Abstract
The Yellow River, with its extremely high sediment loads, and the Yellow River Estuary (YRE) serve as a vital conduit for material exchange between land and marine environments, where sediment–phosphorus interactions profoundly influence nutrient cycling, ecological health and eutrophication potential. This paper reviews the distribution of phosphorus in overlying water and sediment, the characteristics of phosphorus migration and transformation across the sediment–water interface, and the effecting factors of phosphorus migrate, such as sediment properties and environmental factors in the YRE. Inorganic phosphorus was the dominant form in the overlying water and sediment. Suspended sediment acts as a dynamic reservoir for phosphorus transportation in the YRE. The dynamic estuarine environment promotes sediment deposition, which helps reduce phosphorus levels in the water. Upon entering the Bohai Sea, sediment is transformed into the source of phosphorus. The released phosphorus may increase the nutrient load in shallow Bohai Sea waters. Fine particles demonstrate strong adsorption capacity for reactive phosphorus, acting as the primary carriers for phosphorus migration at the sediment–water interface. The grain size of the suspended sediment in the Yellow River exhibited significant sorting characteristics with varying sediment content, consequently affecting the forms of phosphorus. Likewise, the influence of biogeochemical conditions on the transport and transformation of sediment and phosphorus was further analyzed and the partial least squares-path model of related variables on estuarine phosphorus is constructed to interpret the behavior of sediment and phosphorus in the YRE. Finally, the current situation and indeterminacy of water quality models in the estuary were appraised. The priority of analyzing and revealing the environmental behaviors of phosphorus in a sediment-laden river estuary in the future was further proposed against the present deficiencies. This review holds significant practical importance for enhancing the assessment of ecological environment quality and ecological restoration in the YRE.
1. Introduction
Pollutants discharged from human activities migrate through water, ultimately converging in estuaries before entering the ocean, thereby posing a threat to the global marine ecosystem [1]. Estuaries, influenced by river input and tides, emerge as one of the most dynamic regions in terms of water environment and hydrodynamic conditions. In recent years, research on the dynamics, transport and simulation of pollutants in estuarine environments has rapidly evolved from analyzing the pollutant content to identifying pollutant morphology, and subsequently to analyzing pollutant bioavailability in multiple environmental media. Similarly, the spatiotemporal changes of pollutants at the micro-interface have transitioned into simulating spatiotemporal changes at regional and global scales. Therefore, research on the environmental processes and behaviors of pollutants is characterized by multiple processes, interfaces and scales. Estuaries exhibit significant variability in parameters such as salinity, pH and temperature, which significantly affect the migration, accumulation and sedimentation of pollutants. Consequently, numerous scholars have been intrigued and motivated to conduct thorough scientific studies to better understand and explore the behavior of pollutants in these ecosystems [2,3,4].
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient element crucial for the growth and reproduction of all marine phytoplankton [5]. However, excessive phosphorus input into water bodies can lead to eutrophication, causing harm to aquatic organisms. River input and wet/dry deposition collectively influence the dynamic balance of marine phosphorus, with rivers being the primary source of phosphorus in the ocean. The biogeochemical behavior of phosphorus in estuaries directly impacts the flux of phosphorus transported from rivers to the marine system [6,7]. During its migration from rivers to the ocean, the original equilibrium relationship between sediment and phosphorus is disrupted, leading to the gradual formation of a new equilibrium in the estuary. This process involves various mechanisms such as adsorption and desorption, attachment and detachment, dissolution and sedimentation and colloidal flocculation [8,9].
Hyper-concentrated sediment-laden river estuaries are usually associated with rivers carrying a large sediment load, such as the Amazon River, the Mississippi River and the large Asian rivers draining the Himalayas (notably the Yellow, Yangtze, Red, Mekong, Ayeyarwady, Ganges-Brahmaputra and Indus). The Yellow River, as the second longest river in China, serves as an important water source in northern China and ranks among the major sediment-laden rivers globally [10,11]. In 2022, the annual runoff at the hydrologic sites in Lijin was 26.09 billion cubic meters, with an annual sediment discharge of 0.125 billion tons. However, the average annual runoff for the periods 1956–2016 and 1987–2016 stood at 49.004 billion cubic meters and 44.872 billion cubic meters, respectively. Correspondingly, the average sediment discharge in these periods was 619 million tons (1956–2016) and 247.9 million tons (1987–2016) [12]. Additionally, the shallow water in the coastal area outside the estuary results in weak erosion and transport between waves and currents, causing a large amount of sediment from the Yellow River to be deposited near the estuary.
Increasing agricultural pressures have triggered severe alterations to the water–sediment environment of the Yellow River, heightening ecological risks and leading to estuarine eutrophication characterized by excessive inorganic phosphorus levels [13,14]. The Yellow River Estuary (YRE) constitutes a critical interface between terrestrial and marine ecosystems, where sediment–phosphorus interactions profoundly influence nutrient cycling, ecological health and eutrophication potential. Considering the unique role of the YRE, this review aims to achieve three objectives. Firstly, it integrates published data to clarify the spatiotemporal patterns of phosphorus in the water–sediment system of the YRE. Secondly, it elucidates the intrinsic mechanism between sediment properties, environmental factors and the adsorption–desorption of phosphorus, as well as its source–sink transformation. Thirdly, it evaluates the applicability of current estuarine water quality models in simulating phosphorus–sediment interactions in environments with high sediment concentrations. Finally, the priority of analyzing and revealing the environmental behaviors of phosphorus in a sediment-laden river estuary in the future was further proposed against the present deficiencies. An in-depth analysis of sediment and phosphorus accumulation in the estuary holds significant practical importance for enhancing the assessment of ecological environment quality and ecological restoration in the YRE.
2. Distribution of Phosphorus in Overlying Water and Sediment of the YRE
The Yellow River originates on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau at an elevation of 4500 m and extends 5464 km from its source to the Bohai Sea. Not only does it serve as a channel for water flow, energy and materials, but it also provides a vital water source for 114 million people, supporting industrial, residential and agricultural activities. The Yellow River Delta (YRD), located on the southern coast of the Bohai Sea in eastern China, receives the largest sediment load from the Loess Plateau [15]. The Bohai Sea, characterized as a typical semi-enclosed shallow sea on the continental shelf, features a unique marine circulation system and receives abundant river-derived sediments. Consequently, the Yellow River deltaic estuary plays a crucial role as an interface between the continent and the ocean in terms of material fluxes.
Phosphorus in the overlying water of the YRE mainly contains dissolved phosphorus and particulate phosphorus. Dissolved phosphorus includes phosphate (PO43−, HPO4− and H2PO4−), pyrophosphate, metaphosphate, polyphosphate, metal-binding phosphorus (e.g., Fe-P, Al-P) and low valence phosphate (e.g., phosphite, hypophosphite) [16,17,18,19]. Particulate phosphorus has diverse forms, mainly including phosphorus in organisms, high energy phosphates such as intracellular DNA, RNA, ADP and ATP, mineral-bound phosphorus, adsorbed phosphorus on particles and crystalline mineral phosphorus in detritus [16]. Phosphorus in the sediment of the YRE can be divided into inorganic phosphorus and organic phosphorus [17]. Among them, inorganic phosphorus mainly exists in the forms of metal-bound phosphorus, exchangeable phosphorus and dissolved phosphorus in pore water [16], organic phosphorus mainly refers to particulate organic phosphorus in organisms and dissolved organic phosphorus composed of phospholipids, phosphates and phosphonates [17].
The content of phosphorus in the overlying water and sediment of the YRE were analyzed to assess environmental conditions. In the YRE, particulate phosphorus (PP) was the dominant form of total phosphorus (TP), accounting for as much as 76.8%. Dissolved total phosphorus (DTP) concentrations were around 0.008–0.074 mg/L in the overlying water of the YRE, and dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP) concentrations ranged from 0.001 to 0.060 mg/L. Furthermore, TP concentrations were around 594.4–956.9 mg/kg in sediment of the YRE, inorganic phosphorus (IP) were around 475.2–944.2 mg/kg and organic phosphorus (OP) ranged from 27.3 to 108.0 mg/kg in sediment of the YRE. The phosphorus concentrations in the overlying water of the YRE showed significant spatial variation. DIP concentrations in the overlying water dropped to 0.008 mg/L after entering the shallow Bohai Sea waters, while the DTP concentrations slightly rose to 0.021 mg/L [20]. This change indicated that, when transitioning from the estuary to the shallow Bohai Sea waters, the IP concentrations in the water decrease significantly, which may be related to sediment adsorption, biological utilization, or phosphorus form transformation caused by changes in environmental conditions (such as pH and salinity).
Sediment plays a crucial role in controlling phosphate concentrations and the phosphorus cycle in the water (Figure 1) [21]. The Yellow River has a low phosphorus content in the water due to the adsorption of phosphorus by sediment. The dynamic estuarine environment promotes sediment deposition, which helps reduce the phosphorus levels in the water [22]. In the sediment of the YRE, IP is the dominant form of phosphorus, accounting for over 80% of the total phosphorus. Among them, calcium-bound phosphorus (HCl-P) constitutes 94.16% to 98.81% of IP, making it the main component of IP; iron/aluminum/manganese-bound phosphorus (NaOH-P) only accounts for 2.55%, and organic phosphorus accounts for 5.29%. The contents of NaOH-P in the sediment of the shallow Bohai Sea waters increased, while the content of HCl-P remained relatively stable [20]. HCl-P accounts for an extremely high proportion in the sediment of the YRE, and its source is closely related to calcium phosphate minerals in the loess parent material of the basin. Minerals such as calcareous apatite carried by soil erosion from the Loess Plateau are transported by the river and deposited at the estuary, forming the inert phosphorus reservoir. Compared with the content of NaOH-P in the YRE, NaOH-P in the shallow Bohai Sea waters is higher. This is due to the resuspension of estuarine sediments or the adsorption by reactive iron/aluminum oxides in the marine environment [20]. Additionally, the increase in organic phosphorus from the YRE to the Bohai Sea was influenced by regional agricultural activities. OP in the agricultural non-point source pollution carried by the Yellow River gradually accumulated during transportation from the estuary to the shallow Bohai Sea waters due to the stable sedimentary environment.
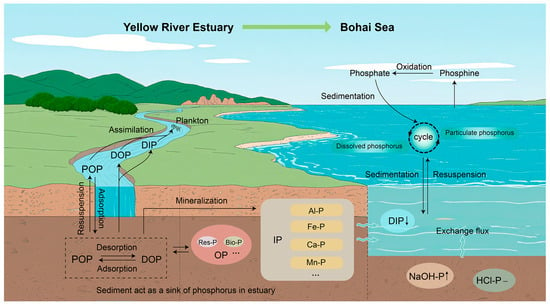
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the source–sink migration process of sediment and phosphorus.
At the estuary, the sediment and water exchange flux of phosphorus accounts for 20.7% of the dissolved phosphorus input flux, playing a vital regulatory role in nutrient inputs. The phosphorus flux at the sediment–water interface in the YRE is closely linked to phosphorus adsorption and release potential. The sediment acts as a sink of phosphorus in the estuary, adsorbing 101.6 tons of phosphorus annually from the water. Upon entering the Bohai Sea, sediment is transformed into the source of phosphorus, releasing 77.3 tons of phosphorus into the seawater each year [12,21]. This transformation is closely related to changes in environmental conditions. From the estuary to the shallow Bohai Sea waters, the pH decreased from 8.35 to 8.00, and the solid concentration dropped from 1.85 g/L to 0.33 g/L in the water. These changes resulted in a rise in the zero-equilibrium phosphorus concentration (EPC0) of sediment, which enhanced its release potential. Notably, the released phosphorus may increase the nutrient load in the shallow Bohai Sea waters, thereby having potential ecological implications for the local marine environment [20].
The estuaries from rivers with hyper-concentrated sediment-laden flows around the world were analyzed, highlighting eight estuaries, including those from China [23,24], USA [25,26,27,28,29,30], Brazil [31] and Vietnam [32,33] (Figure 2a). Notably, the Amazon Estuary, fed by the Amazon River, exhibited the highest mean annual suspended sediment flux at 4.75 × 108 tons/year, followed by the Sai Gon Estuary, YRE and Yangtze Estuary, with mean annual suspended sediment fluxes of 1.6 × 108 tons/year, 1.25 × 108 tons/year and 0.665 × 108 tons/year, respectively. In addition, estuaries such as the Columbia Estuary, Chesapeake Bay Estuary, Lake Pontchartrain Estuary and Breton Sound Estuary were distributed across the Americas. These estuaries originated from the Columbia River, Chesapeake Bay and Mississippi River exhibit annual sediment transport rates of 0.1 × 108 tons/year, 0.0424 × 108 tons/year and 0.0217 × 108 tons/year, respectively.
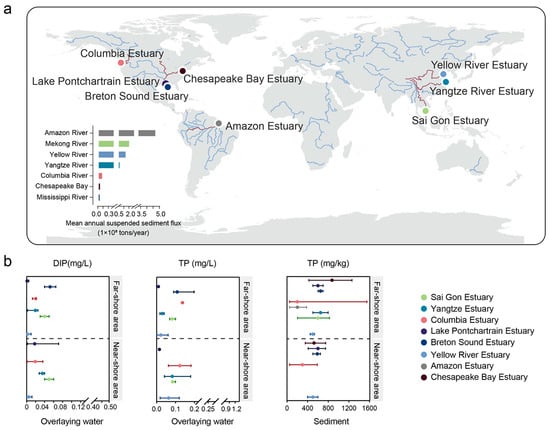
Figure 2.
(a) Localization of 8 estuaries with sediment-laden flows and the mean annual suspended sediment flux of the corresponding river; (b) The content of phosphorus in overlying water and sediment of sandy river estuaries.
The contents of TP and inorganic phosphorus (DIP) in overlying water and sediment on the Yellow River and other estuaries were analyzed to assess the environmental conditions (Figure 2b). TP concentrations were around 0.0152–0.123 mg/L in the overlying water of the near-shore area and 0.0098–0.1367 mg/L in the overlying water of the far-shore area. Similarly, DIP concentrations ranged from 0.005 to 0.05 mg/L in the overlying water of the near-shore area and from 0.002 to 0.0521 mg/L in the overlying water of far-shore area. The YRE exhibits lower concentrations of TP and DIP in overlying water compared to similar estuaries worldwide (Figure 2b). Furthermore, TP concentrations were around 298–600 mg/kg in sediment from the near-shore area and 200–880 mg/kg in sediment from the far-shore area.
3. Characteristics and Dynamics of Sediment in the YRE
An estuary serves as a crucial transition zone where riverine and marine influences converge, making it a major settlement area for terrigenous material and a site of coastal erosion. Consequently, estuarine sediment holds unique biogeochemical information [34]. The development of an estuarine system is influenced by three major factors, including morphological change, hydrodynamics and sedimentology, each of which is further subdivided into three aspects (Figure 3) [35]. Morphological change encompasses three types, including land surface deformation and river valley formation. The morphodynamic equilibrium of estuarine systems is influenced by hydrodynamic forcing, primarily tides, waves and river flows, which shape the landforms. Estuarine sedimentation directly affects the environmental behaviors of pollutants among these dominant factors. Current research on estuarine sedimentation mainly focuses on the physicochemical properties of sediment, sediment dynamics partitioning, sediment transport pattern and the ecological environment effect of sediment [36]. In addition, sediment type (clay, silt and sand) can also affect the morphology. Grain-size characteristics are fundamental sediment properties, encompassing parameters like average grain size, median grain size and sorting coefficient. These characteristics reflect sediment transport, sedimentation and redistribution, providing valuable insights into sedimentation dynamics and transport tendencies. Types of sediment in the YRE are mainly composed of silty clay and clayey silt. Generally, coastal sediment has a low clay content, while the clay content in sediment increases with water depth [37]. Historically, fine-grained sediment in the lower Yellow River facilitated considerable energy for sediment transportation [22]. However, due to the construction of upstream reservoirs and dams and the implementation of sediment regulation measures, the riverbed sediment has become armored [38]. In recent years, a significant reduction in sediment transportation has not only affected the sediment flux into the sea, but has also altered the size grading of surface sediment in the estuary, affecting coastal erosion.
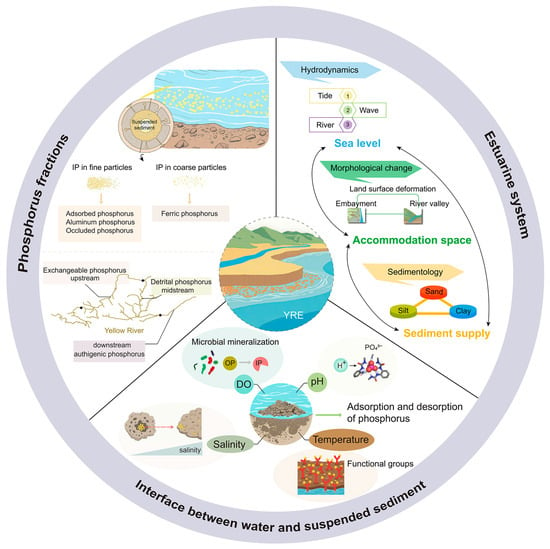
Figure 3.
Dynamic characteristics of sediment and phosphorus in the YRE.
The sediment in the estuary typically contains a clay content of less than 3%. Estuarine sediment transport, primarily influenced by terrestrial input, is characterized by a predominance of silt. In the Yellow River delta, silt constitutes the primary material transported to the sea. The mixing layer, observed in sedimentary profiles, can be related to various factors including disturbance from water and sediment regulation over the years, fluctuations in sediment supply due to a sharp reduction in sediment entering the sea, and marine dynamic events such as strong storms [39]. When sediment concentration is relatively high, suspended particles exhibit larger sizes and coarse particle resuspension is intense, leading to Ca-P becoming the dominant phosphorus migration form. Conversely, lower sediment concentrations correspond to smaller suspended particle sizes and the weaker resuspension of large particles. Under these conditions, fine-sized particles demonstrate strong adsorption capacity for reactive phosphorus, acting as the primary carriers for phosphorus migration at the sediment-water interface [40,41]. In the water environment of the Yellow River, the transformation of highly reactive Fe/Al-P to Ca-P makes suspended particles an important phosphorus sink [42].
The grain size of suspended sediment in the Yellow River exhibited significant sorting characteristics with a varying sediment content, consequently affecting the forms of phosphorus. When the sediment concentration exceeds 15 g/L, the proportion of coarse particles (>31 μm) increased. Under such conditions, the detrital phosphorus (De-P) content demonstrated a linear increase with the rising sediment concentration, with its proportion in total phosphorus escalating from 45% to 75%. This is attributed to the migration of apatite minerals input by erosion in the Loess Plateau with coarse sediment [43]. While fine particles (<8 μm) accounted for over 60% of sediment where the sediment content was less than 5 g/L. Due to the organic matter on the surface of fine particles being more likely to form coordination compounds with phosphorus, the content of organic phosphorus is 1.8 times higher than that in coarse particles [44]. The grain size effect has resulted in detrital phosphorus transported by coarse particles accounting for 68% of the phosphorus flux during the wet season. However, the contribution of organic phosphorus carried by fine particles rose to 34% during the dry season [43,45]. In addition, the variation of phosphorus transformation was observed with the change in sediment content along the upstream, midstream and downstream of the Yellow River. The upstream was dominated by fine particles, where exchangeable phosphorus (Ex-P) accounted for 11.2% in suspended sediments and were further released easily into the water [46]. In the midstream, detrital phosphorus represented more than 60% of the total phosphorus. Coarse particles prevailed and act as the primary sites for inert phosphorus [47]. The estuary was influenced by the mixing of freshwater and seawater, which triggered the flocculation process of sediment, resulting in authigenic phosphorus (Au-P) concentrations in fine particles being 1.3 times higher than those in the upstream [43]. This difference leads to only 18% of particulate phosphorus transported by the Yellow River to the Bohai Sea being available for marine biological cycling, while the remainder deposits as inert forms [43,44].
According to the data from YRE, the average annual sediment content of the Yellow River is 22.1 kg·m−3 and the average annual sediment transport is 6.38 × 108 t. Suspended sediment played a core role in phosphorus transportation. Notably, the interfaces between water and suspended sediment served as the primary bond for the adsorption and desorption of phosphorus in the Yellow River with hyper-concentrated sediment-laden flows. The surface hydroxyl functional groups of clay minerals, such as montmorillonite and illite in the sediment, enable the adsorption of phosphorus to experience exponential growth through the layered structure of clay minerals at a high sediment content level [20,48]. The hysteresis effect in the desorption of phosphorus intensifies with the increasing sediment content, as flocs generated under a high sediment concentration restrict the release of phosphorus [20].
Additionally, the environment at the interface between water and suspended sediment was affected in the YRE with a high sediment content (Figure 3). Dissolved oxygen (DO) exhibited a negative correlation with the sediment content. Microbial mineralization accelerated the decomposition rate of organic phosphorus by 40% when DO was less than 2 mg/L [49], thereby altering the bioavailability of phosphorus. Temperature regulated the adsorption–desorption equilibrium by influencing the activity of functional groups on the surface of sediment. For every 10 °C increase within 20–35 °C, the desorption quantity increased by 20–30% [20]. Salinity altered the interface behavior of phosphorus by influencing the flocculation state of sediment. Internal phosphorus transportation was inhibited in loose flocs derived from the sediment in the low salinity region of the estuary, resulting in a lower desorption quantity of phosphorus compared to the high salinity region [20,44]. Furthermore, the desorption quantity of phosphorus decreased by 30–40% as the pH increased. The coordination of H+ and PO43− promoted the release of phosphorus within the acidic condition [20]. Dynamic characteristics revealed that suspended sediment acts as a dynamic reservoir for phosphorus transportation in the Yellow River.
4. Environmental Behavior of Phosphorus in the YRE
In the Yellow River, catchments where bedrock weathers to produce clay or fine silty soils with high concentrations of Fe and Al (hydro)oxides are expected to yield sediments with a high capacity of phosphorus uptake. Moreover, anthropogenic activities and runoff from agricultural land contribute to phosphorus cycling by increasing nutrient and suspended sediment loadings. Typically, particulate phosphorus dominates in small agricultural catchments, whereas dissolved phosphorus prevails in larger catchments due to downstream wastewater discharges and the increased deposition of suspended solids as the residence time decreases.
The existing seasonal analysis of water in the YRE shows that the maximum values of DIP occur in spring (0.12 ± 0.11 μmol/L), while the minimum values are observed in autumn (0.04 ± 0.04 μmol/L) [50]. The concentration of dissolved organic phosphorus (DOP) is 2–9 times that of DIP. The high concentrations of suspended particulate matter in Yellow River runoff into the sea promote the desorption of DIP during the mixing of seawater and freshwater in the estuary. Consequently, a large amount of DIP is released and diffused from the particulate matter in the estuary, leading to a decrease in TP in the freshwater of the lower Yellow River from 91.2% to 39.8% [43]. DOP mainly originates from biological activities such as phytoplankton secretion and zooplankton excretion, and it is controlled by biological activities in the water environment [51,52]. Water-column processes associated with suspended sediments and uptake by phytoplankton play a significant role in phosphorus cycling, especially in larger rivers with a higher water volume to bed sediment/benthic ratios. As the typical turbid estuary, DIP and DOP exhibit limited seasonal variation due to phosphorus adsorption and desorption [53,54]. DIP and DOP enter the estuary bottom through particle sedimentation, forming crucial phosphorus reservoirs in the sediment [55], and resuspension occurs in response to disturbances in the sediment by wind, wave and water flow (Figure 4) [56,57].
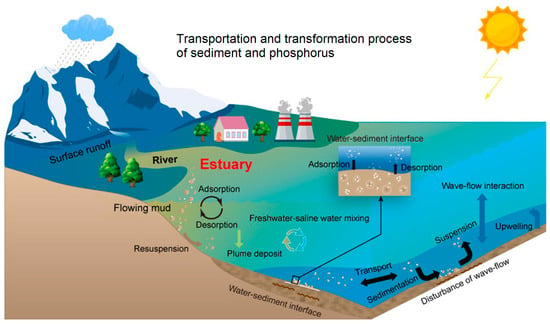
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the adsorption/deposition process of sediment and phosphorus in the estuary.
The sorption reaction of sediment relies on the bonding between metal cations with positive charges on the surface of natural colloids and various phosphate anions in the solution. Inorganic phosphorus (IP) is the main form of phosphorus occurrence in the sediment of the YRE. The content and distribution of organophosphorus (OP) vary substantially, indicating different sources of OP and IP [40,58]. Due to the relatively low organic matter in sediment carried by the Yellow River and since the estuarine sedimentary environment is unstable, OP is more susceptible to physical and biological factors than IP [59,60,61]. Consequently, the proportion of OP is relatively low (<20%) in the YRE. After the mineralization of organic matter in sediment, dissolved phosphorus could be released into pore water. Some phosphorus remains in the sediment, while another portion migrated back to the overlying water for absorption and utilization by phytoplankton [7,62]. Additionally, phosphorus can be adsorbed and preserved by iron-containing oxides in sediment under oxidizing conditions, reducing the concentration of phosphorus in pore water and limiting its diffusion to the overlying water. However, phosphorus combined with organic matter or iron oxides may be released into the overlying water under mild oxidizing conditions [23,24]. Furthermore, the size of sediments directly affects the form and content of phosphorus in particulate matter [61]. According to the rule that grain size dominates the distribution of elements [63], the contents of most elements increased with the decreasing particle size of sediments. Thus, the rule generally applies to various forms of phosphorus in different grain-size sediments [64]. The correlation coefficient matrix between different forms of inorganic phosphorus and the different grain sizes of sediments is shown in Table 1 [61]. Calcium phosphorus (Ca-P) predominates among the total inorganic phosphorus, with Ca-P in the silt fractions having the highest content. Adsorbed phosphorus (Ads-P), aluminum phosphorus (Al-P) and occluded phosphorus (O-P) mainly exist in fine particles (<16 μm), while ferric phosphorus (Fe-P) mainly exist in coarse particles (>31 μm).

Table 1.
Correlation coefficient matrix between the different forms of inorganic phosphorus and the different grain size of sediments [61].
The adsorption and desorption processes at the sediment and overlying water interface play crucial roles in the circulation of phosphorus in the estuarine water environment [58,62]. These processes are primarily determined by the reaction at the interface of sediment and overlying water. The ranges of water temperature, pH, salinity, the concentration of suspended particulate matter, COD and DO are 0.0–28.1 °C, 8.10–8.35, 19.5–31.2%, 0.32 × 103–5.00 × 103 mg/L, 0.68–2.40 mg/L, and 7.51–14.9 mg/L, respectively [50]. Moreover, the properties of sediment particles, such as grain size, specific area and surface charge density, also exert significant influence on the adsorption process of pollutants [65,66].
To investigate the direct and indirect environmental effects of pH, the total organic carbon (TOC), Al, Fe and sediment size distribution (clay: <2 μm, silt: 2–63 μm, sand: >63 μm) on total phosphorus in the YRE [67], the partial least squares path model (PLS-PM) using the plspm package in R, a statistical method that combines principal component analysis and canonical analysis, was used to construct predictive structural equation models (Figure 5b,c). Samples for analysis were from the Bohai Sea in 2018 and the estuarine wetland region located on the north side of the Yellow River in 2014 [68] and 2017 [69] (Table S1). This method is commonly employed to explore the causal relationship between latent variables (Table S2). Notably, pH emerges as the most significant factor (path coefficient 0.610) influencing total phosphorus, exhibiting a significant positive direct effect. This was followed by Fe (path coefficient 0.398) and the size distribution (path coefficient 0.114), both of which had positive effects on the TP (Figure 5b). Conversely, TOC showed significant negative effects on the TP (path coefficient −0.225). In addition, pH and Fe had a notably larger positive total standardized impacts on size distribution (path coefficient 0.523–0.673) compared to TOC (Figure 5c). It can be explained that TOC in the sediments is stabilized and physically protected by binding with active metal oxides like iron, thereby preventing microbial decomposition and reducing phosphorus adsorption. This led to TP correlation when TOC is negative. On the contrary, an increase in pH promoted phosphorus adsorption and resulted in the positive significant correlation observed with pH.
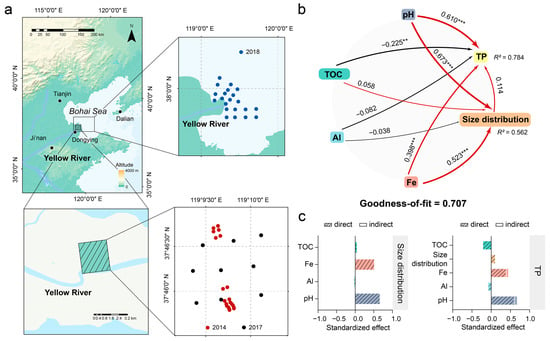
Figure 5.
(a) The sampling sites of the YRE; (b) Partial least squares path model (PLS-PM) and standardized effect based on PLS-PMs. The PLS-PM analyses demonstrate the effects of pH, TOC, Al, Fe and size distribution on TP in the Yellow River Estuary. Arrows indicate the path coefficient, and the red and black lines indicate positive and negative effects, respectively. Numbers adjacent to each arrow denote partial correlation coefficients (significance codes: *** ≤ 0.001 ** ≤ 0.01). R2 values display the proportion of variance explained for each factor; (c) The bar chart shows the standardized total effect of each factor on size distribution and TP in the Yellow River Estuary.
5. Model Simulating of Phosphorus and Sediment
Human activities have severely impacted the migration and transformation of nutrients in ecosystems, leading to the degradation of both freshwater and marine ecosystems. To accurately assess the input patterns of pollutants and the response mechanisms of estuarine deposition, the simulation of water environment models has become a focal point in estuarine, coastal and marine science [70]. Conducting frequent spatiotemporal field monitoring in complex estuarine waters is challenging, and thus, the numerical analysis and model simulation serve as effective supplements and supports [71]. The estuarine hydrodynamic field is validated using measured hydrological data, and simulations are employed to understand the sedimentation, transportation and diffusion of both sediment and phosphorus. These methods can elucidate the migration process of phosphorus in currents, particularly in combined wave and current flows within the estuarine environment [72]. Establishing an estuarine model requires detailed field research data, as estuarine water quality models are highly sensitive to the initial value and boundary condition of environmental factors. Moreover, the data of water flow fields, phosphorus forms, contents and spatiotemporal distribution with different sources and various precision will influence the simulation results of the model. Estuarine and coastal areas constitute complex ecosystems; therefore, establishing an appropriate coupled ecological model for an estuary is crucial, depending on the spatial scale and specificity of the research problems [73,74,75,76,77,78,79] (Table 2).

Table 2.
Commonly used simulation models for water quality in estuaries.
The YRE stands as a typical turbid estuary characterized by intricate hydrological conditions and water environments, susceptible to disturbances from seasonal variation, wave-flow and complex terrain [80]. Understanding the roles of these disturbances across different seasons necessitates the aid of higher-resolution observation models and novel observation methods. Short-term observation at a single point falls short of fully capturing the behavior of pollutants in an estuary with a complex dynamic environment. Given the time intervals between stations in comprehensive sampling, quantifying the diffusion rate of dissolved phosphorus in freshwater poses a challenge. Moreover, the analyses of terrigenous weakly adsorbed phosphorus and iron-bound phosphorus in estuarine sediment are seldom undertaken. Long-term in situ monitoring, sampling and experiments require substantial economic investment. However, it is anticipated that numerical analysis and model simulation will pave the way for breakthroughs in the field.
6. Conclusions and Outlooks
6.1. Conclusions
The Yellow River Estuary plays a crucial role as an interface between the continent and the ocean in terms of material fluxes. In the overlying water and sediment of the YRE, PP and IP were the dominant forms, respectively. The Yellow River has low phosphorus content in water due to the adsorption of phosphorus by suspended sediment. The dynamic estuarine environment promotes sediment deposition, which helps reduce the phosphorus levels in the water. The sediment acts as a sink for phosphorus in the estuary. Upon entering the Bohai Sea, the sediment is transformed into the source of phosphorus. The released phosphorus may increase the nutrient load in the shallow Bohai Sea waters, thereby posing potential ecological implications for the local marine environment. Fine particles demonstrate strong adsorption capacity for reactive phosphorus, acting as the primary carriers for phosphorus migration at the sediment–water interface. The grain size of the suspended sediment in the Yellow River exhibited significant sorting characteristics with a varying sediment content, consequently affecting the forms of phosphorus. Notably, long-term sediment reduction driven by reservoir construction, sediment regulation measures and soil conservation practices in the Yellow River has altered the sediment grain size composition and transport flux in the estuary, further modifying the adsorption–desorption equilibrium of phosphorus between sediment and water, and indirectly affecting the source–sink conversion of phosphorus in the estuary and Bohai Sea [81,82].
As the typical turbid estuary, DIP and DOP exhibit limited seasonal variation due to phosphorus adsorption and desorption. Relatively low organic matter in the sediment carried by the Yellow River and the estuarine sedimentary environment is unstable, and OP is more susceptible to physical and biological factors than IP. After the mineralization of organic matter in the sediment, dissolved phosphorus could be released into pore water. Some phosphorus remains in the sediment, while another portion migrates back to the overlying water for the absorption and utilization by phytoplankton. The further analysis of biogeochemical conditions revealed that environmental factors (e.g., pH, DO) significantly influenced phosphorus transformation. Overall, suspended sediment acts as a dynamic reservoir for phosphorus transportation in the YRE.
6.2. Outlooks
At present, research on the environmental behavior of sediment and phosphorus in the YRE has made significant progress, but some issues still require further in-depth investigation. While the dynamics and mechanisms of sediment deposition in the YRE have been clarified, the spatiotemporal transport patterns of phosphorus accompanying sediment deposition, both vertically and horizontally, warrant deeper exploration. Leveraging existing radionuclide tracing and geochemical methods, employing estuarine dynamic hydrological model to study the three-dimensional spatial distribution characteristics of sediment and the coupling of migration and transformation mechanisms of different pollutant remains a critical and challenging task in current estuarine research.
The estuarine and coastal zones are inherently dynamic systems, exhibiting pronounced seasonal and interannual variations in Chinese coastal areas. By considering the coupling of water, suspended particulate matter and bottom sediment as a dynamic equilibrium system as a whole, comprehensive studies integrating multiple parameters, media and systems will facilitate a deeper understanding of the fundamental variation patterns of pollutants in coastal and marine system. Such holistic approaches will not only aid in predicting future changes in coastal and marine systems but also contribute to the development of the effective management and mitigation strategies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17192794/s1, Table S1: Physicochemical parameter of the YRE from references; Table S2: Inner model of the partial least squares path model (PLS-PM).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, software, writing—original draft and funding acquisition, Y.G.; writing—review and editing, W.L.; methodology, S.L.; data curation, K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Research & Development Foundation of China Institute of Geo-Environment Monitoring (No. 20250101), Operation of National Groundwater Quality Testing and Quality Control Laboratory (DD20251300103), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 42202284).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pan, K.; Wang, W.X. Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, P.M.; Wang, F. Assessing sediment contamination in estuaries. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Pan, K.; Tan, Q.; Guo, L.; Simpson, S.L. Estuarine pollution of metals in China: Science and mitigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9975–9976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Xie, Q.; Xu, H. The evolution process of tidal characteristics in the last 60 years of the Yellow River Estuary. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2019, 38, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Guo, Z.; Cai, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Gao, A. Cyclical patterns and (im)mobilization mechanisms of phosphorus in sediments from a small creek estuary: Evidence from in situ monthly sampling and indoor experiments. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Zhang, P.; Ou, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal nutrient patterns, composition, and implications for eutrophication mitigation in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 266, 107749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Li, B.; Li, F.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, M. Carbon, Nitrogen geochemical character and organic matter source study in the coastal sediment of Yellow River Estuary. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Kettner, A.J.; Green, P. Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean. Science 2005, 308, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.C.; Freidenreich, A.; Wang, W.; Wang, R.; Dai, J. Source quantification and potential risk of mercury, cadmium, arsenic, lead, and chromium in farmland soils of Yellow River Delta. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulskamp, R.; Luijendijk, A.; Maren, V.B.; Moreno-Rodenas, A.; Calkoen, F.; Kras, E.; Lhermitte, S.; Aarninkhof, S. Global distribution and dynamics of muddy coasts. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Nittrouer, J.A.; Naito, K.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Moodie, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Parker, G. The exceptional sediment load of fine-grained dispersal systems: Example of the Yellow River, China. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1603114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellow River Sediment Bulletin. Available online: http://yrcc.gov.cn/gzfw/nsgb (accessed on 21 March 2024).
- Chen, C. Searching for intellectual turning points: Progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5303–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Study on Environmental Evolution and Degradation of Coastal Wetland in Modern Yellow River Delta. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, F.; Yu, J.; Du, S.; Li, Y.; Lv, X.; Ning, K.; Wu, H.; Meng, L. Influences of anthropogenic cultivation on C, N and P stoichiometry of reed-dominated coastal wetlands in the Yellow River Delta. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lou, L.; Cui, X.; Tang, J.; Li, P.; Cao, R. Significance of biological effects on phosphorus transformation processes at the water–sediment interface under different environmental conditions. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Jin, X.; Zhang, R.; Liao, H.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, X. Effects and significance of organic nitrogen and phosphorus in the lake aquatic environment. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cao, R.; Zhang, J.; Han, C.; Gu, X.; Geng, J.; Wang, X.; Qian, X. The non-negligible phosphorus form-reduced phosphorus in water. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 1, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Dai, A. Speciation and release mechanism of phosphorus in sediments and analysis methods for sequential extraction. Rock Miner. Anal. 2011, 30, 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Pan, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Guo, B.; Bao, H. Characteristics of phosphorus sorption on Yellow River sediments from Inner Mongolia reach. Environ. Sci. 2009, 30, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard, C.T.; Planavsky, N.J.; Gill, B.C.; Ozaki, K.; Robbins, L.J.; Lyons, T.W.; Fischer, W.W.; Wang, C.; Cole, D.B.; Konhauser, K.O. Evolution of the global phosphorus cycle. Nature 2017, 541, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P. Preliminary study on the influence of extremely fine particle sediment concentration on the ability of sand carrying in the Yellow River. J. Sediment Res. 1981, 3, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Cao, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, G. Biogeochemistry of bulk organic matter and biogenic elements in surface sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, H.; Wu, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, J. Limited capacity of suspended particulate matter in the Yangtze River Estuary and Hangzhou Bay to carry phosphorus into coastal Seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 258, 107417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolker, A.S.; Miner, M.D.; Weathers, H.D. Depositional dynamics in a river diversion receiving basin: The case of the West Bay Mississippi River diversion. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 106, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, R.R.; Day, J.W.; Justic, D.; Reyes, E.; Marx, B.; Day, J.N.; Hyfield, E. Changes in stoichiometric Si, N and P ratios of Mississippi River water diverted through coastal wetlands to the Gulf of Mexico. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, C.J.; Lane, R.R.; Day, J.W. Spatial and temporal variations in nutrients and water-quality parameters in the Mississippi River-influenced Breton Sound Estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 294, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, E.D.; White, J.R.; Smith, E.A.; Bargu, S.; Li, C. Estuarine ecosystem response to three large-scale Mississippi River flood diversion events. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, E.D.; Nguyen, N.T.; White, J.R. Changes in estuarine sediment phosphorus fractions during a large-scale Mississippi River diversion. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, E.; Palinkas, C.; Cornwell, J. Evaluating estuarine sediment provenance from geochemical patterns in upper Chesapeake Bay. Chem. Geol. 2020, 533, 119404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotovicz Junior, L.C.; Machado, E.d.C.; Brandini, N.; Zem, R.C.; Knoppers, B.A. Distributions of total, inorganic and organic phosphorus in surface and recent sediments of the sub-tropical and semi-pristine Guaratuba Bay Estuary, SE Brazil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Böddeker, S.; Thuyên, L.X.; Schwarz, A.; Huy, H.Đ.; Schwalb, A. Diatom assemblages in surface sediments along nutrient and salinity gradients of Thi Vai Estuary and Can Gio Mangrove Forest, Southern Vietnam. Estuar. Coasts 2017, 40, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noncent, D.; Strady, E.; Némery, J.; Thanh-Nho, N.; Denis, H.; Mourier, B.; Babut, M.; Nguyen, T.A.; Nguyen, T.N.T.; Marchand, C.; et al. Sedimentological and geochemical data in bed sediments from a tropical river-estuary system impacted by a developing megacity, Ho Chi Minh City—Vietnam. Data Brief. 2020, 31, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, R. Comparative observation and analysis of shore tide level and deep water tide level near the Yellow River Estuary. Yellow River 2019, 41, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Coco, G.; Townend, I.; Olabarrieta, M.; van der Wegen, M.; Gong, Z.; D’Alpaos, A.; Gao, S.; Jaffe, B.E.; Gelfenbaum, G.; et al. Is “morphodynamic equilibrium” an oxymoron? Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 165, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qiao, L.; Zhong, Y.; Wan, X.; Xue, W.; Liu, P. Pathways of suspended sediments transported from the Yellow River Mouth to the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 236, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Shan, H.; Yang, X. Sediment and Geologic Hazards in the Estuary of Yellow, China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.; Miao, C.; Wu, J.; Duan, Q.; Sun, Q.; Ye, A.; Di, Z.; Gong, W. The hydro-environmental response on the lower Yellow River to the water–sediment regulation scheme. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 79, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, L.; Bu, R. Spatial variability of the 210Pb sedimentation rates in the Bohai and Huanghai and its influencing factors. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2011, 33, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Wen, W.; Zhuang, F.; Yu, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Y. Universal high-frequency monitoring methods of river water quality in China based on machine learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ma, Q.; Liu, P. Adsorption kinetics of phosphate onto sediments from the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 1901–1905. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Tang, H.; Li, Z.; Yuan, S.; Xiao, Y.; Ji, F. Review of effects of flow and sediment on the transport and transformation of phosphorus in rivers and lakes. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 13, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, C.; Wei, W.; Chen, H.; Mi, T.; Yu, Z. The distribution of dissolved inorganic phosphorus, dissolved organic phosphorus, dissolved total phosphorus in the Yellow River estuary and adjacent water. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2007, 27, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Chen, H.; Yao, Q.; Qin, Y.; Mi, T.; Yu, Z. Behavior of different phosphorus species in suspended particulate matter in the Changjiang estuary. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 2009, 27, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S. Effects and environmental implications of suspended sediment on the transportation and transformation of nitrogen in the Yellow River. Estuar. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2020, 51, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, P.; Ma, Q. Phosphorus fractions and its adsorption thermodynamics onto sediments from the upper reaches of the Yellow River, China. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy and Environmental Protection, Inner Mongolia, China, 23 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Bao, H. Character of phosphorus forms in surface sediments from upper and middle reaches of the Yellow River. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Character of phosphorus forms in surface sediments from middle and lower reaches of Yellow River. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 20, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Chen, H.; Mi, T. The hydrological regime and particulate size control phosphorus form in the suspended solid fraction in the dammed Huanghe (Yellow River). Hydrobiologia 2010, 638, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Lee, K.; Dong, Z.; Di, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Impact of water-sediment regulation scheme on seasonal and spatial variations of biogeochemical factors in the Yellow River Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ke, Y.; Wang, D.; Ji, H.; Chen, S.; Chen, M.; Lyu, M.; Zhou, D. Human impact on suspended particulate matter in the Yellow River Estuary, China: Evidence from remote sensing data fusion using an improved spatiotemporal fusion method. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Qiu, Z. Chemical Oceanography, 2nd ed.; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1982; pp. 122–156. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Yang, D.; Burnett, W.C.; Ran, X.; Yu, Z.; Gao, M.; Diao, S.; Jiang, X. Artificial water sediment regulation scheme influences morphology, hydrodynamics and nutrient behavior in the Yellow River Estuary. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippey, B.; Campbell, J.; McElarney, Y.; Thompson, J.; Gallagher, M. Timescale of reduction of long-term phosphorus release from sediment in lakes. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Song, J.; Li, N. Phosphorus and Silicon in overlying waters and suspended matter near sediment-water interface of the southern Bohai Sea. Marine Sci. 2004, 28, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H.; Wang, C.W. Dissolved and particulate phosphorus species partitioning and distribution in the Danshuei River Estuary, Northern Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.E.; Cai, W.-J.; Raymond, P.A.; Bianchi, T.S.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Regnier, P.A.G. The Changing Carbon Cycle of the Coastal Ocean. Nature 2013, 504, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Yu, L.; Ye, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, D.; Guan, Y.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Dynamics of phosphorus fractions in surface soils of different flooding wetlands before and after flow-sediment regulation in the Yellow River Estuary, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 580, 124256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Dispersal pattern of suspended sediment in the shear frontal zone off the Huanghe (Yellow River) Mouth. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 854–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y. Variability of sediment distribution and analysis of hydrodynamic environment in the Huanghe Estuary and the Mid-South Bohai Sea. J. Ocean. Univ. Qingdao 2004, 34, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Wu, J. Forms of inorganic phosphorus in the sediments near the Huanghe River Estuary. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1992, 23, 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Borgnino, L.; Avena, M.; De Pauli, C. Surface properties of sediments from two argentinean reservoirs and the rate of phosphate release. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2659–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, M. Geochemistry of Sediments of the China Shelf Sea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Yuan, H.; Zheng, G.; Li, N. Sediment record of phosphorus and the primary study of its bioavailability in Jiaozhou Bay sediments. Environ. Sci. 2006, 27, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.E.; Shi, Y.L. Sediment discharge of the Yellow River (China) and its effect on the sedimentation of the Bohai and the Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 1986, 6, 785–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M. Response of nutrient transports to water–sediment regulation events in the Huanghe Basin and its impact on the biogeochemistry of the Bohai. J. Marine Syst. 2015, 141, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenhaus, M.; Esposito, V.; Chatelin, Y.; Lauro, C. PLS path modeling. Comput. Stat. Data. Anal. 2005, 48, 159–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Shao, H.; Meng, L.; Yu, J.; Xia, J.; Sun, J.; Li, Y. Forms and vertical distributions of soil phosphorus in newly formed coastal wetlands in the Yellow River Delta Estuary. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 4219–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Meng, L.; Xia, J.; Huang, H.; Zhan, C.; Li, Y. Soil phosphorus fractions and distributions in estuarine wetlands with different climax vegetation covers in the Yellow River Delta. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Gaffney, O.; Rockström, J.; Öhman, M.C.; Shyamsundar, P.; Steffen, W.; Glaser, G.; Kanie, N.; Noble, I. Sustainable development goals for people and planet. Nature 2013, 495, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yin, B. Model study on Bohai ecosystem: 2. annual cycle of nutrient—Phytoplankton dynamics. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2006, 25, 74–91. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Liu, G.; Yang, J. Review on the marine water quality model. Mar. Forecast. 2017, 34, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, D.; Knightes, C.; Chang, X.; Avant, B. Simulating multiwalled carbon nanotube transport in surface water systems using the Water Quality Analysis Simulation Program (WASP). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11174–11184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, S.; Pei, M.; Geng, B. Development and validation of a coupled one-and three-dimensional water quality model for the Pearl River delta. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2012, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H. Study on Eutrophication in Estuary and Its with Red tide Ecology. Ph.D. Thesis, Hohai University, Nanjing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X. Influence of Waves on Seabed Erosion and Deposition in the Yellow River Estuary. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y. Study on the Influence of Tidal Flat Reclamation in Oujiang Estuary on Hydrodynamics and Water. Master’s Thesis, Hohai University, Nanjing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Dense Current Process of High Concentration in the Yellow River Estuary: Field Observation and Numerical Simulation. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N. Sedimentary Dynamic Process and Topographic of Modern Yellow River Estuary. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Wu, X.; Yuan, L.; Li, H.; Li, F.; Ma, T.; Li, W.; Zheng, Y. Ecological environmental changes and its impact on water resources and water-sediments relationship in Beiluo River Basin. Hydro. Eng. Geol. 2023, 50, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Yao, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Effects of riverine nutrient enrichment and sediment reduction on high primary productivity zone in the Yangtze River estuary: Historical reconstruction and future perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1529744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Miao, C.; Gou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Su, T. Sediment reduction in the middle Yellow River basin over the past six decades: Attribution, sustainability, and implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).