Abstract
As intelligent transportation systems continue to advance, on-board surveillance video has become essential for train safety and intelligent scheduling. However, high-resolution video transmission faces bandwidth limitations, and existing deep learning-based super-resolution models find it difficult to meet real-time requirements due to high computational complexity. To address this, this paper proposes an “edge–end” collaborative multi-terminal task inference framework, which improves inference speed by integrating resources of in-vehicle end devices and edge servers. The framework establishes a real-time-priority mathematical model, uses game theory to solve the problem of minimizing multi-terminal task inference latency, and proposes a multi-terminal task model partitioning strategy and an adaptive adjustment mechanism. It can dynamically partition the model according to device performance and network status, prioritizing real-time performance and minimizing the maximum inference delay. Experimental results show that the dynamic model partitioning mechanism can adaptively determine the optimal partition point, effectively reducing the inference delay of each end device in high-speed mobile and bandwidth-constrained scenarios and providing high-quality video data support for safety monitoring and intelligent analysis.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of intelligent transportation systems, on-board surveillance video has become a core component for ensuring train safety, enabling intelligent scheduling, and supporting efficient management. In scenarios such as high-speed trains, urban rail transit, and autonomous driving, the real-time video data captured by on-board cameras are not only used for driver (or system) monitoring but also serve as critical basis for accident early warning, fault diagnosis, post-event analysis, and intelligent video-based applications such as object detection, abnormal behavior recognition, and track condition monitoring. These application scenarios impose stringent requirements on video clarity and detail integrity—clear video enables the accurate identification of distant obstacles, minor fault signs, or pedestrian movement details, directly impacting the accuracy and timeliness of safety decisions.
One of the key parameters affecting video clarity is video resolution [1]. Due to the increased bandwidth requirements for higher-resolution videos [2], current in-vehicle surveillance systems face multiple technical bottlenecks during data acquisition and transmission, making it challenging to support the real-time transmission of large-scale high-definition video streams and ensuring consistent video quality. More specifically, the following issues can be identified: (1) Severe limitations on transmission bandwidth. In-vehicle video transmission typically relies on wireless communication networks such as 4G/5G, V2X, and vehicle-to-ground wireless communication. However, the stability of wireless channels is poor in high-speed mobile environments, and bandwidth resources are limited. To ensure real-time transmission, vehicle-mounted cameras often use high-compression-rate encoding, which significantly degrades visual quality and negatively impacts the accuracy of intelligent analysis models. (2) Challenges in capturing complex dynamic scenes. The high-speed motion of vehicles leads to significant inter-frame movement and noticeable motion blur. Additionally, factors such as lighting changes (e.g., backlighting and glare at tunnel entrances/exits), adverse weather conditions (rain, snow, and fog), and other environmental variations further exacerbate video quality degradation.
To address the above issues, super-resolution technology has become a key approach for enhancing the quality of in-vehicle video. It can generate high-resolution video from low-resolution input, thereby improving video clarity and detail. The main algorithms of super-resolution technology are generally categorized into interpolation-based [3], reconstruction-based [4], and deep learning-based methods [5]. Currently, video super-resolution models based on deep neural networks have achieved promising results and are widely applied. Most conventional super-resolution models process the original low-resolution video frames through multi-layer convolution with varying kernel sizes and channel numbers to produce high-resolution outputs [6]. However, these deep learning-based models typically have a large number of parameters and high computational complexity, making it difficult to achieve real-time performance at the video acquisition or receiving end, where computational resources are limited. Real-time super-resolution requires that the inference speed of high-definition video be faster than the frame acquisition rate. Due to computational constraints, most existing real-time super-resolution systems either reduce the input data size or use lightweight super-resolution models [7,8,9,10], which limits the application of high-quality super-resolution models and reduces the overall performance [11]. Another approach is to offload the inference tasks to more powerful cloud servers [12], but this significantly increases the bandwidth pressure on the data center network. Moreover, under poor network conditions, transferring the inference tasks to the cloud may result in communication delays exceeding 100 ms, thus compromising the real-time performance of super-resolution video. Therefore, applying a full deep neural network-based super-resolution model to real-time low-resolution video while ensuring its real-time execution remains a critical research challenge in the field of super-resolution applications.
“Edge–end” collaborative computing provides a new approach for real-time video super-resolution in in-vehicle surveillance systems. By leveraging the collaboration between in-vehicle end devices and edge servers, the computing, storage, and network resources of both can be integrated to enhance inference speed. Specifically, the in-vehicle playback device first receives low-resolution video captured by on-board cameras through in-vehicle wired or wireless links (e.g., automotive Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or V2X) and can perform partial super-resolution inference locally. If the end device’s computational capability is insufficient, the intermediate results are transmitted via a low-latency vehicle-to-edge communication link to the nearest edge server for further inference, after which the high-definition video stream is returned. This approach effectively mitigates the limitations of slow inference on weak end devices and the high transmission latency associated with cloud offloading. However, “edge–end” collaborative super-resolution in-vehicle scenarios still face several challenges, outlined as follows: (1) Due to varying conditions such as computation load, network load, and heat dissipation capabilities, the available resources in the edge computing environment change dynamically. (2) In-vehicle end devices are limited by size and power consumption, resulting in extremely constrained computing and storage resources [13]. Although edge servers are more powerful than end devices, they are still resource-constrained devices compared to cloud servers and thus struggle to support large-scale concurrent high-complexity super-resolution tasks. Therefore, “edge–end cooperative” inference requires the design of efficient dynamic task load distribution and adjustment algorithms to better adapt to the dynamic and constrained nature of the edge computing environment, thereby maximizing the utilization of limited resources while meeting user requirements.
To address the limitations of existing approaches, we propose an “edge–end” collaborative multi-terminal task inference framework as follows: (1) Based on the “edge–end” environmental factors, we establish a real-time-priority mathematical model to minimize the inference delay of multi-terminal tasks and use game theory to solve the problem. (2) We propose a multi-terminal task model partitioning strategy and an adaptive adjustment mechanism. The proposed strategy adaptively partitions the model based on the performance of end devices and edge servers, as well as the network state between them, prioritizing real-time requirements and minimizing the maximum inference delay across all end devices. (3) We conduct experiments using real “edge–end” environment data. The results demonstrate that the edge environment-aware dynamic model partitioning mechanism for multi-terminal super-resolution tasks can adaptively determine the optimal model partitioning position based on end device performance and network conditions, ensuring real-time execution while reducing the inference latency of each end device. This mechanism effectively addresses the issue of video quality degradation in high-speed mobility and bandwidth-limited scenarios, providing high-quality video data support for safety monitoring and intelligent analysis.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Edge–End Collaborative Inference Framework
In modern smart devices, deep learning inference tasks are typically executed using cloud computing architectures [14], where data are collected by sensors such as on-board cameras and then uploaded to the cloud for complex computations. However, this approach is constrained by network conditions, which may introduce delays in time-sensitive tasks such as real-time video super-resolution processing. To address this issue, edge computing has emerged as a promising solution, enabling the deployment of part of the inference tasks on edge servers located close to the data source, thereby reducing response time.
Li et al. [15] proposed a cloud-edge collaborative inference framework based on network pruning, which utilizes a sparse-aware feature bias minimization method to reduce feature bias during the pruning process and prevent the model from becoming overly sparse. By employing task-oriented asymmetric feature encoding, they significantly reduce the communication overhead associated with transmitting intermediate data, thereby achieving a notable decrease in inference latency. Pagliari et al. [16] introduced a collaborative inference engine named CRIME, aimed at addressing the inference complexity of recurrent neural networks (RNNs). The framework dynamically selects the optimal inference device based on input characteristics, and by distributing the inference tasks among multiple devices, it achieves more than a 25% reduction in execution time or end-node energy consumption. Kou et al. [17] proposed an adaptive partitioning framework that addresses the challenge of selecting the optimal partition point for cloud-edge collaborative deep inference in dynamic network environments. This approach uses the weighted joint optimization of inference delay and quantization loss to achieve adaptive partitioning and introduces a fast decision-making mechanism to identify the optimal partition point, thereby significantly improving the performance of collaborative inference.
Li et al. [18] proposed a DNN collaborative inference framework based on deep reinforcement learning, suitable for mobile edge computing environments. The framework integrates energy harvesting strategies, edge station selection, and DNN partitioning strategies, and it solves the constrained Markov decision process using Lyapunov optimization techniques, resulting in a significant reduction in inference latency and improved battery stability for mobile devices. Hao et al. [19] proposed a multi-agent collaborative inference framework that compresses intermediate features using a lightweight auto-encoder and applies a multi-agent hybrid proximal policy optimization algorithm to solve the optimization problem. Experimental results show that this approach reduces inference latency by 56% and saves 72% of energy consumption. Xiao et al. [20] introduced an energy-efficient collaborative inference scheme based on multi-agent reinforcement learning, enabling each mobile device to select partition points and collaborate with the appropriate edge nodes based on the number of images, channel conditions, and previous inference performance. The experimental results demonstrate that this approach significantly reduces inference latency and saves energy.
In summary, existing edge–end collaborative inference frameworks can reduce inference latency and improve energy efficiency to some extent [21]. However, most studies focus on single tasks or static network conditions, without fully addressing the continuity and dynamic nature of real-time video processing. Therefore, a way to further optimize collaborative inference frameworks for complex applications such as video super-resolution remains an open research issue.
2.2. Video Super-Resolution Techniques
Toraldo Francia [22] first introduced the concept of super-resolution to recover data beyond the diffraction limit. With the increasing application of super-resolution techniques in image processing, Harris [23] and Goodman [24] proposed the concept of image super-resolution in 1969. Since then, super-resolution technology has developed rapidly [25]. Currently, super-resolution algorithms are mainly categorized into the following four types: interpolation-based, reconstruction-based, traditional learning-based, and deep learning-based methods.
The principle of interpolation-based algorithms is exemplified by bicubic interpolation [26], which estimates the value of a target pixel using a surrounding 4 × 4 pixel matrix. This method considers not only linear but also non-linear relationships among pixels, thereby better preserving image details and structures. Since its introduction, bicubic interpolation has been widely adopted in many fields. However, one limitation is that it may introduce ringing artifacts, manifested as unnatural ripples near edges. To address this issue, various improvements have been proposed, such as Wei’s [27] contrast-guided interpolation method and Zhang’s [28] directionally adaptive gradient-based interpolation technique.
Reconstruction-based algorithms, on the other hand, leverage the prior knowledge of the image to impose constraints on the solution space, thereby transforming ill-posed problems into well-posed ones. Representative approaches include spatial-domain methods, such as the convex set projection method [29]. In addition, some methods enhance reconstruction quality by focusing on specific image regions. For example, Liu [30] exploited directional characteristics to establish local smoothness priors and non-local similarity priors, extracting edge directional information and incorporating it into a total variation and non-local mean reconstruction framework to better preserve sharp image edges.
Learning-based algorithms reconstruct high-resolution images by leveraging large amounts of external data to learn the mapping from low-resolution to high-resolution images. For example, Freeman [31] employed Markov networks to model the mapping between low- and high-resolution images, while Yang [32] utilized sparse representation within the compressive sensing framework to learn dictionaries. Furthermore, Mora-Martinez [33] applied edge correction in the wavelet domain and then reconstructed the wavelet subbands of the frame using a pre-trained dictionary, finally obtaining the high-resolution image through an inverse discrete wavelet transform.
Research on deep learning-based super-resolution began with the SRCNN (Super-Resolution CNN) network proposed by Dong et al. at the Chinese University of Hong Kong at the 2014 ECCV conference [34]. Since then, various high-performance super-resolution neural networks have been proposed. For example, FSRCNN [35], which is based on a transposed convolutional network, first performs a series of convolution operations on the low-resolution input image and then uses transposed convolution for upsampling to obtain the final high-resolution image. This approach avoids the large number of convolution operations caused by interpolation followed by convolution in SRCNN and achieves better super-resolution performance. VDSR [36] and SRNTT [37], which are based on residual networks, allow intermediate information to skip certain layers and propagate directly forward, thereby avoiding the issue of gradient vanishing when constructing deeper models. DRCN [38] and DRRN [39], based on recursive learning, build deep network structures by recursively stacking convolutional layers. Each recursive unit includes one convolutional layer and a recursive connection that introduces information from previous layers, enabling the effective capture of both the local and global features of the image. SRGAN [40], based on generative adversarial networks, consists of a generator and a discriminator that compete during training to continuously improve performance.
EDSR and MDSR [41], based on multi-scale networks, employ different branches to process input data at varying scales, achieving targeted optimization. SRDenseNet [42], based on densely connected networks, connects each layer directly to all previous layers, using feature reuse to enhance feature transmission, reduce parameter count, and improve efficiency. RCAN [43], which utilizes an attention mechanism, enhances useful features while suppressing irrelevant ones through channel attention, significantly improving the quality of image super-resolution reconstruction. In summary, the general workflow of neural network-based image super-resolution involves the feature extraction, feature transformation, upsampling, and reconstruction of the input image, ultimately producing a high-resolution output. Due to the superior performance of deep learning-based super-resolution algorithms compared to traditional methods, they have become the mainstream in current super-resolution research. Additionally, there are video super-resolution models that take a sequence of video frames as input, such as SOFVSR, FRVSR, FFCVSR, BasicVSR, and BasicVSR++ [44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51]. These models leverage inter-frame similarity through feature alignment and feature fusion techniques to enhance super-resolution quality.
However, most of the above studies focus solely on improving super-resolution quality as the optimization objective. The super-resolution models used in these works typically have a large number of parameters and high computational complexity, making them unsuitable for “edge–end” environments where computational resources are limited. Therefore, it is necessary to further balance the trade-off between computational cost and super-resolution performance. Additionally, the selection of an appropriate super-resolution model structure that supports hierarchical offloading in edge–end environments remains a critical issue requiring further investigation.
3. Edge-Aware Dynamic Model Partitioning for Super-Resolution Inference
In this chapter, we aim to address the issue of high inference latency on end devices caused by the computationally intensive nature of video super-resolution deep neural network inference tasks, which may even prevent real-time video playback. To tackle this problem, we explore the use of “edge–end” collaborative inference techniques to accelerate the execution of video super-resolution inference tasks while ensuring real-time video playback. This chapter first proposes an “edge–end” collaborative multi-terminal task inference framework and then establishes a mathematical model for minimizing multi-terminal task inference latency, with real-time performance as the priority, based on the “edge–end” environmental factors. To solve this problem, we employ game theory as a theoretical foundation and propose a multi-terminal task model partitioning strategy and an adaptive adjustment strategy. These strategies can dynamically divide the model based on the performance of the end devices and edge servers, as well as the network state between them, to prioritize real-time requirements and minimize the maximum task inference latency.
3.1. Overview
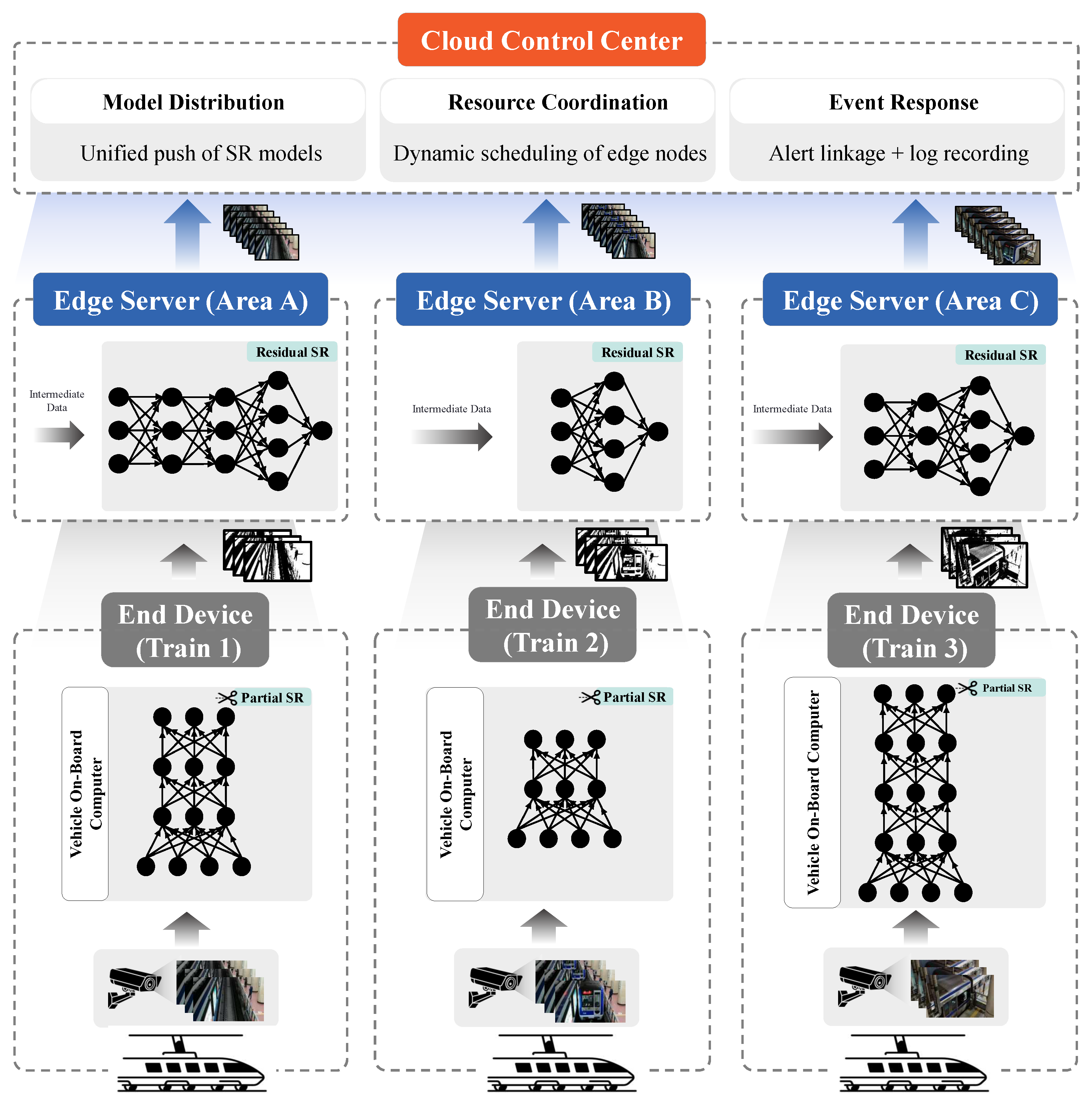
In video super-resolution inference, the inference computation of the neural network model used is much higher than that of classification and recognition models. Executing video super-resolution inference on weak end devices tends to have high inference latency, while completely offloading the task to the edge server will increase the load on the edge server, especially when there are more video super-resolution tasks. In order to meet the real-time playback demand of video super-resolution applications, this chapter considers accelerating video super-resolution task reasoning by using the following “edge–end” cooperative technique: each end device can perform part of the super-resolution reasoning according to the existing conditions, and it can transmit the intermediate reasoning data to the edge server, which will use the intermediate data as input to complete the remaining reasoning of the model. The edge server will use the intermediate data as input to complete the remaining inference of the model. Based on the above execution mode, the “edge–end” cooperative multi-terminal task inference framework is shown in Figure 1.
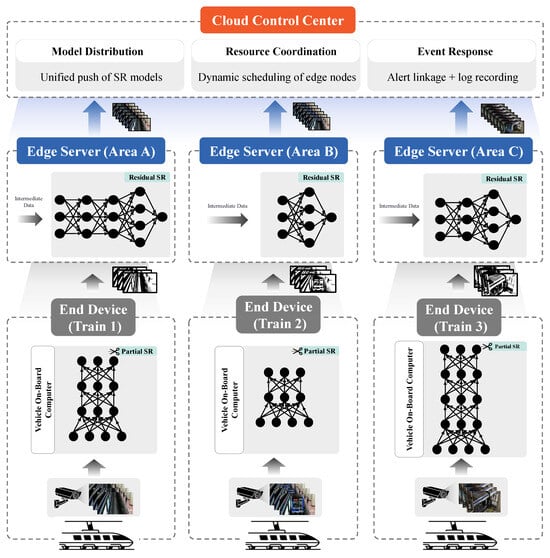
Figure 1.
Edge–end collaborative multi-terminal task inference framework.
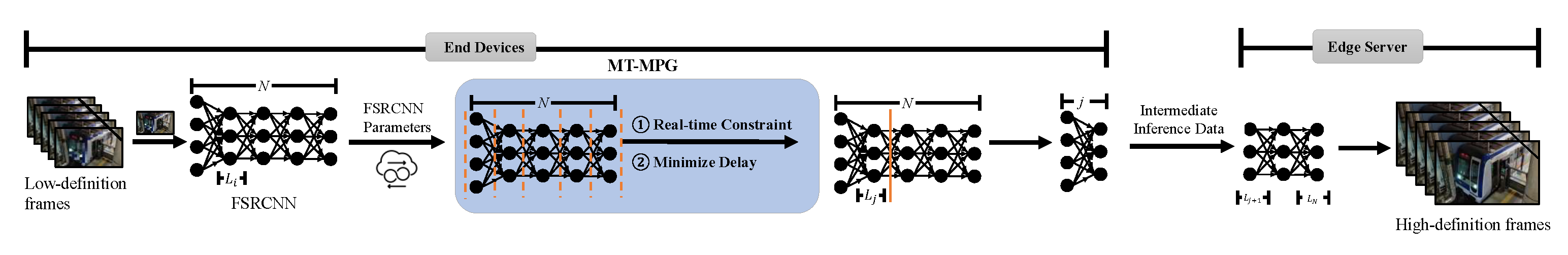
The principle of edge–end collaborative video super-resolution is as follows: After receiving the original low-resolution video stream, the video playback device determines the different offloading strategies based on the edge environment to allocate inference tasks between end devices and edge servers. The task allocation must consider constraints such as the computational capabilities of edge servers and the bandwidth between the edge and end devices. Depending on the task partitioning strategy, there are two main offloading approaches, as follows: frame-based offloading [52] and neural network layer-based offloading [16]. As shown in Figure 2, the edge–end environment and neural network partitioning offloading strategy involves selecting a division point within the neural network. To formally describe and optimize this process across multiple heterogeneous terminals, we define it as a Multi-Terminal Model Partition Game (MT-MPG). For input frames from the low-resolution video stream, the end device performs partial super-resolution inference and sends the intermediate results to the edge server for further processing. This process is applied sequentially to all frames to achieve real-time video stream super-resolution. By leveraging pipeline parallelism, computational resource utilization can be significantly improved. Therefore, the edge–end environment-aware neural network partitioning offloading mechanism is particularly suitable for real-time video super-resolution systems in scenarios such as live streaming, where higher resolution video is required while maintaining real-time performance.
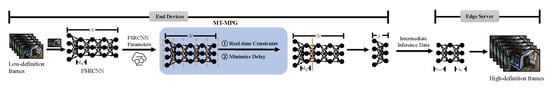
Figure 2.
Edge–end collaborative neural network partitioning offloading.
Edge–end collaborative computing can flexibly utilize the computational resources of end devices and edge servers, thereby reducing the inference latency of computationally intensive tasks such as video super-resolution. However, there are some shortcomings and limitations in existing edge–end collaborative research when applied to multi-terminal task inference for video super-resolution, outlined as follows:
- Existing research efforts typically focus on optimizing the total inference latency. However, in video super-resolution tasks, it is more critical to prioritize real-time guarantees for video playback. Specifically, there are strict latency constraints for each part of every frame. If existing approaches are directly applied to video super-resolution tasks, they may result in noticeable video stuttering or lag.
- In edge–end environments where the computational capabilities of end devices differ significantly, it is essential to take into account the computing power of each device and balance the inference latency across end devices, making it challenging to determine the optimal model partitioning strategy.
- Changes in the “edge–end” environment can affect the model partitioning strategy. For example, when other tasks are running on the edge server, increasing its computational load, it may lead to longer inference latency for the super-resolution task. Additionally, end devices often have limited cooling capabilities, and under high loads, they may experience frequency throttling, which degrades their computational performance and increases inference latency. Moreover, unstable network bandwidth between the edge and end devices can also impact transmission latency. Therefore, static neural network partitioning approaches are likely unable to adapt to the dynamic and real-time nature of the edge–end environment.
In response to the above-mentioned shortcomings and challenges, we have designed an edge-aware dynamic partitioning mechanism for super-resolution models based on “edge–end” collaboration. This mechanism can adaptively determine the optimal model partitioning points for each end device’s super-resolution inference task based on the real-time computing performance of end devices and edge servers, as well as the real-time network bandwidth between the edge and the end. It prioritizes real-time requirements and minimizes the maximum inference latency of tasks.
3.2. Problem Formulation
In formulating the potential game model, several simplifying assumptions are introduced to make the problem tractable. (1) Task independence: the inference tasks of different terminals are independent at the computational level, meaning that one terminal’s video inference does not directly alter another terminal’s input. This allows the partitioning decision of each terminal to be modeled as a self-interested choice. (2) Queuing effect: when multiple terminals simultaneously offload tasks to the edge server, they share the same computing resources, similar to users waiting in a queue for service. Thus, each terminal’s latency depends not only on its own partitioning point but also indirectly on the strategies of others. (3) Equilibrium under bounded rationality: each terminal tends to select the partitioning point that minimizes its own latency given the environment. When multiple terminals make such decisions simultaneously, the overall system outcome can be characterized as the Nash equilibrium of the potential game. These assumptions serve as abstractions of the complex edge–end environment, preserving key characteristics (task independence, resource sharing, and decision coupling) while enabling game-theoretic analysis.
3.2.1. Parameter Modeling
We consider modeling the video super-resolution deep neural network inference task in an “edge–end” environment consisting of Z endpoints and a single edge server, prioritizing real-time performance to reduce the inference latency of the worst endpoint task and to improve the user experience. The key variables required for modeling this optimization problem are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Main notations.
For the Z video super-resolution tasks that require inference on Z end devices, it is necessary to decide the partitioning positions of Z deep neural network (DNN) models. , , , and () represent the current input data volume for end device j, the partitioning position of the DNN model for inference tasks, the inference latency per unit computational volume on end device j, and the transmission latency per unit data volume on end device j, respectively. N represents the number of layers in the super-resolution DNN. and () represent the output data volume of the i-th layer of the DNN under a specific input data volume and the computational volume of the i-th layer of the DNN under a specific input data volume, respectively. represents the specific input data volume. represents the inference latency per unit computational volume on the edge server. F represents the frame rate of video playback.
3.2.2. Constraint Conditions and Objective Function Modeling
We model the optimal inference time for real-time guaranteed “edge–end” collaborative multi-terminal task inference by solving for the optimal model partition location . In particular, indicates that end device j offloads the entire inference task to the edge server, while means that end device j performs the full neural network inference locally. For a given end device j, once its model partition location is determined, the local inference latency can be calculated. end device j only needs to execute the neural network inference up to layer . Based on the current input data volume of end device j, the computation cost of the first layers under the specific input data volume, and the average inference latency per unit computation volume of end device j, the inference time on the end device can be computed as follows:
The intermediate inference data to be transmitted by end device j consist of the intermediate features output by model layer . Based on the current input data volume of end device j, the output data volume of model layer under a specific input data volume, and the transmission latency per unit data volume of end device j, the corresponding transmission time for the intermediate inference data can be expressed as shown in Equation (2).
The inference task of end device j requires executing the deep neural network layers from to N on the edge server. Based on the current input data volume of end device j, the inference computation cost of the layers following under a specific input data volume, and the recent inference latency per unit computation volume of the edge server, the inference time for the task of end device j on the edge server is calculated by the following equation:
Based on the above analysis, the inference latency of end device j’s task consists of three components as follows: the inference time on end device j, the transmission time of the intermediate inference data corresponding to end device j, and the inference time of the task on the edge server. This can be represented as follows:
Since end device j’s inference execution, intermediate data transmission, and edge server inference execution can be pipelined and executed in parallel for continuous video frames, to ensure the real-time performance of the video super-resolution task, the inference time of a single frame on end device j, the intermediate data transmission time, and the inference time on the edge server should all be less than the single-frame playback time. This can be expressed as follows:
Since the super-resolution inference tasks of each end device are independent, the latency in multi-terminal task inference can be defined as the maximum inference latency among all tasks, denoted as follows:
The objective of the optimization problem is to minimize the multi-terminal task inference latency while ensuring the real-time performance of each terminal task by determining the optimal model partitioning position p, which can be expressed as follows:
where Equation (8) denotes the real-time constraint for the video super-resolution task, and Equation (9) denotes the range of values for the end device and model partitioning positions.
Based on the above analysis, the optimization problem formulated in this section is an integer programming problem, where the solution space is determined by the number of model partitioning decisions. Specifically, each model partitioning decision involves Z terminal-based deep neural networks, with the value range of each partitioning position being . Consequently, the size of the solution space for the multi-terminal task model partitioning decision is . However, traditional optimization algorithms face significant challenges in solving this problem within a low time complexity.
3.3. Design Details
In order to address the above optimization problem, this section proposes a dynamic partitioning mechanism for multi-terminal task super-resolution models that is aware of the edge environment, based on “edge–end” collaboration. The mechanism includes a model partitioning strategy and an adaptive adjustment strategy. The model partitioning strategy first considers the single-terminal task solution approach, and it then transforms problem (7) into a game-theoretic problem known as MT-MPG. It proves the existence of a pure-strategy Nash equilibrium in MT-MPG and proposes a decision-making algorithm for multi-terminal task model partitioning. The adaptive adjustment strategy re-executes the multi-terminal task model partitioning decision-making algorithm to update the model partitioning strategy at regular time intervals or when the inference latency exceeds a threshold. The following presents the detailed description of the mechanism.
3.3.1. Model Partitioning Strategy
When the number of end devices in the “edge–end” environment, the problem reduces to a single-terminal task model partitioning scenario. In this case, the size of the solution space for the model partitioning decision is . By traversing all possible partitioning positions and selecting the one that minimizes objective function (7) among those satisfying the constraints, the problem can be solved. If constraint (8) cannot be satisfied, it indicates that no partitioning strategy can guarantee the real-time performance of the video super-resolution task, and thus real-time requirements should be prioritized. For end device j, the optimization objective at this point is to minimize the maximum of the inference time on the end devices and edge servers for a single frame, as well as the intermediate data transmission time from the end device, which can be expressed as follows:
The solution to the real-time optimization problem follows the same approach as the inference latency minimization problem. For the super-resolution deep neural network with partitioning positions, Equations (1)–(3) are evaluated, and the partitioning strategy that minimizes objective function (10) is selected.
In summary, the detailed steps of the model partitioning strategy for the single-terminal task are shown in Algorithm 1, whose inputs include the neural network model parameters, the “edge–end” environment parameters, and the video frame rate parameters, and the outputs are the model partitioning locations with the lowest inference latency or the best real-time performance. Lines 1 to 3 of Algorithm 1 evaluate the inference latency of the device to each layer of the neural network, and lines 4 to 7 represent the judgment of constraints (8). If there is a division position that satisfies constraints (8), it then return to the division position that minimizes the inference latency, as shown in line 9, or return to the division position that optimizes the real-time performance, as shown in line 11.
Algorithm 1 consists of the following two parallel loops: the first loop (rows 1–3) runs for iterations, and the second loop (rows 4–7) also runs for iterations. Therefore, the time complexity of Algorithm 1 is .
However, an edge server often needs to serve multiple end devices in practice. When the number of end devices , the solution space for multi-terminal task model partitioning is . Continuing to use the algorithm of traversing all partitioning positions to solve the problem is too expensive and not suitable for deployment in an edge–end environment with limited computational resources and high sensitivity to latency. According to the analysis in Section 3.2, Equation (7) is affected by the model partitioning location of each end device. Each end device aims to minimize its own latency through model partitioning decisions. Therefore, the model partitioning decision for each end device can be defined as a congestion game , where denotes the participants of the game, i.e., all end devices; denotes the decision space of all end devices, i.e., the model partitioning locations for all end devices; and denotes the reasoning latency of the task of end device j. This section refers to the game problem as the Multi-Terminal Model Partition Game (MT-MPG).
| Algorithm 1 Single-terminal task model partitioning algorithm |
| Input: |
| N: Number of DNN layers |
| : Layer sizes of the DNN |
| : Output data volumes of each DNN layer |
| L: Transmission latency per unit data volume |
| : Inference latency function for layer |
| F: Video frame rate |
| Output: Optimal partition position with minimal latency or best real-time performance |
|
If MT-MPG admits a pure strategy Nash equilibrium, then its equilibrium solution corresponds to the optimal solution of problem (7). The definition of a pure strategy Nash equilibrium is given in Definition 1.
Definition 1
(Pure Strategy Nash Equilibrium). Given a strategy combination , a strategy is said to be a better response for end device j with respect to if . A strategy is said to be an optimal response for end device j if, for all , the condition holds. If a strategy combination satisfies that all end devices have made optimal responses, i.e., it satisfies the relationship shown in Equation (11), then the strategy combination is said to be a pure strategy Nash equilibrium for MTMPG. Here, denotes the combination of model partitioning decisions for the remaining end devices, excluding end device j.
According to [53], a finite strategy potential game must have a pure strategy Nash equilibrium if it admits an ordinal potential function. Therefore, an ordinal potential function can be constructed for MTMPG to prove the existence of a pure strategy Nash equilibrium. The definition of the ordinal potential function is given in Definition 2.
Definition 2
(Ordinal Potential Function). For a finite strategy potential game , if the function satisfies Equation (12) for any two strategy combinations and , then this function is called an ordinal potential function for the finite strategy potential game Γ. More specifically,
where represents the latency of end device j’s task. The ordinal potential function can be viewed as the global inference latency, which is the sum of the inference latency of all end devices’ tasks, expressed as follows:
where denotes the frame inference latency of end device j under strategy , denotes the intermediate data transmission latency of end device j’s task, and denotes the inference latency of edge server processing end device j’s task.
Proof.
(1) Proof that when , we have . For any end device j, can be expanded as follows:
According to the definition of , we have , thus . Additionally, for all , . Therefore, when , we have .
(2) Proof that when , we have . If strategy is a better response to strategy , according to Definition 1, it is clear that . If strategy is a better response to strategy , i.e., , then by part (1), we have , which contradicts the given condition . Thus, this case is invalid. Therefore, when , we have .
Combining parts (1) and (2), we obtain the following:
□
In summary, MT-MPG admits a pure strategy Nash equilibrium, and the equilibrium solution corresponds to the set of model partitioning strategies that minimize the total inference latency across all end devices. The steps for solving the multi-terminal task model partitioning strategy are outlined in Algorithm 2. The inputs include the neural network model parameters listed in Algorithm 1, the “edge–end” environment parameters, the video frame rate parameters, and the number of end devices. Lines 1–3 of Algorithm 2 iterate through each end device, and Line 2 determines the optimal model partitioning decision for the current end device. This algorithm requires traversing all end devices once, resulting in a time complexity of . Since Algorithm 1 is executed for each end device, which has a time complexity of , the overall time complexity of this algorithm is .
| Algorithm 2: Multi-terminal task model partitioning algorithm |
| Input: |
| Edge–end environment, model structure parameters |
| Z: Number of end devices |
| Output: |
| Minimum latency partition positions that prioritize real-time performance |
|
3.3.2. Adaptive Adjustment Strategy
Although the algorithm in the previous section can derive the optimal partitioning strategy based on the current “edge–end” environment, model parameters, video frame rate, and other conditions, several challenges arise in real-world scenarios. When the edge server is handling multiple tasks, leading to increased computational load, the available resources for super-resolution inference may decrease, thereby affecting the reasoning time of the offloaded tasks. Additionally, end devices often have limited thermal dissipation capabilities, and under high-load or high-temperature conditions, chip downclocking occurs, which degrades computational performance and increases local inference latency. Furthermore, fluctuations in the network bandwidth between the edge servers and end devices also impact transmission times.
Static neural network partitioning strategies are likely unable to adapt to the dynamic “edge–end” environment, potentially increasing inference latency and compromising the real-time performance and minimal inference latency required for video super-resolution tasks. Therefore, “edge–end” collaborative multi-terminal task model inference must adaptively update the model partitioning strategy based on the real-time “edge–end” environment. The ideal approach is to determine the optimal partitioning location for each frame’s multi-terminal task model. However, executing the model partitioning algorithm itself introduces additional overhead. Thus, it is necessary to reduce the frequency of executing the model partitioning algorithm while ensuring negligible impact on normal inference latency to adapt to the current “edge–end” environment.
From the experiments, it can be observed that the time overhead for determining the optimal partitioning location using FSRCNN for five end devices is less than 1 ms. Even when simulating scenarios with 10 devices and 100-layer models, the execution overhead of the model partitioning strategy remains below 5 ms. Therefore, if the model partitioning strategy algorithm is executed periodically at a second-level interval, the additional time overhead compared to normal inference is less than 1%, which is within an acceptable range. Moreover, in the edge–end environment, network latency and bandwidth conditions typically vary on a minute-level timescale. The probability of experiencing more than three changes within a single minute is about 37% [54], which suggests that sharp fluctuations within a few seconds are unlikely. As a result, users perceive latency variations to be relatively infrequent. In addition, since the proposed model partitioning strategy can adapt and update within seconds, the duration of user-perceived impact remains minimal.
Therefore, the adaptive adjustment strategy in this section consists of the following two components: periodic execution and triggered execution. The periodic execution is performed every 5 s, while the triggered execution is activated when the inference latency on the current end device exceeds 50% of the expected inference latency based on the model partitioning strategy. When the periodic time arrives, the adaptive adjustment strategy determines the optimal model partitioning position for all end devices, i.e., it executes Algorithm 2 and waits for the completion of the current frame’s inference before performing “edge–end” collaborative inference according to the obtained strategy. In this paper, we adopt a 5-s adjustment window as a representative intermediate setting to balance responsiveness and stability. Nevertheless, our method is lightweight, with an adjustment overhead of less than 1 ms when determining the optimal partition point across five terminal devices running FSRCNN inference. Even under larger-scale simulations (e.g., 10 devices and 100-layer models), the overhead remains below 5 ms. Therefore, smaller adjustment windows (e.g., 1 s [55]) can also be supported without introducing noticeable additional latency. In the case of a triggered execution, the adaptive adjustment strategy only re-partitions the model for the affected end device, i.e., it runs Algorithm 1 and performs “edge–end” collaborative inference after the current frame’s inference is completed.
4. Experiment and Results
In this chapter, we construct a real “edge–end” environment and conduct experiments using the REDS4 dataset and the FSRCNN super-resolution model. The REDS dataset was first introduced in the 2019 NTIRE competition and has since been widely used in various research fields. It consists of 240 training video sequences, 30 validation video sequences, and 30 test video sequences, each containing 100 consecutive frames. REDS4 is a subset composed of the following four sequences: 000, 011, 015, and 020, selected from the original training set, and it is commonly used for performance evaluation. This section details the experimental setup and implementation, and it provides analysis and conclusions based on the experimental results to validate the effectiveness of the dynamic model partitioning mechanism for multi-terminal tasks under edge-aware environments.
4.1. Experimental Setup
In order to simulate a real “edge–end” environment, this experiment selects a variety of heterogeneous devices as the end devices. These include two desktop computers equipped with Intel® Core™ I5-4590 processors, two laptops with Intel® Core™ I5-7200U and AMD® Ryzen™ R7-5800U processors, and one NVIDIA Jetson Nano. The edge server is a server with an Intel® Xeon™ Bronze 3204 processor and an NVIDIA RTX2080Ti GPU. The NVIDIA Jetson Nano runs on Ubuntu 18.04, with CUDA version 11.4 and cuDNN version 8.2. The edge server runs Ubuntu 20.04 with the same CUDA and cuDNN versions to ensure compatibility. The super-resolution models were implemented in PyTorch 1.12.1 with Python 3.10.8. In this experiment, the end devices and the edge server are connected via a local area network (LAN) to enable data communication. A router is used to control the upstream bandwidth of the end devices, simulating different network bandwidth conditions in the “edge–end” environment. To simulate varying computational workloads on the edge server, this experiment employed the nvidia-smi tool to adjust the core and memory frequencies of the GPU. Three load levels were defined at 0%, 33%, and 50%, representing different degrees of GPU resource utilization. A 0% load indicates that the GPU remains idle and only executes the super-resolution inference task in this experiment. In contrast, 33% and 50% loads correspond to scenarios where additional background tasks occupy approximately one-third and one-half of the GPU’s computational capacity, respectively. Under these conditions, the effective computational capacity available for the super-resolution task corresponds to 100%, about 67%, and about 50%, forming the three load levels used in the experiments. While such a simulated network environment cannot fully represent the complexity of real-world mobile or wide-area communication conditions, we believe this setting can provide a reasonable approximation of bandwidth fluctuations and transmission instability observed in practice.
According to the “edge–end” collaborative multi-terminal task inference framework proposed in this chapter, the experiments in this section use the aforementioned devices to construct an “edge–end” collaborative multi-terminal task inference dynamic acceleration system. First, the end device initiates a task request and performs super-resolution model inference using specific input data, and it then transmits the corresponding intermediate data to the edge server for the performance evaluation of the end device’s inference capability and its uplink bandwidth. The model partitioning decision module deployed on the edge server receives the task request and related parameters, completes the model partitioning decision, and informs the end device. Subsequently, the end device’s layered inference module executes the inference on the video frames based on the model partitioning decision, and it uploads the intermediate results to the edge server. Finally, the edge server’s layered inference module processes the remaining layers of the model.
Due to the wide variety of super-resolution neural network model structures, it is necessary to select an appropriate one for the “edge–end” collaborative inference scenario. Among common neural network architectures, parallel and residual structures involve complex data dependencies between layers, where the input of a given layer may depend on the outputs of multiple previous layers. If such models are partitioned into layers, they generate significantly more intermediate data compared to serial structures, where the input of each layer depends only on the output of the previous layer. This increases the bandwidth requirements between devices exponentially, making them unsuitable for layered collaborative inference in the “edge–end” environment. Additionally, video super-resolution models that take a sequence of frames as input are computationally intensive and not suitable for latency-sensitive real-time video inference. Therefore, in the “edge–end” environment, it is preferable to use a super-resolution neural network model with a single frame as input and only a serial structure for hierarchical partitioning and collaborative inference. Hence, this section adopts FSRCNN as the super-resolution model for testing, and it performs 4-fold super-resolution inference on the original video according to conventional super-resolution scaling factors.
In order to conduct the performance test of the “edge–end” collaborative multi-terminal task inference, all terminal inference tasks in this experiment use the video sequence No. 000 from the REDS4 dataset, which has been downsampled to a resolution of 160 × 90. The processing time for each part of each terminal task is recorded. In our experiments, we report the following two performance metrics: (1) Single-frame response time: The time required for a video frame to produce a displayable result, defined as the maximum among terminal inference time, intermediate data transmission time, and edge inference time. This metric reflects the real-time performance perceived by the user. (2) Total inference latency: The overall time consumed by all stages for a video frame, calculated as the sum of terminal inference time, intermediate transmission time, and edge inference time. This metric reflects the overall computational and transmission cost of the system.
Since the edge–end collaborative system executes tasks in a pipelined and parallel manner, the user experience is mainly constrained by the single-frame response time, while the total inference latency provides additional insight into system-level resource consumption and throughput.
4.2. Comparison Algorithm Setup
To evaluate the effectiveness of the dynamic model partitioning mechanism for the multi-terminal task super-resolution based on edge environment awareness proposed in this chapter, two classical algorithms that do not utilize “edge–end” collaboration are selected for comparison as follows: terminal-only inference, edge-only inference, and a static model partitioning “edge–end” collaborative inference algorithm. The details of the compared algorithms are as follows:
- (1)
- Terminal-only: The inference task is executed solely on the end devices without the involvement of the edge server.
- (2)
- Edge-only: All end devices send raw data to the edge server, and the entire inference task is offloaded to the edge for execution.
- (3)
- Static collaboration: A fixed model partitioning point is determined based on the assumption that the computational load between the front and back parts of the deep neural network model is approximately equal, and the “edge–end” collaborative inference is performed accordingly.
- (4)
- Dynamic collaboration: This refers to the dynamic model partitioning mechanism for multi-terminal task super-resolution based on “edge–end” collaboration, which is proposed in this paper.
4.3. Analysis of Experimental Results
This section presents the following three experimental aspects to validate the effectiveness of the mechanism proposed in this chapter: (1) a comparative analysis of the acceleration performance of the dynamic cooperative algorithm under different edge load conditions; (2) a comparative analysis of the acceleration performance of the dynamic cooperative algorithm under varying network bandwidths; and (3) a comparative analysis of the acceleration performance of the dynamic cooperative algorithm across different terminal inference tasks. Each experiment was independently repeated five times. We report the mean latency together with the standard deviation. Unless otherwise stated, all figures present the average values with error bars indicating ±1 standard deviation to reflect the stability of results.
4.3.1. Acceleration Performance Under Varying Edge Load Conditions
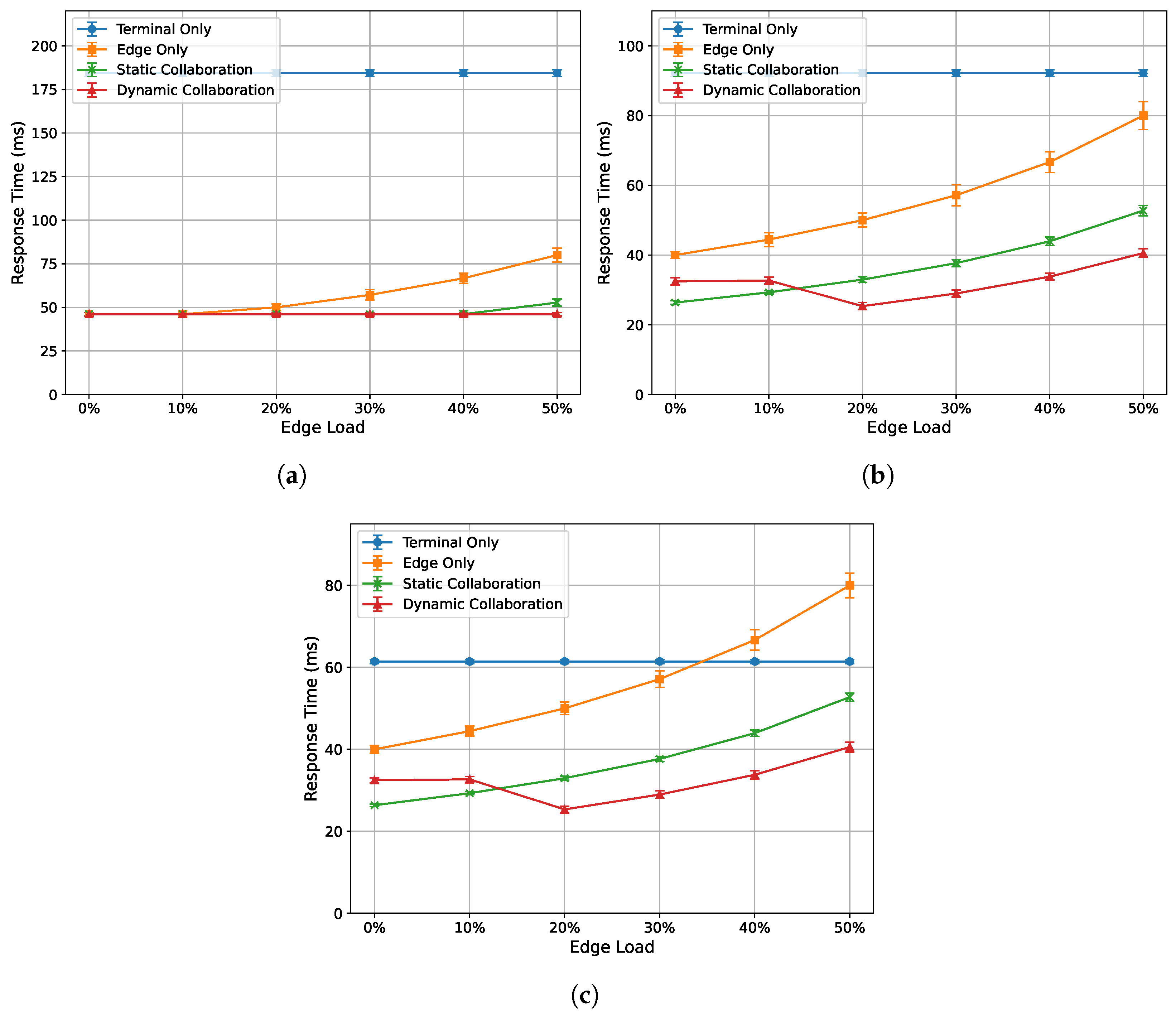
To evaluate the acceleration performance of the algorithm proposed in this paper under varying edge loads, the experiment is conducted under three network bandwidth conditions as follows: 30 Mbps, 60 Mbps, and 90 Mbps. The single-frame response time and total inference latency of the end device (NVIDIA Jetson Nano) are recorded for edge loads ranging from 0% to 50%. The experimental results are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. In the terminal-only comparison, the curves reported in this paper are based primarily on the weak terminal device, Jetson Nano, in order to highlight the acceleration benefits of edge–end collaboration for low-computational-power devices. The other terminal devices achieved noticeably lower response times and inference latencies under the terminal-only setting. The overall ranking is as follows: Ryzen R7-5800U laptop < I5-4590 desktop < I5-7200U laptop < Jetson Nano.
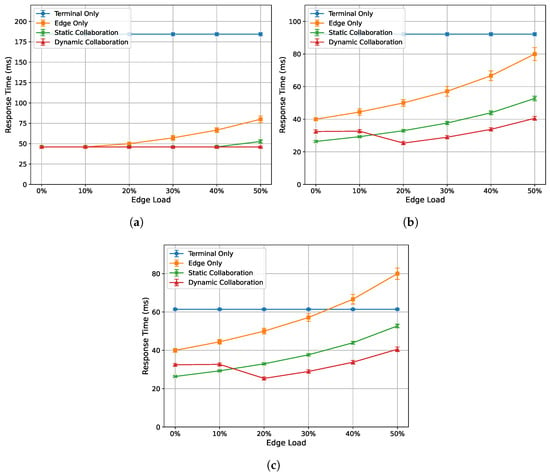
Figure 3.
Relationship between single-frame response time and edge load under different network dandwidths: (a) 30 Mbps. (b) 60 Mbps. (c) 90 Mbps.
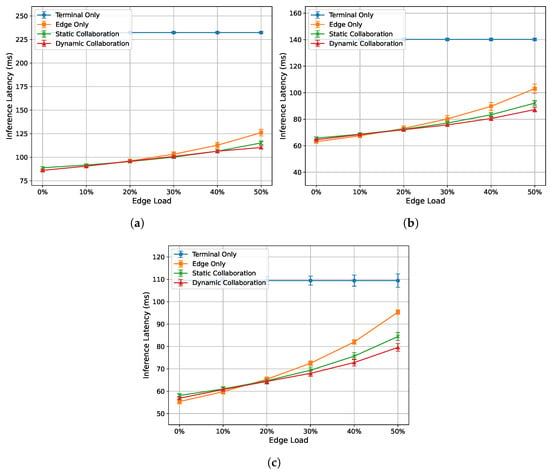
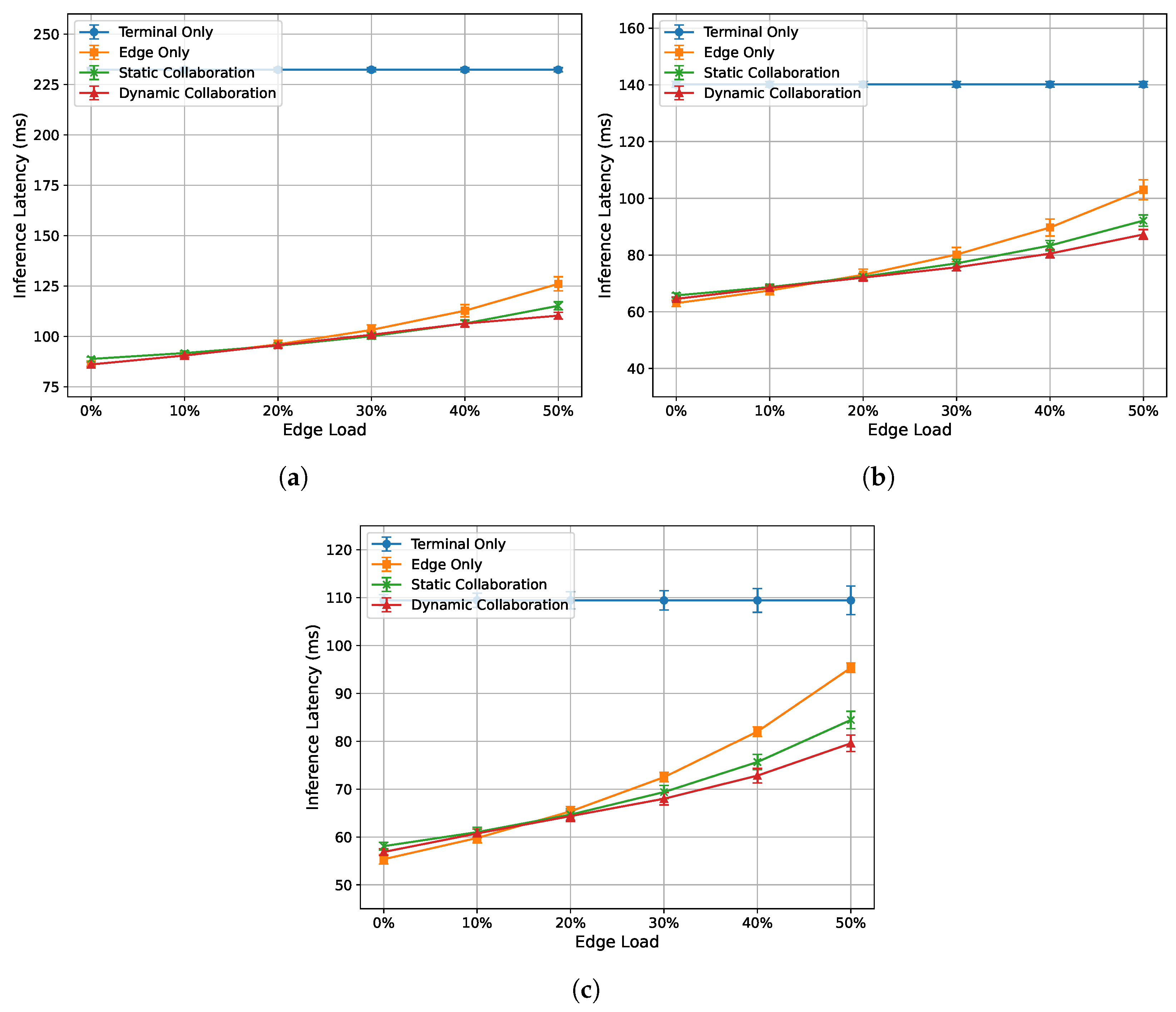
Figure 4.
Relationship between single-frame inference latency and edge load under different network bandwidths: (a) 30 Mbps. (b) 60 Mbps. (c) 90 Mbps.
Figure 3a–c show the relationship between the single-frame response time of each algorithm and edge load at 30 Mbps, 60 Mbps, and 90 Mbps bandwidths, respectively. Overall, the performance from best to worst is as follows: dynamic collaborative inference algorithm, static collaborative inference algorithm, edge-only inference algorithm, and terminal-only inference algorithm. More specifically, the following are observed: (1) The response time for terminal-only inference is independent of the edge server’s load, so its single-frame response time does not fluctuate significantly with changes in edge load. (2) The response time for edge-only inference shows a clear upward trend as the load increases, and the higher the load, the faster the growth rate of the response time. (3) The response time for static collaborative inference exhibits stronger stability under poor bandwidth conditions but is still affected by edge load even under good bandwidth conditions. (4) The response time for the proposed dynamic collaborative inference algorithm is also influenced by bandwidth, but the impact is smaller compared to static collaborative inference. Additionally, when the edge server load reaches 20%, the response time decreases because this algorithm prioritizes real-time performance by changing the optimization objective from minimizing inference latency to minimizing response time.
Figure 4a–c show the relationship between the single-frame inference latency of each algorithm and edge load at 30 Mbps, 60 Mbps, and 90 Mbps bandwidths, respectively. Overall, the performance ranking from best to worst is as follows: dynamic collaborative inference algorithm, static collaborative inference algorithm, edge-only inference algorithm, and terminal-only inference algorithm. Except for the terminal-only inference algorithm, the inference latency of the other three algorithms increases with an increase in edge load. Additionally, the inference latency of the proposed dynamic inference algorithm is less affected by edge load compared to the edge-only and static collaborative inference algorithms.
4.3.2. Acceleration Performance Under Varying Network Bandwidth Conditions
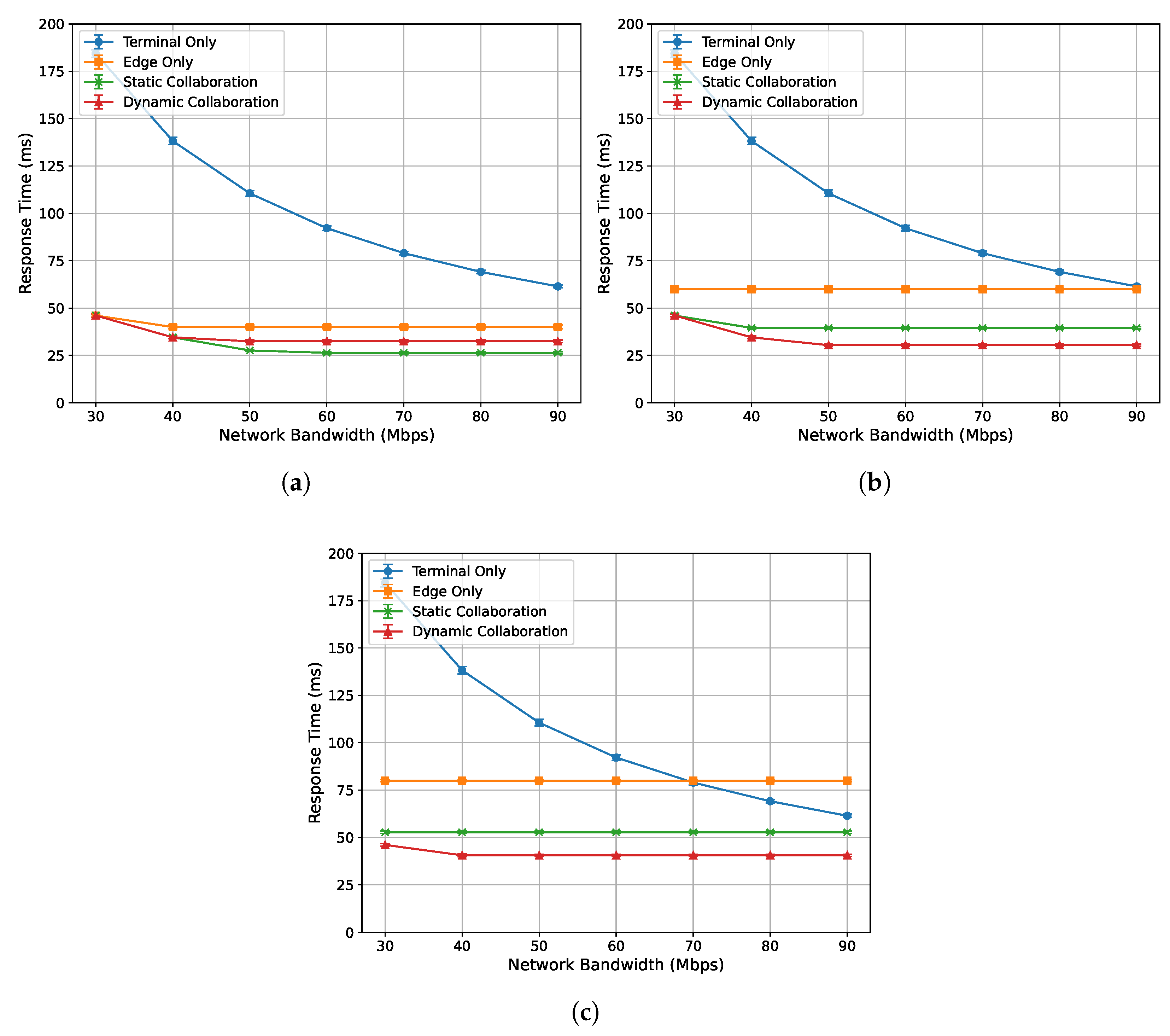
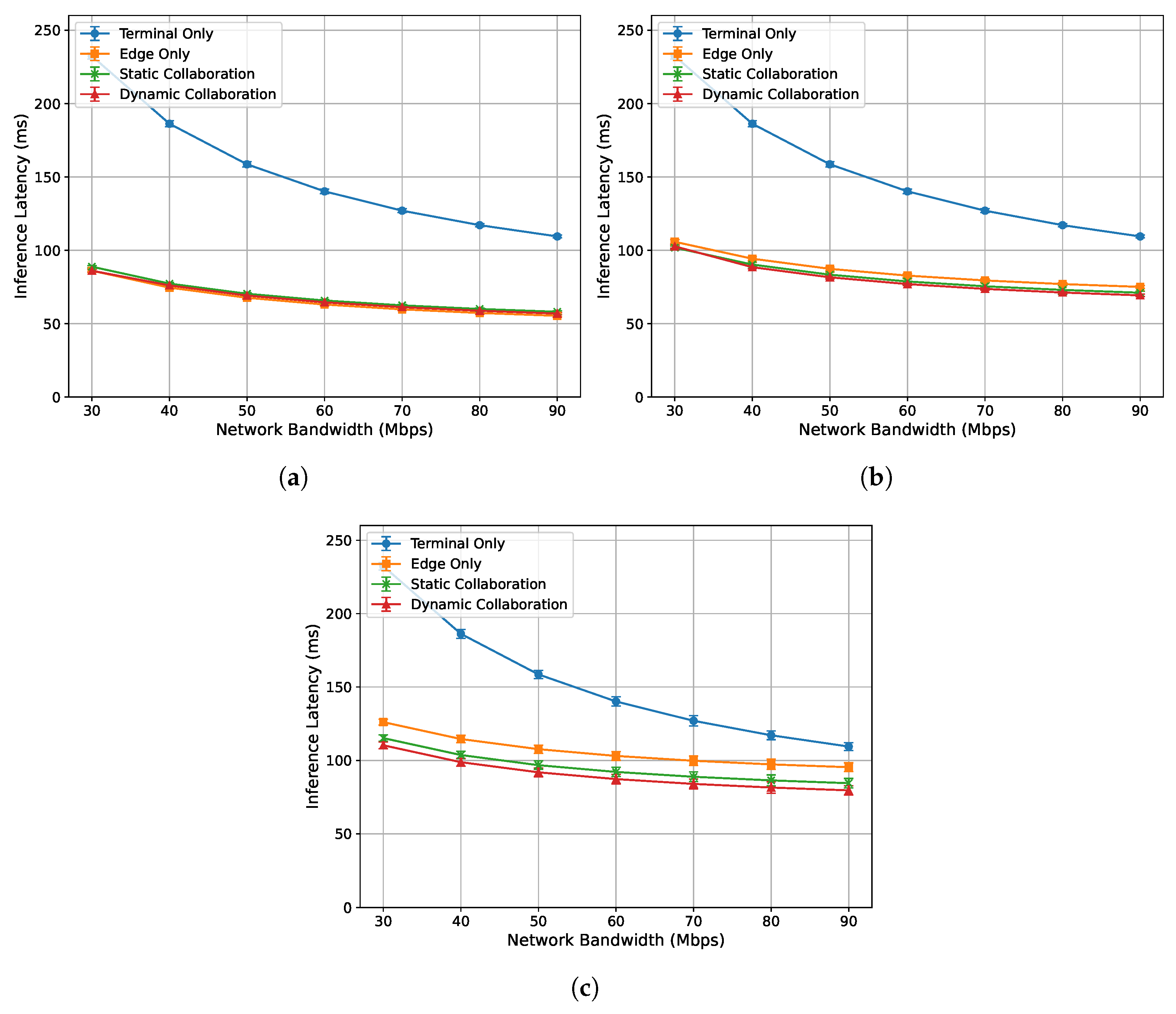
To evaluate the acceleration performance of the algorithm proposed in this paper under different network bandwidth conditions, this experiment measures the single-frame response time and inference latency of the end device (NVIDIA Jetson Nano) for network bandwidths ranging from 30 Mbps to 90 Mbps, under edge loads of 0%, 33%, and 50%, respectively. The experimental results are presented in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
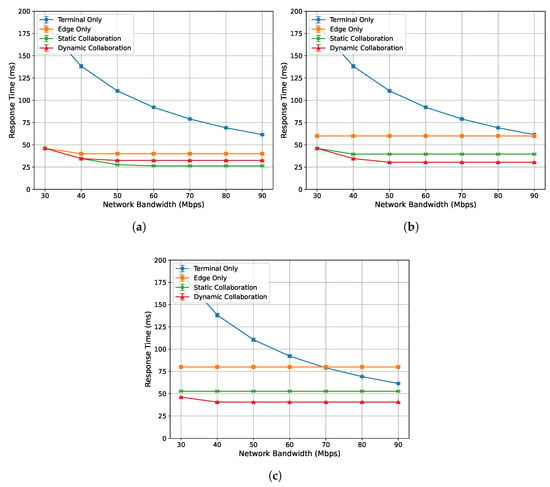
Figure 5.
Relationship between single-frame response time and network bandwidth under varying edge load conditions: (a) 0%. (b) 33%. (c) 50%.
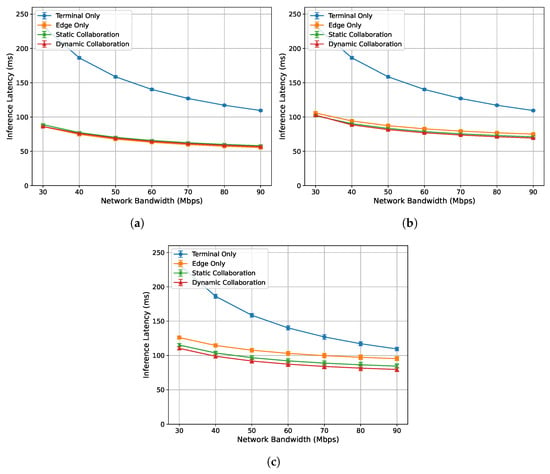
Figure 6.
Relationship between single-frame inference latency and network bandwidth under varying edge load conditions: (a) 0%. (b) 33%. (c) 50%.
Figure 5a–c show the relationship between the single-frame response time of each algorithm and network bandwidth under edge loads of 0%, 33%, and 50%, respectively. Overall, as the network bandwidth increases and transmission bottlenecks are alleviated, the response times of all algorithms decrease and stabilize. The performance ranking from best to worst is as follows: dynamic collaborative inference, static collaborative inference, edge-only inference, and terminal-only inference. Specifically, when the edge load is 0% and the bandwidth exceeds 40 Mbps, the single-frame response time of the proposed dynamic collaborative inference algorithm is higher than that of static collaborative inference. This is because, in this case, the response time is below the single-frame playback time, satisfying real-time requirements. Therefore, the optimization objective shifts to minimizing the single-frame inference latency.
Figure 6a–c show the relationship between the single-frame inference latency of each algorithm and network bandwidth under edge loads of 0%, 33%, and 50%, respectively. Overall, the inference latency of all algorithms decreases as the network bandwidth increases, and the performance ranking from best to worst is as follows: dynamic collaborative inference algorithm, static collaborative inference algorithm, edge-only inference algorithm, and terminal-only inference algorithm. It can be observed that the acceleration effect of the proposed dynamic collaborative inference algorithm becomes more pronounced with higher edge load. This is because the algorithm adaptively determines the model partitioning location based on the edge computing capacity. Specifically, when the edge load is high, the algorithm reduces the number of inference layers executed on the edge server to mitigate the impact of its inference latency.
For the sake of comparability across methods, the terminal-only setup retained the same acquisition/encoding/display pipeline as the other methods. Specifically, low-resolution frames were read and processed locally on the terminal, but the super-resolved results were still encoded on the device and transmitted over the controlled bandwidth-limited link to the display endpoint. Therefore, the reported single-frame response time is an end-to-end metric that includes local inference, encoding/buffering, and transmission/playout, rather than pure computation latency alone. This explains why in Figure 6 and Figure 7 the terminal-only curve decreases as bandwidth increases; higher bandwidth alleviates the encoding/transmission bottleneck, thereby reducing the end-to-end response time, while the computation component itself remains bandwidth-independent.
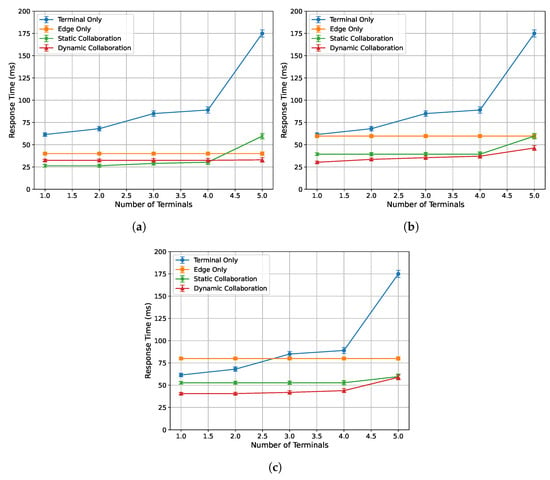
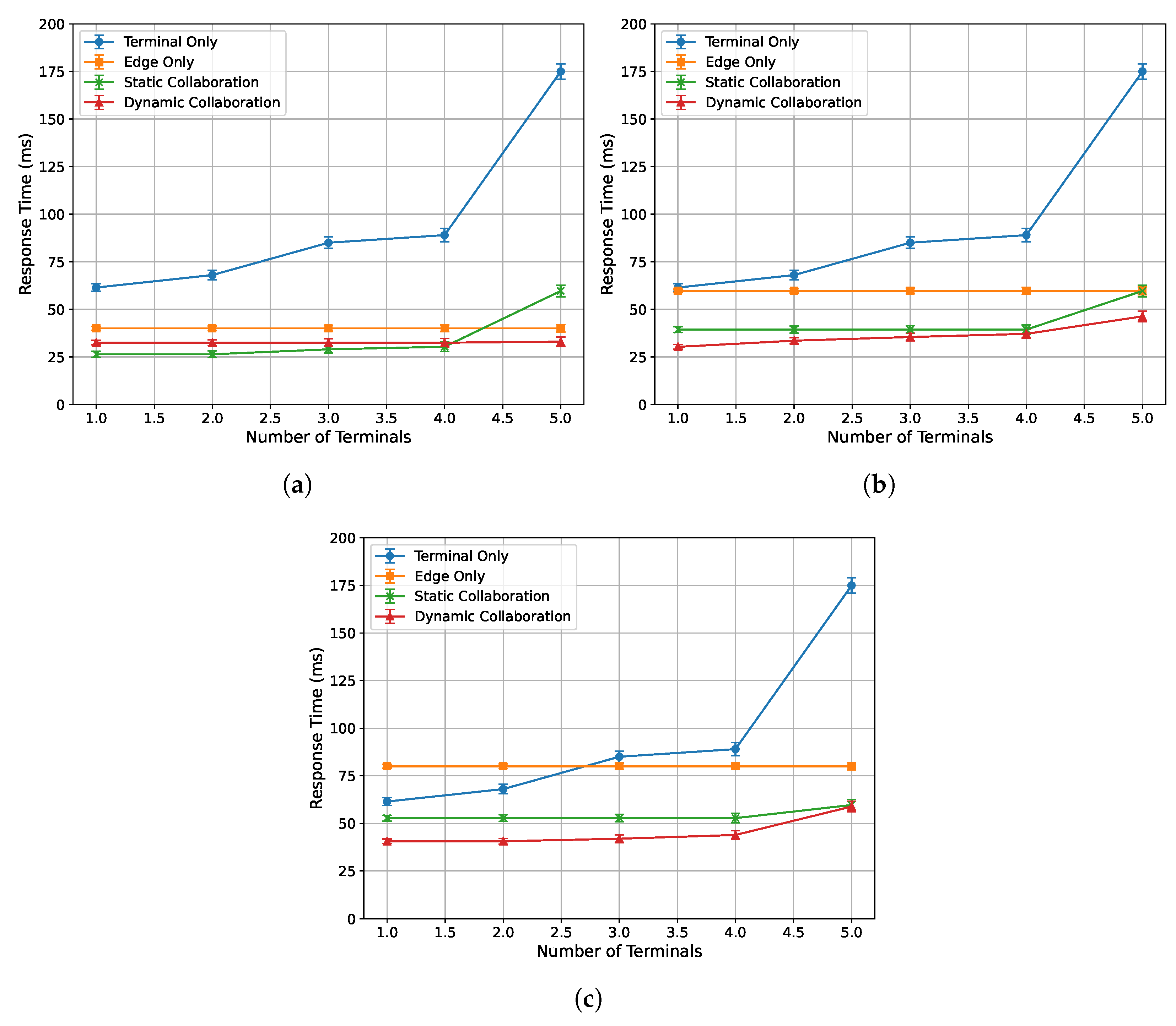
Figure 7.
Relationship between single-frame response time and number of devices under varying edge load conditions: (a) 0%. (b) 33%. (c) 50%.
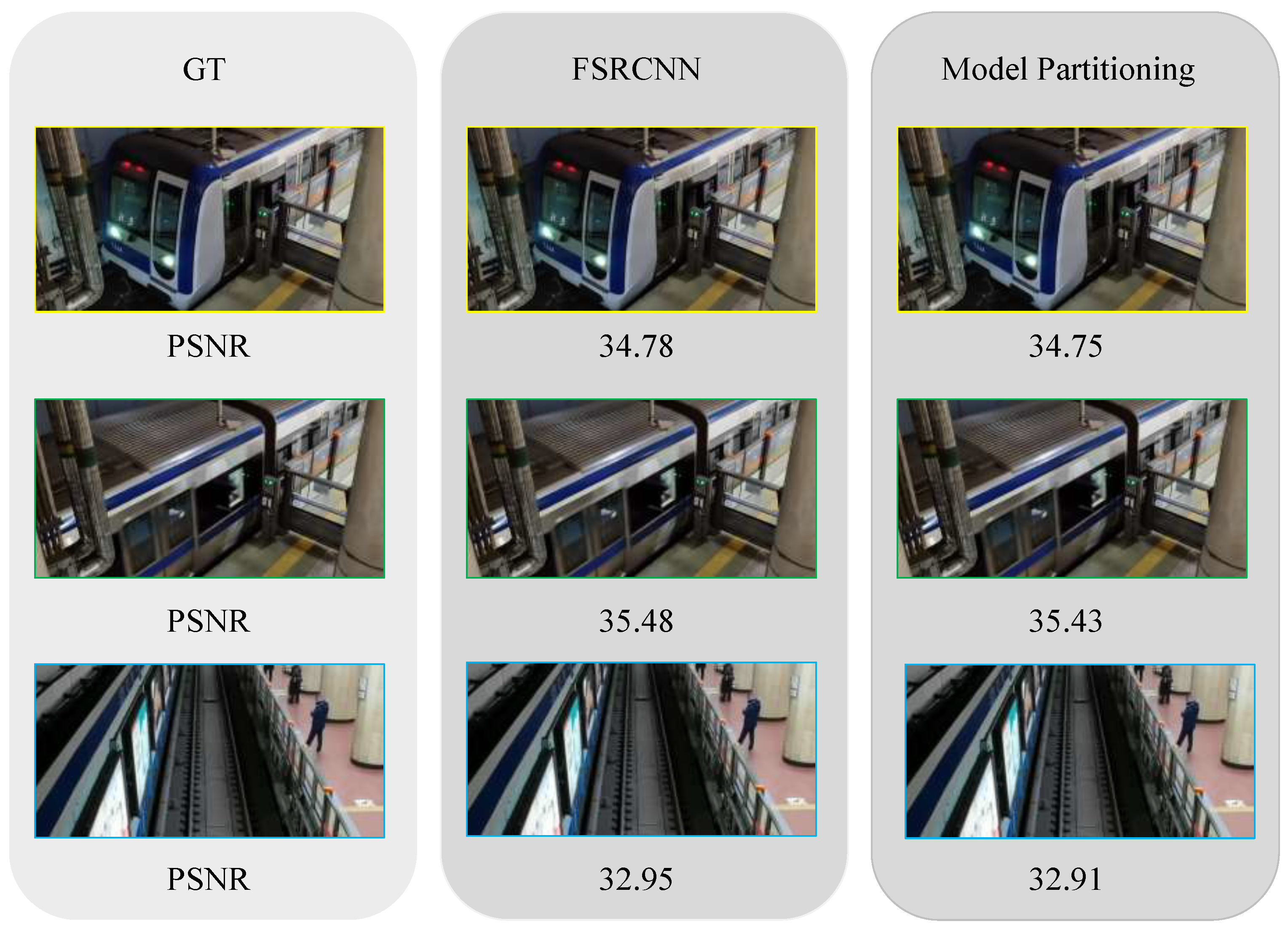
Although the main focus of this work is on reducing inference latency, we additionally verify that model partitioning does not compromise super-resolution quality. Figure 8 compares the PSNR of outputs from the full FSRCNN model and the partitioned model against the ground-truth images. The results show that the differences are negligible (≤0.05 dB across the tested frames), indicating that the proposed partitioning strategy maintains image fidelity while achieving latency reduction.

Figure 8.
PSNR-based quality comparison between FSRCNN and model partitioning.
4.3.3. Acceleration Performance Under Varying Terminal Inference Tasks
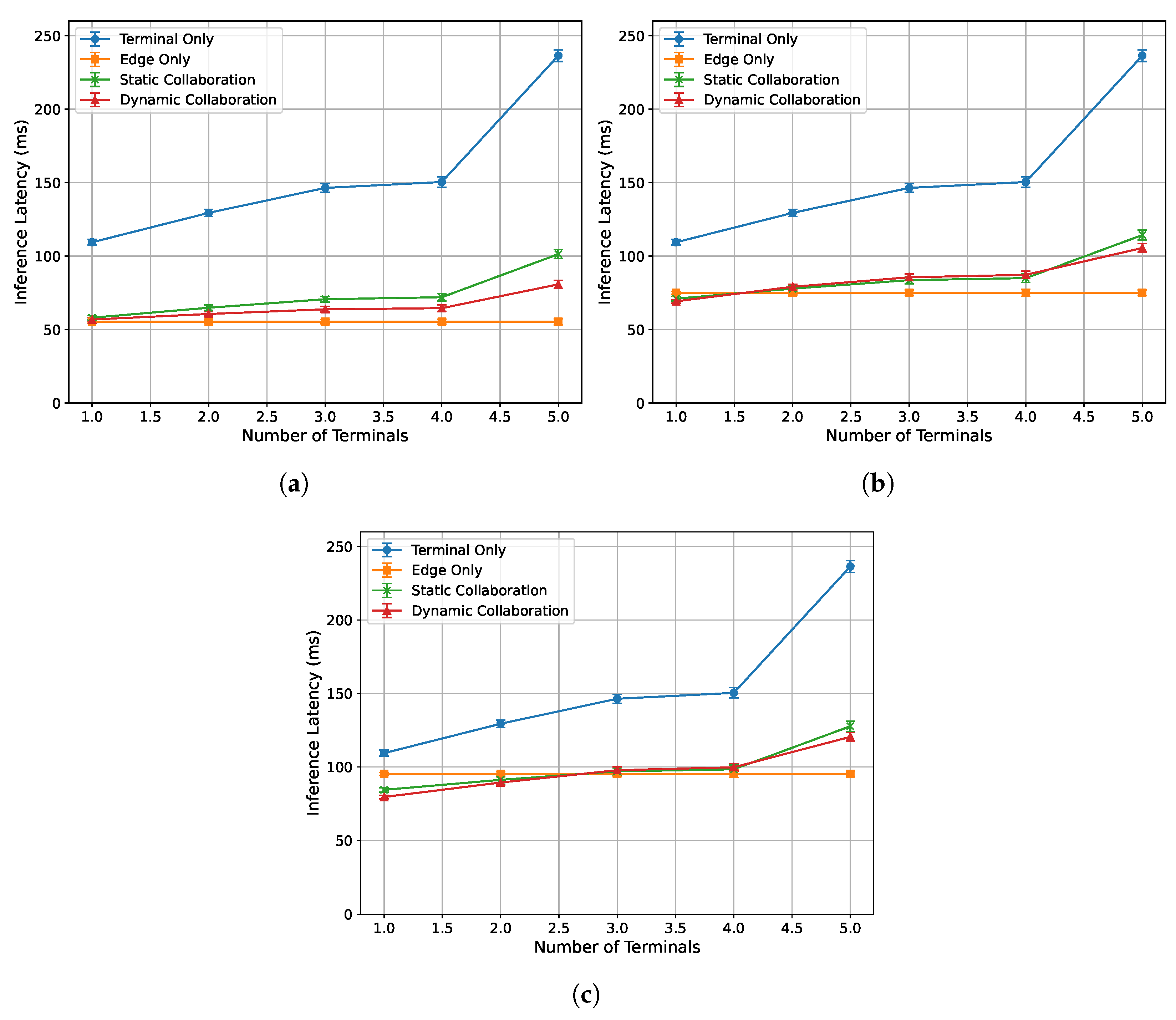
To evaluate the acceleration performance of the algorithm proposed in this paper under different numbers of terminal tasks, this experiment is conducted under edge loads of 0%, 33%, and 50%, with a fixed network bandwidth of 90 Mbps between each end device and the edge server. The single-frame response time and inference latency are recorded for end counts ranging from 1 to 5. Specifically, end device 1 is an NVIDIA Jetson Nano, end device 2 is an AMD® Ryzen™ R7-5800U processor laptop, and end devices 3 and 4 are both Intel® Core™ I5-4590 processor desktop computers. End device 5 is an Intel® Core™ I5-7200U processor laptop. The experimental results are presented in Figure 7 and Figure 9.
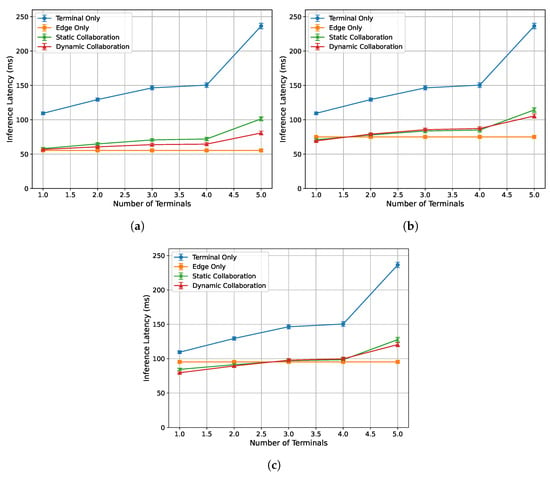
Figure 9.
Relationship between single-frame inference latency and number of devices under varying edge load conditions: (a) 0%. (b) 33%. (c) 50%.
Figure 7a–c illustrate the relationship between the single-frame response time of each algorithm and the number of end devices under edge loads of 0%, 33%, and 50%, respectively. It can be observed that the single-frame response time of all algorithms increases as the number of end devices increases. Among them, the terminal-only inference algorithm is most affected, as the computational performance bottleneck of the weakest end device determines the inference latency. Specifically, since the inference tasks are executed independently on each end device, the latency of the weakest device dictates the overall multi-terminal inference response time. In addition, the dynamic collaborative inference algorithm achieves the highest proportion of response times that satisfy the frame playback duration constraint, effectively ensuring real-time performance in multi-terminal inference tasks.
Figure 9a–c illustrate the relationship between the single-frame inference latency of each algorithm and the number of end devices under edge loads of 0%, 33%, and 50%, respectively. It can be observed that the single-frame inference latency of all algorithms increases as the number of end devices increases. Among them, the total inference latency of the edge-only inference algorithm remains relatively stable, as it is not affected by the performance of end devices. Compared to the static collaborative inference algorithm, the proposed dynamic collaborative inference algorithm optimizes the inference latency while ensuring real-time performance. Therefore, in most cases, the proposed dynamic collaborative inference algorithm achieves the lowest single-frame inference latency.
The above experimental results demonstrate that the dynamic collaborative inference algorithm can adaptively determine the optimal model partitioning position for each end device based on the “edge–end” environment, including device performance and network conditions. It should be emphasized that in the multi-terminal collaborative experiments, each terminal device has its own optimal partition point due to differences in computational capacity and uplink bandwidth. For example, for the low-performance Jetson Nano, the optimal split is usually located earlier in the network to reduce the local inference burden, whereas higher-performance devices such as the Ryzen laptop or desktop computers can process more front-end layers locally. The collaborative decision-making in our experiments dynamically adapts to these device-specific characteristics, thereby ensuring overall real-time performance.
It should also be noted that the experiments in this study were primarily conducted under a controlled LAN environment to isolate computation and bandwidth effects. More realistic wide-area network conditions such as 4G/5G mobile communications were not covered, where fluctuations can be more significant and pose greater challenges to real-time performance. Future work will extend the evaluation to actual vehicular network environments to further validate the robustness and effectiveness of the proposed mechanism.
5. Conclusions
This paper addresses the challenges of high computational complexity, the difficulty in ensuring real-time performance, and dynamic changes in the edge–end environment in in-vehicle real-time video super-resolution tasks by proposing a multi-terminal task inference framework based on edge–end collaboration. The framework establishes a real-time-priority mathematical model, solves the problem of minimizing multi-terminal task inference latency using game theory, and designs a dynamic model partitioning strategy and an adaptive adjustment mechanism. It can adaptively determine the optimal model partitioning point according to the performance of end devices, edge servers, and network status, thereby prioritizing real-time performance and minimizing the maximum inference latency of each end device.
Experimental results show that the proposed dynamic collaborative inference algorithm can effectively reduce single-frame response time and inference latency in scenarios with different edge loads, network bandwidths, and numbers of terminal tasks, outperforming comparative algorithms such as terminal-only inference, edge-only inference, and static collaborative inference. Especially under high edge load and bandwidth-constrained conditions, the algorithm can better adapt to dynamic environmental changes, providing high-quality video data support for in-vehicle safety monitoring and intelligent analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z. and Y.F.; methodology, L.Z. and Y.F.; software, L.Z. and D.S.; validation, L.Z., Y.F. and H.W.; formal analysis, L.Z. and Y.L.; investigation, L.Z. and Y.F.; resources, Y.L. and F.D.; data curation, L.Z. and D.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.F., Y.L., D.S., H.W. and F.D.; visualization, L.Z. and D.S.; supervision, Y.L. and F.D.; project administration, Y.L. and F.D.; funding acquisition, Y.L. and F.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Guangxi Science and Technology Achievement Transformation Program No.2025ZGZG02003, Science and Technology Major Special Program of Jiangsu Grants No. BG2024028, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant No. BK20253020, BK20230083, CRRC S&T Project No. KYHT019202500007, and in part by the Collaborative Innovation Center of Novel Software Technology and Industrialization.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Liming Zhou, Yulong Feng and Hui Wang were employed by the company CRRC Nanjing Puzhen Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Barman, N.; Martini, M.G. QoE modeling for HTTP adaptive video streaming–a survey and open challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 30831–30859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.; Jain, S.; Andra, U.; Khurana, T. Cisco Visual Networking Index (VNI) Complete Forecast Update, 2017–2022. In Americas/EMEAR Cisco Knowledge Network (CKN) Presentation; Cisco: San Jose, CA, USA, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Ruan, Z.; Zhao, P.; Dong, C.; Shang, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Timofte, R. Video super-resolution based on deep learning: A comprehensive survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 5981–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Hoi, S.C.H. Deep learning for image super-resolution: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 3365–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, K.; Patel, S.N.; Kumhar, M.; Bhatia, J.; Tanwar, S.; Davidson, I.E.; Mazibuko, T.F.; Sharma, R. Deep Learning-based Single-image Super-resolution: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 21811–21830. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, X. Fast and Accurate Single Image Super-Resolution via Information Distillation Network. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 723–731. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, R.; Venieris, S.I.; Dudziak, L.; Bhattacharya, S.; Lane, N.D. Mobisr: Efficient on-device super-resolution through heterogeneous mobile processors. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Los Cabos, Mexico, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Zhao, H.; Qiao, Y.; Dong, C. Classsr: A general framework to accelerate super-resolution networks by data characteristic. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 12016–12025. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Choi, S. Supremo: Cloud-assisted low-latency super-resolution in mobile devices. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2020, 21, 1847–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Z.; Gao, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Lightweight image super-resolution with information multi-distillation network. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 2024–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Xu, H.; Joe, Y.J.; Seo, D.; Cai, Z. Lightweight Super-Resolution Model for Complete Model Copyright Protection. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2023, 29, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgazzar, K.; Martin, P.; Hassanein, H.S. Cloud-Assisted Computation Offloading to Support Mobile Services. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2016, 4, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, M.O.; Giordano, S.; Procissi, G.; Seitanidis, I.N. A Review of Low-End, Middle-End, and High-End IoT Devices. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 70528–70554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akherfi, K.; Gerndt, M.; Harroud, H. Mobile cloud computing for computation offloading: Issues and challenges. Appl. Comput. Inform. 2018, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Li, F. Cloud–Edge Collaborative Inference with Network Pruning. Electronics 2023, 12, 3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliari, D.J.; Chiaro, R.; Macii, E.; Poncino, M. Crime: Input-dependent collaborative inference for recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2020, 70, 1626–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; He, X. Adaptive Deep Inference Framework for Cloud-Edge Collaboration. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Computers, Information Processing and Advanced Education (CIPAE), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 26–28 August 2023; IEEE: Now York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yang, L.; Huang, J. A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach for DNN Collaborative Inference in Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2023 10th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ICEEE), Istanbul, Türkiye, 8–10 May 2023; IEEE: Now York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.; Xu, G.; Luo, Y.; Hu, H.; An, J.; Mao, S. Multi-agent collaborative inference via DNN decoupling: Intermediate feature compression and edge learning. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 22, 6041–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wan, K.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Reinforcement learning based energy-efficient collaborative inference for mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 71, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Esquivel, J.A. LSTM network-based adaptation approach for dynamic integration in intelligent end-edge-cloud systems. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2024, 29, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francia, G.T. Resolving power and information. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1955, 45, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.L. Diffraction and resolving power. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1964, 54, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Introduction to Fourier Optics; Roberts and Company Publishers: Greenwood Village, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Tian, S. Transformer and GAN-based super-resolution reconstruction network for medical images. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2023, 29, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.E.; Williams, L. View interpolation for image synthesis. Semin. Graph. Pap. Push. Boundaries 2023, 2, 423–432. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Ma, K.-K. Contrast-guided image interpolation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 4271–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, W. Nonlocal edge-directed interpolation. In Pacific-Rim Conference on Multimedia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1197–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, T.; Haseyama, M. Missing intensity interpolation using a kernel PCA-based POCS algorithm and its applications. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 20, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xue, R.; Li, Y. Single image super-resolution reconstruction based on multi-directionality of the edge. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Digital Image Processing (ICDIP 2019), Guangzhou, China, 10–13 May 2019; Volume 11179, pp. 306–313. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, W.T.; Jones, T.R.; Pasztor, E.C. Example-based super-resolution. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2002, 22, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wright, J.; Huang, T.; Ma, Y. Image super-resolution as sparse representation of raw image patches. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; IEEE: Now York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mora-Martinez, Y.G.; Ponomaryov, V.I.; Garcia-Salgado, B.P.; Reyes-Reyes, R.; Cruz-Ramos, C. Real-time video super-resolution reconstruction using wavelet transforms and sparse representation. In Real-Time Processing of Image, Depth and Video Information; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2023; Volume 12571, pp. 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014, 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part IV 13. Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 184–199. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016, 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part II 14. Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 391–407. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, K.M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1646–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Qi, H. Image super-resolution by neural texture transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7982–7991. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, K.M. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1637–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, X. Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3147–3155. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4681–4690. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Mu Lee, K. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, T.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Gao, Q. Image super-resolution using dense skip connections. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22 –29 October 2017; pp. 4799–4807. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 286–301. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Lin, Z.; Deng, X.; An, W. Learning for video super-resolution through HR optical flow estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ACCV 2018, 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2–6 December 2018; Revised Selected Papers, Part I 14. Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 514–529. [Google Scholar]
- Sajjadi, M.S.M.; Vemulapalli, R.; Brown, M. Frame-recurrent video super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6626–6634. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Lin, C.; Tan, W. Frame and feature-context video super-resolution. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 5597–5604. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.C.; Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Dong, C.; Loy, C.C. BasicVSR: The search for essential components in video super-resolution and beyond. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4947–4956. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.C.; Zhou, S.; Xu, X.; Loy, C.C. Investigating tradeoffs in real-world video super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5962–5971. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Fu, J.; Qian, X. Learning trajectory-aware transformer for video super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5687–5696. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, W.; Ren, W.; Shi, Y.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, X. Video super-resolution via a spatio-temporal alignment network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.; Zhou, S.; Xu, X.; Loy, C.C. BasicVSR++: Improving video super-resolution with enhanced propagation and alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5972–5981. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Miao, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z. Edgeduet: Tiling small object detection for edge assisted autonomous mobile vision. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2022, 31, 1765–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monderer, D.; Shapley, L.S. Potential games. Games Econ. Behav. 1996, 14, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, K.; Li, T.; Zheng, K.; Peng, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Shen, M.; Mijumbi, R. A measurement study on multi-path TCP with multiple cellular carriers on high speed rails. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Budapest, Hungary, 20–25 August 2018; pp. 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Raca, D.; Quinlan, J.J.; Zahran, A.H.; Sreenan, C.J. Beyond throughput: A 4G LTE dataset with channel and context metrics. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM Multimedia Systems Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 12–15 June 2018; pp. 460–465. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).