The Tribological Behavior of Electron Beam Powder Bed Fused Ti-6Al-4V: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
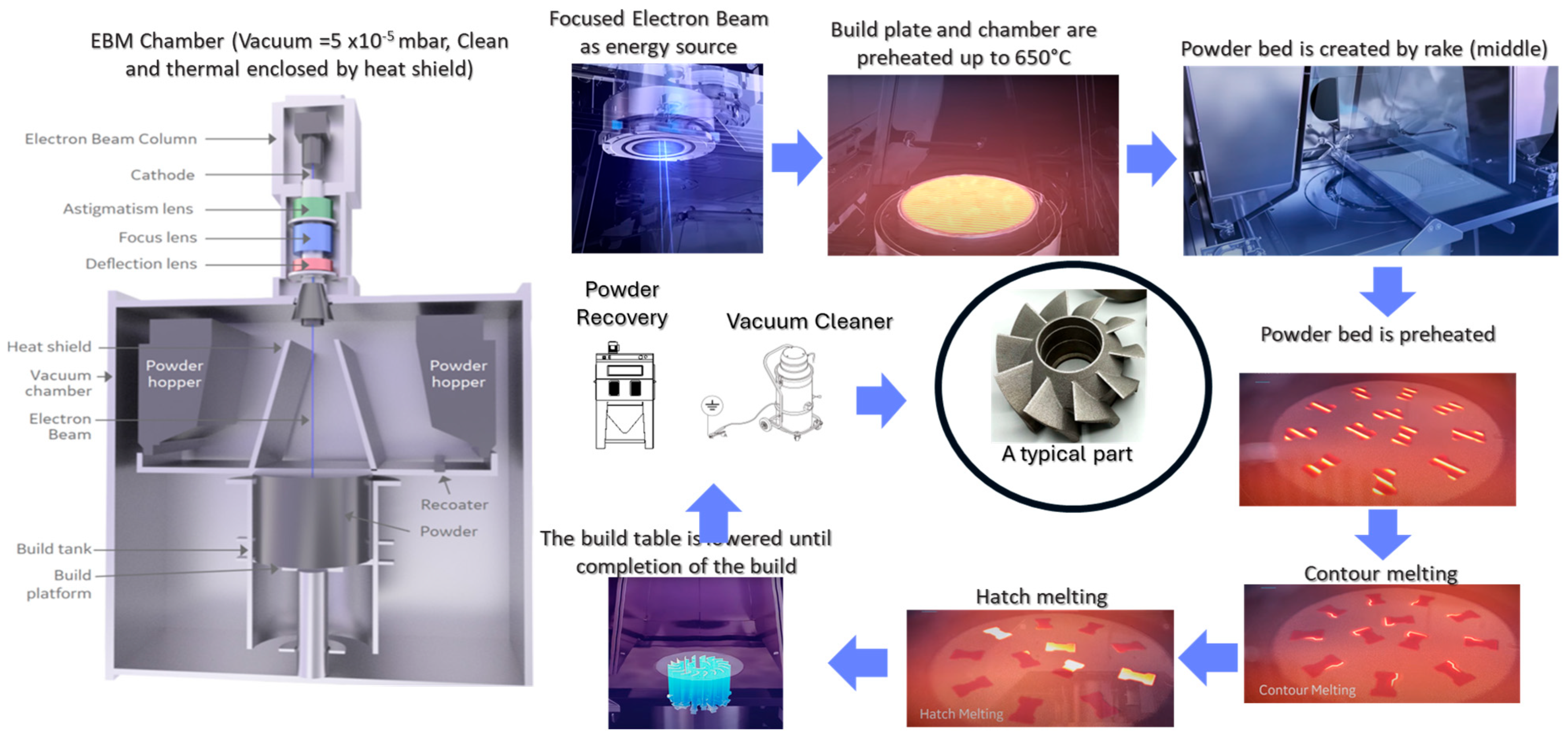
2. EB-PBF Process
3. Tribological Theories and Tribological Studies of EB-PBF Ti-6Al-4V
3.1. Sliding Wear
3.1.1. Block-on-Ring Test
3.1.2. Pin-on-Disc Test
3.1.3. Ball-on-Disc Test
3.1.4. Abrasive Wheel and Rotary Abrasion Test
3.1.5. Scratch Test
3.1.6. Cylinder-on-Plate Test
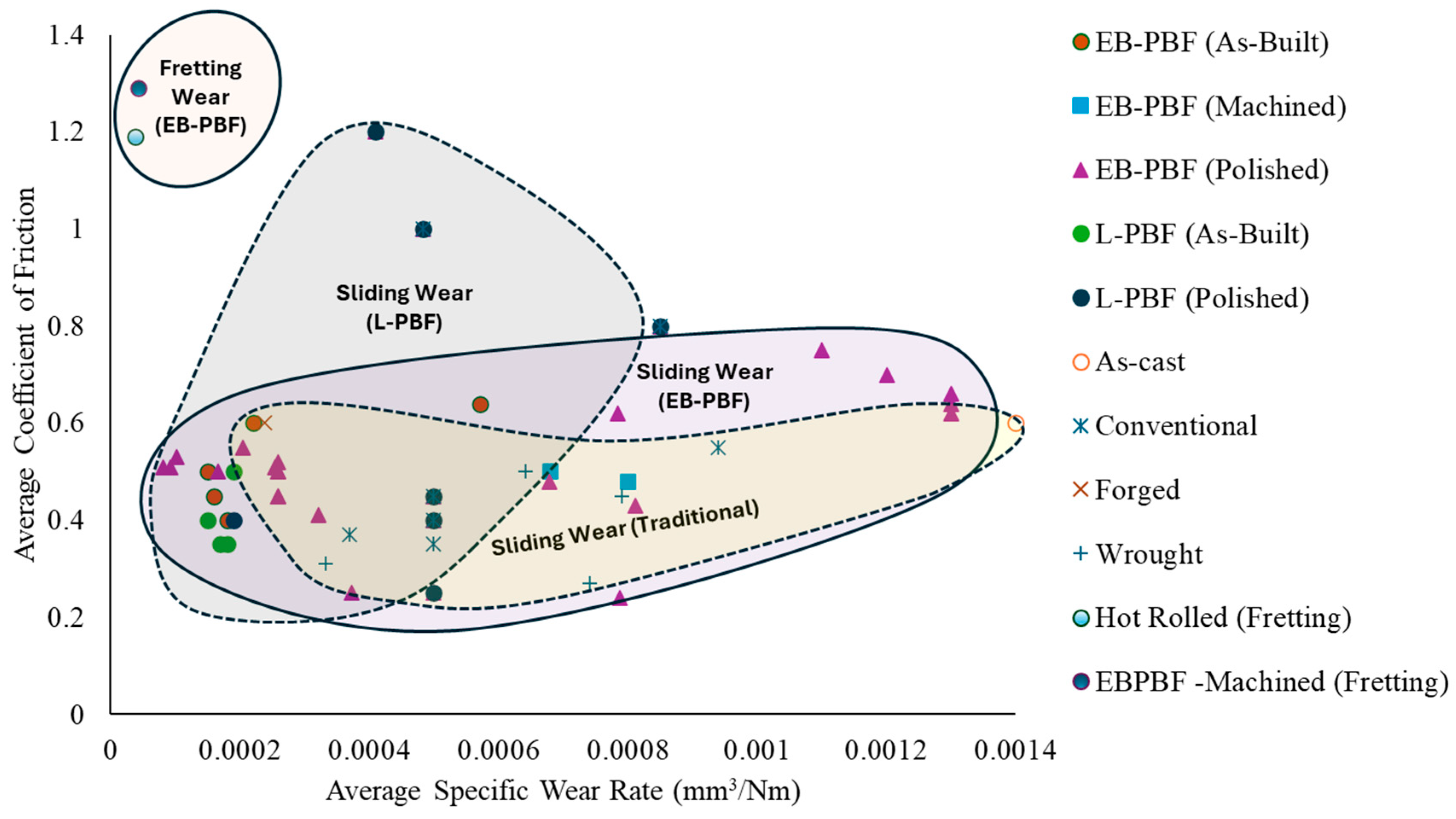
3.2. Fretting Wear
3.3. Erosive Wear
3.4. Tribo-Corrosion Wear
4. Effects of Testing Environment, Build Variability, Process Variability, and Post-Processing on Tribological Properties of EB-PBF Ti-6Al-4V
4.1. Effects of Testing Environment
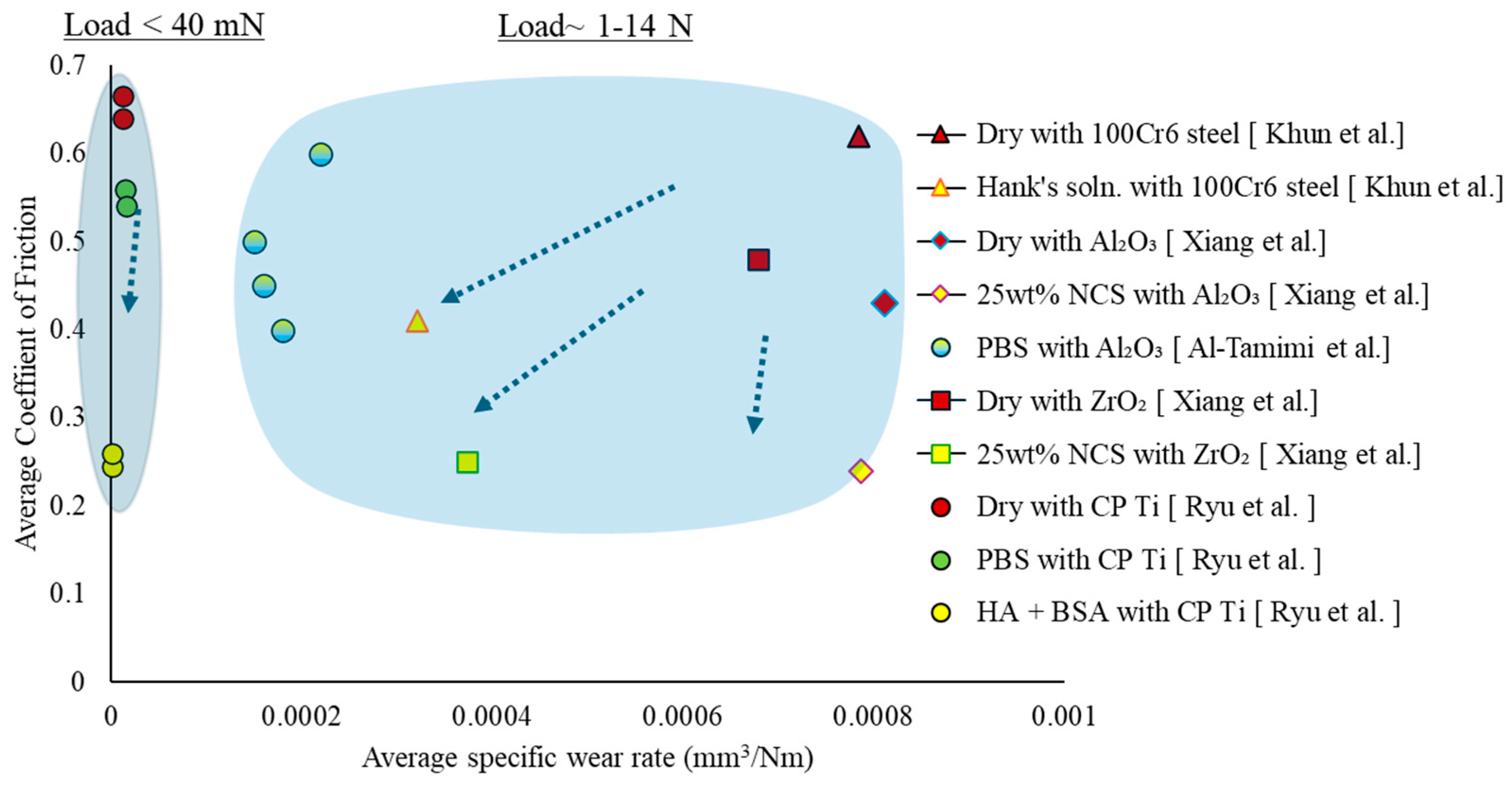
4.1.1. Applied Load and Frequency
4.1.2. Lubrication and Passivating Media
4.1.3. Counterparts
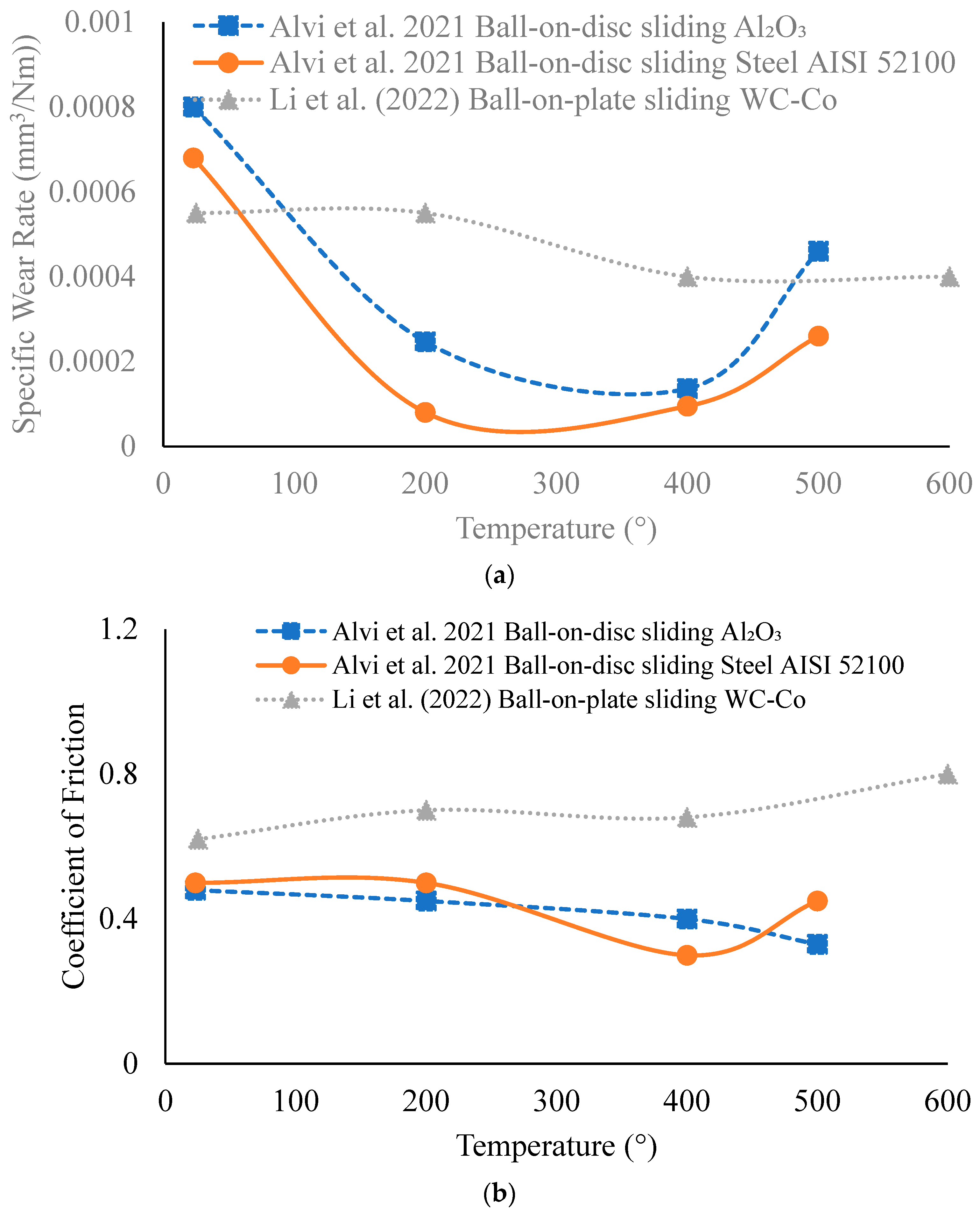
4.1.4. Temperature
4.1.5. EB-PBF Ti-6Al-4V as a Counterpart
4.2. Effects of Build Variability of EB-PBF Ti-6Al-4V on Tribological Properties
4.2.1. Specimen Thickness
4.2.2. Build Orientation
4.2.3. Build Location
4.2.4. Lattice/Cellular Structure with Designed Porosity
4.3. Effects of Post-Processing on Tribological Properties of PBF Ti6Al4V
4.3.1. Heat Treatment
4.3.2. Machining
4.3.3. Combined Machining and Heat Treatment
4.4. Implications of EB-PBF Process’s Influence on Tribological Properties of Ti6Al4V
4.4.1. Influence of Process-Induced Roughness
4.4.2. Powder Reuse and Wear Properties
4.4.3. EB-PBF Process Parameters and Tribological Properties
4.5. Mechanical and Tribological Properties
5. Wear Mechanism
5.1. General Wear Mechanism of EB-PBF Ti-6Al-4V
5.2. Influence of Microstructure and Process on Wear Mechanism
6. Summary, Challenges, and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewandowski, J.J.; Seifi, M. Metal Additive Manufacturing: A Review of Mechanical Properties. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 151–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, A.H.; Nandwana, P.; Yuan, T.; Kirka, M.M.; Dehoff, R.R.; Liaw, P.K.; Duty, C.E. A Review on the Fatigue Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated by Electron Beam Melting Additive Manufacturing. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 119, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shin, Y.C. Additive Manufacturing of Ti6Al4V Alloy: A Review. Mater. Des. 2019, 164, 107552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolie, O.; Stachurek, I.; Kandasubramanian, B.; Njuguna, J. Material Challenges and Opportunities in 3D Printing for Hip Implant Applications. Recent Prog. Mater. 2022, 4, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakey-Milner, B.; Gradl, P.; Snedden, G.; Brooks, M.; Pitot, J.; Lopez, E.; Leary, M.; Berto, F.; Du Plessis, A. Metal Additive Manufacturing in Aerospace: A Review. Mater. Des. 2021, 209, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeyta, A.; Nouwens, C.; Jones, A.M.; Haworth, T.A.; Montelione, A.; Ramulu, M.; Arola, D.D. Characterizing Gas Flow in the Build Chamber of Laser Powder Bed Fusion Systems Utilizing Particle Image Velocimetry: A Path to Improvements. Addit. Manuf. 2025, 106, 104810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, S.J.; Harrison, N.D. Why Aircraft Fail. Mater. Today 2002, 5, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- America Makes & ANSI Additive Manufacturing; Standardization Collaborative (AMSC); America Makes Standardization Roadmap for Additive Manufacturing Version 3 2023. Available online: https://www.ansi.org/standards-coordination/collaboratives-activities/additive-manufacturing-collaborative (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Bin Abdullah, M.S. Characterization of Tribological Behavior Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated by Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Orgeldinger, C.; Seynstahl, A.; Rosnitschek, T.; Tremmel, S. Surface Properties and Tribological Behavior of Additively Manufactured Components: A Systematic Review. Lubricants 2023, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralls, A.M.; Kumar, P.; Menezes, P.L. Tribological Properties of Additive Manufactured Materials for Energy Applications: A Review. Processes 2020, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, A.; Moridi, A. State of the Art in Directed Energy Deposition: From Additive Manufacturing to Materials Design. Coatings 2019, 9, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Pai, N.; Rosenkranz, A.; Shirvani, K.; Marian, M. Tribological Behavior of Additively Manufactured Metal Components. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2022, 6, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.V.U.; Santos, A.A.; Pinto, B.O.; Capelin, G.R.; Pintão, C.A.F.; Correa, D.R.N.; Grandini, C.R.; Lisboa-Filho, P.N. Tribological Behavior Study of New Titanium Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng Part. J J. Eng. Tribol. 2025, 239, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Roy, S. Metallic Dental Implants Wear Mechanisms, Materials, and Manufacturing Processes: A Literature Review. Materials 2022, 16, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods, S.; Schultz, E.; Wisdom, C.; Schur, R.; Pahuja, R.; Montelione, A.; Arola, D.; Ramulu, M. Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing of Ti6Al4V: Evolution of Powder Morphology and Part Microstructure with Powder Reuse. Materialia 2020, 9, 100631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Rafi, K.; Starr, T.; Stucker, B. The Effects of Processing Parameters on Defect Regularity in Ti-6Al-4V Parts Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting and Electron Beam Melting. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium—An Additive Manufacturing Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 12–14 August 2013; pp. 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- GE Additive Inside Electron Beam Melting 2025. Available online: https://go.additive.ge.com/rs/706-JIU-273/images/GE%20Additive_EBM_White%20paper_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Fu, Z.; Körner, C. Actual State-of-the-Art of Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion. Eur. J. Mater. 2022, 2, 54–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
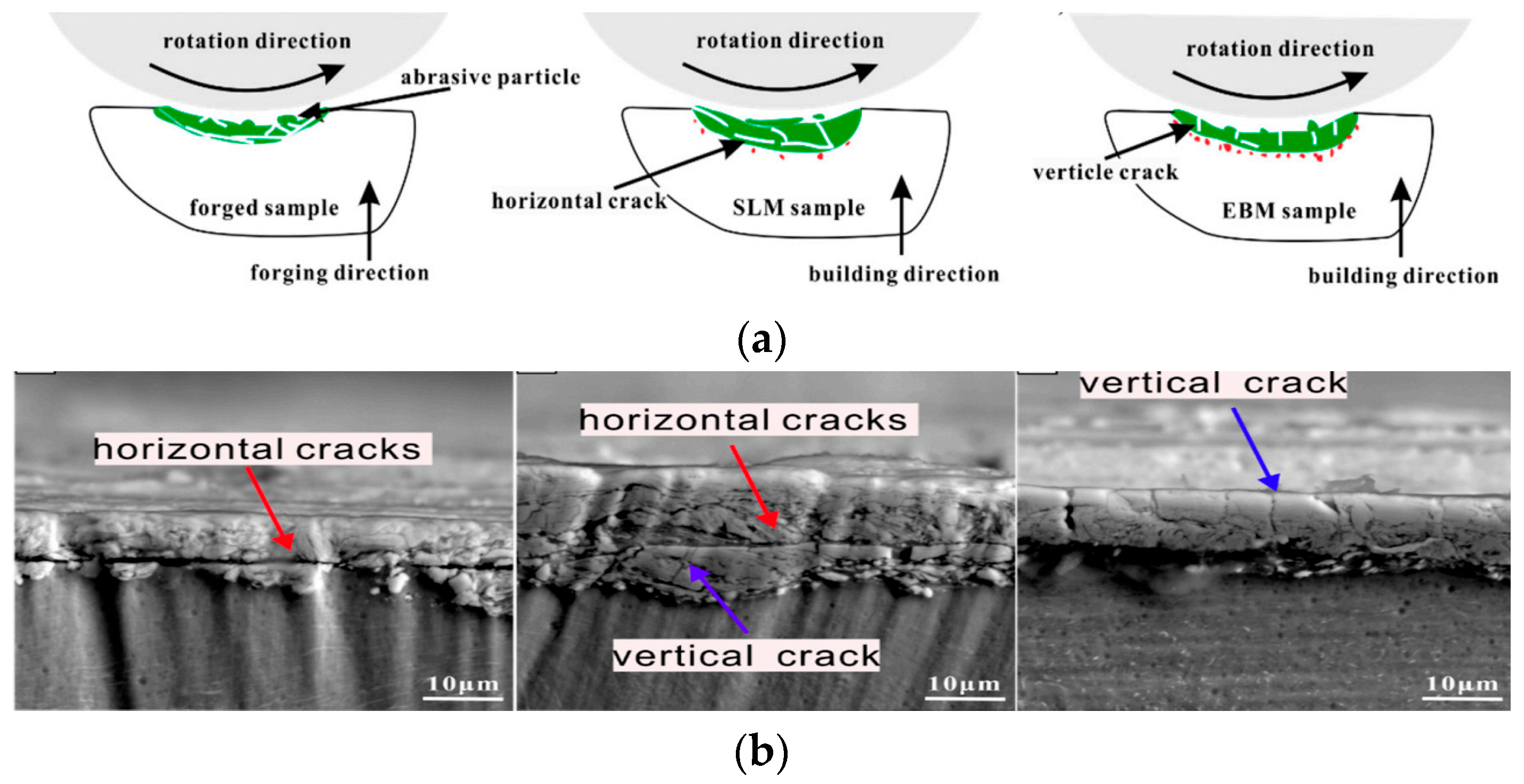
- Zhang, W.; Qin, P.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Kollo, L.; Grzesiak, D.; Prashanth, K. Superior Wear Resistance in EBM-Processed TC4 Alloy Compared with SLM and Forged Samples. Materials 2019, 12, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, W.; Wang, P.; Tan, X.; Nai, M.; Liu, E.; Tor, S. Microstructure and Wear Properties of Electron Beam Melted Ti-6Al-4V Parts: A Comparison Study against As-Cast Form. Metals 2016, 6, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TriboNet Pin on Disk Test 2022. Available online: https://www.tribonet.org/wiki/pin-on-disk-test/ (accessed on 20 September 2025).
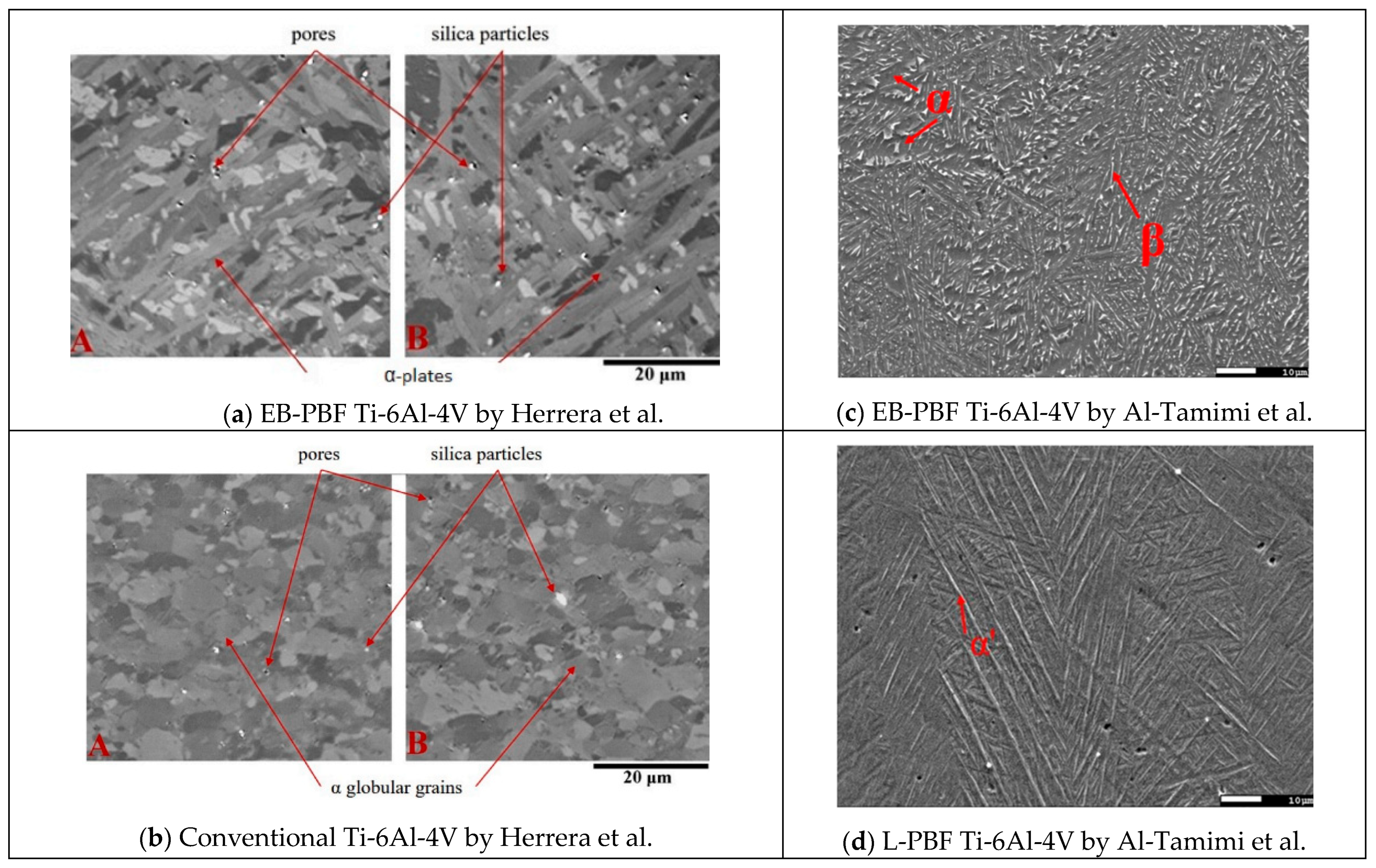
- Herrera, P.; Hernandez-Nava, E.; Thornton, R.; Slatter, T. Abrasive Wear Resistance of Ti-6AL-4V Obtained by the Conventional Manufacturing Process and by Electron Beam Melting (EBM). Wear 2023, 524–525, 204879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni, O.C. Microstructural, Mechanical and Tribological Studies of Ti-6Al-4V Thin Plates Produced by EBM Process. Master’s Thesis, Dalarna University, Borlänge, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Tamimi, A.A.; Hernandez, M.A.; Omar, A.; Morales-Aldana, D.F.; Peach, C.; Bartolo, P. Mechanical, Biological and Tribological Behaviour of Fixation Plates 3D Printed by Electron Beam and Selective Laser Melting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 109, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Kamran, M.; Paraye, N.K.; Anant, R. Insights into the Wear Behaviour of Electron Beam Melted Ti–6Al–4V Alloy in the as-Built and the Heat-Treated Conditions. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 71, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khun, N.W.; Toh, W.Q.; Tan, X.P.; Liu, E.; Tor, S.B. Tribological Properties of Three-Dimensionally Printed Ti–6Al–4V Material Via Electron Beam Melting Process Tested Against 100Cr6 Steel Without and With Hank’s Solution. J. Tribol. 2018, 140, 061606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, W.Q.; Tan, X.; Sun, Z.; Liu, E.; Tor, S.B.; Chua, C.K. Comparative Study on Tribological Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V and Co-Cr-Mo Samples Additively Manufactured with Electron Beam Melting. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Progress on Additive Manufacturing Conference, Singapore, 16–19 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ramezani, M.; Chen, Z.W. Dry Sliding Wear Performance and Behaviour of Powder Bed Fusion Processed Ti–6Al–4V Alloy. Wear 2019, 440–441, 203103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Z.W.; Ramezani, M. Effect of Temperature on Sliding Wear Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Processed by Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing Techniques. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 8940–8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Shrestha, S.; Manogharan, G.; Jung, J. Sliding Contact Wear Damage of EBM Built Ti6Al4V: Influence of Process Induced Anisotropic Microstructure. Metals 2018, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S. Wear Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V for Joint Implants Manufactured by Electron Beam Melting. Master’s Thesis, Youngstown State University, Youngstown, OH, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Riaz, M.Q.; Caputo, M.; Ferraro, M.M.; Ryu, J.J. Influence of Process-Induced Anisotropy and Synovial Environment on Wear of EBM Built Ti6Al4V Joint Implants. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 3460–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Tan, X.; Liao, Z.; He, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Shu, B.T. Comparison of Wear Properties of Ti6Al4V Fabricated by Wrought and Electron Beam Melting Processes in Simulated Body Fluids. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2020, 26, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Abdullah, M.S.; Mamidala, R. Sliding Wear Behavior of Electron Beam Melted (EBM) Ti6Al4V. In Proceedings of the ASME 2022 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Volume 2B: Advanced Manufacturing, Columbus, OH, USA, 30 October–3 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi, S.; Bertolini, R.; Medeossi, F.; Ghiotti, A.; Savio, E.; Shivpuri, R. Case Study: The Application of Machining-Conditioning to Improve the Wear Resistance of Ti6Al4V Surfaces for Human Hip Implants. Wear 2018, 394–395, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, S.; Bertolini, R.; Ghiotti, A. Coupling Machining and Heat Treatment to Enhance the Wear Behaviour of an Additive Manufactured Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy. Tribol. Int. 2017, 116, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, S.; Bertolini, R.; Bordin, A.; Medea, F.; Ghiotti, A. Influence of the Machining Parameters and Cooling Strategies on the Wear Behavior of Wrought and Additive Manufactured Ti6Al4V for Biomedical Applications. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, S.R.; Soul, H.; Bergant, M.; Yawny, A. Fretting Wear Behaviour of Biomedical Grade Ti6Al4V Produced by Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 86, 104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Fang, W.; Yi, Y. Tribology Properties of Additively Manufactured Ti6Al4V Alloy after Heat Treatment. Tribol. Int. 2023, 185, 108485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Abdullah, M.S.; Alajmi, A.F.; Ramulu, M. Solid Particle Erosion Behavior of Electron Beam Melted (EBM) Ti6Al4V at Different Built Orientation. In Proceedings of the ASME 2021 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Volume 2A: Advanced Manufacturing, Virtual, 1–5 November 2021; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2021; p. V02AT02A016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhitano, G.A.; García, I.M.; Arenas, M.A.; De Damborenea, J.J.; Maciel Filho, R.; Conde, A. Effect of Designed Pore Size on Electrochemical, Wear, and Tribocorrosion Behavior of Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Lattice Structures. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 79, 103931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, F.; Varmaziar, S.; Atapour, M.; Iuliano, L.; Saboori, A. In Vitro Corrosion and Bio-Tribocorrosion Performance of Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion Ti6Al4V Specimens with Lapping and Superfinishing Treatments. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2025, 10, 9117–9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, R.; Bruschi, S.; Ghiotti, A.; Pezzato, L.; Dabalà, M. Influence of the Machining Cooling Strategies on the Dental Tribocorrosion Behaviour of Wrought and Additive Manufactured Ti6Al4V. Biotribology 2017, 11, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, S.; Neikter, M.; Antti, M.-L.; Akhtar, F. Tribological Performance of Ti6Al4V at Elevated Temperatures Fabricated by Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushilina, N.S.; Stepanova, E.N.; Kudiiarov, V.N.; Laptev, R.S.; Syrtanov, M.S. Heat Treatment of the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Manufactured by Electron Beam Melting. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2167, 020290. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadhosseini, A.; Fraser, D.; Masood, S.H.; Jahedi, M. Investigation of Wear Properties of EBM Processed Ti6Al4V with UHMWPE for Biomedical Applications. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 811, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Kok, Y.; Tan, Y.J.; Descoins, M.; Mangelinck, D.; Tor, S.B.; Leong, K.F.; Chua, C.K. Graded Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Additive Manufactured Ti–6Al–4V via Electron Beam Melting. Acta Mater. 2015, 97, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Abdullah, M.S.; Bol, E.; Kelley, G.; Doyle, C.; Schleusener, R.; Mojib, M.; Chen, X.; Arola, D.; Ramulu, M. Microstructure and Microhardness of Electron Beam Melted Ti–6Al–4V Components with Differential Thickness in Initial Deposition Layers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 6493–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, R.; Narra, S.P.; Ozturk, T.; Beuth, J.; Rollett, A.D. Evaluating the Effect of Processing Parameters on Porosity in Electron Beam Melted Ti-6Al-4V via Synchrotron X-Ray Microtomography. Jom 2016, 68, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Narra, S.P.; Rollett, A. Exploring the Fabrication Limits of Thin-Wall Structures in a Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 110, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, E.; Ramulu, M. Dimensional Accuracy of Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion with Ti-6Al-4V. Designs 2023, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, P. Effect of Cryogenic Treatment on the Abrasive Wear Resistance of Engineering Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bin Abdullah, M.S.; Mojib, N.M.; Atmadja, N.; Ramulu, M. Machinability of Electron Beam Powder Bed Fused Ti-6Al-4V in Face Milling with Coated Carbide End Mill. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 21430–21444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montelione, A.; Ghods, S.; Schur, R.; Wisdom, C.; Arola, D.; Ramulu, M. Powder Reuse in Electron Beam Melting Additive Manufacturing of Ti6Al4V: Particle Microstructure, Oxygen Content and Mechanical Properties. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, W.A.; Solis-Ramos, E.; Clark, E.; Lucon, E.; Garboczi, E.J.; Predecki, P.K.; Loftus, Z.; Kumosa, M. Effect of Powder Oxidation on the Impact Toughness of Electron Beam Melting Ti-6Al-4V. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 17, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Wang, H.; Tao, X.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Oleksander, M. Investigation on Microstructure, Hardness and Wear Resistance of Electron Beam Wire-Feeding Deposited Inconel 718 Alloy Coatings. Met. Mater. Int. 2019, 27, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, A.H.; Nandwana, P.; McDaniels, R.; Dehoff, R.R.; Liaw, P.K.; Tryon, R.; Duty, C.E. Build Orientation, Surface Roughness, and Scan Path Influence on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Flexural Fatigue Behavior of Ti–6Al–4V Fabricated by Electron Beam Melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Tang, J.; Huang, D.; Yan, M.; Dargusch, M.S. Surface Modification of Biomedical Ti and Ti Alloys: A Review on Current Advances. Materials 2022, 15, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reference | Key Objective/Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Toh et al. [21,28] | Ball-on-disc sliding wear to understand the effects of build thickness on wear properties, microstructure, and hardness and to compare with cast Ti6Al4V (metal on metal). |
| Xiang et al. [34] | Ball-on-disc reciprocating tests against ZrO2 and Al2O3 to compare with wrought Ti64 in a dry condition and a lubricated condition with 5 wt.% newborn calf serum (NCS) (ceramic on metal). |
| Ryu et al. [31], Shrestha [32], Riaz et al. [33] | Reciprocating sliding contact wear by a titanium sphere (ball-on-disc test) to understand the influence of anisotropy in dry and lubricated (PBS) conditions (metal on metal). |
| Khun et al. [27] | Ball-on-disc tests using a 100Cr6 steel ball to understand the tribological properties (sliding wear) in dry conditions, in PBS, and in Hunk’s solution (metal on metal). |
| Li et al. [29,30] | Ball-on-disc (linear reciprocating) tests using WC-Co counterparts on EB-PBF, L-PBF, and conventional Ti6Al4V at room temperature and an elevated temperature (ceramic on metal). |
| Sanni [24] | A scratch test against a diamond stylus to measure the friction coefficients of thin plates (ceramic on metal). |
| Zhang et al. [20] | Block-on-ring sliding wear test using GCr15 steel to compare results with forged and LPBF Ti6Al4V (metal on metal). |
| Herrera et al. [23] | A sand–rubber wheel (DSRW) abrasive wear test at a higher load (130 N) to compare with conventional Ti6Al4V (ceramic on metal). |
| Bin Abdullah and Ramulu [35] | Understanding the influence of build orientation in as-built and machined conditions on sliding wear by abrasive alumina particles (ceramic abrasive on metal). |
| Alvi et al. [45] | Ball-on-disc sliding tests in dry conditions using steel and alumina counterparts to understand the wear behavior up to 400 °C (metal on metal and ceramic on metal). |
| Pushilina et al. [46] | A preliminary study on the effects of heat treatment on wear resistance. However, it did not mention of wear test method or the wear analysis procedure. |
| Sharma et al. [26] | Dry pin-on-disc sliding using EN-31 steel to study the influence of heat treatment on wear resistance (metal on metal). |
| Huang et al. [40] | A reciprocating friction test using Si3N4 ceramic balls to study the influence of the duration of heat treatment at 600 °C, followed by cooling by 100 °C/h. |
| Al Tamimi et al. (2020) [25] | Dry pin-on-disc sliding using an alumina counterpart to study the wear resistance of EB-PBF and L-PBF Ti-6Al-4V (ceramic on metal). |
| Bruschi et al. [36,37,38] | Studied the friction and wear properties of EB-PBF Ti6Al4V after machining in dry and cryogenic conditions; studied the effects of both cryogenic machining and wet machining in increasing wear resistance; and studied the wear behavior of EB-PBF titanium after a combination of machining and heat treatment (metal on metal). |
| Soria et al. [39] | Measured fretting wear by Ti-6Al-4V counterparts to compare with hot-rolled Ti-6Al-4V (metal on metal). |
| Bin Abdullah et al. [41] | Understanding the solid particle erosion mechanism in as-built and machined conditions due to silica impingement (abrasive impingement on metal). |
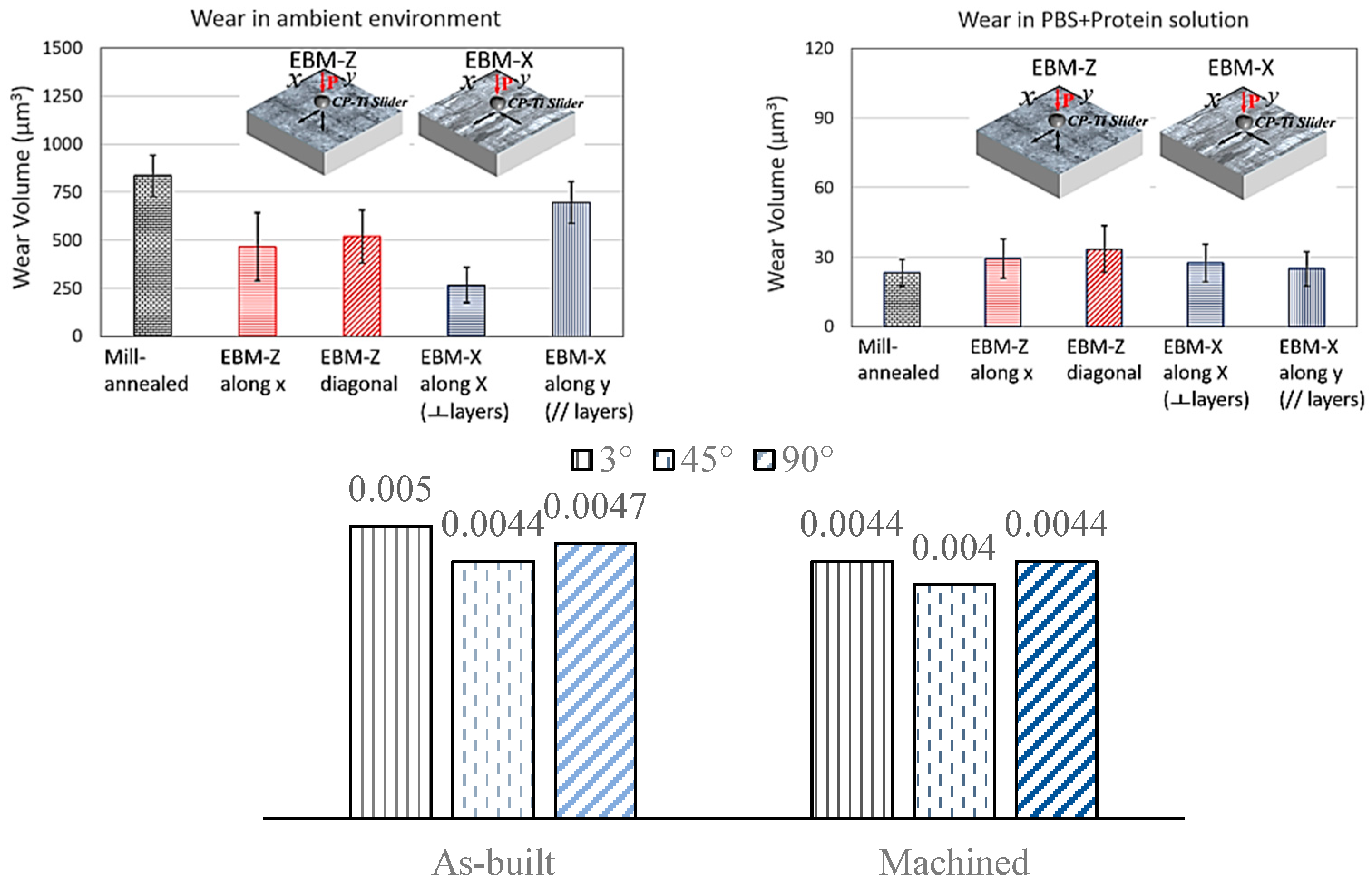
| Bin Abdullah [9] | Understanding the influence of build anisotropy and powder reuse in the sliding and erosion wear of EB-PBF Ti-6Al-4V in as-built and machined conditions (ceramic abrasive on metal and abrasive impingement on metal). |
| Longhitano et al. [42] | The effect of the pore size on the electrochemical properties, wear, and tribo-corrosion behavior of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V lattice structures designed for orthopedic implants (ceramic on metal). |
| Mohammadhosseini et al. [47] | The behavior of an EB-PBF Ti-6Al-4V pin on plastics during a pin-on-disc test (metal on plastic). |
| Ring-on-Block Experimental and Counterpart Details | Process | Wear Rate | Avg. Friction Coefficient | Hardness | Wear Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm3 N−1 m−1) | (HV) | (mm) | |||
| Zhang et al. [20] Load = 50 N GCr15 steel, dry (Ø47.15 mm, 630 HV) | Forged | 23.9 ± 4.6 × 10−5 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 368 ± 12 | 0.24 |
| EB-PBF | 16.6 ± 4.2 × 10−5 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 383 ± 13 | 0.17 | |
| L-PBF | 19.0 ± 3.7 × 10−5 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 399 ± 14 | 0.21 | |
| Ball-on-Disc Experimental and Counterpart Details | Process | ~Wear Rate | ~Avg. Friction Coefficient | ~Hardness | ~Wear Depth |
| (mm3 N−1 m−1) | (HV) | (mm) | |||
| Al-Tamimi et al. [25] Load = 2–14 N Al2O3 ball, PBS Soln. | EB-PBF | 0.15–0.22 × 10−3 | 0.35–0.67 | 337.40 ± 17.60 | 0.125 at 14 N |
| (Ø5 mm) | L-PBF | 0.15–0.19 × 10−3 | 0.37–0.60 | 312.60 ± 7.37 | 0.136 at 14 N |
| Toh et al. [28] Load = 1 N 100Cr6 steel ball, dry (Ø6 mm) | Cast | 140 × 10−5 | 0.62 | 300 | 0.05–0.06 |
| As-built EB-PBF | 110–135 × 10−5 | 0.62–0.71 | 330–370 | 0.06 | |
| Experimental and Counterpart Details | Process | ~Wear Rate | ~Avg. Friction Coefficient | ~Hardness | ~Wear Depth |
| (mm3m−1) | (HV) | (μm) | |||
| Li et al. [29] Load = 2–10 N; Freq = 2–8 Hz WC-Co ball, dry (Ø10 mm) | Conventional | 1–5 × 10−3 | 0.35–0.45 | 324 | - |
| EB-PBF | 1–4.3 × 10−3 | 0.25–0.45 | 359 | - | |
| L-PBF | 1–5 × 10−3 | 0.25–0.45 | 428 | - | |
| Experimental and Counterpart Details | Process | ~Wear Rate | ~Avg. Friction Coefficient | ~Hardness | ~Wear Depth |
| (m3 N−1 m−1) | (HV) | (μm) | |||
| Khun et al. [27] Load = 1 N 100Cr6 steel ball, dry and Hank’s Soln. (Ø6 mm) | Commercial (dry) | 93.9 × 10−14 | 0.55 | 371 | - |
| Commercial (Hank’s) | 36.9 × 10−14 | 0.37 | 376 | - | |
| EB-PBF (dry) | 78.4 × 10−14 | 0.62 | 371 | - | |
| EB-PBF (Hank’s) | 32.1 × 10−14 | 0.41 | 376 | ||
| Fretting Wear Experimental and Counterpart Details | Process | ~Wear Rate | ~Avg. Friction Coefficient | ~Hardness | ~Wear Depth |
| (Pa−1) | (HV) | (μm) | |||
| Soria et al. [39] Load = 10 N Amplitude = 50 μm EB-PBF Ti-6Al-4V | EB-PBF (as-built) | N/A | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 280 | 25 |
| EB-PBF (machined) | 43 ± 5 × 10−15 | 1.29 ± 0.05 | 300–360 | 35 | |
| Hot-rolled | 38.0 ± 0.1 × 10−15 | 1.19 ± 0.01 | 40 |
| Reference | Surface Condition | Process and Orientation | ~CoF | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryu et al. [31] | Polished Load: 0.032–0.032 N | EB-PBF Z (Along X) | ~0.65 | 420 HV |
| EB-PBF X (Along X) | ~0.60 | 385 HV | ||
| EB-PBF X (Along Y) | ~0.68 | 385 HV | ||
| Sanni * [24] | As-built Load: 1–5 N | Along X | ~0.05–0.30 | 389 HV |
| Along Z | ~0.10–0.32 | 389 HV | ||
| Transverse | ~0.10–0.40 | 465 HV |
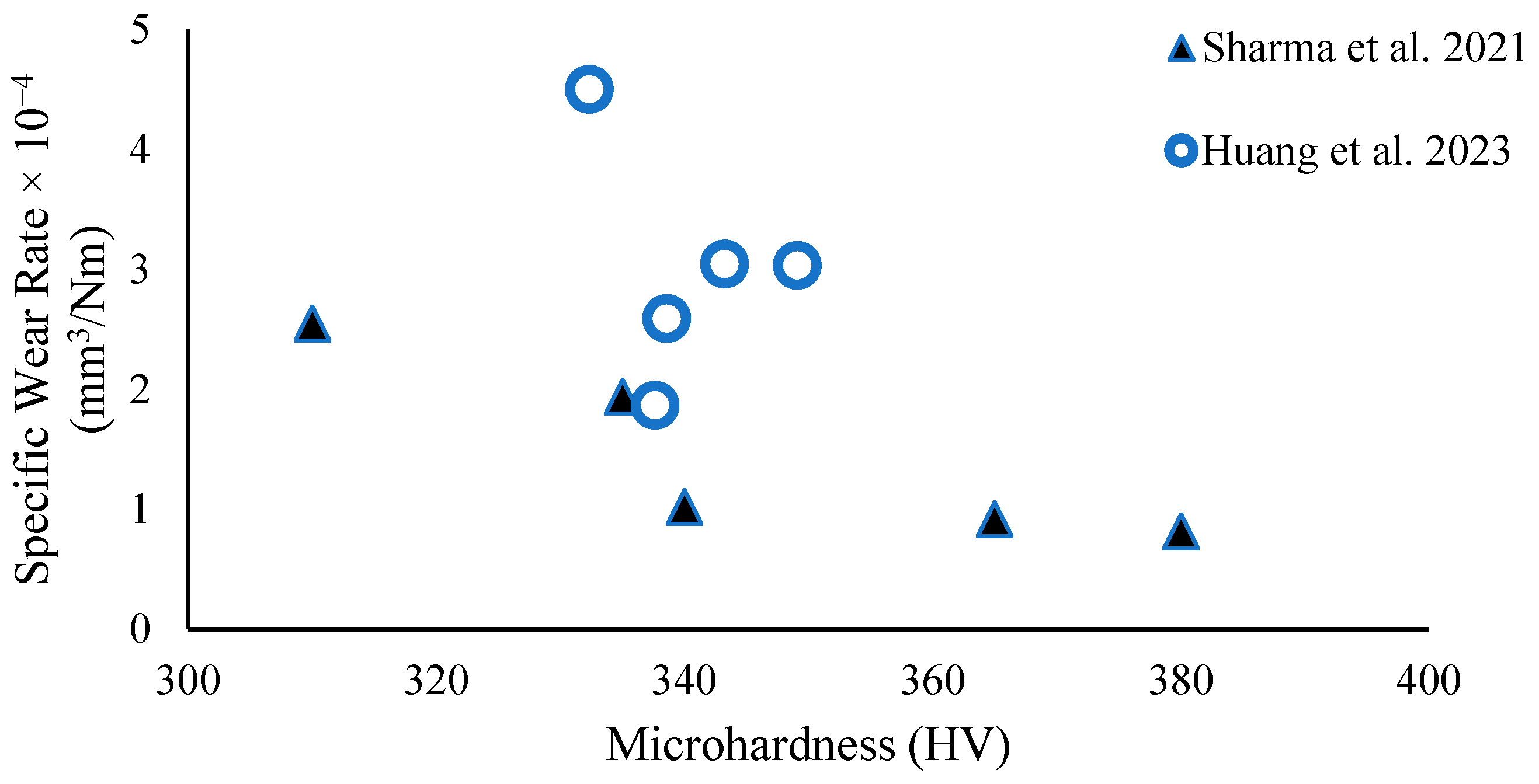
| Reference | Heat Treatment Method | ~CoF | ~Hardness (HV) | ~Specific Wear Rate (mm3/Nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pushilina et al. [46] | As-EB-PBF | N/A | 416 | 0.62 × 10−3 |
| 750 °C/1 h | N/A | 377 | 0.57 × 10−3 | |
| Sharma et al. [26] | As-Built | 0.53 | 340 | 1.02 × 10−4 |
| 1040 °C/2 h-FC | 0.53 | 310 | 2.55 × 10−4 | |
| 1040 °C/2 h-WQ | 0.51 | 380 | 0.82 × 10−4 | |
| 920 °C/2 h-FC | 0.55 | 335 | 1.94 × 10−4 | |
| 920 °C/2 h-WQ | 0.51 | 365 | 0.92 × 10−4 | |
| Huang et al. [40] | 600 °C/1 h-FC | 0.50 | 339 | 2.59 × 10−4 |
| 600 °C/3 h-FC | 0.45 | 332 | 4.50 × 10−4 | |
| 600 °C/5 h-FC | 0.50 | 349 | 3.03 × 10−4 | |
| 600 °C/7 h-FC | 0.52 | 343 | 3.04 × 10−4 | |
| 600 °C/9 h-FC | 0.45 | 338 | 1.87 × 10−4 |
| Condition | Feed Rate, (mm/rev) | Speed Vc (m/min) | Microhardness, HV0.05 | Coefficient of Friction | ~Wear (Weight Loss in %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machining Condition (Bruschi et al., 2016 [38]) | Wrought | EB-PBF | Wrought | EB-PBF | Wrought | EB-PBF | ||
| Dry | 0.1 | 50 | 365 ± 5 | 379 ± 6 | 0.43 | 0.54 | −0.0070 | −0.0008 |
| 0.1 | 80 | 364 ± 6 | 370 ± 4 | 0.44 | 0.46 | −0.0030 | −0.0038 | |
| 0.2 | 50 | 366 ± 4 | 372 ± 7 | 0.42 | 0.51 | −0.0015 | −0.0022 | |
| 0.2 | 80 | 340 ± 4 | 367 ± 5 | 0.39 | 0.42 | −0.0012 | −0.0022 | |
| Cryogenic | 0.1 | 50 | 393 ± 7 | 409 ± 8 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.0038 | 0.0038 |
| 0.1 | 80 | 391 ± 8 | 400 ± 5 | 0.58 | 0.41 | −0.0020 | 0.0038 | |
| 0.2 | 50 | 408 ± 6 | 389 ± 7 | 0.40 | 0.37 | 0.0010 | 0.0039 | |
| 0.2 | 80 | 403 ± 4 | 385 ± 5 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.0025 | 0.0035 | |
| Reference | Post-Processing | Hardness | ~Mean Wear volume | |||||
| Bruschi et al., 2018 [36] | EB-PBF + wet machining (1 pass) | - | 0.011 mm3 | |||||
| EB-PBF + wet machining (5 passes) | 290–295 HV | 0.013 mm3 | ||||||
| EB-PBF + cryogenic machining (1 pass) | 325–350 HV | 0.010 mm3 | ||||||
| EB-PBF + cryogenic machining (5 passes) | 315–350 HV | 0.007 mm3 | ||||||
| Parameters | ~ COF | ~ Hardness (HV) | ~ Wear Volume (mm3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed, Vc (m/s) | Feed Rate (mm/rev) | Turned | Turned + HT | Turned | Turned + HT | Turned | Turned + HT |
| 80 | 0.1 | 0.56 | 0.45 | 355 | 440 | 7.6 ± 1 × 10−3 | 0.5 ± 0.8 × 10−3 |
| 110 | 0.1 | 0.55 | 0.48 | 360 | 420 | 3.8 ± 2 × 10−3 | 1.5 ± 1 × 10−3 |
| 80 | 0.2 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 360 | 425 | 7.6 ± 3 × 10−3 | 1.7 ± 1 × 10−3 |
| 110 | 0.2 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 365 | 425 | 2.9 ± 1.5 × 10−3 | 0.8 ± 1.3 × 10−3 |
| Test Type | Surface conditions | Roughness, Ra (μm) | Specific Wear Rate (mm3/Nm) | Avg. CoF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin-on-disc test in PBS Soln. using alumina ball [25] (Al-Tamimi et al.) | As-built | 19.16 | 1.5–2.2 × 10−4 | 0.4–0.6 |
| Fretting wear in dry conditions using EB-PBF Ti-6Al-4V [39] | As-built | 8.82 | - | 2.2 |
| Machined | 1 | 4.3 × 10−5 | 1.29 | |
| Rotary abrasion in dry conditions using abrasive alumina [35] | As-built at 3° orientation | 19.29 | 5.0 × 10−3 | - |
| As-built at 45° orientation | 18.49 | 4.4 × 10−3 | - | |
| As-built at 90° orientation | 17.85 | 4.7 × 10−3 | - | |
| Machined at 3° orientation | 9.45 | 4.4 × 10−3 | - | |
| Machined at 45° orientation | 10.46 | 4.0 × 10−3 | - | |
| Machined at 90° orientation | 3.34 | 4.4 × 10−3 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bin Abdullah, M.S.; Ramulu, M. The Tribological Behavior of Electron Beam Powder Bed Fused Ti-6Al-4V: A Review. Metals 2025, 15, 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111170
Bin Abdullah MS, Ramulu M. The Tribological Behavior of Electron Beam Powder Bed Fused Ti-6Al-4V: A Review. Metals. 2025; 15(11):1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111170
Chicago/Turabian StyleBin Abdullah, Mohammad Sayem, and Mamidala Ramulu. 2025. "The Tribological Behavior of Electron Beam Powder Bed Fused Ti-6Al-4V: A Review" Metals 15, no. 11: 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111170
APA StyleBin Abdullah, M. S., & Ramulu, M. (2025). The Tribological Behavior of Electron Beam Powder Bed Fused Ti-6Al-4V: A Review. Metals, 15(11), 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111170