Deciphering Escherichia coli ESBL/pAmpC Plasmids Through High-Throughput Third-Generation Sequencing and Hybrid Assembly
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates
2.2. Library Preparation and Whole-Genome Sequencing
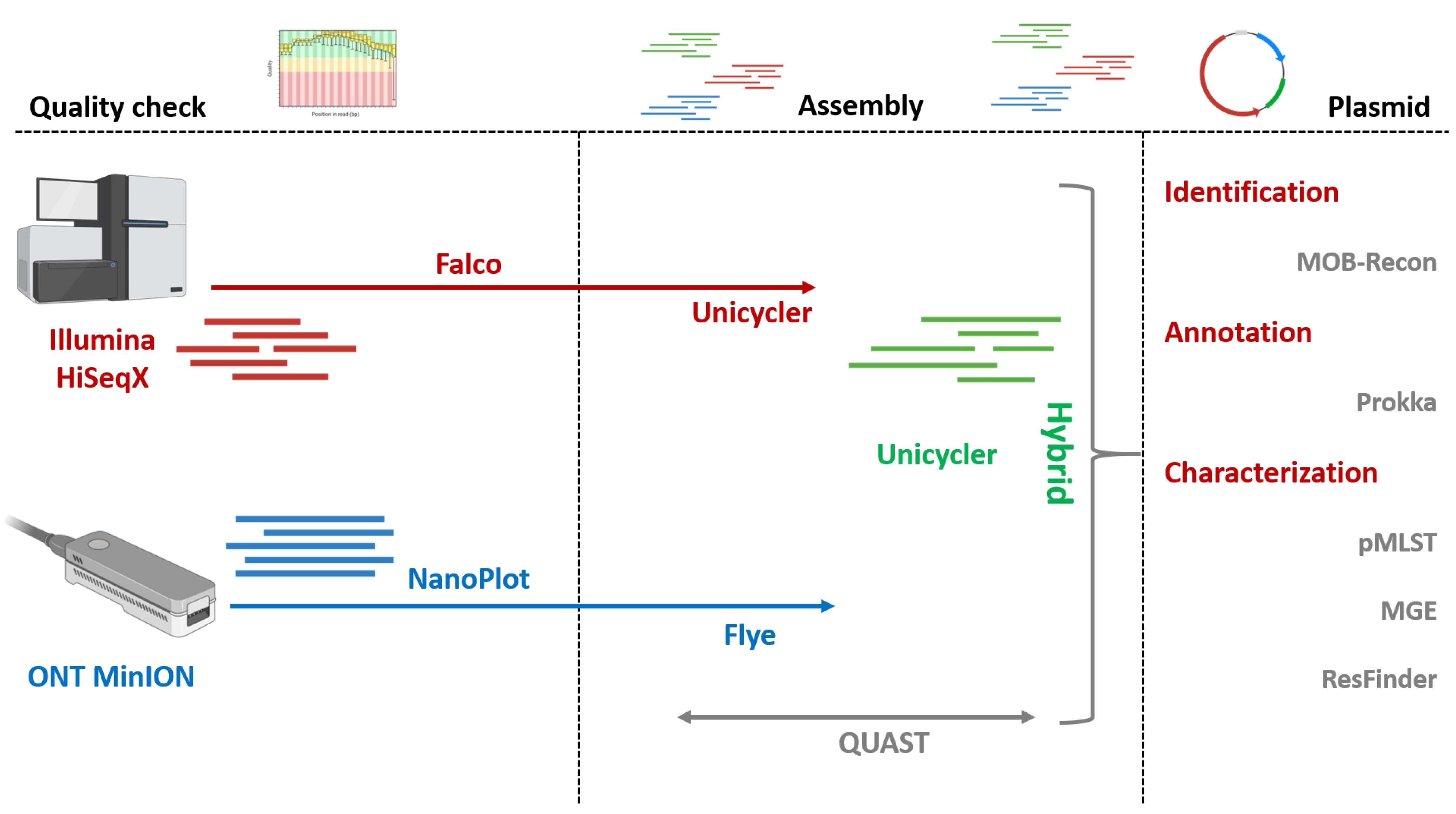
2.3. Raw Reads Quality Control
2.4. Bacterial and Plasmid Whole-Genome Assembly
2.5. Identification, Annotation, and Characterization of ESBL/pAmpC-Carrying Plasmids
2.6. Resistance and Virulence Genes Detection
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Statistics of Short and Long Reads
3.2. Performances of Short, Long, and Hybrid Assemblies
3.3. Identification, Annotation and Characterization of ESBL/pAmpC-Carrying Plasmids in Short, Long, and Hybrid Assemblies
3.4. Identification of Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors in Short, Long and Hybrid Assemblies
3.5. Characterization of Other Plasmids in Short, Long and Hybrid Assemblies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3GCs | Third-generation cephalosporins |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| AmpCs | AmpC β-lactamases |
| ARGs | Antimicrobial resistance genes |
| bp | Base pairs |
| CC | Clonal complex |
| CDS | Coding DNA sequence |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| CTX-EMB | Cefotaxime Eosin Methylene Blue |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| EMB | Eosin Methylene Blue |
| ESBLs | Extended-spectrum β-lactamases |
| HGT | Horizontal gene transfer |
| IS | Insertion sequence |
| kb | Kilobase pairs |
| MGEs | Mobile genetic elements |
| N50 | Assembly contiguity statistic |
| NA | Not assigned/applicable |
| ONT | Oxford Nanopore Technologies |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| pMLST | Plasmid multilocus sequence typing |
| pST | Plasmid sequence type |
| Q | Quality score (Phred) |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| ST | Sequence type |
| Tn | Transposon |
| VF | Virulence factor |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
References
- Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Wang, J.; Han, B.; Tao, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Bacterial Resistance to Antibacterial Agents: Mechanisms, Control Strategies, and Implications for Global Health. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 860, 160461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghnieh, R.; Estaitieh, N.; Mugharbil, A.; Jisr, T.; Abdallah, D.I.; Ziade, F.; Sinno, L.; Ibrahim, A. Third Generation Cephalosporin Resistant Enterobacteriaceae and Multidrug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria Causing Bacteremia in Febrile Neutropenia Adult Cancer Patients in Lebanon, Broad Spectrum Antibiotics Use as a Major Risk Factor, and Correlation with Poor Prognosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, R. Growing Group of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases: The CTX-M Enzymes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A. Plasmids and the Spread of Resistance. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebana, E.; Carattoli, A.; Coque, T.M.; Hasman, H.; Magiorakos, A.-P.; Mevius, D.; Peixe, L.; Poirel, L.; Schuepbach-Regula, G.; Torneke, K.; et al. Public Health Risks of Enterobacterial Isolates Producing Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases or AmpC β-Lactamases in Food and Food-Producing Animals: An EU Perspective of Epidemiology, Analytical Methods, Risk Factors, and Control Options. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trongjit, S.; Chuanchuen, R. Whole Genome Sequencing and Characteristics of Escherichia coli with Co-Existence of ESBL and mcr Genes from Pigs. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvegna, M.; Tomassone, L.; Christensen, H.; Olsen, J.E. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) Analysis of Virulence and AMR Genes in Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Escherichia coli from Animal and Environmental Samples in Four Italian Swine Farms. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, N.; Shaw, L.P.; Hubbard, A.; George, S.; Sanderson, N.D.; Swann, J.; Wick, R.; AbuOun, M.; Stubberfield, E.; Hoosdally, S.J.; et al. Comparison of Long-Read Sequencing Technologies in the Hybrid Assembly of Complex Bacterial Genomes. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.; Pankhurst, L.; Hubbard, A.; Votintseva, A.; Stoesser, N.; Sheppard, A.E.; Mathers, A.; Norris, R.; Navickaite, I.; Eaton, C.; et al. Resolving Plasmid Structures in Enterobacteriaceae Using the MinION Nanopore Sequencer: Assessment of MinION and MinION/Illumina Hybrid Data Assembly Approaches. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, H.; McCarthy, M.C.; Nnajide, C.R.; Sparrow, J.; Rubin, J.E.; Dillon, J.-A.R.; White, A.P. Identification of Plasmids in Avian-Associated Escherichia coli Using Nanopore and Illumina Sequencing. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolakos, I.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Fasolato, L.; Piccirillo, A. Assessing the Occurrence and Transfer Dynamics of ESBL/pAmpC-Producing Escherichia coli Across the Broiler Production Pyramid. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; ISBN 156238838X. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolakos, I.; Feudi, C.; Eichhorn, I.; Palmieri, N.; Fasolato, L.; Schwarz, S.; Piccirillo, A. High-Resolution Characterisation of ESBL/pAmpC-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from the Broiler Production Pyramid. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandine, G.d.S.; Smith, A.D. Falco: High-Speed FastQC Emulation for Quality Control of Sequencing Data. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coster, W.; Rademakers, R. NanoPack2: Population-Scale Evaluation of Long-Read Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coster, W.; D’Hert, S.; Schultz, D.T.; Cruts, M.; Van Broeckhoven, C. NanoPack: Visualizing and Processing Long-Read Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2666–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving Bacterial Genome Assemblies from Short and Long Sequencing Reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yuan, J.; Kolmogorov, M.; Shen, M.W.; Chaisson, M.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of Long Error-Prone Reads Using de Bruijn Graphs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8396–E8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheenko, A.; Prjibelski, A.; Saveliev, V.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A. Versatile Genome Assembly Evaluation with QUAST-LG. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i142–i150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; Nash, J.H.E. MOB-Suite: Software Tools for Clustering, Reconstruction and Typing of Plasmids from Draft Assemblies. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernandez, A.; Larsen, M.V.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.H.K.; Bortolaia, V.; Tansirichaiya, S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Roberts, A.P.; Petersen, T.N. Detection of Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella enterica Using a Newly Developed Web Tool: MobileElementFinder. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 76, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for Predictions of Phenotypes from Genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydenham, T.V.; Overballe-Petersen, S.; Hasman, H.; Wexler, H.; Kemp, M.; Justesen, U.S. Complete Hybrid Genome Assembly of Clinical Multidrug-Resistant Bacteroides fragilis Isolates Enables Comprehensive Identification of Antimicrobial-Resistance Genes and Plasmids. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, A.; Avershina, E.; Ahmad, R. Hybrid Assembly Provides Improved Resolution of Plasmids, Antimicrobial Resistance Genes, and Virulence Factors in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxt, A.M.; Avershina, E.; Frye, S.A.; Naseer, U.; Ahmad, R. Rapid Identification of Pathogens, Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Plasmids in Blood Cultures by Nanopore Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, O.; Chueiri, A.; O’Connor, L.; Lahiff, S.; Burke, L.; Morris, D.; Pfeifer, N.M.; Santamarina, B.G.; Berens, C.; Menge, C.; et al. Portable Differential Detection of CTX-M ESBL Gene Variants, blaCTX-M-1 and blaCTX-M-15, from Escherichia coli Isolates and Animal Fecal Samples Using Loop-Primer Endonuclease Cleavage Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03316-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, C.; Hall, R. IS26-Mediate Formation of Transposons Carrying Antibiotic Resistance Genes. mSphere 2016, 1, e00038-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, L.; Cárdenas, P.; Graham, J.P.; Trueba, G. IS26 Drives the Dissemination of blaCTX-M Genes in an Ecuadorian Community. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e02504-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, S.; Li, D.; Gillings, M.R.; Ren, H.; Mao, D.; Guo, J.; Luo, Y. Inter-Plasmid Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes Accelerates Antibiotic Resistance in Bacterial Pathogens. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrad032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Qin, X.; Yue, M.; Wu, L.; Li, N.; Su, J.; Jiang, M. IS26 Carrying blaKPC−2 Mediates Carbapenem Resistance Heterogeneity in Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Clinical Sites. Mob. DNA 2025, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boostrom, I.; Portal, E.A.R.; Spiller, O.B.; Walsh, T.R.; Sands, K. Comparing Long-Read Assemblers to Explore the Potential of a Sustainable Low-Cost, Low-Infrastructure Approach to Sequence Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria with Oxford Nanopore Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 796465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Kastanis, G.J.; Timme, R.; Roberson, D.; Balkey, M.; Tallent, S.M. Closed Genome Sequences of 28 Foodborne Pathogens from the CFSAN Verification Set, Determined by a Combination of Long and Short Reads. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00152-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Strain | Sample-Type | Production Stage | Phylogroup | Sequence Type (ST) | Serotype | ESBL/pAmpC Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC-7 | cloacal swab | breeders | C | 88 | O8:H4 | blaCMY-2 |
| EC-33 | cloacal swab | breeders | A | 695 | H38 | blaTEM-52B |
| EC-40 | cloacal swab | broiler-chicks | B1 | 155 | O120:H51 | blaSHV-12 |
| EC-56 | cloacal swab | broilers | D | 38 | H15 | blaCTX-M-1 |
| EC-78 | cloacal swab | broilers | A | 4980 | O88:H7 | blaCTX-M-2 |
| EC-91 | carcass | carcass | D | 69 | O15:H18 | blaCTX-M-15 |
| EC-94 | carcass | carcass | A | 4937 | O126:H38 | blaCTX-M-1 |
| EC-115 | carcass | carcass | A | 3107 | O98:H12 | blaCTX-M-1 |
| MinION | Illumina | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Name | Read Length N50 (bp) | Mean Quality Read (Q) | Number of Reads | Total (bp) | Coverage | Number of Reads | Total (bp) | Mean Read Quality | Coverage |
| EC-7 | 2950 | 10.4 | 241,235 | 295,518,677 | 58.15 | 2,124,877 | 318,731,588 | 32.2 | 62.72 |
| EC-33 | 1019 | 17.9 | 1,723,479 | 792,066,859 | 155.9 | 8,684,972 | 1,302,745,812 | 38.9 | 256.3 |
| EC-40 | 3802 | 10.6 | 276,487 | 443,816,606 | 87.3 | 6,253,992 | 938,098,804 | 37.1 | 184.6 |
| EC-56 | 7930 | 10.5 | 173,356 | 377,261,099 | 74.2 | 9,190,283 | 1,378,542,592 | 37.9 | 271.3 |
| EC-78 | 1826 | 10.5 | 292,564 | 293,709,850 | 57.8 | 5,779,896 | 866,984,404 | 38.0 | 170.6 |
| EC-91 | 4880 | 10.6 | 584,008 | 1,252,722,910 | 246.5 | 9,143,314 | 1,371,497,130 | 37.7 | 269.9 |
| EC-94 | 3506 | 10.5 | 271,096 | 506,846,144 | 99.7 | 7,078,484 | 1,061,772,709 | 37.5 | 208.9 |
| EC-115 | 1018 | 10.5 | 304,842 | 216,993,948 | 42.7 | 9,640,675 | 1,446,101,361 | 37.9 | 284.6 |
| Mean | 3366.4 | 11.4 | 483,383.4 | 522,367,011.6 | 102.8 | 7,237,062 | 1,085,559,300 | 36.9 | 213.6 |
| SD | 2295.9 | 2.6 | 515,319.1 | 344,470,921.0 | 67.8 | 2,523,376.8 | 378,506,526.8 | 1.8 | 74.5 |
| Illumina | MinION | Hybrid | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLST | MLST | MLST | ||||||||||
| Sample Name | IncType | Circular | pST | CC | IncType | Circular | pST | CC | IncType | Circular | pST | CC |
| EC-7 | IncA/C2 | N | 3 | - | IncA/C2 | Y | 3 | NA | IncA/C2 | Y | 3 | - |
| EC-33 | IncX1 | Y | NA | NA | IncX1 | Y | NA | NA | IncX1 | Y | NA | NA |
| EC-40 | IncI1 | N | 26 | 2 | IncI1 | N | 26 * | NA | IncI1 | N | New | 26 |
| EC-56 | IncI2 | N | NA | NA | IncI2 | N | NA | NA | IncI2 | Y | NA | NA |
| EC-78 | IncHI2 | N | 4 | - | IncHI2 | N | 11 * | NA | IncHI2 | Y | 4 | - |
| EC-91 | IncY | N | NA | NA | IncY | N | NA | NA | IncY | N | NA | NA |
| EC-94 | Unknown | N | NA | NA | IncFII | N | Failed | Failed | IncFII | N | Failed | Failed |
| EC-115 | IncI1 | N | 80 | 31 | IncFI1 | N | New * | NA | IncI1 | N | 80 | 31 |
| Illumina | MinION | Hybrid | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Name | ESBL/pAmpC | IS/Tn | Other ARGs | ESBL/pAmpC | IS/Tn | Other ARGs | ESBL/pAmpC | IS/Tn | Other ARGs |
| EC-7 | blaCMY-2 | ISEc9 | tet(A), sul2, aph(6)-Id, floR, aph(3”), qacE, sul1, aac(3)-Vla, qacL, sul3 *, aadA2b *, cmlA1 * | blaCMY-2 | ISEc9 | tet(A), sul2, aph(6)-Id, qacE, floR, aadA1, aph(3”), sul1, aac(3)-Vla | blaCMY-2 | ISEc9 | tet(A), sul2, aph(6)-Id, qacE, florR, aadA1, aph(3”)-Ib, sul1, aac(3)-Vla |
| EC-33 | blaTEM-52B | Tn2 | none | blaTEM-52B | Tn2 | none | blaTEM-52B | Tn2 | none |
| EC-40 | blaSHV-12 | IS26 | sul3, aadA1, qacL, aadA2b, cmlA, tet(A) | blaSHV-12 | IS26 | sul3, aadA1, tet(A), qacL, aadA2b, cmla1 | blaSHV-12 | IS26 | sul3, aadA1, tet(A), qacL, aadA2b, cmla1 |
| EC-56 | blaCTX-M-1 | None | none | blaCTX-M-1 | IS102 | none | blaCTX-M-1 | IS102 | none |
| EC-78 | blaCTX-M-2 | None | dfrA1, aph(6)-Id, qacE, sul1, tet(A), aph(3”)-Ib, aadA1, sul2, blaTEM-1 | blaCTX-M-2 | IS26 | dfrA1, aadA1, aph(6)-Id, qacE, sul1, tet(A), aph(3”)-Ib, sul2, blaTEM-1 | blaCTX-M-2 | IS26 | dfrA1, aadA1, aph(6)-Id, qacE, sul1, tet(A), aph(3”)-Ib, sul2, blaTEM-1 |
| EC-91 | blaCTX-M-15 | ISEc9 | blaTEM-1, sul2, aph(6)-Id, aph(3”)-Ib, qnrS1, tet(A) | blaCTX-M-15 | ISEc9 | blaTEM-1, sul2, aph(6)-Id, aph(3”)-Ib, qnrS1, tet(A) | blaCTX-M-15 | ISEc9 | blaTEM-1, sul2, aph(6)-Id, aph(3”)-Ib, qnrS1, tet(A) |
| EC-94 | blaCTX-M-1 | None | mph(A) | blaCTX-M-1 | Cn_5325_IS26 | mph(A) | blaCTX-M-1 | Cn_5325_IS26 | mph(A) |
| EC-115 | blaCTX-M-1 | None | aac(3)-IId, dfrA14 | blaCTX-M-1 | IS26 | dfrA14, aac(3)-IId | blaCTX-M-1 | IS26 | dfrA14, aac(3)-IId |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laconi, A.; Ovedani, E.; Tolosi, R.; Apostolakos, I.; Piccirillo, A. Deciphering Escherichia coli ESBL/pAmpC Plasmids Through High-Throughput Third-Generation Sequencing and Hybrid Assembly. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101039
Laconi A, Ovedani E, Tolosi R, Apostolakos I, Piccirillo A. Deciphering Escherichia coli ESBL/pAmpC Plasmids Through High-Throughput Third-Generation Sequencing and Hybrid Assembly. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101039
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaconi, Andrea, Enea Ovedani, Roberta Tolosi, Ilias Apostolakos, and Alessandra Piccirillo. 2025. "Deciphering Escherichia coli ESBL/pAmpC Plasmids Through High-Throughput Third-Generation Sequencing and Hybrid Assembly" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101039
APA StyleLaconi, A., Ovedani, E., Tolosi, R., Apostolakos, I., & Piccirillo, A. (2025). Deciphering Escherichia coli ESBL/pAmpC Plasmids Through High-Throughput Third-Generation Sequencing and Hybrid Assembly. Pathogens, 14(10), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101039







