Abstract
The coronavirus pandemic is the greatest crisis of our time, having claimed over 2 million lives and shocking the global economy. Scientists and governments have suggested the idea of a digital COVID-19 certificate, to identify vaccinated persons easily. This paper assesses the positions of stakeholders on COVID-19 vaccination certificates, their presentation, and their importance. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) was applied in this study. Search terms with Boolean and/or operators were combined to increase relevant results. Four large digital databases were used for the search. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were used to screen 298 collated studies. Two reviewers independently assessed search results, extracted data, and assessed the quality of the included studies. It is essential to re-examine digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates, considering their benefits, such as real-time detection of fake vaccination certificates and identifying and mapping non-vaccinated areas for strategic vaccination planning. The use of a single electronic platform globally will ease verification processes while bringing economies back to their feet. Digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates may provide balance in this pandemic era. With digital COVID-19 certificate exceeding documentation purposes, it is important to recognise factors such as global economy and human rights, boosting free movements of persons.
1. Introduction
Global economy and health have been affected since the outbreak of acute community-based atypical pneumonia of unknown aetiology was reported in Wuhan, capital of Hubei province in China, in December 2019 [1]. Scores of researchers observe that global initiatives have been established for the deployment of vaccines to tackle the COVID-19 virus [2,3,4,5]. A vaccination certificate is issued out to any individual who is vaccinated against the virus. This vaccination certificate serves as proof to grant the holder access to public events, air travel, etc., without being restricted from accessing facilities in these areas [6]. A study by Hernández-Ramos et al. [7] shows that COVID-19 certificates have been given to vaccinated persons to ease restrictions imposed by governments. Although COVID-19 vaccination certificates can help ease restrictions, the processes involved in obtaining and using them should not be seen as agents of promoting the spread of the virus. Failure to focus on security systems to store patients’ information may raise data privacy concerns that can discourage many from partaking in the vaccination process [8].
The work of Schlagenhauf et al. [9] discusses whether COVID-19 vaccination certificates should be digitalised or in paper format. Should the COVID-19 vaccination certificate be an enhanced version of the International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis, potentially in the form of an electronic record? Another studies by Kowalewski et al. [10] proposes that digital tools play a vital role in mitigating the spread of COVID-19. Digitalising COVID-19 vaccination certificates can minimise physical contact during verification of vaccination status at public events and local and international airports. However, an online representative study conducted in Germany on a sample of 599 participants assessing user perception of vaccination certificates indicated that the majority of participants favoured paper-based COVID-19 vaccination certificates over digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates [10]. Obligatory COVID-19 certification (showing recent negative test, proof of recovery, or vaccination) has been tabled in some countries [11]. As part of global efforts to enhance the vaccination rate, scientists and governments have suggested the idea of COVID-19 immunity certificates. The COVID-19 immunity certificate is for those fully vaccinated or recovered from the coronavirus disease. The COVID-19 immunity certificate is an incentive to drive public interest in vaccination campaigns [12].
Vaccination is gaining global ground. The idea of a COVID-19 vaccination certificate is gaining popularity. Hence, there is the need for international health bodies (such as the World Health Organisation) to be specific as to whether COVID-19 vaccination certificates should be digitalised or paper-based [13]. Artificial intelligence can be applied to detect fake COVID-19 vaccination certificates if the certificate is in a digital format. Furthermore, artificial intelligence can help identify and map non-vaccinated regions for strategic planning if digital COVID-19 vaccination certification systems are deployed. Furthermore, through the application of artificial intelligence, digital COVID-19 vaccination certification systems can organise migration patterns of migrants, based on data stored in the verification application, and assist in contact tracing. Blockchain (BC) technology, which is an immutable, transparent, and decentralised technology that provides a secured way of sending information, may ensure patients’ personal data confidentiality [14]. Internet of Things and BC technology can be used to remotely access COVID-19 vaccination certificates. The paper-based vaccination certificate mostly serves “documenting” and “manual verification” purposes [15]. Although the European Union named its COVID-19 vaccination certificate the “EU Digital COVID Certificate”, some member states still combine digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates with paper-based COVID-19 vaccination certificates [16]. This paper assesses the positions of stakeholders on COVID-19 vaccination certificates and evaluates the formats stakeholders propose a COVID-19 vaccination certificate must take. The study also expounds on the importance of digitalising COVID-19 vaccination certificates.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification: Data Sources and Search Strategy
Keywords were defined to obtain relevant kinds of literature that address the learning objective. Search keywords were created to ensure the quality of the reviews. This was done by combining search terms with Boolean and/or operators to increase relevant results. With constraints on the search, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) were used in the search. Keywords for this review were: COVID-19; Travel Pass; COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate; Digital COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate; Paper-based COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate; COVID-19 Passport Policies. Four digital databases were used for the search, and they were: ProQuest, PubMed, Sage Pub, and Science Direct (see Table 1). The rationale behind selecting these search engines was that they suit the study areas of this review, which are health/medical science and information systems. ProQuest, PubMed, Sage Pub, and Science Direct have a filter feature to screen literature based on year of publication, type of literature, study area, etc. The study title and keywords were used to search for related literature. The plan was to collate all results for each keyword search. The search was conducted from 23 October 2021 to 3 January 2022. A total of 298 studies were collated at the end of search. Two reviewers independently assessed search results, extracted data, and assessed the quality of the included studies.

Table 1.
Databases and number of studies used in this review.
2.2. Screening: Selecting Studies Based on Listed Criteria
The following inclusion criteria were used to screen the 298 collated studies. The paper needs to: (1) be written in English; (2) be a journal paper; (3) address review objectives; (4) be related to specified keywords. Duplicated papers and papers not in full text were excluded. This is depicted in Table 2.

Table 2.
Inclusion and exclusion of studies based on criteria.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) was applied in this study. Streamlining literature availability and finding best-fit literature for this review was the reason for using PRISMA flow diagram. This is shown in Figure 1.
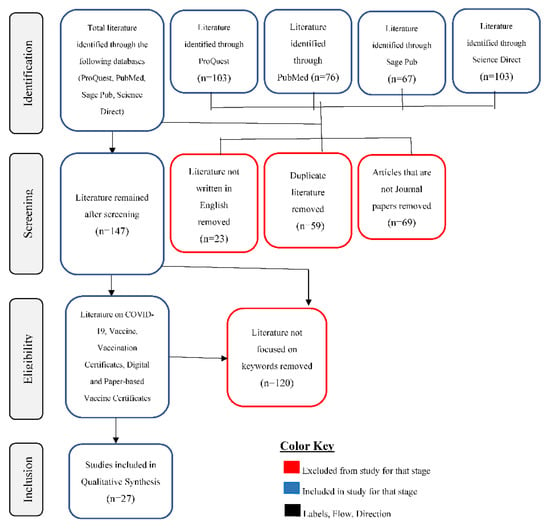
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow for process of article inclusion and exclusion.
3. Results
Out of the two hundred and seventy-one (271) excluded papers, twenty-three (23) papers, representing 9%, were excluded for not been written in English. There were fifty-nine (59) duplicates excluded, representing 22%. Sixty-nine (69) papers, representing 25%, were excluded because they were not journal papers. A total of one hundred and twenty (120) papers, representing 44%, were excluded for not relating to the subject matter. This is depicted in Figure 1.
Twenty-seven (27) papers were included in the qualitative synthesis (see Table 3). The inclusions consisted of three (3) articles, representing 11%, used for introduction to the study synthesis (see Table 4); three (3) articles, representing 11%, on the background of COVID-19 (see Table 5); four (4) articles, representing 15%, on the history of vaccination certificates (see Table 6); eleven (11) articles, representing 41%, that expounded on the positions of stakeholders on COVID-19 vaccination certificates (see Table 7); three (3) articles, representing 11%, that elaborated on the advantages and disadvantages of digital and paper-based COVID-19 vaccination certificates (see Table 8); and three (3) papers, representing 11%, on privacy concern issues around digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates (see Table 9).

Table 3.
Results of Included Articles.

Table 4.
Introduction to study analysis.

Table 5.
Background of COVID-19.

Table 6.
History of vaccination certificates.

Table 7.
Positions of stakeholders on COVID-19 vaccination certificates.

Table 8.
Digital and paper-based COVID-19 vaccination certificates: the advantages and disadvantages.

Table 9.
Addressing issues of privacy concerns for digital COVID-19 vaccine certificates.
Papers included in the review were from seventeen (17) different countries.
Figure 2 shows the distribution based on countries.
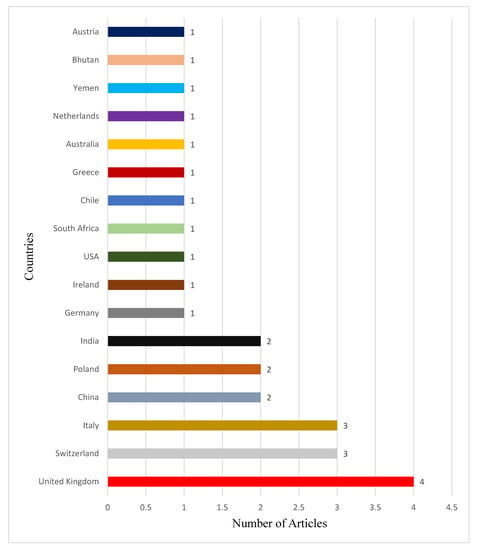
Figure 2.
Distribution of countries based on their respective number of articles. Summary characteristics of studies included.
4. Discussion
The review explores the positions of various stakeholders (the World Health Organisation, the International Civil Aviation Organisation, continental unions, countries, and global citizens) on COVID-19 vaccination certificates and evaluates the formats stakeholders propose a COVID-19 vaccination certificate must take. The study also expounds on the importance of digitalising COVID-19 vaccination certificates.
4.1. The Positions of Stakeholders on COVID-19 Vaccination Certificates
The World Health Organisation (WHO) suggests that COVID-19 vaccination requirements for international travels should not be implemented [22]. This may be a public health decision to limit the spread of the virus by limiting physical contacts that COVID-19 vaccination requirements introduce. The aviation industry was one of the sectors that took major hits as a result of the coronavirus pandemic [19]. The International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) has indicated its intent to accept proof of COVID-19 immunisation in the form of a WHO yellow card [4]. Is this an economic decision to bring the aviation sector back to its feet or a decision to balance global public health and economy? At a regional level, the European Union (EU) has developed its own EU Digital COVID-19 certificate, which has been accepted by all member states [16]. Although the name of the European Union’s certificate is the EU Digital COVID-19 Certificate, its implementation is a blend of digital and paper-based certificates. At a national level, while some countries such as Lithuania use strict measures to ensure high vaccination rates, others such as Poland are adapting the voluntary option [26]. Compulsory COVID-19 certification has been initiated in some countries [11]. The Chilean government has initiated and implemented a “release passport” policy, which is similar to an immunity passport, a position opposed by the World Health Organisation [3]. Bhutan “encourages” visitors to be vaccinated but does not mandate them to be vaccinated [13]. Other studies have been conducted to assess the perception of citizens around the world of COVID-19 vaccination certificates [24,25]. A study conducted in the United Kingdom showed that most people were inclined towards accepting the COVID-19 vaccine because of the COVID-19 vaccination certificate [25]. Another study that assessed behavioural responses of participants to COVID-19 health certification indicated that public attitudes towards the use of immunity certificates for international travels were favourable. However, the public opposed the idea of using immunity certificates for work and other activities [24].
From international, regional, national, and citizenry levels, all stakeholders agreed on the need for COVID-19 vaccination programmes [4,5,22]. While some stakeholders suggested that COVID-19 certificates should not be used as evidence for international travels, others made known their intent to accept proof of COVID-19 vaccination for international travels [4,22]. This is a policy conflict between stance of public health and that of global economy [12]. Striking a balance between public health and bringing the global economy back to its feet is the solution. Digitalising COVID-19 vaccination certificates will reduce public health risks associated with vaccination certification policies. Bringing the global economy back to its feet must not be done in a hurried manner that may escalate the COVID-19 virus [19,20].
While some countries are mandating COVID-19 vaccination certificates, others suggest it must be a voluntary decision [3,11,13,26]. This is a conflict between human rights and public health. Should the rights of people be infringed upon in a quest to implement public health policies? A COVID-19 vaccination certificate is now a requirement to attend public events and to travel locally and internationally [24,25]. A COVID-19 vaccination certificate is also required to allow people to work in some jurisdictions [26]. How can a policy strike a balance between public health and human rights?
4.2. Policy Recommendation on the Positions of Stakeholders on COVID-19 Vaccination Certificates
Score of researchers has postulated that policies from the World Health Organisation recognising factors such as global economy and human rights while showing a framework to implement a COVID-19 vaccination certification programme globally will help to promote uniformity in COVID-19 vaccination certificate programmes and promote the onboarding of all stakeholders [3,4,9,15,22,23,24,25].
4.3. The Format COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate Must Take
The EU Digital COVID-19 Certificate introduced by the European Union includes three certificate types: test certificates, vaccination certificates, and recovery certificates [23]. While issues of falsification or counterfeit COVID-19 vaccine certificates surround the paper-based approach, privacy issues also surround the digital approach [9]. A web-based study evaluated user perception of COVID-19 vaccination certificates. Two paper-based variants and three digital app variants were used. Digital and paper-based vaccine certificates were used for documentation purposes only [assumed]. The results showed that paper-based vaccination certificates were generally favoured over digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates [10]. In addition, benefits of digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates and paper-based COVID-19 vaccination certificates should not be limited to documentation purposes only, as cited in [10]. Digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates can be used to execute various functions. By applying artificial intelligence, fake COVID-19 vaccination certificates can be easily detected, non-vaccinated areas can be identified and mapped for strategic vaccination planning, and contact tracing can be improved. Furthermore, Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) and blockchain technology can be applied in areas with remote access to COVID-19 vaccination certificates, ensuring data privacy [15]. The study conducted by Mbunge et al. [15] highlights the need for global adaptation towards use of digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates and uniform global implementation of digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates.
4.4. Policy Recommendation on Format of COVID-19 Vaccination Certificates
According to Sharif et al. [5], the use of a single electronic platform globally will ease verification processes while bringing economies back to their feet. A policy that initiates global digitalisation of COVID-19 vaccination certificates while highlighting technologies to mitigate data privacy issues associated with digitalised COVID-19 vaccination certificates will enhance stakeholders’ buy-in.
4.5. Addressing Challenges Associated with Digital COVID-19 Vaccination Certificates: A Focus on Data Privacy
Data privacy is the main challenge that hinders people from buying into the idea of digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates [25]. In addressing privacy challenges, blockchain technology can be a major solution [7]. The immutability, transparency, and decentralisation characteristics of blockchain technology provide a trustworthy and secured way of sharing confidential and personal data [14]. One vulnerability of blockchain technology is apparent when resolution of an on-chain mapping of an identifier is specified to a key in public-permissioned blockchain systems, which results in redirection to central servers [27]. Encrypting on-chain mapping processes of an identifier could mitigate this limitation.
4.6. Policy Recommendation Addressing Challenges Associated with Digital COVID-19 Vaccination Certificates: Focus on Data Privacy
A policy recommendation inferred from Foy et al. [27] stipulates that resolution of on-chain mapping of an identifier to a key in public-permissioned blockchain systems must not be specified, as it will redirect results to central servers, exposing data of vaccinated persons.
5. Conclusions
Digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates may provide balance in this pandemic era [16]. Studies postulate them as negotiating the thin line between public health and bringing the global economy back to its feet [19,20]. With use of digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates exceeding documentation purposes, recognising factors such as global economy and human rights while showing a framework to implement uniform global digital COVID-19 vaccination certification will mitigate COVID-19 spread while boosting international travels [14]. It is essential to re-examine digital COVID-19 vaccination certificates, taking into account their benefits, such as: real-time detection of fake COVID-19 vaccination certificates, identifying and mapping non-vaccinated areas for strategic vaccination planning, aiding in contact tracing, and supporting areas with remote access to COVID-19 vaccination certificates [15]. In addressing privacy challenges, blockchain technology can be a major solution [7]. Several studies expound on the stances of stakeholders on COVID-19 vaccination certificates and the format they must take as has been stipulated in this review study. Hence, there is a need for a global policy in that direction by the World Health Organisation to promote uniformity in its implementation.
Quintessential of academic studies, there were some limitations to this study. For instance, the literature search was conducted in only four databases. This may create an impression that studies outside the selected databases were ignored. Some studies with relevant information were disregarded after screening of downloaded studies using inclusive and exclusive criteria. To some extent, methodological limitations of included studies that utilised primary data may have influenced findings of this review. Furthermore, generalisability of findings of this study may be limited, because included studies did not clearly elaborate on how participants were selected. With respect to secondary research-based included studies, limitations regarding the process of sampling were disclosed. This may also limit findings of this research. The included articles in this study did not equally cover all the geographical areas of the world but were limited to only seventeen countries, as shown in Figure 2. It must be reemphasised that only English-language articles were included. This also limits the generalisability of the findings to other contexts. This review is a contribution to the strategies and recommendations for implementing COVID-19 vaccination certificates based on the included databases. Further primary-data-based studies must investigate how paper-based vaccination certificates may have contributed to the spread of COVID-19 and projections into the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K.; formal analysis, investigation, and data curation, J.K. and C.A.; formal data analysis and results interpretation, J.K., C.A. and J.N.L.; writing, original draft preparation, J.K. and C.A.; writing, review and editing, E.K.A. and N.K.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Looking Back at a Year That Changed the World: WHO’s Response to COVID-19; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- To, K.K.; Sridhar, S.; Chiu, K.H.; Hung, D.L.; Li, X.; Hung, I.F.; Raymond Tam, A.; Wai-Hin Chung, T.; Fuk-Woo Chan, J.; Jian-Xia Zhang, A.; et al. Lessons learned 1 year after SARS-CoV-2 emergence leading to COVID-19 pandemic. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 507–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, B. Chile plans controversial COVID-19 certificates. Lancet 2020, 395, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.; Lucey, D.; Blumberg, L.; Kramer, L.D.; Al-Abri, S.; Lee, S.S.; Pinto, T.D.C.A.; Obiero, C.W.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Yapi, R.; et al. COVID-19 vaccines under the International Health Regulations–We must use the WHO International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.; Botlero, R.; Hoque, N.; Alif, S.M.; Karim, M.N.; Islam, S.M.S. A pragmatic approach to COVID-19 vaccine passport. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e006956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.L.; Malik, A.; Ruhi, U.; Al-Busaidi, A. Conflicting attitudes: Analyzing social media data to understand the early discourse on COVID-19 passports. Technol. Soc. 2022, 68, 101830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Ramos, J.L.; Karopoulos, G.; Geneiatakis, D.; Martin, T.; Kambourakis, G.; Fovino, I.N. Sharing Pandemic Vaccination Certificates through Blockchain: Case Study and Performance Evaluation. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 2427896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, O.P.; Priyanka, I.S. Vaccination certificate: An initiative to mitigate COVID-19 waves in India? J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2021, 120, 1931–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlagenhauf, P.; Patel, D.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Gautret, P.; Grobusch, M.P.; Leder, K. Variants, vaccines and vaccination passports: Challenges and chances for travel medicine in 2021. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 101996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalewski, M.; Herbert, F.; Schnitzler, T.; Dürmuth, M. Proof-of-Vax: Studying User Preferences and Perception of Covid Vaccination Certificates. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2106.11676 (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Mills, M.C.; Rüttenauer, T. The effect of mandatory COVID-19 certificates on vaccine uptake: Synthetic-control modelling of six countries. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e15–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Jia, H.; Xie, Y. Passport to a mighty nation: Exploring sociocultural foundation of chinese public’s attitude to covid-19 vaccine certificates. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, S.T.; Lhendup, K.; Dorji, T. Control of travel-related COVID-19 in Bhutan. J. Travel Med. 2021, 28, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.; Shah, M.; Tanwar, S.; Kumar, N. Blockchain for COVID-19: A comprehensive review. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2021, 1, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbunge, E.; Dzinamarira, T.; Fashoto, S.G.; Batani, J. Emerging technologies and COVID-19 digital vaccination certificates and passports. Public Health Pract. 2021, 2, 100136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raciborski, F.; Samel-Kowalik, P.; Gujski, M.; Pinkas, J.; Arcimowicz, M.; Jankowski, M. Factors associated with a lack of willingness to vaccinate against COVID-19 in poland: A 2021 nationwide cross-sectional survey. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nueangnong, V.; Hasan Subih, A.A.S.; Al-Hattami, H.M. The 2020’s world deadliest pandemic: Corona Virus (COVID-19) and International Medical Law (IML). Cogent Soc. Sci. 2020, 6, 1818936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A. Aadhaar in a Box? Legitimizing Digital Identity in Times of Crises. Surveill. Soc. 2021, 19, 104–108. Available online: https://ojs.library.queensu.ca/index.php/surveillance-and-society/index| (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Sotis, C.; Allena, M.; Reyes, R.; Romano, A. COVID-19 vaccine passport and international traveling: The combined effect of two nudges on americans’ support for the pass. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, K.T.; Janny, A.; Riesinger, K. Austria’s digital vaccination registry: Stakeholder views and implications for governance. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, M.A.; Paladino, M.E.; Brambilla, S.; Belingheri, M. COVID-19 health passes: Lessons from the past. J. Travel Med. 2021, 28, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavli, A.; Maltezou, H.C. COVID-19 vaccine passport for safe resumption of travel. J. Travel Med. 2021, 28, taab079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergallo, G.M.; Zaami, S.; Negro, F.; Brunetti, P.; del Rio, A.; Marinelli, E. Does the eu covid digital certificate strike a reasonable balance between mobility needs and public health? Medicina 2021, 57, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, J.; Mao, G.; John, A.; Kamal, A.; Rubin, G.J.; Stott, C.; Vandrevala, T.; Marteau, T.M. Behavioural responses to COVID-19 health certification: A rapid review. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Figueiredo, A.; Larson, H.J.; Reicher, S.D. The potential impact of vaccine passports on inclination to accept COVID-19 vaccinations in the United Kingdom: Evidence from a large cross-sectional survey and modeling study. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 40, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkowiak, M.P.; Walkowiak, J.B.; Walkowiak, D. COVID-19 passport as a factor determining the success of national vaccination campaigns: Does it work? the case of lithuania vs. Poland. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foy, M.; Martyn, D.; Daly, D.; Byrne, A.; Aguneche, C.; Brennan, R. Blockchain-based governance models for COVID-19 digital health certificates: A legal, technical, ethical and security requirements analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 198, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).