Detailed Analysis of Thrombus Composition and Endovascular Thrombectomy Efficiency in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Undergoing Thrombectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Analysis
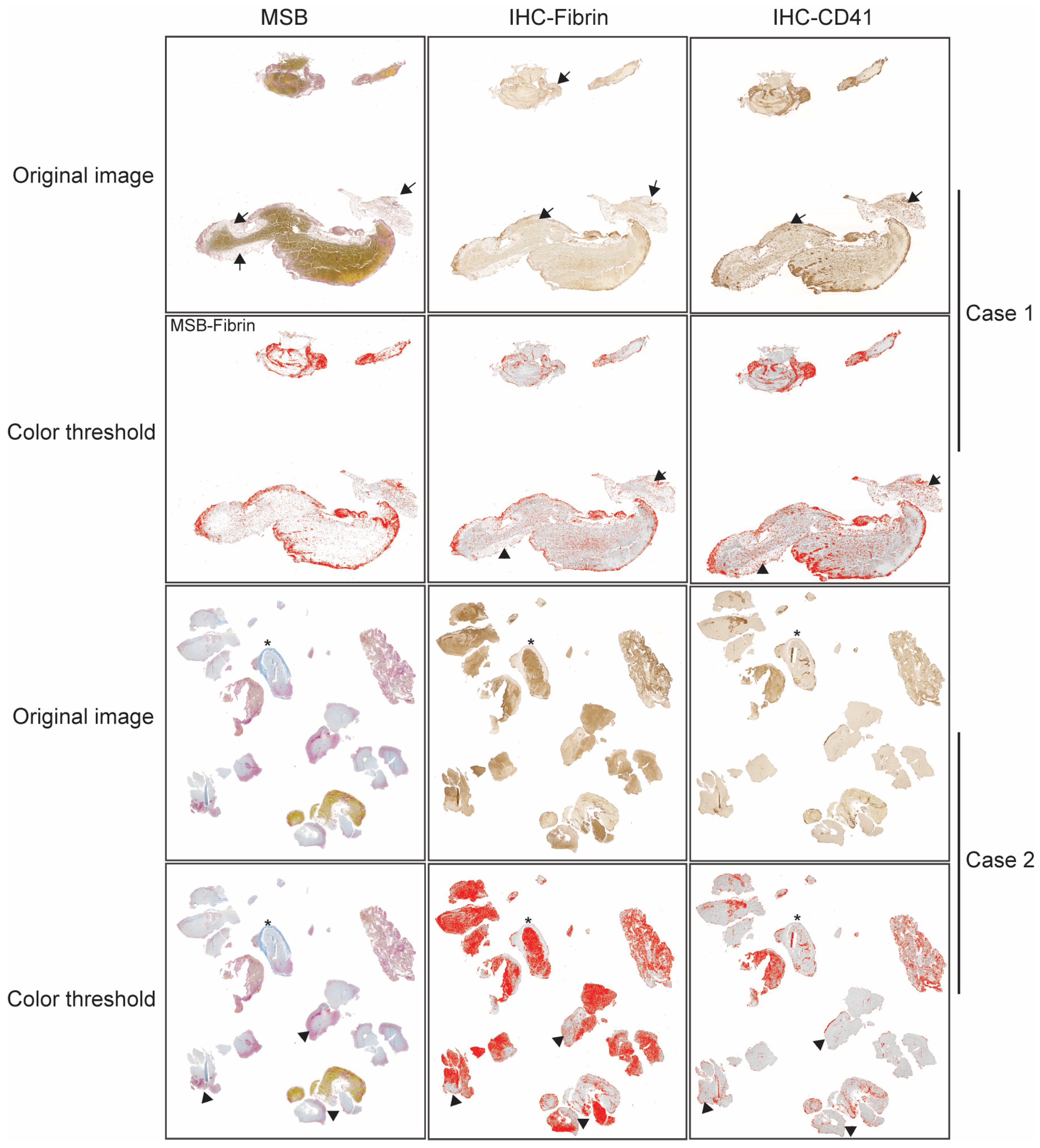
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis by RBC Tertiles
3.2. Thrombus Composition and Modified First Pass Effect
3.3. Relationship Between EVT Efficiency and Thrombus Composition
3.4. Final Reperfusion Outcomes and Thrombus Composition
3.5. Association Between Clinical Outcomes and Thrombus Composition
4. Discussions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, K.S.; Ko, S.B.; Yu, K.H.; Jung, C.; Park, S.Q.; Kim, B.M.; Chang, C.H.; Bae, H.J.; Heo, J.H.; Oh, C.W.; et al. Update of the Korean Clinical Practice Guidelines for Endovascular Recanalization Therapy in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke 2016, 18, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyer, S.F.; Andersson, T.; Baxter, B.; Bendszus, M.; Brouwer, P.; Brinjikji, W.; Campbell, B.C.; Costalat, V.; Davalos, A.; Demchuk, A.; et al. Analyses of thrombi in acute ischemic stroke: A consensus statement on current knowledge and future directions. Int. J. Stroke 2017, 12, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinjikji, W.; Duffy, S.; Burrows, A.; Hacke, W.; Liebeskind, D.; Majoie, C.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Khatri, P.; Baxter, B.; et al. Correlation of imaging and histopathology of thrombi in acute ischemic stroke with etiology and outcome: A systematic review. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.H.; Park, G.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, J.M. Erythrocyte Fraction Within Retrieved Thrombi Contributes to Thrombolytic Response in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, S.T.; Wang, S.; Dai, D.; Douglas, A.; Kadirvel, R.; Gounis, M.J.; Chueh, J.; Puri, A.S.; Layton, K.F.; Thacker, I.C.; et al. Platelet-rich clots as identified by Martius Scarlet Blue staining are isodense on NCCT. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessens, S.; Denorme, F.; Francois, O.; Desender, L.; Dewaele, T.; Vanacker, P.; Deckmyn, H.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Andersson, T.; De Meyer, S.F. Structural analysis of ischemic stroke thrombi: Histological indications for therapy resistance. Haematologica 2020, 105, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H. Traditional Thrombus Composition and Related Endovascular Outcomes: Catching up with the Recent Evidence. Neurointervention 2024, 19, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Yoo, A.J.; Khatri, P.; Tomsick, T.A.; von Kummer, R.; Saver, J.L.; Marks, M.P.; Prabhakaran, S.; Kallmes, D.F.; Fitzsimmons, B.F.; et al. Recommendations on angiographic revascularization grading standards for acute ischemic stroke: A consensus statement. Stroke 2013, 44, 2650–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.J.; Yoo, J.S.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Kang, D.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hong, J.M.; Choi, J.W.; et al. Prognosis of Acute Intracranial Atherosclerosis-Related Occlusion after Endovascular Treatment. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E., 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hong, J.M.; Kim, J.S. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies for Acute Intracranial Atherosclerosis-related Occlusions. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, P.A.; Demchuk, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Buchan, A.M. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. ASPECTS Study Group. Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score. Lancet 2000, 355, 1670–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Jung, W.S.; Choi, M.H.; Hong, J.M.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, J.W. Optimal Multiphase Computed Tomographic Angiography-based Infarct Core Estimations for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puetz, V.; Dzialowski, I.; Hill, M.D.; Subramaniam, S.; Sylaja, P.N.; Krol, A.; O’Reilly, C.; Hudon, M.E.; Hu, W.Y.; Coutts, S.B.; et al. Intracranial thrombus extent predicts clinical outcome, final infarct size and hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke: The clot burden score. Int. J. Stroke 2008, 3, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargazanli, C.; Fahed, R.; Blanc, R.; Gory, B.; Labreuche, J.; Duhamel, A.; Marnat, G.; Saleme, S.; Costalat, V.; Bracard, S.; et al. Modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction 2C/Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction 3 Reperfusion Should Be the Aim of Mechanical Thrombectomy: Insights From the ASTER Trial (Contact Aspiration Versus Stent Retriever for Successful Revascularization). Stroke 2018, 49, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Castonguay, A.C.; Linfante, I.; Gupta, R.; Martin, C.O.; Holloway, W.E.; Mueller-Kronast, N.; English, J.D.; Dabus, G.; Malisch, T.W.; et al. First Pass Effect: A New Measure for Stroke Thrombectomy Devices. Stroke 2018, 49, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Hong, J.M.; Lee, S.E.; Kang, D.R.; Ovbiagele, B.; Demchuk, A.M.; Lee, J.S. Association of fibrinogen level with early neurological deterioration among acute ischemic stroke patients with diabetes. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebeskind, D.S.; Sanossian, N.; Yong, W.H.; Starkman, S.; Tsang, M.P.; Moya, A.L.; Zheng, D.D.; Abolian, A.M.; Kim, D.; Ali, L.K.; et al. CT and MRI early vessel signs reflect clot composition in acute stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.; McCarthy, R.; Farrell, M.; Thomas, S.; Brennan, P.; Power, S.; O’Hare, A.; Morris, L.; Rainsford, E.; MacCarthy, E.; et al. Per-Pass Analysis of Thrombus Composition in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy. Stroke 2019, 50, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoglu, H. User’s guide to correlation coefficients. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, G.M.; McArdle, K.; Mirza, M.; Duffy, S.; Gilvarry, M.; Brouwer, P.A. Clot friction variation with fibrin content; implications for resistance to thrombectomy. J. Neurointerv Surg. 2018, 10, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagargoje, M.S.; Fregona, V.; Luraghi, G.; Migliavacca, F.; Pero, G.; Rodriguez Matas, J.F. The role of friction forces in arterial mechanical thrombectomy: A review. J. Biomech. 2025, 192, 112966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitriu LaGrange, D.; Bernava, G.; Reymond, P.; Wanke, I.; Vargas, M.I.; Machi, P.; Lovblad, K.O. A high resolution scanning electron microscopy analysis of intracranial thrombi embedded along the stent retrievers. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M. Causes and Solutions of Endovascular Treatment Failure. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolugbo, P.; Ariens, R.A.S. Thrombus Composition and Efficacy of Thrombolysis and Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2021, 52, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.H.; Nam, H.S.; Kim, Y.D.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, D.J.; Kwon, I. Pathophysiologic and Therapeutic Perspectives Based on Thrombus Histology in Stroke. J. Stroke 2020, 22, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereuta, O.M.; Rossi, R.; Douglas, A.; Gil, S.M.; Fitzgerald, S.; Pandit, A.; McCarthy, R.; Gilvarry, M.; Ceder, E.; Dunker, D.; et al. Characterization of the ‘White’ Appearing Clots that Cause Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 106127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, B.; Furie, B.C. Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirek, S.; Ozyurt, G.M.; Ozen, A.; Olmaz, R.; Esen, K. Thrombus stiffness as an independent predictor of endovascular treatment success in hemodialysis fistulas: A study using ultrasound elastography. Ultrasonography 2025, 44, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackman, N.; Hisada, Y. Circulating Tumor Cells and Cancer-Associated Venous Thrombosis: A Missing Link. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2023, 43, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laridan, E.; Denorme, F.; Desender, L.; Francois, O.; Andersson, T.; Deckmyn, H.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; De Meyer, S.F. Neutrophil extracellular traps in ischemic stroke thrombi. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, T.; Hori, Y.; Okazaki, S.; Shimada, Y.; Iwamoto, T.; Kanki, H.; Sugiyama, S.; Sasaki, T.; Nakamura, H.; Oyama, N.; et al. An Older Thrombus Delays Reperfusion after Mechanical Thrombectomy for Ischemic Stroke. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 122, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; Kwon, I.; Kim, S.; Nam, H.S.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, D.J.; Song, T.J.; Heo, J.H. Thrombi with a Higher Erythrocyte Composition Are More Fragile in Acute Stroke. J. Stroke 2024, 26, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaesmacher, J.; Boeckh-Behrens, T.; Simon, S.; Maegerlein, C.; Kleine, J.F.; Zimmer, C.; Schirmer, L.; Poppert, H.; Huber, T. Risk of Thrombus Fragmentation during Endovascular Stroke Treatment. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fereidoonnezhad, B.; Dwivedi, A.; Johnson, S.; McCarthy, R.; McGarry, P. Blood clot fracture properties are dependent on red blood cell and fibrin content. Acta Biomater. 2021, 127, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santo, B.A.; Patel, T.R.; Mousavi Janbeh Sarayi, S.M.; Poppenberg, K.E.; Balghonaim, S.; Scotti, A.; Jenkins, T.D.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Kolega, J.; et al. CT Radiomic Signatures of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Ischemic Stroke Thrombi. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussen, D.C.; Al-Bayati, A.R.; Grossberg, J.A.; Bouslama, M.; Barreira, C.; Bianchi, N.; Frankel, M.R.; Nogueira, R.G. Longer stent retrievers enhance thrombectomy performance in acute stroke. J. Neurointerventional Surg. 2019, 11, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Bozorgchami, H.; Ribo, M.; Saver, J.L.; Mattle, H.P.; Chapot, R.; Narata, A.P.; Francois, O.; Jadhav, A.P.; Grossberg, J.A.; et al. Primary Results of the Multicenter ARISE II Study (Analysis of Revascularization in Ischemic Stroke with EmboTrap). Stroke 2018, 49, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 1st Tertile | 2nd Tertile | 3rd Tertile | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 19) | (N = 20) | (N = 20) | ||
| Thrombus components | ||||
| Surface area (mm2) | 22.7 ± 13.5 | 40.4 ± 66.7 | 32.4 ± 45.9 | 0.517 |
| H&E RBC (%) | 22.8 ± 11.3 | 42.4 ± 6.8 | 57.6 ± 17.4 | <0.001 * |
| H&E WBC (%) | 4.3 ± 1.9 | 4.3 ± 1.9 | 4.6 ± 2.0 | 0.854 |
| H&E fibrin/platelet/others (%) | 72.9 ± 11.4 | 53.3 ± 6.8 | 37.8 ± 17.4 | <0.001 * |
| MSB RBC (%) | 18.7 ± 9.1 | 39.1 ± 4.9 | 58.6 ± 10.5 | <0.001 * |
| MSB WBC (%) | 3.8 ± 1.6 | 4.9 ± 3.1 | 4.2 ± 1.8 | 0.372 |
| MSB fibrin (%) | 29.1 ± 11.6 | 26.1 ± 14.0 | 21.4 ± 7.2 | 0.114 |
| MSB platelet/others (%) | 48.4 ± 11.5 | 29.9 ± 13.7 | 15.8 ± 12.5 | <0.001 † |
| IHC fibrin (%) | 26.7 ± 16.0 | 27.4 ± 14.6 | 18.8 ± 7.9 | 0.085 |
| IHC platelet (%) | 34.9 ± 15.8 | 23.4 ± 10.7 | 20.4 ± 10.3 | 0.002 ‡ |
| Clinical parameters | ||||
| Age | 73 ± 11 | 67 ± 15 | 73 ± 12 | 0.225 |
| Sex, male | 10 (52.6%) | 15 (75.0%) | 13 (65.0%) | 0.345 |
| NIHSS | 18 [12–19] | 15 [13–19.75] | 17.5 [13.25–19.75] | 0.718 |
| HTN | 15 (78.9%) | 9 (45.0%) | 14 (70.0%) | 0.070 |
| DM | 6 (31.6%) | 3 (15.0%) | 3 (15.0%) | 0.335 |
| A-fib | 13 (68.4%) | 10 (50.0%) | 12 (60.0%) | 0.503 |
| Stroke etiology | 0.177 | |||
| Cardioembolic | 17 (89.5%) | 11 (55.0%) | 13 (65.0%) | |
| Large artery disease | 1 (5.3%) | 5 (25.0%) | 5 (25.0%) | |
| Others | 1 (5.3%) | 4 (20.0%) | 2 (10.0%) | |
| Tandem occlusion | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (25.0%) | 5 (25.0%) | 0.057 |
| CT collaterals | 3 [2–4] | 3 [3–3.75] | 2.5 [1.25–4.0] | 0.541 |
| Clot burden score | 6 [6–7] | 6 [5–6] | 6.0 [60–6.0] | 0.929 |
| EVT outcomes | ||||
| Stent retrieval as primary modality | 18 (94.7%) | 16 (80.0%) | 17 (85.0%) | 0.395 |
| Thrombectomy trials | 2 [1–3] | 2 [1–3] | 2 [2–3] | 0.917 |
| Toral thrombectomy time, min | 47 [35–60] | 66.5 [35–91.5] | 61.5 [45–82.25] | 0.173 |
| Working EVT time, min | 32 [19–39] | 31 [17.5–51.5] | 37 [24.0–42.75] | 0.703 |
| mFPE (2b–3) | 9 (47.4%) | 11 (55.0%) | 9 (45.0%) | 0.804 |
| mFPE (2c–3) | 7 (36.8%) | 6 (30.6%) | 4 (20.0%) | 0.505 |
| Functional outcomes | ||||
| END | 4 (21.1%) | 4 (20.0%) | 5 (25.0%) | 0.923 |
| Good functional outcomes | 11 (61.1%) | 9 (45.0%) | 7 (35.0%) | 0.269 |
| For mFPE of mTICI 2b or Higher | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| mFPE (+) | mFPE (−) | p Value | |
| N = 29 | N = 30 | ||
| Surface area (mm2) | 16.0 ± 11.6 | 47.4 ± 62.3 | 0.005 |
| H&E RBC (%) | 40.8 ± 20.6 | 41.7 ± 17.5 | 0.431 |
| H&E WBC (%) | 4.2 ± 1.5 | 4.6 ± 2.3 | 0.216 |
| H&E fibrin/platelet/others (%) | 55.0 ± 20.3 | 53.7 ± 18.1 | 0.400 |
| MSB RBC (%) | 38.5 ± 19.7 | 39.8 ± 17.1% | 0.399 |
| MSB WBC (%) | 4.1 ± 1.3 | 4.5 ± 3.0 | 0.230 |
| MSB fibrin (%) | 29.8 ± 10.7 | 21.3 ± 10.9 | 0.002 |
| MSB platelet/others (%) | 27.6 ± 20.9 | 34.4 ± 14.9 | 0.078 |
| IHC fibrin (%) | 28.5 ± 14.5 | 20.1 ± 11.4 | 0.008 |
| IHC platelet (%) | 26.4 ± 14.6 | 28.7 ± 13.1 | 0.868 |
| For mFPE of mTICI 2c or higher | |||
| mFPE (+) | mFPE (−) | p Value | |
| N = 17 | N = 42 | ||
| Surface area (mm2) | 17.8 ± 11.9 | 37.7 ± 55.0 | 0.015 |
| H&E RBC (%) | 36.3 ± 23.2 | 43.2 ± 16.9 | 0.102 |
| H&E WBC (%) | 4.3 ± 1.6 | 4.4 ± 2.1 | 0.409 |
| H&E fibrin/platelet/others (%) | 59.4 ± 23.0 | 52.3 ± 17.1 | 0.100 |
| MSB RBC (%) | 33.4 ± 20.2 | 41.5 ± 17.3 | 0.062 |
| MSB WBC (%) | 4.0 ± 1.3 | 4.4 ± 2.6 | 0.291 |
| MSB fibrin (%) | 32.1 ± 10.3 | 22.8 ± 11.0 | 0.002 |
| MSB platelet/others (%) | 30.4 ± 23.5 | 31.3 ± 16.0 | 0.448 |
| IHC fibrin (%) | 28.5 ± 15.9 | 22.5 ± 12.4 | 0.065 |
| IHC platelet (%) | 29.7 ± 17.4 | 24.6 ± 11.9 | 0.137 |
| For Total Thrombectomy Trials | R | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Surface area | 0.310 | 0.017 |
| MSB fibrin | −0.304 | 0.019 |
| MSB platelet/others | 0.109 | 0.413 |
| For Total Procedure Time | ||
| Surface area | 0.319 | 0.014 |
| MSB RBC | 0.267 | 0.041 |
| MSB WBC | 0.265 | 0.042 |
| MSB fibrin | −0.502 | <0.001 |
| MSB platelet/others | 0.015 | 0.911 |
| IHC fibrin | −0.326 | 0.012 |
| IHC platelets | −0.361 | 0.005 |
| For Working EVT Time | ||
| Surface area | 0.277 | 0.034 |
| MSB fibrin | −0.421 | <0.001 |
| IHC Fibrin | −0.285 | 0.028 |
| mTICI 2c–3 | mTICI 2b | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = 39 | N = 20 | ||
| Surface area (mm2) | 33.1 ± 54.2 | 29.8 ± 31.5 | 0.402 |
| H&E RBC (%) | 40.0 ± 21.4 | 43.7 ± 13.1 | 0.209 |
| H&E WBC (%) | 4.4 ± 1.9 | 4.4 ± 2.1 | 0.463 |
| H&E fibrin/platelet/others (%) | 55.6 ± 21.8 | 52.0 ± 12.2 | 0.209 |
| MSB RBC (%) | 38.5 ± 20.2 | 40.4 ± 14.4 | 0.356 |
| MSB WBC (%) | 4.0 ± 1.9 | 4.8 ± 3.0 | 0.099 |
| MSB fibrin (%) | 27.3 ± 11.1 | 22.1 ± 11.9 | 0.051 |
| MSB platelet/others (%) | 30.2 ± 19.0 | 32.7 ± 16.9 | 0.312 |
| IHC fibrin (%) | 25.5 ± 13.0 | 21.9 ± 14.8 | 0.173 |
| IHC platelet (%) | 27.6 ± 14.9 | 23.0 ± 10.9 | 0.092 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-J.; Nguyen, M.T.; Seo, J.E.; Jung, W.S.; Choi, J.W.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.S. Detailed Analysis of Thrombus Composition and Endovascular Thrombectomy Efficiency in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Undergoing Thrombectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8088. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228088
Lee S-J, Nguyen MT, Seo JE, Jung WS, Choi JW, Park SY, Lee JS. Detailed Analysis of Thrombus Composition and Endovascular Thrombectomy Efficiency in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Undergoing Thrombectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8088. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seong-Joon, Mai Tuyet Nguyen, Jeong Eun Seo, Woo Sang Jung, Jin Wook Choi, So Young Park, and Jin Soo Lee. 2025. "Detailed Analysis of Thrombus Composition and Endovascular Thrombectomy Efficiency in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Undergoing Thrombectomy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8088. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228088
APA StyleLee, S.-J., Nguyen, M. T., Seo, J. E., Jung, W. S., Choi, J. W., Park, S. Y., & Lee, J. S. (2025). Detailed Analysis of Thrombus Composition and Endovascular Thrombectomy Efficiency in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Undergoing Thrombectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8088. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228088






