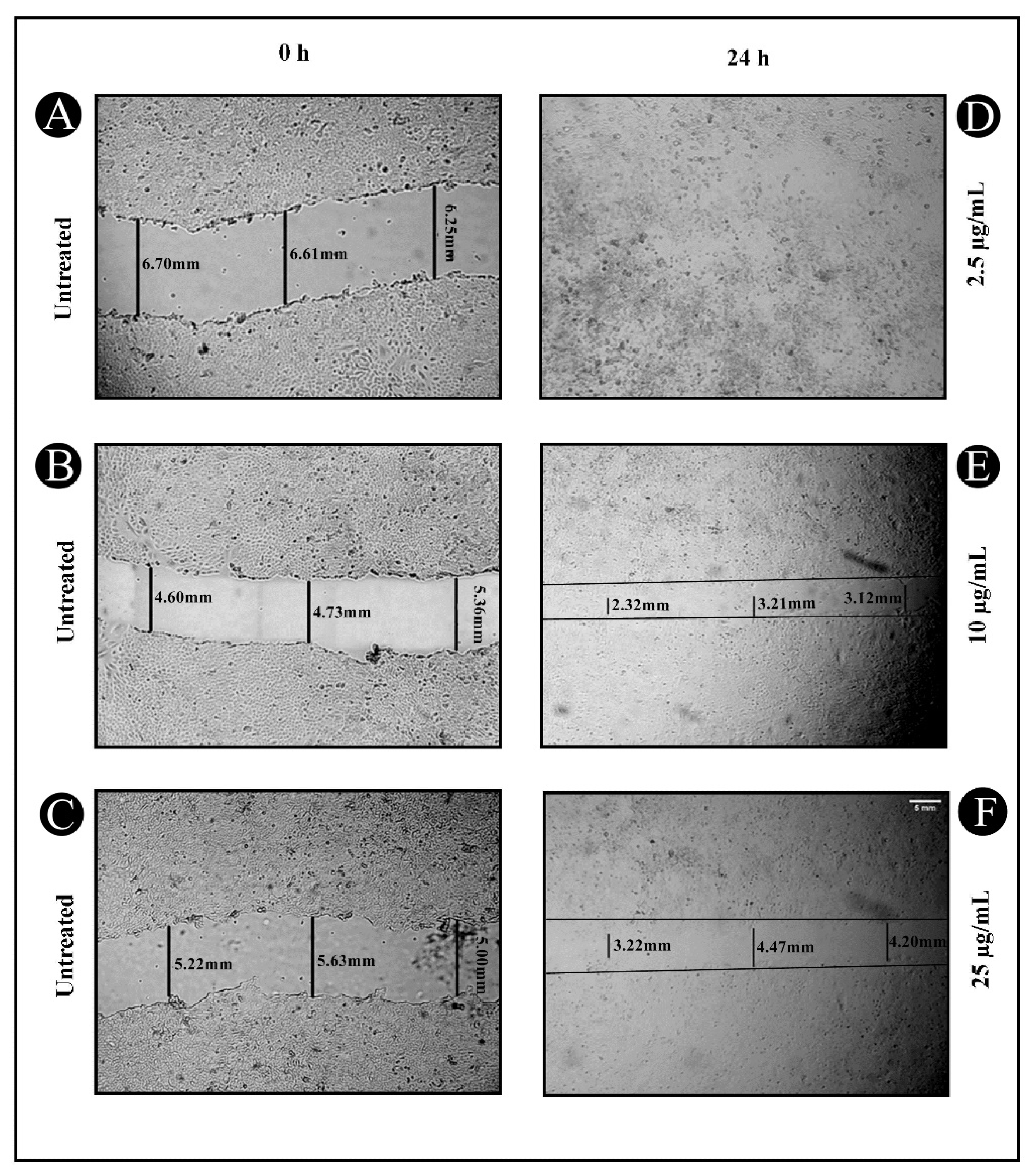
2.2. Anticancer Potential of Synthesized AgNPs
2.3. Antibacterial Activity of Synthesized AgNPs
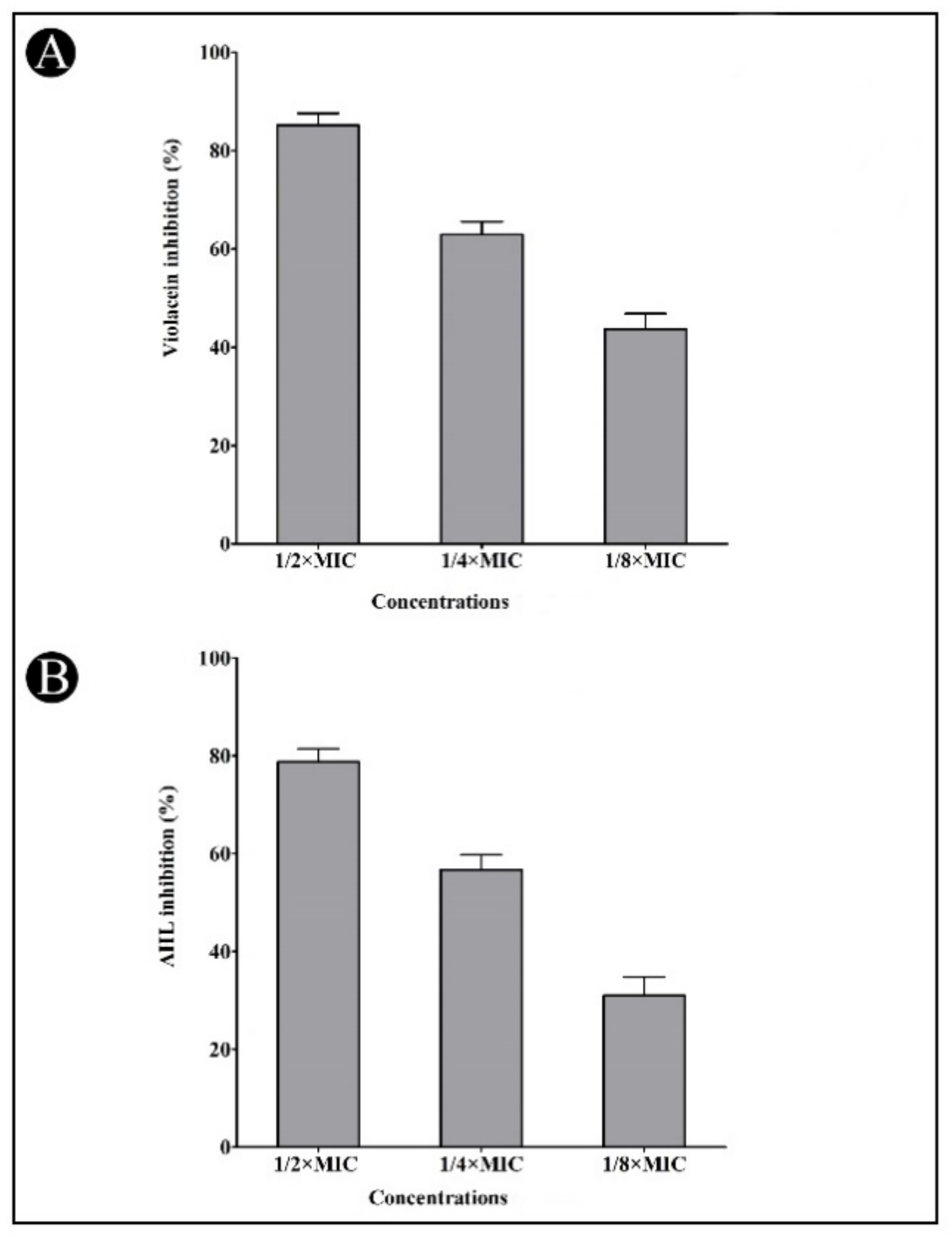
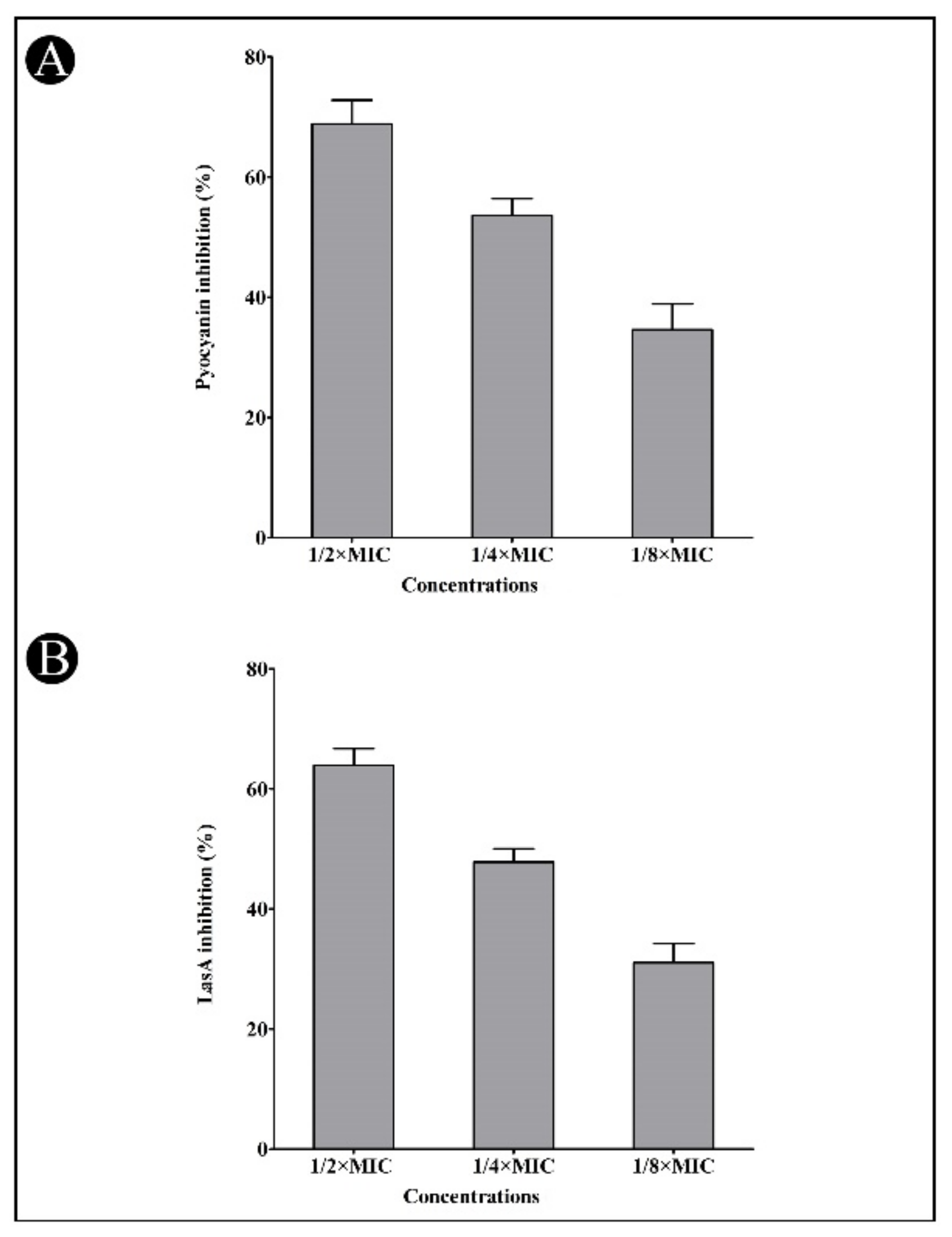
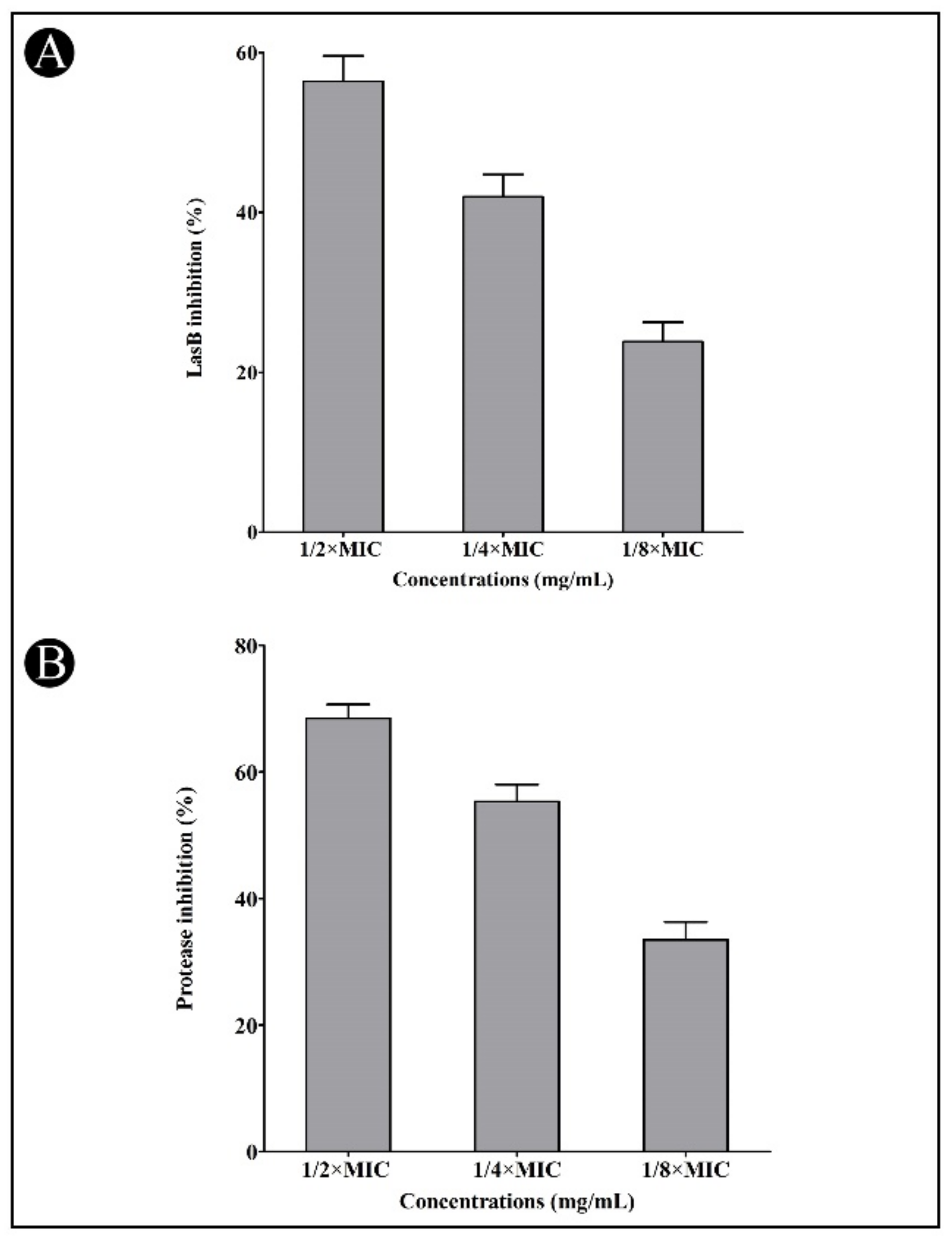
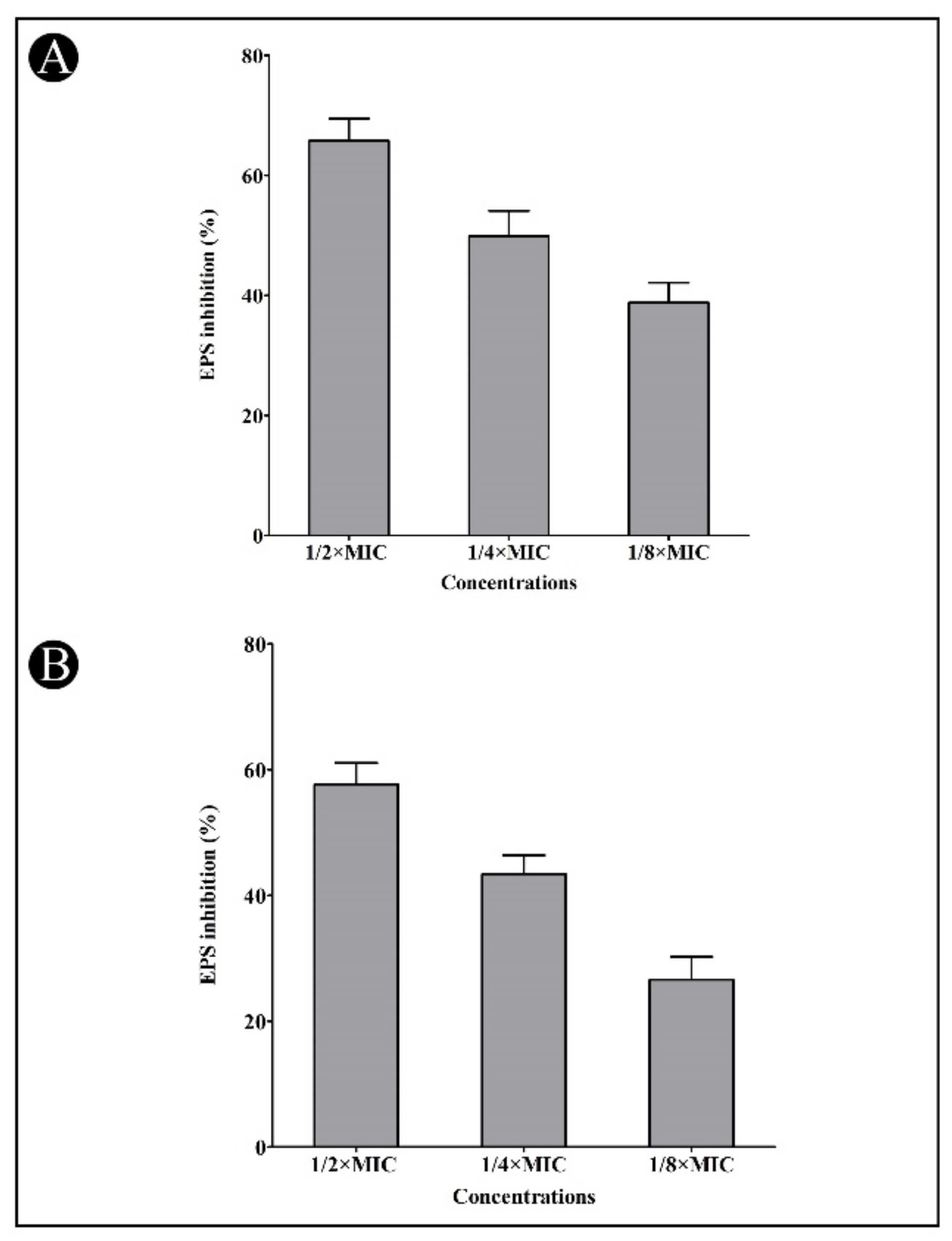
2.4. Effect of Synthesized AgNPs on Quorum-Sensing (QS)-Regulated Virulence Factors
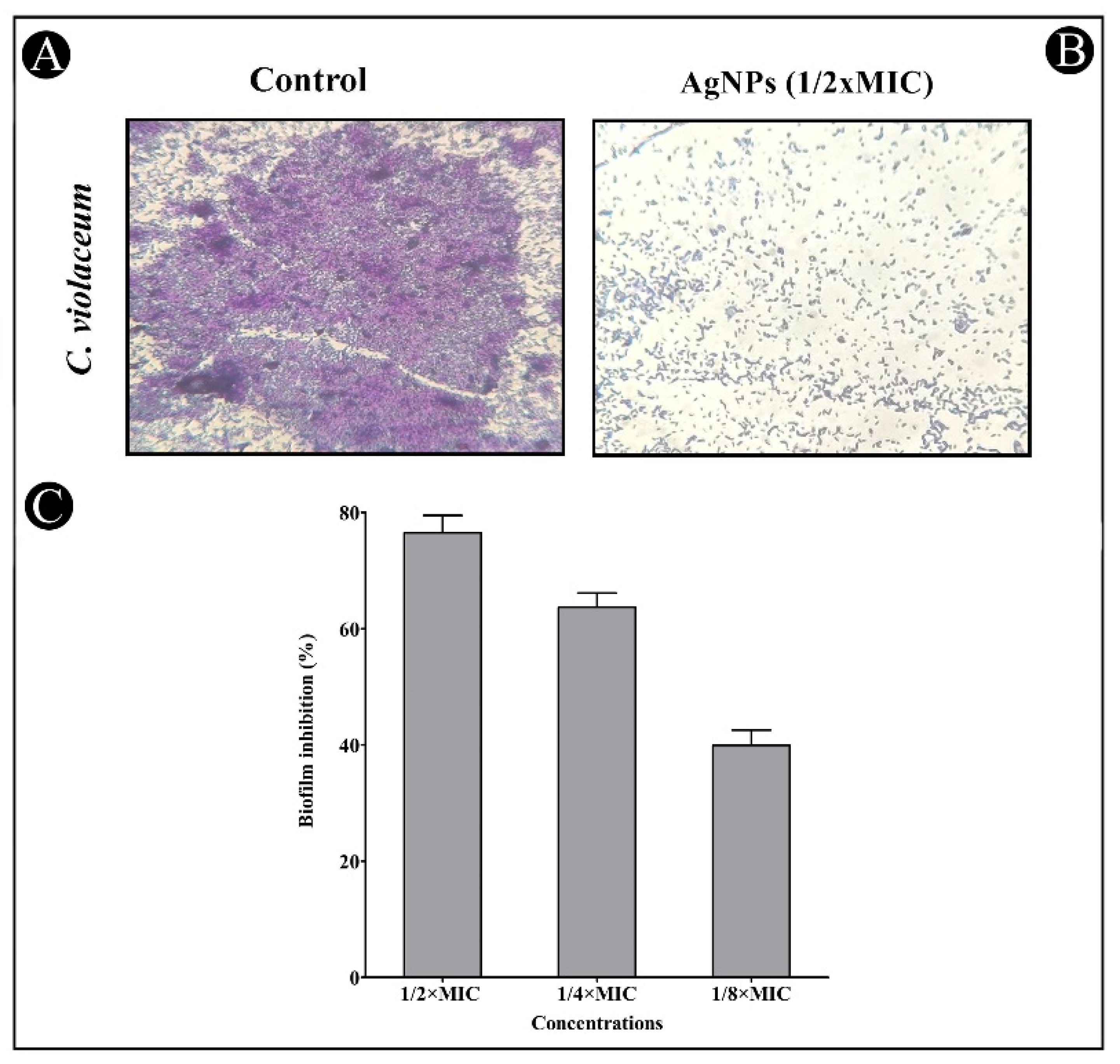
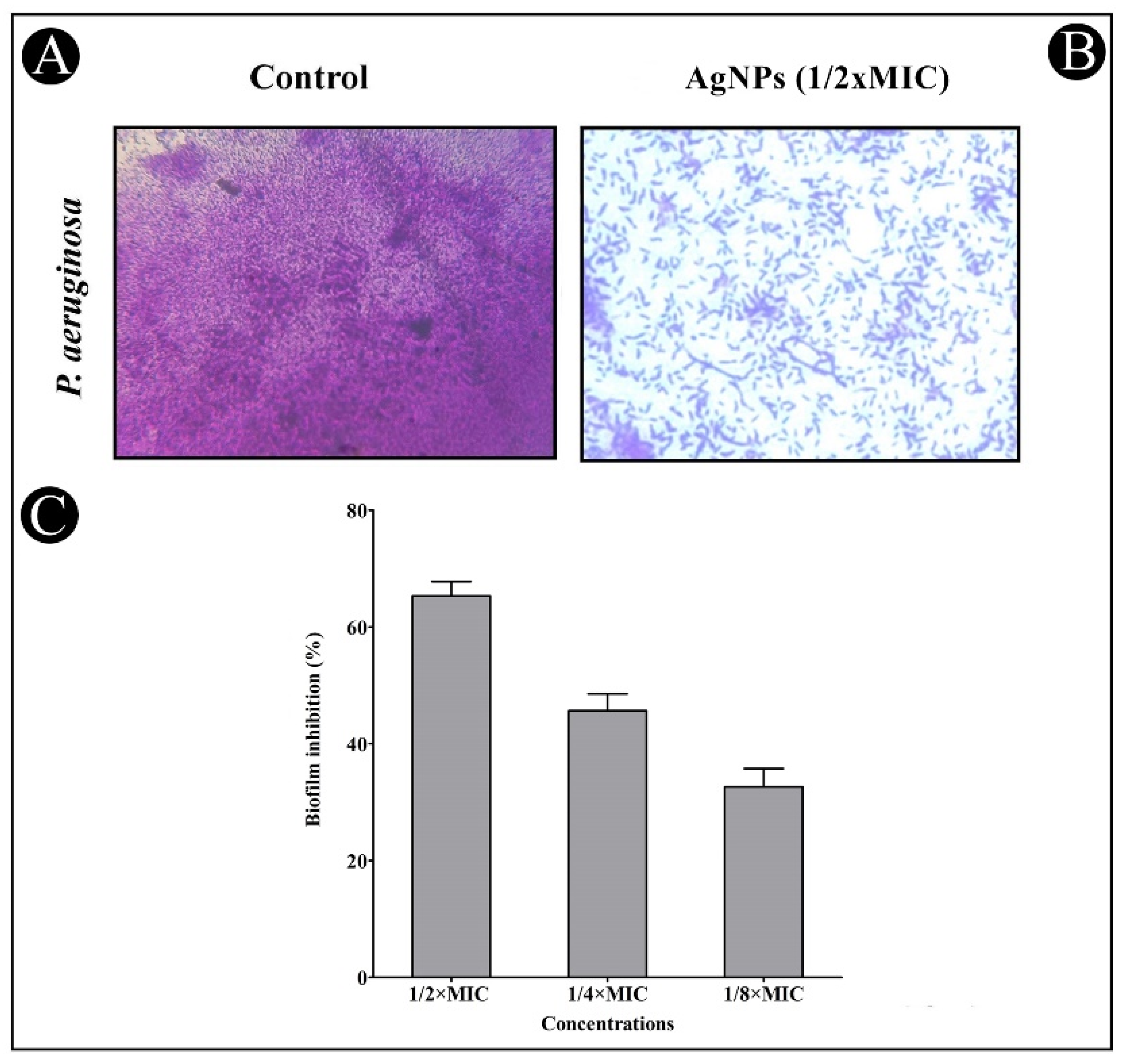
2.5. Antibiofilm Potential of AgNPs
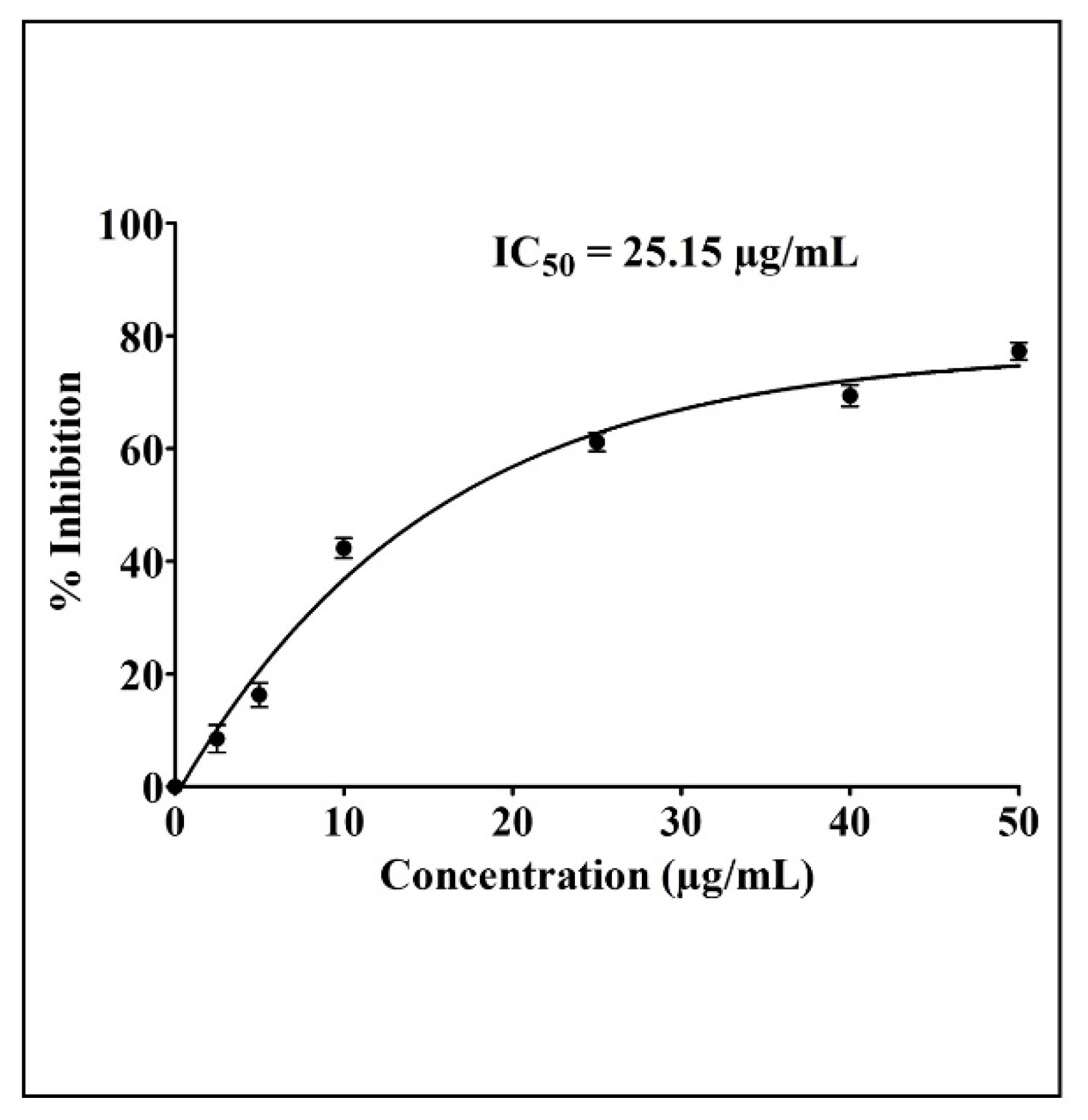
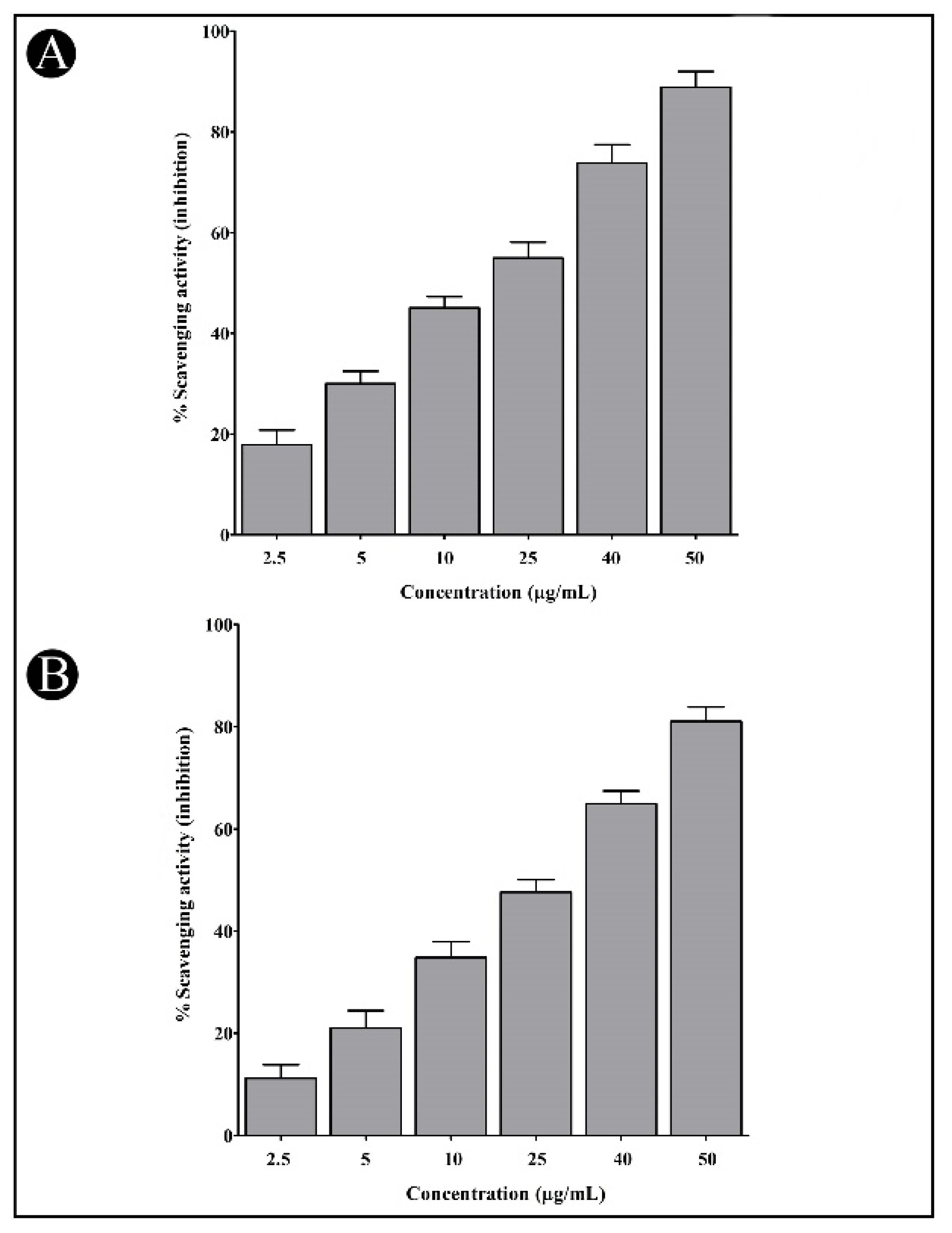
2.6. Antioxidant Potential of Synthesized AgNPs
2.7. Identification of Phytochemical Constituents by GC–MS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Extract Preparation and Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles
4.2. Biophysical Characterization of Synthesized AgNPs
4.3. Cytotoxic Assay (MTT Assay)
4.4. Wound-Healing Assay
4.5. Transwell Migration Assay
4.6. Screening of Antibacterial Activity of Synthesized AgNPs
4.6.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.6.2. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
4.7. Quorum Sensing Inhibitory Activity in C. violaceum
4.7.1. Evaluation of Anti-Quorum-Sensing (QS) Activity
4.7.2. Violacein Inhibition Assay
4.7.3. Quantification of Acyl Homoserine Lactones (AHLs)
4.8. Quorum-Sensing Inhibitory Activity in P. aeruginosa
4.8.1. Quantitative Analysis of Pyocyanin Production in P. aeruginosa
4.8.2. LasA Staphylolytic Assay
4.8.3. LasB Elastase Assay
4.8.4. Azocasein Assay for Proteolytic Activity
4.8.5. Extraction and Estimation of Exopolysaccharides (EPS)
4.9. Antibiofilm Assay
In Situ Visualization of Biofilms
4.10. Determination of DPPH Free-Radical-Scavenging Activity
4.11. Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide Scavenging Activity
4.12. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrophotometry (GC–MS) Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Weiderpass, E. The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer 2021, 127, 3029–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Estimates 2020: Deaths by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country andby Region, 2000–2019; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muteeb, G.; Rehman, M.T.; Ali, S.Z.; Al-Shahrani, A.M.; Kamal, M.A.; Ashraf, G.M. Phage Display Technique: A Novel Medicinal Approach to Overcome an tibiotic Resistance by Using Peptide-Based Inhibitors Against β-Lactamases. Curr. Drug Metab. 2017, 18, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oves, M.; Aslam, M.; Rauf, M.A.; Qayyum, S.; Qari, H.A.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, M.Z.; Tabrez, S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Ismail, I.M.I. Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from the root hair extract of Phoenix dactylifera. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 89, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, V.V.; Siwale, R.; Singh, A.; Mody, H.R. Introduction to metallic nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Jiménez, B.; Johnson, M.E.; Montoro Bustos, A.R.; Murphy, K.E.; Winchester, M.R.; Vega Baudrit, J.R. Silver Nanoparticles: Technological Advances, Societal Impacts, and Metrological Challenges. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gengan, R.M.; Anand, K.; Phulukdaree, A.; Chuturgoon, A. A549 lung cell line activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Albizia adianthifolia leaf. Colloids Surfaces. B Biointerfaces 2013, 105, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraj, M.; Rajesh, M.; Arun, R.; MubarakAli, D.; Sathishkumar, G.; Sivanandhan, G.; Dev, G.K.; Manickavasagam, M.; Premkumar, K.; Thajuddin, N.; et al. An investigation on the cytotoxicity and caspase-mediated apoptotic effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using Podophyllum hexandrum on human cervical carcinoma cells. Colloids Surfaces. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanpui, P.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Induction of apoptosis in cancer cells at low silver nanoparticle concentrations using chitosan nanocarrier. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Deng, K.K.; Kim, N.J.; Ross, L., Jr.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Hu, Z. The inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles, silver ions, and silver chloride colloids on microbial growth. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3066–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Kong, Y.; Wang, X.; Ginoble Pandoli, O.; Gao, G. Synergetic Antibacterial Effects of Silver Nanoparticles@Aloe Vera Prepared via a Green Method. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2010, 2, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, B.R.; Naqvi, A.H.; Singh, H.B. Potential of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Stenotrophomonas sp. BHU-S7 (MTCC 5978) for management of soil-borne and foliar phytopathogens. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, H.; Banihashemi, S. Sol-gel-based silver nanoparticles-doped silica—Polydiphenylamine nanocomposite for micro-solid-phase extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 886, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, S.; Nakashima, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Wada, S. Synthesis of Silver-Strontium Titanate Hybrid Nanoparticles by Sol-Gel-Hydrothermal Method. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, K.; Ahmed, B.; Dwivedi, S.; Saquib, Q.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Musarrat, J. Microwave Accelerated Green Synthesis of Stable Silver Nanoparticles with Eucalyptus globulus Leaf Extract and Their Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity on Clinical Isolates. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddinedi, S.B.; Mandal, B.K.; Maddili, S.K. Biofabrication of size controllable silver nanoparticles—A green approach. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 167, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmath, P.; Baker, S.; Rakshith, D.; Satish, S. Corrigendum to “Mycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles bearing antibacterial activity”. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K.; Shim, M.S. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Marine Algae Ecklonia cava. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjikar, A.P.; Hugar, A.L.; Londonkar, R.L. Characterization of phyto-nanoparticles from Ficus krishnae for their antibacterial and anticancer activities. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulfraz, M.; Sadiq, A.; Tariq, H.; Imran, M.; Qureshi, R. Phytochemical analysis and antibacterial activity of Eruca sativa seed. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Di Gioia, F.; Avato, P.; Serio, F.; Argentieri, M.P. Glucosinolate profile of Eruca sativa, Diplotaxis tenuifolia and Diplotaxis erucoides grown in soil and soilless systems. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 69, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqasoumi, S.; Al-Sohaibani, M.; Al-Howiriny, T.; Al-Yahya, M.; Rafatullah, S. Rocket “Eruca sativa”: A salad herb with potential gastric anti-ulcer activity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1958–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhair, T. Phytochemicals Screening by GC/MS and Determination of Some Flavonol in Cultivated Iraqi Eruca sativa Dried Leaves Extract and its Biological Activity as Antioxidant. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2016, 8, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar]
- Nurzyńska-Wierdak, R. Nutritional and energetic value of Eruca sativa Mill. leaves. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2015, 14, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Jirovetz, L.; Smith, D.; Buchbauer, G. Aroma compound analysis of Eruca sativa (Brassicaceae) SPME headspace leaf samples using GC, GC-MS, and olfactometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4643–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazif, N.M.; Habib, A.A.E.; Tawfik, W.A.M.; Hassan, R.A. Chemical composition and cytotoxic activity of Eruca sativa L. Seeds cultivated in Egypt. Asian J. Chem. 2010, 22, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, S.A. Phytochemical Study of Vsome Medicinal Compounds Present in Hedera helix L. Plant Cultivated in Iraq. Master’s Thesis, Baghdad University, Baghdad, Iraq, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alaraidh, I.A.; Ibrahim, M.M.; El-Gaaly, G.A. Evaluation of Green Synthesis of Ag Nanoparticles Using Eruca sativa and Spinacia oleracea Leaf Extracts and Their Antimicrobial Activity. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 12, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cushing, B.L.; Kolesnichenko, V.L.; O’Connor, C.J. Recent Advances in the Liquid-Phase Syntheses of Inorganic Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 3893–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajitha, B.; Ashok Kumar Reddy, Y.; Sreedhara Reddy, P. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Lantana camara leaf extract. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 49, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, A.; Wu, S.; Senyuan, C.; Zhang, H.; Shao, W.; Xiao, Z. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles with Tunable Morphologies via a Reverse Nano-Emulsion Route. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aritonang, H.F.; Onggo, D.; Ciptati, C.; Radiman, C.L. Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles from K2PtCl4 Solution Using Bacterial Cellulose Matrix. J. Nanoparticles 2014, 2014, 285954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dos Santos, M.M.; Queiroz, M.J.; Baptista, P.V. Enhancement of antibiotic effect via gold:silver-alloy nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Muñoz, R.; Borrego, B.; Juárez-Moreno, K.; García-García, M.; Mota Morales, J.D.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Huerta-Saquero, A. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in biological systems: Does the complexity of biological systems matter? Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 276, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kwon, S.; Ostler, E. Antimicrobial effect of silver-impregnated cellulose: Potential for antimicrobial therapy. J. Biol. Eng. 2009, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zielińska, A.; Skwarek, E.; Zaleska, A.; Gazda, M.; Hupka, J. Preparation of silver nanoparticles with controlled particle size. Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulfinger, L.; Solomon, S.; Bahadory, M.; Jeyarajasingam, A.; Rutkowsky, S.; Boritz, C. Synthesis and Study of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Educ. 2007, 84, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirovetz, L.; Buchbauer, G.; Shafi, M.P.; Leela, N.K. Analysis of the essential oils of the leaves, stems, rhizomes and roots of the medicinal plant Alpinia galanga from southern India. Acta Pharm. 2003, 53, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Chandran, S.P.; Chaudhary, M.; Pasricha, R.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Synthesis of gold nanotriangles and silver nanoparticles using Aloe vera plant extract. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.-Y.; et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.V.; Parkinson, C.V.; Choi, Y.W.; Speshock, J.L.; Hussain, S.M. A Preliminary Assessment of Silver Nanoparticle Inhibition of Monkeypox Virus Plaque Formation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galdiero, S.; Falanga, A.; Vitiello, M.; Cantisani, M.; Marra, V.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antiviral agents. Molecules 2011, 16, 8894–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Zaidi, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Ahmed, F.; Ahmad, E.; Sherwani, A.; Owais, M.; Azam, A. Antibacterial and cytotoxic efficacy of extracellular silver nanoparticles biofabricated from chromium reducing novel OS4 strain of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhuyan, T.; Mishra, K.; Khanuja, M.; Prasad, R.; Varma, A. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 32, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.; Pandey, R.; Barman, I.; Prasad, R. Leveraging the Attributes of Mucor hiemalis-Derived Silver Nanoparticles for a Synergistic Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Platform. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awadelkareem, A.M.; Al-Shammari, E.; Elkhalifa, A.E.O. Phytochemical and In Silico ADME/Tox Analysis of Eruca sativa Extract with Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Anticancer Potential against Caco-2 and HCT-116 Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Lines. Molecules 2022, 27, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadelkareem, A.M.; Al-Shammari, E.; Elkhalifa, A.O. Anti-Adhesion and Antibiofilm Activity of Eruca sativa Miller Extract Targeting Cell Adhesion Proteins of Food-Borne Bacteria as a Potential Mechanism: Combined In Vitro-In Silico Approach. Plants 2022, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.G.; Mamidyala, S.K. Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles using culture supernatant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Colloids Surfaces. B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamal, G.; Sharmila, P.; Rao, K.S.; Pardha-Saradhi, P. Inbuilt Potential of YEM Medium and Its Constituents to Generate Ag/Ag2O Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvi, B.; Madhavan, J.; Santhanam, A. Cytotoxic effect of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Padina tetrastromatica on breast cancer cell line. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Beulaja, M.; Thiagarajan, R.; Palanisamy, S.; Goutham, G.; Koodalingam, A.; Prabhu, N.M.; Kannapiran, E.; Basu, M.J.; Arulvasu, C.; et al. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Phyllanthus acidus L. fruits and characterization of its anti-inflammatory effect against H2O2 exposed rat peritoneal macrophages. Process Biochem. 2017, 55, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeshehy, E.K.; Elazzazy, A.M.; Aggelis, G. Silver nanoparticles synthesis mediated by new isolates of Bacillus spp., nanoparticle characterization and their activity against Bean Yellow Mosaic Virus and human pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahmoud, W.M.; Abdelmoneim, T.S.; Elazzazy, A.M. The Impact of Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Bacillus pumilus as Antimicrobial and Nematicide. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elkhalifa, A.E.O.; Al-Shammari, E.; Alam, M.J.; Alcantara, J.C.; Khan, M.A.; Eltoum, N.E.; Ashraf, S.A. Okra-Derived Dietary Carotenoid Lutein against Breast Cancer, with an Approach towards Developing a Nutraceutical Product: A Meta-Analysis Study. JPRI 2021, 33, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghlin, C.; Murray, G.I. Current and emerging concepts in tumour metastasis. J. Pathol. 2010, 222, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Lin, H.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Wang, C.J.; Chiang, T.A.; Chen, J.H. Inhibitory effects of andrographolide on migration and invasion in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells via down-regulation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 632, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.A. An attractive force in metastasis. Nature 2001, 410, 24–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Ahmad, W.; Andleeb, S.; Jalil, F.; Imran, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ali, M.; Rafiq, M.; Kamil, M.A. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. JCMA 2018, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Patel, M.; Deshpande, S.; Alreshidi, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Reddy, M.N.; Emira, N.; De Feo, V. Effect of Adiantum philippense Extract on Biofilm Formation, Adhesion with Its Antibacterial Activities against Foodborne Pathogens, and Characterization of Bioactive Metabolites: An in vitro-in silico Approach. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegari, A.; Kheyrolahzadeh, K.; Hosseiniyan Khatibi, S.M.; Sharifi, S.; Memar, M.Y.; Zununi Vahed, S. The Battle of Probiotics and Their Derivatives against Biofilms. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Upadhyay, A.; Upadhyaya, I.; Kollanoor-Johny, A.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Antibiofilm effect of plant derived antimicrobials on Listeria monocytogenes. Food Microbiol. 2013, 36, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onbas, T.; Osmanagaoglu, O.; Kiran, F. Potential Properties of Lactobacillus plantarum F-10 as a Bio-control Strategy for Wound Infections. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Contreras, R.; Nuñez-López, L.; Jasso-Chávez, R.; Kwan, B.W.; Belmont, J.A.; Rangel-Vega, A.; Maeda, T.; Wood, T.K. Quorum sensing enhancement of the stress response promotes resistance to quorum quenching and prevents social cheating. ISME J. 2015, 9, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sybiya Vasantha Packiavathy, I.A.; Agilandeswari, P.; Musthafa, K.S.; Karutha Pandian, S.; Veera Ravi, A. Antibiofilm and quorum sensing inhibitory potential of Cuminum cyminum and its secondary metabolite methyl eugenol against Gram negative bacterial pathogens. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, F.M.; Ahmad, I. Doxycycline interferes with quorum sensing-mediated virulence factors and biofilm formation in gram-negative bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adonizio, A.; Kong, K.F.; Mathee, K. Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by South Florida plant extracts. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessler, E.; Safrin, M.; Olson, J.C.; Ohman, D.E. Secreted LasA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a staphylolytic protease. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 7503–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winstanley, C.; Fothergill, J.L. The role of quorum sensing in chronic cystic fibrosis Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 290, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vattem, D.A.; Mihalik, K.; Crixell, S.H.; McLean, R.J. Dietary phytochemicals as quorum sensing inhibitors. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Makris, G.C. Probiotic bacteria and biosurfactants for nosocomial infection control: A hypothesis. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 71, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, B.; Rostami, A.; Momeni, S.S. Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using seed aqueous extract of Pistacia atlantica and its antibacterial activity. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 134, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Jagan, E.G.; Rajasekar, S.; Selvakumar, P.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Mohan, N. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acalypha indica leaf extracts and its antibacterial activity against water borne pathogens. Colloids Surfaces. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.; Tripathi, R.M.; Zafar, F.; Singh, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous solution of Ficus benghalensis leaf extract and characterization of their antibacterial activity. Mater. Lett. 2012, 67, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, A.; Salem, N. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Mulberry Leaves Extract. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidhu, V.K.; Aromal, S.A.; Philip, D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Macrotyloma uniflorum. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 83, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, H.; Bhui, D.K.; Sahoo, G.P.; Sarkar, P.; Pyne, S.; Misra, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using seed extract of Jatropha curcas. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 348, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, C.; Chávez, V.H.; Barriga-Castro, E.D.; Núñez, N.O.; Mendoza-Reséndez, R. Biosynthesis of silver fine particles and particles decorated with nanoparticles using the extract of Illicium verum (star anise) seeds. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 141, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cruz Paula, A. Characterization of Different Breast Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes in Proliferative, Pre-malignant and Neoplastic Lesions of the Breast: Associations with Breast Cancer Behavior and Progression. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- El-Naggar, N.E.-A.; Hussein, M.H.; El-Sawah, A.A. Bio-fabrication of silver nanoparticles by phycocyanin, characterization, in vitro anticancer activity against breast cancer cell line and in vivo cytotxicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, M.N.; Adnan, M.; Alreshidi, M.M.; Saeed, M.; Patel, M. Evaluation of Anticancer, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties of a Medicinally Treasured Fern Tectaria coadunata with its Phytoconstituents Analysis by HR-LCMS. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnan, M.; Siddiqui, A.J. Deciphering the Molecular Mechanism Responsible for Efficiently Inhibiting Metastasis of Human Non-Small Cell Lung and Colorectal Cancer Cells Targeting the Matrix Metalloproteinases by Selaginella repanda. Plants 2021, 10, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-G.; Ma, L.; Lin, S.-H.; Wu, Y.-B.; Yi, J.; Yang, B.-J.; Wu, J.-Z.; Wong, K.-H. Anticancer and anti-angiogenic activities of extract from Actinidia eriantha Benth root. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 203, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, F.M.; Ahmad, I.; Al-Thubiani, A.S.; Abulreesh, H.H.; AlHazza, I.M.; Aqil, F. Leaf Extracts of Mangifera indica L. Inhibit Quorum Sensing—Regulated Production of Virulence Factors and Biofilm in Test Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blosser, R.S.; Gray, K.M. Extraction of violacein from Chromobacterium violaceum provides a new quantitative bioassay for N-acyl homoserine lactone autoinducers. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghadosi, R.; Shakibaie, M.R.; Masoumi, S. Biochemical detection of N-Acyl homoserine lactone from biofilm-forming uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from urinary tract infection samples. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 3, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Essar, D.W.; Eberly, L.; Hadero, A.; Crawford, I.P. Identification and characterization of genes for a second anthranilate synthase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Interchangeability of the two anthranilate synthases and evolutionary implications. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huston, A.L.; Methe, B.; Deming, J.W. Purification, characterization, and sequencing of an extracellular cold-active aminopeptidase produced by marine psychrophile Colwellia psychrerythraea strain 34H. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3321–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkatramanan, M.; Sankar Ganesh, P.; Senthil, R.; Akshay, J.; Veera Ravi, A.; Langeswaran, K.; Vadivelu, J.; Nagarajan, S.; Rajendran, K.; Shankar, E.M. Inhibition of Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in Chromobacterium violaceum by Fruit Extracts of Passiflora edulis. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 25605–25616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musthafa, K.S.; Ravi, A.V.; Annapoorani, A.; Packiavathy, I.S.; Pandian, S.K. Evaluation of anti-quorum-sensing activity of edible plants and fruits through inhibition of the N-acyl-homoserine lactone system in Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chemotherapy 2010, 56, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruch, R.J.; Cheng, S.J.; Klaunig, J.E. Prevention of cytotoxicity and inhibition of intercellular communication by antioxidant catechins isolated from Chinese green tea. Carcinogenesis 1989, 10, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, S.A.; Al-Shammari, E.; Hussain, T.; Tajuddin, S.; Panda, B.P. In-vitro antimicrobial activity and identification of bioactive components using GC-MS of commercially available essential oils in Saudi Arabia. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3948–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Bacterial Strains | MIC of AgNPs (µg/mL) | Sub MICs of AgNPs Selected for Assays (µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ½ MIC | ¼ MIC | 1/8 MIC | ||
| C. violaceum | 12.5 | 6.25 | 3.12 | 1.56 |
| P. aeruginosa | 25 | 12.5 | 6.25 | 3.12 |
| Compounds | RT (min.) | Molecular Formula | Structure | Fragmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tricyclo[5.3.0.0(4,8)]decane | 7.138 | C10H16 | 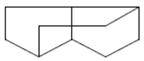 | 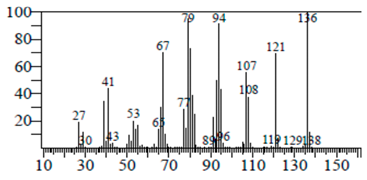 |
| Thiepane | 7.918 | C4H4S |  |  |
| 4H-Pyran-4-one, 2,3-dihydro-3,5 | 8.205 | C6H8O4 |  |  |
| Dodecane | 8.597 | C12H26 |  |  |
| D-Glucitol, 4-O-hexyl- | 8.966 | C18H26O12 |  |  |
| Tetradecane, 1-iodo- | 10.198 | C14H29I | 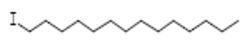 | 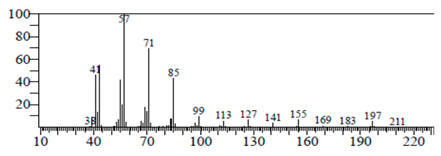 |
| Phenol, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl | 11.044 | C27H50OP2 | 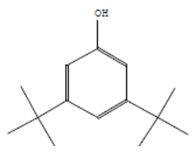 | 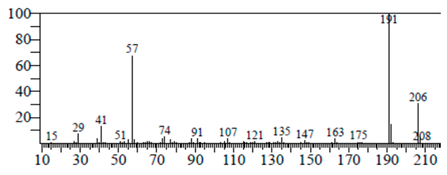 |
| Sulforaphane nitrile | 11.131 | C6H11NOS2 |  | 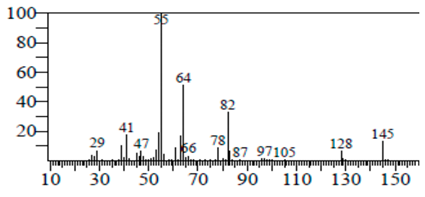 |
| Piperidine, 1-methanesulfonyl-4-methoxy | 12.533 | C13H19NO3S |  | 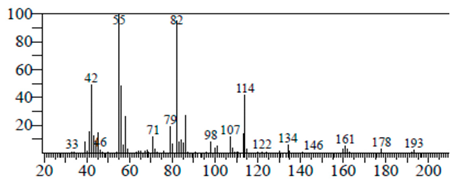 |
| 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid | 14.912 | C18H30O2 |  | 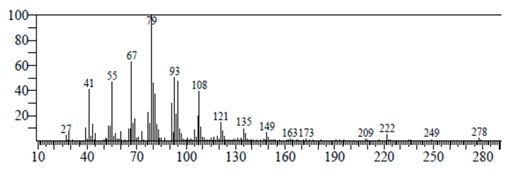 |
| Phytol | 17.807 | C20H40O |  | 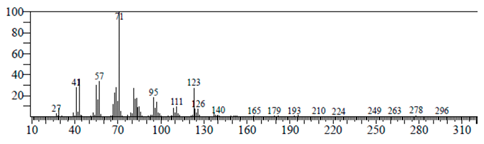 |
| Dicyclohexyl sulfide | 18.711 | C12H22S2 | 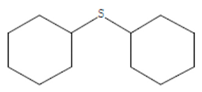 |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Awadelkareem, A.M.; Al-Shammari, E.; Elkhalifa, A.O.; Adnan, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Patel, M.; Khan, M.I.; Mehmood, K.; Ashfaq, F.; Badraoui, R.; et al. Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Eruca sativa Miller Leaf Extract Exhibits Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Antibiofilm, and Anti-Metastatic Activities. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070853
Awadelkareem AM, Al-Shammari E, Elkhalifa AO, Adnan M, Siddiqui AJ, Patel M, Khan MI, Mehmood K, Ashfaq F, Badraoui R, et al. Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Eruca sativa Miller Leaf Extract Exhibits Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Antibiofilm, and Anti-Metastatic Activities. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(7):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070853
Chicago/Turabian StyleAwadelkareem, Amir Mahgoub, Eyad Al-Shammari, AbdElmoneim O. Elkhalifa, Mohd Adnan, Arif Jamal Siddiqui, Mitesh Patel, Mohammad Idreesh Khan, Khalid Mehmood, Fauzia Ashfaq, Riadh Badraoui, and et al. 2022. "Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Eruca sativa Miller Leaf Extract Exhibits Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Antibiofilm, and Anti-Metastatic Activities" Antibiotics 11, no. 7: 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070853
APA StyleAwadelkareem, A. M., Al-Shammari, E., Elkhalifa, A. O., Adnan, M., Siddiqui, A. J., Patel, M., Khan, M. I., Mehmood, K., Ashfaq, F., Badraoui, R., & Ashraf, S. A. (2022). Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Eruca sativa Miller Leaf Extract Exhibits Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Antibiofilm, and Anti-Metastatic Activities. Antibiotics, 11(7), 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070853













