Expanding Horizons in Advancements of FRET Biosensing Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
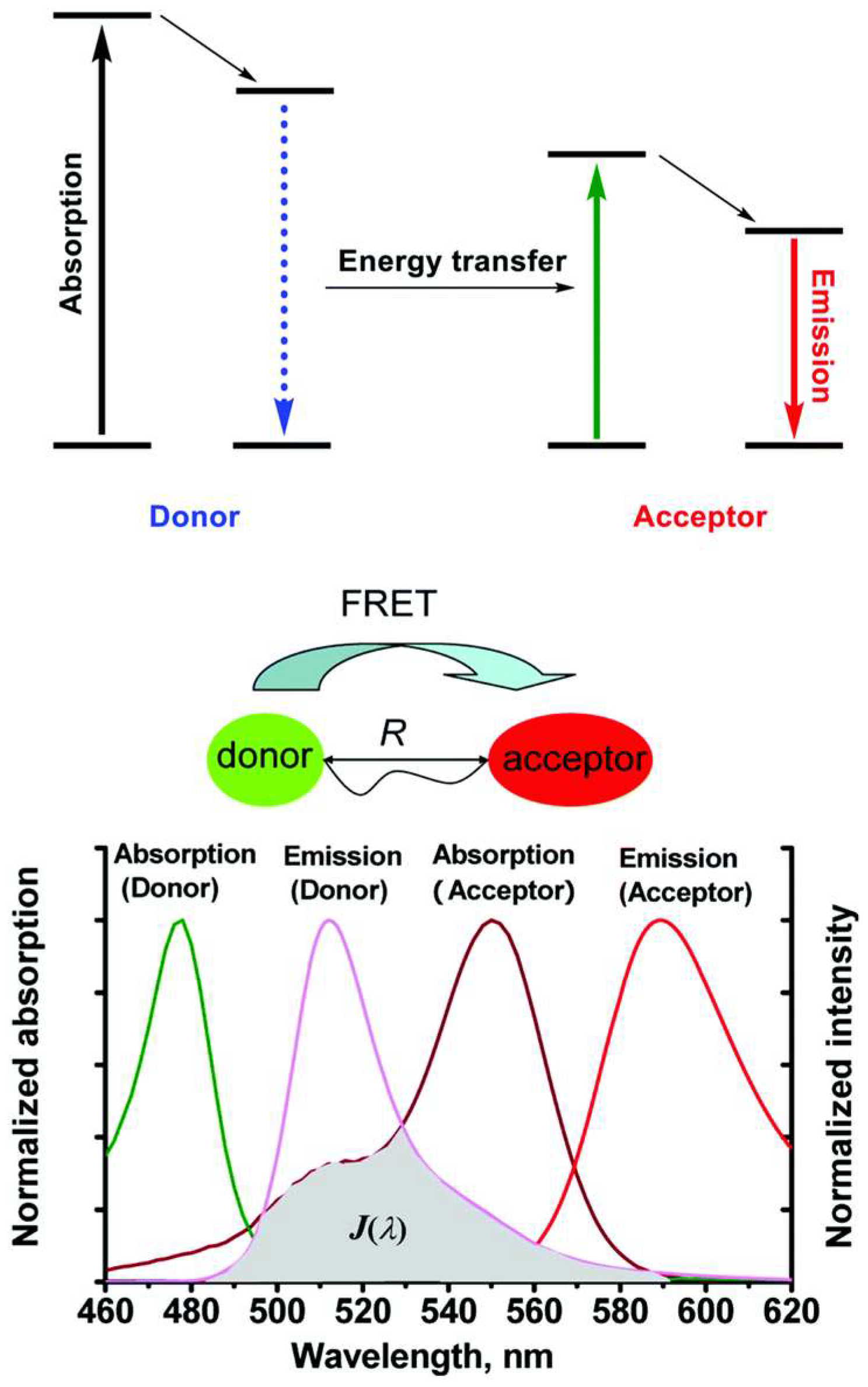
Principle of FRET
2. Applications for FRET Biosensors
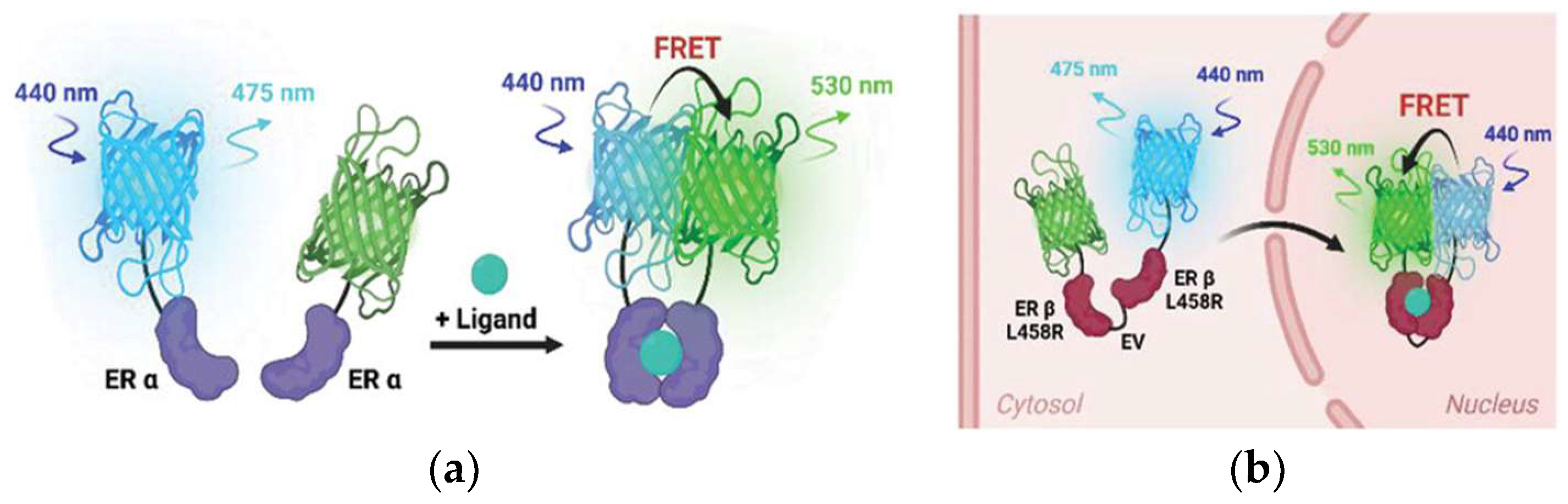
2.1. Cellular Imaging
2.1.1. Disease-Targeted Cellular Imaging Using FRET Biosensors
2.1.2. Enhancing the Signal Stability and Imaging Quality in Live Cells
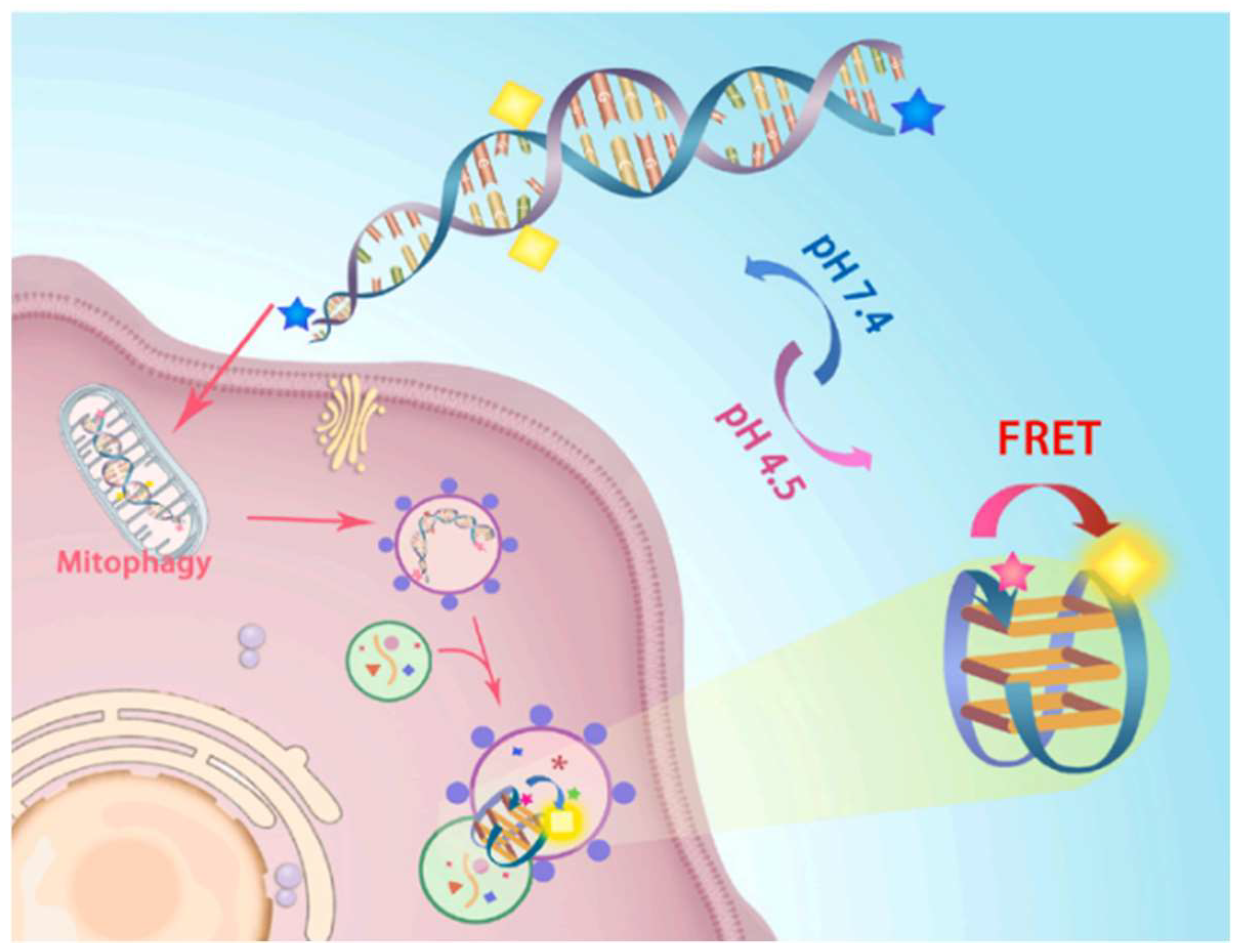
2.1.3. FRET Biosensor for Monitoring Mitochondrial Autophagy
2.1.4. FRET Biosensor for Cardiac and Kinase Activity
2.2. Drug Discovery
2.2.1. FcRn Antagonist Screening Using Phase Transition-Based FRET (PT-FRET)
2.2.2. FRET-Based Drug Efficacy Screening in Cancer Models
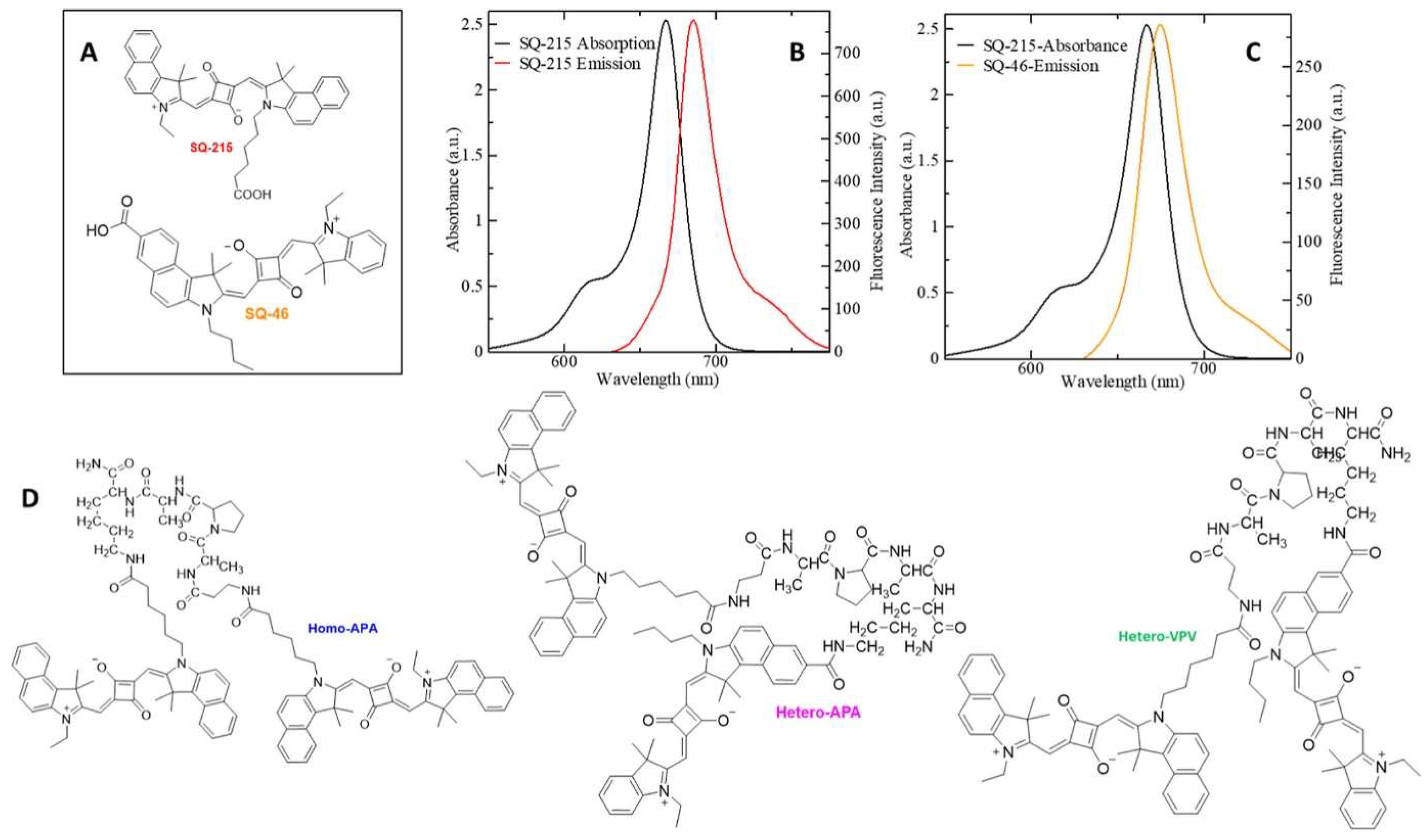
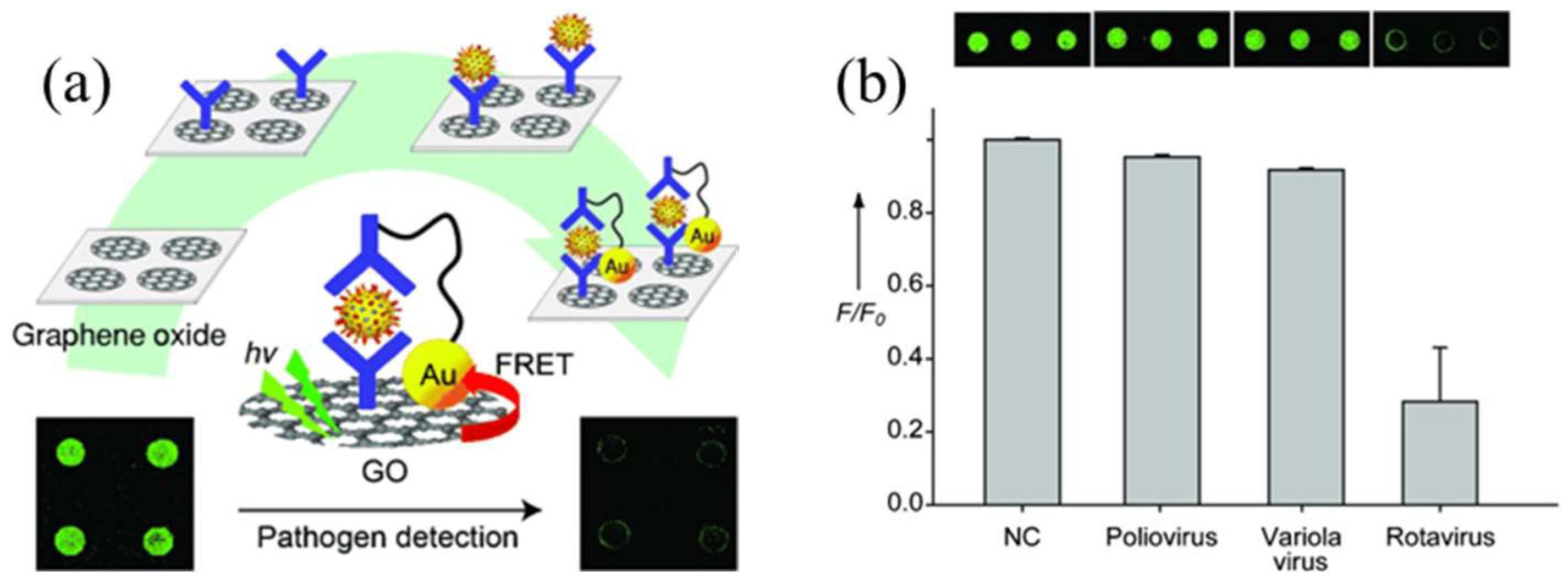
2.3. FRET Biosensors for Pathogen Detection
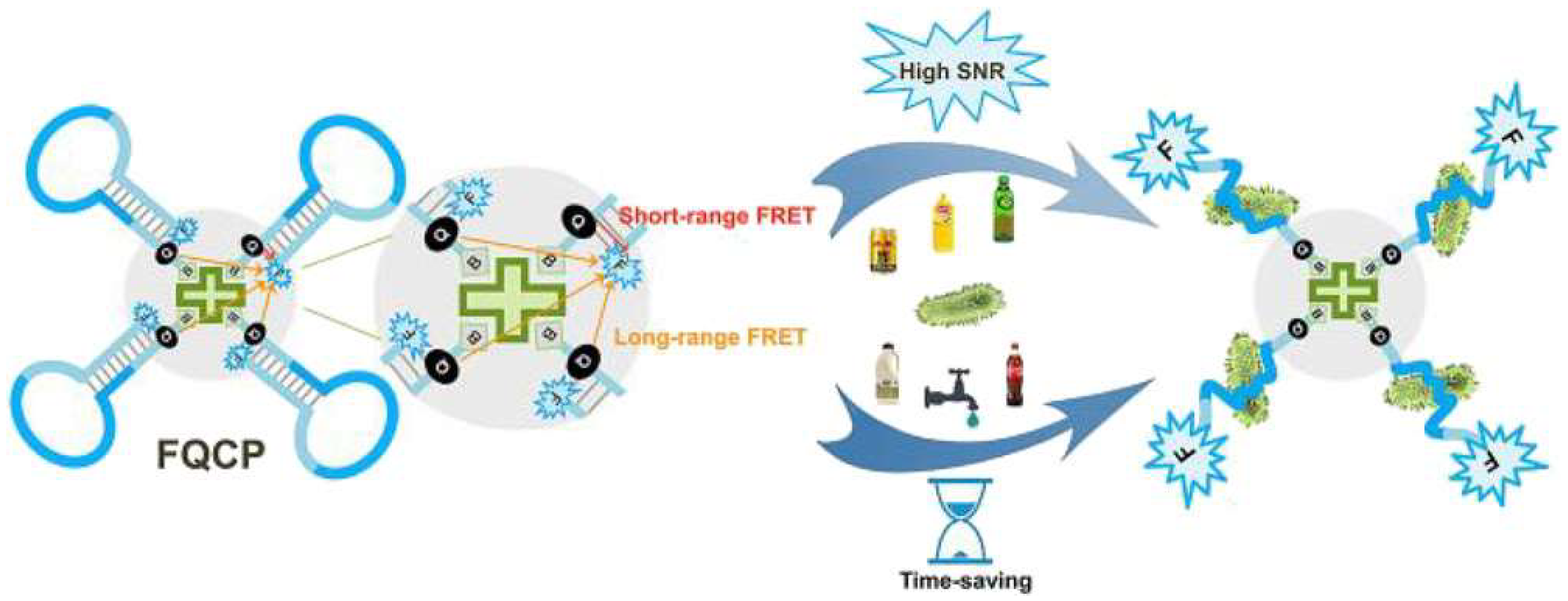
2.3.1. Detection of Bacterial Pathogens
2.3.2. Detection of Viral Pathogens
2.3.3. Detection of Fungal Pathogens
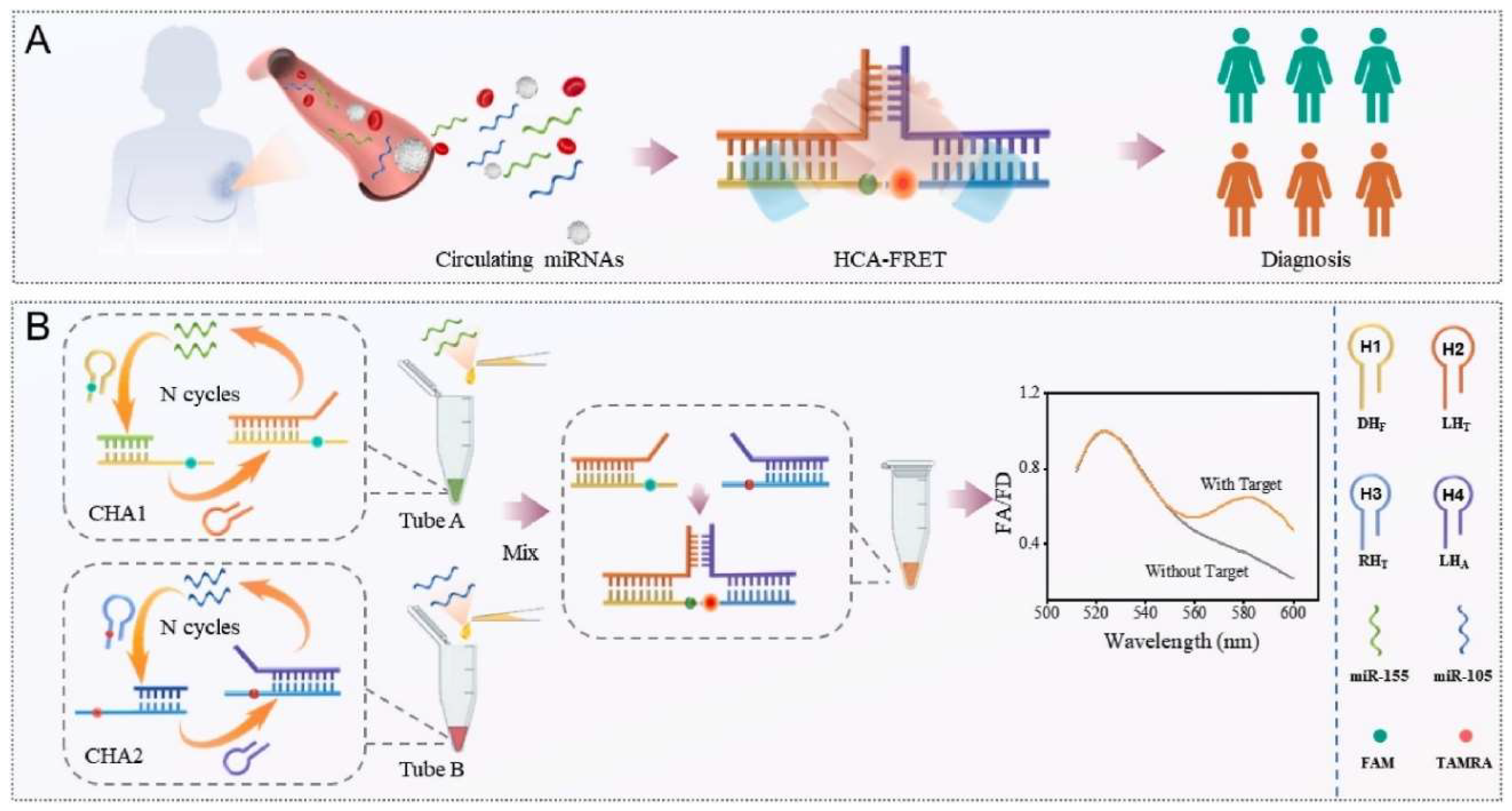
2.4. Cancer Research
3. Challenges and Limitations of FRET Biosensors
4. Summary and Outlook of FRET Biosensors
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zadran, S.; Standley, S.; Wong, K.; Otiniano, E.; Amighi, A.; Baudry, M. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based biosensors: Visualizing cellular dynamics and bioenergetics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Xie, K.; Zou, G. Advances in spiropyrans/spirooxazines and applications based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) with fluorescent materials. Molecules 2017, 22, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapp, A.R.; Medintz, I.L.; Mattoussi, H. Förster resonance energy transfer investigations using quantum-dot fluorophores. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Song, F.; Xiong, X.; Peng, X. Fluorescent nanosensors based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 11228–11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Huang, C.; Emery, B.P.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Bull, S.D.; He, X.-P.; Tian, H.; Yoon, J.; Sessler, J.L.; James, T.D. Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based small-molecule sensors and imaging agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5110–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Lin, W.; Zheng, K.; Zhu, S. FRET-based small-molecule fluorescent probes: Rational design and bioimaging applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Samson, A.A.S.; Song, J.M. Application of fluorescence resonance energy transfer to bioprinting. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.C.; Li, S.Y.; Ni, S.; Liu, G. Advances in FRET-based biosensors from donor-acceptor design to applications. Aggregate 2024, 5, e460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Plaxco, K.W.; Heeger, A.J. Biosensors based on binding-modulated donor–acceptor distances. TRENDS Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, T.M.; Li, A.; Grant, B.D.; Peterson, K.; Yuen, S.; Bawaskar, P.; Kleinboehl, E.; Li, J.; Thomas, D.D.; Gillispie, G.D. Red-shifted FRET biosensors for high-throughput fluorescence lifetime screening. Biosensors 2018, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, E.; Kiyokawa, E. Future perspective of single-molecule FRET biosensors and intravital FRET microscopy. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Komatsu, N.; Hirata, E.; Kamioka, Y.; Matsuda, M. Stable expression of FRET biosensors: A new light in cancer research. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, W.; Rubart, M.; Ryan, J.; Xiao, X.; Qiao, C.; Hato, T.; Davidson, M.W.; Dunn, K.W.; Day, R.N. A practical method for monitoring FRET-based biosensors in living animals using two-photon microscopy. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2015, 309, C724–C735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-W.; Yang, J.-M.; Chen, C.-C.; Au, G.; Wang, S.; Chern, G.-W.; Huang, C.-H. Calibration of FRET-based biosensors using multiplexed biosensor barcoding. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Bazan, G.C.; Liu, B. Conjugated-polymer-amplified sensing, imaging, and therapy. Chem 2017, 2, 760–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, F.; Francés-Soriano, L.; Andrigo, V.; Natile, M.M.; Hildebrandt, N. Optimizing upconversion nanoparticles for FRET biosensing. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 4971–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Nir, E.; Hamadani, K.; Weiss, S. Photobleaching pathways in single-molecule FRET experiments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 4643–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, J.A.; Poland, S.P.; Krstajic, N.; Pfisterer, K.; Erdogan, A.; Barber, P.R.; Parsons, M.; Henderson, R.K.; Ameer-Beg, S.M. Quantitative real-time imaging of intracellular FRET biosensor dynamics using rapid multi-beam confocal FLIM. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Chen, L.; Pan, M.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, D. Tailored biosensors for drug screening, efficacy assessment, and toxicity evaluation. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 3146–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Xu, Q.; Xu, H. Bacterial detection based on Förster resonance energy transfer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 255, 116244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, N.; Hong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shafi, S.; Pan, J.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Hou, W. Application of fluorescent nano-biosensor for the detection of cancer bio-macromolecular markers. Polym. Test. 2022, 115, 107746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Kaur, P.; Ahuja, S. Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and applications thereof. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 5532–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Zhang, P.; Beratan, D.N. Predicting dexter energy transfer interactions from molecular orbital overlaps. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 18956–18960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baibakov, M.; Patra, S.; Claude, J.-B.; Moreau, A.; Lumeau, J.; Wenger, J. Extending single-molecule Forster resonance energy transfer (FRET) Range beyond 10 nanometers in zero-mode waveguides. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8469–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhong, H.; Yang, K.; Pan, K.; Zhao, B.; Deng, J. Energy transfer for constructing circularly polarized luminescence materials: Recent progress and future prospects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2417308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, C.E.; Brown, C.W.; Medintz, I.L.; Delehanty, J.B. Intracellular FRET-based probes: A review. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2015, 3, 042006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Dridi, N.; Palui, G.; Palomo, V.; Jokerst, J.V.; Dawson, P.E.; Sang, Q.-X.A.; Mattoussi, H. Quantum Dot–Peptide Conjugates as Energy Transfer Probes for Sensing the Proteolytic Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase-14. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Deb, S.; Hussain, S.; Dey, D.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Alodhayb, A.N.; Hussain, S.; Hussain, S.A. Spectroscopic investigation of two xanthane dyes and design of a FRET based pesticide sensor. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Akram, W.; Ye, F.; Jin, J.; Niu, F.; Ahmed, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Dong, S.C.; Li, G. Förster Resonance Energy Transfer in Metal Halide Perovskite: Current Status and Future Prospects. ChemistryOpen 2025, 14, e202400118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryer, L. Fluorescence energy transfer as a spectroscopic ruler. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1978, 47, 819–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Hohng, S.; Ha, T. A practical guide to single-molecule FRET. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Foote, A.; Ogasawara, H.; Al Abdullatif, S.; Batista, V.S.; Salaita, K. Digital and Tunable Genetically Encoded Tension Sensors Based on Engineered Coiled-Coils. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2025, 64, e202407359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Long, S.; Xiong, T.; Zhao, X.; Sun, W.; Du, J.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. Single-Molecule Förster Resonance Energy Transfer-Based Photosensitizer for Synergistic Photodynamic/Photothermal Therapy. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marras, A.E.; Shi, Z.; Lindell, M.G., III; Patton, R.A.; Huang, C.-M.; Zhou, L.; Su, H.-J.; Arya, G.; Castro, C.E. Cation-Activated Avidity for Rapid Reconfiguration of DNA Nanodevices. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9484–9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbott, J.M.; Wills, R.; Shirke, R.; Hassanein, L.; Weinshenker, D.; Raj, M. Spatiotemporal Imaging of Catechol Aldehydes in Neural Tissue. JACS Au 2025, 5, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavileti, S.K.; Bila, G.; Utka, V.; Bilyy, R., Jr.; Bila, E.; Butoi, E.; Gupta, S.; Balyan, P.; Kato, T.; Bilyy, R.; et al. Squaraine-Peptide Conjugates as Efficient Reporters of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps-Mediated Chronic Inflammation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 9140–9154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lai, S.; Yang, S.; Zhao, S.; Blanco, F.A.; Lyons, A.C.; Merino-Urteaga, R.; Ahrens, J.F.; Nguyen, N.A.; Liu, H.; et al. Bright and photostable yellow fluorescent proteins for extended imaging. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, T.; Gabay, M.; Meenakshisundaram, A.; Levi, Y.; Eid, S.; Malchenko, N.; Maman, M.; Nitzan, A.; Ravotto, L.; Zaidel-Bar, R. Genetically encoded biosensor for fluorescence lifetime imaging of PTEN dynamics in the intact brain. Nat. Methods 2025, 22, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleja, N.; Mohsin, M. Exploring the landscape of FRET-based molecular sensors: Design strategies and recent advances in emerging applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 77, 108466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.Q.; Arai, S. Quantitative Imaging of Genetically Encoded Fluorescence Lifetime Biosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Noumani, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Solanki, P.R. FRET Based Biosensor: Principle Applications Recent Advances and Challenges. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ding, F.; Zhou, Z.; He, X.; Shen, J. FRET-based sensor for visualizing pH variation with colorimetric/ratiometric strategy and application for bioimaging in living cells, bacteria and zebrafish. Analyst 2020, 145, 4283–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Sun, R.; Sun, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, L.; Yao, L.; Tang, Y. A FRET biosensor constructed using pH sensitive G-quadruplex DNA for detecting mitochondrial autophagy. Talanta 2025, 281, 126885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, B.; Nitu, F.R.; Rebbeck, R.T.; McGurran, L.M.; Oda, T.; Thomas, D.D.; Bers, D.M.; Cornea, R.L. Molecular Mechanism of a FRET Biosensor for the Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor Pathologically Leaky State. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Pan, Y.; Deng, L. Development of FRET Biosensor to Characterize CSK Subcellular Regulation. Biosensors 2024, 14, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Sun, J.; Chien, S.; Wang, Y. Determination of hierarchical relationship of Src and Rac at subcellular locations with FRET biosensors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14353–14358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, X. Application of Fluorescence- and Bioluminescence-Based Biosensors in Cancer Drug Discovery. Biosensors 2024, 14, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Clemens, S.; Gao, P.; Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, P.; Johnsson, K.; Wang, L. Fluorogenic rhodamine-based chemigenetic biosensor for monitoring cellular NADPH dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 20569–20576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopnarine, O.; Yuen, S.L.; Thompson, A.R.; Roelike, L.N.; Rebbeck, R.T.; Bidwell, P.A.; Aldrich, C.C.; Cornea, R.L.; Thomas, D.D. Fluorescence lifetime FRET assay for live-cell high-throughput screening of the cardiac SERCA pump yields multiple classes of small-molecule allosteric modulators. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muretta, J.M.; Rajasekaran, D.; Blat, Y.; Little, S.; Myers, M.; Nair, C.; Burdekin, B.; Yuen, S.L.; Jimenez, N.; Guhathakurta, P.; et al. HTS driven by fluorescence lifetime detection of FRET identifies activators and inhibitors of cardiac myosin. SLAS Discov. 2023, 28, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, R.L.; Yuen, S.L.; Rebbeck, R.T.; Svensson, B.; Roopnarine, O.; Thomas, D.D. Live-cell FRET biosensors for high-throughput screening targeting the SERCA2A-DWORF complex. Biophys. J. 2024, 123, 397a–398a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Feng, R.; Chen, F.; Wu, Z.; Li, D.; Qiu, X. Rapid FRET Assay for the Early Detection of Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation in Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, A.R.; Kochen, N.N.; Yuen, S.L.; Liao, E.E.; Cornea, R.L.; Thomas, D.D.; Sachs, J.N. Advancements in a FRET Biosensor for Live-Cell Fluorescence-Lifetime High-Throughput Screening of Alpha-Synuclein. ASN Neuro 2023, 15, 17590914231184086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, C.; Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Li, Y. Virtual Screening Combined with Phase Transition-FRET for Discovery of Small-Molecule FcRn Antagonists. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 10661–10670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funato, Y.; Mimura, M.; Nunomura, K.; Lin, B.; Fujii, S.; Haruta, J.; Miki, H. Development of a high-throughput screening system targeting the protein-protein interactions between PRL and CNNM. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Ai, N.; Huang, S.; Jiang, C.; Mughal, M.J.; Ge, W.; Wang, G.; Deng, C.-X. An In Vivo Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer-Based Imaging Platform for Targeted Drug Discovery and Cancer Therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 839078. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Lv, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J. Accurate and highly sensitive detection of Alzheimer’s disease-related extracellular vesicles via förster resonance energy transfer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1314, 342779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan Kochen, N.; Murray, M.; Vunnam, N.; Liao, E.E.; Chen, L.; Braun, A.R.; Sachs, J.N. Fluorescence lifetime-based FRET biosensors for monitoring N-terminal domain interactions of TDP-43 in living cells: A novel resource for ALS and FTD drug discovery. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Heo, K.; Lee, S. Single-molecule FRET–based approach for protein-targeted drug discovery. Mol. Cells 2024, 47, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Suh, J.S.; Choi, G.; Jang, Y.K.; Ahn, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, T.J. Novel FRET-Based Biosensors for Real-Time Monitoring of Estrogen Receptor Dimerization and Translocation Dynamics in Living Cells. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2406907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, K.M.; Sabbih, G.; Algama, C.H.; Syed, R.; Danquah, M.K.; Dhakal, S. FRET-Based Single-Molecule Detection of Pathogen Protein IsdA Using Computationally Selected Aptamers. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 9839–9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Yan, C.; Yao, L.; Shang, H.; Chen, W. A Short- and Long-Range Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer-Cofunctionalized Fluorescence Quenching Collapsar Probe Regulates Amplified and Accelerated Detection of Salmonella. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 14294–14301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heli, B.; Ajji, A. Toward a nanopaper-based and solid phase immunoassay using FRET for the rapid detection of bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Tao, X.; Song, E. Rapid detection of pathogenic bacteria based on a universal dual-recognition FRET sensing system constructed with aptamer-quantum dots and lectin-gold nanoparticles. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, R.; Ou, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shen, Y.; Ling, N.; Ye, Y. A novel fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based paper sensor with smartphone for quantitative detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food Control 2023, 145, 109412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Miao, X. A novel “signal off–triggered on” Förster resonance energy transfer biosensor for the ratiometric detection of pathogenic bacteria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 372, 132598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, K.; Wu, S.-Y.; Takahashi-Yamashiro, K.; Shen, Y.; Campbell, R.E. Biosensor Optimization Using a Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Pair Based on mScarlet Red Fluorescent Protein and an mScarlet-Derived Green Fluorescent Protein. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Surve, J.; Parmar, J.; Ahmed, K.; Bui, F.M.; Al-Zahrani, F.A. Recent Advances in Biosensors for Detection of COVID-19 and Other Viruses. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 16, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.M.; Yasin, G.; Zourob, M.; Lu, J. Fluorescent Biosensors for the Detection of Viruses Using Graphene and Two-Dimensional Carbon Nanomaterials. Biosensors 2022, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Han, D.; Yao, N.; Zhao, H.; Chu, X.; Liang, X.; Bi, C.; Wang, C.; et al. Fluorescent immunosensor based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between CdSe/ZnS quantum dots and Au nanorods for PRRSV detection. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2022, 32, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Dos Santos, M.; Colin, I.; Ribeiro Dos Santos, G.; Susumu, K.; Demarque, M.; Medintz, I.L.; Hildebrandt, N. Time-Gated FRET Nanoprobes for Autofluorescence-Free Long-Term In Vivo Imaging of Developing Zebrafish. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2003912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Cheon, D.S.; Liu, F.; Lee, K.B.; Seo, T.S. A graphene oxide based immuno-biosensor for pathogen detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 5708–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaddare, S.H.; Salimi, A. Amplified fluorescent sensing of DNA using luminescent carbon dots and AuNPs/GO as a sensing platform: A novel coupling of FRET and DNA hybridization for homogeneous HIV-1 gene detection at femtomolar level. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Song, M.; Ma, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, G.; Hao, J. Plasmon-enhanced FRET biosensor based on Tm3+/Er3+ co-doped core-shell upconversion nanoparticles for ultrasensitive virus detection. Aggregate 2024, 5, e448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Song, M.; Li, L.; Lao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wong, M.-c.; Yang, M.; Chen, H.; Hao, J. Attomolar-level detection of respiratory virus long-chain oligonucleotides based on FRET biosensor with upconversion nanoparticles and Au–Au dimer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 243, 115778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgazar, A.; Sabouni, R.; Ghommem, M.; Majdalawieh, A.F. Novel metal–organic framework biosensing platform for detection of COVID-19 RNA. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; He, B.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Xue, X.; Qiu, T.; Hao, X.; Lv, F.; Wang, S. A Rapid, Visible, and Highly Sensitive Method for Recognizing and Distinguishing Invasive Fungal Infections via CCP-FRET Technology. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 2816–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Yilmaz, T.; Cohen, S.; Beyhan, S.; Argun, A.A. A novel biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of fungal genes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 222, 114986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, B.; Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Yang, N.; Mao, H. A Detection Method for Crop Fungal Spores Based on Microfluidic Separation Enrichment and AC Impedance Characteristics. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, S.; Huang, X.; Pan, D.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q.-A.; Zhu, Z. Recent advances of integrated microfluidic systems for fungal and bacterial analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulumati, A.; Pulumati, A.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Verma, A.; Papineni, R.V.L. Technological advancements in cancer diagnostics: Improvements and limitations. Cancer Rep. 2023, 6, e1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Lyu, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, M. A fluorescence turn-on biosensor based on graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets for epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Chen, W.; Mi, D.; Wang, B.; Li, H.; Wu, G.; Ding, P.; Liang, J.; Zhou, Z. A highly sensitive strategy for glypican-3 detection based on aptamer/gold carbon dots/magnetic graphene oxide nanosheets as fluorescent biosensor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 6441–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshan, N.; Cheng, T.; Yu, J.; Jiao, K.; Li, L.; Jiao, J.; Jiao, J. Hand in hand catalytic hairpin assembly-based FÖrster resonance energy transfer biosensor for simultaneous detection of multiple MicroRNAs from breast cancer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1352, 343925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennick, J.J.; Nowell, C.J.; Pouton, C.W.; Johnston, A.P.R. Resolving subcellular pH with a quantitative fluorescent lifetime biosensor. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.K.; Bhattacharya, S.C. Implication toward a simple strategy to generate pH tunable FRET-based biosensing. Spectrochim. Acta Part. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 282, 121687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavesley, S.J.; Rich, T.C. Overcoming limitations of FRET measurements. Cytom. A 2016, 89, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, D.P.; Stoneman, M.R.; Raicu, V. Impact of photobleaching of fluorescent proteins on FRET measurements under two-photon excitation. Spectrochim. Acta Part. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 326, 125294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, D.; Basler, K.; Aegerter, C.M. Challenging FRET-based E-Cadherin force measurements in Drosophila. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; He, F.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y. Application of FRET Biosensors in Mechanobiology and Mechanopharmacological Screening. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 595497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, E.; Klauß, A.; Toro-Nahuelpan, M.; Schüler, D.; Hille, C.; Faivre, D. The in vivo mechanics of the magnetotactic backbone as revealed by correlative FLIM-FRET and STED microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.T.; Sinsuebphon, N.; Rudkouskaya, A.; Michalet, X.; Intes, X.; Barroso, M. In vivo quantitative FRET small animal imaging: Intensity versus lifetime-based FRET. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 3, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fatima, M.; Abbas, N. Expanding Horizons in Advancements of FRET Biosensing Technologies. Biosensors 2025, 15, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070452
Fatima M, Abbas N. Expanding Horizons in Advancements of FRET Biosensing Technologies. Biosensors. 2025; 15(7):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070452
Chicago/Turabian StyleFatima, Munazza, and Naseem Abbas. 2025. "Expanding Horizons in Advancements of FRET Biosensing Technologies" Biosensors 15, no. 7: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070452
APA StyleFatima, M., & Abbas, N. (2025). Expanding Horizons in Advancements of FRET Biosensing Technologies. Biosensors, 15(7), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070452





