Abstract
In this paper, we introduce the notion of multivalued interpolative Kannan-type contractions. We also introduce a more general version of this notion by relaxing the degrees of freedom of the powers arising in the contractive condition. Gaba et al. (2021) recently pointed out a significant error in the paper of Gaba and Karapinar (2019), showing that a particular type of generalized interpolative Kannan-type contraction does not posses a fixed point in general in a complete metric space. Thus, the study of generalized Kannan-type mappings remains an interesting and mathematically challenging area of research. The main aim of this article is to address such existing results for multivalued mappings. We also investigate common fixed points for this type of contractions. Our results extend and unify some existing results in the literature.
Keywords:
fixed point; Kannan-type contraction; interpolative map; multivalued map; contraction map; common fixed point; differential equation; integral equation; metric space AMS Subject Classification:
47H10; 54H25; 54E50
1. Introduction
Some well-known fixed point results obtained for multivalued mappings were established by Nadler [1] in 1969. This generalization is based on the idea of the Hausdorff concept—i.e., the distance between two arbitrary sets. The concept of Hausdorff metric space is defined as follows:
Consider a complete metric space (MS) and the class of all nonempty closed and bounded subsets of the nonempty set ℑ. Then, construct a map , such that for ,
where . The pair is known as Pompeiu–Hausdorff metric space, which is induced by .
Definition 1
([1]). Suppose is a multivalued map. Then, is said to be a fixed point of Υ if and denotes the set of all fixed points of Υ.
Remark 1.
- Suppose is an MS; is a fixed point of Υ if and only if .
- We know that the metric function is continuous if are two sequences in ℑ with for some , as . Additionally, as . This implies that the function Δ is continuous if as . Additionally, as , for any .
It is well known that a map satisfying the Banach contraction principle is continuous. In 1968, Kannan [2,3] reported that there are also discontinuous maps which satisfy certain contractive conditions and possess fixed points. Since then, Kannan’s results have been studied and extended in multiple directions (see [4,5,6,7,8]). Recently, Karapinar [9] and Gaba and Karapinar [10] extended Kannan’s theorem via interpolation and produced more general results.
However, in [11], Gaba, Aydi, and Mlaiki pointed out a significant error in the paper published by Gaba and Karapinar [10]. They showed that a interpolative Kannan contraction does not necessarily posses a fixed point in a complete MS. Our current work is also an improvement in that direction where we discuss the existence of a fixed point by assuming that the images of the multivalued mapping under consideration are compact.
For some recent results on interpolative contractions, we refer to the works of Aydi et al. [12,13], Karapinar et al. [14,15], Debnath et al. [16], and Debnath [17], as well as the recent monographs [18,19,20].
Recently, Debnath and Srivastava [21] studied common BPPs for multivalued contractive pairs of mappings. Debnath and Srivastava [22] also proved new extensions of Kannan’s and Reich’s theorems. Another Kannan-type contraction for multivalued asymptotic regular maps was presented by Debnath et al. [23]. Furthermore, a very significant application of fixed points of -contractions to fractional differential equations was recently provided by Srivastava et al. [24].
Some important results for the present context are listed below:
Lemma 1
([25,26]). Consider an MS and suppose . Then,
- (1)
- for any and ;
- (2)
- for any .
Lemma 2
([1]). Suppose that and . Then, for any , there exists , such that:
However, in every situation there may not be a point , such that:
If is compact, then such a point ξ exists—i.e.,
Lemma 3
([1]). Suppose is a sequence in and for some , = 0. If and for some , , then .
In the current paper, our aim is to introduce and establish a multivalued version of Kannan-type contractions via interpolation. The rest of the paper is organised as follows. In Section 2, we introduce multivalued interpolative Kannan-type (MVIK-type, in short) contractions and show that they admit fixed points. We also provide a more general version of this result as a corollary by relaxing the degrees of freedom of the power occurring in the contractive condition. In Section 3, we present a common fixed point theorem for MVIK-type contractions. Section 4 provides our conclusions.
2. MVIK-Type Contractions
First of all, we introduce the definition of MVIK-type contractions and present the corresponding existing result.
Definition 2.
Suppose that is an MS. A map is called an MVIK-type contraction if there exist and , such that:
for all with .
Theorem 1.
Suppose that is a complete MS and Υ is an MVIK-type contraction, such that is compact for each . Then,
Proof.
Consider and choose . Since is compact, from Lemma 2 we can select , such that . Similarly, we may consider , such that and so on. Continuing in a similar manner, we can create a sequence satisfying , such that .
Suppose that ∀. Otherwise, we can trivially obtain a fixed point. Thus, , ∀.
Taking and in Definition 2, we have:
Therefore, is a non-increasing and non-negative sequence of real numbers; therefore, it converges to some real numbers l. We show that .
From Equation (2):
Since , taking the limit in (3) as , we have .
Next, we verify that is a Cauchy sequence.
Taking and in Definition 2, we have:
From (4),
For any positive integer k:
Letting in (6), we obtain . Therefore, is a Cauchy sequence. Since is complete, for some .
Next, we show that is a fixed point of . Putting and in (2), we have:
Taking the limit in the above inequality as , we find that (using of Remark 1 and the fact that ). Therefore, —i.e., —is a fixed point of . □
Next, we introduce a more general version of the notion of MVIK-type contraction by relaxing the degrees of freedom of the powers arising in the contractive condition. We call this -interpolative Kannan-type contraction.
Definition 3.
Suppose that is an MS and is a multivalued map. Then, Υ is called a -interpolative Kannan-type contraction if there exist and with , such that:
for all with , and .
Remark 2.
In Definition 3, if we admit , we have a direct reference to Definition 2 (). Hence, the condition allows the parameters to admit various values and still provides the interpolative results.
The corresponding existing result follows as a corollary to Theorem 1.
Corollary 1.
Suppose that is a complete MS and is a -interpolative Kannan-type contraction, such that is compact for each . Then, .
Proof.
Fix . Applying similar techniques as those in Theorem 1, we construct a sequence satisfying:
Taking and in Definition 3, we have:
Next, adopting a similar procedure as in the proof of Theorem 1, we can prove that is a Cauchy sequence. Furthermore, since is complete, converges to a fixed point of . □
The example below validates Corollary 1 and consequently Theorem 1.
Example 1.
Consider and . Then, is a complete MS.
Construct , such that:
Let . Then, . Now, .
Thus, Υ is a -interpolative Kannan-type contraction for any and with . Hence, all the conditions of Corollary 1 and consequently Theorem 1 are satisfied and Υ has infinitely many fixed points.
3. Common Fixed Point Theorem for MVIK-Type Contractions
Throughout this section, we present existing results for common fixed points of MVIK-type contractions.
Theorem 2.
Suppose that is a complete MS and are two multivalued maps, such that and are compact for each . Suppose there exist and , satisfying:
for all , such that and .
Then, Υ and S have a common fixed point.
Proof.
Consider with , so that . Choose . Using Lemma 2, we can select , such that:
Similarly, we may choose , such that:
Continuing in a similar manner, we construct a sequence , such that and for all , satisfying:
and
Now,
Similarly,
Taking the limits on both sides of the last inequality, we have:
Similarly, we have:
Again taking the limit, we have:
Now,
Similarly,
Now, using similar techniques as those in Theorem 1, we can show that the sequence is a Cauchy sequence.
Since is complete, there exists , such that , as .
Next, we claim that is a common fixed point of and S. Now,
Additionally, we have:
Hence, is a common fixed point of and S. □
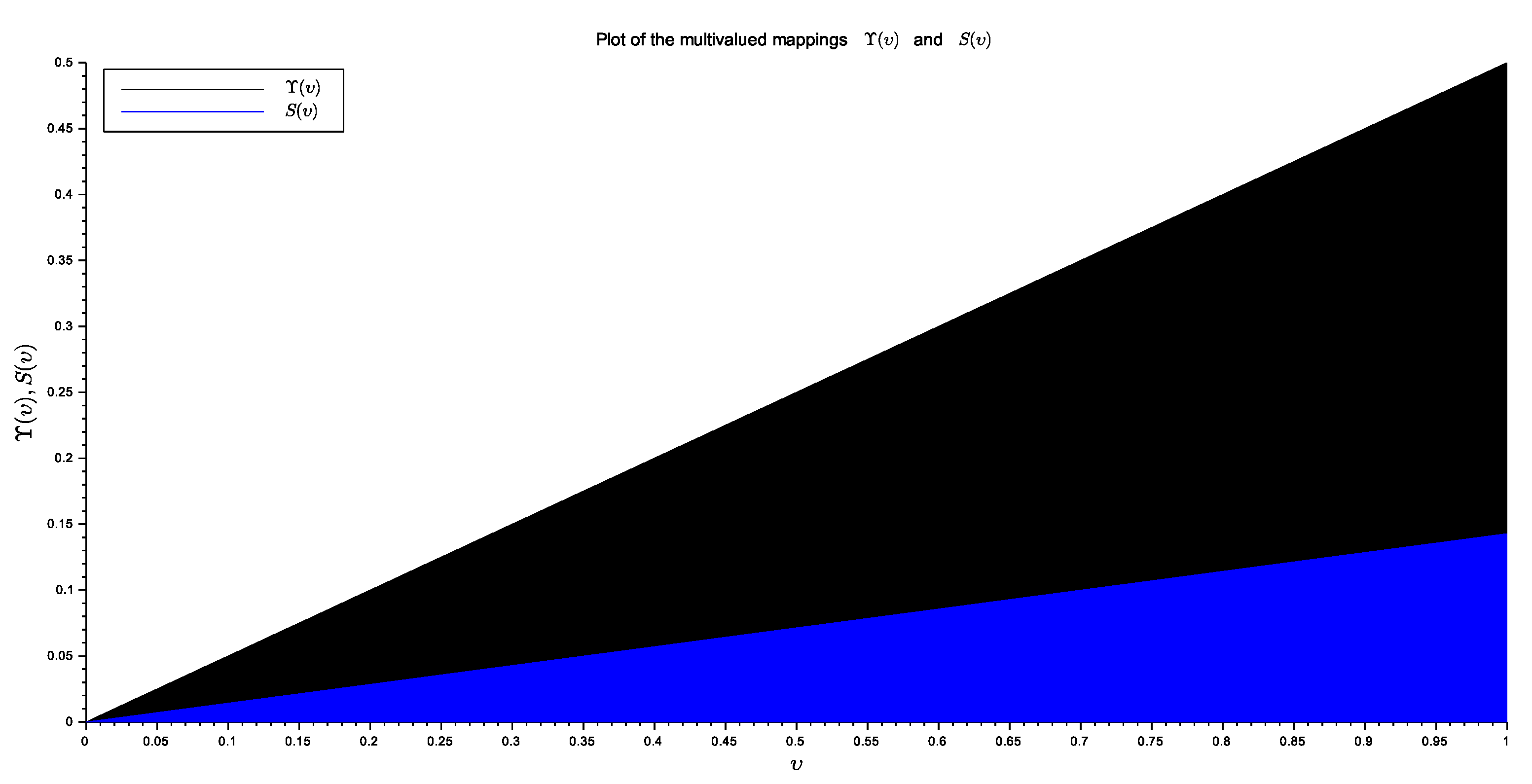
Example 2.

Assume with usual metric . Construct , such that:
and
for all (see Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Combined plot of the multivalued mappings and S.
Without a loss of generality, suppose that , , and . Then,
, and .
Therefore, we can check that is satisfied for , and for all , such that and .
Hence, all the conditions of Theorem 2 are satisfied and hence is a common fixed point of Υ and S.
4. Conclusions and Future Work
In this paper, we introduced MVIK-type contraction and multivalued (, , )-interpolative Kannan-type contraction mappings. The existence of fixed point results was investigated for such maps. The existence of common fixed points for MVIK-type contractions was also established. We provided a new and easier technique of proof for common fixed point theorems of multivalued maps. As mentioned earlier, it was observed that all generalized interpolative Kannan-type contractions need not have a fixed point in a complete MS. Hence, we attempted to address this question of existence for certain multivalued mappings. However, we assumed stronger conditions in our hypothesis, such as the compactness of the images of the map under consideration. It would be interesting to investigate, in future work, if this condition can be relaxed and the existence of these mappings can still be proven.
In Definition 2, in place of , it may be sufficient to use a real increasing function f, such that has suitable properties. In place of , it may be sufficient to assume a real decreasing function g, such that has suitable properties. Definition 3 and Theorem 2 may also be revised in light of these considerations. All these factors will lead to an important extension of the current results.
Establishing the conditions that imply the uniqueness of a fixed point for multivalued mappings is always of special interest.
Author Contributions
Author N.K. contributed to the Investigation, Methodology, and Writing of the original draft; Author R.S. contributed to the Investigation, Validation, Writing, and Editing; Author P.D. contributed to the Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing of the original draft, Validation, and Editing; Author H.M.S. contributed to the Investigation, Validation, Writing, and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the learned referees for their valuable comments, which helped with the correction of several errors, as well as for suggesting some future research directions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Nadler, S.B. Multi-valued contraction mappings. Pac. J. Math. 1969, 30, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R. Some results on fixed points. Bull. Calc. Math. Soc. 1968, 60, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, R. Some results on fixed points–II. Am. Math. Mon. 1969, 76, 405–408. [Google Scholar]
- Bojor, F. Fixed points of Kannan mappings in metric spaces endowed with a graph. Analele Univ. Ovidius Constanta-Ser. Mat. 2012, 20, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornicki, J. Fixed point theorems for Kannan type mappings. J. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2017, 19, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reich, S. Fixed points of contractive functions. Boll. Unione Mat. Ital. 1972, 5, 26–42. [Google Scholar]
- Reich, S. Kannan’s fixed point theorem. Boll. Unione Mat. Ital. 1971, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam, P.V. Completeness and fixed points. Monatshefte Math. 1975, 80, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapinar, E. Revisiting the Kannan type contractions via interpolation. Adv. Theory Nonlinear Anal. Appl. 2018, 2, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaba, Y.U.; Karapinar, E. A new approach to the interpolative contractions. Axioms 2019, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaba, Y.U.; Aydi, H.; Mlaiki, N. (ρ,η,μ)-Interpolative Kannan contractions I. Axioms 2021, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydi, H.; Chen, C.M.; Karapinar, E. Interpolative Ćirić-Reich-Rus type contractions via the Branciari distance. Mathematics 2019, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydi, H.; Karapinar, E.; Hierro, A.F.R. ω-Interpolative Ćirić-Reich-Rus-type contractions. Mathematics 2019, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karapinar, E.; Agarwal, R.P.; Aydi, H. Interpolative Reich-Rus-Ćirić type contractions on partial metric spaces. Mathematics 2018, 6, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karapinar, E.; Alahtani, O.; Aydi, H. On interpolative Hardy-Rogers type contractions. Symmetry 2018, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debnath, P.; Mitrović, Z.; Radenović, S. Interpolative Hardy-Rogers and Reich-Rus-Ćirić type contractions in b-metric spaces and rectangular b-metric spaces. Math. Vesnik. 2020, 72, 368–374. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, P. Banach, Kannan, Chatterjea, and Reich-type contractive inequalities for multivalued mappings and their common fixed points. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 2022, 45, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, P.; Konwar, N.; Radenović, S. Metric Fixed Point Theory: Applications in Science, Engineering and Behavioural Sciences; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, W.A.; Shahzad, N. Fixed Point Theory in Distance Spaces; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, H.K. An Introduction to Nonlinear Analysis and Fixed Point Theory; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, P.; Srivastava, H.M. Global optimization and common best proximity points for some multivalued contractive pairs of mappings. Axioms 2020, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, P.; Srivastava, H.M. New extensions of Kannan’s and Reich’s fixed point theorems for multivalued maps using Wardowski’s technique with application to integral equations. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, P.; Mitrović, Z.D.; Srivastava, H.M. Fixed points of some asymptotically regular multivalued mappings satisfying a Kannan-type condition. Axioms 2021, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, H.M.; Shehata, A.; Moustafa, S.I. Some fixed point theorems for F(ψ,φ)-contractions and their application to fractional differential equations. Russ. J. Math. Phys. 2020, 27, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriceanu, M.; Petrusel, A.; Rus, I. Fixed point theorems for some multivalued generalized contraction in b-metric spaces. Int. J. Math. Stat. 2010, 6, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Czerwik, S. Nonlinear set-valued contraction mappings in b-metric spaces. Atti Sem. Mat. Univ. Modena 1998, 46, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).