Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules Using Ultrasound Cine-Loop Video Sequences
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
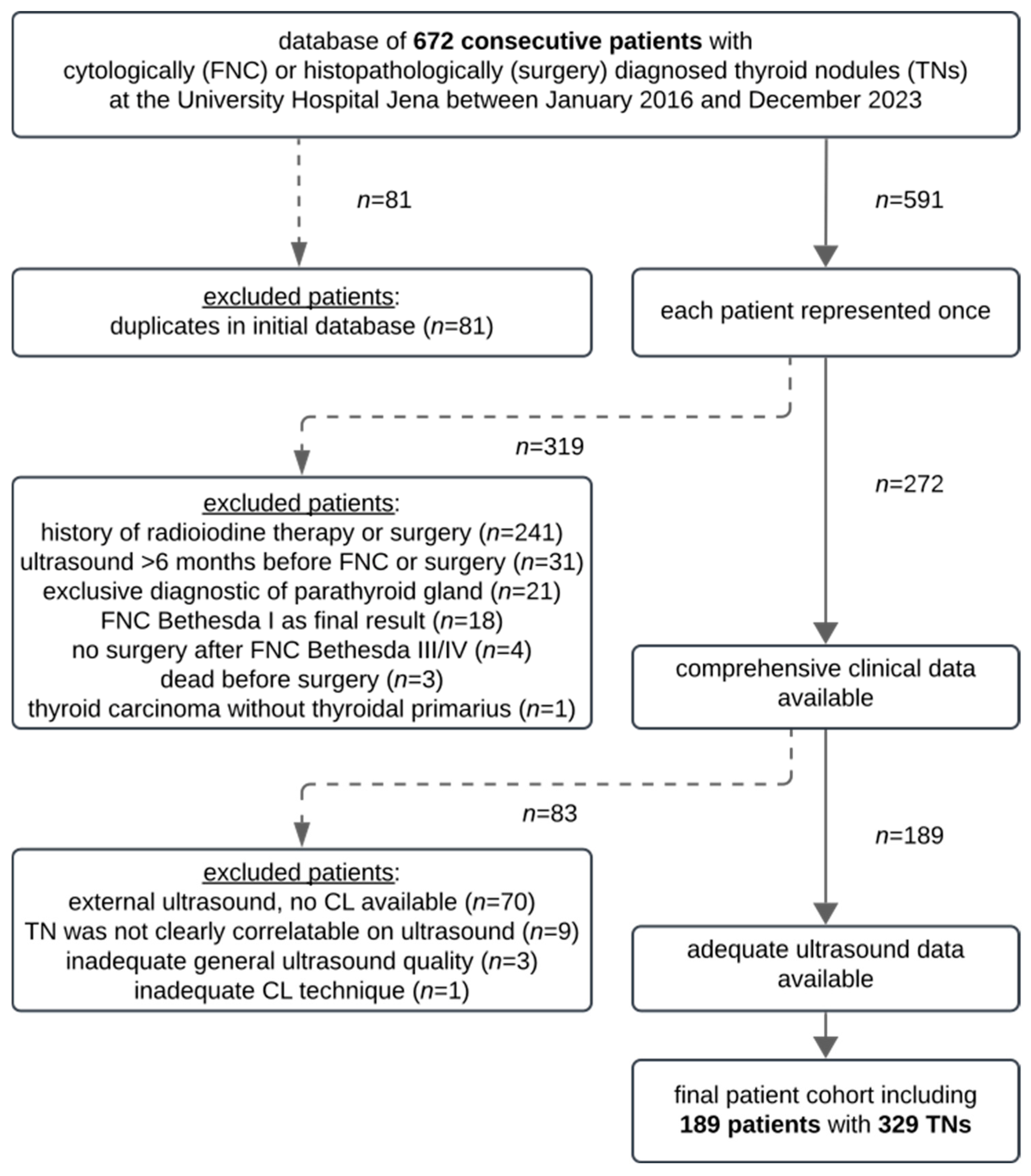
2.1. Study Design and Patients
- -
- The CL of TNs available on the PACS (transverse and sagittal planes);
- -
- Ultrasound performed <6 months prior to FNC/surgery;
- -
- Cytological and/or histopathological results of TNs available (Bethesda II without subsequent surgery and Bethesda III, IV, and V with subsequent surgery).
- -
- A history of radioiodine therapy or thyroid surgery;
- -
- Ultrasound > 6 months before FNC/surgery;
- -
- No CLs available (external pre-interventional ultrasound);
- -
- Inadequate CL techniques (e.g., missing transverse or sagittal scans);
- -
- Inadequate ultrasound image quality (images were not reasonably assessable);
- -
- Inconclusive final diagnosis (e.g., missing histopathological results after ambiguous FNC);
- -
- Bethesda I as the final result;
- -
- Bethesda III/IV/V without subsequent surgery;
- -
- Thyroid carcinoma detected in metastases, and no primary tumor identified in the thyroid gland;
- -
- The localization of cytologically/histopathologically diagnosed TN was not relatable to TNs on ultrasound.
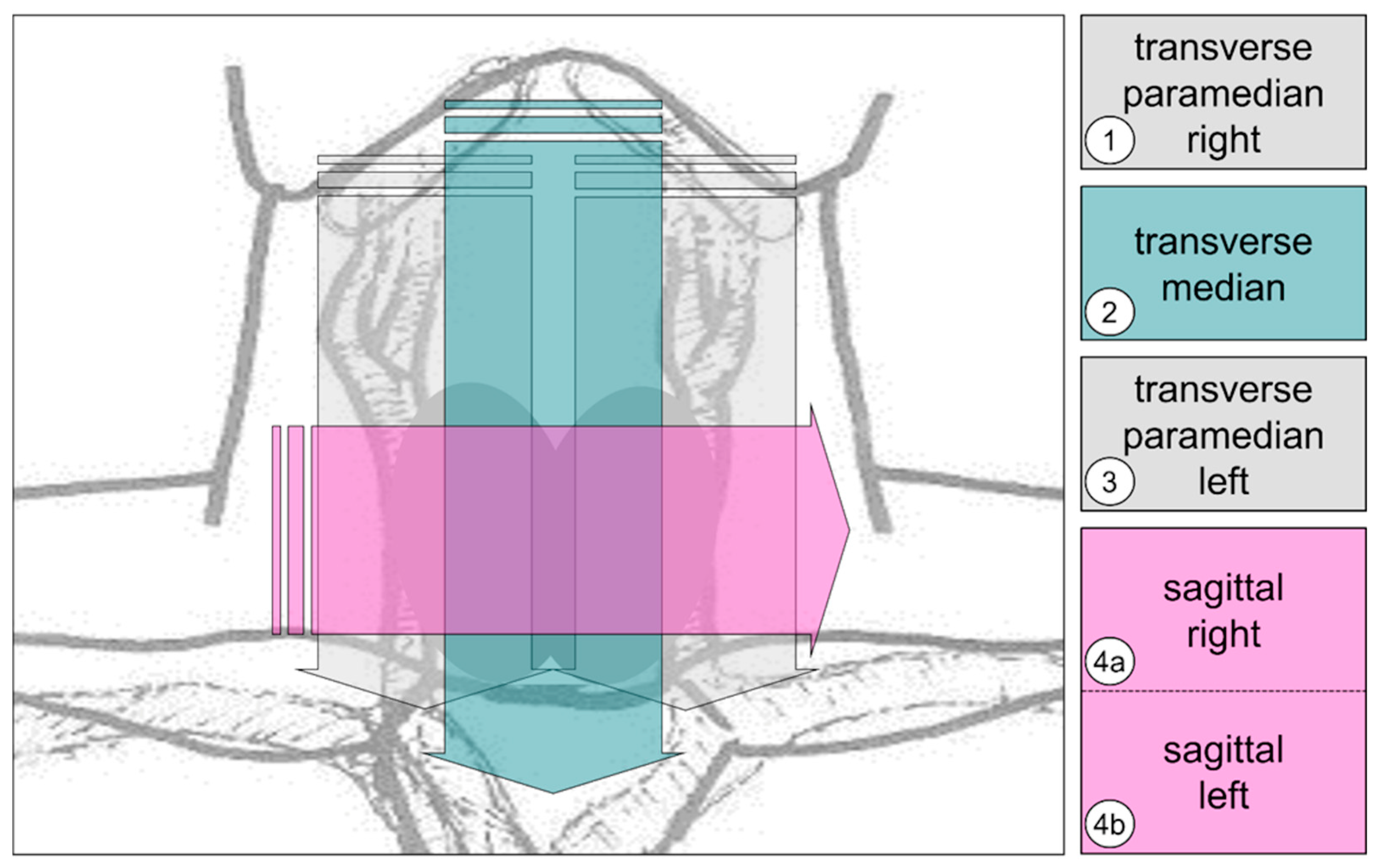
2.2. Ultrasound Examinations
- -
- 1: Right-sided medial thyroid compartment; transverse plane; and cranio-caudal movement.
- -
- 2: Median thyroid compartment, transverse plane and cranio-caudal movement.
- -
- 3: Left-sided medial thyroid compartment; transverse plane; and cranio-caudal movement.
- -
- 4a/4b: Thyroid compartment; sagittal plane; right–left; and possibly two single scans (depending on the prominence of the larynx).
2.3. Data Assessment
2.4. Data Analyses and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Data and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Ultrasound Features
3.3. Risk Stratification Systems
3.4. Technical Ultrasound Features
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | diagnostic accuracy |
| ACR | American College of Radiology |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| CL | cine loops (video sequences on ultrasound) |
| FNC | fine-needle cytology |
| NPV | negative predictive value |
| PACS | Picture Archiving and Communication System |
| PPV | positive predictive value |
| pts. | points |
| RSSs | risk stratification systems |
| SENS | sensitivity |
| SICs | static image captures |
| SPEC | specificity |
| SOP | standard operating procedure |
| TIRADS | Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System |
| TN(s) | thyroid nodule(s) |
References
- Kobaly, K.; Kim, C.S.; Mandel, S.J. Contemporary Management of Thyroid Nodules. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, G.; Leboulleux, S.; Leenhardt, L.; Hegedus, L. Thyroid incidentalomas: Epidemiology, risk stratification with ultrasound and workup. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2014, 3, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, E.K.; Cibas, E.S. Diagnosis of thyroid nodules. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boers, T.; Braak, S.J.; Rikken, N.E.T.; Versluis, M.; Manohar, S. Ultrasound imaging in thyroid nodule diagnosis, therapy, and follow-up: Current status and future trends. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2023, 51, 1087–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, L.; Freitas, C.; Martins, R.; Saraiva, C.; Manita, I.; Oliveira, M.J.; Marques, A.P.; Marques, B.; Rocha, G.; Martins, T.; et al. Malignancy risk of thyroid nodules: Quality assessment of the thyroid ultrasound report. BMC Med. Imaging 2022, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, C.; Offi, C.; Clarizia, G.; Romano, R.M.; Cozzolino, I.; Montella, M.; Di Crescenzo, R.M.; Mascolo, M.; Cangiano, A.; Di Martino, S.; et al. Medullary thyroid carcinoma with double negative calcitonin and CEA: A case report and update of literature review. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessler, F.N.; Middleton, W.D.; Grant, E.G.; Hoang, J.K.; Berland, L.L.; Teefey, S.A.; Cronan, J.J.; Beland, M.D.; Desser, T.S.; Frates, M.C.; et al. ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS): White Paper of the ACR TI-RADS Committee. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2017, 14, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, G.; Bonnema, S.J.; Erdogan, M.F.; Durante, C.; Ngu, R.; Leenhardt, L. European Thyroid Association Guidelines for Ultrasound Malignancy Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules in Adults: The EU-TIRADS. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2017, 6, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.Y.; Han, K.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Moon, H.J.; Son, E.J.; Park, S.H.; Jung, H.K.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, E.K. Thyroid imaging reporting and data system for US features of nodules: A step in establishing better stratification of cancer risk. Radiology 2011, 260, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lin, M.; Wu, S. Validating and Comparing C-TIRADS, K-TIRADS and ACR-TIRADS in Stratifying the Malignancy Risk of Thyroid Nodules. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 899575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, P.; Kuhnel, C.; Reissmann, I.; Winkens, T.; Freesmeyer, M. Standardized acquisition and documentation of cine loops on conventional thyroid ultrasound. Laryngorhinootologie 2024, 103, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, P.; Maikowski, I.; Winkens, T.; Kuhnel, C.; Guhne, F.; Drescher, R.; Freesmeyer, M. Ultrasound Cine Loop Standard Operating Procedure for Benign Thyroid Diseases-Evaluation of Non-Physician Application. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, K.; Burke, L.; McGettigan, M. Use of cine images in standard ultrasound imaging: A survey of sonologists. Abdom. Radiol. 2023, 48, 3530–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Yang, B.; Wei, L.; Xue, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Qin, M.; Zhang, S.; Dai, Q.; Yang, M. Real-time carotid plaque recognition from dynamic ultrasound videos based on artificial neural network. Ultraschall Med. 2024, 45, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, T.E.; Jones, J.; Rosenberg, H.; Thomson, A.; Ghandehari, H.; Rosta, N.; Jozkow, K.; Stromer, M.; Swan, H. Increasing the detection rate of congenital heart disease during routine obstetric screening using cine loop sweeps. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, C.; Wang, H.; Cheng, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ni, D.; Huang, W.; et al. Locating Multiple Standard Planes in First-Trimester Ultrasound Videos via the Detection and Scoring of Key Anatomical Structures. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2023, 49, 2006–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopuschek, M.P.; Freesmeyer, M.; Winkens, T.; Kuhnel, C.; Petersen, M.; Guhne, F.; Werner, A.; Seifert, P. Standard operating procedure (SOP) for cervical ultrasound cine loop video sequences in the follow-up of differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC). Endocrine 2024, 87, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenke, S.A.; Petersen, M.; Gorges, R.; Ruhlmann, V.; Zimny, M.; Richter, J.P.; Groener, D.; Baumgarten, J.; Kreissl, M.C.; Stahl, A.R.; et al. Interobserver Agreement in Ultrasound Risk Stratification Systems for Thyroid Nodules on Static Images Versus Cine-Loop Video Sequences. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibas, E.S.; Ali, S.Z. The 2017 Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. Thyroid 2017, 27, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoglu, H. User’s guide to correlation coefficients. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fat, I.; Kulaga, M.; Dodis, R.; Carling, T.; Theoharis, C.; Rennert, N.J. Insular variant of poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Endocr. Pract. 2011, 17, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Midorikawa, S.; Fukushima, T.; Shimura, H.; Ohira, T.; Ohtsuru, A.; Abe, M.; Shibata, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Suzuki, S.; et al. Systematic determination of thyroid volume by ultrasound examination from infancy to adolescence in Japan: The Fukushima Health Management Survey. Endocr. J. 2015, 62, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dormagen, J.B.; Gaarder, M.; Drolsum, A. Standardized cine-loop documentation in abdominal ultrasound facilitates offline image interpretation. Acta Radiol. 2015, 56, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, E.J.; Moon, W.J.; Na, D.G.; Lee, Y.H.; Choi, N.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.K. A Multicenter Prospective Validation Study for the Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System in Patients with Thyroid Nodules. Korean J. Radiol. 2016, 17, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.R.; Ahn, H.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Yoo, R.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Sung, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Baek, J.H. Diagnostic Performance of the Modified Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System for Thyroid Malignancy: A Multicenter Validation Study. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, P.; Gorges, R.; Zimny, M.; Kreissl, M.C.; Schenke, S. Interobserver agreement and efficacy of consensus reading in Kwak-, EU-, and ACR-thyroid imaging recording and data systems and ATA guidelines for the ultrasound risk stratification of thyroid nodules. Endocrine 2020, 67, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, P.; Schenke, S.; Zimny, M.; Stahl, A.; Grunert, M.; Klemenz, B.; Freesmeyer, M.; Kreissl, M.C.; Herrmann, K.; Gorges, R. Diagnostic Performance of Kwak, EU, ACR, and Korean TIRADS as Well as ATA Guidelines for the Ultrasound Risk Stratification of Non-Autonomously Functioning Thyroid Nodules in a Region with Long History of Iodine Deficiency: A German Multicenter Trial. Cancers 2021, 13, 4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piticchio, T.; Russ, G.; Radzina, M.; Frasca, F.; Durante, C.; Trimboli, P. Head-to-head comparison of American, European, and Asian TIRADSs in thyroid nodule assessment: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Chung, S.R.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, K.W. Accuracy of thyroid imaging reporting and data system category 4 or 5 for diagnosing malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 5611–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xi, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Lai, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, B. Comparison among TIRADS (ACR TI-RADS and KWAK- TI-RADS) and 2015 ATA Guidelines in the diagnostic efficiency of thyroid nodules. Endocrine 2019, 64, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Moon, H.J.; Park, V.Y.; Kwak, J.Y. Comparison of diagnostic performance of the ACR and Kwak TIRADS applying the ACR TIRADS’ size thresholds for FNA. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 5243–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studen, K.B.; Domagala, B.; Gaberscek, S.; Zaletel, K.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A. Diagnosing and management of thyroid nodules and goiter-current perspectives. Endocrine 2024, 87, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; He, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Diagnostic efficiency among Eu-/C-/ACR-TIRADS and S-Detect for thyroid nodules: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1227339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, S.J.; Kwak, J.Y. Thyroid ultrasonography: Pitfalls and techniques. Korean J. Radiol. 2014, 15, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carlos, J.; Garcia, J.; Basterra, F.J.; Pineda, J.J.; Dolores Ollero, M.; Toni, M.; Munarriz, P.; Anda, E. Interobserver variability in thyroid ultrasound. Endocrine 2024, 85, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileva, M.; Stoilovska, B.; Jovanovska, A.; Ugrinska, A.; Petrushevska, G.; Kostadinova-Kunovska, S.; Miladinova, D.; Majstorov, V. Thyroid cancer detection rate and associated risk factors in patients with thyroid nodules classified as Bethesda category III. Radiol. Oncol. 2018, 52, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freesmeyer, M.; Winkens, T.; Weissenrieder, L.; Kuhnel, C.; Guhne, F.; Schenke, S.; Drescher, R.; Seifert, P. Fusion iENA Scholar Study: Sensor-Navigated I-124-PET/US Fusion Imaging versus Conventional Diagnostics for Retrospective Functional Assessment of Thyroid Nodules by Medical Students. Sensors 2020, 20, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkens, T.; Seifert, P.; Hollenbach, C.; Kuhnel, C.; Guhne, F.; Freesmeyer, M. The FUSION iENA Study: Comparison of I-124-PET/US Fusion Imaging with Conventional Diagnostics for the Functional Assessment of Thyroid Nodules by Multiple Observers. Nuklearmedizin 2019, 58, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenke, S.; Seifert, P.; Zimny, M.; Winkens, T.; Binse, I.; Gorges, R. Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules Using the Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS): The Omission of Thyroid Scintigraphy Increases the Rate of Falsely Suspected Lesions. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.; Beck, M.; Muller, S.K.; Iro, H.; Koch, M.; Sievert, M. Thyroid nodules as an incidental finding : Value of sonography and scintigraphy in primary diagnostics. HNO 2024, 72, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potipimpanon, P.; Charakorn, N.; Hirunwiwatkul, P. A comparison of artificial intelligence versus radiologists in the diagnosis of thyroid nodules using ultrasonography: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 5363–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildman-Tobriner, B.; Buda, M.; Hoang, J.K.; Middleton, W.D.; Thayer, D.; Short, R.G.; Tessler, F.N.; Mazurowski, M.A. Using Artificial Intelligence to Revise ACR TI-RADS Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules: Diagnostic Accuracy and Utility. Radiology 2019, 292, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Qian, L.; Wang, Z.; Hu, X. Deep learning diagnostic performance and visual insights in differentiating benign and malignant thyroid nodules on ultrasound images. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 2538–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnabatu, C.J.; Fetzer, D.T.; Tessnow, A.; Holt, S.; Sant, V.R. Avoidable biopsies? Validating artificial intelligence-based decision support software in indeterminate thyroid nodules. Surgery 2025, 177, 108829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez Velasco, P.; Perez Lopez, P.; Torres Torres, B.; Delgado, E.; de Luis, D.; Diaz Soto, G. Clinical Evaluation of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Decision Support System for the Diagnosis and American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System Classification of Thyroid Nodules. Thyroid 2024, 34, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodoque-Cubas, J.; Fernandez-Saez, J.; Martinez-Hervas, S.; Perez-Lacasta, M.J.; Carles-Lavila, M.; Pallares-Gasulla, R.M.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.J.; Gil-Boix, J.V.; Miret-Llaurado, M.; Aulinas-Maso, A.; et al. Integrating Artificial Intelligence in Thyroid Nodule Management: Clinical Outcomes and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 00, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zheng, L.L.; Zhang, C.J.; Wei, H.F.; Xu, L.L.; Zhang, M.R.; Li, Q.; He, G.F.; Ghamor-Amegavi, E.P.; Li, S.Y. Comparison of S-Detect and thyroid imaging reporting and data system classifications in the diagnosis of cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1098031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, C. Diagnostic accuracy of S-Detect in distinguishing benign and malignant thyroid nodules: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildman-Tobriner, B.; Taghi-Zadeh, E.; Mazurowski, M.A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools for Thyroid Nodules on Ultrasound, from the AJR Special Series on AI Applications. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 219, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinov, L.; Jairaj, A.; Middleton, W.D.; Beland Kirsch, J.; Filice, R.W.; Reverter, J.L.; Arguelles, I.; Grant, E.G. Improving the Efficacy of ACR TI-RADS Through Deep Learning-Based Descriptor Augmentation. J. Digit. Imaging 2023, 36, 2392–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronke, M.; Eilers, C.; Dimova, D.; Kohler, M.; Buschner, G.; Schweiger, L.; Konstantinidou, L.; Makowski, M.; Nagarajah, J.; Navab, N.; et al. Tracked 3D ultrasound and deep neural network-based thyroid segmentation reduce interobserver variability in thyroid volumetry. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munsterman, R. Deep Learning Segmentation of 3D Ultrasound Thyroid Scans. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Faculty of Science and Technology, Biomedical Engineering, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, A.; Lee, J.W.K.; Ngiam, K.Y. Use of 3D ultrasound to characterise temporal changes in thyroid nodules: An in vitro study. J. Ultrasound 2023, 26, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ultrasound Features | CL (n = 329) | SIC (n = 271) | Chi2 | Spearman’s Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | ||||
| Cystic or almost completely cystic | 59 (17.9) | 39 (14.4) | p = 0.243 | r = 0.657 p < 0.001 |
| Spongiform | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.4) | p = 0.891 | |
| Mixed cystic and solid | 123 (37.4) | 120 (44.3) | p = 0.087 | |
| Solid or almost completely solid | 146 (44.4) | 111 (41.0) | p = 0.400 | |
| Echogenicity | ||||
| Anechoic | 24 (7.3) | 10 (3.7) | p = 0.057 | r = 0.574 p < 0.001 |
| Hyperechoic or isoechoic | 129 (39.2) | 97 (35.8) | p = 0.390 | |
| Hypoechoic | 157 (47.7) | 133 (49.1) | p = 0.741 | |
| Very hypoechoic | 19 (5.8) | 31 (11.4) | p = 0.013 | |
| Shape | ||||
| Wider than tall | 300 (91.2) | 234 (86.3) | p = 0.059 | r = 0.380 p < 0.001 |
| Taller than wide | 29 (8.8) | 37 (13.7) | p = 0.059 | |
| Margin | ||||
| Smooth | 103 (31.3) | 136 (50.2) | p < 0.001 | r = 0.406 p < 0.001 |
| Ill-defined | 205 (62.3) | 112 (41.3) | p < 0.001 | |
| Lobulated or irregular | 21 (6.4) | 23 (8.5) | p = 0.325 | |
| Extra-thyroidal extension | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - * | |
| Echogenic Foci | ||||
| None or large comet-tail artifacts | 245 (74.5) | 203 (74.9) | p = 0.902 | r = 0.523 p < 0.001 |
| Macrocalcifications | 51 (15.5) | 43 (15.9) | p = 0.902 | |
| Peripheral (rim) calcifications | 6 (1.8) | 10 (3.7) | p = 0.158 | |
| Punctate echogenic foci | 27 (8.2) | 15 (5.5) | p = 0.202 | |
| Result | CL (n = 329) | SIC (n = 271) | Chi2 | Spearman’s Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACR TIRADS | ||||
| TR1 | 23 (7.0) | 10 (3.0) | p = 0.078 | r = 0.475 p < 0.001 |
| TR2 | 37 (11.2) | 37 (11.2) | p = 0.372 | |
| TR3 | 89 (27.1) | 60 (18.2) | p = 0.166 | |
| TR4 | 142 (43.2) | 125 (38.0) | p = 0.467 | |
| TR4 (4 pts.) | 81 (24.6) | 84 (31.0) | p = 0.082 | |
| TR4 (5 pts.) | 36 (10.9) | 29 (10.7) | p = 0.925 | |
| TR4 (6 pts.) | 25 (7.6) | 12 (4.4) | p = 0.108 | |
| TR5 | 38 (11.6) | 39 (11.8) | p = 0.301 | |
| Kwak TIRADS | ||||
| 3 | 65 (19.8) | 51 (15.5) | p = 0.772 | r = 0.569 p < 0.001 |
| 4A | 107 (32.5) | 84 (25.5) | p = 0.690 | |
| 4B | 124 (37.7) | 103 (31.3) | p = 0.936 | |
| 4C | 33 (10.0) | 33 (10.0) | p = 0.403 | |
| 4C (3 pts.) | 28 (8.5) | 27 (8.2) | p = 0.540 | |
| 4C (4 pts.) | 5 (1.5) | 6 (1.8) | p = 0.528 | |
| 5 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - * | |
| Assessment Confidence | ||||
| Very confident | 120 (36.5) | 143 (43.5) | p < 0.001 | r = 0.239 p < 0.001 |
| Confident | 163 (49.5) | 116 (35.3) | p = 0.100 | |
| Ambiguous | 41 (12.5) | 11 (3.3) | p < 0.001 | |
| Uncertain | 5 (1.5) | 1 (0.3) | p = 0.156 | |
| Cutoff | Ultrasound Method | SENS | SPEC | PPV | NPV | ACC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACR TIRADS | ||||||
| TR4 TR4 (4 pts.) | CL | 68.1 | 47.5 | 17.8 | 89.9 | 50.5 |
| SIC | 76.7 | 42.9 | 22.0 | 89.7 | 48.7 | |
| TR4 (5 pts.) | CL | 51.1 | 73.4 | 24.2 | 90.0 | 70.2 |
| SIC | 57.4 | 76.3 | 33.8 | 89.5 | 73.1 | |
| TR4 (6 pts.) | CL | 40.4 | 58.8 | 30.2 | 89.5 | 78.1 |
| SIC | 44.7 | 86.6 | 41.2 | 88.2 | 79.3 | |
| TR5 | CL | 36.2 | 92.6 | 44.7 | 89.7 | 84.5 |
| SIC | 34.0 | 89.7 | 41.0 | 86.6 | 80.1 | |
| Kwak TIRADS | ||||||
| 4C 4C (3 pts.) | CL | 37.2 | 94.3 | 48.5 | 86.6 | 85.4 |
| SIC | 34.9 | 92.8 | 45.5 | 89.5 | 81.5 | |
| 4C (4 pts.) | CL | 9.3 | 100.0 | 80.0 | 86.7 | 86.6 |
| SIC | 9.3 | 100.0 | 66.7 | 83.8 | 83.4 | |
| Ultrasound Method | Affected Ultrasound Plane | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL (n = 658) * | SIC (n = 542) * | More Frequently in (CL) | More Frequently in (SIC) | Chi2 | |
| No artifacts | 406 (61.7) | 433 (79.9) | transverse | transverse | p < 0.001 |
| Bad image quality | 90 (13.7) | 32 (5.9) | transverse | transverse | p < 0.001 |
| Indistinguishable TNs | 105 (16.0) | 51 (9.4) | sagittal | sagittal | p < 0.001 |
| TNs cut/interfered | 50 (7.6) | 14 (2.6) | sagittal | sagittal | p < 0.001 |
| Acoustic shadowing | 7 (1.1) | 12 (2.2) | sagittal | equally | p = 0.112 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmidt, T.N.; Freesmeyer, M.; Kühnel, C.; Gühne, F.; Rosenbaum, L.; Drescher, R.; Seifert, P. Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules Using Ultrasound Cine-Loop Video Sequences. Cancers 2025, 17, 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162616
Schmidt TN, Freesmeyer M, Kühnel C, Gühne F, Rosenbaum L, Drescher R, Seifert P. Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules Using Ultrasound Cine-Loop Video Sequences. Cancers. 2025; 17(16):2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162616
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmidt, Tabea Nikola, Martin Freesmeyer, Christian Kühnel, Falk Gühne, Larissa Rosenbaum, Robert Drescher, and Philipp Seifert. 2025. "Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules Using Ultrasound Cine-Loop Video Sequences" Cancers 17, no. 16: 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162616
APA StyleSchmidt, T. N., Freesmeyer, M., Kühnel, C., Gühne, F., Rosenbaum, L., Drescher, R., & Seifert, P. (2025). Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules Using Ultrasound Cine-Loop Video Sequences. Cancers, 17(16), 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162616






