Abstract
Introduction: Nutrition literacy has garnered growing research attention worldwide, yet only a few instruments have been developed to specifically measure this construct among adolescents. Accordingly, the present research sought to examine the validity and reliability of the Adolescent Nutrition Literacy Scale (ANLS) within a group of Lebanese adolescents. Methods: A cross-sectional study was carried out from December 2022 to March 2023, targeting a nationally representative sample. Results: Fit indices of the three-factor structure were good. Internal reliability was adequate for the following three subscales: Functional Nutrition Literacy (FNL) (ω = 0.88/α = 0.88), Interactive Nutrition Literacy (INL) (ω = 0.87/α = 0.86) and Critical Nutrition Literacy (CNL) (ω = 0.89/α = 0.89). Invariance was established across genders at configural, metric, and scalar levels. A significantly higher mean FNL and INL scores were found in males compared to females, with no significant difference between the two genders in terms of CNL. Higher FNL, but not CNL and INL scores were significantly associated with lower child food security. Conclusions: The Arabic ANLS has exhibited robust psychometric reliability, validity, and cost-effectiveness as a tool for assessing nutrition literacy. By utilizing the Arabic version of the ANLS, we can more efficiently and accurately assess the nutritional literacy of adolescents.
1. Introduction
Adolescence is a crucial stage for developing healthy habits that often persist into adulthood. Eating behaviors, a core part of lifestyle, are largely shaped during this period [1]. However, recent studies indicate that many adolescents are moving away from the traditional Mediterranean Diet (MD)—rich in plant-based foods, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates– and are instead adopting a Western-style diet high in calories, ultra-processed foods, and saturated fats but low in essential nutrients [2,3,4]. In addition, about 80% of adolescents do not meet recommended physical activity levels, with sedentary behaviors such as excessive screen time being common [5,6]. Data from Mexico [7] reported that 36.3% of adolescents aged 12–19 years were overweight or obese, with higher rates observed among females. Recent evidence further links nutrition-related behaviors and issues in youth to their level of nutrition literacy [1,8,9].
Nutritional Literacy (NL) is a multidimensional construct that reflects an individual’s capacity to obtain, comprehend, interpret, and use nutrition-related information. It is commonly divided into three domains: functional, interactive, and critical nutrition literacy [10,11]. Functional Nutrition Literacy (FNL) refers to basic reading, writing, and numeracy skills needed to understand nutrition information. Interactive Nutrition Literacy (INL) involves the ability to communicate and actively engage with nutritional information, while Critical Nutrition Literacy (CNL) encompasses the skills to critically analyze and evaluate the reliability and relevance of such information [12]. As a fundamental, cost-effective, and practical tool, NL plays a vital role in promoting healthy nutrition and improving national health outcomes [9]. Consequently, investigating NL during adolescence is particularly important, as it can guide the development of sustainable nutrition interventions [11].
Appropriate nutritional literacy fosters healthier eating habits, enhances dietary quality, promotes better nutritional/food choices, and improves overall nutritional status. It also plays a critical role in preventing and managing nutrition-related non-communicable diseases [9,13,14,15]. These benefits are associated with factors such as improved nutrient adequacy, the ability to read food labels effectively, and greater food security [1,16,17]. Children with strong nutritional literacy are more inclined to develop healthy eating habits and make well-informed food choices, whereas low nutritional literacy has been linked to unhealthy dietary patterns [9,18,19]. Studies among adolescents have shown that nutrition literacy is linked to factors such as Body Mass Index, daily lifestyle practices, and overall eating behaviors [1]. Likewise, research has found that higher levels of nutrition literacy are associated with selecting smaller portion sizes when consuming fast food and consuming packaged or processed snacks less frequently among children and adolescents in school settings [20]. In the same way, a reciprocal relationship exists between food security and nutrition literacy, where limited food and nutrition literacy can contribute to food insecurity, and experiencing food insecurity may hinder the use of food literacy skills to maintain a nutritious diet [21].
Nutrition literacy has garnered growing research attention worldwide, yet only a few instruments have been specifically designed to assess this construct in children and adolescents. Most available tools focus primarily on adults [22,23,24,25]. A 2021 systematic review [26] identified four tools that measured NL or its subcomponents in children [26,27,28,29]. Of these, two addressed critical NL [27,28], one evaluated menu board literacy [29], and another focused on food label literacy [30]. Furthermore, in 2017, Asakura et al. developed the Nutrition Knowledge Questionnaire for primary school students. This tool comprises four sections that assess understanding of nutritional terms, knowledge of dietary guidelines, the application of information to food choices, and awareness of diet–disease relationships [31]. Another widely cited instrument is the Food and Nutrition Literacy (FNL) tool that evaluates both cognitive and practical skills of food and nutrition literacy in children [25]. However, these instruments often fall short in assessing deeper cognitive comprehension and critical evaluation of nutritional information. In China, Liao et al. created a nutrition literacy assessment for college students [32], while other researchers developed core NL items tailored for preschool-aged children [33,34]. It is important to note that cultural and social contexts strongly influence individuals’ beliefs and attitudes, thereby shaping their NL [35].
To better reflect the multifaceted nature of nutrition literacy, Bari (2012) developed the Adolescent Nutrition Literacy Scale (ANLS) [36], that was later on adapted into Turkish by Türkmen et al. [37]. It includes 22 attitude statements across three sub-dimensions [38]: Functional Nutrition Literacy (seven items); Interactive Nutrition Literacy (six items); and Critical Nutrition Literacy (nine items). The Cronbach’s alpha for internal consistency has been reported as 0.80 in its original development, indicating a good level of reliability. In studies adapting the scale to different languages and populations (e.g., Turkish), the Cronbach’s alpha increased to 0.86, further affirming its reliability in varied contexts. The Adolescent Nutrition Literacy Scale has been widely used in research to assess relationships between nutrition literacy and behaviors such as physical activity [39], dietary choices and health outcomes [40]. Thus, it is regarded as a reliable instrument for evaluating NL among adolescents.
Malnutrition remains a significant challenge in many Arab countries, highlighting the immense difficulty the region faces in achieving the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development goal of “zero hunger” and eliminating all forms of malnutrition [41]. The Arab region grapples with significant challenges related to food insecurity, malnutrition, and obesity, with an estimated 116 million people experiencing food insecurity, 43 million suffering from undernutrition, and 115 million obese [42]. Recent evidence shows a dramatic rise in malnutrition, with the number of undernourished individuals increasing from 4.8 million to 69 million between 2019 and 2020 [43].
In Lebanon, where the population faces the dual burden of macro- and micro-traumas, increasing their vulnerability to mental health disorders [44], recent studies highlight a concerning shift in adolescents’ dietary habits. This shift, characterized by the adoption of a Westernized lifestyle and greater sedentary behavior, has been linked to rising rates of overweight, obesity, and associated health complications [45,46,47]. These conditions often persist into adulthood, posing significant health challenges [48,49].
Moreover, with the rise of social media, the younger generation has become its primary user group. In Lebanon, this demographic is grappling with declining diet quality and increasing obesity rates [50]. Notably, adolescents are experiencing higher dietary fat consumption alongside reduced protein and carbohydrate intake, as well as the risk of insufficient mineral intake [51]. These trends may stem from a preference for fast food, frequent skipping of breakfast, and a general dislike of home cooking [52,53]. While the immediate health effects may not always be evident, these unhealthy lifestyles and dietary patterns significantly heighten the long-term risk of chronic diseases [54].
Addressing this issue requires urgent efforts to improve adolescent’s nutritional literacy through targeted education [55]. Before implementing specialized nutritional care and educational programs for specific groups, it is essential to thoroughly understand their perceived nutritional literacy. This study focuses on culturally adapting the ANLS. We hypothesized that the Adolescent Nutrition Literacy Scale would (1) show three factors similar to the original version, (2) exhibit robust psychometric validity and reliability and invariance between males vs. females, and (3) correlate with child food security.
2. Methods
2.1. Human Ethics and Consent to Participate Declarations
The study was carried out according to the ethical principles of the Helsinki Declaration (2013 version). The Ethics Committee of the Al-Zahraa University Medical Center, Beirut, Lebanon (Reference # 10-12-2022) provided their ethical approval to conduct this study. Informed written consent was obtained from all participants prior to their inclusion in the study.
2.2. Study Design
A cross-sectional survey was carried out between 11 December 2022 and 18 March 2023, targeting a nationally representative sample of Lebanese adolescents. Participants were selected through a probability cluster sampling approach and recruited from all eight Lebanese governorates. Participants’ distribution across the governorates is shown in Figure 1. To ensure relevance to the goals of the study, participants were recruited based on the following eligibility criteria: All the participants had to be Lebanese, aged between 10 and 18 years, and free of chronic diseases. Moreover, from each household, only one adolescent child was recruited after dissemination of the survey announcement in several public areas, social media, and healthcare settings.
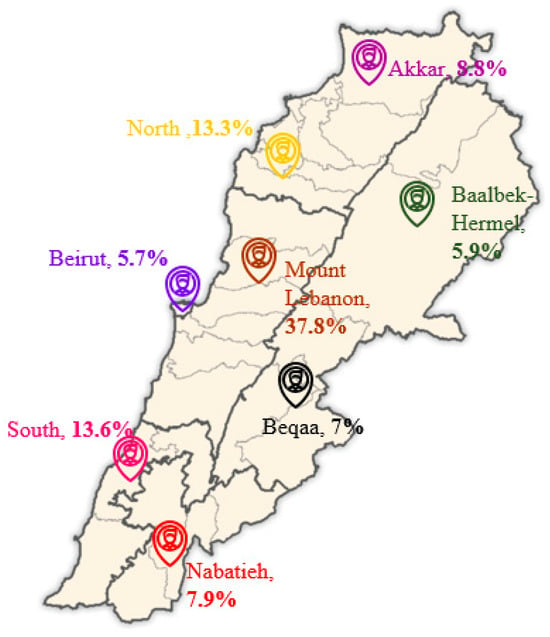
Figure 1.
Distribution of study participants across governorates [56].
2.3. Data Collection and Measures
Using a pre-tested questionnaire, the following information was collected during a face-to-face interview with the participants: age, gender, residency, primary caregiver, whether currently working, education level, school type, and whether the adolescent receives nutrition education in their schools. Information regarding nutrition literacy was collected during the same interview where the Adolescent Nutrition Literacy Scale (ANLS) was utilized to assess the nutrition literacy levels of adolescents. Originally developed by Bari [36], the scale was forward and backward translated to Arabic by two different translators. The original and translated English versions were then compared by the research team and the two translators to solve any discrepancies. A pilot study was conducted on 30 adolescents to make sure that all questions were clear to them; no changes were made afterwards. The ANLS comprises 22 items, each rated on a five-point Likert scale, where 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = undecided, 4 = agree, and 5 = strongly agree. Scores on the scale range from a minimum of 22 to a maximum of 110. A score between 22 and 57.2 reflects “low nutrition literacy”, 57.2 to 74.8 indicates “moderate nutrition literacy”, and 74.8 to 110 represents “high nutrition literacy”.
Child food security: The child questionnaire consists of 14 items designed to assess food insecurity experiences among children. It has been previously validated in Arabic and refined based on prior research [57]. The 14 items are organized into five key domains: cognitive, emotional, and physical awareness of food scarcity, coping strategies, and shared responsibility with caregivers for managing resources. The questionnaire covers experiences from the past 6 months, specifically from the end of the last academic year to the beginning of the summer. Participants respond with options of “sometimes” (a little of the time), “often” (a lot of the time), or “never.” In this study, the Cronbach’s α = 0.94.
2.4. Analytic Strategy
A confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was performed using SPSS AMOS v.28. The required sample size was estimated at a minimum of 440 participants, following the guideline of 20 times per variable of the scale [58]. Parameter estimates were obtained through the maximum likelihood method. Several fit indices were computed to evaluate model fit [59], including Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA; ≤0.08), Standardized Root Mean Square Residual (SRMR; ≤0.05), Tucker–Lewis Index (TLI; ≥0.90) and Comparative Fit Index (CFI; ≥0.90). Convergent validity was assessed through the average variance extracted (AVE), with values of ≥0.50 considered acceptable [60]. Since multivariate normality was initially not met (Bollen-Stine bootstrap p = 0.002), a non-parametric bootstrapping procedure was applied.
A multi-group CFA was conducted to test measurement invariance of ANLS scores across genders [61] at the configural, metric, and scalar levels [62]. Evidence of invariance was supported when ΔCFI was ≤0.010 and ΔRMSEA was ≤0.015 or ΔSRMR was ≤0.010 [63]. Gender differences in ANLS scores were examined using the Mann–Whitney test.
Internal reliability was evaluated through McDonald’s ω and Cronbach’s α, with values above 0.70 indicating satisfactory reliability [64]. Associations between ANLS and child food security scores were analyzed using Spearman’s correlation test.
3. Results
Descriptive statistics of the sample can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Sociodemographic and other characteristics of the sample (N = 442).
3.1. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
The fit indices were good (RMSEA = 0.066 (90% CI 0.060, 0.072), SRMR = 0.062, CFI = 0.924, TLI = 0.913). The standardized estimates of factor loadings were all adequate (Figure 2). Internal reliability was adequate for the three subscales: Functional Nutrition Literacy (ω = 0.88/α = 0.88), F2 = Interactive Nutrition Literacy (ω = 0.87/α = 0.86), and F3 = Critical Nutrition Literacy (ω = 0.89/α = 0.89).
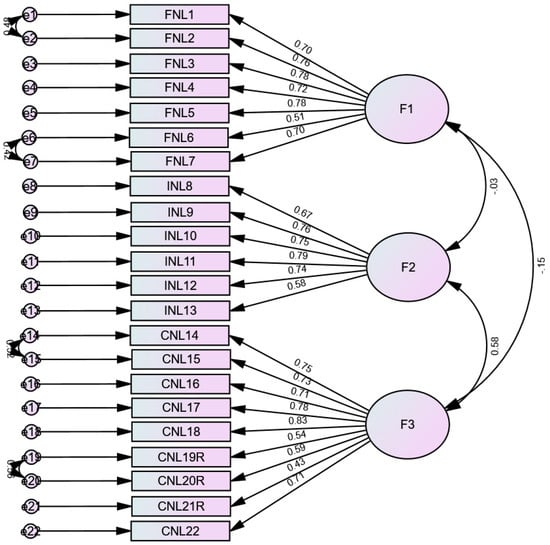
Figure 2.
Standardized loading factors deriving from the confirmatory factor analysis of the Adolescent Nutrition Literacy Scale in Arabic. F1 = Functional Nutrition Literacy; F2 = Interactive Nutrition Literacy; F3 = Critical Nutrition Literacy.
3.2. Gender Invariance
Invariance was shown at the metric and scalar levels in terms of genders (Table 2). A significantly higher mean FNL (23.22 ± 5.64 vs. 21.45 ± 6.00; p = 0.001, Cohen’s d = 0.304) and INL (18.20 ± 4.88 vs. 17.07 ± 5.45; p = 0.018, Cohen’s d = 0.220) were found in males compared to females, with no significant difference between the two genders in terms of CNL (30.41 ± 6.92 vs. 29.72 ± 7.33; p = 0.161, Cohen’s d = 0.096).

Table 2.
Measurement invariance of the Adolescent Nutrition Literacy Scale across genders.
3.3. Concurrent Validity
Higher FNL (r = −0.15; p = 0.002), but not CNL (r = −0.06; p = 0.196) and INL (r = 0.001; p = 0.981), scores were significantly associated with lower child food security.
4. Discussion
This study’s findings demonstrate that the ANLS is a reliable and valid instrument for assessing nutrition literacy in adolescents, making it a valuable tool for nutritional monitoring. The results further affirm its reliability, validity, and suitability for use among Arabic-speaking adolescents.
4.1. Factor Structure
Regarding the factorial validity of the Arabic version of the ANLS, our findings are consistent with the original study [36] and the Turkish validation [37], confirming that the scale includes three sub-categories: Functional, Interactive, and Critical nutrition literacy. These dimensions highlight the complex nature of nutrition literacy and emphasize the need for tailored educational interventions. The factor structure of the ANLS offers a strong framework for evaluating nutrition literacy among adolescents [37]. By identifying the distinct dimensions—functional, interactive, and critical nutrition literacy—the scale not only assesses adolescents’ current abilities but also informs targeted interventions aimed at fostering healthier lifestyles. Future research should continue to validate the ANLS in diverse populations and examine its potential to predict long-term dietary behaviors and health outcomes.
4.2. Internal Reliability
In our study, the reliability coefficients were very good: Functional Nutrition Literacy (ω = 0.88/α = 0.88), Interactive Nutrition Literacy (ω = 0.87/α = 0.86), and Critical Nutrition Literacy (ω = 0.89/α = 0.89), with higher values than the Turkish validation [37]. Cronbach’s alpha values were 0.66 for FNL, 0.71 for INL, 0.84 for CNL, and 0.80 for the total score obtained in the tool. Similarly, in the scale development study [36], the internal consistency coefficient was reported to be 0.80 for the overall scale. Subscales exhibited reliability values ranging from 0.648 to 0.942, indicating acceptable to excellent internal consistency across different dimensions of nutrition literacy. Accordingly, based on the findings of this research, the Arabic ANLS appears to exhibit robust psychometric reliability, indicating that this tool measures nutrition literacy with an acceptable level of accuracy.
4.3. Sex Invariance
In this study, notable differences were observed between males and females in ANLS scores, with higher mean FNL and INL in males compared to females, and with no significant difference between the two genders in terms of CNL. It is worth noting that the developmental scale and Turkish validation do not report gender invariance, highlighting the originality of our findings.
A study conducted across 10 Arab countries [40] reported that female adolescents had higher nutritional literacy than males. The same results were found in two Turkish [1,65] and two Iranian [17,66] studies. One possible explanation for these gender differences is that females tend to prioritize healthy eating and focus more on the nutritional value of food [67]. Women often have greater nutrition knowledge and view nutrition as an integral component of their overall health [68].
Regarding CNL, a previous study [69] found that a higher proportion of women (60%) than men (42%) struggled to differentiate between scientific and non-scientific dietary information. Additionally, women were more likely than men to be influenced by dietary advice in the media (42% vs. 27%) and to find alternative medicine advice credible (38% vs. 25%) [69]. In contrast, our findings suggest no significant gender differences in CNL, possibly indicating that both genders face similar challenges in critically assessing complex nutritional information. Research suggests that men and women alike may struggle to discern credible from non-credible nutritional advice, underscoring a universal need to improve critical thinking skills in this area [40].
One possible explanation for the higher scores in FNL and INL among males in this study may relate to contextual factors such as demographic characteristics, educational level, or evolving health behaviors. Recent evidence suggests that men have become increasingly engaged in health and nutrition topics, especially in populations where health promotion campaigns and fitness culture are widespread [70]. Cultural norms and media exposure may also influence gender-specific information-seeking behavior, with some studies showing that men are more likely to seek out functional health information when it aligns with their personal goals, such as physical performance or body image [71]. Differences in sampling methods and measurement tools across studies may further account for discrepancies in findings [71].
These findings emphasize the importance of developing gender-sensitive nutrition education strategies that address specific gaps while leveraging strengths across different literacy domains.
4.4. Concurrent Validity
In the current study, higher FNL, but not CNL and INL, scores were significantly associated with lower child food security, in line with many studies demonstrating a strong link between high food insecurity and unfavorable eating behaviors, which ultimately lead to poor dietary quality [72,73,74]. For instance, research involving children aged nine to twelve found that those experiencing high food insecurity exhibited lower levels of nutritional knowledge and struggled to comprehend food and nutrition information [75]. Additionally, their food choice literacy scores were significantly lower compared to their food-secure peers. Moreover, Landry et al. reported that food-insecure children had poorer diet quality, scoring lower on greens and beans, seafood, and plant proteins, while consuming more added sugars compared to their food-secure peers [72]. Likewise, a study of 3790 food-insufficient, low-income families found that adolescents consumed fewer calories, carbohydrates, and fruits, but had higher cholesterol intake [76]. Moreover, adolescents experiencing food insecurity often shop at stores dominated by less-healthy options and are more likely to choose unhealthy snacks and sugar-sweetened beverages [77]. While food literacy—an essential factor in shaping eating behaviors—can help food-insecure adolescents improve their food choices by building critical skills, several unmodifiable factors contribute to poor dietary decisions. Contributing factors include household income, restricted availability of healthy foods, and the elevated cost of nutritious choices.
4.5. Clinical Implications
Developing a valid Arabic version of the ANLS would enable the collection of precise epidemiologic data on nutrition literacy across Arab countries. This, in turn, could guide initiatives to enhance nutrition literacy among adolescents, a critical step in fostering healthy eating habits and lifestyle behaviors. Raising adolescents’ awareness is essential, and health policies should prioritize the development of appropriate educational resources to support this objective. Moreover, Arab schools can present an excellent opportunity to integrate efforts toward sustainable development by leveraging the formal education system to enhance students’ nutrition literacy [78]. All school-based activities promoting healthy eating—both inside and outside the classroom—can form part of a broader nutrition education strategy known as a “macro-curriculum” [79].
4.6. Limitations
When interpreting the results and conclusions of this study, several limitations must be considered. First, the use of snowball sampling for participant recruitment may limit the generalizability of the findings. In the context of Lebanon where private schools often serve students with higher socioeconomic backgrounds, the overrepresentation of children from private schools (almost twice as many as from public schools) could have influenced the results. Second, cross-sectional design restricts our ability to assess certain psychometric properties, such as test–retest reliability. Third, key psychometric properties, including inter-rater and test–retest reliability, and discriminant and convergent validity, were not evaluated. Fourth, the reliance on self-reported data from participants introduces the potential for information bias. Fifth, as the sample was drawn from the Lebanese population, the findings may not be applicable to all Arabic-speaking countries. Further research is needed to explore cultural differences across the Arabic-speaking world. The face-to-face data collection may have introduced social desirability bias, and the lack of a separate validation sample limits generalizability.
5. Conclusions
The Arabic Adolescent Nutrition Literacy Scale (ANLS) has exhibited robust psychometric reliability, validity, and cost-effectiveness as a tool for assessing nutrition literacy. The adapted and validated version of the ANLS is well suited for Arabic-speaking adolescents, and its potential for use in other countries warrants further investigation. By utilizing the Arabic version of the ANLS, we can more efficiently and accurately assess the nutritional literacy of adolescents. This, in turn, facilitates the development of targeted nutrition education programs and public health policies. Additionally, it allows for the identification of high-risk groups, enabling the provision of necessary support and interventions to enhance the overall nutritional health of society.
Author Contributions
M.H. (Maha Hoteit) designed the study; S.O., S.H. and F.F.-R. drafted the manuscript; S.H., L.S. and N.T. carried out the analysis and interpreted the results; M.H. (Maha Hoteit), A.S., Y.S. and M.H. (Marie Hokayem) reviewed the paper for intellectual content. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was carried out according to the Helsinki Declaration’s ethical guidelines. The Ethics Committee of the Al-Zahraa University Medical Center, Beirut, Lebanon (Reference Nb12/10-December-2022) provided their ethical approval to conduct this study. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations (in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Data Availability Statement
Data is provided within the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the assistance of Hala Mohsen, Nour Yazbeck, Dalia Hachem, Zahraa Al Hassani, and Joanna Nohra for their contribution to the data collection of the participants information.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Koca, B.; Arkan, G. The relationship between adolescents’ nutrition literacy and food habits, and affecting factors. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santi, M.; Callari, F.; Brandi, G.; Toscano, R.V.; Scarlata, L.; Amagliani, G.; Schiavano, G.F. Mediterranean diet adherence and weight status among Sicilian Middle school adolescents. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim, N.E.; Çalışkan, G.; Beşler, Z.N. Assessment of adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and behaviors of fruit and vegetable consumption in adolescents. Sağlık Bilim. Değer 2022, 12, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nota, M.H.; Nicolas, S.; O’Leary, O.F.; Nolan, Y.M. Outrunning a bad diet: Interactions between exercise and a Western-style diet for adolescent mental health, metabolism and microbes. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 149, 105147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetou, V.; Kanellopoulou, A.; Kanavou, E.; Fotiou, A.; Stavrou, M.; Richardson, C.; Orfanos, P.; Kokkevi, A. Diet-related behaviors and diet quality among school-aged adolescents living in Greece. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Ding, L.; Zhang, R.; Ding, M.; Wang, B.; Yi, X. Physical activity, screen-based sedentary behavior and physical fitness in Chinese adolescents: A cross-sectional study. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 722079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamah-Levy, T.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Gaona-Pineda, E.B.; Gómez-Acosta, L.M.; del Carmen Morales-Ruán, M.; Hernández-Ávila, M.; Rivera-Dommarco, J.Á. Sobrepeso y obesidad en niños y adolescentes en México, actualización de la Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición de Medio Camino 2016. Salud Pública México 2018, 60, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, S.; Itani, L. Nutrition literacy among adolescents and its association with eating habits and BMI in Tripoli, Lebanon. Diseases 2021, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.K.; Sullivan, D.K.; Ellerbeck, E.F.; Gajewski, B.J.; Gibbs, H.D. Nutrition literacy predicts adherence to healthy/unhealthy diet patterns in adults with a nutrition-related chronic condition. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, C.; Sommerhalder, K.; Beer-Borst, S.; Abel, T. Just a subtle difference? Findings from a systematic review on definitions of nutrition literacy and food literacy. Health Promot. Int. 2018, 33, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silk, K.J.; Sherry, J.; Winn, B.; Keesecker, N.; Horodynski, M.A.; Sayir, A. Increasing nutrition literacy: Testing the effectiveness of print, web site, and game modalities. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2008, 40, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutbeam, D. The evolving concept of health literacy. Soc. Sci. Med. 2008, 67, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, T.; Jung, H. The relationships between food literacy, health promotion literacy and healthy eating habits among young adults in South Korea. Foods 2022, 11, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, B.R.; Makarova, A.; Sidig, D.; Niazi, S.; Abddelgader, R.; Mirza, S.; Joud, H.; Urfi, M.; Ahmed, A.; Jureyda, O. Nutritional literacy among uninsured patients with diabetes mellitus: A free clinic study. Cureus 2021, 13, e16355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotaiuti, P.; Girelli, L.; Mancone, S.; Valente, G.; Bellizzi, F.; Misiti, F.; Cavicchiolo, E. Psychometric properties and measurement invariance across gender of the Italian version of the tempest self-regulation questionnaire for eating adapted for young adults. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 941784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natour, N.; Al-Tell, M.; Ikhdour, O. Nutrition literacy is associated with income and place of residence but not with diet behavior and food security in the Palestinian society. BMC Nutr. 2021, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Doustmohammadian, A.; Omidvar, N.; Keshavarz-Mohammadi, N.; Eini-Zinab, H.; Amini, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Amirhamidi, Z.; Haidari, H. Low food and nutrition literacy (FNLIT): A barrier to dietary diversity and nutrient adequacy in school age children. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkan, I. The impact of nutrition literacy on the food habits among young adults in Turkey. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2019, 13, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaló, M.I.; Gibbons, S.; Naylor, P.-J. Using food models to enhance sugar literacy among older adolescents: Evaluation of a brief experiential nutrition education intervention. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doustmohammadinan, A.; Omidvar, N.; Keshavarz Mohammadi, N.; Eini-Zinab, H.; Amini, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Esfandyari, S.; Amirhamidi, Z. Food and nutrition literacy (FNLIT) is associated to healthy eating behaviors in children. Nutr. Food Sci. Res. 2021, 8, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, R.; Adinolfi, P.; Annarumma, C.; Catinello, G.; Tonelli, M.; Troiano, E.; Vezzosi, S.; Manna, R. Unravelling the food literacy puzzle: Evidence from Italy. Food Policy 2019, 83, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, H.D.; Ellerbeck, E.F.; Gajewski, B.; Zhang, C.; Sullivan, D.K. The nutrition literacy assessment instrument is a valid and reliable measure of nutrition literacy in adults with chronic disease. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2018, 50, 247–257.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, H.D.; Kennett, A.R.; Kerling, E.H.; Yu, Q.; Gajewski, B.; Ptomey, L.T.; Sullivan, D.K. Assessing the nutrition literacy of parents and its relationship with child diet quality. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2016, 48, 505–509.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, H.D.; Ellerbeck, E.F.; Befort, C.; Gajewski, B.; Kennett, A.R.; Yu, Q.; Christifano, D.; Sullivan, D.K. Measuring nutrition literacy in breast cancer patients: Development of a novel instrument. J. Cancer Educ. 2016, 31, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doustmohammadian, A.; Omidvar, N.; Keshavarz-Mohammadi, N.; Abdollahi, M.; Amini, M.; Eini-Zinab, H. Developing and validating a scale to measure Food and Nutrition Literacy (FNLIT) in elementary school children in Iran. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deesamer, S.; Piaseu, N.; Maneesriwongul, W.; Orathai, P.; Schepp, K.G. Development and Psychometric Testing of the Thai-Nutrition Literacy Assessment Tool for Adolescents. Pac. Rim Int. J. Nurs. Res. 2020, 24, 5–19. [Google Scholar]
- Guttersrud, Ø.; Petterson, K.S. Young adolescents’ engagement in dietary behaviour–the impact of gender, socio-economic status, self-efficacy and scientific literacy. Methodological aspects of constructing measures in nutrition literacy research using the Rasch model. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 2565–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naigaga, D.A.; Pettersen, K.S.; Henjum, S.; Guttersrud, Ø. Assessing adolescents’ perceived proficiency in critically evaluating nutrition information. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2018, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, O.; Quinn, E.L.-H.; Ramirez, M.; Sawyer, V.; Eimicke, J.P.; Teresi, J.A. Development of a menu board literacy and self-efficacy scale for children. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2017, 49, 867–871.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.S.; Treu, J.A.; Njike, V.; Walker, J.; Smith, E.; Katz, C.S.; Katz, D.L. The validation of a food label literacy questionnaire for elementary school children. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2012, 44, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, K.; Todoriki, H.; Sasaki, S. Relationship between nutrition knowledge and dietary intake among primary school children in Japan: Combined effect of children’s and their guardians’ knowledge. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, L.-L.; Lai, I.-J. Construction of nutrition literacy indicators for college students in Taiwan: A Delphi consensus study. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2017, 49, 734–742.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Su, X.; Li, N.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, G.; Zhu, W. Delphi method on food and nutrition literacy core components for school-age children. Chin. J. Health. Educ. 2020, 36, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wen, J.; Ma, H.; Yin, X.; Wang, J. Establishment of nutrition literacy core items for Chinese preschool children. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 54, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Medicine, I.O.; Neuroscience, B.O.; Health, B.; Literacy, C.O.H. Health Literacy: A Prescription to End Confusion; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bari, N.N. Nutrition Literacy Status of Adolescent Students in Kampala District, Uganda. Master’s Thesis, Oslo and Akershus University College of Applied Sciences, Lillestrøm, Norway, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Türkmen, A.S.; Kalkan, I.; Filiz, E. Adaptation of adolescent nutrition literacy scale into Turkish: A validity and reliability study. Int. Peer-Rev. J. Nutr. Res. 2017, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joulaei, H.; Keshani, P.; Kaveh, M.H. Nutrition literacy as a determinant for diet quality amongst young adolescents: A cross sectional study. Prog. Nutr. 2018, 20, 455–464. [Google Scholar]
- Depboylu, G.Y.; Kaner, G.; Süer, M.; Kanyılmaz, M.; Alpan, D. Nutrition literacy status and its association with adherence to the Mediterranean diet, anthropometric parameters and lifestyle behaviours among early adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2023, 26, 2108–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoteit, M.; Mansour, R.; Mohsen, H.; Bookari, K.; Hammouh, F.; Allehdan, S.; Alkazemi, D.; Al Sabbah, H.; Benkirane, H.; Kamel, I.; et al. Status and correlates of food and nutrition literacy among parents-adolescents’ dyads: Findings from 10 Arab countries. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1151498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger and Malnutrition in the Arab Region Stand in the Way of Achieving Zero Hunger by 2030. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/mena/press-releases/hunger-and-malnutrition-arab-region-stand-way-achieving-zero-hunger-2030-un-report (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Food and Agricultural Organization; International Fund for Agricultural Development; United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund; World Food Program; World Health Organization, Economic SCfWA. Near East and North Africa Regional Overview of Food Security and Nutrition 2020: Enhancing Resilience of food Systems in the Arab States. 2021. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/275622ec-df5b-4198-b72c-757f681e236c/content (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Agence France-Presse. A Third of People in 420m-Strong Arab World Do Not Have Enough to Eat Arab News. 2021. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/1988326/middle-east (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- El Zouki, C.-J.; Chahine, A.; Mhanna, M.; Obeid, S.; Hallit, S. Rate and correlates of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) following the Beirut blast and the economic crisis among Lebanese University students: A cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naja, F.; Hwalla, N.; Itani, L.; Karam, S.; Sibai, A.M.; Nasreddine, L. A Western dietary pattern is associated with overweight and obesity in a national sample of Lebanese adolescents (13–19 years): A cross-sectional study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, H.; Zind, M.; Garnier, S.; Fazah, A.; Jacob, C.; Moussa, E.; Gratas-Delamarche, A.; Groussard, C. Overweight and obesity related factors among Lebanese adolescents: An explanation for gender and socioeconomic differences. Epidemiology 2017, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraj, S.S. Physical Activity Among a Representative Sample of Lebanese Adolescents Aged 12–18 Years: A National Cross-Sectional Study. Ph.D. Thesis, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Accelerated Action for the Health of Adolescents (AA-HA!): Guidance to Support Country Implementation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Laska, M.N.; Larson, N.I.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Story, M. Does involvement in food preparation track from adolescence to young adulthood and is it associated with better dietary quality? Findings from a 10-year longitudinal study. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoghby, H.B.; Sfeir, E.; Akel, M.; Malaeb, D.; Obeid, S.; Hallit, S. Knowledge, attitude and practice of Lebanese parents towards childhood overweight/obesity: The role of parent-physician communication. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B. Intakes of energy and macronutrient from Chinses 15 provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities) adults aged 18 to 35 in 1989-2018. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu J. Hyg. Res. 2022, 51, 361–380. [Google Scholar]
- Desbouys, L.; De Ridder, K.; Rouche, M.; Castetbon, K. Food consumption in adolescents and young adults: Age-specific socio-economic and cultural disparities (Belgian Food Consumption Survey 2014). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, F.; Azadbakht, L. A systematic review on diet quality among Iranian youth: Focusing on reports from Tehran and Isfahan. Arch. Iran. Med. 2014, 17, 574–584. [Google Scholar]
- Vella-Zarb, R.A.; Elgar, F.J. The ‘freshman 5’: A meta-analysis of weight gain in the freshman year of college. J. Am. Coll. Health 2009, 58, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, E.T.; Zoellner, J.M. Nutrition and health literacy: A systematic review to inform nutrition research and practice. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikimedia Commons. Lebanon Districts. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lebanon_districts.png (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Jamaluddine, Z.; Sahyoun, N.R.; Choufani, J.; Sassine, A.J.; Ghattas, H. Child-Reported Food Insecurity Is Negatively Associated with Household Food Security, Socioeconomic Status, Diet Diversity, and School Performance among Children Attending UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees Schools in Lebanon. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 2228–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundfrom, D.J.; Shaw, D.G.; Ke, T.L. Minimum sample size recommendations for conducting factor analyses. Int. J. Test. 2005, 5, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu Lt Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, N.; Dash, S. Marketing Research: An Applied Orientation; Pearson-Dorling Kindersley: Delhi, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen FF: Sensitivity of goodness of fit indexes to lack of measurement invariance. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 2007, 14, 464–504. [CrossRef]
- Vadenberg, R.; Lance, C. A review and synthesis of the measurement in variance literature: Suggestions, practices, and recommendations for organizational research. Organ Res. Methods 2000, 3, 4–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, V.; Todd, J.; Azzi, V.; Malaeb, D.; El Dine, A.S.; Obeid, S.; Hallit, S. Psychometric properties of an Arabic translation of the Functionality Appreciation Scale (FAS) in Lebanese adults. Body Image 2022, 42, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, T.J.; Baguley, T.; Brunsden, V. From alpha to omega: A practical solution to the pervasive problem of internal consistency estimation. Br. J. Psychol. 2014, 105, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmazel, G.; Bozdogan, S. Nutrition literacy, dietary habits and food label use among Turkish adolescents. Prog. Nutr. 2021, 23, e2021007. [Google Scholar]
- Ashoori, M.; Omidvar, N.; Eini-Zinab, H.; Shakibazadeh, E.; Doustmohamadian, A.; Abdar-Esfahani, B.; Mazandaranian, M. Food and nutrition literacy status and its correlates in Iranian senior high-school students. BMC Nutr. 2021, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, J.; Haase, A.M.; Steptoe, A. Body image and weight control in young adults: International comparisons in university students from 22 countries. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-P. Gender differences in nutrition knowledge, attitude, and practice among elderly people. Int. J. Manag. Econ. Soc. Sci. (IJMESS) 2017, 6, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Svendsen, K.; Torheim, L.E.; Fjelberg, V.; Sorprud, A.; Narverud, I.; Retterstøl, K.; Bogsrud, M.P.; Holven, K.B.; Myhrstad, M.C.; Telle-Hansen, V.H. Gender differences in nutrition literacy levels among university students and employees: A descriptive study. J. Nutr. Sci. 2021, 10, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullan, B.A.; Wong, C.; Kothe, E.J. Predicting adolescents’ safe food handling using an extended theory of planned behavior. Food Control 2013, 31, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliffe, J.L.; Rossnagel, E.; Kelly, M.T.; Bottorff, J.L.; Seaton, C.; Darroch, F. Men’s health literacy: A review and recommendations. Health Promot. Int. 2020, 35, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, M.J.; van den Berg, A.E.; Asigbee, F.M.; Vandyousefi, S.; Ghaddar, R.; Davis, J.N. Child-report of food insecurity is associated with diet quality in children. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, S.A.; Tangney, C.C.; Crane, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Appelhans, B.M. Nutrition quality of food purchases varies by household income: The SHoPPER study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J.; Frongillo, E.A.; Rivera, J.A. Food insecurity reported by children, but not by mothers, is associated with lower quality of diet and shifts in foods consumed. Matern. Child Nutr. 2016, 12, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorramrouz, F.; Doustmohammadian, A.; Eslami, O.; Khadem-Rezaiyan, M.; Pourmohammadi, P.; Amini, M.; Khosravi, M. Relationship between household food insecurity and food and nutrition literacy among children of 9–12 years of age: A cross-sectional study in a city of Iran. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, P.H.; Szeto, K.; Lensing, S.; Bogle, M.; Weber, J. Children in food-insufficient, low-income families: Prevalence, health, and nutrition status. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2001, 155, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liese, A.D.; Bell, B.A.; Martini, L.; Hibbert, J.; Draper, C.; Burke, M.P.; Jones, S.J. Perceived and geographic food access and food security status among households with children. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 2781–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- School Health and Nutrition. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/en/health-education/nutrition (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Hunter, D.; Giyose, B.; PoloGalante, A.; Tartanac, F.; Bundy, D.; Mitchell, A.; Moleah, T.; Friedrich, J.; Alderman, A.; Drake, L.; et al. Schools as a System to Improve Nutrition: A New Statement for School-Based Food and Nutrition Interventions; United Nations System Standing Committee on Nutrition: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).