Stakeholder Analysis for Climate Change Adaptation: A Case Study from the Living Lab Schouwen-Duiveland, The Netherlands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Overview of Recent Reviews on SA
2.2. Critique of SA
2.3. SA in the Environmental Management Domain
| Domain | Review Reference | Focus | Methodological Approach and Evidence Base (Database/Search Engine; Period; Final Included N of Studies) | Key Findings | Identified Knowledge Gaps Regarding SA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business administration | Mahajan et al. (2023) [8] | Assess stakeholder theory (ST) in business ethics and organisational management | Systematic literature review: Scopus: searches up to 2021; N = 988 publications included |
Four major research streams identified:
|
|
| Project management | Achterkamp & Vos (2008) [37] | How the stakeholder notion and SA methods are used and applied in project management literature | Literature search and meta-analysis within two project management journals: International Journal of Project Management (IJPM) and Project Management Journal (PMJ); 1995–2006 N = 42 articles included |
|
|
| Education | Syed et al. (2024) [35] | Discover interfaces between the concept of higher education institutions (HEIs) and stakeholder analysis | Bibliometric and content analysis: Scopus: last 25 years, 1996–2020; N = 469 publications included |
Four topical clusters identified:
|
|
| Construction industry | Agyemang et al. (2025) [51] | Systematically review stakeholder and shareholder theories in construction studies | Systematic scoping review and thematic analysis: Scopus and Google Scholar, 2000–2024; N = 31 publications included |
|
|
| Health innovation | Franco-Trigo et al. (2020) [36] | To provide an overview of the use and reporting of stakeholder analyses in health innovation planning processes | Systematic scoping review: PubMed, Scopus, and DOAJ (+Google), searches up to 2017; N = 51 publications included |
|
|
| Environmental management | Bendtsen et al. (2021) [6] | State of the art of SA within environmental management and regulation | Systematic literature review: Scopus and WoS: no time limits; N = 48 publications included |
|
|
3. Materials and Methods
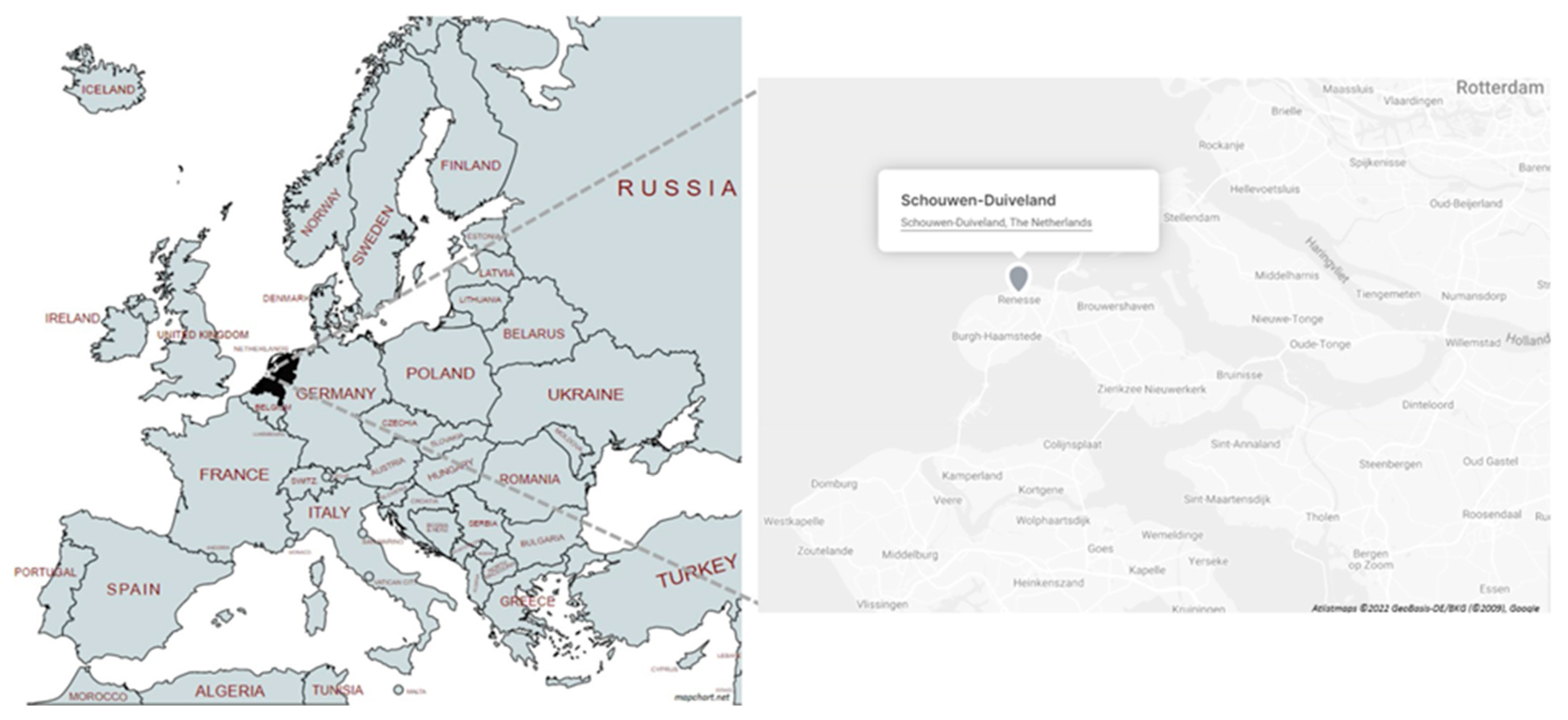
3.1. Case Study of Stakeholder Analysis of Drought on the Island of Schouwen-Duiveland
3.1.1. Case Study Area and Methodology
3.1.2. Data Collection
Early Stakeholder Identification
Survey Questionnaire
Interviews
Workshop
3.2. Data Analysis
4. Results
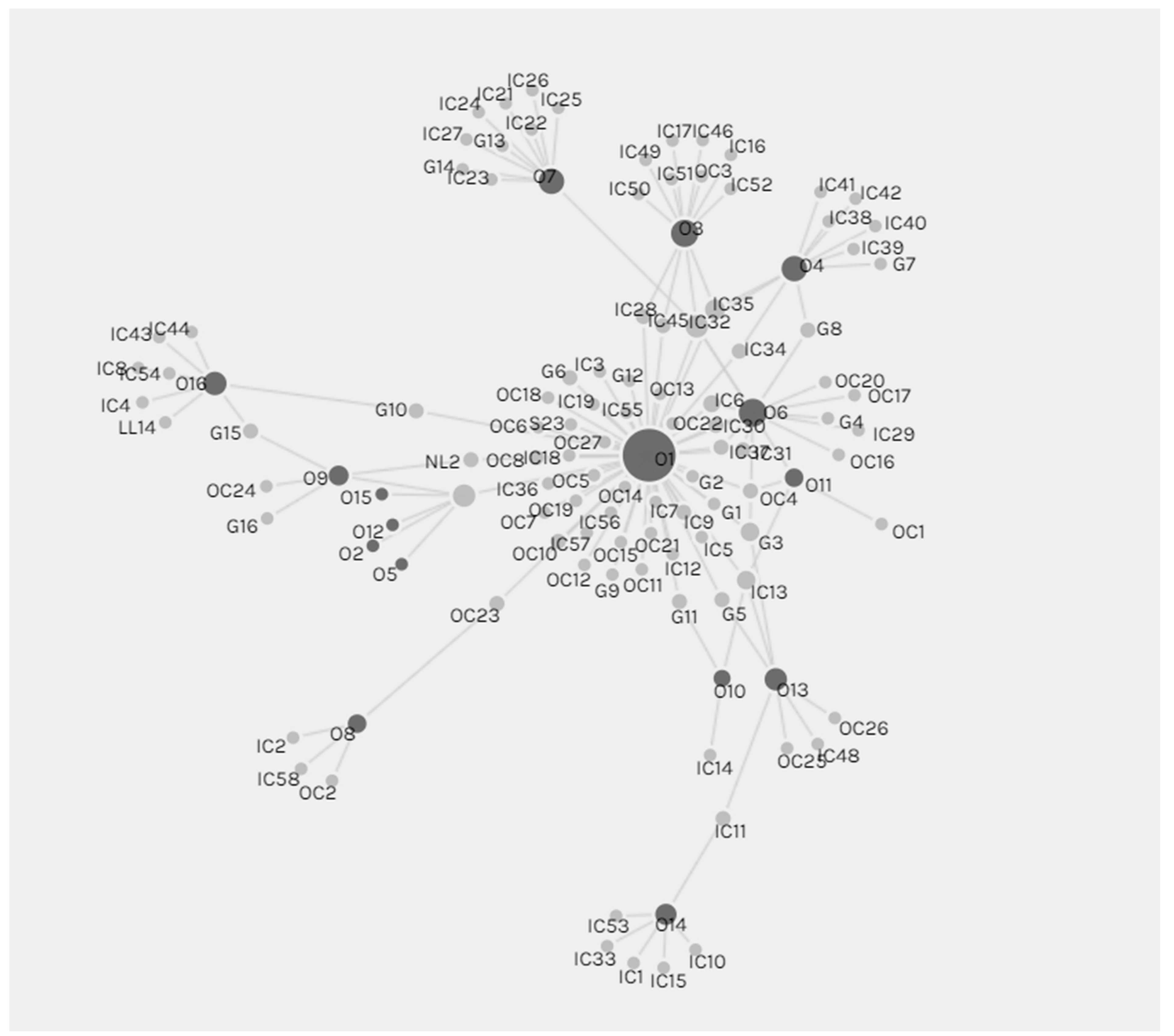
4.1. Stakeholder Identification
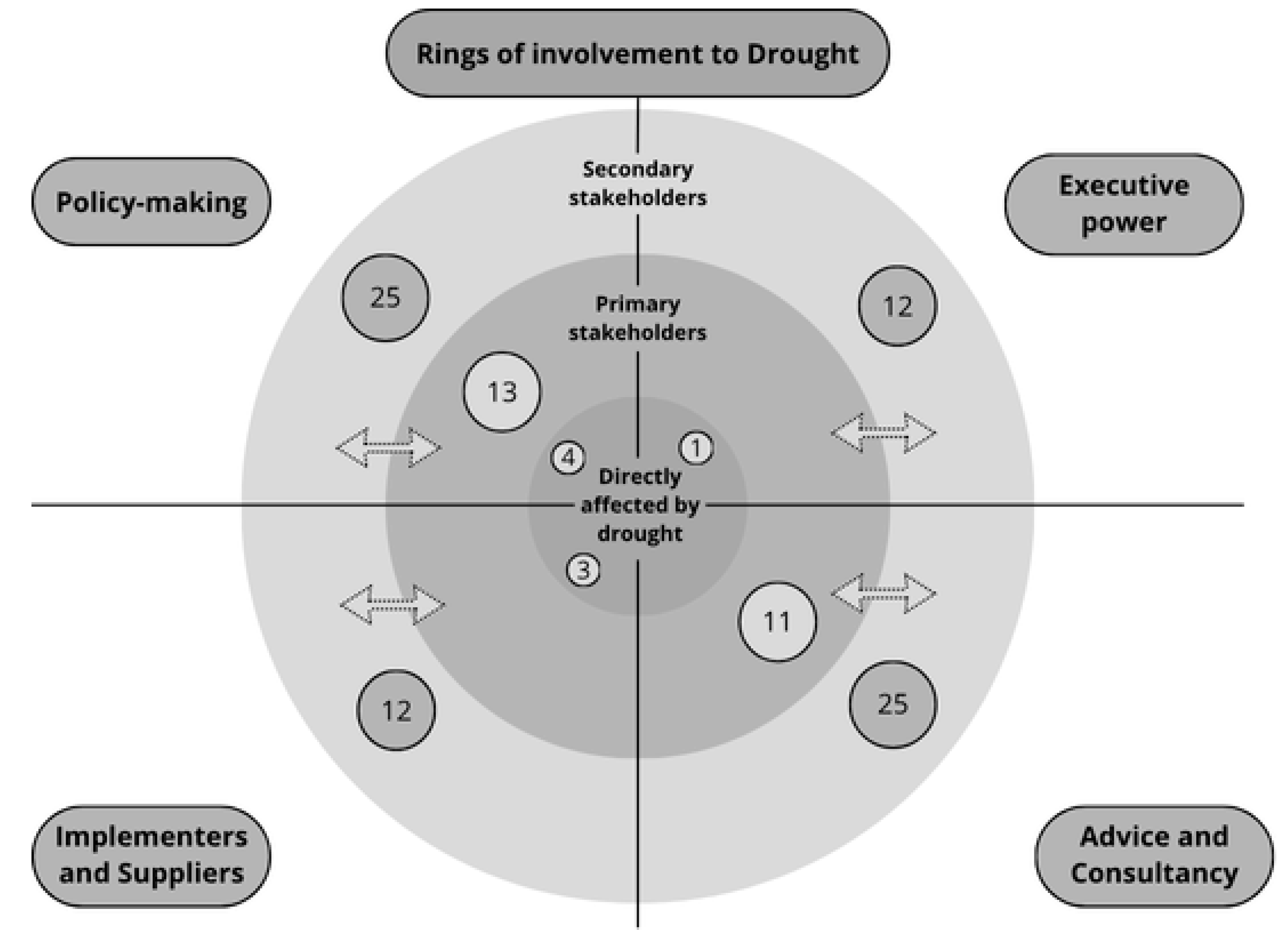
4.2. Stakeholder Analysis: Categorisation
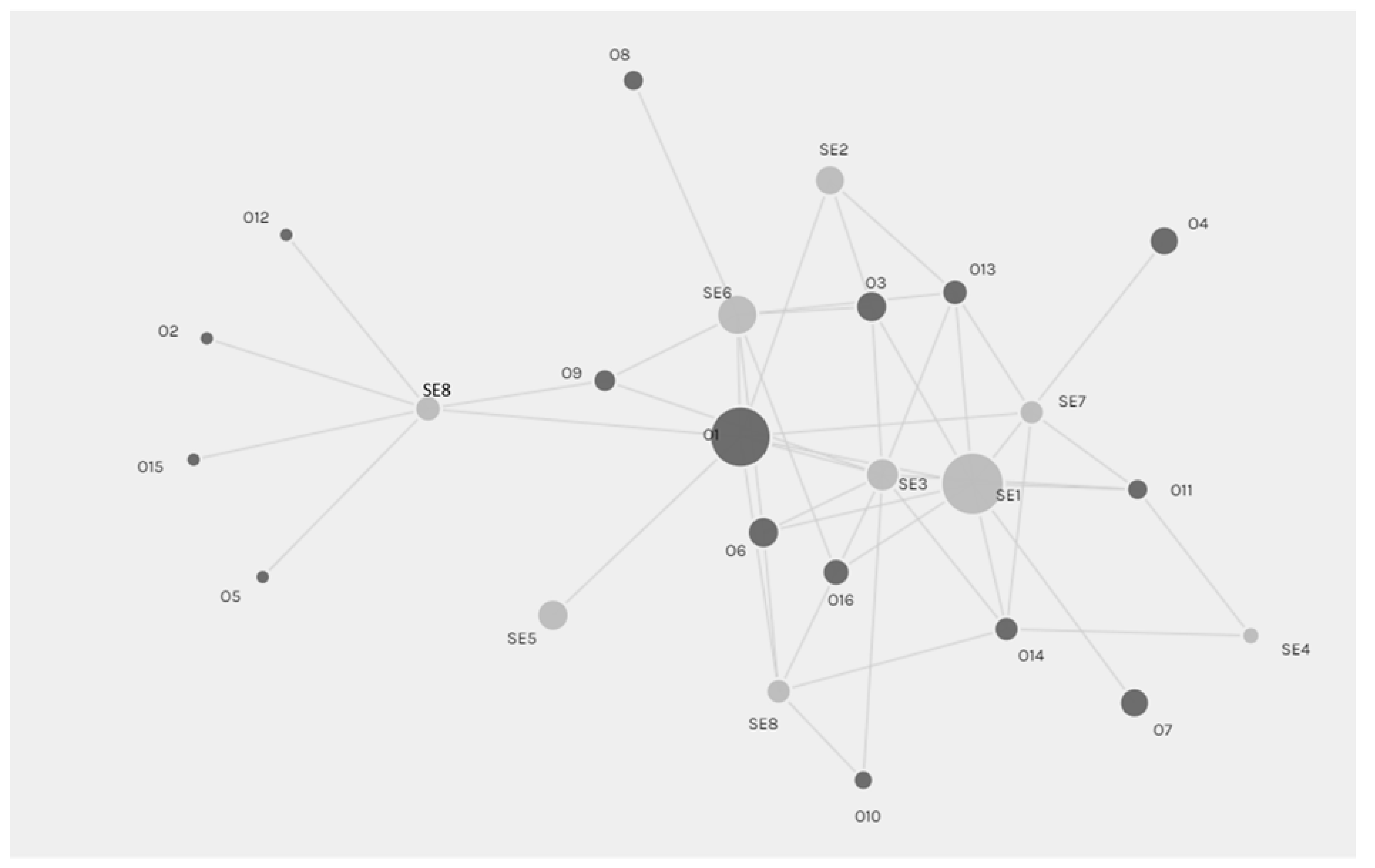
4.3. Stakeholder Analysis: Interrelationships
5. Discussion
5.1. Role of Intermediaries in SA
5.2. Methodological Reflections
5.3. Limitations and Recommendations for Future Research
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shukla, P.R.; Skea, J.; Calvo Buendia, E.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Pörtner, H.O.; Roberts, D.G.; Zhai, P.; Slade, R.; Connors, S.; van Diemen, R.; et al. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorino, D.J. Citizen participation and environmental risk: A survey of institutional mechanisms. Sci. Technol. Hum. Values 1990, 15, 226–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.S.; Graves, A.; Dandy, N.; Posthumus, H.; Hubacek, K.; Morris, J.; Prell, C.; Quinn, C.H.; Stringer, L.C. Who’s in and why? A typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1933–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; ISBN 9781139192675. [Google Scholar]
- Billgren, C.; Holmén, H. Approaching reality: Comparing stakeholder analysis and cultural theory in the context of natural resource management. Land Use Policy 2008, 25, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, E.B.; Clausen, L.P.W.; Hansen, S.F. A review of the state-of-the-art for stakeholder analysis with regard to environmental management and regulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, R.E.; Wicks, A.C.; Parmar, B. Stakeholder Theory and “The Corporate Objective Revisited”. Organ. Sci. 2004, 15, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, R.; Lim, W.M.; Sareen, M.; Kumar, S.; Panwar, R. Stakeholder theory. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 166, 114104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimble, R.; Wellard, K. Stakeholder methodologies in natural resource management: A review of principles, contexts, experiences and opportunities. Agric. Syst. 1997, 55, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, R.M.; Witt, G.B.; Lacey, J. Power, perspective, and privilege: The challenge of translating stakeholder theory from business management to environmental and natural resource management. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushove, P.; Vogel, C. Heads or tails? Stakeholder analysis as a tool for conservation area management. Glob. Environ. Change 2005, 15, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Badola, R.; Hussain, S.A.; Hickey, G.M. Assessing the utility of stakeholder analysis to Protected Areas management: The case of Corbett National Park, India. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 2956–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannetti, L.M.; Göttert, T.; Zeller, U.; Esler, K.J. Identifying and categorizing stakeholders for protected area expansion around a national park in Namibia. Ecol. Soc. 2019, 24, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalsen, K.H.; Jentoft, S. From user-groups to stakeholders? The public interest in fisheries management. Mar. Policy 2001, 25, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbakidze, M.; Angelstam, P.; Axelsson, R. Stakeholder identification and analysis for adaptive governance in the Kovdozersky Model Forest, Russian Federation. For. Chron. 2012, 88, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, O.; Harvey, J.; Tollin, N. Stakeholder analysis for industrial waste management systems. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeleliere, E.; Nyamekye, A.B.; Antwi-Agyei, P.; Boamah, E.F. Strengthening climate adaptation in the northern region of Ghana: Insights from a stakeholder analysis. Clim. Policy 2022, 22, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.E.; Chan, F.K.S.; Scheffran, J. Climate change, water management and stakeholder analysis in the Dongjiang River basin in South China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2016, 34, 166–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, L.; García, J.A.; Bodoque, J.M. Stakeholder analysis: Mapping the river networks for integrated flood risk management. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 124, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter-Mkrtchyan, A.V.; Franklin, A.L. Stakeholder analysis in the context of natural disaster mitigation: The case of flooding in three U.S. cities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, V.; Piadeh, F.; Chen, A.S.; Behzadian, K. Stakeholder analysis in the application of cutting-edge digital visualisation technologies for urban flood risk management: A critical review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 236, 121426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, D.; Borg, M.; Hallett, S.H.; Sakrabani, R.S.; Thompson, A.; Papadimitriou, L.; Knox, J.W. Multi-stakeholder analysis to improve agricultural water management policy and practice in Malta. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 229, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, K.; Simonsson, L.; Swartling, Å.G.; Linnér, B. Method Development for Identifying and Analysing Stakeholders in Climate Change Adaptation Processes. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2012, 14, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrich, V.M.; Elliff, C.; de Andrade, M.M.; Grilli, N.M.; Turra, A. Stakeholder Analysis as a strategic tool in framing collaborative governance arenas for marine litter monitoring. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 198, 115799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingault, N.; Caron, P.; Kolmans, A.; Lemke, S.; Kalafatic, C.; Zikeli, S.; Waters-Bayer, A.; Callenius, C.; Qin, Y. Moving beyond the opposition of diverse knowledge systems for food security and nutrition. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods (Applied Social Research Methods), 5th ed.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2013; p. 312. ISBN 978-1452242569. [Google Scholar]
- Kemmis, S.; McTaggart, R.; Nixon, R. The Action Research Planner: Doing Critical Participatory Action Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, B.G.; Hannon, B. Center for Environmental Philosophy, The University of North Texas Environmental Values. Environ. Ethics 1997, 19, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.S.; Merkle, B.G.; Cook, E.J.; Hafferty, C.; Hejnowicz, A.P.; Holliman, R.; Marder, I.D.; Pool, U.; Raymond, C.M.; Wallen, K.E.; et al. Reimagining the language of engagement in a post-stakeholder world. Sustain. Sci. 2024, 19, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, T.; Vargas, E. Drought management plans in the European Union: The case of Spain. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 1537–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, N. IWRM in England: Bridging the gap between top-down and bottom-up implementation. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2014, 30, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.E. The politics of stakeholder theory: Some future directions. Bus. Ethics Q. 1994, 4, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugha, R.; Varvasovszky, Z. Stakeholder analysis: A review. Health Policy Plan. 2000, 15, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Cook, C.N.; Nguyen, V.M.; Walsh, J.C.; Young, N.; Cvitanovic, C.; Grainger, M.J.; Randall, N.P.; Muir, M.; Kadykalo, A.N.; et al. Environmental evidence in action: On the science and practice of evidence synthesis and evidence-based decision-making. Environ. Evid. 2023, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, R.T.; Singh, D.; Agrawal, R.; Spicer, D. Higher education institutions and stakeholder analysis: Theoretical roots, development of themes and future research directions. Ind. High. Educ. 2024, 38, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Trigo, L.; Fernandez-Llimos, F.; Martínez-Martínez, F.; Benrimoj, S.I.; Sabater-Hernández, D. Stakeholder analysis in health innovation planning processes: A systematic scoping review. Health Policy 2020, 124, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achterkamp, M.C.; Vos, J.F.J. Investigating the use of the stakeholder notion in project management literature, a meta-analysis. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2008, 26, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.; Freeman, R.E.; Wicks, A.C. What stakeholder theory is not. Bus. Ethics Q. 2003, 13, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.K.; Agle, B.R.; Wood, D.J. Toward a theory of stakeholder identification and salience: Defining the principle of who and what really counts. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1997, 22, 853–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.C. Value maximization, stakeholder theory, and the corporate objective function. Bus. Ethics Q. 2002, 12, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, M. Stakeholder engagement: Beyond the myth of corporate responsibility. J. Bus. Ethics 2007, 74, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortetmäki, T.; Heikkinen, A.; Jokinen, A. Particularizing nonhuman nature in stakeholder theory: The recognition approach. J. Bus. Ethics 2023, 185, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, H.; Baek, J.S. Assemblage-based stakeholder analysis in design: A conceptual framework through the lenses of post–anthropocentrism. CoDesign 2024, 20, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prell, C.; Hubacek, K.; Reed, M. Stakeholder analysis and social network analysis in natural resource management. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2009, 22, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weible, C.M. An Advocacy Coalition Framework Approach to Stakeholder Analysis: Understanding the Political Context of California Marine Protected Area Policy. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2006, 17, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastran, M. Stakeholder analysis in a protected natural park: Case study from Slovenia. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2014, 57, 1359–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukristiyono, S.; Purwanto, R.H.; Suryatmojo, H.; Sumardi, S. Stakeholder analysis on sungai wain protected forest management in Balikpapan city, East Kalimantan Province. J. Sylva Lestari 2021, 9, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovacool, B.K. A critical stakeholder analysis of the Trans-ASEAN Gas Pipeline (TAGP) Network. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaltonen, K. Project stakeholder analysis as an environmental interpretation process. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2011, 29, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaginalkar, A.; Kumar, S.; Gargava, P.; Niyogi, D. Stakeholder analysis for designing an urban air quality data governance ecosystem in smart cities. Urban Clim. 2023, 48, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyemang, E.A.; Musonda, I.; Zulu, S. Stakeholder theory and shareholder theory application in construction field: Systematic scoping review. Constr. Econ. Build. 2025, 25, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, V.R.; Field, C.B.; Dokken, D.J.; Mastrandrea, M.D.; Mach, K.J. (Eds.) Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Working Group II Contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report of the Integovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; ISBN 9781107415386. [Google Scholar]
- Municipality of Schouwen-Duiveland. Verslag Klimaatstresstest SchouwenDuiveland. Municipality of Schouwen-Duiveland; Municipality of Schouwen-Duiveland: Schouwen-Duiveland, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous (Scheldestromen Water Board, Middelburg, The Netherlands). Personal communication, 2020.
- CBS; PBL; RIVM; WUR. Jaarlijkse Hoeveelheid Neerslag in Nederland, 1910–2019. Available online: https://www.clo.nl/indicatoren/nl050808-jaarlijkse-hoeveelheid-neerslag-in-nederland-1910-2019 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Rijkswaterstaat. Bescherming Tegen het Water. Rijkswaterstaat Ministerie van Infrastructuur en Waterstaat; Rijkswaterstaat: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- KNMI. KNMI’s Klimaatscenario’s Voor Nederland 14: Herziene Uitgave 2015. Koninklijk Nederlands Meteorologisch Instituut Ministerie van Infrastractuur en Milieu. Available online: https://cdn.knmi.nl/system/data_center_publications/files/000/070/616/original/Brochure_KNMI14_NL.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Living Lab Schouwen-Duiveland Living Lab Schouwen-Duiveland. Available online: https://livinglabschouwen-duiveland.nl/ (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Maas, T.; van den Broek, J.; Deuten, J. Living labs in Nederland: Van Open Testfaciliteit tot Levend Lab; Rathenau Instituut: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Baungaard, C.; Kok, K.P.W.; den Boer, A.C.L.; Brierley, C.; van der Meij, M.G.; Gjefsen, M.D.; Wenink, J.; Wagner, P.; Gemen, R.; Regeer, B.J.; et al. FIT4FOOD2030: Future-proofing Europe’s Food Systems with Tools for Transformation and a Sustainable Food Systems Network. Nutr. Bull. 2021, 46, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisman, J.C.; Feenstra, L.D.; Broerse, J.E.W.; Grijseels, M.; Gudek, L.; de Hoop, E.; Jones, T.S.; Loeber, A.M.C.; Luger, J.; van der Meij, M.G.; et al. Labbing for sustainability transformations: Learning about challenges and strategies for impact. GAIA—Ecol. Perspect. Sci. Soc. 2024, 33, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flyvbjerg, B. Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research. Qual. Inq. 2006, 12, 219–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, H. The Logic of Qualitative Survey Research and its Position in the Field of Social Research Methods. Forum Qual. Sozialforschung/Forum Qual. Soc. Res. 2010, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiers, J. A Decision-Support Tool for Assessing Areas Facing Drought: A Case Study of Living Lab Schouwen-Duiveland, Zeeland, The Netherlands. Master’s Thesis, Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, Venice, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rijksoverheid Ringen van Invloed. Available online: https://communicatiekompas.nl/hulpmiddelen/ringen-van-invloed (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- Chevalier, J.; Buckles, D. SAS2: A Guide to Collaborative Inquiry and Social Engagement; SAGE Publications India Pvt Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2008; ISBN 9788178298900. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, J.W.; Neal, Z.P.; Brutzman, B. Defining brokers, intermediaries, and boundary spanners: A systematic review. Evid. Policy 2021, 18, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.; Robson-Williams, M.; Edwards, S. A close examination of the role and needed expertise of brokers in bridging and building science policy boundaries in environmental decision making. Palgrave Commun. 2020, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegleb, V.; Bruns, A. Working the boundary: Science–policy interactions and uneven knowledge politics in IPBES. Sustain. Sci. 2023, 18, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guston, D.H. Boundary organizations in environmental policy and science: An introduction. Sci. Technol. Hum. Values 2001, 26, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.C.; Tomich, T.P.; van Noordwijk, M.; Guston, D.; Catacutan, D.; Dickson, N.M.; McNie, E. Boundary work for sustainable development: Natural resource management at the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4615–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma-aho, V.; Vos, M. Towards a more dynamic stakeholder model: Acknowledging multiple issue arenas. Corp. Commun. Int. J. 2010, 15, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Manji, S.; Lovett, J.; Mitchell, G. Factors affecting disaster resilience in oman: Integrating stakeholder analysis and fuzzy cognitive mapping. Risks Hazards Crisis Public Policy 2021, 12, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, I.J.; Roca, E.; Villares, M. Integrating climate change adaptation in coastal governance of the Barcelona metropolitan area. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2021, 26, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, E.; McDermott, R.; Snyder, W.P. Cultivating Communities of Practice; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; ISBN 1-57851-330-8. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suškevičs, M.; Swiers, J.; Prakofjewa, J.; Sõukand, R.; Prūse, B. Stakeholder Analysis for Climate Change Adaptation: A Case Study from the Living Lab Schouwen-Duiveland, The Netherlands. Land 2025, 14, 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112209
Suškevičs M, Swiers J, Prakofjewa J, Sõukand R, Prūse B. Stakeholder Analysis for Climate Change Adaptation: A Case Study from the Living Lab Schouwen-Duiveland, The Netherlands. Land. 2025; 14(11):2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112209
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuškevičs, Monika, Joost Swiers, Julia Prakofjewa, Renata Sõukand, and Baiba Prūse. 2025. "Stakeholder Analysis for Climate Change Adaptation: A Case Study from the Living Lab Schouwen-Duiveland, The Netherlands" Land 14, no. 11: 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112209
APA StyleSuškevičs, M., Swiers, J., Prakofjewa, J., Sõukand, R., & Prūse, B. (2025). Stakeholder Analysis for Climate Change Adaptation: A Case Study from the Living Lab Schouwen-Duiveland, The Netherlands. Land, 14(11), 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112209









