Simple Summary
In the treatment of colorectal cancer, classic chemotherapy drugs such as 5-fluorouracil, capecitabine, irinotecan, oxaliplatin, trifluridine, and tipiracil have played a crucial role. Through the analysis of the top 100 most influential articles, we examined the evolution in research and current relevance, confirming the continued significance of this group of drugs despite the emergence of new treatments. The research reveals global collaboration among institutions, countries (primarily the United States, China, and Europe), and researchers, with three main themes driving the study: pharmacogenetics, new pharmaceutical formulations, and the use of adjuvants.
Abstract
In the landscape of colorectal cancer treatment, classical chemotherapeutic agents such as 5-fluorouracil, capecitabine, irinotecan, oxaliplatin, trifluridine, and tipiracil have historically played a pivotal role. This study presents a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most influential articles focusing on these classic chemotherapy drugs in the management of colorectal cancer. With this, we shed light on their current importance, despite the emergence of new therapeutic targets and treatments in the field of oncology. Systematically evaluating research outputs, this analysis reveals a prevalence of co-authorship among institutions, countries (led by the United States, China, and Europe), and researchers highlighting the global and collaborative nature of efforts in research, utilization, and development of these drugs. Three thematic axes lead the research: pharmacogenetics, the development of new pharmaceutical forms, and the use of adjuvants. This research serves as a foundation for future endeavors, aiding researchers, clinicians, and policymakers in making informed decisions about the direction of research and development in the dynamic field of colorectal cancer therapy.
1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer, comprising cancers of the colon and rectum, has demonstrated the highest incidence and mortality rates among all cancer types in the United States, as per the NIH data presented in its Cancer Facts and Figures 2020 document [1]. In 2020, 147,950 new cases were diagnosed, and 53,200 patients succumbed to the disease. Drug therapy represents one of the primary modalities available for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Traditional or standard chemotherapy [2] utilizing cytotoxic drugs (5-fluorouracil, capecitabine, irinotecan, oxaliplatin, trifluridine, and tipiracil) [3,4] to eliminate tumor cells continues to be an option despite the emergence of new pharmaceutical technologies. These drugs can be administered alone or in combination. The significant scientific interest in discovering new drugs against colorectal cancer or investigating existing drugs has resulted in a voluminous number of publications on these substances. Bibliometrics employs mathematical and statistical methods to quantitatively analyze scientific activity, making it possible to compare, measure, and objectify scientific activity. As a result, it provides valuable insights into the behavior of science and scientists [5].
In our study, we will leverage the two main and distinctive functions of bibliometrics. Firstly, we will utilize the mathematical and statistical methods provided by bibliometrics to select the most relevant articles. Given the existence of thousands of publications on the use of cytotoxic drugs in the treatment of colorectal cancer, it would be impractical for any researcher to review them all. Therefore, through bibliometrics, we will identify the 100 most important articles that will be crucial for our analysis, allowing us to evaluate whether chemotherapy still has a role in the investigation of treatments for this disease, as well as identifying current and potential lines of research for the future.
Secondly, we will use bibliometrics as an analytical tool to identify the key players who have led the research in this field. We will explore the existing collaborations among them, which will allow us to gain a better understanding of the research networks and the interaction among key researchers. This approach will provide us with a more comprehensive view of the scientific landscape regarding the use of cytotoxic drugs in the treatment of colorectal cancer.
We can identify the emerging themes that will guide future research, the authors or institutions that have been instrumental in exploring the most effective treatments, and the geographic distribution of countries at the forefront of research. Furthermore, we can ascertain the scientific journals with the broadest dissemination and acceptance among the research community. Citations serve as the foundation of bibliometric analysis and are among the best indicators of the quality of a study [6] and an objective criterion for selecting works to conduct research.
2. Materials and Methods
On 20 April 2023, we performed the last bibliographic search in Web of Science (WOS, Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA) for all articles containing the terms “5-fluorouracil”, “5-FU”, “capecitabine”, “xeloda”, “irinotecan”, “camptosar”, “oxaliplatin” eloxatin”, “trifluridine and tipiracil”, in order to collect the different names of the main chemotherapy treatments used in colorectal cancer, both conventional drugs and new therapeutic targets. To ensure comprehensive drug selection, we used the cancer.gov website as a reference and extracted both the trade name and the FDA-accepted active ingredient name for each medication belonging to the American Cancer Society, and in the bibliography provided by this society [7].
The databases used to obtain the papers were: SCI-EXPANDED, Social Science Citation Index (SSCI), Arts and Humanities Citation Index (A & HCI), Conference Proceedings Citation Index-Science (CPCI-S), Conference Proceedings Citation Index-Social Science and Humanities (CPCI-SSH), Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), Current Chemical Reactions-Expanded (CCR-EXPANDED) and Index Chemicus (IC). No filters were applied by time, article language, authors, participating institutions, topics or article funding.
After conducting preliminary searches to contextualize the study and in accordance with the total number of researchers, it was decided that the final analysis would be limited to entries that included the name of the drug as part of the article title, excluding those in which it appeared only in the abstract.
A total of 42,276 articles were identified. To focus exclusively on original research articles, we excluded Meeting Abstracts, Review Articles, Proceedings Papers, Editorial Materials, Early Access, Corrections, News Items, Book Chapters, Retracted Publications, and Retractions. This left us with a total of 11,024 articles, consisting of 10,610 Articles and 414 Letters. On the day of the search, these articles collectively had accumulated 172,123 citations, with an average of 15.61 citations per article.
To narrow our focus to articles specifically related to colorectal cancer, we implemented a secondary filter using keywords such as “colorectal”, “colon”, and “rectal”. Subsequently, we organized the articles based on their citation counts and selected the top 100 most cited articles (T100). Within this subset of articles, we conducted an analysis of various variables, including subject matter, authorship, title, citation count, source, author identification, the specific institution or country where each T100 article was published, citation density (citations per year), and citations per record.
The data obtained from this search were exported to a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet located in Redmond, WA, USA. It is worth noting that none of the authors of this manuscript have affiliations or associations with pharmaceutical industries involved in the research or production of these drugs.
3. Results
On 20 April 2023, a search was conducted to gather articles for a subsequent bibliometric study focused on the chemotherapeutic treatment of colorectal cancer. Initially, a total of 42,486 articles were retrieved by entering relevant terms into the Web of Science (WOS) database. However, after refining the search to include only original publications, we selected a total of 11,131 papers, comprising 10,621 articles and 510 letters. These publications collectively amassed 178,433 citations, resulting in an average citation density of 16.03 citations per article.
Subsequently, we applied a filter to isolate articles related to colorectal cancer, which yielded a total of 2504 papers, including 2132 articles and 372 letters. The cumulative number of these papers accumulated 48,009 citations, with an average citation density of 19.17 citations per article. Among these, the top 100 most cited articles (Table 1) received a total of 12,329 citations, with an average citation density of 123.29 citations per article.

Table 1.
Bibliometric information associated with the top 100 (T100) cited articles.
The highest-cited article, published in 2004 in Annals of Oncology, garnered a total of 778 citations. It focused on the analysis of adverse reactions to chemotherapy in 153 patients with colorectal cancer, specifically examining the use of oxaliplatin. The list of the top 100 articles was completed with an article published in 2016 in the journal Biochemical Pharmacology, which received a total of 60 citations. This study investigated the addition of a natural diterpenoid called Andrographolide to enhance the response of 5-FU in the treatment of colorectal cancer.
The year 2017 stands out as having the most influential papers, with 8 articles from the top 100 published during that year. Additionally, from 2010 to the present, 55 out of the 100 articles were published, with 22 of them appearing in the last five years (since 2017). The last decade (2013–2022) contributed 41 articles, reflecting research trends in pharmacogenetics, adjuvant substances, and the synthesis of nanoparticles and liposomes.
In total, 734 authors contributed to the T100 articles. The top 3 authors with the highest number of published articles within the T100, each having authored 4 articles, are Falcone A and Loupakis F, accumulating a total of 382 citations and a citation density of 95.5 citations per article. Ranking third is Goel A, with 343 citations across his 4 articles, resulting in an average of 85.75 citations per article.
From a geographical perspective, the United States leads in production with 25 articles, amassing a total of 3939 citations. China closely follows with 24 papers, which received 2057 citations. Spain secures the third position with 6 papers, contributing to a total of 559 citations. France boasts the highest citation density per article, achieving 2306 citations across its 12 papers, resulting in an impressive density of 192.17 citations per article (Table 2).

Table 2.
Countries publishing more than 25 of the T100 cited articles.
Funding sources reveal that the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) supported 13 of the T100 papers, while US institutions such as the National Institutes Of Health and National Cancer Institute also funded 3 T100 papers each. It is worth noting that all T100 articles were composed in English.
Among the journals featuring T100 articles, Annals of Oncology takes the lead with a total of 11 articles. Furthermore, it boasts an impressive impact factor of 32.97 for the year 2021.
4. Discussion
The research on cytotoxic drugs is of significant current relevance, representing the primary key finding from our analysis. When examining the temporal evolution of the most relevant articles, it becomes evident that the publication distribution from year to year underscores the contemporary and substantial nature of this topic. Specifically, 55 out of the 100 relevant articles have been published from 2010 to the present day. Within the last decade, spanning from 2013 to 2022, 41 articles have been contributed. Furthermore, in the past five years, from 2017 to the present, our ranking includes 22 papers (see Figure 1).
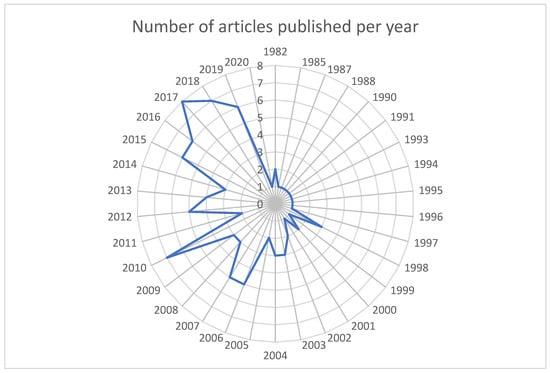
Figure 1.
Annual distribution of T100.
Moreover, the year 2017 stands out with the highest number of contributions to the T100. It is noteworthy that our analysis exclusively focused on original articles, leading us to identify a total of 2470 papers with a collective citation count of 46,189, indicative of a considerable impact. This pronounced impact is also evident in the T100 dataset (refer to Table 1), where the 100 most cited articles amass a total of 12,329 citations, yielding an average citation density surpassing 120 citations per article.
To ascertain the prevailing research trends in the realm of colorectal cancer treatment, we conducted an extensive analysis of the content within the 41 articles published in the top 100 journals (T100) over the past decade. Our examination revealed three key areas of research that are currently attracting substantial attention.
The first area of research revolves around pharmacogenetics, which delves into how genetic variations influence a patient’s response to chemotherapeutic drugs used in colorectal cancer treatment [8,9]. Researchers are investigating how individual genetic differences can impact drug efficacy and toxicity, with the aim of optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing side effects [10,11,12].
The second area of research focuses on the utilization of adjuvant substances. These are additional agents administered alongside chemotherapeutic drugs to enhance their effects. Such substances may encompass other drugs or natural compounds that have demonstrated the ability to improve drug delivery, enhance drug efficacy, or reduce drug resistance.
Lastly, the third area of research revolves around the development of more efficient pharmaceutical forms. Researchers are exploring novel drug delivery systems designed to enhance drug bioavailability and pharmacokinetics while simultaneously reducing toxicity and side effects. This includes the creation of targeted drug delivery systems capable of specifically targeting cancer cells while sparing healthy ones from harm.
In summary, our analysis of the literature indicates that these three research areas are currently the most active and promising within the field of colorectal cancer treatment.
The articles focusing on the pharmacogenetic study within the T100 dataset are #15, #21, #31, #37, #49, #51, #54, #57, #66, #67, #68, #71, #72, #73, #75, #87, and #89.
In the realm of pharmacogenetic variability in colorectal cancer therapy, it is noteworthy that non-coding molecules play a pivotal role in regulating the expression of genes associated with chemotherapeutic drug metabolism, rather than changes in coding genes. Recent research has concentrated on the study of microRNAs, which are small single-stranded RNA fragments that regulate other genes through ribo-interference. Despite their inability to produce proteins, microRNA molecules can significantly influence the effectiveness and toxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs.
Several non-coding RNA molecules have been identified as participants in regulating chemoresistance in colon cancer cells. These include MALAT1, lncRNA-like microRNA #15, Linc00152 #21, microRNA-625-3p #51, and lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 #54 and #57, all of which enhance oxaliplatin chemoresistance by targeting the miR-34a/ATG4B pathway. Conversely, miR-19b-3p promotes colon cancer cell proliferation while also fostering oxaliplatin-based chemoresistance by targeting SMAD4 #71. Additionally, miR-136 promotes metastasis and drug resistance through the long non-coding RNA CRNDE #72, while miR-637 achieves this through autophagy #75.
However, miR-506 enhances the sensitivity of human colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin by suppressing MDR1/P-gp expression (#89). Genetic variability also affects another chemotherapeutic drug, 5-fluorouracil, due to certain microsatellites. In one study, it was discovered that miR 139-5p, which targets NOTCH-1, and microRNA-34a, which inhibits the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, sensitize colon cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil. Additionally, overexpression of MicroRNA-122 re-sensitizes 5-FU-resistant colon cancer cells to 5-FU by inhibiting PKM2 in vitro and in vivo (#73).
BRAF V600E and KRAS mutations have been extensively studied and found to be significantly associated with shorter disease-free survival and overall survival in patients with microsatellite-stable tumors but not in patients with microsatellite-unstable tumors. Investigating the impact of microorganisms on variable gene expression that can influence pharmacogenetics is crucial (#31). Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil by positively regulating BIRC3 expression in colorectal cancer (#37). Furthermore, the analysis of the functional capacity of the gut microbiota using PICRUSt revealed that genes involved in amino acid metabolism, replication and translation repair, and nucleotide metabolism were better expressed in a healthy microbiota (#49).
The second trending topic involves the study of adjuvant substances that enhance the properties of chemotherapy drugs used in colorectal cancer therapy. Articles #22, #39, #43, #50, #56, #69, #79, #86, #94, #95, and #100 explore the use of adjuvant substances, such as melatonin, curcumin, or resveratrol, as well as Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, which exhibit positive effects when administered alongside cytotoxic therapy [13,14,15].
Study #22 suggests that the hormone melatonin can enhance the effectiveness of 5-fluorouracil in treating colon cancer by suppressing two signaling pathways, namely PI3K/AKT and NF-κB/Inos. Additionally, melatonin in combination with 5-fluorouracil can work together to suppress colon cancer stem cells by regulating the cellular prion protein axis (#95).
In study #43, resveratrol is found to sensitize colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil treatment by positively regulating intercellular junctions, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and apoptosis. Resveratrol also enhances the effect of TNF-beta-induced cell death in 5-fluorouracil-treated colorectal cancer cells (#94).
Study #50 demonstrates that curcumin can reverse resistance to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer cells by modulating the CXC-chemokine/NF-κB signaling pathway. Curcumin also sensitizes 5-fluorouracil-resistant MMR-deficient human colon cancer cells in high-density culture (#56).
In article #69, a combination of drugs and supramolecular therapy administered with oxaliplatin is shown to have adjuvant efficacy. Furthermore, cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors can increase the efficacy and delivery of carboxylated pilar [6] and decrease cytotoxicity.
Two studies (#38 and #86) demonstrate that epigallocatechin-3-gallate can target cancer stem cells and enhance the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil by inhibiting the GRP78/NF-kappa B/miR-155-5p/MDR1 pathway.
Work #100 reveals that andrographolide can reverse 5-fluorouracil resistance in human colorectal cancer cells by upregulating BAX expression.
Lastly, recent developments in new pharmaceutical forms aim to improve the efficacy and safety of drugs [16,17,18]. Pharmaceutical technology is being utilized to discover new delivery vehicles capable of accurately delivering drugs to their intended targets. The use of nanoparticles and liposomes has emerged as a promising approach to drug delivery, as highlighted in articles #47, #56, #92, #93, and #98.
As an example of this approach, researchers have developed Eudragit S100-coated citrus pectin nanoparticles for targeted delivery of 5-fluorouracil in the colon (#47). Another study employed enteric coating to achieve sustained and localized release of 5-fluorouracil (#56). Additionally, pH-sensitive double-layered alginate/chitosan/kappa-carrageenan microspheres were designed for controlled release of 5-fluorouracil in the colon (#92).
In addition to nanoparticles, liposomes are also under investigation for targeted drug delivery. For instance, a novel delivery system using folic acid-conjugated liposomes was developed for 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer therapy (#93). Another study explored the use of pH-sensitive ZnO/carboxymethylcellulose/chitosan bionanocomposite beads to achieve colon-specific release of 5-fluorouracil (#98).
Overall, the development of these new pharmaceutical forms represents an exciting area of research with the potential to significantly improve the effectiveness and safety of drug treatments. By leveraging advanced technology to precisely deliver drugs to their intended targets, researchers can reduce the risk of side effects and enhance the efficacy of treatments for various diseases, including cancer.
Regarding the analysis of authors who participated in the T100 articles, it is evident that strong co-authorship is prevalent among them. Collaborative efforts involving multiple professionals in research and article publication are regarded as a quality parameter, providing a broader perspective, potential multidisciplinarity, and access to a wider network of readers. Over 700 authors contributed to the T100. Co-authorship serves as an indicator of collaboration and teamwork among researchers, measuring collaboration between institutions and countries in scientific output [19].
Furthermore, co-authorship is significant for assessing the quality and impact of research, as collaboration among authors from different institutions and disciplines can bring diverse perspectives and expertise to a research project. Co-authorship also aids in evaluating researchers’ productivity and the influence of their work within the scientific community (see Figure 2 and Figure 3).
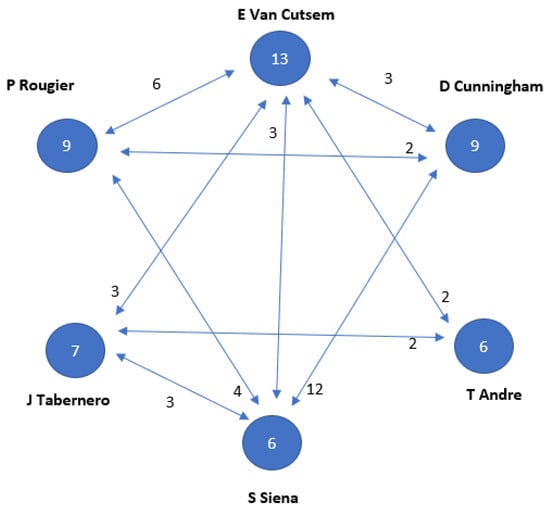
Figure 2.
Relationship between the authors with 6 or more publications on a topic. Numbers inside the circles indicate the number of articles published. Connecting arrows and numbers affixed indicate number of papers together, respectively.
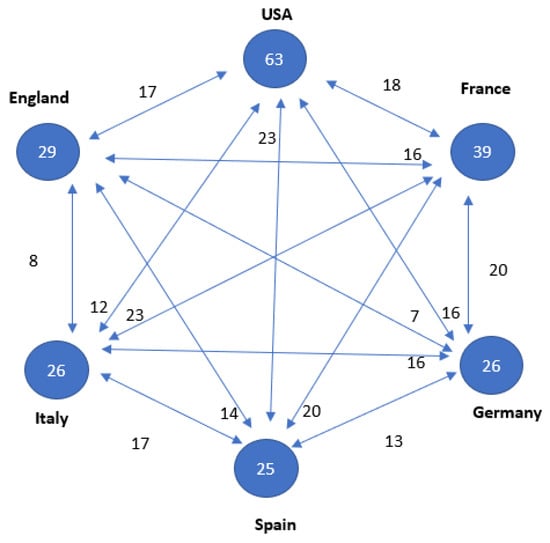
Figure 3.
Relationship between the countries with 25 or more publications on a topic. Numbers inside the circles indicate the number of articles published. Connecting arrows and numbers affixed indicate number of papers together, respectively.
The bibliometric analysis of the authors reveals that the Lotka law of productivity does not apply in this case, as the production of articles is distributed quite evenly among many authors. This law typically suggests that a small group of authors produces the majority of relevant publications and, consequently, accumulates the majority of citations. While three authors have authored 4 articles each, making them the most prolific, they have received just over 300 citations collectively. However, it is important to note that this citation count might not be considered high when considering the high citation density per article [19].
In terms of research leadership, both the United States and China are at the forefront of this field, with nearly equal numbers of articles (25 versus 24, respectively). However, it is noteworthy that articles in which the United States participated received nearly twice as many citations. It is worth mentioning that China entered the research arena later, with its first article published in the T100 in 2006. Additionally, four European countries also contribute significantly to this field (see Table 2 and Figure 4).
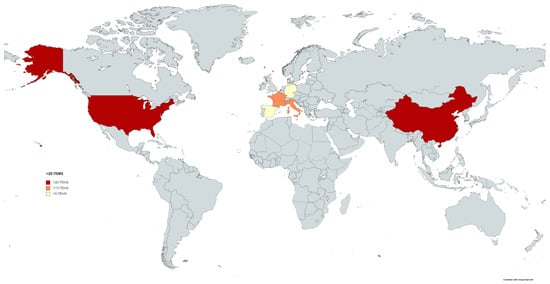
Figure 4.
Map depicting countries with the highest number of publications within the Top 100 articles, based on a map created using MapaChart.net.
These results underscore the exponential growth in research within China. According to data from the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, the Chinese government has substantially increased its investment in research over the past decade. In 2019, the total investment in research and development (R & D) in China reached CNY 2.44 trillion (approximately USD 371.7 billion), marking a 12.5% increase compared to the previous year. Moreover, investment in R & D has steadily risen in recent years, growing from 1.42% of GDP in 2009 to 2.23% in 2019 [20].
It is noteworthy that English serves as the essential tool for scientific communication, even in research related to the use of colorectal chemotherapy. All articles in the T100 are written in English [21]. This is understandable because, for an article to be considered relevant, it must reach the widest possible audience, and there is no language more universal than English. All articles are published in high-impact journals, with the journal Annals of Oncology being the most prolific in the T100. It is a specific journal focused on cancer research and had an impact factor of 32.97 in 2021 (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Journals publishing 4 or more than 4 of the top 100 (T100) papers are arranged by the number of T100 records.
Additionally, the primary institutions that have funded these papers underscore the significance of this topic. Public institutions from two of the world’s most influential countries, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) and American institutions such as the National Institutes of Health and National Cancer Institute, have provided funding various of the T100 papers. The NSFC has funded 13 papers, while American institutions have funded 3 papers within the T100, according to the data obtained from WOS (see Figure 5).
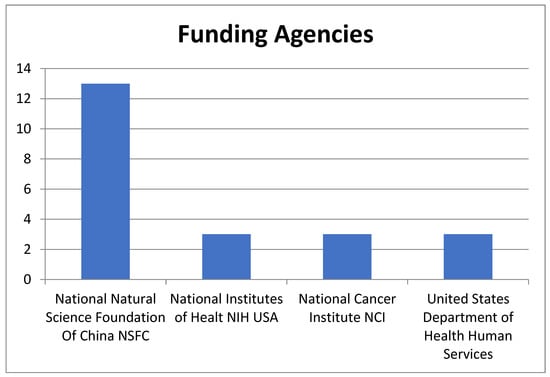
Figure 5.
Funding agencies for more than 14 of the T100 manuscripts are arranged by the number of T100 records.
Analyzing institutions in a bibliometric analysis is crucial as it allows for the identification of organizations that finance and support research in a specific field [22]. This information can be valuable for understanding resource allocation, funding trends, and collaboration among institutions in a particular area of research [23]. Moreover, it can help identify the most influential institutions in a field and those making the most significant contributions to scientific production in that area. In summary, the analysis of institutions provides an overview of the research landscape in a specific field and informs policies and decisions related to research investments.
5. Conclusions
The analysis of bibliometric data underscores the sustained significance and impact of research on cytotoxic drugs for the treatment of colorectal cancer. This is evident through the substantial volume of articles and high citation density observed in both the initial search and the subsequent refined results. Currently, research in this field is primarily concentrated in three key areas: pharmacogenetics, adjuvant substances, and advancements in pharmaceutical forms.
The leading countries actively contributing to this research are the United States and China, both of which have made substantial public investments in research endeavors. Institutions from these countries play a prominent role in funding, with the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) leading the way with funding for 13 papers, closely followed by prominent American institutions such as the National Institutes of Health and National Cancer Institute.
Collaboration among authors is common, and the predominant language of publication is English. High-impact journals are the preferred choice for publication, with the Annals of Oncology being particularly noteworthy in this regard.
Author Contributions
H.C.-M., A.E.G.-F. and F.J.G.-F. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2020|American Cancer Society. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2020.html (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Kim, J.H. Chemotherapy for colorectal cancer in the elderly. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2015, 21, 5158–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comprehensive Review of Targeted Therapy for Colorectal Cancer|Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-020-0116-z (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Role of Targeted Therapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer-PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5027019/ (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Ellegaard, O.; Wallin, J.A. The bibliometric analysis of scholarly production: How great is the impact? Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1809–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, J.d.A.; Silva, L.F.d. Knowledge management in project management: Mapping bibliographic convergence. Knowl. Manag. Res. Pract. 2022, 20, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treatment by Cancer Type. NCCN. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category_1 (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Pharmacogenomics: Challenges and Opportunities|Annals of Internal Medicine. Available online: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/abs/10.7326/0003-4819-145-10-200611210-00007 (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Evans, W.E.; Relling, M.V. Moving towards individualized medicine with pharmacogenomics. Nature 2004, 429, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relling, M.V.; Evans, W.E. Pharmacogenomics in the clinic. Nature 2015, 526, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbarino, J.M.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB: A worldwide resource for pharmacogenomic information. WIREs Syst. Biol. Med. 2018, 10, e1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PharmGKB: The Pharmacogenetics Knowledge Base|Nucleic Acids Research|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/30/1/163/1332715?login=false (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Piwowarczyk, L.; Stawny, M.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Muszalska-Kolos, I.; Goslinski, T.; Jelińska, A. Role of Curcumin and (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-O-Gallate in Bladder Cancer Treatment: A Review. Cancers 2020, 12, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effects of Resveratrol, Curcumin, Berberine and Other Nutraceuticals on Aging, Cancer Development, Cancer Stem Cells and microRNAs|Aging. Available online: https://www.aging-us.com/article/101250/text (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Life|Free Full-Text|Resveratrol, Epigallocatechin Gallate and Curcumin for Cancer Therapy: Challenges from Their Pro-Apoptotic Properties. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-1729/13/2/261?type=check_update&version=1 (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Fan, Y.; Marioli, M.; Zhang, K. Analytical characterization of liposomes and other lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Full Article: Recent Advances on Liposomal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Biomedical Applications. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/21691401.2017.1282496 (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Lipid Nanoparticles—From Liposomes to mRNA Vaccine Delivery, a Landscape of Research Diversity and Advancement|ACS Nano. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsnano.1c04996 (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Bookstein, A. Patterns of Scientific Productivity and Social Change: A Discussion of Lotka’s Law and Bibliometric Symmetry. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1977, 28, 206–210. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. DEA-based Achievements Estimate of Technology Investment. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Smart Technologies and Systems for Internet of Things (STS-IOT 2021), Shanghai, China, 17–18 September 2021; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- García-Fernández, F.J.; García-Fernández, A.E.; Nava, E.; Del Pozo, J.S.G.; Ikuta, I.; Jordan, J.; Galindo, M.F. A bibliometric evaluation of the top 100 cited natalizumab articles. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 349, 577379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Fernández, F.J.; García-Fernández, A.E.; Ikuta, I.; Nava, E.; Solis García del Pozo, J.; Jordan, J.; Galindo, M.F. A bibliometric evaluation of the top 100 cited dimethyl fumarate articles. Molecules 2021, 26, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nunen, K.; Li, J.; Reniers, G.; Ponnet, K. Bibliometric analysis of safety culture research. Saf. Sci. 2018, 108, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).