Simple Summary
Aflatoxin B1 frequently contaminates animal feed, posing a considerable risk to the poultry industry. There is an urgent necessity to develop effective strategies for mitigating the harmful effects of aflatoxin B1 on poultry health. This study aimed at assessing the efficacy of dietary supplementation with the novel aflatoxin oxidase CotA in mitigating the adverse effects of an aflatoxin B1-contaminated diet in Japanese quails. The findings indicate that aflatoxin oxidase CotA effectively detoxified dietary aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity and reduced liver aflatoxin B1 residues in Japanese quails. These results underscore the potential application of aflatoxin oxidase CotA as a promising agent for aflatoxin B1 degradation in the feed industry.
Abstract
This research explored the role of aflatoxin oxidase CotA in mitigating aflatoxin B1 (AFB1)-induced hepatotoxicity in Japanese quails. A total of 225 female Japanese quails, aged two weeks, were randomly assigned to three dietary groups: a control diet, an AFB1-contaminated diet, and an AFB1-contaminated diet supplemented with aflatoxin oxidase CotA for three weeks. The results indicate that quails receiving the AFB1-contaminated diet exhibited reduced body weight gain, pronounced vacuolar degeneration within hepatocytes, and inflammatory cell infiltration. Additionally, the AFB1 group demonstrated an increased liver index and elevated serum liver enzyme activities (ALT, AST, and ALP). Supplementation with CotA improved body weight gain and conferred protection against AFB1-induced liver injury. Furthermore, the addition of CotA significantly enhanced liver antioxidant enzyme activities (T-AOC, GST, GSH-Px, POD, and CAT), reduced hepatic H2O2 and MDA levels, and upregulated the mRNA expression levels of genes in the Nrf2 pathway in quails exposed to AFB1. AFB1 exposure led to lipid droplet accumulation in liver tissues and elevated serum TG and LDL-C levels. However, the introduction of CotA mitigated AFB1-induced alterations in lipid metabolism. Furthermore, dietary supplementation with CotA inhibited AFB1-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and decreased the mRNA expression of apoptosis-related genes, including Bax, caspase-9, and caspase-3. Notably, the AFB1+CotA group exhibited a significant reduction in AFB1 residues and AFB1-DNA adducts in quail liver tissues compared to the AFB1 group. These findings indicate that aflatoxin oxidase CotA holds promise as a feed additive to alleviate AFB1-induced hepatotoxicity.
1. Introduction
Aflatoxins are a class of toxic secondary metabolites mainly produced by Aspergillus parasiticus and Aspergillus flavus. Aflatoxins were initially identified in 1961 by Van der Zijden et al. [1] as the primary etiological agent of “Turkey X disease”, which led to the deaths of more than 100,000 turkeys [2]. To date, over 20 types of aflatoxins have been discovered. Among them, aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) exhibits the highest toxicity and is classified as a Group I carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) [3]. In the liver, aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) undergoes bioactivation through phase I metabolic enzymes, specifically cytochrome P450 (CYP450), resulting in the formation of exo-AFB1-8,9-epoxide (AFBO) [4]. This epoxide subsequently forms adducts with DNA, leading to cytotoxicity, mutation, and DNA damage [5]. Poultry, including chickens, ducks, turkeys, and quails, are among the animal species that are vulnerable to the toxic impacts of AFB1. Dietary AFB1 exposure can lead to serious organ damage, reduced production performance, immune suppression, intestinal microbiota disorder, increased morbidity and mortality rates, and meat quality deterioration in poultry [6]. There is an urgent necessity to explore effective strategies for preventing or alleviating the deleterious impacts of AFB1 on poultry [7].
The utilization of mycotoxin binders for preventing aflatoxicosis has gained prominence in poultry production. Numerous studies have demonstrated that mineral and organic adsorbents, including zeolite, bentonite, aluminosilicate, montmorillonite, and yeast cell wall, can partially or completely mitigate the deleterious effects of dietary AFB1 [8]. Nevertheless, these adsorbents may also sequester essential nutrients such as minerals and vitamins. Biological degradation, characterized by the microbial and enzymatic conversion of AFB1 into less harmful metabolites, is regarded as a promising approach due to its high specificity, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. Various enzymes, including peroxidases [9,10], laccases [11,12], N-acyl endolipases [13], and F420H2-dependent reductases [14], have been identified as capable of degrading AFB1. Currently, research on AFB1-degrading enzymes predominantly concentrates on verifying AFB1 degradation in vitro, with relatively few in vivo studies evaluating the efficacy of these enzymes in animal production [15]. Our previous research established that CotA laccase derived from Bacillus licheniformis exhibited aflatoxin oxidase activity, which could catalyze the C3-hydroxylation of AFB1 to non-toxic aflatoxin Q1 and epi-aflatoxin Q1 [12]. Moreover, CotA laccase significantly enhanced growth performance, intestinal health, and hepatic AFB1 metabolism in ducks consuming a diet naturally contaminated with AFB1. Dietary supplementation of CotA reduced AFB1-DNA adducts in the liver and decreased AFB1 residues in both the liver and feces [16]. These findings underscore the potential of CotA as a safe and effective aflatoxin oxidase.
Raising Japanese quails has become increasingly popular within the poultry industry, especially in developing countries, as an alternative protein source for humans. Previous research has demonstrated that the intake of diets contaminated with AFB1 adversely affects hepatic function in Japanese quails, leading to a loss of production performance and reduction in egg weight [17]. Additional studies have reported the immunosuppressive effects of AFB1 exposure in Japanese quails [18,19]. However, there is limited information available on biological detoxification strategies for quail diets contaminated with AFB1. Therefore, the current study was conducted to examine the protective effects of the novel aflatoxin oxidase CotA in mitigating AFB1-induced liver damage in Japanese quails.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Animal Trial Design
AFB1 (purity ≥ 98%) was procured from Pribolab Biological Technical Company, Qingdao, China. The aflatoxin oxidase CotA from Bacillus licheniformis ANSB821 was expressed in Pichia pastoris and subsequently freeze-dried under vacuum conditions for 24 h [12,20]. Japanese quail chicks (1 week of age, female) were purchased from Henan Aoxiang Quail Breeding Base (Henan, China). After acclimation for 1 week, a total of 225 Japanese quail chicks were randomly allocated into three groups, each comprising five replicates with 15 quail chicks per replicate. The experimental groups included: (1) a basal diet serving as the control group (CON); (2) a basal diet with 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1 (AFB1 group); and (3) a basal diet with 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1 and 1 U kg−1 of aflatoxin oxidase CotA (AFB1+CotA group). The AFB1 level in the diet and the dose of aflatoxin oxidase CotA included in this study were set according to our previous study [16]. The basal diet was formulated following the NRC (1994) guidelines for growing Japanese quails (Table S1). The birds had free access to feed and water. Quails within each replicate were housed in cages measuring 90 × 40 × 40 cm, with the ambient temperature being maintained at 25 °C ± 2 °C throughout the duration of the 21-day feeding trial.
2.2. Growth Performance and Sample Collection
Upon the completion of the feeding trial, the quails were fasted for 12 h and weighed to determine average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADFI), and feed conversion ratio (FCR). Subsequently, three birds from each replicate were selected for the collection of blood and tissue samples. Blood samples were taken from the brachial vein, clotted at room temperature for 2 h, and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min to separate the serum. The serum was then stored at −80 °C for subsequent analysis. Following blood collection, the birds were dissected, and whole liver tissues were promptly isolated and blotted with absorbent paper to eliminate surface moisture. The liver index was calculated by measuring liver weight with an electronic balance. A portion of the liver samples was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, while another portion was stored at −80 °C for further analysis.
2.3. H&E Staining
Liver tissue specimens were initially fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, followed by dehydration in ethanol, and subsequently embedded in paraffin. The specimens were sectioned into slices of 5 µm thickness and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for pathological examination using a digital microscopy scanner (3DHistech Ltd., Budapest, Hungary).
2.4. Oil Red O Staining
To assess hepatic lipid droplet deposition, the Oil Red O staining method was employed. Liver tissues were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in the Tissue-Tek O.C.T. compound, and sectioned into slices approximately 5 μm thick. The sections were then stained with Oil Red O and counterstained with hematoxylin, with the visualization of the red lipid droplets performed using a Nikon microscope (Nikon, Melville, NY, USA).
2.5. TUNEL Staining
Apoptosis in liver tissues was evaluated using TUNEL staining. Briefly, liver tissues were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, dehydrated, embedded in paraffin, and dewaxed post-sectioning. The sections were permeabilized with proteinase K, followed by labeling with BrightRed Labeling Mix at 37 °C for 1 h. After washing with PBS, DAPI counterstaining was performed at room temperature. Apoptotic cells were imaged using a confocal microscope (Eclipse Ti2, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
2.6. Serum Biochemical Analysis
The activities of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and the contents of triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in serum were measured by commercial kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China).
2.7. Liver Antioxidant and Oxidative Biomarkers
Liver samples were homogenized in ice-cold PBS using a homogenizer (XU-YM-24, Xi Niu Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The resultant homogenate was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 30 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was promptly transferred into sterile tubes and stored at −80 °C until further analysis. The activities of total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD), glutathione S-transferase (GST), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT), as well as the concentrations of malondialdehyde (MDA) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) were assessed using commercial kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China).
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Total RNA was extracted from liver tissues employing a total RNA extraction kit (TransGen Biotech Co. Ltd, Beijing, China). The integrity and concentration of the extracted RNA were assessed through agarose gel electrophoresis and spectrophotometric analysis. Complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis was performed utilizing a reverse transcription kit (Takara, Dalian, China). The quantification of gene expression was conducted using the SYBR Green quantitative PCR Master Mix (Takara, Dalian, China) and analyzed with the 2−ΔΔCt method. β-actin served as the reference gene for the normalization of target gene expression levels. The primer sequences for the target genes are detailed in Table S2.
2.9. Determination of AFB1 Residues and AFB1-DNA Adduct Levels
AFB1 residues in liver samples were extracted utilizing the total aflatoxin immunoaffinity column (Clover Technology Group, Beijing, China), following the manufacturer’s protocol. The extracted samples containing AFB1 were subsequently analyzed through high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Specifically, the samples were filtered using a 0.22 μm RC filter, and a 20 μL aliquot was injected into the HPLC system. The detection of AFB1 was conducted using excitation and emission wavelengths of 360 nm and 440 nm, respectively. The mobile phase was a methanol–water mixture (45:55, v/v) with a flow rate of 1 mL min−1. The AFB1-DNA adduct contents in liver were determined by a commercial kit (HB253-NC, Hengyuan Biological Institute, Shanghai, China).
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test using the IBM SPSS Statistics software (v26.0). Before conducting the ANOVA, the normality of the data was confirmed via the Shapiro–Wilk test and homogeneity of variances via the Levene’s test. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All data were expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). GraphPad Prism v7.0 was used to draw all the graphs.
3. Results
3.1. Aflatoxin Oxidase CotA Improved the Growth Performance of Japanese Quails Fed with AFB1-Contaminated Diet
The initial body weight of the quails selected for the experiment did not differ significantly (p > 0.05, Table 1). After a 21-day feeding trial, a significant reduction (p < 0.01) in the final body weight and ADG was observed in quails from the AFB1 group compared to the CON group. The addition of aflatoxin oxidase CotA to the AFB1-contaminated diet ameliorated the decrease in the final body weight and ADG. Moreover, there were no notable differences (p > 0.05) in ADFI and FCR among the different groups of quails.

Table 1.
Effect of dietary supplementation with aflatoxin oxidase CotA on the growth performance of Japanese quails fed with AFB1-contaminated diet.
3.2. Aflatoxin Oxidase CotA Protected Japanese Quails from AFB1-Induced Liver Injury
As depicted in Figure 1A, the liver histopathological sections from the CON group and the AFB1+CotA group displayed no notable pathological alterations, whereas the AFB1 group exhibited pronounced vacuolar degeneration within hepatocytes and notable inflammatory cell infiltration. The significant increase in the liver index of quails was also observed following AFB1 exposure (p < 0.05, Figure 1B). Moreover, serum ALT, AST, and ALP activities were significantly higher in the AFB1 group compared to the CON group (p < 0.05, Figure 1C–E), further indicating hepatocyte damage. Dietary supplementation with aflatoxin oxidase CotA protected quails from AFB1-induced hepatotoxicity, as indicated by the normalization of these key serum liver function biomarkers.
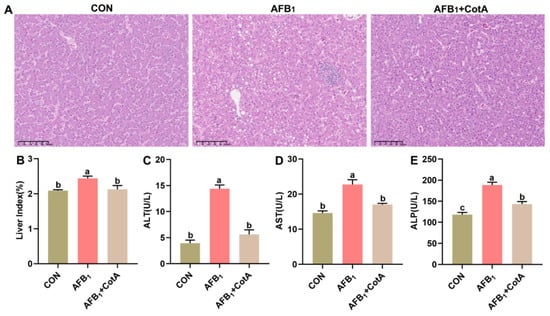
Figure 1.
Protective effect of aflatoxin oxidase CotA on AFB1-induced liver injury of Japanese quails. (A) The liver histopathology observed using HE staining. (B) Liver index. (C) Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity. (D) Serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activity. (E) Serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, and different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05. CON = fed with basal diet; AFB1 = fed with basal diet + 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1; AFB1+CotA = fed with basal diet + 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1 + 1U kg−1 of aflatoxin oxidase CotA.
3.3. Aflatoxin Oxidase CotA Alleviated AFB1-Induced Oxidative Stress in Liver
The effect of dietary supplementation with aflatoxin oxidase CotA on the hepatic redox homeostasis of Japanese quails fed with AFB1-contaminated diet was investigated. As presented in Table 2, hepatic T-AOC level and the activities of antioxidant enzymes, including GST, GSH-Px, POD, and CAT, were significantly reduced in quails exposed to AFB1 compared to the CON group (p < 0.05). Concurrently, the AFB1 group showed a significant increase in liver H2O2 and MDA levels (p < 0.05). The addition of aflatoxin oxidase CotA enhanced antioxidant enzyme activities and reduced H2O2 and MDA levels in the hepatic tissues of quails compared to the AFB1 group. Moreover, AFB1 exposure significantly down-regulated Nrf2, HO-1, NQO1, and SOD1 mRNA expression (p < 0.05), which was mitigated by the dietary inclusion of aflatoxin oxidase CotA (Figure 2).

Table 2.
Effect of dietary supplementation with aflatoxin oxidase CotA on antioxidant and oxidative stress-related biomarkers in liver tissues of Japanese quails fed with AFB1-contaminated diet.
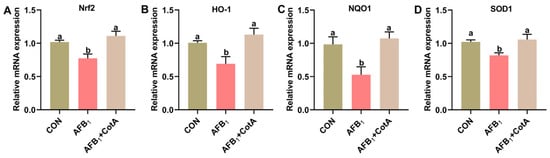
Figure 2.
The mRNA expression of the transcription factor Nrf2 and its downstream genes in the liver of quails. (A–D) The relative expression of Nrf2, HO-1, NQO1, and SOD1. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, and different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05. CON = fed with basal diet; AFB1 = fed with basal diet + 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1; AFB1+CotA = fed with basal diet + 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1 + 1U kg−1 of aflatoxin oxidase CotA.
3.4. Aflatoxin Oxidase CotA Ameliorated AFB1-Induced Lipid Metabolism Disorder in Liver
Oil Red staining revealed extensive hepatocellular vacuoles due to lipid droplets in the AFB1 group (Figure 3A), aligning with the increased serum TG levels in quails consuming an AFB1-contaminated diet (p < 0.05, Figure 3B). No significant difference in serum TC content was found between the AFB1 group and the CON group (p > 0.05, Figure 3C). Moreover, quails in the AFB1 group exhibited higher serum LDL-C level and lower serum HDL-C level than the CON group (p < 0.05, Figure 3D,E). The addition of aflatoxin oxidase CotA to AFB1-contaminated diet effectively reversed these biochemical alterations.
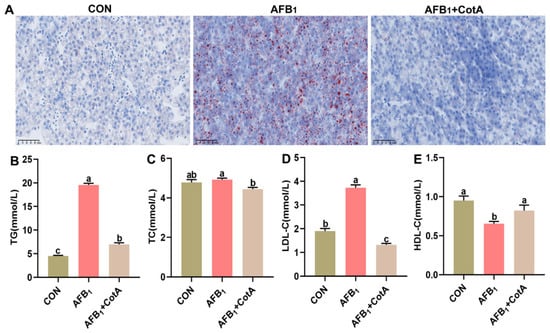
Figure 3.
Effect of aflatoxin oxidase CotA on the hepatic lipid accumulation in Japanese quails fed with AFB1-contaminated diet. (A) Oil Red O staining of liver tissue sections. (B) Serum triglyceride (TG) content. (C) Serum total cholesterol (TC) content. (D) Serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) content. (E) Serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) content. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, and different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05. CON = fed with basal diet; AFB1 = fed with basal diet + 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1; AFB1+CotA = fed with basal diet + 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1 + 1U kg−1 of aflatoxin oxidase CotA.
3.5. Aflatoxin Oxidase CotA Mitigated AFB1-Induced Liver Apoptosis
The apoptosis rate in quail hepatocytes was detected via the TUNEL assay (Figure 4A). The AFB1 group exhibited a significant increase in apoptotic cells (positive-stained red) compared to the CON group. The addition of aflatoxin oxidase CotA to the AFB1 diet significantly reduced apoptotic cells in the liver. As shown in Figure 4B–E, compared with the CON group, the AFB1 group exhibited a significant increase (p < 0.05) in the mRNA expression levels of Bax, caspase-3, and caspase-9, while the expression of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 significantly decreased (p < 0.05). The addition of aflatoxin oxidase CotA significantly (p < 0.05) decreased the mRNA expression of Bax, caspase-3, and caspase-9 compared to the AFB1 group. The AFB1+CotA group exhibited a significant (p < 0.05) increase in the Bcl-2 mRNA expression level compared to the AFB1 group.
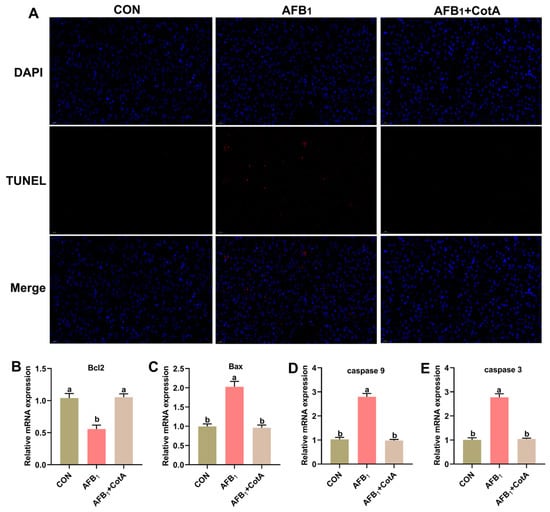
Figure 4.
Effect of aflatoxin oxidase CotA on hepatocyte apoptosis and apoptosis-related gene expression of Japanese quails fed with AFB1-contaminated diet. (A) TUNEL stained paraffin sections from liver tissues. The relative mRNA expression of (B) B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), (C) Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), (D) caspase 9, and (E) caspase 3 in the liver. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, and different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05. CON = fed with basal diet; AFB1 = fed with basal diet + 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1; AFB1+CotA = fed with basal diet + 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1 + 1U kg−1 of aflatoxin oxidase CotA.
3.6. Aflatoxin Oxidase CotA Reduced AFB1 Residues and AFB1-DNA Adduct Content in Liver
The impact of dietary aflatoxin oxidase CotA on AFB1 residues and AFB1-DNA adduct content in the liver of quails is illustrated in Figure 5. In the control group, neither AFB1 residues nor AFB1-DNA adduct were detectable in the liver. In comparison to the AFB1 group, there was a significant reduction (p < 0.05) in both AFB1 residues and AFB1-DNA adduct content in the liver tissues of quails in the AFB1+CotA group.
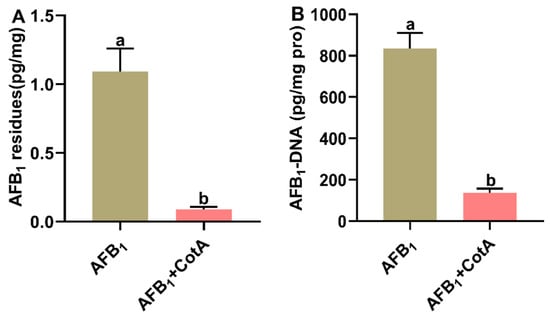
Figure 5.
Aflatoxin oxidase CotA reduced AFB1 residues and AFB1-DNA adduct content in liver of quails. (A) AFB1 residues in liver. (B) AFB1-DNA adduct content in liver. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, and different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05. CON = fed with basal diet; AFB1 = fed with basal diet + 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1; AFB1+CotA = fed with basal diet + 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1 + 1U kg−1 of aflatoxin oxidase CotA.
4. Discussion
AFB1 contamination in feed poses a substantial toxicological threat to poultry, resulting in decreased body weight, lower feed intake, and liver damage [21]. Consequently, the development and implementation of effective AFB1 detoxification strategies are of paramount importance to the poultry industry. Multiple strategies, encompassing chemical, physical, and biological techniques, have been investigated to mitigate the harmful impact of AFB1 in poultry. Among these, biological methods have emerged as particularly promising, offering the potential to counteract AFB1 toxicity without inducing negative side effects in birds. Notably, CotA laccase, a novel aflatoxin oxidase, has demonstrated the capability to degrade AFB1 in both experimental and natural settings [12,16]. The present study was conducted to investigate whether the dietary supplementation of aflatoxin oxidase CotA could effectively ameliorate aflatoxicosis in Japanese quails. In this study, quails exposed to 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1 exhibited significant reduction in both final body weight and average daily gain. These metrics are among the most prevalent clinical manifestations observed following the ingestion of AFB1-contaminated diets in poultry models. Ma et al. [16] investigated ducks consuming a diet with 20 μg kg−1 of AFB1 and documented a notable decrease in average daily gain and body weight at 28 d of age. Similarly, broilers subjected to 40 μg kg−1 of AFB1 in diet for 42 d led to a notable decrease in body weight gain [22]. The inability to achieve the expected body weight can result in economic losses. The growth depression observed in quails exposed to AFB1 was mitigated by the dietary inclusion of aflatoxin oxidase CotA in this study. The liver, as the principal site of AFB1 metabolism, is also the primary target for its pathological impacts. Histological examination using H&E staining revealed increased hepatic morphological alterations and structural disarray in quails fed an AFB1-containing diet. Consistent with histopathological image analysis, the AFB1-treated group exhibited significantly higher liver index and serum liver enzyme activities (ALT, AST, and ALP) than the control group. The findings collectively demonstrate that AFB1 induces significant hepatic damage, thereby validating the successful establishment of the quail AFB1 poisoning model. The incorporation of aflatoxin oxidase CotA into the AFB1-contaminated diet mitigates hepatic damage, normalizes tissue morphology, and restores serum liver enzyme activity. Thus, dietary supplementation with CotA exhibits a substantial protective effect against AFB1-induced hepatic injuries.
Oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between oxidants and antioxidants within the body, is a pivotal factor in the pathogenesis of AFB1-induced hepatic damage [21]. T-AOC serves as a marker reflecting the antioxidant status, while antioxidant enzymes, including SOD, GST, GSH-Px, POD, and CAT, are crucial for eliminating free radicals and peroxides [23]. H2O2 is formed starting from the superoxide anion (O2−), and MDA is the end product of lipid peroxidation, both of which are commonly employed as indicators of oxidative stress [24,25]. In the present study, quails exposed to AFB1 showed signs of oxidative stress, indicated by a notable rise in hepatic H2O2 and MDA levels, alongside a marked decrease in antioxidant enzymes, including T-AOC, GST, GSH-Px, POD, and CAT. These findings align with prior research showing that AFB1 exposure significantly elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS), H2O2, and MDA levels while suppressing T-AOC, SOD, and CAT activities in the livers of mice, thereby suggesting that oxidative stress may serve as the initial trigger in exacerbating AFB1-induced liver injury [26]. The supplementation of aflatoxin oxidase CotA in the diet of quails enhanced T-AOC, GST, GSH-Px, POD, and CAT activities and lowered H2O2 and MDA concentrations in the liver, thereby mitigating oxidative stress induced by AFB1. Nrf2 is a key transcription factor involved in oxidative stress caused by AFB1 [27,28]. Intracellular oxidative stress prompts the translocation of Nrf2 to the nucleus, where it attaches to the antioxidant response element to control the expression of antioxidant genes, such as HO-1, NQO1, and SOD [29]. The present study demonstrated that exposure to AFB1 inhibited the mRNA expression of Nrf2 and its downstream genes HO-1, NQO1, and SOD in the liver of quails. These findings align with earlier research showing that AFB1 exposure inhibits Nrf2 nuclear translocation [27,28]. Dietary supplementation with aflatoxin oxidase CotA ameliorated the AFB1-induced suppression of Nrf2 and enhanced antioxidant gene expression.
Changes in lipids and lipoproteins contribute to the development of aflatoxicosis [30]. In this study, AFB1 exposure was found to cause hepatic steatosis in quails, marked by excessive lipid accumulation in liver tissues. Moreover, AFB1 exposure elevated serum TG and LDL-C levels and reduced HDL-C level. The mechanisms by which AFB1 induces lipid metabolism disorders are multifaceted. A previous study has revealed that AFB1 can increase cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression, subsequently raising mitophagy levels and disrupting normal mitochondrial lipid metabolism [31]. Additionally, AFB1 exposure has been linked to changes in bile acid metabolism, which is crucial for lipid digestion and absorption [32]. In addition to these direct effects on lipid metabolism, AFB1 also interacts with other metabolic pathways. For example, AFB1 exposure in Hep3B cells has been shown to induce dynamic metabolic reprogramming, affecting pathways such as fatty acid synthesis and oxidation, glycerophospholipid metabolism, and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle [33]. These alterations further contribute to the overall disruption of lipid metabolism in the liver. The dietary supplementation of aflatoxin oxidase CotA could ameliorate the negative impact of AFB1 on lipid metabolism.
Apoptosis, an essential and programmed form of cell death, is integral to the normal physiological processes in avian species. Prior studies have shown that AFB1 can compromise the structural integrity of hepatocyte mitochondria, reduce mitochondrial membrane potential, and initiate mitochondrion-dependent apoptotic pathways [26,28]. In alignment with these findings, TUNEL staining revealed that AFB1 treatment markedly elevated hepatocyte apoptosis compared to the CON group in this study. Conversely, the AFB1+CotA group exhibited a notable decrease in the liver cell apoptosis index relative to the AFB1 group. Mitochondrial apoptosis is modulated by the Bcl-2 protein family, which includes the pro-apoptotic Bax and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 [34]. The anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 inhibits apoptosis by neutralizing Bax, which facilitates the permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane, a vital step in the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Upon release from mitochondria, the pro-apoptotic molecule cytochrome c (Cyt-C) interacts with apoptotic protease activating factor 1 (Apaf-1) to form apoptosome complex. This complex subsequently activates pro-caspase-9, which in turn converts pro-caspase-3 into caspase-3, culminating in the execution phase of apoptosis. Prior research has demonstrated that AFB1 can enhance the mRNA expression of Bax, caspase-9, and caspase-3, while reducing Bcl-2 mRNA expression level, thereby promoting cellular apoptosis [26,35]. This study further assessed the expression profiles of mitochondrial pathway-related apoptosis genes in the liver tissue of quails. The findings reveal the significant up-regulation of Bax, caspase-9, and caspase-3 mRNA expression, alongside a notable down-regulation of Bcl-2 mRNA level in the AFB1 group in comparison with the CON group. Moreover, the dietary supplementation of aflatoxin oxidase CotA in the AFB1 diet notably decreased the mRNA expression levels of Bax, caspase-9, and caspase-3, while enhancing Bcl-2 mRNA expression. These results indicate that aflatoxin oxidase CotA effectively mitigated AFB1-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in quails.
The liver is the primary site for AFB1 metabolism, where cytochrome P450 enzymes convert AFB1 into exo-AFB1-8,9-epoxide (AFBO) [4]. Subsequently, AFBO interacts with biomacromolecules such as DNA, resulting in AFB1-DNA adduct formation [36]. These adducts serve as promising biomarkers for assessing AFB1 exposure and AFBO production in animals [5]. Our study found that dietary supplementation with aflatoxin oxidase CotA significantly reduced AFB1 residues and AFB1-DNA adducts in the liver of quails exposed to AFB1. These findings collectively suggest that aflatoxin oxidase CotA possesses a robust AFB1 degradation capability within the gastrointestinal tract of quails, thereby reducing the concentration of AFB1 absorbed by enterocytes and maintaining normal hepatic function.
5. Conclusions
In summary, Japanese quails fed with diet contaminated with 50 μg kg−1 of AFB1 for 21 days presented reduced growth performance. The hepatoxicity of AFB1 may closely associate with oxidative stress, lipid metabolism disorder, and apoptosis. The dietary supplementation of aflatoxin oxidase CotA could effectively detoxify aflatoxicosis in Japanese quails fed with AFB1-contaminated diet and reduced AFB1 residues and AFB1-DNA adduct content in the liver. These results emphasize the potential application of aflatoxin oxidase CotA as a promising AFB1 detoxification agent in the feed industry. Given that the feeding trial in this study was limited to a duration of three weeks, it is imperative to investigate further the long-term protective effects of aflatoxin oxidase CotA in Japanese quails exposed to AFB1. Additionally, further research is warranted to assess the AFB1-detoxifying efficacy of CotA in other poultry species.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani15111555/s1. Table S1: Ingredients and nutrient contents of the basal diet; Table S2: Primers used in the real-time quantitative PCR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z. and Y.G.; methodology, H.L. and Z.R.; validation, W.Z. and Z.W.; formal analysis, H.L.; investigation, Y.L.; data curation, H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.L. and Z.R.; writing—review and editing, Y.G.; visualization, L.Z.; supervision, Y.G.; project administration, H.L., Z.R. and Y.L.; funding acquisition, Y.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Science and Technology Project of Henan Province (242102111006), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2023M730998), Postgraduate Education Reform and Quality Improvement Project of Henan Province (24JX0098), and Young Talents Fund of Henan Agricultural University (30501327).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The experiment was approved by the Animal Care Committee at Henan Agricultural University (Approval No. HNND2022030838; Approval date: 7 February 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data in this study are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Van der Zijden, A.S.M.; Koelensmid, W.; Boldingh, J.; Barrett, C.B.; Ord, W.O.; Philip, J. Aspergillus flavus and Turkey X disease: Isolation in crystalline form of a toxin responsible for Turkey X-disease. Nature 1962, 195, 1060–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blount, W.P. Turkey “X” disease. J. Br. Turkey 1961, 9, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ostry, V.; Malir, F.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y. Mycotoxins as human carcinogens-the IARC Monographs classification. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Q.; Ji, C. Novel strategies for degradation of aflatoxins in food and feed: A review. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkerroum, N. Retrospective and prospective look at aflatoxin research and development from a practical standpoint. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, A.M.; Ruan, D.; El-Senousey, H.K.; Chen, W.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, C. Harmful effects and control strategies of aflatoxin B1 produced by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus strains on poultry: Review. Toxins 2019, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Q. Aflatoxin B1 in poultry liver: Toxic mechanism. Toxicon 2023, 233, 107262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, L.; Li, J. Complicated interactions between bio-adsorbents and mycotoxins during mycotoxin adsorption: Current research and future prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 96, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xu, C.; Lu, P.; Wu, M.; Chen, A.; Zhang, M.; Xie, Y.; Han, G. Widespread distribution of the DyP-carrying bacteria involved in the aflatoxin B1 biotransformation in Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, T.V.; Yang, B.; Tian, X.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, G.; Si, P.; Li, R.; Xing, F. Simultaneous degradation of aflatoxin B1 and zearalenone by porin and peroxiredoxin enzymes cloned from Acinetobacter nosocomialis Y1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, M.; Fanelli, F.; Zucca, P.; Liuzzi, V.C.; Quintieri, L.; Cimmarusti, M.T.; Monaci, L.; Haidukowski, M.; Logrieco, A.F.; Sanjust, E.; et al. Aflatoxin B1 and M1 degradation by Lac2 from Pleurotus pulmonarius and redox mediators. Toxins 2016, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Qin, X.; Tang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L. CotA laccase, a novel aflatoxin oxidase from Bacillus licheniformis, transforms aflatoxin B1 to aflatoxin Q1 and epi-aflatoxin Q1. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Wu, T.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Mwabulili, F.; Xie, Y.; Sun, S.; Ma, W.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; et al. Mining lactonase gene from aflatoxin B1-degrading strain Bacillus megaterium and degrading properties of the recombinant enzyme. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 20762–20771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.E. A new role for coenzyme F420 in aflatoxin reduction by soil mycobacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, L.; Gong, G.; Zhang, L.; Shi, L.; Dai, J.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Khalil, M.M.; Sun, L. Invited review: Remediation strategies for mycotoxin control in feed. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Wang, G.; Guo, Y.; Huang, S.; Ma, Q.; Ji, C.; et al. Bacillus CotA laccase improved the intestinal health, amino acid metabolism and hepatic metabolic capacity of Pekin ducks fed naturally contaminated AFB1 diet. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, M.I.; Murakami, A.E.; Fernandes, A.M.; Ospina-Rojas, I.C.; Nunes, K.C.; Hirata, A.K. Performance and serum biochemical profile of Japanese quail supplemented with silymarin and contaminated with aflatoxin B1. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh Kasmani, F.; Karimi Torshizi, M.A.; Allameh, A.; Shariatmadari, F. A novel aflatoxin-binding Bacillus probiotic: Performance, serum biochemistry, and immunological parameters in Japanese quail. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, F.N.; Magnoli, A.P.; Dalcero, A.M.; Marin, R.H. Effect of feed contamination with aflatoxin B1 and administration of exogenous corticosterone on Japanese quail biochemical and immunological parameters. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, L. Combined strategies for improving aflatoxin B1 degradation ability and yield of a Bacillus licheniformis CotA laccase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, S.; Kim, J.E.; Coulombe, R. Aflatoxin B1 in poultry: Toxicology, metabolism and prevention. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Ding, K.; Wang, J.; Deng, Q.; Gu, K.; Wang, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and smectite after aflatoxin B1 challenge on the growth performance, nutrient digestibility and blood parameters of broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habashy, W.S.; Milfort, M.C.; Rekaya, R.; Aggrey, S.E. Cellular antioxidant enzyme activity and biomarkers for oxidative stress are affected by heat stress. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, 63, 1569–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennicke, C.; Rahn, J.; Lichtenfels, R.; Wessjohann, L.A.; Seliger, B. Hydrogen peroxide—Production, fate and role in redox signaling of tumor cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W. AFB1-induced mice liver injury involves mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by mitochondrial biogenesis inhibition. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yan, W.; Tang, J.; Jin, X.; Xue, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q.; Liang, Z. Dietary phillygenin supplementation ameliorates aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in chicken liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; San, J.; Pang, H.; Du, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Hu, J.; Yang, J. Taurine attenuates AFB1-induced liver injury by alleviating oxidative stress and regulating mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Toxicon 2022, 215, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kensler, T.W.; Wakabayashi, N.; Biswal, S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 89–116. [Google Scholar]
- Rotimi, O.; Rotimi, S.; Duru, C.; Ebebeinwe, O.; Abiodun, A.; Oyeniyi, B.; Faduyile, F. Acute aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity alters gene expression and disrupts lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 4, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.L.; Han, P.; Meng, Y. Aflatoxin B1-induced COX-2 expression promotes mitophagy and contributes to lipid accumulation in hepatocytes in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Toxicol. 2020, 39, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Kang, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, K. Aflatoxin B1 induces liver injury by disturbing gut microbiota-bile acid-FXR axis in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 176, 113751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; He, K.; Wang, H. Comprehensive metabolomic analysis reveals dynamic metabolic reprogramming in Hep3B cells with aflatoxin B1 exposure. Toxins 2021, 13, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiraz, Y.; Adan, A.; Kartal Yandim, M.; Baran, Y. Major apoptotic mechanisms and genes involved in apoptosis. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 8471–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, F.; Tao, W.; Ye, R.; Li, Z.; Lu, Q.; Shang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fang, J.; Bhutto, Z.; Liu, J. Penthorum Chinense Pursh extract alleviates aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury and oxidative stress through mitochondrial pathways in broilers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 822259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, L.L.; Massey, T.E. Aflatoxin B1-induced DNA damage and its repair. Cancer Lett. 2006, 241, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).