Influence of Leadership on Human–Artificial Intelligence Collaboration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Human Intelligence
2.2. Artificial Intelligence
2.3. Leadership
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
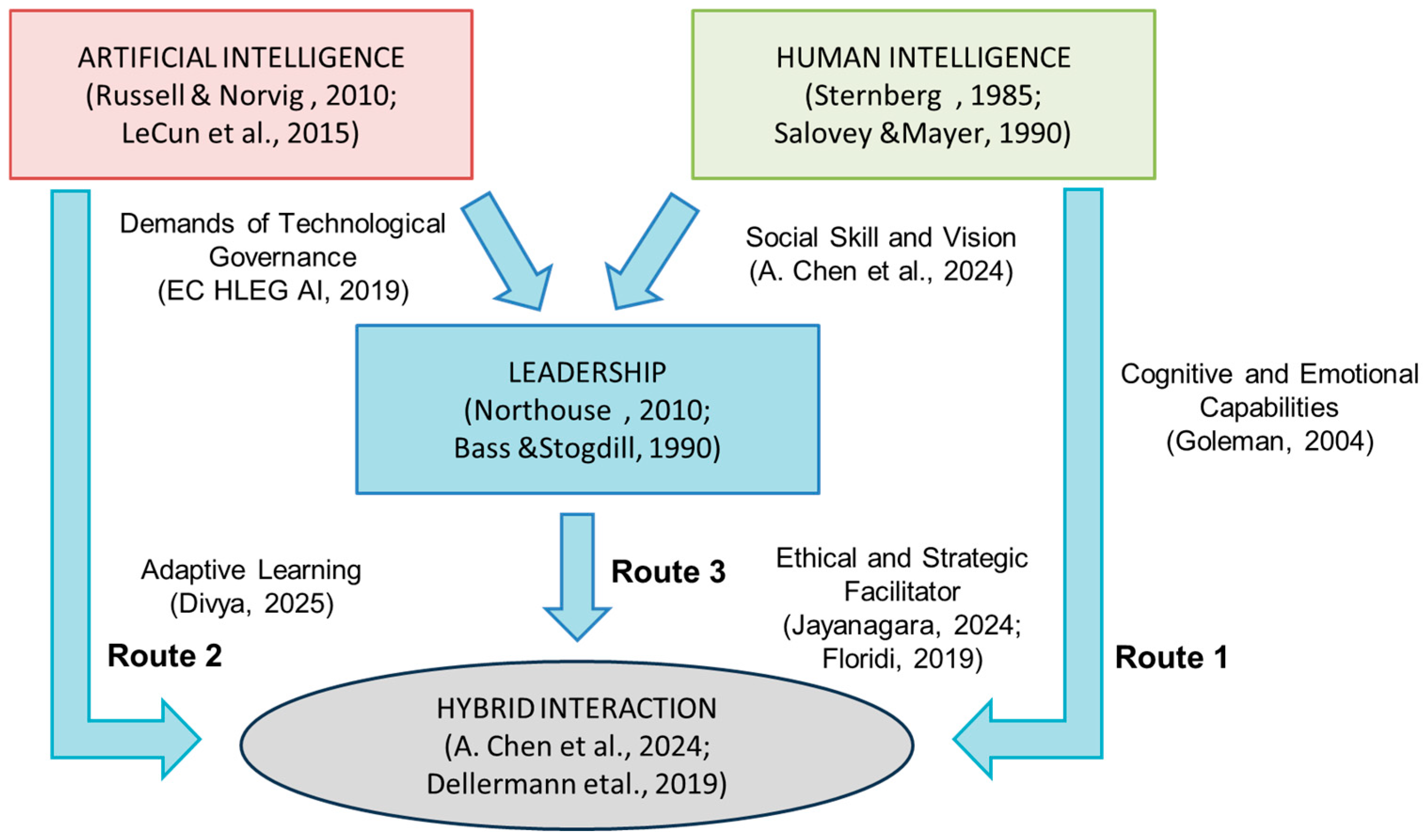
4.1. Leadership Mediation Model in Human–AI Interaction
Conceptual Model of Hybrid Interaction
4.2. Applicability of the Proposed Model
5. Discussion
5.1. Interaction Between Human–AI
5.2. Influence of Leadership on Human–AI Collaboration
6. Conclusions
6.1. Limitations
6.2. Future Lines of Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HI | Human Intelligence |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Adeniyi, I. S., Al Hamad, N. M., Adewusi, O. E., Unachukwu, C., Osawaru, B., Onyebuchi, C. N., Omolawal, S. A., Aliu, A. O., & David, I. O. (2024). Organizational culture and leadership development: A human resources review of trends and best practices. Magna Scientia Advanced Research and Reviews, 10(1), 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinrinola, O., Okoye, C. C., Ofodile, O. C., & Ugochukwu, C. E. (2024). Navigating and reviewing ethical dilemmas in AI development: Strategies for transparency, fairness, and accountability. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews, 18(3), 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J. F. (1998). AI growing up: The changes and opportunities. AI Magazine, 19(4), 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaibani, E., Bakir, A., & Al-Atwi, A. (2025). The impact of leadership behaviors on organizational innovative performance and learning in AI-driven Industry 5.0 environments. Development and Learning in Organizations, 39(3), 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taneiji, S. (2006). Transformational leadership and teacher learning in model schools. Journal of Faculty of Education UAEU, 23(6), 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Baczyńska, A., & Thornton, G. C. (2017). Relationships of analytical, practical, and emotional intelligence with behavioral dimensions of performance of top managers. International Journal of Selection and Assessment, 25(2), 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baez, M. D. (2025). AI-powered leadership: Transforming organizations in the digital age. IGI Global. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrammirzaee, A. (2010). A comparative survey of artificial intelligence applications in finance: Artificial neural networks, expert system and hybrid intelligent systems. Neural Computing and Applications, 19(8), 1165–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, N., Kauppinen, M., Hiekkanen, K., & Kujala, S. (2022). Transparency and explainability of AI systems: Ethical guidelines in practice. In Requirements engineering: Foundation for software quality (pp. 3–18). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbey, A. K., Colom, R., & Grafman, J. (2013). Architecture of cognitive flexibility revealed by lesion mapping. Neuroimage, 82, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, B. M. (1985). Leadership and performance beyond expectations. Free Press. Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=NCd-QgAACAAJ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Bass, B. M., & Riggio, R. E. (2006). Transformational leadership. Psychology Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, B. M., & Stogdill, R. M. (1990). Bass & Stogdill’s handbook of leadership: Theory, research, and managerial applications. Simon and Schuster. [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua, S., Masárová, J., Perotti, F. A., & Ferraris, A. (2025). Enhancing top managers’ leadership with artificial intelligence: Insights from a systematic literature review. Review of Managerial Science, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binet, A., & Simon, T. (1904). Méthodes nouvelles pour le diagnostic du niveau intellectuel des anormaux. L’Année Psychologique, 11(1), 191–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, R. R., & Mouton, J. S. (1985). The managerial grid III: A new look at the classic that has boosted productivity and profits for thousands of corporations worldwide. Gulf Publishing Company. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, T., & von der Oelsnitz, D. (2025). Leadership competences in the era of artificial intelligence—A structured review. Strategy and Leadership, 53(3), 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredeweg, B., & Kragten, M. (2022). Requirements and challenges for hybrid intelligence: A case-study in education. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 5, 891630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M. E., & Treviño, L. K. (2006). Ethical leadership: A review and future directions. The Leadership Quarterly, 17(6), 595–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruch, H., & Walter, F. (2007). Leadership in context: Investigating hierarchical impacts on transformational leadership. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 28(8), 710–726. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, J. A. (2016). Improving the peer review of narrative literature reviews. Research Integrity and Peer Review, 1(12). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cath, C., Wachter, S., Mittelstadt, B., Taddeo, M., & Floridi, L. (2017). Artificial Intelligence and the ‘Good Society’: The US, EU, and UK approach. Science and Engineering Ethics, 24, 505–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A., Lyu, A., & Lu, Y. (2024). Member’s performance in human–AI hybrid teams: A perspective of adaptability theory. Information Technology & People. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L., Chen, P., & Lin, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence in education: A review. IEEE Access, 8, 75264–75278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. (2017, July 21–26). Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (pp. 1800–1807), Honolulu, HI, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. (2019). On the measure of intelligence. arXiv, arXiv:1911.01547. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C., & Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 20(3), 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyert, R. M. (1990). Defining leadership and explicating the process. Non-profit Management and Leadership, 1(1), 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, D. M., & Mandvikar, S. (2023). Augmented intelligence: Human-AI collaboration in the era of digital transformation. International Journal of Engineering Applied Sciences and Technology, 8(6), 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellermann, D., Calma, A., Lipusch, N., Weber, T., Weigel, S., & Ebel, P. (2019, January 8–11). The future of human-AI collaboration: A taxonomy of design knowledge for hybrid intelligence systems. Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebojoh, S., & Högberg, K. (2024). Exploring leadership in the hybrid workplace. International Journal of Advanced Corporate Learning (iJAC), 17(4), 16–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC HLEG AI-European Commission. (2019). Ethics guidelines for trustworthy AI [Informe técnico]. Available online: https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/library/ethics-guidelines-trustworthy-ai (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Elfighi, M. M. S. (2025). Advancements and challenges in neuromorphic computing: Bridging neuroscience and artificial intelligence. International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology, 13(1), 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbart, D. C. (1962). Augmenting human intellect: A conceptual framework (pp. 13–29). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough, M. J., & Hart, R. K. (2008). Emotions in leadership development: A critique of emotional intelligence. Advances in Developing Human Resources, 10(5), 740–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R. (2015). Writing narrative style literature reviews. Medical Writing, 24(4), 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, N. V., & Croitoru, G. (2025). The impact of artificial intelligence on communication dynamics and performance in organizational leadership. Administrative Sciences, 15(2), 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floridi, L. (2019). Establishing the rules for building trustworthy AI. Nature Machine Intelligence, 1(6), 261–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, M. (2018). Architects of intelligence: The truth about AI from the people building it. Packt Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, Y., & Schapire, R. E. (1997). A decision-theoretic generalization of online learning and an application to boosting. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 55(1), 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, H. E. (2000). Intelligence reframed: Multiple intelligences for the 21st century. Hachette UK. [Google Scholar]
- Gignac, G. E. (2018). Conceptualizing and measuring intelligence. In SAGE handbook of personality and individual differences (pp. 439–464). SAGE Publications Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Gignac, G. E., & Szodorai, E. T. (2024). Defining intelligence: Bridging the gap between human and artificial perspectives. Intelligence, 104, 101832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givigi, S., & Jardine, P. T. (2018). Machine learning for data-driven control of robots. IEEE Potentials, 37(4), 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glikson, E., & Woolley, A. W. (2020). Human trust in artificial intelligence: Review of empirical research. Academy of Management Annals, 14(2), 627–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goleman, D. (1995). Emotional intelligence. Bantam Books. [Google Scholar]
- Goleman, D. (2004). What makes a leader? Harvard Business Review, 82(1), 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Luna, E., Fernando-Navas, D., Aponte-Mayor, G., & Betancourt-Buitrago, L. A. (2014). Metodología para la revisión bibliográfica y la gestión de información de temas científicos, a través de su estructuración y sistematización. Dyna, 81(184), 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, R. W., & Moorhead, G. (2013). Organizational behavior: Managing people and organizations. Cengage Learning. Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=yRuJK0w-htEC (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Grover, P., Kar, A. K., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2022). Understanding artificial intelligence adoption in operations management: Insights from the review of academic literature and social media discussions. Annals of Operations Research, 308(1–2), 177–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirao, S. J. A. (2015). Utilidad y tipos de revisión de literatura. Ene, 9(2), 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S., & Jaiswal, R. (2024). How can we improve AI competencies for tomorrow’s leaders: Insights from multi-stakeholders’ interaction. International Journal of Management Education, 22(3), 101070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamet, P., & Tremblay, J. (2017). Artificial intelligence in medicine. Metabolism, 69(4), S36–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M. (2015). A study on principles of leadership and conditions of a leader. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 8(25), 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, H., Silva, E. S., Unger, S., TajMazinani, M., & Mac Feely, S. (2020). Artificial Intelligence (AI) or Intelligence Augmentation (IA): What is the future? AI, 1(2), 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heifetz, R. A., Grashow, A., & Linsky, M. (2009). The practice of adaptive leadership: Tools and tactics for changing your organization and the world. Harvard Business Press. [Google Scholar]
- Henkel, T., & Bourdeau, D. (2018). A field study: An examination of managers’ situational leadership styles. Journal of Diversity Management (JDM), 13(2), 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansyah, M., Najib, A., Farida, A., Sacipto, R., & Rintyarna, B. S. (2023). Artificial intelligence and ethics: Building an artificial intelligence system that ensures privacy and social justice. International Journal of Science and Society, 5(1), 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G., Srivastava, N., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Salakhutdinov, R. R. (2012). Improving neural networks by preventing coadaptation of feature detectors. arXiv, arXiv:1207.0580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, A., Langs, G., Denk, H., Zatloukal, K., & Müller, H. (2019). Causability and explainability of artificial intelligence in medicine. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 9(4), e1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayounirad, A. (2023). Designing the built environment through hybrid intelligence. HHAI 2023: Augmenting Human Intellect, 368, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S., Fernando, M., & Akter, S. (2025). Digital leadership: Towards a dynamic managerial capability perspective of artificial intelligence-driven leader capabilities. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 32(2), 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahi, M. H. (2018). Artificial intelligence and the future of work: Human-AI symbiosis in organizational decision making. Business Horizons, 61(4), 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanagara, O. (2024). The evolution of leadership in the modern professional landscape: Shifting paradigms and their impacts. Feedforward: Journal of Human Resource, 4(1), 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A. R. (1998). The g factor and the design of education. In The g factor (pp. 111–132). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y., Li, X., Luo, H., Yin, S., & Kaynak, O. (2022). Quovadis artificial intelligence? Discover Artificial Intelligence, 2(1), 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D. L., & Newman, D. A. (2010). Emotional intelligence: An integrative meta-analysis and cascading model. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95(1), 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A., & Haenlein, M. (2019). Siri, Siri, in my hand: Who’s the fairest in the land? On the interpretations, illustrations, and implications of artificial intelligence. Business Horizons, 62(1), 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, D., Maccoby, N., Gurin, G., & Floor, L. G. (1951). Productivity, supervision and morale among railroad workers. Institute for Social Research, University of Michigan. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1130282271921984384.bib?lang=ja (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Kelly, K. (2016). The inevitable: Understanding the 12 technological forces that will shape our future. Viking. Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=4bogDAAAQBAJ (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Kouzes, J. M., & Posner, B. Z. (2017). The leadership challenge: How to make extraordinary things happen in organizations. Wiley. Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=u-5xDgAAQBAJ (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Kumari, J., Gupta, C., & Jindal, P. (2024). Ethical leadership. In Handbook of research on leadership (pp. 148–158). IGI Global. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyllonen, P. C., Roberts, R. D., & Stankov, L. (2008). Extending intelligence: Enhancement and new constructs. Taylor & Francis. [Google Scholar]
- Ladkin, D. (2010). Rethinking leadership: A new look at old leadership questions. Edward Elgar Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legg, S., & Hutter, M. (2007). A collection of definitions of intelligence. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and applications, 157, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M., & Bitterly, T. B. (2024). How perceived lack of benevolence harms trust of artificial intelligence management. Journal of Applied Psychology, 109(11), 1794–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, R. G., & Maher, K. J. (2002). Leadership and information processing. Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhmann, N. (1998). Social systems. Stanford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Maletzki, C., Rietzke, E., & Bergmann, R. (2024). Empowering large language models in hybrid intelligence systems through data-centric process models. Proceedings of the AAAI Symposium Series, 3(1), 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M. L., Minsky, M., Rochester, N., & Shannon, C. E. (1955). A proposal for the Dartmouth summer research project on artificial intelligence. AI Magazine, 27(4), 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidan, Y., Lerner, B., Rabinowitz, G., & Hassoun, M. (2011). Cycle-time key factor identification and prediction in semiconductor manufacturing using machine learning and data mining. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 24(2), 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L., Yang, M., Yao, J., Huang, Y., & Wang, D. (2024, September 22–24). Design of labor capacity management system based on artificial intelligence and machine learning. 2024 International Conference on Electronics and Devices, Computational Science (ICEDCS) (pp. 875–879), Marseille, France. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q., Wu, T. J., Duan, W., & Li, S. (2025). Effects of Employee–Artificial Intelligence (AI) Collaboration on Counterproductive Work Behaviors (CWBs): Leader Emotional Support as a Moderator. Behavioral Sciences, 15(5), 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menouar, H., Guvenc, I., Akkaya, K., Uluagac, A. S., Kadri, A., & Tuncer, A. (2017). UAV-enabled intelligent transportation systems for the smart city: Applications and challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(3), 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minsky, M. (1968). Semantic information processing. MIT Press. Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=XPTOnQAACAAJ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Morin, E. (2001). El método 1. La naturaleza de la naturaleza. Ediciones Cátedra. [Google Scholar]
- Musanga, V., Chibaya, C., & Viriri, S. (2024). A scoping review of literature on deep learning and symbolic AI-based framework for detecting COVID-19 using computerized tomography scans. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science, 13(2), 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvaez, D. (2002). Individual differences that influence reading comprehension. In Comprehension instruction: Research-based best practices (pp. 158–175). Springer Nature. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolescu, B. (2006). Transdisciplinariedad: Pasado, presente y futuro (1ª parte). Visión docente Con-ciencia, 6(31), 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, N. J. (1998). Artificial intelligence: A new synthesis. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Northouse, P. G. (2010). Leadership: Theory and practice. SAGE Publications. Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=BiqT_CZbBegC (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Oesch, N. (2024). Social brain perspectives on the social and evolutionary neuroscience of human language. Brain Sciences, 14(2), 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J., Eden, J., Oetomo, D., & Johal, W. (2024). Using Fitts’ law to benchmark assisted human-robot performance. arXiv. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:274597067 (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Parchment, A. (2025). Ethical leadership and its communication implications: Navigating artificial intelligence, technological advancements, and employee well-being. In AI-powered leadership: Transforming organizations in the digital age (pp. 73–107). IGI Global Scientific Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, K., Cohen, M., & Bhattacharya, S. (2016). Rise of the Machines. Group & Organization Management, 41(5), 571–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, L., & Topaz, M. (2022). Artificial intelligence in health care: Implications for nurse managers. Journal of Nursing Management, 30(8), 3641–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pileggi, S. F. (2024). Ontology in hybrid intelligence: A concise literature review. Future Internet, 16(8), 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomin, R. (2019). Blueprint: How DNA makes us who we are. MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, M., & Srivastava, A. K. (2023). Leadership and supply chain management: A systematic literature review. Journal of Modelling in Management, 18(2), 524–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, A., Braines, D., Cerutti, F., & Pham, T. (2019). Explainable AI for Intelligence Augmentation in Multi-Domain Operations. arXiv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J. R. (1986). Induction of decision trees. Machine Learning, 1(1), 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisch, S., & Krakowski, S. (2021). Artificial intelligence and management: The automation–augmentation paradox. Academy of Management Review, 46(1), 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rest, J. R., Narvaez, D., Thoma, S. J., & Bebeau, M. J. (1999). DIT2: Devising and testing a revised instrument of moral judgment. Journal of Educational Psychology, 91(4), 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S. (2023). Hybrid AI models for balancing privacy and innovation in government infrastructure. The Review of Contemporary Scientific and Academic Studies, 3(12), 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rue, L. W., & Byars, L. L. (2005). Management: Skills and application. McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=-LahtyVud_gC (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Rukadikar, A., & Khandelwal, K. (2024). Leadership development through self-upskilling: Role of generative artificial intelligence. Development and Learning in Organizations, 38(4), 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., & Williams, R. J. (1986). Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 323(6088), 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S., & Norvig, P. (2002). Inteligencia Artificial: Un enfoque moderno (2nd ed). Prentice Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S., & Norvig, P. (2010). Artificial intelligence: A modern approach (3rd ed.). Pearson. [Google Scholar]
- Salovey, P., & Mayer, J. D. (1990). Emotional intelligence. Imagination. Cognition and Personality, 9(3), 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuering, B., & Schmid, T. (2024). What can computers do now? Dreyfus revisited for the third wave of artificial intelligence. Proceedings of the AAAI Symposium Series, 3(1), 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyaningrum, R. P., & Muafi, M. (2023). Managing job burnout from workplace telepressure: A three-way interaction. SA Journal of Human Resource Management, 21, a2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M. M., & Ghodoosi, F. (2022). The ethics of blockchain in organizations. Journal of Business Ethics, 178(4), 1009–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H., Prins, C., & Schrijvers, E. (2023). Mission AI. Springer International Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skagestad, P. (1993). Thinking with machines: Intelligence augmentation, evolutionary epistemology, and semiotic. Journal of Social and Evolutionary Systems, 16(2), 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skagestad, P. (1996). The mind’s machines: The Turing machine, the Memex, and the personal computer. Semiotica, 111(3–4), 217–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosik, J. J. (2005). The role of personal values in the charismatic leadership of corporate managers: A model and preliminary field study. The Leadership Quarterly, 16(2), 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, R. J. (1985). Beyond IQ: A triarchic theory of human intelligence. CUP Archive. [Google Scholar]
- Stogdill, R. M., & Coons, A. E. (1957). Leader behavior: Its description and measurement. Bureau of Business Research, College of Commerce and Administration, Ohio State University. Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=oON4ygAACAAJ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Sun, C., Ma, M., Zhao, Z., Tian, S., Yan, R., & Chen, X. (2019). Deep transfer learning based on sparse autoencoder for remaining useful life prediction of tool in manufacturing. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 15(4), 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H. (2015). Leadership style and organizational performance: A comparative study between transformational and transactional leadership styles. IBT Journal of Business Studies, 11(2), 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebes, S., Lins, S., & Sunyaev, A. (2021). Trustworthy artificial intelligence. Electronic Markets, 31(2), 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P., Rajput, N., & Garg, V. (2022, April 27–29). Artificial intelligence and talent acquisition: Role of HR leaders in adoption. 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Engineering and Management (ICIEM 2022) (pp. 313–317), London, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Turing, A. M. (1950). Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind, 59(236), 433–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Breemen, A. J. J., Farkas, J. I., & Sarbo, J. J. (2011). Knowledge representation as a tool for intelligence augmentation. In Computational modeling and simulation of intellect: Current state and future perspectives (pp. 321–341). IGI Global. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Waa, J., Kunneman, Y., Maccatrozzo, V., & van der Stigchel, B. (2022). H3AI 2022: Hackathon on Hybrid Human Artificial Intelligence. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, 354, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wynsberghe, A. (2021). Sustainable AI: AI for sustainability and the sustainability of AI. AI and Ethics, 1(3), 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, P. (2025). The transformative role of artificial intelligence in leadership and management development: An academic insight. Development and Learning in Organizations. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchiotti, R. (2018). Contemporary leadership: The perspective of a practitioner. Journal of Leadership Studies, 12(2), 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroom, V. H., & Jago, A. G. (2007). The role of the situation in leadership. American Psychologist, 62(1), 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P. (2019). On defining artificial intelligence. Journal of Artificial General Intelligence, 10(2), 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weick, K. E. (1995). Sensemaking in organizations (Vol. 3). Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T. J., Liang, Y., & Wang, Y. (2024). The Buffering Role of Workplace Mindfulness: How Job Insecurity of Human-Artificial Intelligence Collaboration Impacts Employees’ Work–Life-Related Outcomes. Journal of Business and Psychology, 39(6), 1395–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T. J., Zhang, R. X., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Navigating the human-artificial intelligence collaboration landscape: Impact on quality of work life and work engagement. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 62, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, R., & Ebrahim, F. (2016). Leadership styles and organizational commitment: Literature review. Journal of Management Development, 35(2), 190–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetton, P., & Crouch, A. (1983). Social influence and structure: Elements of a general theory of leadership. Australian Journal of Management, 8(2), 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S., Li, X., Gao, H., & Kaynak, O. (2015). Data-based techniques focused on modern industry: An overview. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 62(1), 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y. (2024). Hybrid models for accuracy and explainability in AI systems. In J. Zhang, & N. Sun (Eds.), Third international conference on electronic information engineering, big data, and computer technology (EIBDCT 2024) (p. 309). SPIE. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukl, G. (2006). Leadership in Organizations, 9/e. Pearson Education India. [Google Scholar]
- Yukl, G. (2008). How leaders influence organizational effectiveness. The leadership quarterly, 19(6), 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukl, G. (2012). Leadership: What is it? Cases in leadership (3rd ed., pp. 1–42). Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, K. S., Reaz, M. B. I., Ali, S. H. M., Bakar, A. A. A., & Chowdhury, M. E. H. (2022). Custom hardware architectures for deep learning on portable devices: A review. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 33(11), 6068–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaresefat, M., & Derakhshani, R. (2023). Revolutionizing groundwater management with hybrid AI models: A practical review. Water, 15(9), 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarsky, T. (2016). The trouble with algorithmic decisions. Science, Technology, & Human Values, 41(1), 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D., Han, X., & Deng, C. (2018). Review on the research and practice of deep learning and reinforcement learning in smart grids. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 4(3), 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zárate-Torres, R.; Rey-Sarmiento, C.F.; Acosta-Prado, J.C.; Gómez-Cruz, N.A.; Rodríguez Castro, D.Y.; Camargo, J. Influence of Leadership on Human–Artificial Intelligence Collaboration. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15070873
Zárate-Torres R, Rey-Sarmiento CF, Acosta-Prado JC, Gómez-Cruz NA, Rodríguez Castro DY, Camargo J. Influence of Leadership on Human–Artificial Intelligence Collaboration. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(7):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15070873
Chicago/Turabian StyleZárate-Torres, Rodrigo, C. Fabiola Rey-Sarmiento, Julio César Acosta-Prado, Nelson Alfonso Gómez-Cruz, Dorys Yaneth Rodríguez Castro, and José Camargo. 2025. "Influence of Leadership on Human–Artificial Intelligence Collaboration" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 7: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15070873
APA StyleZárate-Torres, R., Rey-Sarmiento, C. F., Acosta-Prado, J. C., Gómez-Cruz, N. A., Rodríguez Castro, D. Y., & Camargo, J. (2025). Influence of Leadership on Human–Artificial Intelligence Collaboration. Behavioral Sciences, 15(7), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15070873








