Abstract
Freshwater scarcity in arid regions forces farmers to use saline water, reducing durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. subsp. durum) productivity, particularly during early growth stages. This study evaluated two Moroccan varieties, Faraj and Nachit, on silty clay soil under five salinity levels (0.2, 4, 8, 12, and 16 dS m−1) in a randomized complete block design with three replications, aiming to identify tolerance thresholds and characterize physiological and agronomic responses. Key traits measured included germination percentage, germination stress index, mean germination time, root and coleoptile length, plant height, leaf number, chlorophyll fluorescence, grain yield, weight of 200 grains, and straw yield. Germination percentage declined from 8 dS m−1, with delayed germination and inhibited vegetative growth at higher salinity. Both varieties maintained grain yield up to 8 dS m−1 and weight of 200 grains and straw yield up to 12 dS m−1, with Nachit showing higher tolerance. Multivariate analyses, including principal component analysis and heatmaps, linked soil sodium, chloride, and electrical conductivity negatively to growth and yield, whereas potassium, calcium, and magnesium supported plant growth and physiological activity. These findings provide insights for breeding and irrigation strategies to sustain durum wheat under salinity stress.
1. Introduction
Freshwater scarcity is a major challenge in arid and semi-arid regions, where increasing water demand due to climatic pressures and population growth threatens agricultural productivity and food security [1,2].
In Morocco, approximately 700,000 hectares of land is affected by soil salinity, with nearly half of this area located in irrigated perimeters [3]. This situation highlights the critical need for efficient water management and the adoption of innovative agricultural practices to sustain crop yields under salinity stress. Saline irrigation, while providing an alternative water source, inevitably introduces salts into the soil, potentially altering soil physicochemical properties, reducing nutrient availability, and impairing crop performance [4,5,6]. The extent of these impacts is influenced by soil texture, initial salinity levels, irrigation practices, and crop characteristics [7].
Durum wheat is a major cereal crop cultivated across Mediterranean regions, including Morocco, where it provides an important source of staple foods such as flour and pasta [8,9,10]. Its productivity, however, is increasingly challenged by environmental stresses, particularly in arid and semi-arid areas. Irregular rainfall, high temperatures, soil degradation, and salinity significantly constrain growth and yield, reducing the crop’s overall resilience [11,12,13,14,15]. Salinity, in particular, limits water uptake, disrupts ionic balance, and impairs photosynthesis, ultimately affecting biomass accumulation and grain production [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. In Morocco, durum wheat is often grown under rainfed conditions, making it highly sensitive to fluctuations in water availability and climatic extremes [23]. Additional factors, including soil quality, nutrient management, pests, and diseases, further influence crop performance. Consequently, the identification and cultivation of durum wheat varieties with enhanced tolerance to salinity, combined with optimized irrigation and agronomic practices, are essential to sustain productivity and ensure food security in the country’s dryland regions [24,25].
Seed germination is the earliest and most vulnerable stage in the plant life cycle, critically influencing crop establishment and yield potential. This stage is particularly sensitive to salinity, which imposes osmotic stress, limiting water uptake, and ionic stress, caused by excessive sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) ions [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. These stresses disrupt physiological and biochemical processes, including nutrient absorption, photosynthesis [27], protein synthesis, and energy metabolism [28], while inducing oxidative damage through reactive oxygen species (ROS). As a result, germination can be delayed or inhibited, reducing seedling establishment and compromising subsequent growth. The severity of these effects varies with salinity level and varietal tolerance, with osmotic stress predominating at lower concentrations and ion toxicity at higher levels. Importantly, salinity continues to affect growth at later vegetative stages, further limiting biomass accumulation and overall crop productivity [29,30,31].
Beyond germination, salinity continues to affect vegetative growth by reducing leaf expansion, photosynthetic efficiency, nutrient uptake, and chlorophyll content. Prolonged irrigation with saline water can result in soil salinization, increasing electrical conductivity (EC) and sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), while decreasing nutrient availability and microbial activity [32,33,34,35]. The intensity of these effects is influenced by soil texture, initial salinity, irrigation practices, climate, and cultivar characteristics [36]. Implementing strategies such as alternating saline and fresh water, controlled leaching, optimized irrigation scheduling, and cultivating salt-tolerant varieties can mitigate these negative impacts on both soil and crop performance [37].
Enhancing salt tolerance in durum wheat, particularly in local cultivars such as Faraj and Nachit, is critical for maintaining stable productivity under saline irrigation conditions. Salinity imposes both osmotic and ionic stresses that disrupt physiological processes, including water uptake, nutrient assimilation, and photosynthesis, ultimately limiting growth, biomass accumulation, and grain yield [38]. Local durum wheat varieties often exhibit differential responses to salt stress, reflecting inherent genetic variability that can be exploited in breeding and agronomic programs [39]. Evaluating growth and yield-related parameters such as plant height, leaf number, biomass, grain yield, and straw yield under controlled saline irrigation allows for the identification of cultivars capable of sustaining performance under stress. This approach supports the selection of resilient varieties and contributes to the sustainability of cereal cropping systems in silty clay soils under dryland conditions, ensuring both crop productivity and long-term soil health [40]. Ultimately, targeted evaluation and selection of durum wheat varieties adapted to salinity represent a cornerstone for improving food security and agricultural resilience in arid and semi-arid regions [41,42].
This study aims to evaluate the responses of durum wheat to saline irrigation in silty clay soils. It compares the performance of two local Moroccan durum wheat varieties, Faraj and Nachit, across key growth stages, including seed germination, vegetative development, physiological traits, and yield components. By assessing performance under varying salinity levels, the study objectives are to determine the tolerance thresholds of each variety at different growth stages, linking early stress responses to final agronomic outcomes. Specifically, the research focuses on (i) quantifying the effects of salinity on growth, physiology, and yield, (ii) identifying the variety with superior salt resilience, and (iii) establishing actionable selection criteria for improved variety choice under saline irrigation. The findings are intended to provide practical recommendations for irrigation management and variety selection, promoting water-use efficiency and sustainable durum wheat production in dry and semi-arid regions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Soil Sampling, and Assessment of Physicochemical Properties
This study was carried out at the Regional Center of Rabat of the National Institute of Agricultural Research (INRA), within the Research Unit for Environment and Natural Resource Conservation (URECRN). The experiment was conducted in a greenhouse at this center, located at 34°03′50″ N latitude and 06°50′40″ W longitude, approximately 70 m above sea level, representing the typical coastal area of Rabat. Soil samples were manually collected from an agricultural field in the Temara region (latitude 33°53′29.6″ N, longitude 6°56′15.8″ W; altitude 78.42 m), approximately 30 km south of Rabat. This field was selected for its fine-textured soils, which are particularly prone to salinization and degradation under irrigation. Samples were taken from the top 0–40 cm soil layer using an auger, as this layer represents the most biologically active and agriculturally important portion of the profile. Climate data for Témara were obtained from the local meteorological station. Minimum and maximum temperatures, precipitation, humidity, and rainy days cover the period 1991–2021, while average sunshine hours are available for 1999–2019 [43]. The region has a Mediterranean climate with oceanic influences, characterized by mild, wet winters (January minimum 8.2 °C, maximum 16.8 °C, 69 mm rainfall, 6 rainy days) and warm, dry summers (July minimum 18.3 °C, maximum 30.3 °C, 1 mm rainfall, 0 rainy days). Monthly average temperatures range from 12 °C (January) to 24.2 °C (August), relative humidity varies between 67% and 79%, average annual rainfall is around 451 mm, and average annual sunshine is approximately 9.2 h/day. These data provide a precise and location-specific climatic context for the experimental and soil sampling sites (Figure 1).
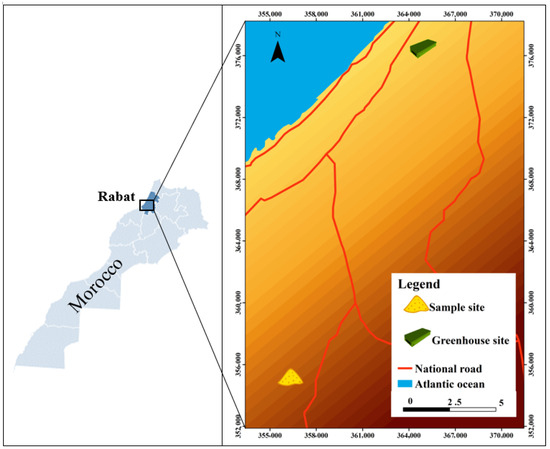
Figure 1.
Location of the soil sampling site and the greenhouse experimental setup.
The assessment of the soil’s physicochemical characteristics was conducted following the procedures reported by Manhou et al. (2024) [43]. Soil samples were collected from the top 0–40 cm layer in the Temara region, air-dried, and sieved for analysis of pH, electrical conductivity (EC), exchangeable cations (Na, K, Ca, Mg), total nitrogen (N), available phosphorus (P), and organic matter (OM). Particle size distribution was determined using the sedimentation method. The soil was characterized as a silty clay soil, comprising 52.6% clay, 34.3% silt, and 13.1% sand, with an alkaline pH of 7.8, low electrical conductivity (0.20 dS m−1), and low organic matter content (1.33%). According to the World Reference Base for Soil Resources [44], this soil can be classified as a Calcaric Cambisol, reflecting its non-saline character, moderate fertility, and limited nutrient retention. Total nitrogen (N) is 0.078%, available phosphorus (P) is 120 mg kg−1, and exchangeable potassium (K) is 229 mg kg−1. The soil exhibits relatively low levels of sodium (Na), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and chloride (Cl). The initial physicochemical characterization of the soil is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of the soil prior to the experiment.
2.2. Plant Material, Experimental Setup, and Crop Management Practices
The experiment was conducted using the durum wheat varieties Nachit and Faraj under controlled greenhouse conditions. Seeds were sown in plastic containers (28 × 21 cm) filled with 4 kg of silty clay soil, representative of the study area, with a gravel layer at the base for drainage. The selected varieties were chosen for their adaptability, yield potential, tolerance to drought and salinity, and quality traits such as protein content and yellow pigment index (Table 2). A completely randomized design (CRD) with three replicates per treatment was used, totaling fifteen containers for five salinity levels: I0 (0.2 dS m−1, control), I1 (4 dS m−1), I2 (8 dS m−1), I3 (12 dS m−1), and I4 (16 dS m−1) NaCl. Greenhouse temperature was maintained at 22 ± 1 °C. Irrigation started with freshwater during the first week, then saline treatments were applied three times per week (0.5 L per container) to maintain soil near field capacity. Nutrient management included split nitrogen fertilization (120 kg ha−1) at sowing, stem elongation, and heading, along with phosphorus and potassium based on soil tests. Pest management followed integrated pest management (IPM) principles. Standard agronomic practices were maintained throughout the experiment to ensure optimal growth.

Table 2.
Key agronomic and quality characteristics of the durum wheat varieties.
2.3. Germination Test and Germination Indicators
The germination and early seedling development of the durum wheat varieties Nachit and Faraj were evaluated under fully controlled greenhouse conditions to eliminate field variability. Uniform, healthy seeds were selected, surface-sterilized with 0.5% sodium hypochlorite, and rinsed with distilled water. For each treatment, 75 seeds per variety were divided into three replicates of 25 seeds each and placed in sterile vessels lined with filter paper. Salinity treatments included a control (0.2 dS m−1 freshwater) and four NaCl concentrations (4, 8, 12, and 16 dS m−1). Containers were kept in darkness at 21 °C, with moisture consistently maintained to prevent desiccation. Seedling emergence was monitored daily and was generally uniform, although slight delays were observed at higher salinity levels. A factorial design considering the two varieties and five salinity levels allowed for assessment of variety × salinity interactions on germination and early seedling growth. Germination parameters were subsequently calculated as follows:
Germination Capacity (GC %): Germination Capacity (GC %): This parameter helps determine the salinity level at which durum wheat seed germination starts to decline. It is calculated by expressing the percentage of seeds that successfully germinate by the end of the test relative to the total seeds sown [45]:
where g is the number of germinated seeds and G is the total number of seeds.
Germination percentage (GP %): This parameter indicates the fraction of seeds that have sprouted by a specific day (n) and is calculated using the following formula:
where denotes the total seeds sprouted up to day n, Ng refers to the initial seed count, and n indicates the specific day of observation (1, 2, …, n).
Germination speed index (GSI): This is calculated by tracking seed germination each day and computed using the formula [46]:
where Pi is the number of seeds that germinated on day i, and Di is the number of days elapsed since the beginning of the test.
Mean Germination Time (MGT): This parameter indicates the average duration. required for seeds to germinate under specific conditions. It was calculated using the formula [47]:
where is the time from day one to the last day of observation, is the number of seeds germinated on day , and is the last day of germination.
To evaluate the relationship between salinity levels and the mean daily germination percentage (DGP), linear regression analysis was performed. The mean DGP was calculated over 7 days (Day 1 to Day 8) using the following formula:
where G8 and G1 represent the cumulative germination percentages recorded on Day 8 and Day 1, respectively.
Seedling Length Measurement: On day 6 of germination, five seedlings were randomly selected from each replicate for each variety and salinity treatment. Radicle and coleoptile lengths were measured using a graduated ruler, keeping seedlings on a moist surface to prevent desiccation. This measurement provided an accurate evaluation of early growth responses to salinity stress. Figure 2 summarizes the germination test methodology, including seed selection and sterilization, placement on moistened filter paper, application of salinity treatments, and assessment of seedling growth parameters.
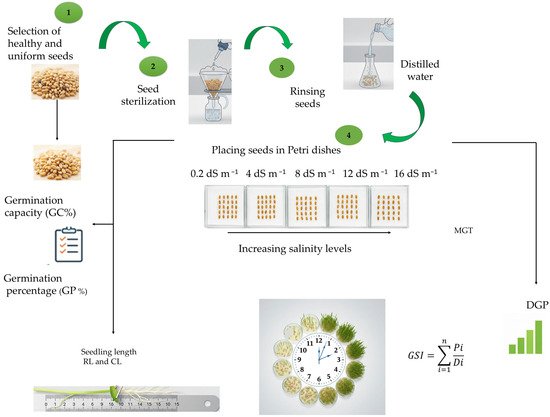
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the germination test methodology for durum wheat varieties. DGP: Daily Germination Percentage; MGT: Mean Germination Time; GSI: Germination Stress Index; RL: Root Length; CL: Coleoptile Length.
2.4. Measurement of Growth Parameters and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Under Controlled Conditions
All measurements were conducted at key phenological stages of durum wheat: tillering, stem elongation, heading, and maturation. Each container contained 10 plants, ensuring uniform plant density across treatments. Durum wheat seeds were directly sown in the same containers used throughout the experiment, from sowing to harvest. Plant height was measured on three representative plants per container from the stem base to the tip of the uppermost leaf using a vertically oriented graduated ruler, and mean values were calculated. Leaf number was recorded manually on the same plants at each stage to ensure consistency. Chlorophyll a fluorescence (Fᵥ/Fₘ) was assessed on fully expanded leaves using a portable pulse-amplitude modulated fluorometer (OS-30p, Opti-Sciences, Hudson, NH, USA) with red LEDs (660 nm) delivering a saturating light pulse of up to 6000 µmol photons m−2 s−1. Leaves were dark-adapted for at least 30 min prior to measurement. Minimum fluorescence (F0) and maximum fluorescence (Fₘ) were recorded, allowing the calculation of variable fluorescence (Fᵥ) and the Fᵥ/Fₘ ratio, which reflects the maximum photochemical efficiency of photosystem II [48,49].
Fv = Fm − F0
The maximum quantum efficiency of PSII was then calculated as:
2.5. Yield Component Analysis
At the final growth stage, key yield-related traits of durum wheat were carefully assessed. Spikes were hand-harvested to avoid grain loss or damage. Grains were meticulously cleaned to eliminate debris and impurities. For uniformity in weight determination, a representative sample of 200 grains per batch was oven-dried at 105 °C for 45 min to remove residual moisture and weighed using a high-precision balance (Ohaus, Parsippany, NJ, USA). The total grain count per container was determined with an automated seed counter (Numigral, Villeneuve-la-Garenne Cedex, France). Straw yield was measured as the remaining biomass after threshing, using the same high-precision balance to ensure consistency across treatments. Planting density (PD), considering each container covered 0.04 m2, was calculated using the following formula:
where TNP is the total number of plants, and TSA is the total surface area in square meters.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software, version 25. To assess the effect of different salinity levels on germination parameters of the two durum wheat varieties, analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted. This analysis revealed significant effects of salinity treatments on key germination indicators, as well as varietal differences, enabling identification of the variety with the greatest tolerance to saline conditions. When significant differences were detected, a post hoc test was applied to determine which treatments differed statistically. Linear regression analyses were also performed between salinity concentrations and individual germination parameters, in order to quantify the strength and direction of these relationships. In the second phase of the experiment, conducted in a greenhouse, data related to growth parameters, chlorophyll fluorescence, and yield components were analyzed using two- or three-way ANOVA (variety, salinity, and, where applicable, sampling period). This approach allowed evaluation of main. effects and interactions among factors. A significance level of 0.05 was adopted. When significant differences were found, Duncan’s post hoc test was used to identify homogeneous groups and perform pairwise comparisons. Additionally, a Principal PCA was performed to explore the responses of the two durum wheat varieties under different salinity levels, using six key variables (EC, K, Pth, ChlF, GY, 200-GW) selected from the original dataset. The ten observations corresponded to the two varieties across five salinity treatments. The suitability of the data for PCA was confirmed by the KMO measure and Bartlett’s test of sphericity. PCA was applied as an exploratory tool to visualize patterns, examine correlations, and identify variables most strongly associated with plant performance under saline conditions.
3. Results
3.1. Daily Germination Progress of Two Durum Wheat Varieties Under Varying Salinity Levels
Germination of durum wheat progressively declined with increasing salinity. Under freshwater irrigation (0.2 dS m−1), both Faraj and Nachit achieved high germination rates of 98.7% and 98.8%, respectively. Moderate salinity (4 dS m−1) slightly reduced germination to 88.2% for Faraj and 88.4% for Nachit, indicating tolerance to low salt levels. At 8 dS m−1, germination dropped to 75.2% and 75.5%, marking moderate stress, with Nachit consistently slightly higher. Severe salinity (12–16 dS m−1) strongly inhibited seedling emergence, with final germination decreasing to 47.4% and 40.5% for Faraj, and 47.5% and 40.7% for Nachit, representing over 50% reductions relative to the control. Daily germination dynamics highlighted a clear salinity effect. Under control conditions, 25–28% of seeds germinated by day two, reaching 80–81% by day five, and 98.7–98.8% by day eight. At 4 dS m−1, germination started at 18–20%, reached 65% by day five, and exceeded 88% by day eight. At 8 dS m−1, only 12–14% germinated on day two, 42–44% by day five, and 75.2–75.5% by day eight. High salinity (12–16 dS m−1) strongly suppressed germination, with 47–47.5% and 40–40.7% germinating by day eight (Figure 3).
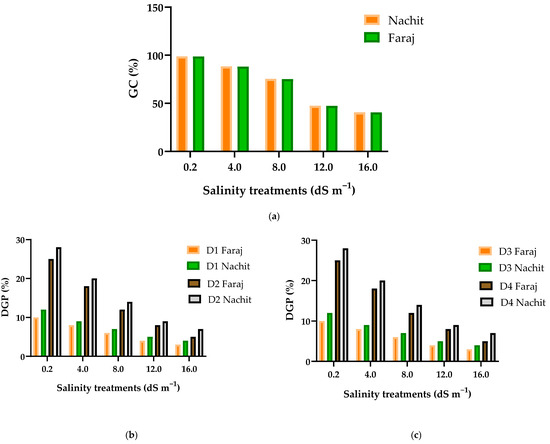
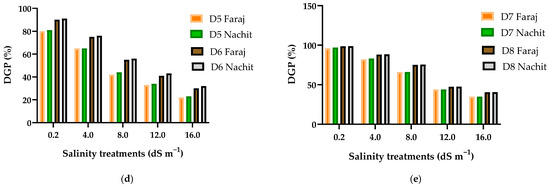
Figure 3.
Germination dynamics of durum wheat varieties (Nachit and Faraj) under different salinity levels: (a) Germination capacity; (b–e) Changes in daily germination percentage during 8 days of observation.
3.2. Effects of NaCl Treatments on Germination Stress Index (GSI) and Mean Germination Time (MGT) in Two Durum Wheat Varieties
Irrigation with saline water markedly affected germination performance in both durum wheat varieties (Table 3). The highest germination speed index (GSI) and the shortest mean germination time (MGT) were obtained under freshwater irrigation (0.2 dS m−1), indicating optimal germination conditions. As salinity increased, GSI declined progressively, whereas MGT showed an opposite trend, reflecting delayed and inhibited germination. Under moderate salinity (4–8 dS m−1), GSI decreased by up to 22%, while MGT nearly doubled compared to the control, highlighting the sensitivity of both varieties to ionic and osmotic stress. Severe salinity (12–16 dS m−1) caused a marked reduction in germination rate and uniformity, particularly in Faraj, confirming the adverse impact of saline irrigation on seed vigor and germination efficiency.

Table 3.
Effect of salinity and durum wheat varieties on germination speed index (GSI) and mean germination time (MGT, days). Values are presented as mean ± SE (n = 75, from three sets of 25 seeds). Means followed by different letters within a row are significantly different according to Duncan’s test (p < 0.05). The table also shows the ANOVA results for the effects of salinity, variety, and their interaction.
3.3. Response of Durum Wheat Root and Coleoptile Growth to Gradual Salinity Stress
Root length (RL) and coleoptile length (CL) of the two durum wheat varieties, Nachit and Faraj, exhibited a gradual decline as NaCl concentrations increased from 0.2 to 16 dS m−1 (Figure 4). At the lowest salinity level (0.2 dS m−1), Nachit showed an RL of 4.53 cm and a CL of 3.86 cm, while Faraj recorded slightly lower values with 4.25 cm and 3.59 cm for RL and CL, respectively. At 4 dS m−1, both varieties experienced a reduction in growth, with RL decreasing to 3.98 cm in Nachit and 3.65 cm in Faraj, and CL to 3.27 cm and 2.94 cm, respectively. Further increases in salinity to 8 dS m−1 resulted in RL values of 2.83 cm for Nachit and 2.51 cm for Faraj, whereas CL decreased to 2.28 cm and 1.96 cm. At 12 dS m−1, RL dropped to 1.87 cm in Nachit and 1.59 cm in Faraj, while CL measured 1.45 cm and 1.22 cm, respectively. Under the highest salinity level of 16 dS m−1, the most pronounced reductions were observed, with RL reaching 1.23 cm in Nachit and 1.04 cm in Faraj, and CL decreasing to 0.91 cm and 0.75 cm, respectively. Overall, the data show a consistent decline in both RL and CL across increasing salinity levels, with Nachit maintaining slightly higher measurements than Faraj at each concentration.
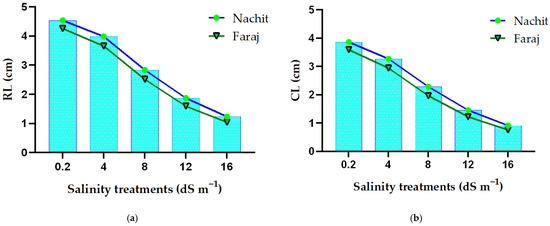
Figure 4.
Response of root length (RL) and coleoptile length (CL) in durum wheat varieties (Faraj and Nachit) under increasing salinity levels. (a) Root length; (b) Coleoptile length.
3.4. Relationships Between Salinity Treatments, Germination and Early Seedling Growth Parameters
Linear regression analyses revealed strong relationships between salinity treatments and all measured germination and early seedling growth parameters (Figure 5). For both durum wheat varieties, germination capacity (GC) exhibited a strong negative correlation with salinity (R2 = 0.96 for Nachit and R2 = 0.96 for Faraj). Similarly, daily germination percentage (DGP) showed a pronounced negative relationship with salinity (R2 = 0.96 for Nachit and R2 = 0.95 for Faraj), indicating that increasing NaCl concentrations reduced both the speed and uniformity of germination. The germination speed index (GSI) also declined significantly with salinity (R2 = 0.98 for the two varieties). In contrast, mean germination time (MGT) was positively correlated with salinity (R2 = 0.97 for both varieties), reflecting a prolongation of the germination process at higher salt levels. Early seedling growth parameters, including root length (RL) (R2 = 0.98) and coleoptile length (CL) (R2 = 0.99 for Nachit and R2 = 0.98 for Faraj), were negatively affected by increasing salinity.
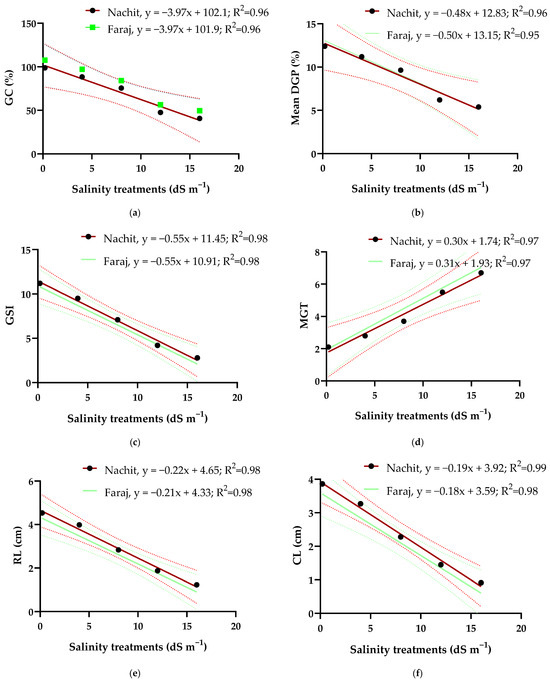
Figure 5.
Linear regression analysis of durum wheat germination responses under different salinity levels: (a): Germination capacity (GC); (b): Daily germination percentage (DGP); (c): Germination speed index (GSI); (d): Mean germination time (MGT); (e): Root length (RL) and (f): Coleoptile length (CL).
3.5. Effects of Salinity on Plant Development, Leaf Number, and Chlorophyll Fluorescence (Fv/Fm) in Durum Wheat
Figure 6 illustrates the effects of increasing salinity on plant height, chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm), and leaf number in durum wheat cultivated on silty clay soil across key vegetative and reproductive stages. Plant height showed little difference between tillering and stem elongation, even under moderate salinity (4–8 dS m−1), but progressively declined with higher NaCl concentrations, particularly at heading and maturity under severe salinity (16 dS m−1), reaching only 30–32 cm at maturity. Chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm) followed a similar pattern: slightly affected at early stages, but markedly reduced at heading and maturity, dropping below 0.32 under the highest salinity. Leaf number per plant also decreased with salinity, with reductions of approximately 25% at maturity compared to the control. Across all stages, Nachit consistently maintained slightly higher plant height, Fv/Fm, and leaf number than Faraj, indicating a marginally better tolerance to saline irrigation.
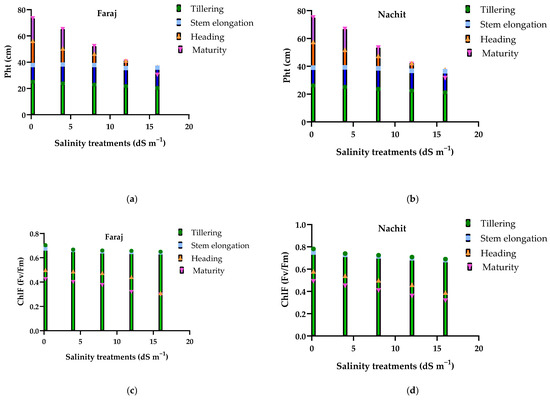
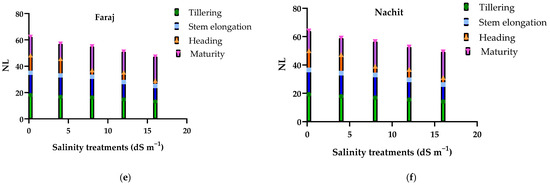
Figure 6.
Responses of plant height, chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm), and number of leaves to increasing salinity in two durum wheat varieties across growth stages: (a,b) Plant height; (c,d) Chlorophyll fluorescence; (e,f) Number of leaves.
3.6. Evaluation of Yield Components and Salinity Tolerance Limits in Two Durum Wheat Varieties
The interaction between durum wheat varieties (Faraj and Nachit) and salinity levels significantly influenced grain yield, 200-grain weight, and straw yield (Table 4). Grain yield declined progressively with increasing salinity, with the highest values under freshwater irrigation (0.2 dS m−1: 1.20 t ha−1 for Nachit, 1.12 t ha−1 for Faraj) and the lowest under severe salinity (16 dS m−1: 0.20 t ha−1 for Nachit, 0.16 t ha−1 for Faraj). 200-grain weight and straw yield followed similar trends, with Nachit consistently outperforming Faraj under moderate and high salinity. For example, at 8 dS m−1, 200-grain weight was 37.5 g for Nachit and 34.6 g for Faraj, while straw yield reached 1.05 t ha−1 and 0.97 t ha−1, respectively.

Table 4.
Yield components of Faraj and Nachit durum wheat varieties under varying salinity levels. Values indicated by the same letter within each column are not significantly different at p < 0.05 according to Duncan’s post hoc test. Values in parentheses indicate standard deviations. ANOVA results show the significance of salinity effects. ns: Not significant; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
ANOVA results showed highly significant effects of salinity on all yield components (p < 0.001). Variety significantly affected grain yield and 200-grain weight, while the variety × salinity interaction was significant for all parameters, indicating that Nachit maintained relatively higher yields than Faraj, especially under moderate and high-salinity conditions.
3.7. Relationships Between Grain Performance and Irrigation Salinity in Durum Wheat
Across all salinity treatments, increasing salinity had a negative impact on the yield traits of durum wheat (Figure 7). Grain yield (GY) showed the strongest response to salinity, with R2 = 0.95 for Nachit and R2 = 0.90 for Faraj, indicating a very high sensitivity of productivity to NaCl stress. Straw yield (SY) also declined, with R2 = 0.95 for Nachit and R2 = 0.97 for Faraj, reflecting a substantial reduction in vegetative biomass under elevated salinity. Similarly, 200-grain weight (200-GW) was strongly affected, with R2 = 0.89 for Nachit and R2 = 0.88 for Faraj, demonstrating that grain filling and individual grain development are significantly impaired at higher salt levels. All correlations were negative, confirming the inverse relationship between salinity and these yield components.
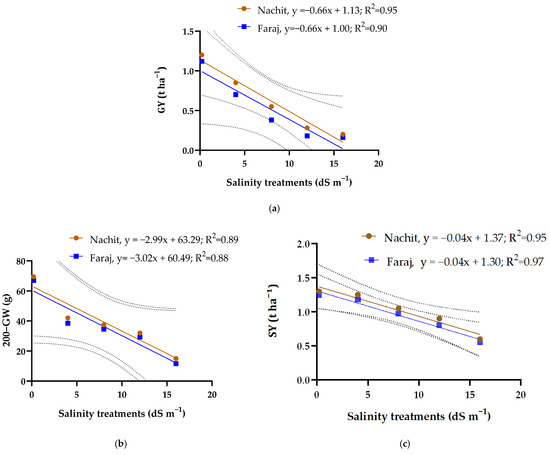
Figure 7.
Linear regression of yield components across increasing salinity concentrations in silty clay soil. (a): Grain yield; (b): 200-grain weight and (c): Straw yield.
3.8. Heatmap of Correlations Between Soil Chemical Parameters, Growth Traits, and Yield Components in Durum Wheat
The heatmap of correlations among soil parameters, growth traits, and yield. components in durum wheat under increasing salinity levels (Figure 8) highlighted distinct relationships between the measured variables. EC, Na, and Cl were strongly and positively correlated with each other, while exhibiting significant negative correlations with plant height (Pth), chlorophyll fluorescence (ChlF), number of leaves (NoL), grain yield (GY), 200-grain weight (200-GW), and straw yield (SY). Among yield components, GY and 200-GW displayed a strong positive correlation, and a moderate positive correlation was observed between 200-GW and SY. Potassium (K) was positively and strongly correlated with growth traits (Pth, ChlF, NoL) across all salinity levels, whereas its correlations with yield components were weakly positive. Similarly, calcium (Ca) exhibited strong positive correlations with vegetative traits, while correlations with GY, 200-GW, and SY were slightly negative under higher salinity. Magnesium (Mg) showed moderate positive correlations with growth traits and weak positive correlations with GY and 200-GW. Growth traits themselves were consistently positively correlated with yield components, with ChlF exhibiting particularly strong positive correlations with Pth, NoL, and GY. Number of leaves (NoL) was positively correlated with GY, 200-GW, and SY, while plant height (Pth) was moderately positively associated with all yield components.
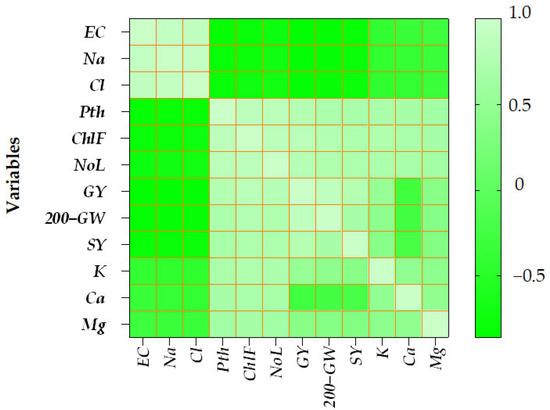
Figure 8.
Heatmap of correlation coefficients among soil parameters, growth traits, and yield components in durum wheat under increasing salinity levels. The heatmap shows the correlation matrix between all measured variables: soil parameters including electrical conductivity (EC), sodium (Na), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and chloride (Cl); growth-related traits such as plant height (Pth), chlorophyll fluorescence (ChlF), and number of leaves (NoL); and yield components including grain yield (GY), 200-grain weight (200-GW), and straw yield (SY).
3.9. Principal Component Analysis Revealing the Relationships Among Soil Chemistry, Growth, and Yield Under Salinity
The principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted to explore the relationships among soil chemical properties, growth traits, and yield components of durum wheat under different salinity levels (Figure 9). In this PCA, the observations corresponded to the two durum wheat varieties (Faraj and Nachit) evaluated under five salinity levels (I0, I1, I2, I3, and I4 dS m−1), resulting in a total of ten observation points. Each point represents the combined response of one variety under a specific salinity treatment.
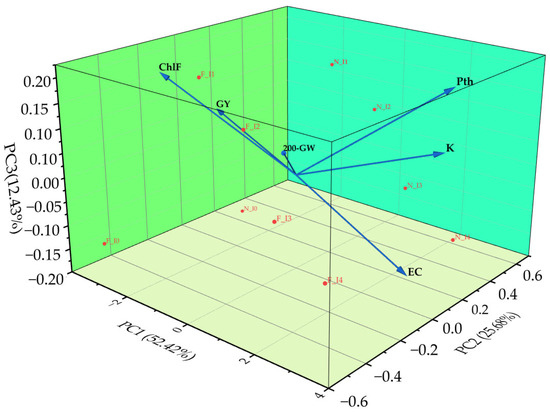
Figure 9.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of selected soil and plant variables in durum wheat under varying salinity levels. The PCA includes six key variables: EC (electrical conductivity), K (potassium), Pth (plant height), ChlF (chlorophyll fluorescence), GY (grain yield), and 200-GW (200-grain weight). Observations correspond to the two varieties at five salinity levels: F = Faraj, N = Nachit; I0–I4 indicate salinity treatments from 0.2 to 16 dS m−1.
To ensure data suitability given the limited number of observations, six key variables were selected: EC, K, Pth, ChlF, GY, and 200-GW. PCA was applied as an exploratory multivariate tool to visualize associations and identify the most discriminating factors influencing plant performance under saline conditions. The first three principal components had eigenvalues ≥ 1 and together explained 90.53% of the total variation, ensuring a robust representation of the dataset. PC1 (52.42%) represented the performance and yield axis, being strongly and positively associated with Pth, ChlF, GY, and 200-GW. The EC vector was nearly perpendicular to this axis, suggesting that PC1 primarily reflects plant performance rather than direct salinity intensity. PC2 (25.68%) was mainly influenced by K, which showed a positive association with Pth, indicating its modulatory role in supporting plant growth under salinity stress. Conversely, EC contributed negatively to this axis, reflecting the contrasting behavior of salinity and nutrient availability. PC3 (12.43%) accounted for additional minor variability without altering the main relationships observed along PC1 and PC2Overall, the PCA clearly highlighted the antagonistic relationship between EC and the performance-related traits (ChlF, GY, and 200-GW).
4. Discussion
The germination and early seedling growth stages constitute crucial phases in the plant life cycle and are highly vulnerable to the quality of irrigation water, particularly its salinity. The impact of salt stress on durum wheat during these stages is reflected through several key indicators such as GP, DGP, GSI, MGT, RL, and CL. These early responses are influenced by both genetic predispositions and environmental cues, which together shape the seed’s capacity to initiate growth under optimal conditions. Elevated salinity often disrupts physiological balance, primarily due to ion toxicity and osmotic effects, which hinder water uptake and impair metabolic activity essential for germination and seedling development [50,51]. Salinity induces osmotic stress that restricts water uptake by seeds and causes ionic toxicity, primarily as a result of the high accumulation of Na+ and Cl− ions. These conditions disrupt nutrient balance and interfere with essential metabolic processes such as germination, thereby reducing GP and GSI, and ultimately impairing seed vigor and early seedling development.
Such physiological and biochemical disruptions under saline conditions are well documented in wheat, where salinity is a major constraint during early growth stages [52,53]. In this study, elevated irrigation salinity reduced germination performance in both Faraj and Nachit, although both maintained rates above 75% at 8 dS m−1, indicating moderate tolerance, with Nachit showing a slight advantage. This aligns with other studies on tetraploid wheat, highlighting the importance of early-stage physiological i ndicators for selecting salt-resilient lines [54,55]. Similar trends have been observed in sorghum, where high salinity delays germination and reduces seedling growth [56]. Salinity imposes osmotic and ionic stresses affecting leaf water potential, stomatal conductance, and evapotranspiration, ultimately reducing crop yield. Wheat is generally classified as salt-tolerant based on soil salinity and water stress indices [57].
A similar trend was observed for root length (RL) and coleoptile length (CL), both progressively decreasing with increasing saline concentrations in the irrigation water for the Faraj and Nachit varieties. This reduction is widely reported across various species, as roots are the first organs to encounter salinity stress and play a crucial role in water uptake and its transport to aerial parts [58,59]. Moreover, salinity stress often inhibits cell expansion and division, thereby limiting elongation of both roots and coleoptiles in the Faraj and Nachit varieties under increasing saline irrigation. As roots are the first organs exposed to salinity, their early development is crucial for plant adaptation. Root branching and growth are tightly regulated processes involving genetic and hormonal controls that determine root length and function [60]. The more pronounced reduction in root length compared to coleoptile length observed in this study could be attributed to the higher sensitivity of root tissues to NaCl toxicity. This is consistent with findings in finger millet showing that salinity stress causes significant growth reduction and cellular. damage in both coleoptile and root tissues, with roots being particularly affected under increasing NaCl concentrations [61]. These findings underline the importance of early root development as a critical factor for salinity tolerance in durum wheat and suggest that selecting genotypes with better root growth under saline irrigation could improve crop performance in salt-affected areas [62].
Overall, irrigation with fresh water promotes the best growth performance in durum wheat. The results indicate that sensitivity to salinity increases as the plant develops. Early growth stages, particularly tillering and stem elongation, are relatively less affected by moderate salinity levels (4–8 dS m−1), with the Nachit variety demonstrating greater tolerance. However, at later stages such as heading and maturity, growth is significantly reduced under high salinity conditions (12–16 dS m−1), although Nachit maintains a slight advantage over Faraj. These findings align with previous studies highlighting that salinity induces osmotic and ionic stress, limiting water uptake and resulting in more pronounced growth retardation during advanced developmental stages [63,64,65]. Moreover, the number of leaves decreases as salinity increases. At 0.2 dS m−1, both varieties develop the maximum number of leaves, whereas at 16 dS m−1, a significant reduction is observed. This decline reflects the plants’ limited ability to sustain leaf growth under salt stress, likely due to disruptions in the cell cycle and reduced cell division in actively growing tissues, as reported in various plant species [66]. It may also be associated with ionic imbalances, particularly increased competition between Na+ and K+, leading to nutrient deficiencies that restrict foliar development [67]. Increased salinity reduces chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm), reflecting lower photosystem II efficiency. Low salinity maintains near-optimal values, whereas 12–16 dS m−1 causes a marked decline, indicating substantial photosynthetic stress. Chlorophyll fluorescence is a reliable, non-invasive indicator of salt-induced alterations in photosynthesis, particularly PSII activity and energy dissipation [68]. Similar Fv/Fm reductions under high NaCl have been observed in rice [69], soybean [70], and barley [71]. Advanced approaches like kinetic chlorophyll fluorescence allow for precise assessment of photosynthetic performance, highlighting traits such as non-photochemical quenching and quantum yield, which are critical for salt tolerance [72] and can aid in selecting resistant genotypes in breeding programs combining high-resolution phenotyping with genomic analyses [73]. These insights emphasize the value of adopting multidisciplinary approaches that integrate genomics, plant physiology, and agronomic management to more comprehensively understand the mechanisms underlying salt tolerance. Recent studies have demonstrated that combining physiological assessments with high-throughput phenotyping and genomic analyses enables the identification of salt-tolerant genotypes while linking cellular mechanisms to agronomic performance [74,75]. Such integrated strategies are essential for developing cultivars that maintain growth and yield under salinity stress, ultimately supporting sustainable crop production
In addition to physiological parameters, grain yield and its components are crucial indicators of salinity tolerance under agronomic conditions. Both varieties maintain a tolerance threshold for grain yield up to 8 dS m−1, which declines beyond this level, whereas 200-grain weight and straw yield are significantly affected only from 12 dS m−1, with Nachit showing a slight advantage over Faraj. Abiotic stresses, particularly salinity, significantly reduce crop yields during the reproductive stage, a critical phase for productivity [76,77]. Plants respond by activating physiological mechanisms, such as partial sodium exclusion from leaves, to maintain ion homeostasis [78], while the K+/Na+ ratio and grain dry matter content strongly influence grain filling and yield quality [79].
Saline irrigation disrupts water relations, nutrient uptake, and stomatal function, inducing oxidative damage that collectively reduces photosynthesis, biomass, and source-sink interactions, accelerating reproductive organ senescence [80,81]. Key reproductive stages, including anthesis and grain filling, are particularly sensitive, with structural leaf changes limiting turgor, assimilate synthesis, and yield potential [82]. Grain yield reductions of ~39.1%, 24.3%, and 13.4% have been reported at flowering, initial booting, and mid-grain filling, respectively [83]. Salinity also diminishes grain quality, reducing gluten, fiber, ash, and essential minerals (Mg, P, Ca, Zn, K, Fe) [84,85], with some species, such as Brassica oleracea var. capitata, showing up to 62% yield loss at 8 dS m−1 [86]. Additionally, salinity impairs stomatal regulation, nitrogen metabolism, photosynthesis, water use efficiency, and plant vigor, collectively limiting biomass and yield [87,88]. These multifaceted effects underscore the profound challenges salinity poses for sustainable agricultural productivity [89].
The results from the heatmap and principal component analysis (PCA) reveal strong correlations between soil parameters (EC, Na, K, Ca, Mg, Cl) and durum wheat growth and yield traits (Pth, ChlF, NoL, GY, 200-GW, SY), clearly illustrating the detrimental impact of salinity on agronomic performance. Increases in Na and Cl concentrations, together with elevated soil EC, were strongly associated with significant reductions in growth parameters (Pth, NoL, ChlF) and yield components (GY, 200-GW, SY). These results are consistent with those of [90], who reported that salinity impairs crop growth and yield through combined osmotic and ionic stresses. Similar findings were observed in previous studies showing that saline irrigation reduces spike formation [91] and grain weight [92], ultimately leading to yield losses [93,94] A yield reduction of up to 90% in durum wheat at 15 dS m−1 has been documented, whereas in the present study, the average decrease reached approximately 40% at 10 dS m−1 and 62% at 15 dS m−1, emphasizing the considerable genetic variability in salinity tolerance among cultivars [95]. Moreover, chlorophyll fluorescence (ChlF) emerged as a sensitive indicator of plant response to salt stress, showing close correlations with growth traits and overall productivity. Although leaf chlorophyll content slightly decreased under saline. conditions, the reduction remained moderate and may have been compensated by morphological adjustments, such as increased leaf thickness, that help sustain photosynthetic efficiency under stress [96,97]. Finally, specific nutrients particularly potassium (K) and magnesium (Mg) appeared to modulate plant responses to salinity. These elements play essential roles in osmotic regulation, membrane stability, and photosynthetic function, suggesting that optimizing nutrient management could help mitigate the adverse effects of salt stress [98,99].
5. Conclusions
This study evaluated the response of two local durum wheat varieties, Faraj and Nachit, to different salinity levels in irrigation water applied to silty-clay soil, from germination to final yield. Salinity progressively affected germination, with moderate tolerance observed up to 8 dS m−1; Nachit maintained higher germination rates than Faraj, indicating greater resilience at early stages. During vegetative growth, plant height, leaf number, and chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm) were moderately resilient under low to moderate salinity, but heading and maturity stages showed significant reductions, particularly in photosynthesis and overall vigor. Regarding yield components, grain yield declined from 8 dS m−1, while 200-grain weight and biomass were more stable up to 12 dS m−1. Nachit consistently outperformed Faraj, largely due to more efficient regulation of toxic ions (Na+, Cl−) and better retention of essential nutrients (K+, Ca2+, Mg2+). These results highlight critical tolerance thresholds and indicate that Nachit is better suited to saline conditions. From an agronomic perspective, these findings support the selection of salt-tolerant varieties and the implementation of management practices such as optimized irrigation, use of organic amendments, and farmer awareness programs. Integrating physiological, genomic, and agronomic strategies will further enhance salt tolerance, helping to sustainably improve durum wheat productivity and quality, particularly in regions facing increasing soil and water salinization.
Author Contributions
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, K.M.; methodology, K.M. and H.D.; software, K.M.; resources, K.M.,H.S. and M.O.L.; validation, K.M., H.D. and D.H.; formal analysis, K.M., H.D., R.M. and A.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, K.M., D.H., H.D., A.G. and A.Z.; writing—review and editing, K.M., H.D., D.H., H.S. and M.O.L.; visualization, K.M. and A.G.; supervision, D.H. and H.D.; funding acquisition, R.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the “MCGP” project (INRA and ICARDA) for their financial and technical support.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study are available upon request. We encourage interested researchers to contact us for further information.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their gratitude to those who contributed to this study, including the field sampling, laboratory analysis, and manuscript-writing teams from the ProcessEngineering and Environment Laboratory at the National Institute of Agricultural Research (INRA)and the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) in Morocco.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- FAO. World Food Day 2023 Highlights the Critical Role of Water in Achieving Food Security; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ingrao, C.; Strippoli, R.; Lagioia, G.; Huisingh, D. Water Scarcity in Agriculture: An Overview of Causes, Impacts and Approaches for Reducing the Risks. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmjid, Z.; Hallam, J.; Dakak, H.; Douaik, A.; Oumaima, I. Soil Salinity: A Challenge for the Resilience of Ecosystems and the Sustainability of Moroccan Agriculture. Afr. Med. Agric. J. 2024, 143, 135–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Šimůnek, J.; Shi, H.; Chen, N.; Hu, Q. Optimizing drip irrigation with alternate use of fresh and brackish waters by analyzing salt stress: The experimental and simulation approaches. Soil. Tillage Res. 2022, 222, 105355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Liu, X. Reclamation effect of freezing saline water irrigation on heavy saline-alkali soil in the Hetao Irrigation District of North China. Catena 2021, 204, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, K.; Mondal, S.; Gorai, S.; Singh, A.P.; Kumari, A.; Ghosh, T.; Roy, A.; Hembram, S.; Gaikwad, D.J.; Mondal, S.; et al. Impacts of salinity stress on crop plants: Improving salt tolerance through genetic and molecular dissection. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1241736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zheng, C.; Ning, S.; Cao, C.; Li, K.; Dang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Impacts of Long-Term Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Properties and Crop Yields under Maize–Wheat Crop Rotation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 280, 108383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, N.; Shehzad, T.; Harrabi, M.; Okuno, K. Mapping Novel QTLs for Tolerance to Salt Stress at the Late Vegetative Stage in Durum Wheat (Triticum durum L.). J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2023, 35, 102506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xynias, I.N.; Mylonas, I.; Korpetis, E.G.; Ninou, E.; Tsaballa, A.; Avdikos, I.D.; Mavromatis, A.G. Durum Wheat Breeding in the Mediterranean Region: Current Status and Future Prospects. Agronomy 2020, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddiq, M.S.; Afzal, I.; Basra, S.M.A.; Iqbal, S.; Ashraf, M. Sodium Exclusion Affects Seed Yield and Physiological Traits of Wheat Genotypes Grown Under Salt Stress. J. Soil. Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2020, 20, 1442–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggini, G.; Namoune, H.; Abecassis, J.; Cuq, B. Other Traditional Durum-Derived Products. In Durum Wheat; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 177–199. ISBN 978-1-891127-65-6. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, P.; Kaur, H.; Tyagi, V.; Saini, P.; Ahmed, N.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Sheikh, I. Nutritional Value and End-Use Quality of Durum Wheat. CEREAL Res. Commun. 2023, 51, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Kumar, A.; Sehrawat, N.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, N.; Lata, C.; Mann, A. Effect of Saline Irrigation on Plant Water Traits, Photosynthesis and Ionic Balance in Durum Wheat Genotypes. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2510–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouras, E.; Jarlan, L.; Khabba, S.; Er-Raki, S.; Dezetter, A.; Sghir, F.; Tramblay, Y. Assessing the Impact of Global Climate Changes on Irrigated Wheat Yields and Water Requirements in a Semi-Arid Environment of Morocco. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X. Environmental Groundwater Depth for Groundwater-Dependent Terrestrial Ecosystems in Arid/Semiarid Regions: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Qureshi, A.S.; Cheraghi, S.A.M. Extent and Characterisation of Salt-affected Soils in Iran and Strategies for Their Amelioration and Management. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; An, F.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Variations on Soil Salinity and Sodicity and Its Driving Factors Analysis under Microtopography in Different Hydrological Conditions. Water 2016, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carillo, P.; Parisi, D.; Woodrow, P.; Pontecorvo, G.; Massaro, G.; Annunziata, M.G.; Fuggi, A.; Sulpice, R. Salt-Induced Accumulation of Glycine Betaine Is Inhibited by High Light in Durum Wheat. Funct. Plant Biol. 2011, 38, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, C.; Soni, S.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, A.; Pooja, P.; Mann, A.; Rani, S. Adaptive Mechanism of Stress Tolerance in Urochondra (Grass Halophyte) Using Roots Study. Ind. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 89, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Comparative Physiology of Salt and Water Stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchimanchi, B.R.; Ripoll-Bosch, R.; Steenstra, F.A.; Thomas, R.; Oosting, S.J. The Impact of Intensive Farming Systems on Groundwater Availability in Dryland Environments: A Watershed Level Study from Telangana, India. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2023, 5, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.-Z.; Darzi-Naftchali, A.; Karandish, F.; Ritzema, H.; Solaimani, K. Enhancing Agricultural Sustainability with Water and Crop Management Strategies in Modern Irrigation and Drainage Networks. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 305, 109110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, P.S.; Ramos, T.B.; Ben-Gal, A.; Pereira, L.S. Coping with Salinity in Irrigated Agriculture: Crop Evapotranspiration and Water Management Issues. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 227, 105832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, H.; Moussadek, R.; Mouhir, L.; Lhaj, M.O.; Dakak, H.; Manhou, K.; Zouahri, A. Monte Carlo Simulation for Evaluating Spatial Dynamics of Toxic Metals and Potential Health Hazards in Sebou Basin Surface Water. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 29471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnilickova, H.; Kraus, K.; Vachova, P.; Hnilicka, F. Salinity Stress Affects Photosynthesis, Malondialdehyde Formation, and Proline Content in Portulaca oleracea L. Plants 2021, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousfi, S.; Serret, M.D.; Márquez, A.J.; Voltas, J.; Araus, J.L. Combined Use of δ13 C, δ18 O and δ15 N Tracks Nitrogen Metabolism and Genotypic Adaptation of Durum Wheat to Salinity and Water Deficit. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdehpour, Z.; Ehsanzadeh, P. Concurrence of Ionic Homeostasis Alteration and Dry Mass Sustainment in Emmer Wheats Exposed to Saline Water: Implications for Tackling Irrigation Water Salinity. Plant Soil 2019, 440, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattabi, D.; Sakar, E.H.; Louahlia, S. Flag Leaf Tolerance Study in Moroccan Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Varieties Submitted to a Severe Salt Stress. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 2787–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousfi, S.; Serret, M.D.; Voltas, J.; Araus, J.L. Effect of Salinity and Water Stress during the Reproductive Stage on Growth, Ion Concentrations, Δ13C, and δ15N of Durum Wheat and Related Amphiploids. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3529–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Soil Salinization Management for Sustainable Development: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, H.; Lan, L.; Huang, R.; Deng, X.; Peng, Y. Effects of Exponential N Application on Soil Exchangeable Base Cations and the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Clonal Chinese Fir Seedlings. Plants 2023, 12, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, F.; Tian, L.; He, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ren, F. Soil Physicochemical Properties and Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Yield under Brackish Water Mulched Drip Irrigation. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Li, F.; Yang, P.; Ren, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wei, R.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Properties, N2O Emission and Yield of Spring Maize under Mulched Drip Irrigation. Water 2019, 11, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Feike, T.; Chen, S.; Shao, L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X. Effects of Saline Irrigation on Soil Salt Accumulation and Grain Yield in the Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Double Cropping System in the Low Plain of North China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2886–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Yao, R.; Yu, S. Impact of Irrigation Volume and Water Salinity on Winter Wheat Productivity and Soil Salinity Distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 149, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Luo, J.; Park, E.; Barcaccia, G.; Masin, R. Soil Salinization in Agriculture: Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies Combining Nature-Based Solutions and Bioengineering. iScience 2024, 27, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rham, I.; Bouchiha, F.; Kharbouche, H.A.; El Maataoui, S.; Radi, H.; Choukrane, B.; Karama, M.; Ouhboun, R.; Hmouni, D.; Mazri, M.A. Effects of Medium Components on Cactus Pear (Opuntia Ficus-Indica (L.) Mill. Genotype ‘M2’) Organogenesis, and Assessment of Transplanting Techniques andVitroplant Fruit Quality. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 2025, 160, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Torre, S.; Garcia-Caparrós, P.; Nogales, A.; Abreu, M.M.; Santos, E.; Cortinhas, A.L.; Caperta, A.D. Sustainable Agricultural Management of Saline Soils in Arid and Semi-Arid Mediterranean Regions through Halophytes, Microbial and Soil-Based Technologies. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 212, 105397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, E.S.A.; El-Sobky, E.-S.E.A.; Farag, H.I.A.; Yasin, M.A.T.; Attia, A.; Rady, M.O.A.; Awad, M.F.; Mansour, E. Sowing Date and Genotype Influence on Yield and Quality of Dual-Purpose Barley in a Salt-Affected Arid Region. Agronomy 2021, 11, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, M.A.; Soccio, M.; Laus, M.N.; Flagella, Z. Influence of Drought and Salt Stress on Durum Wheat Grain Quality and Composition: A Review. Plants 2021, 10, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Moreno, F.; Ammar, K.; Solís, I. Global Changes in Cultivated Area and Breeding Activities of Durum Wheat from 1800 to Date: A Historical Review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate-Data.org. Témara, Morocco–Climate Data by Month. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/africa/morocco/temara-%D8%AA%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%A9/temara-%D8%AA%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%A9-764491/ (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Manhou, K.; Moussadek, R.; Yachou, H.; Zouahri, A.; Douaik, A.; Hilal, I.; Ghanimi, A.; Hmouni, D.; Dakak, H. Assessing the Impact of Saline Irrigation Water on Durum Wheat (Cv. Faraj) Grown on Sandy and Clay Soils. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRB (World Reference Base for Soil Resources). International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; ISBN 978-92-5-136461-5. [Google Scholar]
- Doran, J.C.; Gunn, B.V. Treatments to Promote Seed Germination in Australian Acacias. In Proceedings of the an International Workshop, Gympie, Australia, 4–7 August 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, J.D. Speed of Germination—Aid in Selection and Evaluation for Seedling Emergence and Vigor. Crop Sci. 1962, 2, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenchley, J.L.; Probert, R.J. Seed Germination Responses to Some Environmental Factors in the Seagrass Zostera Capricorni from Eastern Australia. Aquat. Bot. 1998, 62, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murchie, E.H.; Lawson, T. Chlorophyll Fluorescence Analysis: A Guide to Good Practice and Understanding Some New Applications. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3983–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häder, D.-P.; Herrmann, H.; Schäfer, J.; Santas, R. Photosynthetic Fluorescence Induction and Oxygen Production in Two Mediterranean Cladophora Species Measured on Site. Aquat. Bot. 1997, 56, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, D.; Luna, B.; Ourcival, J.-M.; Kavgacı, A.; Sirca, C.; Mouillot, F.; Arianoutsou, M.; Moreno, J.M. Germination Sensitivity to Water Stress in Four Shrubby Species across the Mediterranean Basin. Plant Biol. J. 2017, 19, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nautiyal, P.C.; Sivasubramaniam, K.; Dadlani, M. Seed Dormancy and Regulation of Germination. In Seed Science and Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 39–66. ISBN 978-981-19588-8-5. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramaniam, T.; Shen, G.; Esmaeili, N.; Zhang, H. Plants’ Response Mechanisms to Salinity Stress. Plants 2023, 12, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sabagh, A.; Islam, M.S.; Skalicky, M.; Ali Raza, M.; Singh, K.; Anwar Hossain, M.; Hossain, A.; Mahboob, W.; Iqbal, M.A.; Ratnasekera, D.; et al. Salinity Stress in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the Changing Climate: Adaptation and Management Strategies. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 661932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; James, R.A. Screening Methods for Salinity Tolerance: A Case Study with Tetraploid Wheat. Plant Soil. 2003, 253, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwando, E.; Han, Y.; Angessa, T.T.; Zhou, G.; Hill, C.B.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Li, C. Genome-Wide Association Study of Salinity Tolerance During Germination in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi Dehnavi, A.; Zahedi, M.; Ludwiczak, A.; Cardenas Perez, S.; Piernik, A. Effect of Salinity on Seed Germination and Seedling Development of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) Genotypes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerji, N.; Van Hoorn, J.W.; Hamdy, A.; Mastrorilli, M. Salinity Effect on Crop Development and Yield, Analysis of Salt Tolerance According to Several Classification Methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 62, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Rizwan, M.; Zia Ur Rehman, M.; Zubair, M.; Riaz, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Alharby, H.F.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Ali, S. Application of Co-Composted Farm Manure and Biochar Increased the Wheat Growth and Decreased Cadmium Accumulation in Plants under Different Water Regimes. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Akiba, T.; Moritsugu, M. Effects of High Concentrations of Sodium Chloride and Polyethylene Glycol on the Growth and Ion Absorption in Plants: I. Water Culture Experiments in a Greenhouse. Plant Soil. 1983, 75, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.A.; Rasmussen, A.; Traini, R.; Voß, U.; Sturrock, C.; Mooney, S.J.; Wells, D.M.; Bennett, M.J. Branching Out in Roots: Uncovering Form, Function, and Regulation. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satish, L.; Rathinapriya, P.; Sagina Rency, A.; Antony Ceasar, S.; Prathibha, M.; Pandian, S.; Rameshkumar, R.; Ramesh, M. Effect of Salinity Stress on Finger Millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn): Histochemical and Morphological Analysis of Coleoptile and Coleorhizae. Flora Morphol. Distrib. Funct. Ecol. Plants 2016, 222, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Hao, X.; Song, R.; Chen, S.; Wang, G.; Hua, L. Salt Stress in Wheat: A Physiological and Genetic Perspective. Plant Stress. 2025, 16, 100832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, K.; Karmakar, S.; Dutta, D.; Pal, A.K.; Jana, K. Comparative Physiology of Salinity, Drought and Heavy Metal Stress during Seed Germination in Ricebean [Vigna Umbellata (Thunb.) Ohwi and Ohashi]. J. Crop Weed 2019, 15, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhou, K.; Moussadek, R.; Zouahri, A.; Ghanimi, A.; Sanad, H.; Oueld Lhaj, M.; Hmouni, D.; Dakak, H. Performance, Agro-Morphological, and Quality Traits of Durum Wheat (Triticum turgidum L. Ssp. durum Desf.) Germplasm: A Case Study in Jemâa Shaïm, Morocco. Plants 2025, 14, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.-K. Thriving under Stress: How Plants Balance Growth and the Stress Response. Dev. Cell 2020, 55, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, A.H.K.; Matthew, C.; Uddin, M.J.; Bayazid, K.N. Salinity-Induced Reduction in Root Surface Area and Changes in Major Root and Shoot Traits at the Phytomer Level in Wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3719–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairmansis, A.; Berger, B.; Tester, M.; Roy, S.J. Image-Based Phenotyping for Non-Destructive Screening of Different Salinity Tolerance Traits in Rice. Rice 2014, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-C.; Chen, K.-C.; Cheng, T.-S.; Lee, C.; Lin, S.-H.; Tung, C.-W. Chlorophyll Fluorescence Analysis in Diverse Rice Varieties Reveals the Positive Correlation between the Seedlings Salt Tolerance and Photosynthetic Efficiency. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Lee, T.-Y.; Nah, G.; Kim, D.-S. Potential of Thermal Image Analysis for Screening Salt Stress-Tolerant Soybean (Glycine Max). Plant Genet. Resour. 2014, 12, S134–S136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhodja, R.; Morales, F.; Abadia, A.; Gomez-Aparisi, J.; Abadia, J. Chlorophyll Fluorescence as a Possible Tool for Salinity Tolerance Screening in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Physiol. 1994, 104, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awlia, M.; Nigro, A.; Fajkus, J.; Schmoeckel, S.M.; Negrão, S.; Santelia, D.; Trtílek, M.; Tester, M.; Julkowska, M.M.; Panzarová, K. High-Throughput Non-Destructive Phenotyping of Traits That Contribute to Salinity Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, A.; Huang, Z. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Salt Tolerance at the Seed Germination Stage and Yield-Related Traits in Brassica napus L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Kalhoro, N.; Rajpar, I.; Ali Kalhoro, S.; Ali, A.; Raza, S.; Ahmed, M.; Ali Kalhoro, F.; Ramzan, M.; Wahid, F. Effect of Salts Stress on the Growth and Yield of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Am. J. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 2257–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehtaiwesh, F.A.; Rashed, H.F. Growth and Yield Responses of Libyan Hard Wheat (Triticum durum Desf) Genotypes to Salinity Stress. Zawia Univ. Bull. 2020, 22, 33–58. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Yamaji, N.; Costa, A.; Okuma, E.; Kobayashi, N.I.; Kashiwagi, T.; Katsuhara, M.; Wang, C.; Tanoi, K.; Murata, Y.; et al. OsHKT1;4-Mediated Na+ Transport in Stems Contributes to Na+ Exclusion from Leaf Blades of Rice at the Reproductive Growth Stage upon Salt Stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poustini, K.; Siosemardeh, A. Ion Distribution in Wheat Cultivars in Response to Salinity Stress. Field Crops Res. 2004, 85, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, H.; Nemati, H.; Farsi, M.; Jartoodeh, S.V. How Salinity Affect Germination and Emergence of Tomato Lines. J. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 5, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Oueld Lhaj, M.; Moussadek, R.; Mouhir, L.; Sanad, H.; Manhou, K.; Iben Halima, O.; Yachou, H.; Zouahri, A.; Mdarhri Alaoui, M. Application of Compost as an Organic Amendment for Enhancing Soil Quality and Sweet Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Growth: Agronomic and Ecotoxicological Evaluation. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, C.; Gu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ju, F.; Wang, S.; Hu, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Improving the soil K+/Na+ ratio under moderate salt stress synergistically increases the yield and quality of cotton fiber and cottonseed. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 185, 118441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataar, M.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Shabani, F. Soil Salinity and Matric Potential Interaction on Water Use, Water Use Efficiency and Yield Response Factor of Bean and Wheat. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Asif, S.; Jang, Y.-H.; Park, J.-R.; Zhao, D.-D.; Kim, E.-G.; Kim, K.-M. Effect of Different Salts on Nutrients Uptake, Gene Expression, Antioxidant, and Growth Pattern of Selected Rice Genotypes. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 895282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Ashraf, M. Growth Stage-Based Modulation in Physiological and Biochemical Attributes of Two Genetically Diverse Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Cultivars Grown in Salinized Hydroponic Culture. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 6227–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Tariq, M.N.; Amjad, M.; Sajjad, M.; Akram, M.; Imran, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Gondal, T.A.; Kenijz, N.; Kulikov, D. Salinity-Induced Changes in the Nutritional Quality of Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Genotypes. AGRIVITA J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 42, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, H.; Moussadek, R.; Mouhir, L.; Lhaj, M.O.; Zahidi, K.; Dakak, H.; Manhou, K.; Zouahri, A. Ecological and Human Health Hazards Evaluation of Toxic Metal Contamination in Agricultural Lands Using Multi-Index and Geostatistical Techniques across the Mnasra Area of Morocco’s Gharb Plain Region. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, K.; Fujita, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Salicylic Acid Enhances Growth and Productivity in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. Capitata L.) Grown Under Saline Condition. Foc. Sci. 2017, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chriqui, A.; Mouniane, Y.; Bensaid, A.; Soufiani, A.; Arabi, R.; Manhou, K.; Ameziane, H.; Benkhnigue, O.; Mabrouki, J.; Hmouni, D. Medicinal Flora of the Municipality Asjen of the Ouezzane Region, Morocco: A Comprehensive Look at the Biodiversity of Its Natural Resources—A Review. In Technical and Technological Solutions Towards a Sustainable Society and Circular Economy; Mabrouki, J., Mourade, A., Eds.; World Sustainability Series; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 567–579. ISBN 978-3-031-56291-4. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Oueld Lhaj, M.; Moussadek, R.; Mouhir, L.; Mdarhri Alaoui, M.; Sanad, H.; Iben Halima, O.; Zouahri, A. Assessing the Evolution of Stability and Maturity in Co-Composting Sheep Manure with Green Waste Using Physico-Chemical and Biological Properties and Statistical Analyses: A Case Study of Botanique Garden in Rabat, Morocco. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, K.; Ahamed, K.U.; Islam, M.M.; Haque, M.N. Response of Tomato Plant Under Salt Stress: Role of Exogenous Calcium. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 10, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.R.; Choudhary, M.; Singh, J.; Lal, M.K.; Jha, P.K.; Udawat, P.; Gupta, N.K.; Rajput, V.D.; Garg, N.K.; Maheshwari, C.; et al. Impacts, Tolerance, Adaptation, and Mitigation of Heat Stress on Wheat under Changing Climates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueld Lhaj, M.; Moussadek, R.; Zouahri, A.; Sanad, H.; Saafadi, L.; Mdarhri Alaoui, M.; Mouhir, L. Sustainable Agriculture Through Agricultural Waste Management: A Comprehensive Review of Composting’s Impact on Soil Health in Moroccan Agricultural Ecosystems. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Jiang, C.; Tang, C.; Nie, X.; Du, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, P.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Kang, Z.; et al. Wheat Adaptation to Environmental Stresses under Climate Change: Molecular Basis and Genetic Improvement. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1564–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, A.B.; Bauer, A.; Black, A.L. Effects of Air Temperature and Water Stress on Apex Development in Spring Wheat. Crop Sci. 1987, 27, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Saqib, M.; Rafique, Q.; Rahman, M.; Javaid, A.; Anwar-ul-Haq, M.; Nasim, M. Effect of Salinity on Grain Yield and Grain Quality of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Pak. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 50, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Introduction to Soil Salinity, Sodicity and Diagnostics Techniques. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Zaman, M., Shahid, S.A., Heng, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–42. ISBN 978-3-319-96190-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sorour, S.G. Yield of Wheat Is Increased through Improving the Chemical Properties, Nutrient Availability and Water Productivity of Salt Affected Soils in the North Delta of Egypt. Appl. Ecol. Env. Res. 2019, 17, 8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; Munns, R.; Condon, A.G. (Tony) Effect of Sodium Exclusion Trait on Chlorophyll Retention and Growth of Durum Wheat in Saline Soil. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2003, 54, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; James, R.A.; Sirault, X.R.R.; Furbank, R.T.; Jones, H.G. New Phenotyping Methods for Screening Wheat and Barley for Beneficial Responses to Water Deficit. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3499–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousfi, S.; Serret, M.D.; Araus, J.L. Shoot δ15N Gives a Better Indication than Ion Concentration or Δ13C of Genotypic Differences in the Response of Durum Wheat to Salinity. Funct. Plant Biol. 2009, 36, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, S.R.; Grieve, C.M. Salinity–Mineral Nutrient Relations in Horticultural Crops. Sci. Hortic. 1998, 78, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).