Abstract
Prickly sow thistle, Sonchus asper (L.) Hill, and common sow thistle, Sonchus oleraceus L., are noxious weeds. Probably originating from the Mediterranean region, they have become widespread species. They share similar morphology and are closely related. However, they differ in their chromosome numbers and the precise relationship between them remains uncertain. Understanding their chloroplast genome structure and evolution is an important initial step toward determining their phylogenetic relationships and analyzing accelerating plant invasion processes on a global scale. We assembled four accessions of chloroplast genomes (two S. asper and two S. oleraceus) by the next generation sequencing approach and conducted comparative genomic analyses. All the chloroplast genomes were highly conserved. Their sizes ranged from 151,808 to 151,849 bp, containing 130 genes including 87 coding genes, 6 rRNA genes, and 37 tRNA genes. Phylogenetic analysis based on the whole chloroplast genome sequences showed that S. asper shares a recent common ancestor with S. oleraceus and suggested its likely involvement in a possible amphidiploid origin of S. oleraceus. In total, 79 simple sequence repeats and highly variable regions were identified as the potential chloroplast markers to determine genetic variation and colonization patterns of Sonchus species.
1. Introduction
Prickly (or spiny) sow thistle, Sonchus asper (L.) Hill, and common (or annual) sow thistle, S. oleraceus L., are two well-known worldwide noxious weeds. The seeds can germinate throughout the year over a broad range of temperatures [1,2]. These species are considered to be particularly troublesome weeds across the grain growing regions because they have allelopathic potential to function as interference competition even in weed communities [3] and are prolific seed producers (up to 25,000 seeds per single plant in a fallow); the seeds possess pappi, which helps wind-mediated dispersal [4]. Moreover, the evolution of herbicide resistance found that populations of these species threatens the efficiency of weed control. For example, several populations of S. oleraceus have been reported as resistant to acetolactate synthase (ALS) inhibiting herbicides including chlorsulfuron (Group B) and glyphosate herbicides (Group M) in Australia [5,6]. In addition to being troublesome weeds worldwide, the tender leaves of common sow thistles are consumed as salads and potherbs and the extracts of both sow thistles have been used as medicinal herbs in Brazil, New Zealand, and China [7,8].
Prickly and common sow thistles belong to the subgenus Sonchus of the genus Sonchus L. (Asteraceae); the genus is a member of the subtribe Hyoseridinae Less. (formerly known as Sonchinae sensu K. Bremer) [9,10]. The current, redefined genus Sonchus in its wider circumscription is comprised of ca. 95 species, which are widely distributed globally. They mainly grow in native ranges from most of the Old World (Eurasia and Africa) and mid-Atlantic islands, avoiding the coldest and driest regions, and extend to Australia/New Zealand and the Southeast Pacific islands of the Juan Fernández and Desventuradas [9,10]. Almost half of the species diversity is found in the oceanic insular ranges, which are examples of spectacular adaptive radiation (Macaronesia in the Atlantic and the Juan Fernández and Desventuradas in the Pacific) [11,12,13]. Some of the most common species, both prickly and common sow thistles, have been introduced to America, being particularly widespread in northern temperate regions. The genus seems to have originated in the western Mediterranean region, including areas of western Morocco with a Mediterranean-type climate. The geographical origins of weedy sow thistles have not been formulated with any certainty, but they are also believed to have originated in the Mediterranean region, becoming one of the cosmopolitan species on planet Earth [14]. Both species are widespread and prevalent in Europe, Asia, Africa, and have also been introduced to America and Australia [1,11,15]. They are pioneer species, invade mainly open and disturbed areas, and occur in a wide variety of environments like cultivated fields, gardens, roadsides, pastures, and waste places.
Although some diagnostic features are relevant for species identification, S. asper and S. oleraceus can sometimes be confused morphologically. Both species are erect herbs, annual or biennial weeds, and have yellow florets and hollow and smooth stems. They can be either low-growing rosettes or upright in their growth form and overwinter as achenes, but fall-germinated plants may overwinter as rosettes in milder climates. Despite their similar morphology and phenology, S. asper and S. oleraceus can be distinguished primarily based on the characteristics of their leaves and fruits (Figure 1). The leaves of S. asper are deep, shiny, and green, rarely divided, thick, and have very prickly leaf margins, while those of S. oleraceus are flatter, pinnatifid, and weakly spinous. In addition, the leaf base auricles of S. asper are often recurved or curled and rounded, while those of S. oleraceus are deltate to lanceolate, almost straight, and acute. However, the characteristic of leaf base and degree of prickly dentate leaf margin can be variable in both species, often confusing species identification based on these traits only. The most consistent reproductive diagnostic features are in their fruits: the cypselae of S. oleraceus are slightly compressed, with rounded margins, (2)3(4) ribs per side, two of them furrowed lengthwise, and transversely rugulose or tuberculate across and between ribs, while those of S. asper are strongly compressed, more or less winged, 3 ribs per side, and smooth across and between the ribs [4] (Figure 1). One important karyotype characteristic is their different ploidy levels. S. asper has been represented uniformly by diploid plants (somatic chromosome number 2n = 18) in Europe, USA, and Canada, while S. oleraceus has typically been reported with a chromosome number of 2n = 32 in Eurasia, Africa, and North America [11,16,17,18,19,20]. However, descending aneuploid (2n = 16; from Eurasia) and tetraploid (2n = 36; from North Dakota, USA) chromosome counts also have been rarely reported [16], although the taxonomic identity of the plant material studied remains unclear. Stebbins et al. [21] proposed an amphidiploid origin for S. oleraceus (n = 16, 2 n= 32), which has combined S. asper (n = 9, 2n = 18) and S. tenerrimus L. (n = 7, 2n = 14). Certainly, the morphological characteristics of S. oleraceus reflect a remarkable middle ground between the two putative parental species. It is also plausible that the hybrid origin of S. oleraceus increased ecological amplitude and evolutionary success via (re-)combining two different genomes. Previous molecular phylogenetic studies [13,22,23,24] provided evidence that S. asper and S. oleraceus are closely related to each other, but failed reciprocal monophyly due to poor resolution. It is of great interest to determine the origin of amphidiploid S. oleraceus based on extensive sampling strategy and rigorous molecular and cytological tools.
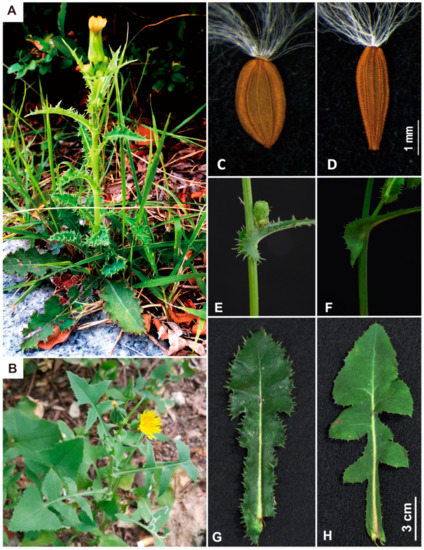

Figure 1.
Pictures of Sonchus asper (prickly sow thistle) and Sonchus oleraceus (common sow thistle). Sonchus asper (A). plant; (C). achene; (E,G). rounded leaf base auricle and prickly leaf margin. Sonchus oleraceus (B). plant; (D). achene; (F,H). pointed leaf base auricle and lobed leaf margin. Photo credits: (C,D) (Jose Mejías); (A,B,E–H) (Jin Hyeong Kim and Myong-Suk Cho).
Chloroplasts in plant cells serve as metabolic centers and encode many key proteins that are involved in photosynthesis and other metabolic processes, primarily participating in photosynthesis, transcription, and translation [25]. Chloroplast (cp) sequence polymorphisms have been extensively used as useful genetic markers at wide ranges of taxonomic levels in plants. They have provided valuable insights into phylogenetic relationships and the origin and evolution of the crop species [26] or introduced/invasive species [27,28,29,30] that are facilitated by maternal inheritance of cp genomes. However, earlier phylogenetic analyses utilizing the partial cpDNA sequences from several regions often resulted in limited sequence variation owing to highly conservative genome evolution, particularly for closely related and recently radiated groups of species [31]. The advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies of next-generation sequencing (NGS) has helped to reveal considerable genome-wide variations in terms of sequences and structures of entire chloroplast genomes. The benefits of genome-wide data have increased phylogenetic resolution and significantly enhanced our understanding of plant evolution and diversity in the field of chloroplast genetics and genomics [25]. The chloroplast phylogeny based on several coding and noncoding cpDNA regions in previous studies has not provided enough resolution to elucidate the phylogenetic relationship among weedy Sonchus species as well as the origin of S. oleraceus. In both of the cpDNA and nuclear DNA phylogenies, S. oleraceus was more closely related to S. asper than to S. tenerrimus, even though the precise relationship between them was not clear [13,22,23,24]. Taking cpDNA phylogeny and maternal inheritance into consideration, it could be hypothesized that S. asper contributed as the maternal parent in the origin of amphidiploid S. oleraceus. To test this hypothesis and to better understand the evolutionary relationships of two weedy sow thistle species, we characterized four accessions of complete chloroplast genomes (two from S. asper and two from S. oleraceus) and conducted the comparative analyses of their whole chloroplast genomes. All but one accession of S. oleraceus was collected from the probable origin of diversity in the Mediterranean region. Considering their global distribution, one accession of S. oleraceus was collected from Dok-do Island in Korea and one more previously published accession of S. oleraceus from Australia (GenBank accession number MG878405) was also included in the comparative analyses.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation, DNA Extraction, Genome Sequencing, and Annotation
The silica-gel dried leaves of four prickly and common sow thistles which were sampled from natural habitats in Spain and Korea were used as sources of DNA. Two accessions of S. asper were sampled from Seville (VIL-1) and Huelva (MAR-1) in Spain, while S. oleraceus was sampled from Huelva (MAR-1) in Spain and Dok-do Island in the East Sea, Korea. Total genomic DNA was isolated using the DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen GmbH, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s protocol. An Illumina paired-end (PE) genomic library was constructed and sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq platform (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, Ca, USA) at Macrogen Corporation (Seoul, Korea). The sequence reads of chloroplast genomes were assembled by the de novo genomic assembler, Velvet 1.2.10 [32] at coverages ranging from 789x to 1354x. Annotation was performed using the Dual Organellar GenoMe Annotator [33], ARAGORN v1.2.36 [34], and RNAmmer 1.2 Server [35]. Using Geneious v8.1.6 (Biomatters Ltd., Auckland, New Zealand), the draft annotation was inspected and corrected manually, performing blast search by comparison with homologous genes in Lactuca sativa (DQ383816), S. oleraceus (MG878405), S. canariensis (NC042381), S. acaulis (NC042382), and S. webbii (NC042383) from the GenBank database at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) as references. The complete plastome sequences were registered in GenBank under the accession numbers MH908962 (S. oleraceus from Korea, Collection # Son0-uDS2), MK371006 (S. oleraceus from Spain, Population # MAR-1), MK371015 (S. asper from Spain, Population # VIL-1), and MK371016 (S. asper from Spain, Population # MAR-1). In addition, the raw HiSeq reads were deposited in the Short Read Archive (SRA) at NCBI under Bioproject ID PRJNA0577793 for MH908962 and PRJNA578572 for MK371006, MK371015, and MK371016. OGDRAW [36] was used to draw circular chloroplast genome maps (Figure 2).
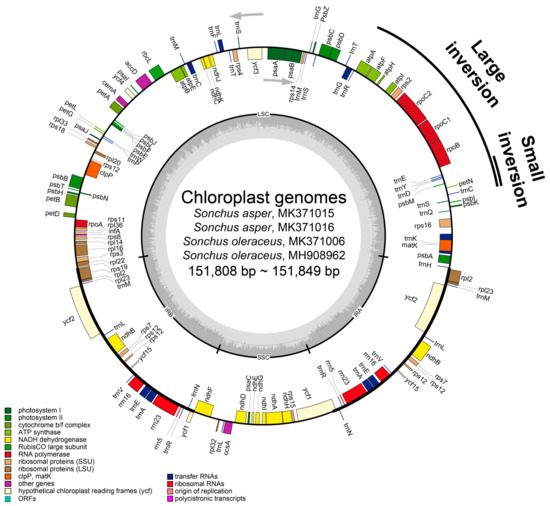
Figure 2.
Merged gene map of four weedy Sonchus chloroplast genomes of two accessions each of S. asper and S. oleraceus that were sequenced in this study. The genes inside and outside of the circle are transcribed in the clockwise and counterclockwise directions, respectively. Genes belonging to different functional groups are shown in different colors. The thick lines indicate the extent of the inverted repeats (IRA and IRB) that separate the genomes into small single copy (SSC) and large single copy (LSC) regions. Large inversion and smaller inversion nested within the large inversion that is unique in Asteraceae are indicated with black lines outside the gene map.
2.2. Repeat Sequence Analysis
Two types of repeat sequences were identified in the five chloroplast genomes of S. asper and S. oleraceus including previously reported S. oleraceus from Australia (GenBank accession number MG878405). REPuter [37] was used to detect the various types of repetitive sequences of the five Sonchus chloroplast genomes. Search parameters were set to: maximum computed repeats = 50, minimum repeat size = 8 bp, and hamming distance = 0. Simple sequence repeats (SSRs) were identified using MISA web (http://pgrc.ipk-gatersleben.de/misa/) with search parameters of 1–15 (unit size-minimum repeats, i.e., mono-nucleotide motifs with 15 minimum numbers of repetition), 2-5, 3-3, 4-3, 5-3, and 6-3 with 0 interruption (maximum difference for two SSRs).
2.3. Identification of Highly Divergent Regions
The five weedy Sonchus chloroplast genomes were compared to the reference genome of S. webbii at the entire chloroplast genomic level using DnaSP [38] and mVISTA [39]. S. webbii is a herbaceous perennial unlike other woody Sonchus species (S. acaulis and S. canariensis) in the Canary Islands and is sister to the clade containing five accessions of weedy Sonchus species. Overall sequence divergence was estimated for the five weedy Sonchus chloroplast genomes that were aligned and compared to the reference genome using the LAGAN alignment mode [40] in mVISTA. Nucleotide diversity (Pi) was calculated using the sliding window analysis (window length = 1000 bp and step size = 200 bp excluding sites with alignment gaps) to detect the most divergent regions (i.e., mutation hotspots) among the five weedy Sonchus genomes in DnaSP. The borders of large single copy (LSC), small single copy (SSC), and inverted repeats (IRs) were compared with the results of DnaSP and mVISTA.
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
To investigate the taxonomic position and phylogenetic relationship of the newly sequenced accessions of S. asper and S. oleraceus, 26 complete chloroplast sequences representing major lineages of the family Asteraceae were obtained from GenBank. In total, full sequences of 30 chloroplast genomes were aligned using MAFFT v.7 [41]. A maximum likelihood tree was produced based on the relationships of whole chloroplast genomes by IQ-TREE [42] with 1000 replicate bootstrap (BS) analyses. The best fit evolutionary model was chosen as TVM + F + I + G4, which was scored according to the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) scores and weights by using ModelFinder [43] implemented in IQ-TREE.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Five Weedy Sonchus Chloroplast Genomes in Content, Order, and Organization
Despite morphological and cytological differences between two weedy Sonchus species (S. asper and S. oleraceus), gene content and arrangement were found to be identical in five chloroplast genomes, displaying 99.98% pairwise similarity in sequences (Table 1). The total length of five cp genomes ranged from 151,808 (S. oleraceus from Spain and Australia) to 151,849 (the two samples of S. asper from Spain and S. oleraceus from Dok-do, Korea) base pairs (bp) and consisted of four typical regions: LSC, SSC, and a pair of inverted repeat regions (IRA and IRB). One large inversion with a size of 22.8 kb and a second smaller inversion of 3.3 kb, nested within the large inversion, were found in all five chloroplast genomes (Figure 2). These inversions are unique to Asteraceae and present in most of the family, but are absent in the species of the basal subfamily Barnadesioideae [44,45]. The overall guanine-cytosine (GC) content of each chloroplast genome was 37.6%, with LSC, SSC, and IR regions having 35.8%, 31.4–31.5%, and 43.1% GC contents, respectively. Each of the five cp genomes contained 130 genes, including 80 protein-coding genes (plus seven duplicated in IR), three rRNA genes (all duplicated in IR), and 30 tRNA genes (plus seven duplicated in IR). Eighteen genes contained introns, including seven tRNA genes. Three genes of clpP, rps12, and ycf3 exhibited two introns. The trnK tRNA gene harbored the largest intron, which contained the matK gene in between. In total, 17 genes were duplicated in the IR regions, including seven tRNAs, three rRNAs, and seven protein genes. The trans-splicing gene rps12, consisting of three exons, was located in the LSC region for exon 1, but exon 2 and exon 3 of the gene were imbedded in the IR regions. Part of ycf1 and rps19, for which we did not annotate in the four weedy Sonchus cp genomes that were sequenced in this study, were duplicated in the IRA region, forming pseudogenes. A pseudo ycf1 gene in IR was extended to the SSC region and overlapped with the near ndhF gene (Figure 2 and Figure 3; Table 1 and Table 2). The genomic features of five weedy Sonchus genomes were nearly identical to congeneric species in the woody Sonchus alliance in the Macaronesian Islands (Atlantic Ocean), S. canariensis (NC042381), S. acaulis (NC042382), and S. webbii (NC042383) in gene content and overall GC rate [46]. The cp genomes of other Asteraceae species were also highly conservative in gene order and content with minor variations in the gene prediction of several genes (e.g., ycf68 protein coding gene, 4.5 rRNA genes and pseudogenes), even though they represent morphologically and genetically diverse tribes of Asteraceae belonging to Anthemideae, Cardueae, Cichoroieae, Eupatorieae, Heliantheae, Millerieae, and Senecioneae [47,48,49].

Table 1.
Summary of the complete chloroplast genome characteristics of five accessions of two weedy species of Sonchus: S. asper and S. oleraceus.
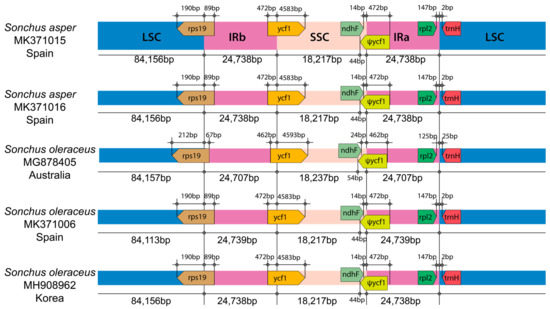
Figure 3.
Comparison of the border positions of the large single copy (LSC), small single copy (SSC), and inverted repeat (IR) regions among five weedy Sonchus chloroplast genomes representing S. asper and S. oleraceus. Gene names are indicated in the boxes and their lengths in the corresponding regions are displayed above the boxes. Ψ indicates a pseudogene.

Table 2.
Genes present in the complete chloroplast genomes of five accessions of two weedy species of Sonchus: S. asper and S. oleraceus.
3.2. SSRs and Large Repeat Sequences
Repeat sequences are considered to play an important role in genome recombination and rearrangement [50,51]. Particularly, SSRs, which represent a unique type of tandemly repeated genomic DNA sequence, have high polymorphisms due to large variations in motifs and number of repetitions. Because of the high level of polymorphisms and genome-wide distribution, they have been considered as powerful tools to measure genetic diversity and address population genetic issues at the level of inter- and intra-specific variations, such as gene flow, parentage, and population structure [52]. We found that all the five cp genomes contained the same numbers and distribution patterns of repeated sequences in each cp genome. There were 79 SSRs detected by MISA [53] based on search parameters set for 1–15 (mono-nucleotide motifs with 15 minimum numbers of repetition), 2–5, 3–3, 4–3, 5–3, and 6–3. The majority of the SSRs were tri-nucleotide motifs (66 SSRs, 84%). Remarkably, there were low proportions of other SSR types, i.e., three mono-nucleotide SSRs (4%), four di-nucleotide SSRs (5%), and six tetra-nucleotide SSRs (7%) (Figure 4A). The abundance of tri-nucleotide SSRs was consistent with previous findings with similar parameter settings [54]; however, the frequency of mono-nucleotide SSRs was significantly lower because of the more stringent search parameter used in this study (i.e., minimum repeat of 15) than in previous studies (minimum repeat of 8 or 10) [47,54]. The most abundant repeat motif was “AAT/ATT” followed by “AAG/CTT” in all five genomes (Figure 4B, Table S1). Interestingly, SSRs were distributed most abundantly in the coding regions (57%), followed by intergenic regions (38%), however much lower numbers were distributed in the non-coding introns (5%) in each cp genome. The coding regions with the highest number of SSRs were ycf genes as shown in Cynara cardunculus (globe artichoke) and other Asteraceae species [47]. Gene ycf2 contained 10 SSRs (five duplicated in each IR) and ycf1, three in SSC, emphasizing that these highly variable regions can be of specific interest to develop future cpSSR markers for phylogenetic studies of Sonchus species. Considering the quadripartite regional occupancy of SSRs, the IR and SSC regions were remarkably lower in overall SSR frequency compared with the LSC region: 19% from the SSC region and 10% from each of the two IR regions versus 61% from the LSC region (Table S2).
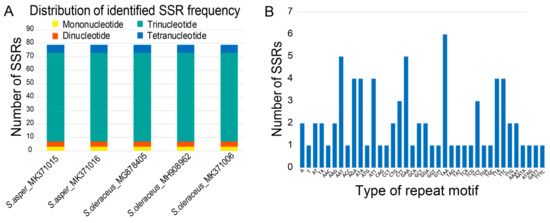
Figure 4.
Simple sequence repeat (SSR) number per distribution and repeat type of five accessions of weedy S. asper and S. oleraceus chloroplast genomes. (A) Variation in the numbers of SSRs detected in five chloroplast genomes of weedy S. asper and S. oleraceus. (B) Number of SSR motifs in different repeat motifs of each weedy Sonchus chloroplast genome.
In the case of the large repeats, we found 49 pairs in each cp genome using the parameters of maximum computed repeats = 50, minimum repeat size = 8 bp, and hamming distance = 0 by REPuter [37]. They contained 21 forward, 6 reverse, 1 complement, and 21 palindromic matches of repeats (Figure 5A). Similar results were reported in previous studies with the majority of repeats in forward (21) and palindromic (13) in other Asteraceae species, Taraxacum plastomes (dandelions) [48]. Most of these large repeats were present in the intergenic spacers, but a large proportion was found within the ycf gene as in Ambrosia trifida (giant ragweed) [54]. Lengths of 20–22 repeats were the most frequent (45%) followed by lengths of 23–26 repeats (37%), with repeats of 27–30 (6%) and > 42 (12%) being quite rare (Figure 5B).
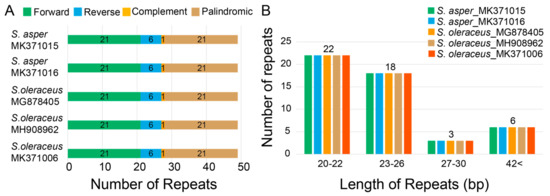
Figure 5.
Repeat numbers per repeat type and repeat length of five chloroplast genomes of two Sonchus species. (A) Variation in the distribution of forward, reverse, complement, and palindromic repeats in each chloroplast genomes of five weedy Sonchus genomes. (B) Number of different repeat lengths of each weedy Sonchus chloroplast genomes.
3.3. Sequence Divergence and Hotspots
Nucleotide diversity among five weedy Sonchus cp genomes was estimated using DnaSP [38] with a sliding window analysis (window length = 1000 bp and step size = 200 bp excluding sites with alignment gaps). The divergence level was compared to the reference genome of S. webbii (Figure 6). Overall nucleotide diversity value (Pi) among Sonchus chloroplast genomes including the two closely related species, S. asper and S. oleraceus, was 0.00117 and ranged from 0 to 0.00807. The SSC region showed the highest nucleotide diversity (0.001629) among the regions of LSC, SSC, and IRs, while the lowest value was in the IR boundary regions (0.000254). Ten divergence hotspots were suggested as the potential chloroplast markers for phylogenetic studies of Sonchus species: four intergenic regions (trnK-rps16, trnT-psbD, accD-psaI, and psbE-petL), two intron regions (trnL intron and rps16 intron), and four protein coding regions (psaA, ycf1, ndhF, and ψycf1). Most of them are located in the LSC region, but the most variable hotspots with the highest divergence values are in the SSC region.
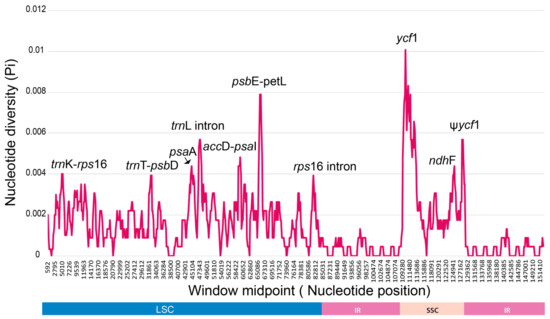
Figure 6.
DNA sequence polymorphisms of three Sonchus chloroplast genomes (S. webbii, S. asper, and S. oleraceus) calculated using a sliding window analysis of 1000 bases and 200 base step sizes using DNAsp. Ten most divergent regions are suggested as mutation hotspots and potential chloroplast markers for Sonchus species.
The result of mVISTA plotted against S. webbii also exhibited a high degree of synteny and gene order conservation among five weedy Sonchus cp genomes. A total of 528 polymorphic sites, which were identified in the DnaSP analysis, were visualized in mVISTA graph from mostly noncoding and intron regions, but also from several protein coding regions. The most divergent coding regions among Sonchus cp genomes were rpoB, rpoC2, atpA, accD, ycf2, ndhF, and ycf1 (Figure 7), while the coding genes of rpoC1, rpoC2, trnL, accD, clpP, psbB, ndhD, ycf1, ndhA, rps16, and ndhF were presented as the most variable regions between Taraxacum and 18 other Asteraceae plastomes [48].
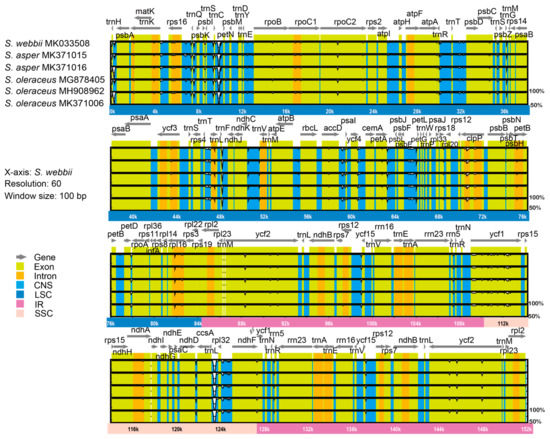
Figure 7.
Comparison of five chloroplast genomes of two weedy Sonchus species, S. asper and S. oleraceus plotted against S. webbii by mVISTA. Sequence identity is portrayed with a cut-off of 50% identity. The Y-scale axis represents the percent identity within 50%–100%. Grey arrows indicate genes with their orientation and position. Genome regions are color-coded as green blocks for the conserved coding genes (exon), aqua blue blocks for the conserved non-coding sequences in intergenic regions (CNS), and orange blocks for introns. Thick lines below the alignment indicate the quadripartite regions of genomes; the LSC region is in dark blue, IR regions are in pink, and the SSC region is in peach. Black bordered white peaks that are shown in genome regions indicate the divergent regions with sequence variation among Sonchus species.
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
The taxonomic position and evolutionary relationship of S. asper and S. oleraceus sequenced in this study were assessed by comparative phylogenetic analysis among 30 representative Asteraceae species based on the sequences of whole cp genomes. For overall phylogenetic relationships within the family Asteraceae, the maximum likelihood tree supported the traditional taxonomy of the family, except the subfamily Asteroideae (Figure 8). Asteroideae failed to form a monophyletic clade, as reported in a previous study [55]. Two tribes of Asteroideae, i.e., Heliantheae and Inuleae, were not nested in the monophyletic clade comprising other tribes of the same subfamily, Anthemideae, Gnaphalieae, Senecioneae, and Astereae. With regard to phylogenetic relationships within Sonchus, the genus formed a monophyletic clade (100% BS) within the tribe Cichorieae of the subfamily Cichorioideae. Sonchus was split into two subclades: i.e., the woody Sonchus alliance in the Canary Islands (100% BS) and the weedy Sonchus species distributed globally (100% BS). S. oleraceus and S. asper were nested in the same subclade, being closely related to each other, even though they were not reciprocally monophyletic. The whole chloroplast genome analysis suggested that both S. asper and S. oleraceus are not monophyletic at the chloroplast level. It is plausible that the species may in fact be monophyletic at the nuclear genome level but is paraphyletic at the chloroplast level, possibly due to incomplete lineage sorting. One lineage of S. oleraceus was represented by two accessions which were sampled from geographically widely separated regions (MK371006 from Spain and MG878405 from Australia) (98% BS) and they shared their most recent common ancestor with S. asper sampled from Spain (MK371016) (weak 33% BS). On the other hand, the accession of S. oleraceus (MH908962) sampled from Dok-do Island in the East Sea (between the Korean peninsula and Japanese archipelago) represented a different plastome type. It was deeply nested within the paraphyletic group of S. asper and, interestingly, the overall length of the whole plastome (151,849 bp) was the same as the ones of S. asper sampled from Spain (MK371015 and MK371016) (Table 1). We consequently confirmed that the plant material studied from Dok-do Island showed typical morphological characteristics of S. oleraceus in its leaves and achenes in order to avoid misinterpretations from our phylogenetic results. The maximum likelihood tree showed that S. oleraceus from Dok-do Island (MH908962) is a sister clade containing one accession of S. asper (MK371016) and two accessions of S. oleraceus (MK371006 from Spain and MG878405 from Australia). Therefore, it is conceivable that S. oleraceus accession on Dok-do Island, which contains a distinct plastome type from two other accessions, represents a distinct lineage of S. oleraceus that is probably spread throughout Eurasia. Nevertheless, our results do not support the existence of clear geographic patterns for plastome lineages since the two accessions of S. asper from Spain (140 km apart, without apparent geographic barriers) seemed to originate from differentiated lineages and the samples of S. oleraceus from Spain and Australia (sampled in geographically remote areas) shared the same plastome profile. The current results generally support the hypothesis that S. asper contributed as the maternal parent in the hybrid origin of S. oleraceus in multiple lineages, a common feature in polyploidy processes [56,57]. However, the origin and evolution of amphidiploid S. oleraceus are yet to be determined precisely, which will likely require the inclusion of nuclear DNA analysis and cytological investigation (e.g., fluorescence in situ hybridization, FISH; or genomic in situ hybridization, GISH) to infer the paternal parents.
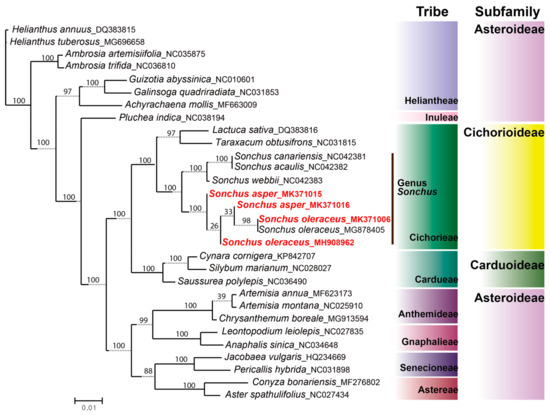
Figure 8.
Phylogenetic position and relationships of weedy Sonchus sow thistles among Asteraceae species based on whole chloroplast genome sequences inferred from maximum likelihood analysis by IQ-TREE. Numbers above nodes are bootstrap values with 1000 replicates. Newly sequenced four chloroplast genomes representing S. asper and S. oleraceus in this study are red colored on the phylogenetic tree.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we sequenced, assembled, and annotated four cp genomes of two weedy Sonchus sow thistles (S. asper and S. oleraceus) and analyzed five cp genomes including an additional cp genome of S. oleraceus (Australia) obtained from GenBank. The results of comparative genomic analyses revealed that the genomes are highly conserved structurally, sharing most common genomic features of sequences, gene content, numbers, and distributions of repeated sequences despite the morphological and cytological differences between S. asper and S. oleraceus. The phylogenetic relationship based on whole chloroplast genome sequences suggested that amphidiploid S. oleraceus most likely originated multiple times from the closely related congeneric species S. asper. We believe that the SSRs, especially longer ones, show potential as useful markers if sample sizes are increased. Lastly, highly variable regions of both coding and noncoding regions were identified as potential phylogenetic markers for Sonchus species.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4425/10/11/881/s1, Table S1: The frequency of SSR candidates (2), Table S2: SSR candidates.
Author Contributions
M.-S.C. and S.-C.K. conceived and designed the experiments. J.A.M. provided plant materials, and M.-S.C. and J.H.K. performed the experiments and analyzed the data. C.-S.K. obtained the funding from the Rural Development Administration, M.-S.C. wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and S.-C.K. and J.A.M. revised the paper. All authors read and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out with the support of “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ01385507)” by Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Holm, L.G.; Plucknett, D.L.; Pancho, J.V.; Herberger, J.P. The World’s Worst Weeds: Distribution and Biology; University Press of Hawaii: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, H.A.; Neilson, J.E. Seed survival and periodicity of seedling emergence in twelve weedy species of Compositae. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1981, 97, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.O.; Gomaa, N.H.; Fahmy, G.M.; González, L.; Hammouda, O.; Atteya, A.M. Interactions between Sonchus oleraceus L. and some weeds in agroecosystems in Egypt. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2014, 59, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, I.A.; Colosi, J.; Lewin, R.A. The biology of Canadian weeds. 63. Sonchus asper (L.) Hill and S. oleraceus L. Can. J. Plant. Sci. 1984, 64, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutsalis, P.; Powles, S.B. Inheritance and mechanism of resistance to herbicides inhibiting acetolactate synthase in Sonchus oleraceus L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1995, 91, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, T.; Davidson, B.; Miller, R. A new glyphosate resistant weed species confirmed for northern New South Wales and the world: Common sowthistle (Sonchus oleraceus). In Proceedings of the 19th Australasian Weeds Conference, Hobart, TAS, Australia, 1–4 September 2014; Tasmanian Weed Society: Hobart, Australia; pp. 206–209. [Google Scholar]
- Cambie, R.C.; Ferguson, L.R. Potential functional foods in the traditional Maori diet. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. 2003, 523, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Yang, P.L. Research progress of Sonchus species. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, N.; Gemeinholzer, B.; Lack, H.W. Cichorieae. In Systematics, Evolution, and Biogeography of Compositae; Funk, V.A., Susanna, A., Stuessy, T.F., Bayer, R.J., Eds.; International Association for Plant Taxonomy: Vienna, Austria, 2009; pp. 343–383. [Google Scholar]
- Kilian, N.; Hand, R.; von Raab-Straube, E. (Eds.) Cichorieae Systematics Portal. Available online: http://cichorieae.e-taxonomy.net/portal/ (accessed on 15 December 2018).
- Boulos, L. Révision systématique du genre Sonchus L. s.l. I. Introduction et classification. Bot. Not. 1972, 125, 287–305. [Google Scholar]
- Mejías, J.A.; Kim, S.-C. Taxonomic treatment of Cichorieae (Asteraceae) endemic to the Juan Fernandez and Desventuradas Islands (SE Pacific). Ann. Bot. Fenn. 2012, 49, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-C.; Lee, C.; Mejias, J. A Phylogenetic analysis of chloroplast DNA matK gene and ITS of nrDNA sequences reveals polyphyly of the genus Sonchus and new relationships among the subtribe Sonchinae (Asteraceae: Cichorieae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 44, 578–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, L. Cytotaxonomic studies in the genus Sonchus 2. The genus Sonchus, a general systematic treatment. Bot. Not. 1960, 3, 400–420. [Google Scholar]
- CABI. Invasive Species Compendium, Sonchus Oleraceus Datasheet. Available online: https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/50584#BE1550BF-EFDC-4477-BBF6-40BF99ECFA6D (accessed on 29 July 2018).
- Hsieh, T.S.; Schooler, A.B.; Hell, A.; Nalewaja, J.A. Cytotaxonomic of three Sonchus species. Am. J. Bot. 1972, 59, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejías, J.A.; Andrés, C. Karyological studies in Iberian Sonchus (Asteraceae: Lactuceae): S. oleraceus, S. microcephalus and S. asper and a general discussion. Folia Geobot. 2004, 39, 275–291. [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan, G.A. Chromosome numbers of canadian weeds. I. Can. J. Bot. 1957, 35, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Ellison, W.L.; King, R.M. Chromosome numbers in the Compositae. IV. North American species with phyletic interpretations. Am. J. Bot. 1961, 48, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, R.; Kuta, E. Cytological and embryological studies in Sonchus L.I. Sonchus asper (L.) HILL and Sonchus oleraceus L. Acta Biol. Cracoviensia Ser. Bot. 1971, 14, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Stebbins, G.L.; Jenkins, J.A.; Walters, M.S. Chromosomes and phylogeny in the Compositae, tribe Cichorieae. Univ. Calif. Publ. Bot. 1953, 26, 401–430. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-C.; Crawford, D.J.; Jansen, R.K. Phylogenetic relationships among the genera of the subtribe Sonchinae (Asteraceae): Evidence from ITS sequences. Syst. Bot. 1996, 21, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-C.; Crawford, D.J.; Francisco-Ortega, J.; Santos-Guerra, A. A common origin for woody Sonchus and five related genera in the Macaronesian islands: Molecular evidence for extensive radiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 7743–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, S.-C.; Lundy, K.; Santos-Guerra, A. Chloroplast DNA phylogeny of the woody Sonchus alliance (Asteraceae: Sonchinae) in the Macaronesian Islands. Am. J. Bot. 2005, 92, 2072–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Miao, H.; Xiong, S. Insights from the complete chloroplast genome into the evolution of Sesamum indicum L. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Iaffaldano, B.J.; Zhuang, X.; Cardina, J.; Cornish, K. Chloroplast genome resources and molecular markers differentiate rubber dandelion species from weedy relatives. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristescu, M.E. Genetic reconstructions of invasion history. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 2212–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudeul, M.; Giraud, T.; Kiss, L.; Shykoff, J.A. Nuclear and chloroplast microsatellites show multiple introductions in the worldwide invasion history of common ragweed, Ambrosia artemissifolia. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnard, G.; Henry, P.; Wille, L.; Cooke, D.; Chapuis, E. On the origin of the invasive olives (Olea europaea L., Oleaceae). Heredity 2007, 99, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, M.; Cronn, R.; Liston, A. Increasing phylogenetic resolution at low taxonomic levels using massively parallel sequencing of chloroplast genomes. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, S.K.; Jansen, R.K.; Boore, J.L. Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3252–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslett, D.; Canback, B. ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rødland, E.A.; Stærfeldt, H.H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNammer: Consistent annotation of rRNA genes in genomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Kahlau, S.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW—A suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W575–W581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudno, M.; Do, C.B.; Cooper, G.M.; Kim, M.F.; Davydov, E.; Green, E.D.; Sidow, A.; Batzoglou, S. NISC Comparative Sequencing Program. LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: Efficient Tools for Large-Scale Multiple Alignment of Genomic DNA. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Choi, K.S.; Jansen, R.K. Two chloroplast DNA inversions originated simultaneously during the early evolution of the sunflower family (Asteraceae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timme, R.E.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. A comparative analysis of the Lactuca and Helianthus (Asteraceae) plastid genomes: Identification of divergent regions and categorization of shared repeats. Am. J. Bot. 2007, 94, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.S.; Yang, J.Y.; Yang, T.J.; Kim, S.-C. Evolutionary Comparison of the Chloroplast Genome in the Woody Sonchus Alliance (Asteraceae) on the Canary Islands. Genes 2019, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curci, P.L.; De Paola, D.; Danzi, D.; Vendramin, G.G.; Sonnante, G. Complete chloroplast genome of the multifunctional crop globe artichoke and comparison with other Asteraceae. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, R.H.; Majeský, Ľ.; Schwarzacher, T.; Gornall, R.; Heslop-Harrison, P. Complete chloroplast genomes from apomictic Taraxacum (Asteraceae): Identity and variation between three microspecies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Cui, L.; Feng, K.; Deng, P.; Du, X.; Wan, F.; Weining, S.; Nie, X. Comparative analysis of Asteraceae chloroplast genomes: Structural organization, RNA editing and evolution. Plant. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1526–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogihara, Y.; Terachi, T.; Sasakuma, T. Intramolecular recombination of chloroplast genome mediated by short direct-repeat sequences in wheat species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8573–8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, B.G.; Hampton, J.N.; Palmer, J.D. Dispersed repeats and structural reorganization in subclover chloroplast DNA. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1989, 6, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.L.; Barkley, N.A.; Jenkins, T.M. Microsatellite markers in plants and insects. Part I: Applications of biotechnology. Genesgenomes Genom. 2009, 3, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Thiel, T.; Michalek, W.; Varshney, R.; Graner, A. Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sablok, G.; Amiryousefi, A.; He, X.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. Sequencing the plastid genome of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida, Asteraceae) from a herbarium specimen. Front. Plant. Sci. 2019, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhou, Z.S.; Liu, G.; Qian, Z.Q. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of the invasive weed Galinsoga quadriradiata (Asterales: Asteraceae). Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2018, 10, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltis, D.E.; Soltis, P.S. Polyploidy: Recurrent formation and genome evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltis, D.E.; Soltis, P.S.; Pires, J.C.; Kovaric, A.; Tate, J.A.; Mavrodiev, E. Recent and recurrent polyploidy in Tragopogon (Asteraceae): Cytogenetic, genomic and genetic comparisons. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2004, 82, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).