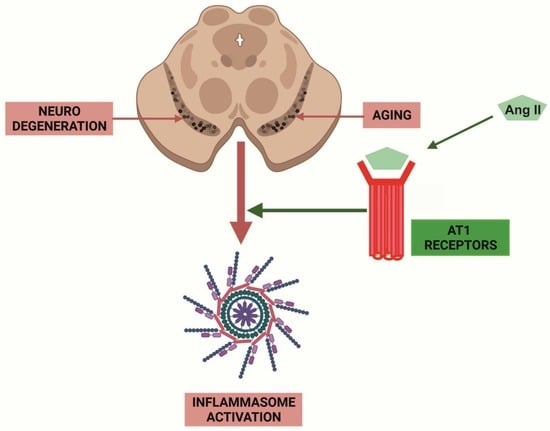
Angiotensin Type-1 Receptor Inhibition Reduces NLRP3 Inflammasome Upregulation Induced by Aging and Neurodegeneration in the Substantia Nigra of Male Rodents and Primary Mesencephalic Cultures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Young Adult and Aged Rats and Mice
2.3. In Vivo Induction of Partial Dopaminergic Degeneration with the Dopaminergic Neurotoxin 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)
2.4. Treatment of Rats with Candesartan
2.5. In Vitro Induction of Dopaminergic Degeneration. Primary Mesencephalic Neuron-Glia Cultures
2.6. Administration of Intraventricular AngII in Rats
2.7. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
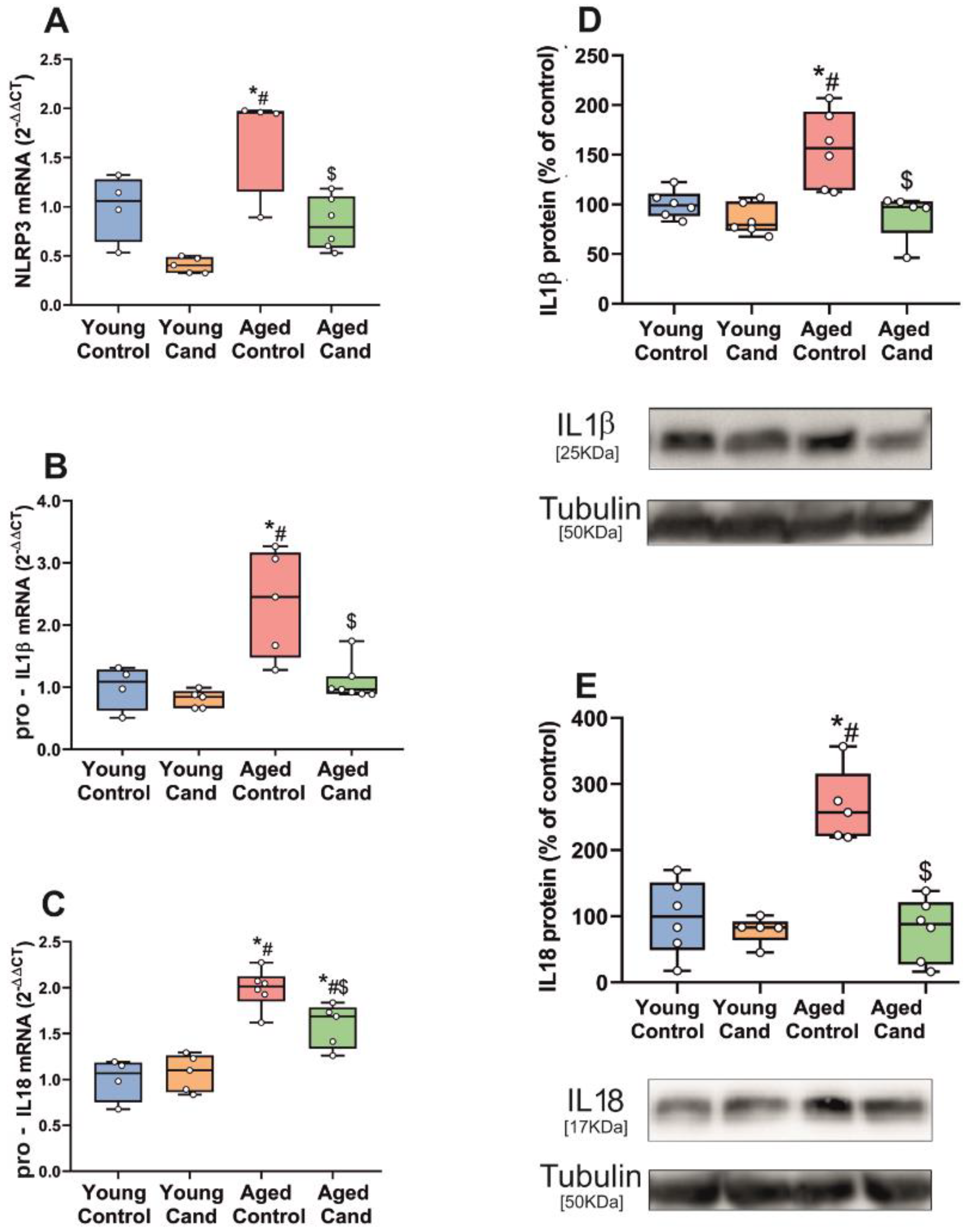
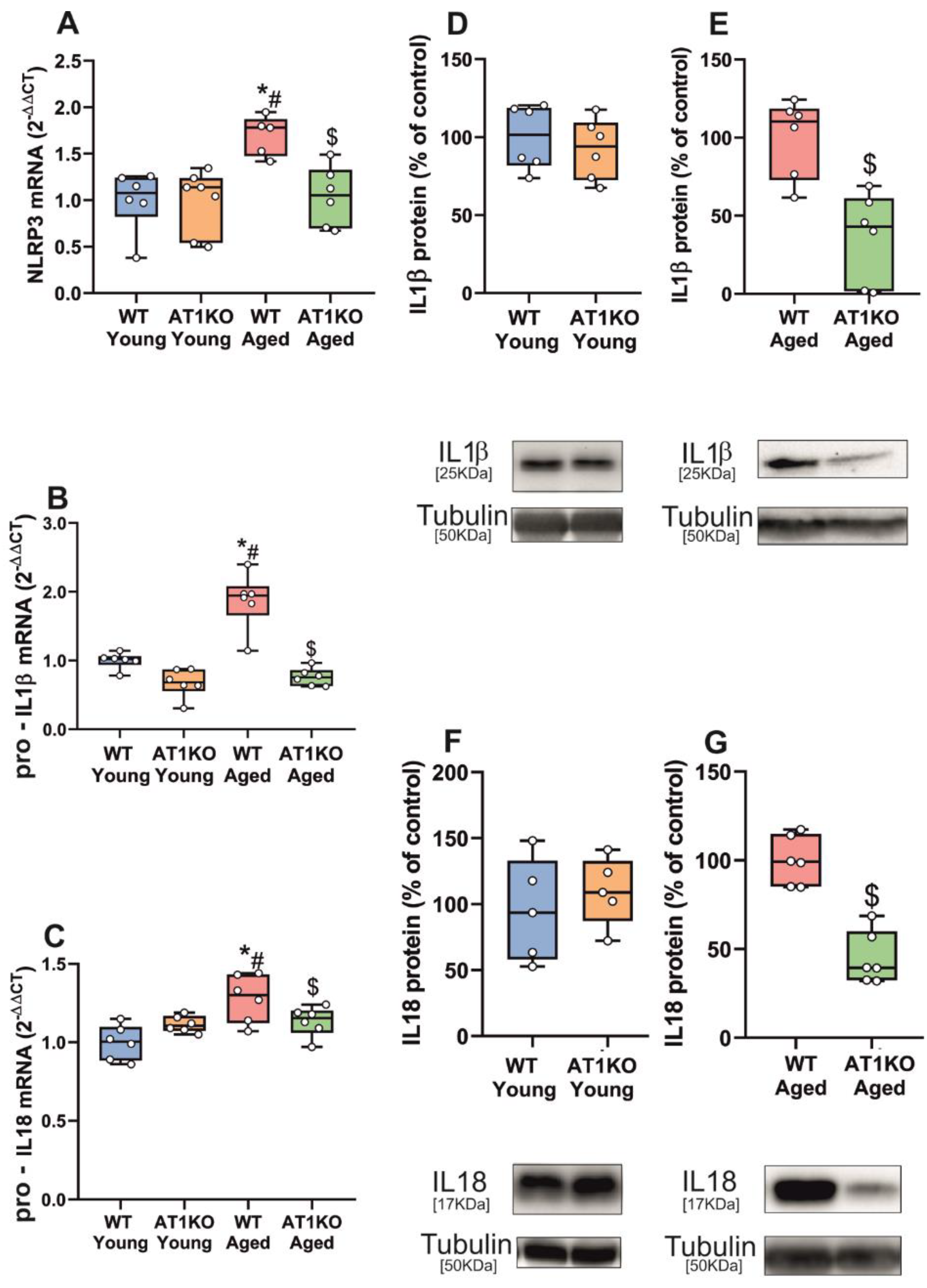
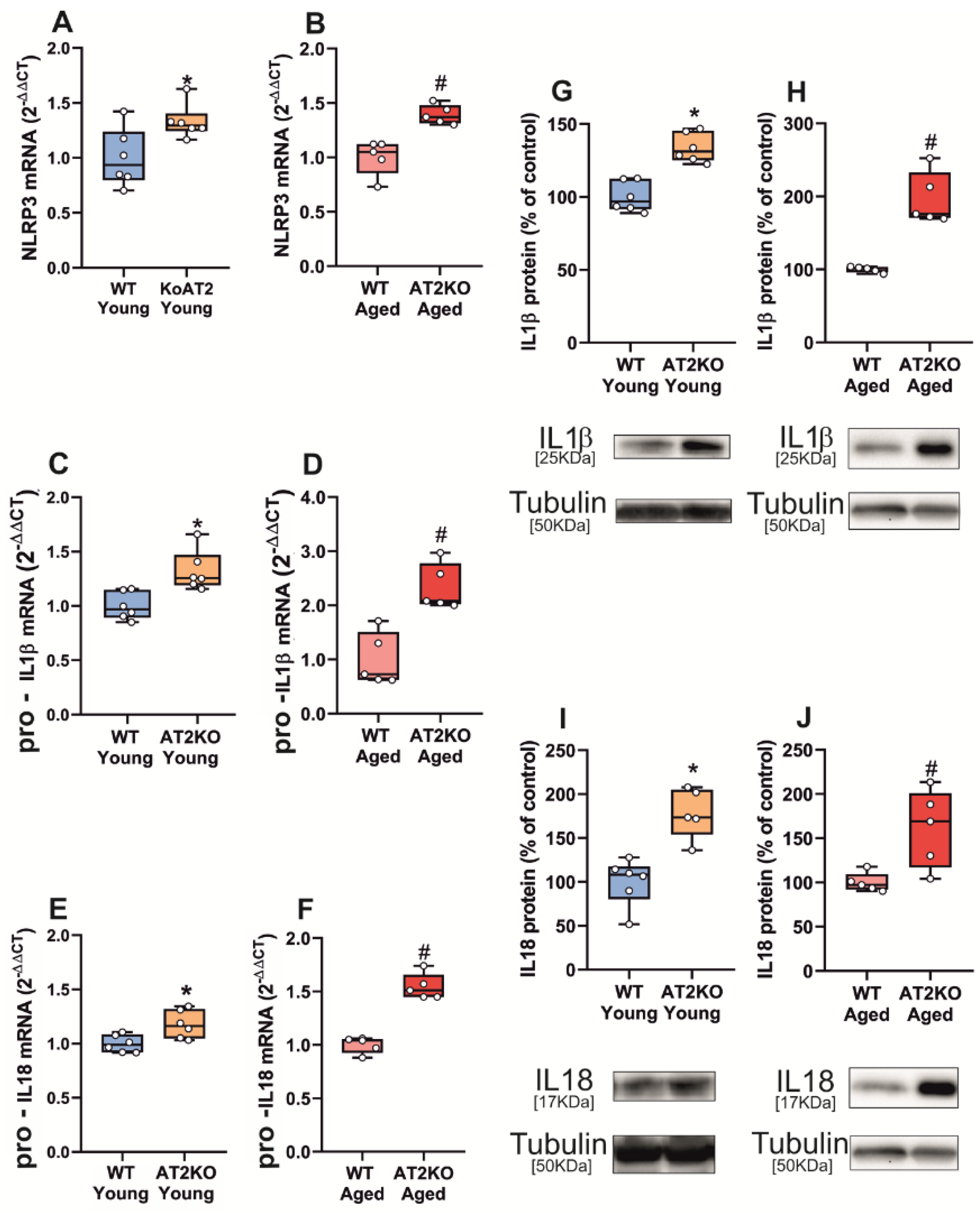
3.1. Aging-Related Upregulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Is Mediated by AT1 Receptors
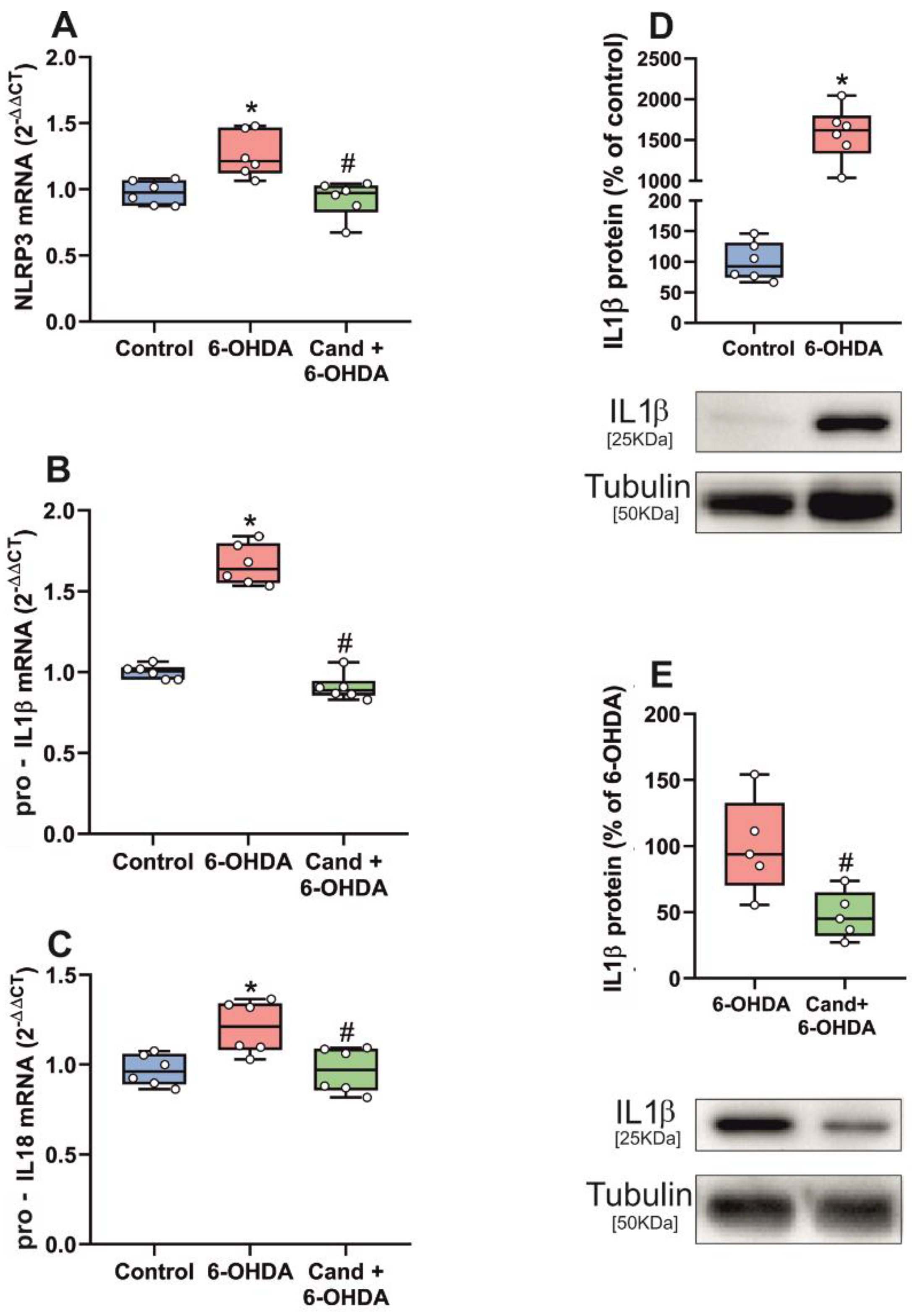
3.2. Up-Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome by 6-OHDA-Induced Neurodegeneration Is Mediated by AT1 Receptors
3.3. Up-Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome by Intraventricular AngII Administration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cevenini, E.; Monti, D.; Franceschi, C. Inflamm-ageing. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, I.M.; Gibson, D.S.; McGilligan, V.; McNerlan, S.E.; Alexander, H.D.; Ross, O.A. Age and Age-Related Diseases: Role of Inflammation Triggers and Cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bernhardi, R.; Eugenin-von Bernhardi, L.; Eugenin, J. Microglial cell dysregulation in brain aging and neurodegeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benigni, A.; Cassis, P.; Remuzzi, G. Angiotensin II revisited: New roles in inflammation, immunology and aging. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosarderelioglu, C.; Nidadavolu, L.S.; George, C.J.; Marx, R.; Powell, L.; Xue, Q.L.; Tian, J.; Salib, J.; Oh, E.; Ferrucci, L.; et al. Higher Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) levels and activity in the post-mortem brains of older persons with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, glab376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Ruiz, C.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Dominguez-Meijide, A.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Aging-Related Overactivity of the Angiotensin/AT1 Axis Decreases Sirtuin 3 Levels in the Substantia Nigra, Which Induces Vulnerability to Oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Cheda, B.; Dominguez-Meijide, A.; Valenzuela, R.; Granado, N.; Moratalla, R.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Aging-related dysregulation of dopamine and angiotensin receptor interaction. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1726–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Cheda, B.; Valenzuela, R.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Aging-related changes in the nigral angiotensin system enhances proinflammatory and pro-oxidative markers and 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic degeneration. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 204.e1–204.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Lanciego, J.L.; Guerra, M.J. Brain Renin-Angiotensin System and Microglial Polarization: Implications for Aging and Neurodegeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzani, R.; Giulietti, F.; Di Pentima, C.; Giordano, P.; Spannella, F. Disequilibrium between the classic renin-angiotensin system and its opposing arm in SARS-CoV-2-related lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell Mol. Physiol. 2020, 319, L325–L336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Sucunza, D.; Pedrosa, M.A.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Kulisevsky, J.; Lanciego, J.L.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Angiotensin Type 1 Receptor Antagonists Protect Against Alpha-Synuclein-Induced Neuroinflammation and Dopaminergic Neuron Death. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 1063–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Rey, P.; Parga, J.A.; Munoz, A.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Brain angiotensin enhances dopaminergic cell death via microglial activation and NADPH-derived ROS. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 31, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Borrajo, A.; Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Interaction between NADPH-oxidase and Rho-kinase in angiotensin II-induced microglial activation. Glia 2015, 63, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Parga, J.A.; Joglar, B.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels enhance angiotensin-induced oxidative damage and dopaminergic neuron degeneration. Relevance for aging-associated susceptibility to Parkinson’s disease. Age 2012, 34, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawada, W.M.; Banninger, G.P.; Thornton, J.; Marriott, B.; Cantu, D.; Rachubinski, A.L.; Das, M.; Griffin, W.S.; Jones, S.M. Generation of reactive oxygen species in 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) treated dopaminergic neurons occurs as an NADPH oxidase-dependent two-wave cascade. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howrylak, J.A.; Nakahira, K. Inflammasomes: Key Mediators of Lung Immunity. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; McManus, R.M.; Latz, E. Inflammasome signalling in brain function and neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.E.; Akther, M.; Jakaria, M.; Kim, I.S.; Azam, S.; Choi, D.K. Targeting the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome and its role in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, B.; Su, Z.; Guo, B.; Qin, L.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, R. The Nrf2-NLRP3-caspase-1 axis mediates the neuroprotective effects of Celastrol in Parkinson’s disease. Redox Biol. 2021, 47, 102134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, M.; Du, R.H.; Qiao, C.; Jiang, C.Y.; Zhang, K.Z.; Ding, J.H.; Hu, G. MicroRNA-7 targets Nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome to modulate neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. Activation and regulation of cellular inflammasomes: Gaps in our knowledge for central nervous system injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2014, 34, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, G.; Cardinali, C.; Morelli, M.B.; Santoni, M.; Nabissi, M.; Amantini, C. Danger- and pathogen-associated molecular patterns recognition by pattern-recognition receptors and ion channels of the transient receptor potential family triggers the inflammasome activation in immune cells and sensory neurons. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso-Loeches, S.; Urena-Peralta, J.R.; Morillo-Bargues, M.J.; Oliver-De La Cruz, J.; Guerri, C. Role of mitochondria ROS generation in ethanol-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death in astroglial cells. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Herrmann, K.M.; Salas, L.A.; Martinez, E.M.; Young, A.L.; Howard, J.M.; Feldman, M.S.; Christensen, B.C.; Wilkins, O.M.; Lee, S.L.; Hickey, W.F.; et al. NLRP3 expression in mesencephalic neurons and characterization of a rare NLRP3 polymorphism associated with decreased risk of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2018, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutterwala, F.S.; Haasken, S.; Cassel, S.L. Mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1319, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, D.E.; Kanneganti, T.D. Recent advances in inflammasome biology. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 50, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.H.; Yang, Y.X.; Meng, X.; Luo, X.Y.; Li, X.M.; Shuai, Z.W.; Ye, D.Q.; Pan, H.F. NLRP3: A promising therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchetti, F.; Brownell, A.L.; Williams, K.; Chen, Y.I.; Livni, E.; Isacson, O. Neuroinflammation of the nigrostriatal pathway during progressive 6-OHDA dopamine degeneration in rats monitored by immunohistochemistry and PET imaging. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Valenzuela, R.; Joglar, B.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Renin angiotensin system and gender differences in dopaminergic degeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Valenzuela, R.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Dopaminergic neuroprotection of hormonal replacement therapy in young and aged menopausal rats: Role of the brain angiotensin system. Brain 2012, 135, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, H.; Oertel, W.H. Progressive degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons following intrastriatal terminal lesions with 6-hydroxydopamine: A combined retrograde tracing and immunocytochemical study in the rat. Neuroscience 1994, 59, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohlke, P.; Von Kugelgen, S.; Jurgensen, T.; Kox, T.; Rascher, W.; Culman, J.; Unger, T. Effects of orally applied candesartan cilexetil on central responses to angiotensin II in conscious rats. J. Hypertens. 2002, 20, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, T. Inhibiting angiotensin receptors in the brain: Possible therapeutic implications. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2003, 19, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Gil, P.; Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Dominguez-Meijide, A.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Brain angiotensin regulates iron homeostasis in dopaminergic neurons and microglial cells. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 250, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Pedrosa, M.A.; Garcia-Garrote, M.; Valenzuela, R.; Navarro, G.; Franco, R.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Angiotensin type 2 receptors: Role in aging and neuroinflammation in the substantia nigra. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, H.M.A.; Sahar, N.E.; ZhuGe, D.L.; Huh, J.Y. Exercise Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Obese Mice via the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Meteorin-like. Cells 2021, 10, 3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.X.; Luo, L.; Fu, J.H.; He, J.Y.; Chen, M.Y.; He, Z.J.; Jia, J. Exercise-induced neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury is mediated via alleviating inflammasome-induced pyroptosis. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 349, 113952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lv, Z.; Gao, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Tang, C.; Xiang, J. Treadmill exercise alleviates neuronal damage by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome and microglial activation in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 174, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, A.; Correa, C.L.; Lopez-Lopez, A.; Costa-Besada, M.A.; Diaz-Ruiz, C.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Physical Exercise Improves Aging-Related Changes in Angiotensin, IGF-1, SIRT1, SIRT3, and VEGF in the Substantia Nigra. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, A.; Correa, C.L.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Costa-Besada, M.A.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Aging-related Increase in Rho Kinase Activity in the Nigral Region Is Counteracted by Physical Exercise. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Babior, B.M. NADPH oxidase. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauernfeind, F.; Bartok, E.; Rieger, A.; Franchi, L.; Nunez, G.; Hornung, V. Cutting edge: Reactive oxygen species inhibitors block priming, but not activation, of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Yazdi, A.S.; Menu, P.; Tschopp, J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature 2011, 469, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.W.; Wang, J.; Dhandapani, K.M.; Brann, D.W. NADPH Oxidase 2 Regulates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in the Brain after Traumatic Brain Injury. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 6057609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.N.; Dechend, R.; Mervaala, E.M.; Park, J.K.; Schmidt, F.; Fiebeler, A.; Theuer, J.; Breu, V.; Ganten, D.; Haller, H.; et al. NF-kappaB inhibition ameliorates angiotensin II-induced inflammatory damage in rats. Hypertension 2000, 35, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Lorenzo, O.; Ruperez, M.; Konig, S.; Wittig, B.; Egido, J. Angiotensin II activates nuclear transcription factor kappaB through AT(1) and AT(2) in vascular smooth muscle cells: Molecular mechanisms. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, J.P.; Sriramula, S.; Mariappan, N.; Agarwal, D.; Francis, J. Angiotensin II-induced hypertension is modulated by nuclear factor-kappaBin the paraventricular nucleus. Hypertension 2012, 59, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancardi, V.C.; Bomfim, G.F.; Reis, W.L.; Al-Gassimi, S.; Nunes, K.P. The interplay between Angiotensin II, TLR4 and hypertension. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 120, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancardi, V.C.; Stranahan, A.M.; Krause, E.G.; de Kloet, A.D.; Stern, J.E. Cross talk between AT1 receptors and Toll-like receptor 4 in microglia contributes to angiotensin II-derived ROS production in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 310, H404–H415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasu, M.R.; Riosvelasco, A.C.; Jialal, I. Candesartan inhibits Toll-like receptor expression and activity both in vitro and in vivo. Atherosclerosis 2009, 202, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, S.; Zhou, H.; DeSantis, D.; Croniger, C.M.; Li, X.; Stark, G.R. Erlotinib protects against LPS-induced endotoxicity because TLR4 needs EGFR to signal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9680–9685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wise, L.; Fukuchi, K.I. TLR4 Cross-Talk With NLRP3 Inflammasome and Complement Signaling Pathways in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearnley, J.M.; Lees, A.J. Ageing and Parkinson’s disease: Substantia nigra regional selectivity. Brain 1991, 114 (Pt 5), 2283–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, T.J.; Lipton, J.; Daley, B.F.; Palfi, S.; Chu, Y.; Sortwell, C.; Bakay, R.A.; Sladek, J.R., Jr.; Kordower, J.H. Aging-related changes in the nigrostriatal dopamine system and the response to MPTP in nonhuman primates: Diminished compensatory mechanisms as a prelude to parkinsonism. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 26, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubis, N.; Faucheux, B.A.; Ransmayr, G.; Damier, P.; Duyckaerts, C.; Henin, D.; Forette, B.; Le Charpentier, Y.; Hauw, J.J.; Agid, Y.; et al. Preservation of midbrain catecholaminergic neurons in very old human subjects. Brain 2000, 123 (Pt 2), 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.Y.; Zhang, J.; Bing, G. Aging enhances the neuroinflammatory response and alpha-synuclein nitration in rats. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 1649–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbin, O. The aging striatal dopamine function. Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colebrooke, R.E.; Humby, T.; Lynch, P.J.; McGowan, D.P.; Xia, J.; Emson, P.C. Age-related decline in striatal dopamine content and motor performance occurs in the absence of nigral cell loss in a genetic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 2622–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chan, G.L.; Holden, J.E.; Dobko, T.; Mak, E.; Schulzer, M.; Huser, J.M.; Snow, B.J.; Ruth, T.J.; Calne, D.B.; et al. Age-dependent decline of dopamine D1 receptors in human brain: A PET study. Synapse 1998, 30, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreola, R.; Alvarez-Herrera, S.; Perez-Sanchez, G.; Becerril-Villanueva, E.; Cruz-Fuentes, C.; Flores-Gutierrez, E.O.; Garces-Alvarez, M.E.; de la Cruz-Aguilera, D.L.; Medina-Rivero, E.; Hurtado-Alvarado, G.; et al. Immunomodulatory Effects Mediated by Dopamine. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 3160486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, C.; Basu, B.; Chakroborty, D.; Dasgupta, P.S.; Basu, S. The immunoregulatory role of dopamine: An update. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Huang, Y.; He, F.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Sun, T.; Ren, W.; Hou, J.; Zhu, L. Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonist A-68930 Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation, Controls Inflammation, and Alleviates Histopathology in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Spine 2016, 41, E330–E334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Ding, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, R. Dopamine controls systemic inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell 2015, 160, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, Z.; Han, X.; Wang, D.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, J.; Xiao, M.; Wang, C.; Lu, M.; Hu, G. Dopamine D2 receptor restricts astrocytic NLRP3 inflammasome activation via enhancing the interaction of beta-arrestin2 and NLRP3. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 2037–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Cheda, B.; Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Valenzuela, R.; Munoz, A.; Guerra, M.J.; Baltatu, O.C.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Nigral and striatal regulation of angiotensin receptor expression by dopamine and angiotensin in rodents: Implications for progression of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugh, G.; Pokkunuri, I.; Asghar, M. Renal dopamine and angiotensin II receptor signaling in age-related hypertension. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2013, 304, F1–F7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Yao, B.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhang, M.Z.; Harris, R.C. Intrarenal dopamine modulates progressive angiotensin II-mediated renal injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2012, 302, F742–F749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Meijide, A.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Diaz-Ruiz, C.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Dopamine modulates astroglial and microglial activity via glial renin-angiotensin system in cultures. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 62, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahooti, B.; Chhibber, T.; Bagchi, S.; Varahachalam, S.P.; Jayant, R.D. Therapeutic role of inflammasome inhibitors in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 91, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quijano, A.; Diaz-Ruiz, C.; Lopez-Lopez, A.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Muñoz, A.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Angiotensin Type-1 Receptor Inhibition Reduces NLRP3 Inflammasome Upregulation Induced by Aging and Neurodegeneration in the Substantia Nigra of Male Rodents and Primary Mesencephalic Cultures. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020329
Quijano A, Diaz-Ruiz C, Lopez-Lopez A, Villar-Cheda B, Muñoz A, Rodriguez-Perez AI, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Angiotensin Type-1 Receptor Inhibition Reduces NLRP3 Inflammasome Upregulation Induced by Aging and Neurodegeneration in the Substantia Nigra of Male Rodents and Primary Mesencephalic Cultures. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(2):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020329
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuijano, Aloia, Carmen Diaz-Ruiz, Andrea Lopez-Lopez, Begoña Villar-Cheda, Ana Muñoz, Ana I. Rodriguez-Perez, and Jose L. Labandeira-Garcia. 2022. "Angiotensin Type-1 Receptor Inhibition Reduces NLRP3 Inflammasome Upregulation Induced by Aging and Neurodegeneration in the Substantia Nigra of Male Rodents and Primary Mesencephalic Cultures" Antioxidants 11, no. 2: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020329
APA StyleQuijano, A., Diaz-Ruiz, C., Lopez-Lopez, A., Villar-Cheda, B., Muñoz, A., Rodriguez-Perez, A. I., & Labandeira-Garcia, J. L. (2022). Angiotensin Type-1 Receptor Inhibition Reduces NLRP3 Inflammasome Upregulation Induced by Aging and Neurodegeneration in the Substantia Nigra of Male Rodents and Primary Mesencephalic Cultures. Antioxidants, 11(2), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020329