Abstract
A multidisciplinary study was conducted to reconstruct the paleoenvironmental evolution of Maladroxia Bay, one of the principal bays of the islet of Sant’Antioco in southwestern Sardinia, over the past eight millennia. As part of an archaeological landscape project, this study explores the paleogeography and environment of the bay from a diachronic perspective to gain insights into the Holocene relative sea level history, shoreline displacements, and the environmental conditions during different phases. This study is based on an analysis of four sediment cores in conjunction with a chronological model that is based on radiocarbon dates. Four relative sea level indicators were produced. These are the first such indicators from the early and middle Holocene for the island of Sant’Antioco. The results indicate that in the early Holocene, the area was a terrestrial, fluvial environment without marine influence. In the 6th millennium BCE, the rising sea level and marine transgression resulted in the formation of a shallow inner lagoon. It reached its maximum extent in the middle of the 5th millennium BCE. Afterwards, a gradual transition from lagoon to floodplain, and a seaward shift of the shoreline occurred. The lagoon potentially served as a valuable source of food and resources during the middle Holocene. During the Nuragic period (2nd to 1st millennium BCE), the Bay of Maladroxia was very similar to how it is today. Its location was ideal for use as an anchorage, due to the calm and sheltered conditions that prevailed.
1. Introduction
The Holocene sea level rise was a significant driving force in the interaction between nature and humans in the Mediterranean region. It resulted in a profound change in the environment available to humans as a habitat [1,2,3]. On the one hand, large areas of living space were lost due to flooding. On the other hand, new habitats were created, including the densely populated coastal plains with their particularly resource-rich shallow lagoons [4,5]. It is imperative to develop a comprehensive understanding of the historical context and the mechanisms of Holocene sea level rise and shoreline evolution for several reasons. Firstly, this fundamental knowledge is indispensable for comprehending the relationship between settlers and the sea in archaeological contexts. Secondly, such understanding is crucial for the development of effective models to predict future sea level rise and to formulate reliable scenarios for the future [6,7,8].
Sardinia is an island in the western Mediterranean with a rich archaeological heritage and an elongated coastline, which is never more than 60 km from the furthest point from the sea (Figure 1a). The island’s landscape evolution and settlement history are, therefore, particularly intertwined with Holocene sea level changes. Despite the plethora of geomorphological and geoarchaeological studies that have been conducted on Holocene sea level development in Sardinia, a consensus has yet to be reached. Discrepancies between sea level index points and limiting points from disparate origins have been observed, particularly in the context of the mid-Holocene period [8]. The islet of Sant’Antioco (Figure 1b), located in the southwest of Sardinia, has remained particularly unexplored. Sea level reconstructions for the middle Holocene period have not yet been conducted for this island. For the late-Holocene, only two sea level index points have been produced [9].
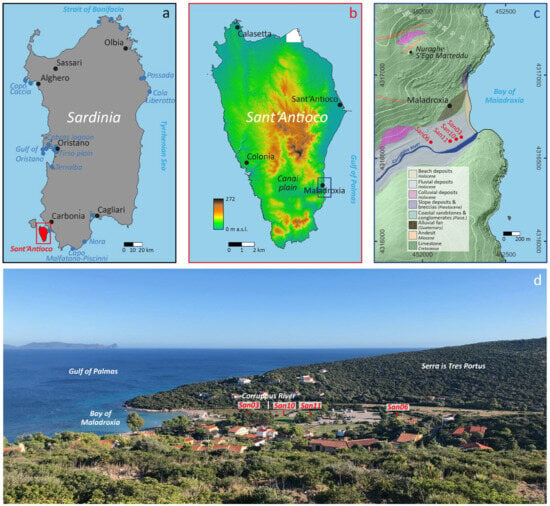
Figure 1.
Overview of the study area. (a) Location of the islet of Sant’Antioco. Black dots represent cities. Blue dots represent locations of sea level index points reviewed by Vacchi et al., 2018 [8] Base map from sardegnageoportale.it (b) Location of the village of Maladroxia on the islet of Sant’Antioco. DEM from Rüden et al., 2023 [10] (c) Geomorphologic–geologic situation of the Bay of Maladroxia, location of the drilling sites of cores San03, San06, San10, and San11. DEM from Rüden et al., 2023 [10]. (d) View from the nuraghe S’Ega Marteddu to the southeast into the Bay of Maladroxia with drilling sites.
Sant’Antioco, and particularly the connection between the settlement history and paleogeographical evolution, is the focus of an archaeological landscape project conducted under the auspices of the “Making Landscape” project of the University of Bochum in cooperation with the cultural foundation “Calderone”. The objective of this endeavor is to undertake a more comprehensive exploration of the mid-Holocene pre- and protohistoric phases of the island that have heretofore been understudied. The project employs a multifaceted approach, integrating remote sensing methodologies, archaeological surveys conducted above and below water, excavations, and geomorphological–geoarchaeological investigations. This comprehensive strategy aims to systematically investigate the existing sites and to explore new ones, thereby enhancing our understanding of the region’s settlement dynamics and the human activities of the past [10].
The Bay of Maladroxia (Figure 1b–d), in the southeast of Sant’Antioco, is among the principal bays of the islet. One of the “Making Landscape” project’s aims is to explore the bay’s paleogeography and environment from a diachronic perspective to gain insights into the Holocene relative sea level history, shoreline displacements, and the environmental conditions during the different phases. This approach will also facilitate the refinement of the search for areas where terrestrial archaeological findings are likely to be found in areas that have already been silted up. As Sant’Antioco was part of a wider Mediterranean seaborne web, a central tenet of this study is to evaluate the respective access of the bay from the sea and to investigate its potential suitability as an anchorage in earlier periods.
This study employs an environmental reconstruction of the Bay of Maladroxia over the past eight millennia. The study is founded upon an analysis of four sediment cores, in conjunction with a chronological model that is based on radiocarbon dates. The production of three new sea level index points (SLIPs) and a terrestrial limiting point (LP) was undertaken. The maximum extent of the bay was determined, and the impact of environmental changes on the usability of the environment for settlers of different epochs was assessed.
2. Study Area
2.1. Physio-Geographical Setting
Maladroxia Bay is one of the principal bays of the islet of Sant’Antioco, which is located in the southwest of Sardinia (Figure 1a). The islet is connected to Sardinia by a narrow sandy isthmus, which forms the northern boundary of the Gulf of Palmas. Maladroxia Bay is located on the western coast of the gulf, 8 km south of the city of Sant’Antioco (Figure 1b). It is characterized by a 350 m-long sandy beach and shallow waters, where the Mediterranean seaweed (Posidonia oceanica) forms extensive subaquatic meadows on the sandy seabed. A thermal spring emerges close to the shoreline at the northern edge of the bay. An alluvial fan as well as the limestone cliffs of the mountains S’Arraigraxiu (134 m above sea level) in the north and Serra is Tres Portus (108 m above sea level) in the south enclose the bay, which is entered from the west by the Corruppus valley (Figure 1c,d). The Corruppus River is an ephemeral stream that drains the southern part of the islet of Sant’Antioco with its mountainous hinterland and the Canai plain (Figure 1b). The Corruppus River’s catchment area is characterized by the presence of marls and carbonatic shelf deposits (dolomitic, oolithic, and bioclastic limestones) of Cretaceous age, as well as by andesitic lavas of the second Miocene volcanic cycle [11].
The islet of Sant’Antioco is part of the Late Eocene–Middle Miocene calc-alkaline volcanic belt that extends along the western coast of Sardinia [12]. As with the majority of Sardinia, Sant’Antioco is tectonically stable since at least the Late Pliocene [13]. Consequently, the area is suitable to obtain reference data for sea level changes since the last interglacial period. In the area surrounding the Maladroxia Bay, sea level markers of the Tyrrhenian warm phase (MIS 5.5), such as littoral Strombus bubonius fossiliferous deposits and tidal notches, have been identified. These markers are located between 2.5 and 4 m above modern mean sea level [9]. The region’s climate is maritime, with warm, dry summers and cold, humid winters, a characteristic of the Mediterranean [14]. Strong winds, especially from the north and west, are prominent features and a significant determinant of the climate [15]. The west coast of Sant’Antioco is typically windier than the east coast, where the study site is located. The Bay of Maladroxia is known for its beaches and nautical tourism due to its physiogeographical setting, and a tourist resort is located close to the modern beach (Figure 1d). The development of tourist infrastructure has had a significant impact on the coastal area.
2.2. Archaeological Setting
The presence of numerous rock shelters, Domus de Janas, menhirs, and surface finds indicates that the islet of Sant’Antioco already experienced vibrant activity during the Neolithic and Chalcolithic phases [16,17]. In the immediate hinterland of the bay, surveys conducted by the ‘Making Landscape’ project in 2018 and 2019 identified what appears to be a large Neolithic settlement. A particularly salient aspect of the island’s archaeological record pertains to the substantial evidence from the Nuragic period (roughly from the 2nd to the early 1st millennium BCE) of over fifty monumental sites across the island. Most of these sites are located in the hilly regions on the periphery of the central Canai plain, which serves as the island’s predominant agricultural epicenter [10,18]. The substantial concentration of Nuragic sites indicates a distinct function for the island during the Bronze Age era. This observation potentially serves as a contributing factor to the establishment of the Phoenician city of Sulky in the northwestern region of the island in the first half of the 1st millennium BCE, thereby enhancing connectivity throughout the Mediterranean region.
A salient question that emerges from the scope of this study pertains to the manner in which the islet’s inhabitants engaged with the sea, no matter whether they perceived it as a sustenance resource or as a conduit for exchange and communication. The western shore of Sant’Antioco is characterized by steep, rocky coastlines and the presence of high-energy zones, which makes access apart from a few bays rather difficult [19]. In contrast, the Gulf of Palmas, located southeast of the island, is distinguished by its tranquil conditions. This is further evidenced by its mention in the portolan description, a medieval guidebook for sailors [20], and a map drawn by the cartographer Joseph Roux in 1764 and published in 1817 by Jean Joseph Allezard. The map indicates that the Gulf of Palma was a favored anchorage for the large sailing ships of that time. Of particular interest is the precise location of an anchorage marked at the height of the Bay of Maladroxia along the eastern coast of Sant’Antioco, where the Corruppus River flows into the sea. It can be posited that this bay also held significant importance during the prehistoric and protohistoric periods, as it provides the most accessible route to the Canai plain. The presence of the nuraghe S’Ega Marteddu on the northern hill overlooking the bay suggests that the Bronze Age population may have exhibited a degree of interest in the area. While the majority of the nuraghe are oriented towards the Canai plain, taking advantage of its agricultural potential, the nuraghe S’Ega Marteddu is oriented towards the bay, thereby enabling its visual and acoustic surveillance [10]. Moreover, an early excavation of Roman remains was conducted in the 1960s in proximity to the coastline in the northern section of the bay, beneath the initial modern housing developments. These building structures have not been published, and their precise nature remains to be elucidated. Evidently, their preliminary assessments have indicated a potential correlation with the nearby thermal spring, as evidenced by the nomenclature of the contemporary coastal street.
3. Methods
The stratigraphy of the transition from the Corruppus valley floor to the modern Bay of Maladroxia has been studied using four sediment cores (San03, San06, San10, and San11). The cores are distributed linearly along an east–west transect and reflect the stratigraphic structure to a depth of approximately 9 m below the modern surface (Figure 1c, Table 1).

Table 1.
List of vibracoring sites.
3.1. Field Work
Sediment cores were collected using an Atlas Copco Cobra TTe vibracorer and 100 cm long, 5 cm wide plastic tubes [21,22]. As field measurements were not possible due to local legal restrictions, borehole elevations were derived from a digital elevation model (DEM) which is based on a high-resolution LiDAR-scan done in 2018 by AIRBORNE Technologies for the project ‘Making landscape’ and was first published in von Rüden et al., 2023 [10]. The DEM version used for this study has a vertical accuracy of ±0.5 m. In the course of a geomorphological field survey, a range of landforms were systematically documented and evaluated, including alluvial fans and river channels.
3.2. Sampling and Description
The description and sampling of the cores was carried out under laboratory conditions. The main sedimentological characteristics, such as grain size composition and calcium carbonate content, were described according to the guidelines of the German Soil Mapping Manual [23]. The colour of the sediments was determined using the Munsell Soil Color Chart.
3.3. Microfossil Analysis
As macroscopic features are often not sufficient to reliably determine the environmental conditions under which a facies formed, 12 samples from selected core sections were analysed for their macro- and microfaunal content. Ostracods and foraminifers are excellent indicators for the interpretation of paleoenvironments due to their well-known ecological requirements [24]. The distribution of species depends on factors such as salinity, temperature, and depth [25,26]. By wet sieving, fractions between 2 mm and 100 μm were extracted from the samples and prepared for microscopic analysis. Four samples were analysed for ostracods and foraminifers by counting the 200 μm fraction to a minimum of 300 individuals. Charophytes and macrofossils such as molluscs were recorded qualitatively. Microfossil counts were listed both absolutely and proportionally and plotted semiquantitatively. In addition, three beach samples were analysed for comparison and counted to approximately 100 individuals.
3.4. Radiocarbon Dating
The sieving remains were also examined for material for radiocarbon dating. Three AMS samples of charcoal and one sample of ostracods were measured at the Poznan Radiocarbon Laboratory. Using OxCal 4.4.4 [27], the AMS 14C dates of the charcoal were calibrated using the IntCal20 calibration curve [28]. The age of the ostracod sample was calibrated with the Marine20 curve [29] and corrected with the ΔR value −109 + −40 [30] (Table 2).

Table 2.
Results of AMS radiocarbon dating of samples from sediment core San03. Calibration is based on the OxCal 4.4.4 software [27].
3.5. Relative Sea Level Reconstruction
Vacchi et al., 2016, 2018 [8,31] have developed a protocol for the Mediterranean to produce SLIPs and LPs from facies whose deposition is linked to the relative sea level. Part of their approach is to classify sedimentary facies and assign attributes such as an indicative range (IR) and a reference water level (RWL). They define the IR as the elevational range over which an indicator forms and the RWL as the midpoint of this range. The chronological model of the approach relies on radiocarbon dating.
Within this study, we followed the protocol of Vacchi et al., 2016 [31] to produce three new SLIPs from samples of an inner lagoon facies. As an IR, we used 0.5 m [8]. Furthermore, a terrestrial LP was created from a sample of the ‘upper beach/foreshore facies’. The significance of the terrestrial LP is that it must be above sea level, although the exact distance to the paleo-sea level cannot be determined. For the SLIPs and the LP, we have calculated errors in terms of elevation, core stretching, sample thickness uncertainty, tidal uncertainty, and angle error (Table 3).
4. Results
The stratigraphy of the study area is represented by the cross-section consisting of cores San03, San06, San10, and San11 (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). Core San03 contains a complete set of all the sedimentary facies and is, therefore, described in detail below (Figure 2). It is the easternmost core of the transect and was retrieved from the alluvial plain of the Corruppus River, approximately 85 m west of the modern coastline (Figure 1c). Drilling was terminated at 9.12 m below the surface due to the presence of an impenetrable layer of clasts.
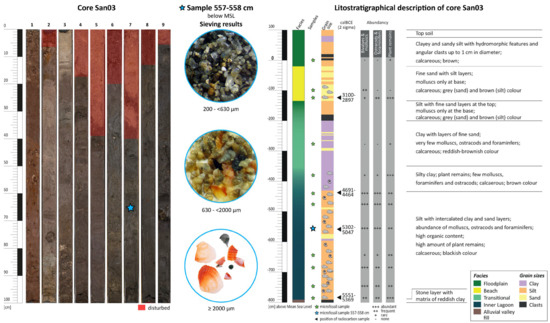
Figure 2.
Stratigraphical features and calibrated radiocarbon dates of core San03.
4.1. Facies Description
4.1.1. Alluvial Deposits
Five sedimentary facies can be distinguished within core San03 (Figure 2). The lowest facies occurs between 8.12 m and 7.93 m below modern mean seal level (MSL), and its sediments consist of reddish brown, sandy, and silty clays with a high proportion of angular clasts. The organic content is very low, and no fossils of any kind are present. The absence of any discernible marine influence suggests that the facies is a terrestrial, alluvial valley fill deposit, formed in a predominantly fluvial environment.
4.1.2. Inner Lagoon Deposits
In the second facies (7.93–3.35 m below MSL), silt is the dominant grain size, with layers of clay and sand interbedded. The sediments are blackish in color, have a high organic content, and contain large amounts of highly decomposed plant remains. Molluscs, ostracods, and foraminifers are abundant, and individuals of a bivalve species (Cerastoderma sp.) and a gastropod species (Hydrobia sp.) have been identified. In the lowest samp–le of the facies, from 7.86 to 7.85 m below MSL, gyrogonites of at least two species of Charophyta spp. were observed. Five species of ostracods were identified (Figure 3).
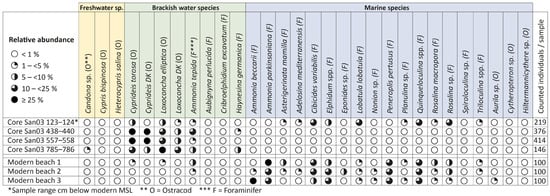
Figure 3.
Semi-quantitative presentation of micropaleontological data of core San03.
The brackish water species Cyprideis torosa and Loxoconcha elliptica are dominant and present in all stages of ontogeny, with a high proportion of double-flapped adults, and almost no juveniles with this feature. The freshwater species Candona sp., Heterocypris salina, and Cypris bispinosa are very rare, with only one or two specimens recorded. The abundance of lagoonal foraminifera is very low. The observed species spectrum corresponds to a lagoonal habitat with a salinity different from that of seawater. The ostracods are typical of a very sheltered lagoon with at most a narrow connection to the sea [32]. The high number of double-flapped ostracods and the presence of charophytes also indicate extremely calm conditions. The absence of juvenile double-flapped ostracods, which would indicate a premature death of individuals, suggests that conditions were conducive to the survival of ostracods such as Cyprideis torosa and Loxoconcha elliptica, which typically inhabit shallow depths with minimal water movement.
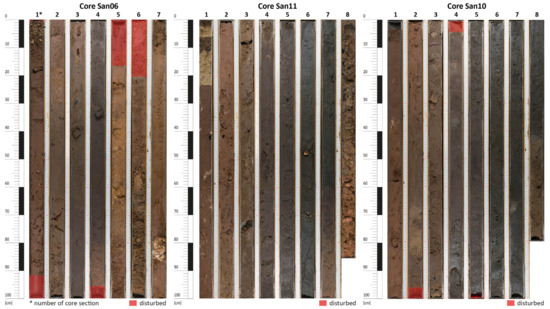
Figure 4.
Images of cores San06, San11, and San10.
4.1.3. Transitional Deposits
At the uppermost level, the shallow brackish lagoon facies gradually transitions into an increasingly terrestrial facies, exhibiting a strong influence from the input of hinterland sediments into the shallow environment. In core San03, this transitional facies is observed from approximately 3.35 to 1.20 m below MSL. The organic content exhibits a decline compared to the underlying sediments, and the color undergoes a shift from black to a reddish-brown hue. While silt is still the dominant grain size at the base, clay dominates in the middle parts. Layers of fossil-free fine sands between c. 1.8 and 1.3 m below MSL indicate single depositional events associated with fluvial deposition in the shallow lagoon environment. A gravel layer between 2.0 and 1.8 m below MSL is interpreted as a channel fill of the Paleo-Corruppus River, indicating a highly variable environment with alternating deposition of clay, sand, and gravel. This suggests a significant range of conditions, from almost stagnant lake-like settings to fast-flowing water within river channels. The fossil content of the facies is significantly lower, with mollusks, ostracods, and foraminifers only occurring in substantial quantities at the base. The facies is present in all the cores examined, extending more than 300 m inland from the present beach.
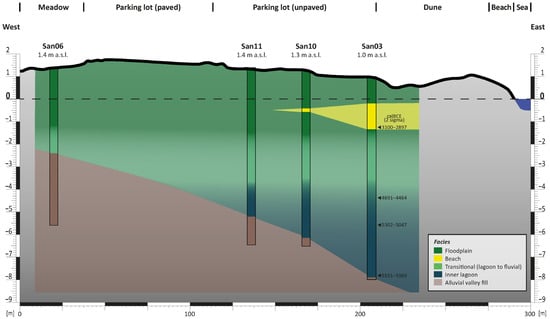
Figure 5.
Stratigraphic section, crossing the silted-up Bay of Maladroxia from east to west.
4.1.4. Beach Deposits
In core San03, the terrestrial facies is overlain by beach sediments from approximately 1.35 to 0.2 m below MSL, which consist of greyish fine sands with interbedded layers of brownish silt. Twelve species of marine foraminifers occur in large numbers (Figure 3). They are considered to be reworked. The most prevalent species are Cibicides variabilis, Elphidium spp., Lobatula lobatula, Quinqueloculina spp., and Rosalina sp. A comparison of the species assemblage with three samples from the present beach demonstrated a high degree of similarity. The microfossils in both the fossil and modern beach sediments are excellently preserved, although they are reworked. This indicates very calm, sheltered conditions in the bay seaward of the beach.
4.1.5. Fluvial Deposits
The sedimentary succession at the uppermost level of core San03, as well as the other three cores (Figure 4), comprises brown colored clayey and sandy silt with angular clasts up to 1 cm in diameter. The sediments are interpreted as terrestrial sediments deposited within an entirely terrestrial floodplain.
4.2. Sea Level Index Points and Limiting Points
Of the five identified facies, two are of clearly marine origin and have a direct relationship to sea level: the lagoon facies and the beach facies. Three samples from the lagoon facies and one sample from the beach facies were dated (Table 2, Figure 2). The calculated SLIPs and the terrestrial LP are shown in Table 3 and Figure 6. The SLIPs from the lagoonal facies are at 7.35 ± 0.79 m, 5.07 ± 0.78 m, and 3.89 ± 0.73 m below modern MSL and date from the middle of the 6th millennium BCE to the middle of the 5th millennium BCE. The terrestrial LP from the beach facies, the significance of which is that it lies above sea level, is 1.23 ± 0.52 m below modern MSL and dates from the beginning of the 3rd millennium BCE.

Table 3.
Calculation of sea level index points from Maladroxia.
Table 3.
Calculation of sea level index points from Maladroxia.
| Mean Depth b.s. | Type | RSLi * | Total Vertical Error Ei ** | Ai Below MSL | RWLi | Error | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e1 | e2 | e3 | e4 | e5 | e6 | ||||||
| Indicative Range *** | Elevation Error **** | Core Stretching/Shortening Error *** | Sample Thickness Uncertainty | Tidal Uncertainty *** | Angle Error | ||||||
| [m] | [m] | [m] | [m] | [m] | [m] | ||||||
| 2.235 | LP | 1.235 | 0.52 | MSL | above MSL | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.02235 | |
| 5.39 | SLIP | 3.89 | 0.73 | 4.39 | −0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.0539 |
| 6.575 | SLIP | 5.075 | 0.78 | 5.575 | −0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.005 | 0.1 | 0.06575 |
| 8.855 | SLIP | 7.355 | 0.79 | 7.855 | −0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.005 | 0.1 | 0.08855 |
* RSLi = Ai − RWLi, ** Ei = (e12 + e22 + e32 + e42 + e52 + e62)1/2, *** value from Vacchi et al., 2018 [8], **** elevation error from DEM.
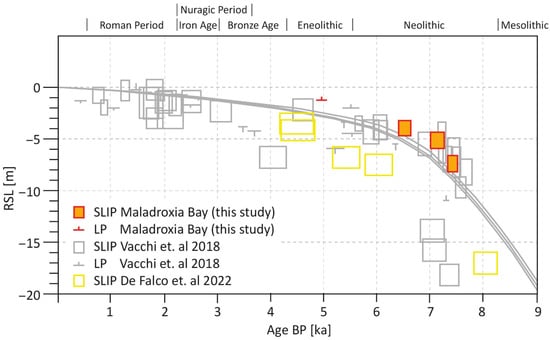
Figure 6.
Sea level index points and limiting points from Maladroxia Bay in relation to the modelled sea level curve and sea level index points presented in Vacchi et al., 2018 [8] and in De Falco et al., 2022 [33]. Grey lines denote the geography of relative sea level predictions calculated using SELEN and adopting the ICE-6G (VM5a) GIA model [8]. Dimensions of boxes (SLIPs) and lines (LPs) are based on errors in elevation and age.
5. Discussion
5.1. Sea Level Rise in the Sardinian Context
The Holocene sea level rise in Sardinia has been investigated in multiple studies. More than 70 SLIPs and limiting points have been produced since the 1980s for about 20 locations along the Sardinian coast (Figure 1 and Figure 6) [8,34]. Vacchi et al., 2018 [8] give a comprehensive review of the available sea level reconstructions from several studies [5,6,9,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. In recent years, additional SLIPs and LPs have been presented by De Falco et al., 2022 [33] and Vacchi et al., 2020 [34].
The available datasets demonstrate discrepancies between the reconstructed sea level, particularly in the early and middle Holocene. The preponderance of SLIPs and LPs, in conjunction with the modelled curve presented by Vacchi et al., 2018 [8], suggests that the sea level rose during the sixth millennium BCE roughly from ten to six meters below its contemporary level, and from six to two meters from the fifth to second millennium BCE. A reduced number of SLIPs and LPs are indicative of a sea level curve that was up to 10 m lower during the corresponding periods. The SLIPs and LPs from the most recent dataset by De Falco et al., 2022 [33] also indicate a lower sea level during the early and middle Holocene. A range of factors are considered to be the causative agents of the observed discrepancies between the sea level reconstructions [8]. Potential errors may be attributed to post-sedimentary compaction of sediments or to erroneous radiometric dating techniques from several decades ago. It is also conceivable that the observed discrepancies are attributable to erroneous estimates of the age of some archaeological SLIPs and LPs.
The three newly produced SLIPs and the terrestrial LP for the Bay of Maladroxia are in good agreement with the SLIPs and LPs indicating a comparatively high sea level, as well as with the modelled curve for Sardinia, as outlined in Vacchi et al., 2018 [8] (Figure 6). These four relative sea level indicators are the first ones from the early and middle Holocene for the island of Sant’Antioco. So far, there have only been two SLIPs derived from archaeological remains (a harbor structure and ceramics cemented in beach rock) that date to the late-Holocene [9].
5.2. Environmental Changes in the Bay of Maladroxia
The facies succession (Figure 5) and sea level reconstruction (Figure 6) presented in the results section show the environmental changes that the Bay of Maladroxia has undergone over the past c. eight millennia (Figure 7). At the beginning of the 6th millennium BCE, the investigated area was a terrestrial, fluvial environment. From the extent of the fluvial facies within the cross-section it can be deduced that the valley sloped eastwards at an average gradient between 3 and 4%. The Paleo-Corruppus River drained this valley and flowed eastwards into the sea, which was about 11 to 13 m below the modern sea level (Figure 6).
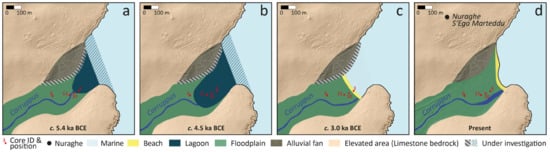
Figure 7.
Schematic reconstruction of the main phases of the Maladroxia Bay evolution as reconstructed by facies analysis and interpretation. (a) The Holocene transgression has reached the Corruppus valley and an inner or semi-enclosed lagoon has developed; (b) The lagoon has reached its maximum extent; (c) The lagoon has been silted up and the shoreline has moved seawards; (d) The shoreline has moved further east to its present position.
In the middle of the 6th millennium BCE, the rising sea reached a level 7.35 ± 0.79 m below modern MSL, intruded into the Corruppus valley, and entered the study area. A shallow lagoon with a water level of c. 0.5 to 1 m with a thriving micro- and macrofauna developed. The species assemblage shows that the lagoon was very sheltered and was either an almost entirely cut off inner lagoon or a semi-enclosed lagoon with a very narrow connection to the sea (Figure 7a). Why the lagoon was protected in this way could not be determined within the scope of this study. It is likely that a coastal barrier system eastward and seaward of the study area separated the bay from the open sea. Such lagoonal barrier systems have been demonstrated, for example, in the Tirso river coastal plain in western Sardinia [33,36] and in the Posada plain in eastern Sardinia [5]. It is also possible that geological structures like reefs, now submerged in the sea, protected at least part of the entrance to the bay from the direct influence of the sea.
The shallow lagoon had reached its maximum extent in the middle of the 5th millennium BCE and extended to approximately 200 m west of the modern shoreline (Figure 7b). At this point in time, the sea reached a level approximately 3.89 ± 0.73 m below modern MSL, and terrestrial sedimentation by the Paleo-Corruppus gradually increased. This led to a significant deterioration in the living conditions of lagoon species. It is most likely that the shift to terrestrial sedimentation was triggered by the significant slowdown in the rate of sea level rise in the 5th millennium BCE (Figure 6). The human factor may also have played a role. It is likely that the increasing agricultural activities of the Neolithic settlers in the hinterland [16,17] led to greater erosion and a higher sediment load in the Corruppus River. However, it is not possible to determine the extent of this effect without a detailed study of the history of erosion and deposition in the hinterland.
In the westernmost sections of the transect (cores San06 and San11), the strongly terrestrially influenced lagoon facies transitions directly into a fluvial facies (Figure 5). Conversely, in the easternmost sections, the lagoonal facies is followed by a beach facies. This observation reflects the still ongoing sea level rise and the resulting inland movement of the shoreline, which before had been eastwards and outside the study area (Figure 7c). The lowermost sands at 1.23 m below modern MSL and hence the beginning of the beach sedimentation dates to the transition from the 4th to the 3rd millennium BCE and the Eneolithic period. At this point in time, the location of core San03 was, for the first time, evidently above the MSL. The absence of beach deposits in cores San06 and San10, and the minimal thickness of the beach facies in core San10 (Figure 5) indicate that the influence of the shoreline advanced only as far as the location of core San10, never reaching further west. The contemporary beach (Figure 7d) is located approximately 80 m east of the position of the beach from the transition from the 4th to the 3rd millennium BCE. This seaward shift in the mid- and late-Holocene can most likely be attributed to the fact that fluvial sedimentation by the river had become the main factor of landscape evolution, and the effects of the henceforth modest sea level rise over the past few millennia became less substantial. The phenomenon of the seaward progradation of the shorelines during the mid- to late-Holocene has been observed on Sardinia [5,44] as well as on a multitude of other coasts in the Mediterranean region [45]. The underlying cause of this phenomenon is believed to be the interaction between three factors: firstly, a decrease in the rate of sea level rise; secondly, climatic variations; and thirdly, a high sediment supply by the rivers. The latter process is frequently ascribed to the impact of human activity, which has resulted in the destabilisation of the landscape, for instance through deforestation, leading to enforced erosion in the hinterland and higher accumulation in the river deltas [1,46]. In view of the paucity of detailed information concerning climatic variations as well as settlement activity and erosional processes in the hinterland, it remains unclear which factors were responsible for the seaward shift of the coastline in Maladroxia Bay.
The current state of research does not allow any valid conclusions to be drawn regarding the influence of the alluvial fan at the northern exit of the Corruppus valley on the development of Maladroxia Bay (Figure 1c). The stratigraphy of the fan has not yet been the subject of investigation, and its temporal origin remains uncertain. It is conceivable that the formation of the alluvial fan may have exerted an influence on the development and subsequent disappearance of the lagoon, as well as on the suitability of the Maladroxia Bay as an anchorage.
5.3. Implications for the Pre- and Protohistory
The sea advanced into the Corruppus valley in the early Neolithic period during the middle of the 6th millennium BCE (Figure 7a). This resulted in a dramatic transformation of the landscape. The fluvial valley, whose suitability for land use was previously not significantly different from the hinterland, was becoming a shallow lagoon teeming with brackish water and marine animals. Consequently, the early Neolithic settlers gained access to a food and material source that potentially had previously been located further to the east in today’s Gulf of Palmas, which might have inhabited an older lagoon. Possibly, a lagoon with such calm and sheltered conditions had not been present at all in the closer vicinity. Given the important role of lagoonal environments for food procurement of Neolithic societies in the Mediterranean region, and Sardinia in particular [5], it is reasonable to assume that the development of the lagoon in the Corruppus valley had a profound positive effect on the local population’s food supply. Moreover, it can be assumed that the termination of the lagoon phase, marked by the gradual desiccation of the lagoon as a substantial source of sustenance, had a profound impact on the inhabitants during the Neolithic.
The temporal extent of the Nuragic period is understood to span from the 2nd to the early 1st millennium BCE. It is not possible to exactly determine which of the sediments from the lithostratigraphic cross-section relate to this period, as no corresponding dates are available for reference. Nonetheless, based on the youngest and uppermost age from the chronological model (3100–2897 calBCE in c. 2.23 m below surface in core San03), it can be deduced that the sediments from the Nuragic period must be contained within the top two meters below the surface. The lithostratigraphy and the facies model (Figure 2) provide evidence that, within this depth range, the lagoonal phase had already concluded, and that terrestrial sedimentation occurred within a fluvial system. In contradistinction to the contemporary situation, which is distinguished by intensive land use, channelized and controlled watercourses, and tourist infrastructure, the valley floor must be regarded as a natural, dynamic floodplain with anastomosing or meandering, often shifting river channels. Only in the easternmost part of the cross-section, as represented by cores San03 and San10, beach sediments fall into the potential depth range of the Nuragic culture. However, due to the absence of dated samples, it remains uncertain whether the Nuragic shoreline was located near the sites of cores San03 and San10, or if it had already migrated further east, closer to the position of the modern shoreline. In both cases, it is evident that the geography of the Corruppus valley and the Bay of Maladroxia exhibited a high degree of similarity to the present situation, and only the shoreline could have been located at a maximum of 100 m, but most likely significantly less, further west than the modern one. The sea level was also close to its present level. According to the curve developed by Vacchi et al., 2018 [8], it was approximately 2 m below modern MSL at the beginning of the second millennium BCE, and less than 1 m at the end of the first millennium BCE. The excellent state of preservation of the marine foraminifera in the fossil and recent beach sands indicates extremely calm conditions and a sheltered location of the bay. The suitability of the Bay of Maladroxia as an anchorage is, therefore, considered to be very high, both for today and for the pre- and protohistoric periods. In addition, it can be assumed that in the Nuragic period the bay was very accessible from the sea, comparable to the present situation.
6. Conclusions
A multidisciplinary study incorporating sedimentology, microfossil analysis, and radiocarbon dating was conducted to facilitate the reconstruction of the paleoenvironmental evolution of the Maladroxia Bay, one of the principal bays of the islet of Sant’Antioco in southwestern Sardinia, during the last eight millennia. It was demonstrated that in the early Holocene epoch, the area constituted a terrestrial, fluvial environment that was drained by the Paleo-Corruppus River. In the 6th millennium BCE, the rising sea intruded into the Corruppus valley, resulting in the formation of a shallow lagoon, possibly protected by a coastal barrier system. The transgression of the sea reached its maximum extent in the middle of the 5th millennium BCE. This was followed by a gradual transition from lagoonal conditions to a fluvial environment, and a seaward movement of the shoreline. Evidence has been presented which suggests that the lagoon potentially functioned as a valuable source of food and resources during the middle Holocene. Prior to and subsequent to this period, these favorable conditions were not observed. During the Nuragic period, which extended from the 2nd to the early 1st millennium BCE, the Bay of Maladroxia exhibited a high degree of similarity to its contemporary state. The location was found to be excellent for use as an anchorage, due to the calm and sheltered conditions that prevailed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S., M.S. and C.v.R.; Funding acquisition, C.v.R.; Investigation, S.S., M.S., A.P. and C.v.R.; Methodology, S.S., M.S., A.P. and C.v.R.; Project administration, C.v.R.; Supervision, C.v.R.; Visualization, S.S.; Writing—original draft, S.S., M.S., A.P. and C.v.R.; Writing—review and editing, S.S., M.S. and C.v.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Geoarchaeological research was part of the project ‘Making Landscape. An Investigation of the Pre- and Proto-historic Taskscapes on the Islet of Sant’Antioco/Sardinia’, which has been funded by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG, project number 497599429) since 2022. Further investigations relating to underwater research were conducted with the University of Haifa and were funded by the Gerda Henkel Foundation, bringing the project to a close in 2024.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our profound gratitude to Giovanna Pietra and the Soprintendenza Archeologia, belle arti e paesaggio per la città metropolitana di Cagliari, Sara Muscuso and the municipality of Sant’Antioco, as well as our esteemed partners from ARCI Il Calderone APS. The organization of numerous on-site studies would be unfeasible without their invaluable support.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Steffen Schneider and Marlen Schlöffel were employed by the company Enreco GbR. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AMS | Accelerator mass spectrometry |
| BCE | Before common era |
| BP | Before present |
| cal | Calibrated |
| CE | Common era |
| IR | Indicative range |
| LP | Limiting point |
| MIS | Marine isotope stage |
| MSL | Mean sea level |
| RWL | Reference water level |
| SLIP | Sea level index point |
References
- Benjamin, J.; Rovere, A.; Fontana, A.; Furlani, S.; Vacchi, M.; Inglis, R.H.; Galili, E.; Antonioli, F.; Sivan, D.; Miko, S.; et al. Late Quaternary Sea-Level Changes and Early Human Societies in the Central and Eastern Mediterranean Basin: An Interdisciplinary Review. Quat. Int. 2017, 449, 29–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner, H.; Kelterbaum, D.; Marunchak, O.; Porotov, A.; Vött, A. The Holocene Sea Level Story since 7500 BP–Lessons from the Eastern Mediterranean, the Black and the Azov Seas. Quat. Int. 2010, 225, 160–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeck, K. Sea-Level Change in the Mediterranean Sea since the LGM: Model Predictions for Tectonically Stable Areas. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2005, 24, 1969–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, A.; Vinci, G.; Tasca, G.; Mozzi, P.; Vacchi, M.; Bivi, G.; Salvador, S.; Rossato, S.; Antonioli, F.; Asioli, A.; et al. Lagoonal Settlements and Relative Sea Level during Bronze Age in Northern Adriatic: Geoarchaeological Evidence and Paleogeographic Constraints. Quat. Int. 2017, 439, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, R.T.; Rita, F.D.; French, C.; Marriner, N.; Montis, F.; Serreli, G.; Sulas, F.; Vacchi, M. 8000 years of Coastal Changes on a Western Mediterranean Island: A Multiproxy Approach from the Posada Plain of Sardinia. Mar. Geol. 2018, 403, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, F.; Anzidei, M.; Lambeck, K.; Auriemma, R.; Gaddi, D.; Furlani, S.; Orrù, P.; Solinas, E.; Gaspari, A.; Karinja, S.; et al. Sea-Level Change during the Holocene in Sardinia and in the Northeastern Adriatic (Central Mediterranean Sea) from Archaeological and Geomorphological Data. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2007, 26, 2463–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsico, A.; Lisco, S.; Presti, V.L.; Antonioli, F.; Amorosi, A.; Anzidei, M.; Deiana, G.; De Falco, G.; Fontana, A.; Fontolan, G.; et al. Flooding Scenario for Four Italian Coastal Plains Using Three Relative Sea Level Rise Models. J. Maps 2017, 13, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, M.; Ghilardi, M.; Melis, R.T.; Spada, G.; Giaime, M.; Marriner, N.; Lorscheid, T.; Morhange, C.; Burjachs, F.; Rovere, A. New Relative Sea-Level Insights into the Isostatic History of the Western Mediterranean. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 201, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrù, P.; Solinas, E.; Puliga, G.; Deiana, G. Palaeo-Shorelines of the Historic Period, Sant’Antioco Island, South-Western Sardinia (Italy). Quat. Int. 2011, 232, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Rüden, C.; Klingenberg, T.; Usadel, M. Grutt’i Acqua and Its Hinterland. Some Preliminary Insights into the Exploration of the Microregion of Sant’Antioco. In Proceedings of the Fifth Festival of the Nuragic Civilization (Orroli, Cagliari); Perra, M., LoSchiavo, F., Eds.; Arkadia Editore: Cagliari, Italy, 2023; pp. 23–45. [Google Scholar]
- Carmignani, L.; Oggiano, G.; Funedda, A.; Conti, P.; Pasci, S. The Geological Map of Sardinia (Italy) at 1:250,000 Scale. J. Maps 2016, 12, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustrino, M.; Morra, V.; Fedele, L.; Franciosi, L. Beginning of the Apennine Subduction System in Central Western Mediterranean: Constraints from Cenozoic “Orogenic” Magmatic Activity of Sardinia, Italy. Tectonics 2009, 28, TC5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferranti, L.; Antonioli, F.; Mauz, B.; Amorosi, A.; Pra, G.D.; Mastronuzzi, G.; Monaco, C.; Orrù, P.; Pappalardo, M.; Radtke, U.; et al. Markers of the Last Interglacial Sea-Level High Stand along the Coast of Italy: Tectonic Implications. Quat. Int. 2006, 145, 30–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pungetti, G.; Marini, A.; Vogiatzakis, I.N. Sardinia. In Mediterranean Island Landscapes; Vogiatzakis, I.N., Pungetti, G., Mannion, A.M., Eds.; Landscape Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 143–169. ISBN 978-90-481-7271-9. [Google Scholar]
- Soldati, M.; Marchetti, M. Landscapes and Landforms of Italy; Soldati, M., Marchetti, M., Eds.; World Geomorphological Landscapes; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 3319261940. [Google Scholar]
- Vacca, G. Tracce. Il Primo Popolamento Dell’isola Di Sant’Antioco; Cagliaritana, C.U.E., Ed.; University Press-Archeologia: Cagliari, Italy, 2009; ISBN 8884675340. [Google Scholar]
- Usai, L.S. Antioco. Area Del Cronicario. Campagne Di Scavo 1983-86. La Ceramica Preistorica Dell’area Del Cronicario. Rev. Studi Fenici 1990, 18, 103–123. [Google Scholar]
- Marras, V. Emergenze Archeologiche Extraurbane Di Età Preistorica Nel Territorio Del Comune Di Sant’Antioco. Quad. Soprintend. Prov. Cagliari Oristano 1996, 13, 87–107. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoloni, P. Porti e Approdi Dell’antica Sulcis. In Naves Plenis Velis Euntes; Mastino, A., Spanu, P.G., Zucca, R., Eds.; Carocci: Roma, Italy, 2009; pp. 178–192. ISBN 978-8843048564. [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer, K. Die Italienischen Portolane des Mittelalters: Ein Beitrag zur Geschichte der Kartographie und Nautik; Reprint of the Berlin 1909 Edition; Olms: Hildesheim, Germany, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Schlöffel, M.; Schneider, S.; Schütt, B. Fluvial Dynamics and Phases of Landscape Development in the Bronze Age Settlement Area of the Sambek Valley (Northeastern Hinterland of the Sea of Azov). Mediterr. J. Geogr. 2016, 126, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Matthaei, A.; Schlöffel, M.; Meyer, C.; Kronwald, M.; Pint, A.; Schütt, B. A Geoarchaeological Case Study in the Chora of Pergamon, Western Turkey, to Reconstruct the Late Holocene Landscape Development and Settlement History. Quat. Int. 2015, 367, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ad-hoc-AG Boden. Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung, 5th ed.; Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe und Niedersächsisches Landesamt für Bodenforschung: Hannover, Germany, 2005; ISBN 9783510959204. [Google Scholar]
- Boomer, I.; Eisenhauer, G. Ostracod Faunas as Palaeoenvironmental Indicators in Marginal Marine Environments. In The Ostracoda: Applications in Quaternary Research; Holmes, J.A., Chivas, A.R., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Volume 131, pp. 135–149. ISBN 9780875909905. [Google Scholar]
- Frenzel, P.; Karasz, R.M.; Viehberg, F. Muschelkrebse Als Zeugen Der Vergangenheit. Zwischen Biologie, Paläontologie Und Umweltforschung. Biol. Unserer Zeit 2006, 36, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, P.; Boomer, I. The Use of Ostracods from Marginal Marine, Brackish Waters as Bioindicators of Modern and Quaternary Environmental Change. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2005, 225, 68–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronk Ramsey, C. Bayesian Analysis of Radiocarbon Dates. Radiocarbon 2009, 51, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, P.J.; Austin, W.E.N.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Blackwell, P.G.; Bronk Ramsey, C.; Butzin, M.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. The IntCal20 Northern Hemisphere Radiocarbon Age Calibration Curve (0–55 Cal KBP). Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 725–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, T.J.; Köhler, P.; Butzin, M.; Bard, E.; Reimer, R.W.; Austin, W.E.N.; Bronk Ramsey, C.; Grootes, P.M.; Hughen, K.A.; Kromer, B.; et al. Marine20—The Marine Radiocarbon Age Calibration Curve (0–55,000 Cal BP). Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 779–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siani, G.; Paterne, M.; Arnold, M.; Bard, E.; Metivier, B.; Tisnerat, N.; Bassinot, F. Radiocarbon Reservoir Ages in the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea. Radiocarbon 2000, 42, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, M.; Marriner, N.; Morhange, C.; Spada, G.; Fontana, A.; Rovere, A. Multiproxy Assessment of Holocene Relative Sea-Level Changes in the Western Mediterranean: Sea-Level Variability and Improvements in the Definition of the Isostatic Signal. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 155, 172–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pint, A.; Frenzel, P. Ostracod Fauna Associated with Cyprideis Torosa—An Overview. J. Micropalaeontol. 2017, 36, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, G.; Carannante, A.; Del Vais, C.; Gasperini, L.; Pascucci, V.; Sanna, I.; Simeone, S.; Conforti, A. Evolution of a Single Incised Valley Related to Inherited Geology, Sea Level Rise and Climate Changes during the Holocene (Tirso River, Sardinia, Western Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Geol. 2022, 451, 106885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, M.; Ghilardi, M.; Stocchi, P.; Furlani, S.; Rossi, V.; Buosi, C.; Rovere, A.; Muro, S.D. Driving Mechanisms of Holocene Coastal Evolution of TheBonifacio Strait (Western Mediterranean). Mar. Geol. 2020, 427, 106265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, G.; Antonioli, F.; Fontolan, G.; Presti, V.L.; Simeone, S.; Tonielli, R. Early Cementation and Accommodation Space Dictate the Evolution of an Overstepping Barrier System during the Holocene. Mar. Geol. 2015, 369, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, R.T.; Depalmas, A.; Rita, F.D.; Montis, F.; Vacchi, M. Mid to Late Holocene Environmental Changes along the Coast of Western Sardinia (Mediterranean Sea). Glob. Planet. Change 2017, 155, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, S.D.; Orrù, P.E. Il Contributo Delle Beach Rock Nello Studio Della Risalita Del Mare Olocenico. Le Beach Rock Post-Glaciali Della Sardegna Nord-Orientale. Il Quat. 1998, 11, 19–39. [Google Scholar]
- Nesteroff, W. Étude de Quelques Grès de Plage Du Sud de La Corse. Maison Orient 1984, 8, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Orrù, P.E.; Mastronuzzi, G.; Deiana, G.; Pignatelli, C.; Piscitelli, A.; Solinas, E.; Spanu, P.; Zucca, R. Sea Level Changes and Geoarchaeology between the Bay of Capo Malfatano and Piscinnì Bay (SW Sardinia) in the Last 4 Kys. Quat. Int. 2014, 336, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrù, P.E.; Antonioli, F.; Lambeck, K.; Verrubbi, V. Holocene Sea Level Change of the Cagliari Coastal Plain (Southern Sardinia, Italy). Quat. Nova 2004, 8, 193–212. [Google Scholar]
- Pascucci, V.; De Falco, G.; Del Vais, C.; Sanna, I.; Melis, R.T.; Andreucci, S. Climate Changes and Human Impact on the Mistras Coastal Barrier System (W Sardinia, Italy). Mar. Geol. 2018, 395, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rita, F.; Melis, R.T. The Cultural Landscape near the Ancient City of Tharros (Central West Sardinia): Vegetation Changes and Human Impact. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 4271–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.M.; Carmona, P.; Gómez-Bellard, C.; Dommelen, P.V. Geomorphology and Environmental Change around the Punic Sites of the Terralba Plain (Oristano Gulf, Sardinia, Italy). Bol. Geol. Min. 2018, 129, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, G.D.; Carannante, A.; Del Vais, C.; Gasperini, L.; Sanna, I.; Cammarano, F.; Cozzolino, M.; Pascucci, V.; Conforti, A. Late Holocene Evolution of the Lagoonal Harbour of the Punic Centre of Othoca (Western Sardinia, Mediterranean Sea). Geoarchaeology 2025, 40, e70010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Marriner, N.; Morhange, C. Human Influence and the Changing Geomorphology of Mediterranean Deltas and Coasts over the Last 6000years: From Progradation to Destruction Phase? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 139, 336–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maselli, V.; Trincardi, F. Man Made Deltas. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).