Spatial Heterogeneity of Vegetation Structure, Plant N Pools and Soil N Content in Relation to Grassland Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Field Sampling
2.3. Soil and Vegetation Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
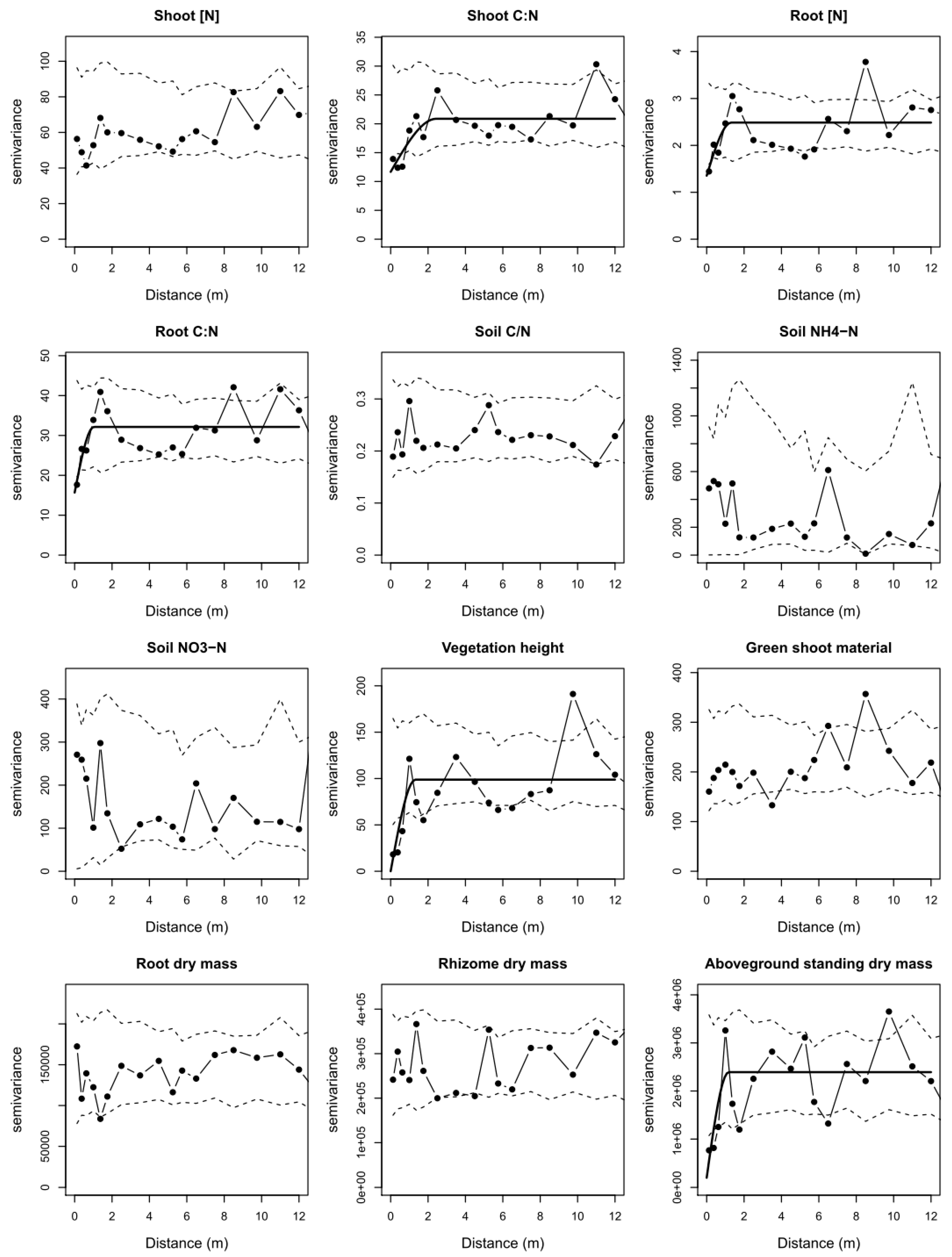
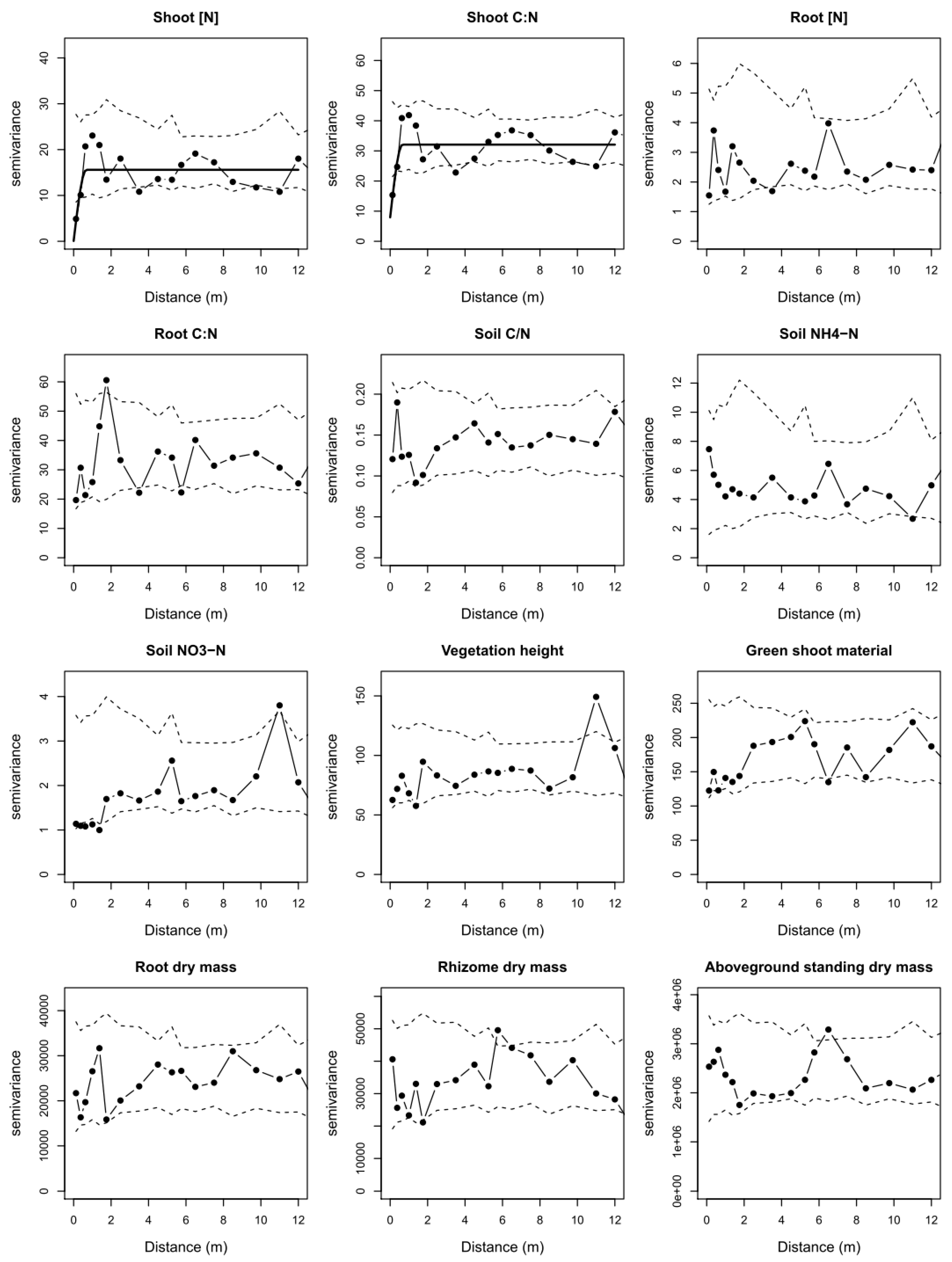
3.1. Impacts of Management on Within-Field Variation
3.2. Spatial Patterns in Relation to Grazing Animal Identity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tilman, D. Dynamics and Structure of Plant Communities; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, I.C.; Lauenroth, W.K.; Riggle, R.; Brannen, P.; Madigan, B.; Beard, S. Spatial variability of soil properties in the shortgrass steppe: The relative importance of topography, grazing, microsite and plant species in controlling spatial patterns. Ecosystems 1999, 2, 422–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloor, J.M.G.; Pottier, J. Grazing and spatial heterogeneity: Implications for grassland structure and function. In Grassland Biodiversity and Conservation in a Changing World; Mariotte, P., Kardol, P., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppage, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 135–162. [Google Scholar]
- García-Palacios, P.; Maestre, F.T.; Bardgett, R.D.; De Kroon, H. Plant responses to soil heterogeneity and global environmental change. J. Ecol. 2012, 100, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGranahan, D.A.; Hovick, T.J.; Elmore, R.D.; Engle, D.M.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. Moderate patchiness optimizes heterogeneity, stability, and beta diversity in mesic grassland. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 5008–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; Donato, D.C.; Romme, W.H. Consequences of spatial heterogeneity for ecosystem services in changing forest landscapes: Priorities for future research. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.P. The impact of soil and crop management practices on soil spatial heterogeneity. In Soil Biota Management in Sustainable Farming Systems; Pankhurse, C.E., Doube, B.M., Gupta, V.V., Grace, P.R., Eds.; CSIRO: East Melbourne, Australia, 1994; pp. 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- Vertes, F.; Delaby, L.; Klumpp, K.; Bloor, J.M.G. C-N-P uncoupling in grazed grasslands and environmental implications of management intensification. In Agroecosystem Diversity; Lemaire, G., Carvalho, P.C.D.F., Kronberg, S., Recous, S., Eds.; Academic Press—Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 15–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dronova, I. Environmental heterogeneity as a bridge between ecosystem service and visual quality objectives in management, planning and design. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 163, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mara, F.P. The role of grasslands in food security and climate change. Ann. Bot. 2012, 110, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, J.; Bullock, J.M.; Egoh, B.; Everson, T.; O’Connor, T.; O’Farrell, P.J.; Smith, H.G.; Lindborg, R. Grasslands—more important for ecosystem services than you might think. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, P.B.; Raff, D.; Lauenroth, W.K. The effect of grazing on the spatial heterogeneity of vegetation. Oecologia 2001, 128, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J.; Williams, P.H. Nutrient cycling and soil fertility in the grazed pasture ecosystem. Adv. Agron 1993, 49, 119–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, A.J.; Dumont, B. Spatial heterogeneity and grazing processes. Anim. Res. 2003, 52, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, N.J.; Olesen, J.E.; Petersen, B.M.; Berntsen, J. Modelling spatial heterogeneity in grazed grassland and its effects on nitrogen cycling and greenhouse gas emissions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milchunas, D.G.; Sala, O.E.; Lauenroth, W.K. A generalized model of the effects of grazing by large herbivores on grassland community structure. Am. Nat. 1988, 132, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Wardle, D.A. Herbivore-mediated linkages between aboveground and belowground communities. Ecology 2003, 84, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Lavorel, S.; McIntyre, S.; Falczuk, V.; Casanoves, F.; Milchunas, D.G.; Skarpe, C.; Rusch, G.M.; Sternberg, M.; Noy-Meir, I.; et al. Plant trait responses to grazing–a global synthesis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 12, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonn, B.; Raab, C.; Isselstein, J. Sward patterns created by patch grazing are stable over more than a decade. Grass Forage Sci. 2019, 74, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, O.J.; Luo, Z.; Jin, H.; Chen, Q.; Han, X. Variation in small-scale spatial heterogeneity of soil properties and vegetation with different land use in semiarid grassland ecosystem. Plant Soil 2008, 310, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirobe, M.; Kondo, J.; Enkhbaatar, A.; Amartuvshin, N.; Fujita, N.; Sakamoto, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; Kielland, K. Effects of livestock grazing on the spatial heterogeneity of net soil nitrogen mineralization in three types of Mongolian grasslands. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, C.; Wang, D.L.; Wang, L.; Wilsey, B.J.; Zhong, Z.W. Impacts of grazing by different large herbivores in grassland depend on plant species diversity. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.K.; Norton, B.E.; Maeno, M.; Malechek, J.C. Paddock size and stocking density affect spatial heterogeneity of grazing. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 61, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hong, M.; Han, G.; Zhao, M.; Bai, Y.; Chang, S.X. Grazing intensity affected spatial patterns of vegetation and soil fertility in a desert steppe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 138, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rook, A.J.; Dumont, B.; Isselstein, J.; Osoro, K.; Wallis DeVries, M.F.; Parente, G.; Mills, J. Matching type of livestock to desired biodiversity outcomes in pastures—A review. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 119, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.S.; Ritchie, M.E.; Olff, H.; Milchunas, D.G.; Knops, J.M.H. Herbivore impact on grassland plant diversity depends on habitat productivity and herbivore size. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogaert, N.; Salomez, J.; Vermoesen, A.; Hofman, G.; Van Cleemput, O.; Van Meirvenne, M. Within-field variability of mineral nitrogen in grassland. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 32, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, N.; Chadoeuf, J.; Carrère, P.; Dumont, B. A hierarchical model for analysing the stability of vegetation patterns created by grazing in temperate pastures. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2011, 14, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaaks, E.H.; Srivastava, R.M. An Introduction to Applied Geostatistics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, K.L.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Burton, A.J. Spatial variation in nitrogen availability in three successional plant communities. J. Ecol. 1995, 83, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S.; Zwanzig, S. An improvement of the nonparametric bootstrap test for the comparison of the coefficient of variations. Commun. Stat. Simulat. 2010, 39, 1726–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, M.J.; Dale, M.R.T. Spatial Analysis: A Guide for Ecologists; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wiens, J.A. Spatial scaling in ecology. Func. Ecol. 1989, 3, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.J.; John, E.A.; Wijesinghe, D.K. Toward understanding the consequences of soil heterogeneity for plant populations and communities. Ecology 2003, 84, 2322–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tälle, M.; Deák, B.; Poschlod, P.; Valkó, O.; Westerberg, L.; Milberg, P. Grazing vs. mowing: A meta-analysis of biodiversity benefits for grassland management. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 222, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oenema, O.; Velthof, G.L.; Yamulki, S.; Jarvis, S.C. Nitrous oxide emissions from grazed grassland. Soil Use Manag. 1997, 13, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.; Cameron, K. Nitrate leaching in temperate agroecosystems: Sources, factors and mitigating strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 64, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwin, K.H.; Bertram, J.E.; Clough, T.J.; Condron, L.M.; Sherlock, R.R.; O’Callaghan, M. Short-term consequences of spatial heterogeneity in soil nitrogen concentrations caused by urine patches of different sizes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 42, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White-Leech, R.; Liu, K.; Sollenberger, L.E.; Woodard, K.R.; Interrante, S.M. Excreta deposition on grassland patches. II. Spatial pattern and duration of forage responses. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Evaluating the effectiveness of landscape metrics in quantifying spatial patterns. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 10, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, M.J.; Anderson, J.M.; Bol, R.; Allen, D.K. Incorporation of 15N from spiked cattle dung pats into soil under two moorland plant communities. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2000, 14, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.L.; Sheffield, R.E.; Washburn, S.P.; King, L.D.; Green, J.T., Jr. Spatial and time distribution of dairy cattle excreta in an intensive pasture system. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 2180–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelena, P.; Sibbald, A.M.; Erhard, H.W.; McLeod, J.E. Effects of group size and personality on social foraging: The distribution of sheep across patches. Behav. Ecol. 2009, 20, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Alves, D.G. The effect of plant spatial pattern within a patch on foraging selectivity of grazing sheep. Landsc. Ecol. 2012, 27, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getzin, S.; Yizhaq, H.; Cramer, M.D.; Tschinkel, W.R. Contrasting global patterns of spatially periodic fairy circles and regular insect nests in drylands. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2019, 124, 3327–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, F.; Kohler, F.; Vandenberghe, C.; Buttler, A. Effect of dung deposition on small-scale patch structure and seasonal vegetation dynamics in mountain pastures. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 135, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheile, T.; Isselstein, J.; Tonn, B. Herbage biomass and uptake under low-input grazing as affected by cattle and sheep excrement patches. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2018, 112, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, N.; Carrère, P.; Bloor, J.M.G. Nitrogen form and spatial pattern promote asynchrony in plant and soil responses to nitrogen inputs in a temperate grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 71, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
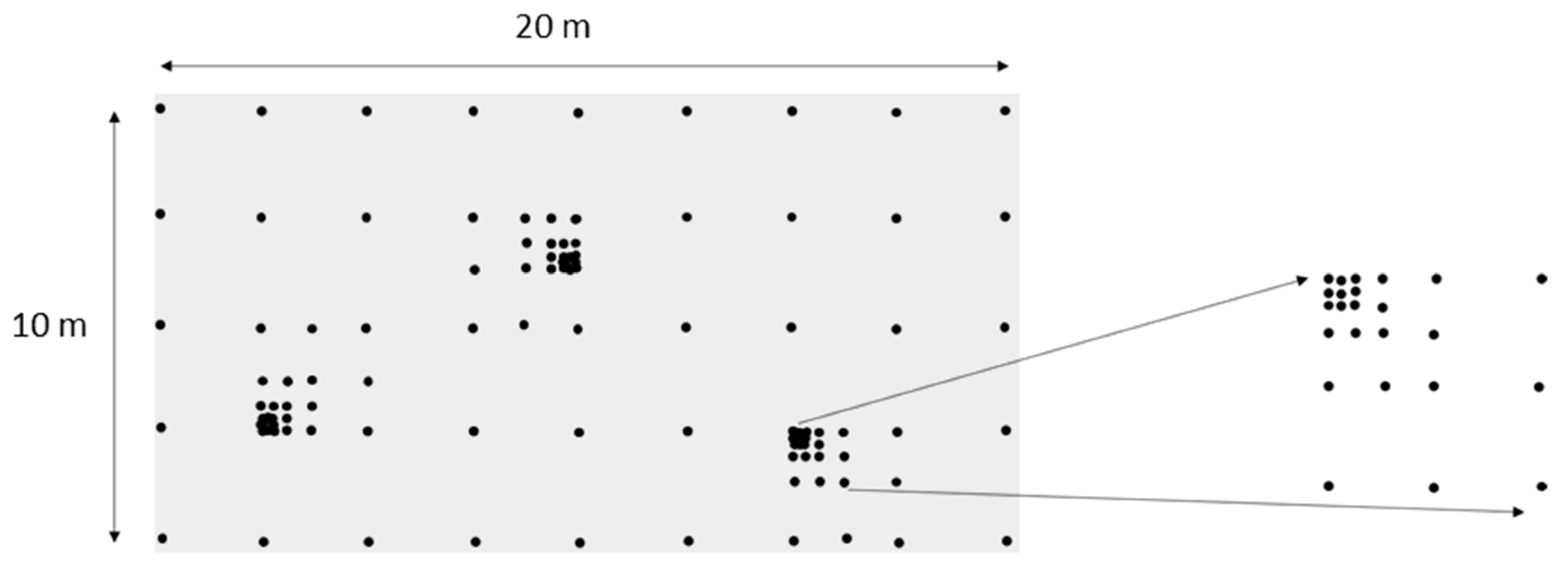
| Variable | Management Treatment § | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mowing+NPK | Sheep-Grazing | Cattle-Grazing | |
| Vegetation height (cm) | 35.4 a | 38.3 a | 54.6 b |
| Aboveground standing dry mass (kg m−2) | 64.6 a | 48.1 b | 65.7 a |
| Green shoot material (%) | 13.9 a | 35.5 b | 72.4 c |
| Shoot [N] * (mg N g−1 shoot dry mass) | 16.5 a | 23.8 b | 28.5 b |
| Shoot C/N* | 19.9 a | 21.6 ab | 27.3 b |
| Rhizome dry mass (kg m−2) | 84.6 a | 83.5 a | 68.9 a |
| Root dry mass (kg m−2) | 80.4 a | 55.8 b | 47.6 b |
| Root [N] (mg N g−1 root dry mass) | 14.2 a | 15.1 a | 13.6 a |
| Root C/N | 14.1 a | 14.6 a | 14.1 a |
| Soil NO3-N (μg N g−1 dry soil) | 128 a | 31.1 b | 192 c |
| Soil NH4-N (μg N g−1 dry soil) | 121 a | 42.4 b | 224 c |
| Soil C/N | 5.44 a | 3.30 b | 4.29 ac |
| Treatment | Variable | Spatial Pattern * | Range (m) | Spatial Dependence (C/[C+C0]) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sheep Grazing | Shoot [N] | Patchy | 0.68 | 1 |
| Shoot C:N | Patchy | 0.66 | 0.75 | |
| Cattle Grazing | Vegetation height | Periodic | 1.83 | 1 |
| Aboveground standing biomass | Periodic | 1.18 | 0.92 | |
| Shoot C:N | Patchy | 2.44 | 0.44 | |
| Root [N] | Patchy | 1.32 | 0.46 | |
| Root C:N | Patchy | 1.03 | 0.51 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bloor, J.M.G.; Tardif, A.; Pottier, J. Spatial Heterogeneity of Vegetation Structure, Plant N Pools and Soil N Content in Relation to Grassland Management. Agronomy 2020, 10, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050716
Bloor JMG, Tardif A, Pottier J. Spatial Heterogeneity of Vegetation Structure, Plant N Pools and Soil N Content in Relation to Grassland Management. Agronomy. 2020; 10(5):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050716
Chicago/Turabian StyleBloor, Juliette M. G., Antoine Tardif, and Julien Pottier. 2020. "Spatial Heterogeneity of Vegetation Structure, Plant N Pools and Soil N Content in Relation to Grassland Management" Agronomy 10, no. 5: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050716
APA StyleBloor, J. M. G., Tardif, A., & Pottier, J. (2020). Spatial Heterogeneity of Vegetation Structure, Plant N Pools and Soil N Content in Relation to Grassland Management. Agronomy, 10(5), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050716





