Abstract
Autochthonous microorganisms play critical roles in shaping the quality of Chinese sausages and may be influenced by local climate and/or processing conditions. The present study aimed to reveal the interprovincial differences in microbial community between Sichuan and Guizhou sausages, as well as driving factors based on high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatic analysis. The results indicated that Cobetia, Debaryomycetaceae, Kurtzmaniella, and Candida zeylanoides served as biomarkers for Sichuan sausages. In contrast, Enterococcus, unclassified Cyanobacteriales, Lactobacillales, Aspergillus vitricola, Mortierella, Fusarium, and Penicillium were identified as biomarkers for Guizhou sausages. Furthermore, salt content and moisture level showed positive correlations with Cobetia, Staphylococcus, Debaryomyces, and Kurtzmaniella, mainly found in Sichuan sausages. Conversely, pH and water activity (Aw) were positively associated with potential pathogenic bacteria (e.g., Vibrio, Cyanobacteria, Enterococcus, and Aeromonas) and fungi (e.g., Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Penicillium), which were mainly distributed in Guizhou sausages. Notably, microbial composition discrepancies between Sichuan and Guizhou sausages were primarily driven by processing conditions rather than regional climate factors. Collectively, these findings provide valuable insight for developing novel specific starters.
1. Introduction
Sausages are traditional fermented meat products widely favored by consumers globally. In European countries, sausages such as salami are typically produced using starters composed of functional microbes and are widely distributed in Italy, Spain, and Germany [1]. In contrast, Chinese sausages are traditionally prepared by mixing pork lean/fat meat with ingredients such as salt, sugar, pepper powder, chili powder, and baijiu. The mixture is then stuffed into a natural casing (e.g., small intestine) and subjected to smoke curing and spontaneous fermentation [2]. Accordingly, autochthonous microorganisms—primarily derived from raw materials, processing tools, human skin, and the environment—colonize the meat matrix due to its nutrient-rich composition. These microorganisms excrete hydrolases to degrade carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, generating flavor precursors and aromatic compounds. Meanwhile, they effectively inhibit undesired microbiota and mitigate the accumulation of harmful metabolites. Collectively, microbial communities play a critical role in determining the flavor, quality, and safety of sausages during spontaneous fermentation [3]. Thus, unveiling the microbial composition of smoke-cured sausages is essential for improving their quality and safety.
Both culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches have been extensively used to characterize microbial diversity in fermented sausages. Initially, functional microorganisms in sausages were isolated and identified using traditional cultivation methods. Staphylococcus species such as S. succinus and S. xylosus were largely isolated during the maturation stage of Italian sausages, as well as lactic acid bacteria (LAB) [4]. Although culture-dependent methods have identified numerous functional microbes, these methods are limited by low reliability, accuracy, and efficiency. Moreover, rare species and unculturable microorganisms often evade isolation, hindering comprehensive profiling of authentic microbial communities [5,6]. Subsequently, polymerase chain reaction–denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE) was employed to analyze microbial profiles in fermented sausages from Italy [7,8], Portugal [9], Argentina [10], and China [11,12]. High-throughput sequencing (HTS) technology has since emerged as a superior tool, offering enhanced accuracy, throughput, robustness, and speed for elucidating microbial community structure and succession in complex ecosystems. HTS-based studies have provided in-depth insights into microbial communities of fermented meat products, including air-dried beef, sausage, and yak jerky, etc. [13,14,15].
Sichuan and Guizhou provinces, located in southwestern China, have traditional practices of homemade smoke-cured sausage production during winter. Sichuan sausages are typically prepared with a lean-to-fat pork ratio of 1.5:1, supplemented with 50–60 g/kg NaCl, 2 g/kg sugar, 5 g/kg chili powder, 50 mg/kg pepper powder, and baijiu (Chinese liquor). In contrast, Guizhou sausages use a lean-to-fat ratio of 1:1, 20–30 g/kg NaCl, 2 g/kg sugar, 50 mg/kg pepper powder, and baijiu. Both sausages undergo smoke curing and air-drying, differing primarily in processing duration. Sichuan sausages are initially smoke-cured for one day using cypress leaf, orange peel, and peanut shell, followed by air-drying for over 20 days. Guizhou sausages, however, are suspended in kitchens and exposed to wood smoke during daily cooking for approximately one month. Sensorily, Sichuan sausages are characterized by spiciness and saltiness, whereas Guizhou sausages exhibit a mild sourness. These taste discrepancies are greatly influenced by microbial composition and processing conditions. Although prior studies have reported microbial communities in Sichuan sausages using HTS [12,14,16], comparative analyses of interprovincial microbial profiles (Sichuan vs. Guizhou) remain scarce [17]. Additionally, the factors driving microbial compositional differences between these sausages are poorly understood.
Therefore, this study aimed to (1) compare microbial compositions of smoke-cured sausages at the interprovincial level and (2) identify key factors driving microbial community divergence. The findings provide critical insights for developing novel specific starters to optimize sausage quality and safety.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sausages Collection
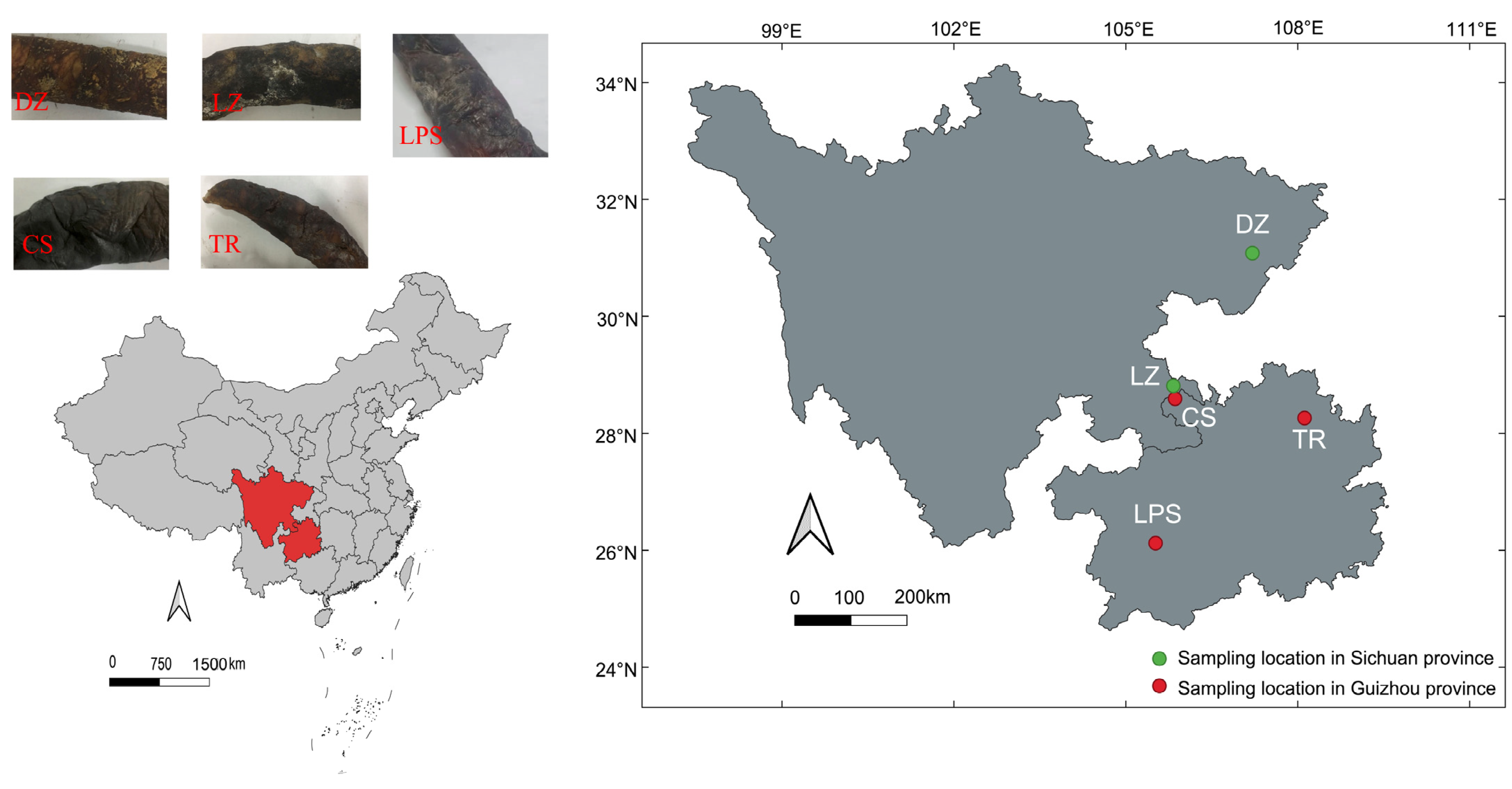
A total of five smoke-cured sausage samples were collected in March 2022. Two samples (labeled DZ and LZ) originated from Dazhou (107.2° E, 31.1° N) and Luzhou (105.8° E, 28.8° N) in Sichuan Province. The three remaining samples—CS, LPS, and TR—were collected from Chishui (105.9° E, 28.6° N), Liupanshui (105.5° E, 26.1° N), and Tongren (108.1° E, 28.3° N) in Guizhou Province, respectively. The geographical locations of the sampling sites are illustrated in Figure 1. All samples were stored in an ice box and transported to the laboratory within 24 h. Subsequently, the sausages were frozen at −20 °C for physicochemical parameter detection and microbial community profiling.
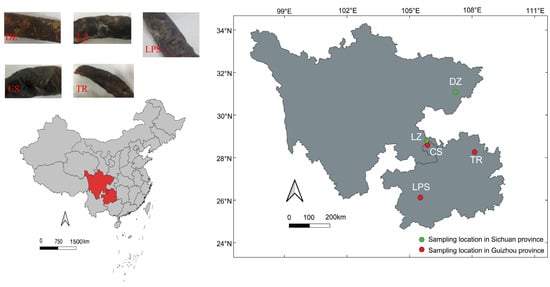
Figure 1.
The appearances and sampling locations of five smoke-cured sausage samples that were collected from Sichuan and Guizhou provinces in southwest China. DZ: Dazhou; LZ: Luzhou; CS: Chishui; LPS: Liupanshui; TR: Tongren. Green and read circles denoted Sichuan and Guizhou sausage samples, respectively.
2.2. Detection of Physicochemical Parameters
The moisture content of sausages was detected by a portable moisture meter (SFY-30, Guanya, Shenzhen, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Water activity (Aw) was determined with a water activity instrument (HD-4B, Huake Apparatus Co., Shenzhen, China) at 25 °C. Briefly, 3 g of a homogenized sausage sample was evenly distributed in the bottom of the water activity apparatus. The pH values of sausages were recorded using a portable pH meter (Testo 205, Lenzkirch, Germany), by directly inserting the probe into the samples. For salt content, 1 g of sausage was homogenized with 9 mL of distilled water, and salinity was quantified using a salt meter (Pal-saltprobe, ATAGO Co., Fukuoka City, Japan). These four physicochemical parameters were measured in triplicate.
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and High-Throughput Sequencing
About 1 g of sausage from each of the 15 duplicates was flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and then ground into powder. Genomic DNA was extracted using the TGuide S96 Magnetic Beads Soil/Fecal DNA extraction kit (TIANGEN, DP812, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Bacterial 16S rRNA gene V3–V4 regions were amplified with primers 338F/806R, and fungal ITS1 regions were amplified with primers ITS1F/ITS2 via a two-step PCR approach. First PCR (10 μL) consisted of 5–50 ng template DNA, 0.3 μL each primer, 5 μL KOD FX Neo Buffer, 2 μL dNTP (2 mM), 0.2 μL KOD FX Neo, and nuclease-free water to 10 µL. The PCR conditions were as shown below: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, 25 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 50 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 40 s, final extension at 72 °C for 7 min. The second PCR reaction system (20 μL) was as follows: 5 μL initial targeting PCR products, 2.5 μL MPPI-a/MPPI-b (2 μM), 10 μL 2 × Q5 High-Fidelity Master Mix. The PCR reaction conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 98 °C for 30 s, 10 cycles of 98 °C for 10 s, 65 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. The agarose gel electrophoresis (1.8% w/v) was used to check the target PCR products. After checked and quantified, the targeted products were used to build a cloning library. The library quality was assessed on the Qubit@2.0 Fluorometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Finally, paired-end sequencing was performed on the Illumina novaseq 6000 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
Raw sequences of bacterial 16S rRNA (V3-V4) and fungal ITS1 regions were firstly filtrated by Trimmomatic (version 0.33). Removal of primer sequences was performed by Cutadapt (version 1.9.1) to obtain clean reads. Then, the paired-end reads obtained were assembled by USEARCH (version 10), followed by Chimera removal using UCHIME (version 8.1). Sequences with ≥97% similarity were clustered into the same operational taxonomic units (OTUs). Taxonomic annotation was performed against the SILVA (v138) and UNITE (v8.3) databases for bacteria and fungi, respectively. Alpha diversity (Chao1, Shannon, Simpson, and PD whole tree, etc.) and beta diversity analyses were performed using QIIME software (Version 1.7.0). Abundance analysis, principal component analysis (PCA), linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe), and Spearman’s correlation heatmaps were visualized using R package (v2.15.3). Raw bacterial and fungal DNA sequences were deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under accession number: PRJNA870249.
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters of Sausages from the Sichuan and Guizhou Region
The pH, moisture content, Aw, and salt content of the sausages were detected and are shown in Table 1. The pH value of the five fermented sausages ranged from 5.51 to 6.22. As expected, sample TR showed the lowest pH value (5.51). Although no linear relationship was observed between Aw and moisture content, a positive correlation was noted. Specifically, sample CS (14.15% moisture) displayed the lowest Aw (0.761), whereas samples with >20% moisture showed Aw > 0.8. Notably, the NaCl content in two Sichuan sausages (DZ and LZ) exceeded 5%, roughly twice that of Guizhou sausages.

Table 1.
Physicochemical parameters of Sichuan sausages and Guizhou sausages.
3.2. α-Diversity Analysis
Representative OTUs obtained from the Illumina Novaseq platform were used to characterize the bacterial and fungal diversities of these 15 sausage duplicates. Abundance-based indices (ACE and Chao1), diversity indices (Shannon and Simpson), and phylogenetic diversity (PD whole tree) are summarized in Table 2. Usually, Shannon and Simpson indices reflect microbial community diversity and evenness, while Chao1 and ACE estimate species richness. For bacterial communities, sample DZ exhibited the lowest ACE, Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson values, indicating reduced diversity and high evenness. In contrast, the remaining four samples displayed bacterial Shannon indices >4.30, suggesting higher diversity. Notably, fungal diversity (Shannon index) surpassed bacterial diversity in sample TR. Furthermore, the fungal Shannon indices were highest in TR and CS, whereas DZ, LZ, and LPS showed minimal fungal diversity. The PD whole-tree values revealed distinct genetic relationships: the bacterial communities in DZ and LPS exhibited the simplest and most complex genetic profiles, respectively. Similarly, the fungal PD values indicated simplified genetic relationships in DZ and LZ, contrasting with the complex profiles observed in TR and CS.

Table 2.
α-diversity indices of bacterial and fungal community of Sichuan and Guizhou fermented sausages.
3.3. Abundance Analyses of the Bacterial and Fungal Community Composition of Sausages at the Phylum and Genus Levels
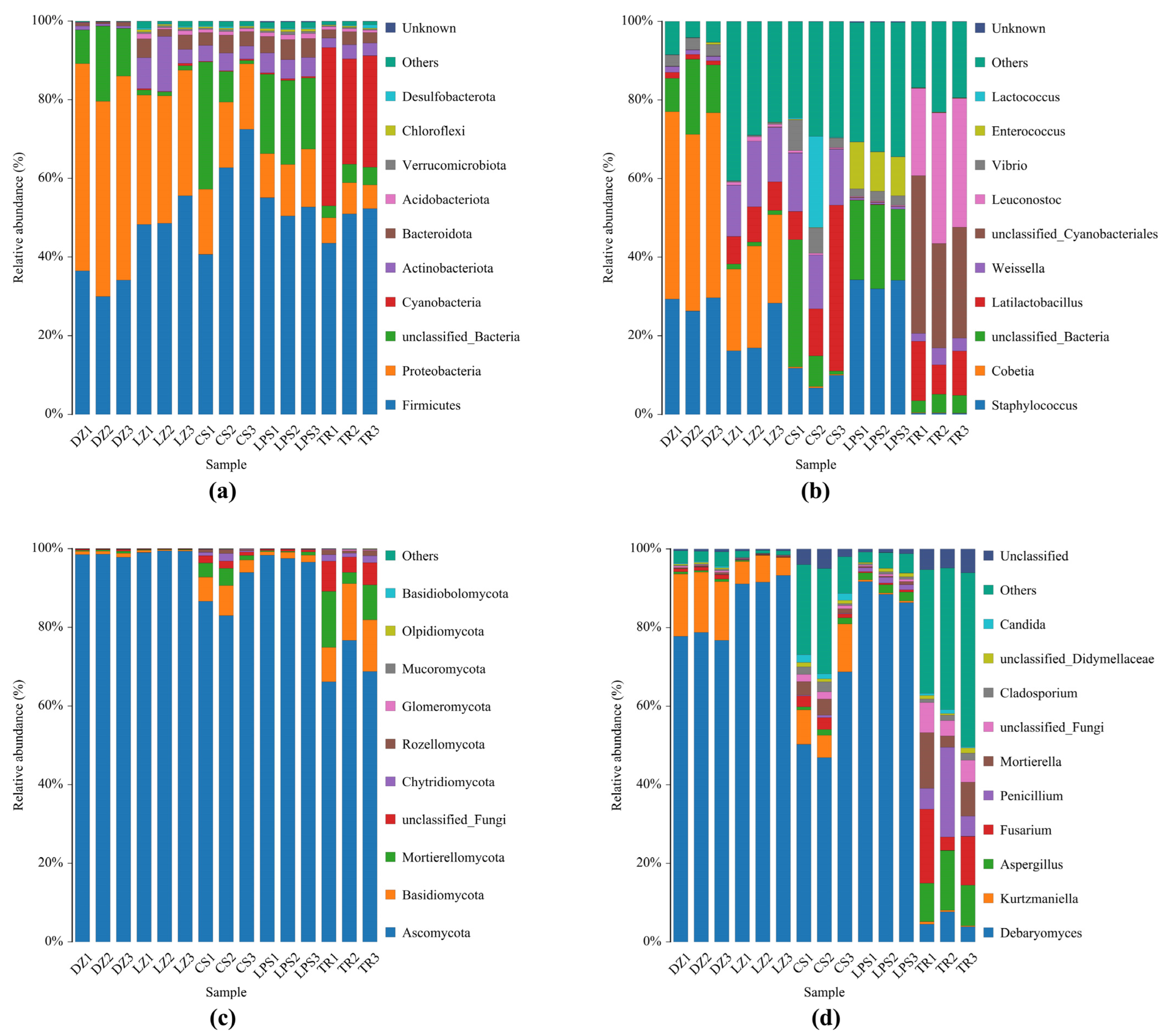
Following taxonomic annotation, the relative abundances of the top 10 abundant microbial phyla and genera are illustrated in Figure 2. At the phylum level, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria, Actinobacteriota, and Bacteroidota were the predominant phyla. Firmicutes and Proteobacteria collectively accounted for >60% of the total abundance (reaching up to 90% in most samples), except in CS1 and TR1. Notably, Firmicutes exhibited a lower relative abundance (~30%) in the Sichuan sample DZ, whereas Proteobacteria accounted for more than 50%. In contrast, the three Guizhou sausage samples displayed an inverse pattern, with Firmicutes significantly surpassing Proteobacteria in abundance. Intriguingly, the phylum Cyanobacteria were exclusively detected in sample TR with a relative abundance >30%, which exhibited the lowest pH and NaCl values (Figure 2a).
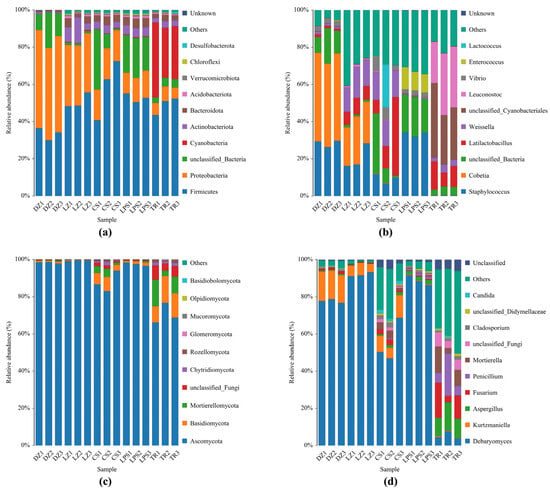
Figure 2.
Abundance analysis of bacteria (a,b) and fungi (c,d) obtained from five sausage samples at the phylum level and genus level. DZ: Dazhou; LZ: Luzhou; CS: Chishui; LPS: Liupanshui; TR: Tongren. These five sausage samples were measured in triplicate.
At the genus level, the predominant bacterial genera in both Sichuan and Guizhou sausages included Staphylococcus, Cobetia, unclassified Cyanobacteriales, Vibrio, and Enterococcus, and lactic acid bacteria (LAB; Latilactobacillus, Leuconostoc, Weissella, and Lactococcus) were found. The genus Staphylococcus was present in all samples except TR, accounting for approximately 15% in LZ and 40% in LPS. Meanwhile, unclassified Cyanobacteriales and LAB (especially Leuconostoc) predominated in TR, which exhibited the lowest pH and saline content. Intriguingly, halophilic Cobetia was exclusively identified in high-salt Sichuan sausages, constituting >45% of DZ and ~20% of LZ. Potential pathogens such as unclassified Cyanobacteriales, Vibrio, Enterococcus were mainly distributed in the Guizhou samples TR, CS, and LPS (Figure 2b).
As regards fungal diversity, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Mortierellomycota were the dominant phyla in sausages. The phylum Ascomycota accounted for 96% of samples DZ, LZ, and LPS, even near 100% in sample LZ. Additionally, the total proportion of both phyla Mortierellomycota and Basidiomycota was 15–25% in sample TR, though Ascomycota was still the dominant fungal phylum (Figure 2c). At the genus level, Debaryomyces, Kurtzmaniella, Aspergillus, Penicillium, Fusarium, and Mortierella were the dominant genera in all sausage samples. As expected, the most abundant genera, Debaryomyces and Kurtzmaniella, accounted for over 90% of samples DZ and LZ with an elevated saline content. In contrast, the genus Debaryomyces in sample TR was the least abundant among all sausage samples, reflected by its <8% proportion. Accordingly, the abundances of the genera Aspergillus, Penicillium, Fusarium, and Mortierella, and some potential pathogenic fungi were high in sample TR, followed by sample CS (Figure 2d).
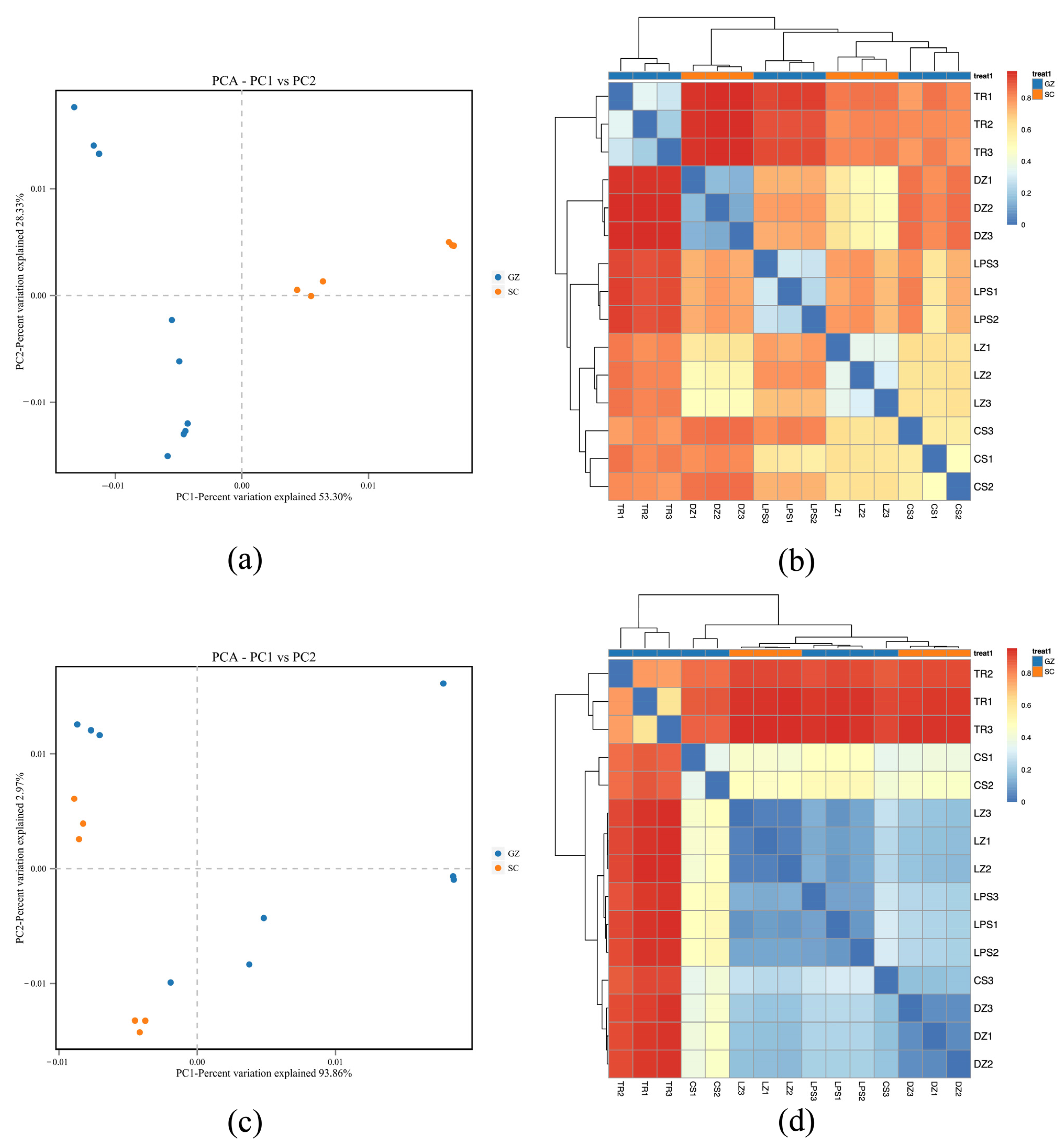
3.4. Principle Component Analysis (PCA) and Heatmap Analysis
PCA was conducted to assess microbial community divergence between sausage samples (Figure 3). Regarding bacterial communities, PC1 and PC2 explained 53.30% and 28.33% of the total variance, respectively. The Sichuan samples exhibited dispersion along PC1 but clustered centrally along PC2, with distinct separation from the Guizhou samples (Figure 3a). Fungal PCA revealed a pronounced variance explained by PC1 (93.86%) and PC2 (2.97%). Similarly, the Sichuan fungal communities clustered tightly along PC1, whereas the Guizhou samples showed broader dispersion (Figure 3c).
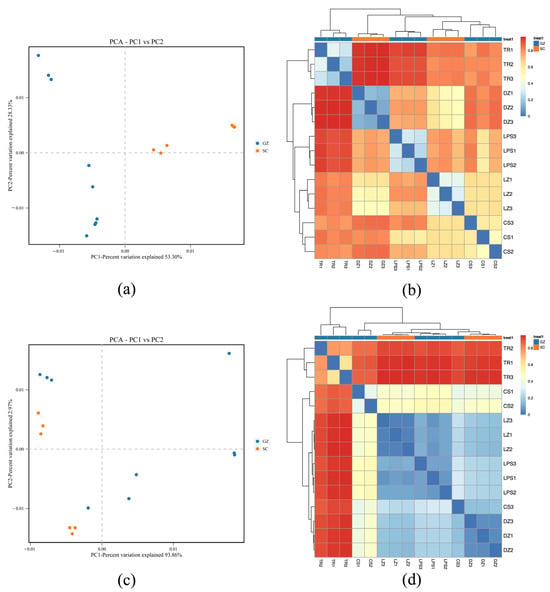
Figure 3.
Principal component analysis (PCA) (a,c) and heatmap plot (b,d) display Bray–Curtis dissimilarity. Red and blue colors in PCA plot denote SC (Sichuan) and GZ (Guizhou) sausages, respectively. Blue indicates high similarity (low distance), and red indicates low similarity (high distance) between microbial communities of sausage samples.
Differentiation and similarities among the five sausage samples were further analyzed based on heatmap clustering. Bacterial heatmap analysis suggested close similarity between samples LZ and CS, which clustered distinctly from DZ. Sample TR exhibited marked divergence from the other four samples (Figure 3b). Similarly, the fungal heatmap results highlighted that sample TR was obviously distinct from the remaining four sausages, whereas DZ, LZ, and LPS formed a cohesive cluster, which was reflected by the blue color in Figure 3d, suggesting shared fungal community features among these three samples.
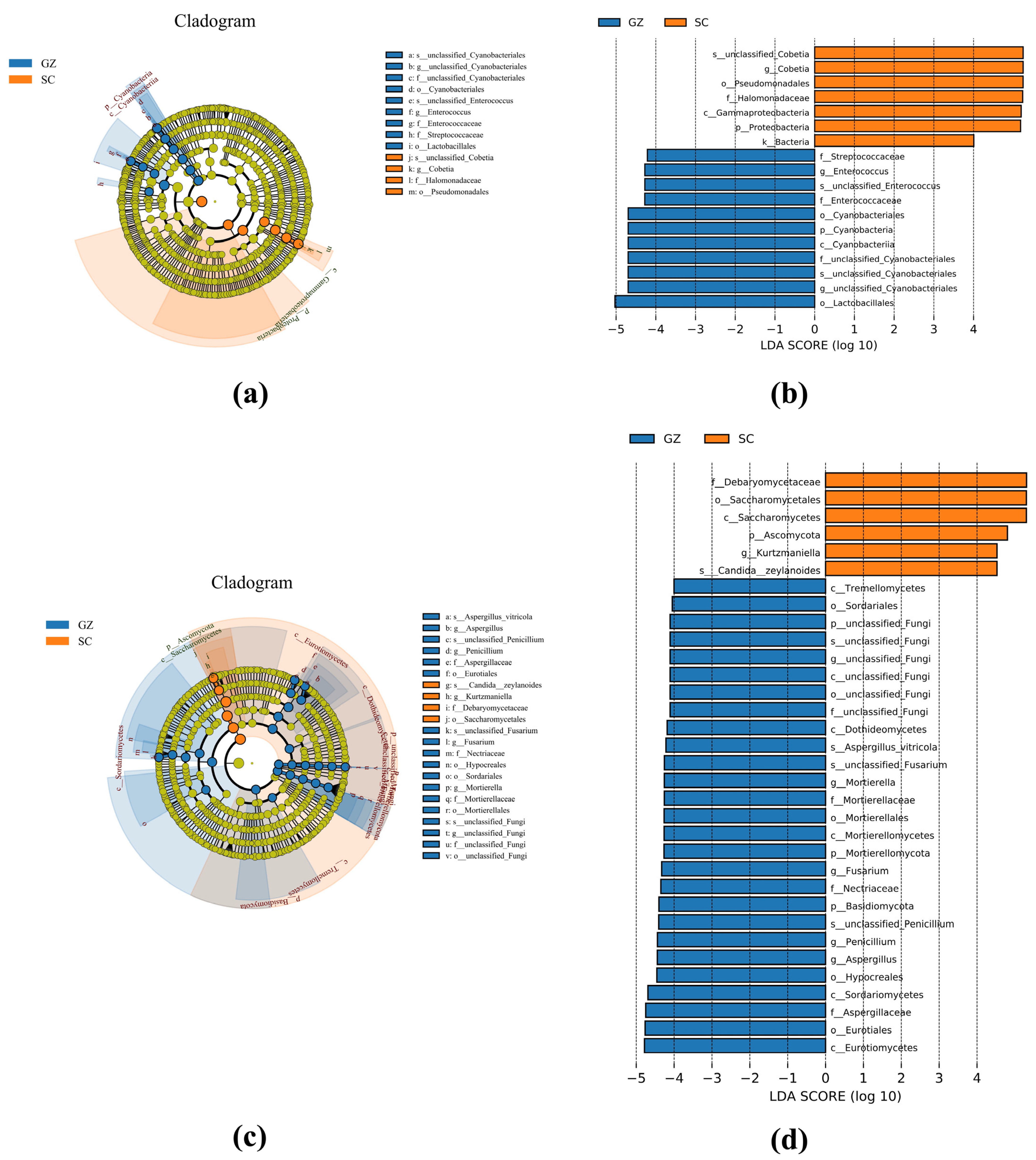
3.5. LEfSe Analysis
Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe), combined with cladogram analysis, was employed to identify microbial biomarkers distinguishing Sichuan and Guizhou sausages (Figure 4). The bacterial biomarkers of the Sichuan sausages were mainly composed of Cobetia and Halomonadaceae. In contrast, Enterococcus, Streptococcaceae, Cyanobacteria, and Lactobacillales were considered biomarkers of the Guizhou sausages (Figure 4a,b). The fungal biomarkers further highlighted that yeasts Debaryomycetaceae, Saccharomycetales, Kurtzmaniella, and Candida zeylanoides were the main biomarkers of the Sichuan sausages. However, the biomarkers of the Guizhou sausages were mainly composed of filamentous molds, such as Aspergillus, Mortierella, Fusarium, and Penicillium (Figure 4c,d).
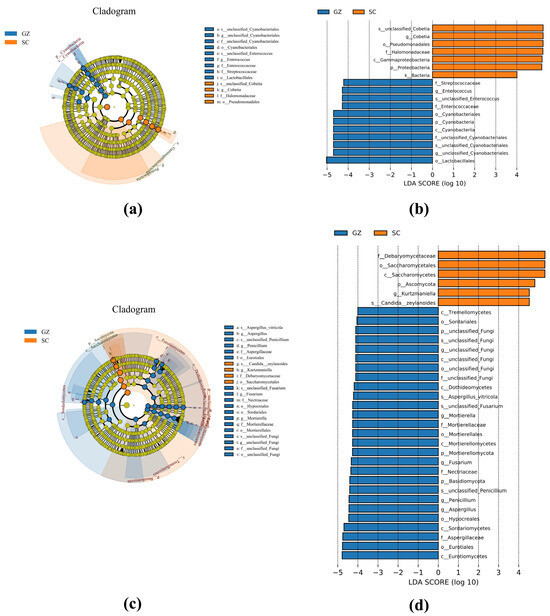
Figure 4.
LEfSe analysis of bacteria (a,b) and fungi (c,d) of two sausage groups. Groups SC and GZ with red and blue colors represent Sichuan and Guizhou sausage samples, respectively.
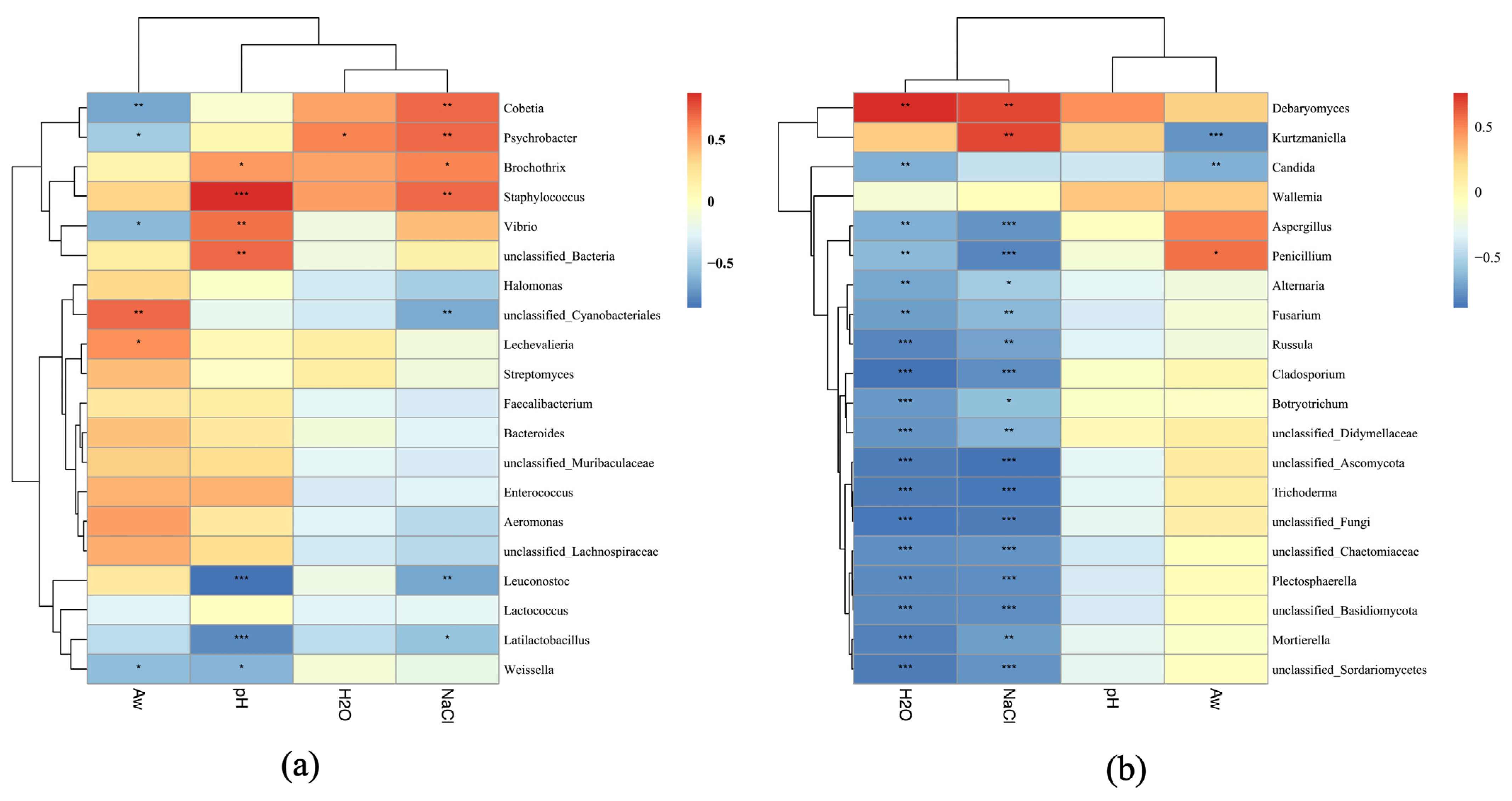
3.6. Correlation Analysis
To further reveal the effects of physiochemical parameters on microbial composition, Spearman’s correlation analysis was conducted between four physicochemical parameters (NaCl, pH, Aw, and moisture) and the top 20 dominating bacterial and fungal taxa (Figure 5). Interestingly, the NaCl content showed positive correlations with the genera Staphylococcus and Cobetia, indicating their adaptation to high-salinity conditions. However, NaCl exhibited negative correlations with unclassified Cyanobacteriales, Leuconostoc, and Latilactobacillus, suggesting inhibitory effects on Cyanobacteria and LAB. Likewise, pH was positively correlated with Vibrio and Brochothrix as well as Staphylococcus, while it was negatively correlated with LAB (Latilactobacillus, Leuconostoc, and Weissella). Aw was positively associated with unclassified Cyanobacteriales, Enterobacter, and Aeromonas (Figure 5a). Furthermore, both NaCl and moisture exhibited positive correlations with Debaryomyces and Kurtzmaniella but negative correlations with filamentous molds including Aspergillus, Penicillium, Mortierella, and Fusarium. The positive correlation between moisture and Debaryomyces implied that the growth of Debaryomyces in sausages is favored by high humidity. Factor Aw showed positive correlations with Penicillium, Aspergillus, and Fusarium, etc., indicating that high water activity facilitates the proliferation of these filamentous molds (Figure 5b).
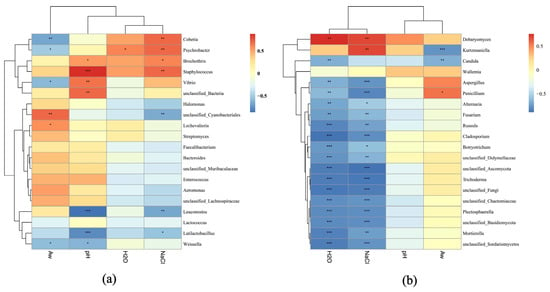
Figure 5.
Correlation analysis between physiochemical parameters and dominant bacteria (a) and fungi (b) from five sausage samples based on Spearman’s algorithm. “*”, “**”, “***” denote significances at the p = 0.05, p = 0.01, p = 0.001 levels, respectively.
4. Discussion
Although the number of sausages was relatively lower and the flavor profile of the sausages was not tested, the present study performed a comparative analysis of the microbial communities of Sichuan and Guizhou sausages at the inter-provincial level. Beneficial and harmful microorganisms were preliminarily revealed. Meanwhile, the combination of the correlation results and geographical information unveiled the factors modifying the microbial composition of sausages.
Beneficial microorganisms, including halotolerant taxa (Staphylococcus, Cobetia, Debaryomyces) and acid-producing bacteria (LAB), exhibited distinctive distribution in Sichuan and Guizhou sausages. These functional microbiota played critical roles in enzyme excretion and flavor development. Consistent with prior studies [18,19], Firmicutes and Proteobacteria were the predominant phyla in both Sichuan and Guizhou sausages. A recent study showed that Proteobacteria the most predominant in Sichuan sausages, followed by Firmicutes. For Cantonese sausages, the dominating phyla included Firmicutes (68.4–80.8%) and Proteobacteria (13.2–18.0%) [20]. In terms of abundance, our findings showed higher values in Cantonese sausages than in Sichuan sausages. At the genus level, Staphylococcus and LAB (Latilactobacillus, Leuconostoc, Weissella, and Lactococcus) were ubiquitously detected in all sausage samples. It is well known that Staphylococcus and LAB are considered functional microorganisms in meat products during the fermentation and ripening periods [21]. Staphylococcus sp., such as S. xylosus and S. carnosus, can excrete protease and lipase to produce polypeptides, free amino acids, and free fatty acids, leading to the synthesis of flavor substances [22,23]. Nitrate-reductase in S. simulans and S. carnosus contributed to redness [24]. S. xylosus exhibited amine oxidase activity, degrading histamine and other biogenic amines [16,25]. This kind of functional genus was not only found in sausages but also other fermented meat products such as dry-curing ham [26], Sichuan smoked bacon [27], and Chinese sour meat [28]. With regard to LAB, Weissella is regarded as a functional LAB because of its useful metabolites such as acids and bacteriocins, which not only contribute to the formation of flavor compounds but also inhibit the growth of pathogens and spoilage microbes. Lactobacillus and Lactococcus were responsible for flavors production in sausages due to protease activity [29]. Hu et al. (2020) observed Leuconostoc dominance in Northeastern Chinese sausages, reinforcing its prevalence across regional styles and supporting our current findings in Guizhou [30]. In terms of application aspect, starters, consisting of Staphylococcus and LAB, reshaped the microbial composition and were facilitated by the production of the desired on-odors, accordingly influencing the quality of sausages [16,31]. For example, inoculation of the starter including Lactobacillus sakei M2 and Staphylococcus xylosus Y4 significantly increased the contents of volatile compounds such as heptanal, octanal, 2-pentanone, and 1-octen-3-ol [32].
Traditionally, the halophilic genus Cobetia inhabits marine environments with high-salinity. Interestingly, Cobetia was obtained from Sichuan sausages characterized by an elevated NaCl content (>5%), mirroring its reported presence in other high-salt fermented meats such as Chinese traditional bacon and dry-cured ham [33,34]. Cobetia contributes to flavor development through enzymatic activity and metabolite synthesis. In Mianning ham, this genus promoted the formation of flavors such as benzaldehyde, 3-methylthio-propanal, trans-2-nonenal, and (E,E)-2,4-decadienal [35,36]. Meanwhile, it also secreted a variety of extracellular hydrolases, such as amylase, lipase, protease, and nuclease, and performed higher hydrolysis activity under high-salinity conditions [37]. Cobetia was positively correlated with five dipeptides and four glycerophospholipids in Chinese bacon [34], which not only contributed to umami flavor but also facilitated biofilm formation via the production of extracellular proteins and polysaccharides. Biofilm further helps Cobetia adapt to high-salt environments like Sichuan sausages [38]. However, the metabolic pathways of Cobetia in meat matrices remain poorly characterized.
Concerning the fungal community in fermented meats, yeasts produce a wide range of esters, higher alcohols, carbonyl compounds, and fatty acid derivatives [39,40]. Molds synthesize volatile compound precursors and flavors as a result of lipolytic and proteolytic activities [41]. Consistent with prior studies on dry sausages [42,43], dominant fungal genera in our study included Debaryomyces, Kurtzmaniella, Aspergillus, Fusarium, Penicillium, and Mortierella. Debaryomyces sp. (e.g., D. hansenii) is indispensable for the fermentation and ripening of dry sausages. This halotolerant yeast stabilizes the redness of fermented sausages due to its ability to degrade peroxides [44]. Regardless of simple in vitro models or complex sausage models, D. hansenii could synthesize volatile compounds in fermented sausages, including esters, acids, branched alcohols, and aldehydes, thus shaping the final volatile profile due to its proteolytic and lipolytic activity [40,45]. As presented in Figure 5, a positive correlation between moisture content and Debaryomyces suggested that the growth of D. hansenii in sausage is favored by high humidity, which was not in agreement with a previous finding reported by Bonaïti [46].
Kurtzmaniella zeylanoides (formerly Candida zeylanoides), a psychrotrophic yeast previously identified in Chinese traditional fermented fish [47], Italian fermented fish sausage [48], and Portuguese cacholeira blood sausage [49], exhibited lipolytic activity [50] and produced flavor compounds such as benzene ethanol and 3-methyl-1-butanol [51]. Furthermore, in the dry fermented sausage models, strains including D. hansenii SH4 and K. C. zeylanoides DQ7 showed significantly positive correlations with volatiles (acetic acid, hexanoic acid, ethanol, phenethyl alcohol, ethyl acetate, and ethyl hexanoate) [52], underscoring their metabolic versatility.
Regarding potential pathogens and spoiling bacteria, since Chinese smoke-cured sausages are produced in an open environment under spontaneous fermentation, Cyanobacteria, Enterococcus, Psychrobacter, Brochothrix, Faecalibacterium, Aeromonas, and Vibrio are generally introduced into sausages during the fermentation and ripening stages. Typically, Cyanobacteria originate from water, soil, or environment. The occurrence of Cyanobacteria was caused by hand-making procedures or unsanitary conditions [15]. Enterococcus faecium has previously been found and isolated from dry fermented sausages [14,19,53]. This species possibly transferred antibiotic resistance genes to Listeria monocytogenes [54]. Meanwhile, E. faecium and E. faecalis produced biogenic amines in dry fermented sausages [55]. Brochothrix, Psychrobacter, Aeromonas, Serratia, Pseudomonas, and Streptococcus were detected from fermented sausages in different regions of China and recognized as spoilage bacteria due to the production of off-odors and off-flavors [19,53]. Overall, Chinese dry fermented sausages are highly susceptible to undesirable pathogenic and spoilage bacteria. In contrast, opportunistic pathogenic and spoilage bacteria merely exist in western sausages due to the use of starters, which was supported by a comparative analysis result [18]. In addition, the inoculation of starters strongly inhibited undesired microorganisms (e.g., Yersinia, Enterobacter, Acinetobacter, Psychrobacter) and off-flavor substances [16,31].
With respect to adverse effects, many filamentous fungi showed an atoxigenic character, while some potential mycotoxin-producing fungi belonged to genera Penicillium, Aspergillus and Fusarium, such as Penicillium nordicum, P. olsonii, P. expansum, P. viridicatum, P. granulatum, P. oxalicum, P. commune, Aspergillus versicolor, A. fischeri, A. ochraceus, and Aspergillus carbonarius [56]. For instance, mycotoxin compound ochratoxin A poses a great risk to human’s health and was primarily produced by P. nordicum in the high Aw condition [57]. Cladosporium oxysporum and Penicillium spp. caused another undesired effect—food spoilage—resulting in the production of off-odors and unpleasant taste [58]. Recently, it was shown that autochthonous microorganism Debaryomyces hansenii and Staphylococcus xylosus in fermented meat products can significantly inhibit the growth of P. nordicum and accordingly reduce the production of ochratoxin A [59,60]. Genera Staphylococcus and Debaryomyces were predominant in the Sichuan and Guizhou sausages, except sample TR, where the abundances of Penicillium and Aspergillus were very low, suggesting a clear inhibitory effect (Figure 2b,d). Meanwhile, Staphylococcus and Debaryomyces are possibly developed as potential sausage starters due to the capacity of flavor production and their antagonistic effect of harmful fungi. With regard to Fusarium, previous studies demonstrated that mycotoxins zearalenone and fumonisins were mainly produced by Fusarium culmorum and Fusarium graminearum. These mycotoxins were distributed in food and feed, posing a risk to animal and human health due to their global propagation and serious economic loss [61,62].
As suggested previously, differences in the microbial communities of other fermented foods, such as traditional Sichuan bacon [63], Tibetan yak jerky [15], and Xinjiang Kazak cheese [64], were attributed to the raw materials, climate conditions, and processing methods. In this case study, from a geographic perspective, although both cities belong to Sichuan Province, Luzhou city is far from Dazhou city, and the climate conditions in winter are different between these two cities. Conversely, Luzhou city and Chishui county are very close, and their climate conditions are also similar (Figure 1). However, the microbial communities, especially the fungal communities, of samples LZ and DZ were highly similar, while the distinction between LZ and CS was significant (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The four physiochemical parameters of samples DZ and LZ were approximate. However, Aw, the water content, and NaCl content of sample CS were much lower than those of two Sichuan sausages (Table 1). Accordingly, the argument that differences in microbial community of sausages between Sichuan sausages and Guizhou sausages are possibly caused by processing conditions such as the addition of salt rather than climate factors is made.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, a comparative analysis of the bacterial and fungal communities in Sichuan and Guizhou sausages was conducted in the present study despite limitations in sample size and flavor profile characterization. The dominating bacteria Staphylococcus and Cobetia, and yeasts Debaryomyces, Kurtzmaniella mainly inhabited Sichuan sausages. However, acid-tolerant lactic acid bacteria (Lactococcus, Leuconostoc, Weissella, and Lactobacillus) and molds (Aspergillus, Mortierella, Fusarium, and Penicillium) were largely distributed in Guizhou sausages, especially TR. Integrative analysis of geographic, climatic, and physiochemical data suggested that the discrepancy in the microbial composition of sausages from Sichuan and Guizhou provinces was possibly attributed to the processing conditions (salt addition) rather than climate. Key beneficial microbiota (e.g., Staphylococcus, Debaryomyces, Cobetia, LAB) and potential harmful microbes (Cyanobacteria, Enterococcus, Penicillium, Aspergillus and Fusarium) were identified, which are facilitated by the development of novel starters composed of defined functional microorganisms. Subsequently, isolating functional strains and characterizing flavor profiles are required in further studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z.; methodology, X.Z.; formal analysis, Q.L. and X.Z.; investigation, X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Z.; writing—review and editing, W.C., C.W., D.L. and Q.L.; visualization, D.L. and Q.L.; supervision, X.Z.; project administration, W.C.; funding acquisition, X.Z., C.W., D.L. and Q.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Liquor Making Biological Technology and Application of key laboratory of Sichuan Province (NJ2024-06), the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Projects (ZK [2022] 114, ZK [2023] 088), and the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (2025ZNSFSC0292).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article, the raw sequences data can be acquired in SRA database with accession No. PRJNA870249. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The bioinformatic analysis was performed on the BioMarker cloud platform.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| HTS | High-throughput sequencing |
| ITS | Internal transcribed spacer |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic unit |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
References
- Oliveira, M.; Ferreira, V.; Magalhães, R.; Teixeira, P. Biocontrol strategies for Mediterranean-style fermented sausages. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, M.; Piornos, J.A. Fermented meat sausages and the challenge of their plant-based alternatives: A comparative review on aroma-related aspects. Meat Sci. 2021, 182, 108636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ji, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Bai, T.; Hou, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; et al. A review: Microbial diversity and function of fermented meat products in China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 645435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocolin, L.; Dolci, P.; Rantsiou, K.; Urso, R.; Cantoni, C.; Comi, G. Lactic acid bacteria ecology of three traditional fermented sausages produced in the North of Italy as determined by molecular methods. Meat Sci. 2009, 82, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.H.; Tahon, G.; Geesink, P.; Sousa, D.Z.; Ettema, T.J.G. Innovations to culturing the uncultured microbial majority. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.H.T.; Kim, J. Cultivation of unculturable soil bacteria. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaiotta, G.; Pennacchia, C.; Ercolini, D.; Moschetti, G.; Villani, F. Combining denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of 16S rDNA V3 region and 16S-23S rDNA spacer region polymorphism analyses for the identification of staphylococci from Italian fermented sausages. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 26, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocolin, L.; Manzano, M.; Aggio, D.; Cantoni, C.; Comi, G. A novel polymerase chain reaction (PCR)—Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) for the identification of Micrococcaceae strains involved in meat fermentations. Its application to naturally fermented Italian sausages. Meat Sci. 2001, 58, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, H.C.P.; Henriques, I.; Correia, A.C.M.; Hogg, T.A.; Teixeira, P. Characterization of microbial population of ‘Alheira’ (a traditional Portuguese fermented sausage) by PCR-DGGE and traditional cultural microbiological methods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 2187–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, C.; Vignolo, G.; Cocconcelli, P.S. PCR-DGGE analysis for the identification of microbial populations from Argentinean dry fermented sausages. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 63, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ji, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Li, K.; Xu, C.; Jiang, C. The effects of starter cultures and plant extracts on the biogenic amine accumulation in traditional Chinese smoked horsemeat sausages. Food Control 2015, 50, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Yu, Q.; Chen, S.; He, L.; et al. Investigation of diverse bacteria encoding histidine decarboxylase gene in Sichuan-style sausages by culture-dependent techniques, polymerase chain reaction–denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis, and high-throughput sequencing. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2021, 139, 110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; He, L.; Li, C. Determination of bacterial community and its correlation to volatile compounds in Guizhou Niuganba, a traditional Chinese fermented dry-cured beef. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2022, 161, 113380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H. Unraveling microbial community diversity and succession of Chinese Sichuan sausages during spontaneous fermentation by high-throughput sequencing. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3254–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, R.; Lv, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. High-throughput sequencing approach to reveal the bacterial diversity of traditional yak jerky from the Tibetan regions. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X. Effect of a compound starter cultures inoculation on bacterial profile and biogenic amine accumulation in Chinese Sichuan sausages. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.; Xiong, Y. Two efficient nitrite-reducing Lactobacillus strains isolated from traditional fermented pork (Nanx Wudl) as competitive starter cultures for Chinese fermented dry sausage. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhan, Y. Comparison of bacterial diversity profiles and microbial safety assessment of salami, Chinese dry-cured sausage and Chinese smoked-cured sausage by high-throughput sequencing. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2018, 90, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, M.; Chen, X.H.; Dong, M.S. Comparative analysis of the bacterial diversity of Chinese fermented sausages using high-throughput sequencing. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2021, 150, 111975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, F.; Qu, D.; Wan, T.; Xi, L.; Hu, C.Y. Aroma characterization of Sichuan and Cantonese sausages using electronic nose, gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, gas chromatography-olfactometry, odor activity values and metagenomic. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjo, M.; Potes, M.E.; Elias, M. Role of starter cultures on the safety of fermented meat products. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Xia, X.; Liu, Q.; Sun, F.; Kong, B. Flavour formation from hydrolysis of pork meat protein extract by the protease from Staphylococcus carnosus isolated from Harbin dry sausage. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2022, 163, 113525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Fu, L. High-throughput sequencing-based characterization of the predominant microbial community associated with characteristic flavor formation in Jinhua Ham. Food Microbiol. 2021, 94, 103643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gøtterup, J.; Olsen, K.; Knøchel, S.; Tjener, K.; Stahnke, L.H.; Møller, J.K.S. Colour formation in fermented sausages by meat-associated staphylococci with different nitrite- and nitrate-reductase activities. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, T.; Li, J.; Zhu, W. Effects of inoculation of commercial starter cultures on the quality and histamine accumulation in fermented sausages. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, M377–M383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, S.; Chen, G.; Zheng, Z.; Ren, R.; Liao, G. Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties and microbial community structure in five types of Yunnan dry-cured hams. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2025, 215, 117293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, W.; Wen, P. Effects of storage methods on the microbial community and quality of Sichuan smoked bacon. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2022, 158, 113115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Li, T.; Liu, K.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Peng, C.; Li, Z. Correlations between microbiota succession and volatile profiles development and biogenic amine formation involved in the ripening of Chinese sour meat. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2025, 215, 117238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wen, R.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Technological characterization and flavor-producing potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional dry fermented sausages in northeast China. Food Microbiol. 2022, 106, 104059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. The potential correlation between bacterial diversity and the characteristic volatile flavour of traditional dry sausages from Northeast China. Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Xie, T.; Li, P. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum and Staphylococcus xylosus on flavour development and bacterial communities in Chinese dry fermented sausages. Food Res. Int. 2020, 135, 109247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, K.; Li, C.; Xu, B. Microbiota dynamics and volatile metabolite generation during sausage fermentation. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Su, W.; Mu, Y.; Jiang, L. Combined application of high-throughput sequencing and metabolomics reveals metabolically active microorganisms during Panxian ham processing. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Han, Q.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, K.; Li, X.; Xu, B. Comprehensive insights into the evolution of microbiological and metabolic characteristics of the fat portion during the processing of traditional Chinese bacon. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 110987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Ji, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Bai, T.; Gan, L.; Chen, L. Comparative studies on physicochemical properties, volatile flavor substances and microbial community of Mianning ham at different altitudes. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1536749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gan, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Ji, L.; Chen, L. Study on the changes and correlation of microorganisms and flavor in different processing stages of Mianning ham. Foods 2024, 13, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, T. Extracellular hydrolytic enzyme screening of culturable heterotrophic bacteria from deep-sea sediments of the Southern Okinawa Trough. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wuertz, S. Bacteria and archaea on Earth and their abundance in biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzialo, M.C.; Park, R.; Steensels, J.; Lievens, B.; Verstrepen, K.J. Physiology, ecology and industrial applications of aroma formation in yeast. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41 (Suppl. 1), S95–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, M.; Corral, S.; Cano-García, L.; Salvador, A.; Belloch, C. Yeast strains as potential aroma enhancers in dry fermented sausages. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 212, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunesen, L.O.; Stahnke, L.H. Mould starter cultures for dry sausages-selection, application and effects. Meat Sci. 2003, 65, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleggia, L.; Ferrocino, I.; Reale, A.; Haouet, M.N.; Corvaglia, M.R.; Milanović, V.; Boscaino, F.; Di Renzo, T.; Di Bella, S.; Borghi, M.; et al. Unravelling microbial populations and volatile organic compounds of artisan fermented liver sausages manufactured in Central Italy. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 111019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, R.; Sun, F.; Li, X.-A.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. The potential correlations between the fungal communities and volatile compounds of traditional dry sausages from Northeast China. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, H.; Yen, Y.; Ku, M.S.B. Characterization of a salt-induced DhAHP, a gene coding for alkyl hydroperoxide reductase, from the extremely halophilic yeast Debaryomyces hansenii. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, M.A.; Marongiu, A.; Aponte, M.; Blaiotta, G.; Deiana, P.; Mangia, N.P. Impact of a selected Debaryomyces hansenii strain’s inoculation on the quality of Sardinian fermented sausages. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaïti, C.; Leclercq-Perlat, M.N.; Latrille, E.; Corrieu, G. Deacidification by Debaryomyces hansenii of smear soft cheeses ripened under controlled conditions: Relative humidity and temperature influences. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 3976–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W.; Yu, D.; Gao, P.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, F. Dynamics and diversity of microbial community succession during fermentation of Suan yu, a Chinese traditional fermented fish, determined by high throughput sequencing. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleggia, L.; Ferrocino, I.; Rita Corvaglia, M.; Cesaro, C.; Milanović, V.; Cardinali, F.; Garofalo, C.; Cocolin, L.; Aquilanti, L.; Osimani, A. Profiling of autochthonous microbiota and characterization of the dominant lactic acid bacteria occurring in fermented fish sausages. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 110990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleggia, L.; Ferrocino, I.; Reale, A.; Boscaino, F.; Di Renzo, T.; Corvaglia, M.R.; Cocolin, L.; Milanović, V.; Cardinali, F.; Garofalo, C.; et al. Portuguese cacholeira blood sausage: A first taste of its microbiota and volatile organic compounds. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, L.M.; Padilla, B.; Belloch, C.; Vignolo, G. Diversity and enzymatic profile of yeasts isolated from traditional llama meat sausages from north-western Andean region of Argentina. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, R.; Chen, X.; Xiong, S.; Qi, B.; Li, J.; Qiao, X.; Chen, W.; Qu, C.; Wang, S. Predominant yeasts in Chinese Dong fermented pork (Nanx Wudl) and their aroma-producing properties in fermented sausage condition. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Yin, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Technological properties and flavour formation potential of yeast strains isolated from traditional dry fermented sausages in Northeast China. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2022, 154, 112853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Huang, X.; Qiao, M.; He, R.K.; Song, L. Microbial diversity of representative traditional fermented sausages in different regions of China. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.; Holley, R.A. Transfer of antibiotic resistance from Enterococcus faecium of fermented meat origin to Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komprda, T.; Sládková, P.; Petirová, E.; Dohnal, V.; Burdychová, R. Tyrosine- and histidine-decarboxylase positive lactic acid bacteria and enterococci in dry fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidari, R.; Tofalo, R. Dual role of yeasts and filamentous fungi in fermented sausages. Foods 2024, 13, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, J.; Rondan, J.J.; Nunez, F.; Rodriguez, A. Influence of an industrial dry-fermented sausage processing on ochratoxin A production by Penicillium nordicum. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 339, 109016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Ojalvo, D.; Rodriguez, A.; Cordero, M.; Bernaldez, V.; Reyes-Prieto, M.; Cordoba, J.J. Characterisation and detection of spoilage mould responsible for black spot in dry-cured fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncero, E.; Andrade, M.J.; Álvarez, M.; Cebrián, E.; Rodríguez, M. Debaryomyces hansenii reduces ochratoxin A production by Penicillium nordicum on dry-cured ham agar through volatile compounds. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2024, 213, 117030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrián, E.; Núñez, F.; Álvarez, M.; Roncero, E.; Rodríguez, M. Biocontrol of ochratoxigenic Penicillium nordicum in dry-cured fermented sausages by Debaryomyces hansenii and Staphylococcus xylosus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 375, 109744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, S.; Longobardi, C.; Ferrara, G.; Piscopo, N.; Riccio, L.; Russo, V.; Meucci, V.; De Marchi, L.; Esposito, L.; Florio, S.; et al. Oxidative status and histological evaluation of wild boars’ tissues positive for zearalenone contamination in the campania region, southern Italy. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartinger, T.; Grabher, L.; Pacífico, C.; Angelmayr, B.; Faas, J.; Zebeli, Q. Short-term exposure to the mycotoxins zearalenone or fumonisins affects rumen fermentation and microbiota, and health variables in cattle. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 162, 112900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Pan, W.; Liu, A.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Zou, L. Evaluation of Bacterial Diversity and Quality Features of Traditional Sichuan Bacon from Different Geographical Region. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, F.; Li, K.; Shi, X.; Ni, Y.; Li, B.; Zhuge, B. Evaluating the microbial ecology and metabolite profile in Kazak artisanal cheeses from Xinjiang, China. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).