Flavone C-Glycosides from Dianthus superbus L. Attenuate Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) via Multi-Pathway Regulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Plant Sample Origin
2.3. Zebrafish Maintenance
2.4. Isolation and Purity of Sample
2.5. Network Pharmacology Analysis
2.5.1. Identification of Compound-Disease Intersection Targets
2.5.2. PPI Network and Core Target Analysis
2.5.3. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Potential Targets
2.5.4. Construction of the Compound-Target-Pathway Network
2.5.5. Molecular Docking Analyses
2.6. Animal Experiments
2.6.1. Zebrafish Treatment
2.6.2. Weight, Length, and BMI Measurements
2.6.3. Lipid Metabolism Biochemical Assays
2.6.4. Oil Red O Staining of Whole Zebrafish
2.6.5. Liver Tissue Sectioning and Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) Staining
2.6.6. Behavioral Analysis
2.6.7. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Assays
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
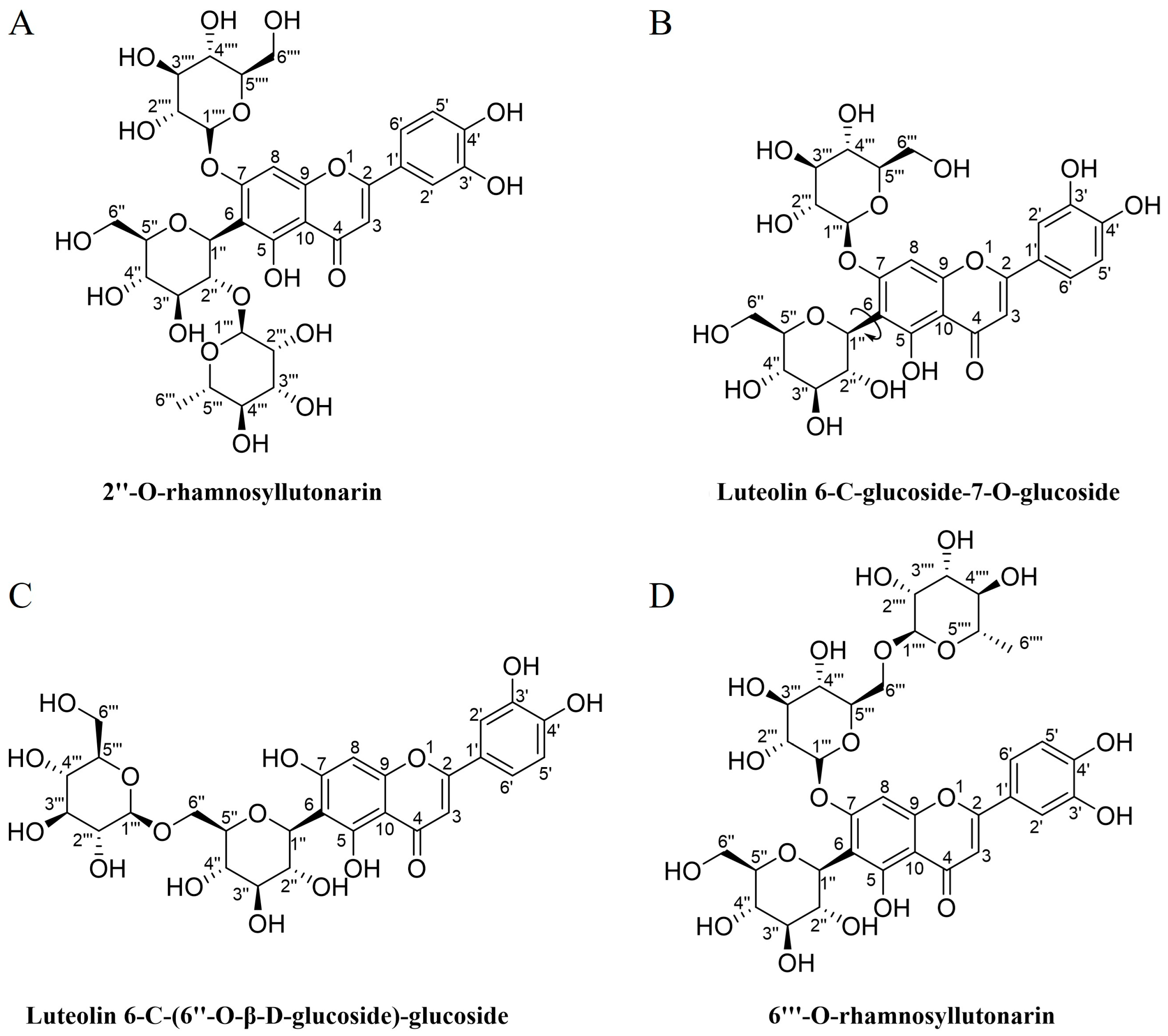
3.1. Preparative Isolation, Purity Analysis and Structural Characterization of Compounds
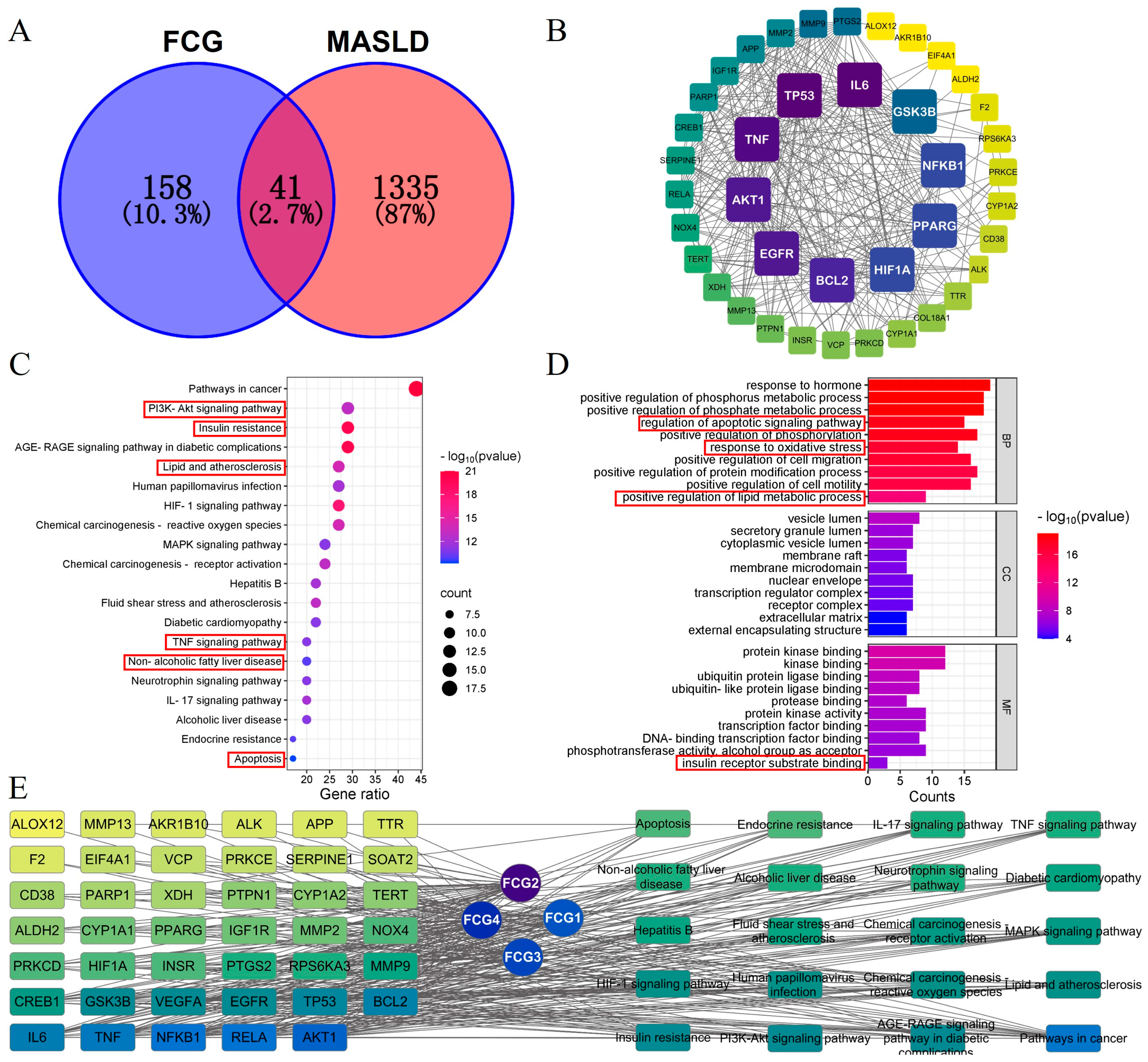
3.2. Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis of Potential Targets and Pathways for FCGs in the Treatment of MASLD
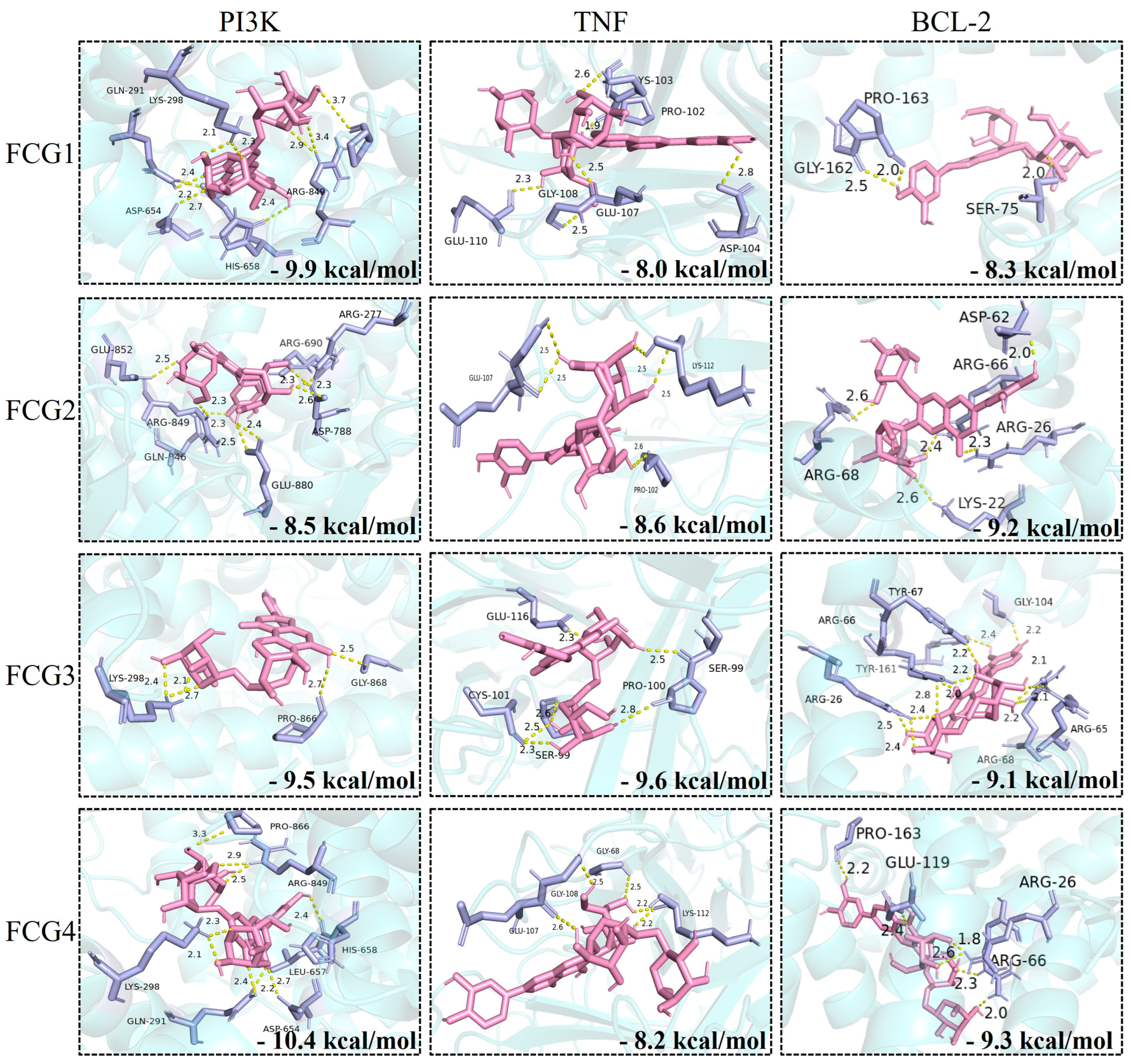
3.3. Molecular Docking Analysis of FCGs with Core Therapeutic Targets
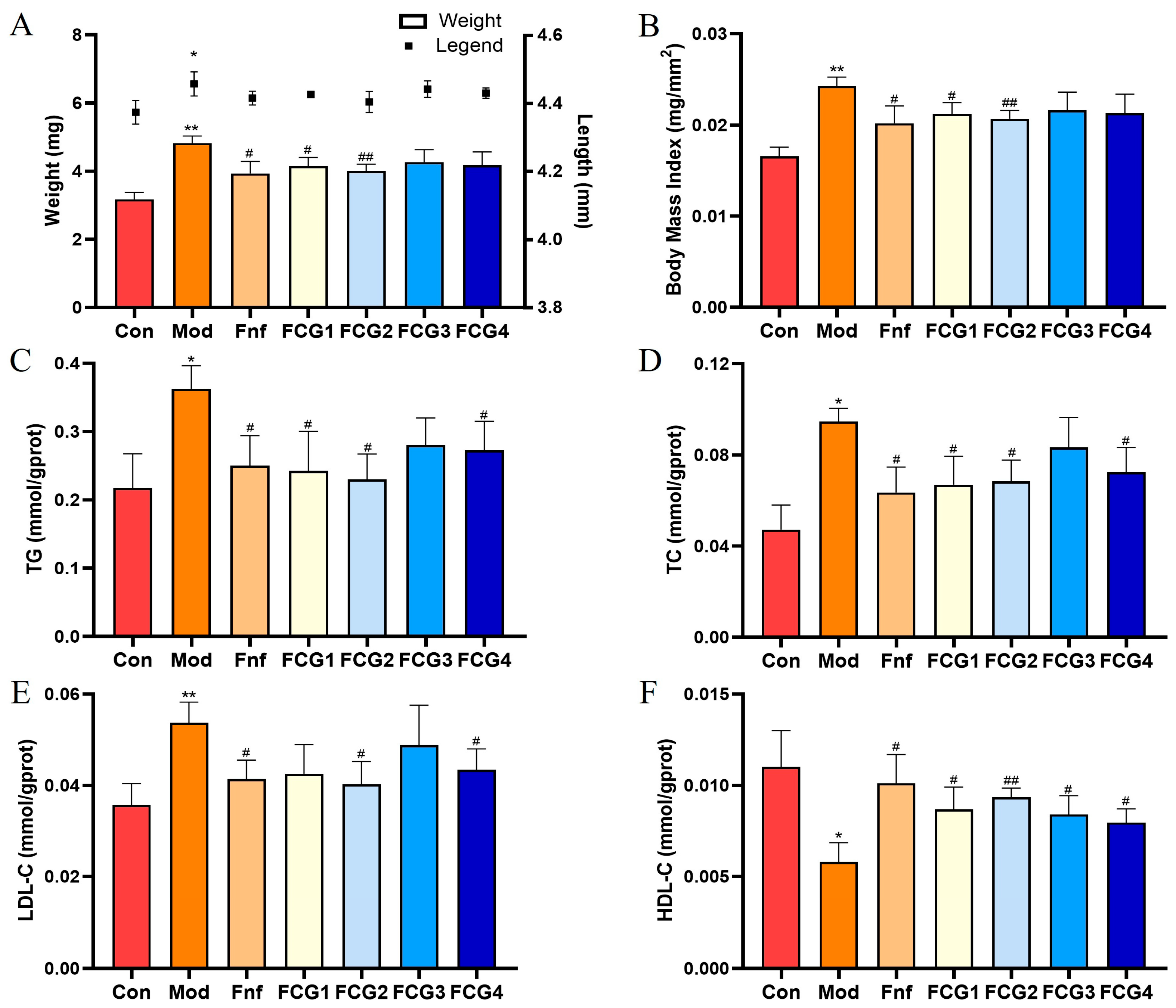
3.4. Effect of FCGs on Obesity in MASLD Zebrafish
3.5. Effect of FCGs on Lipid Metabolism in MASLD Zebrafish
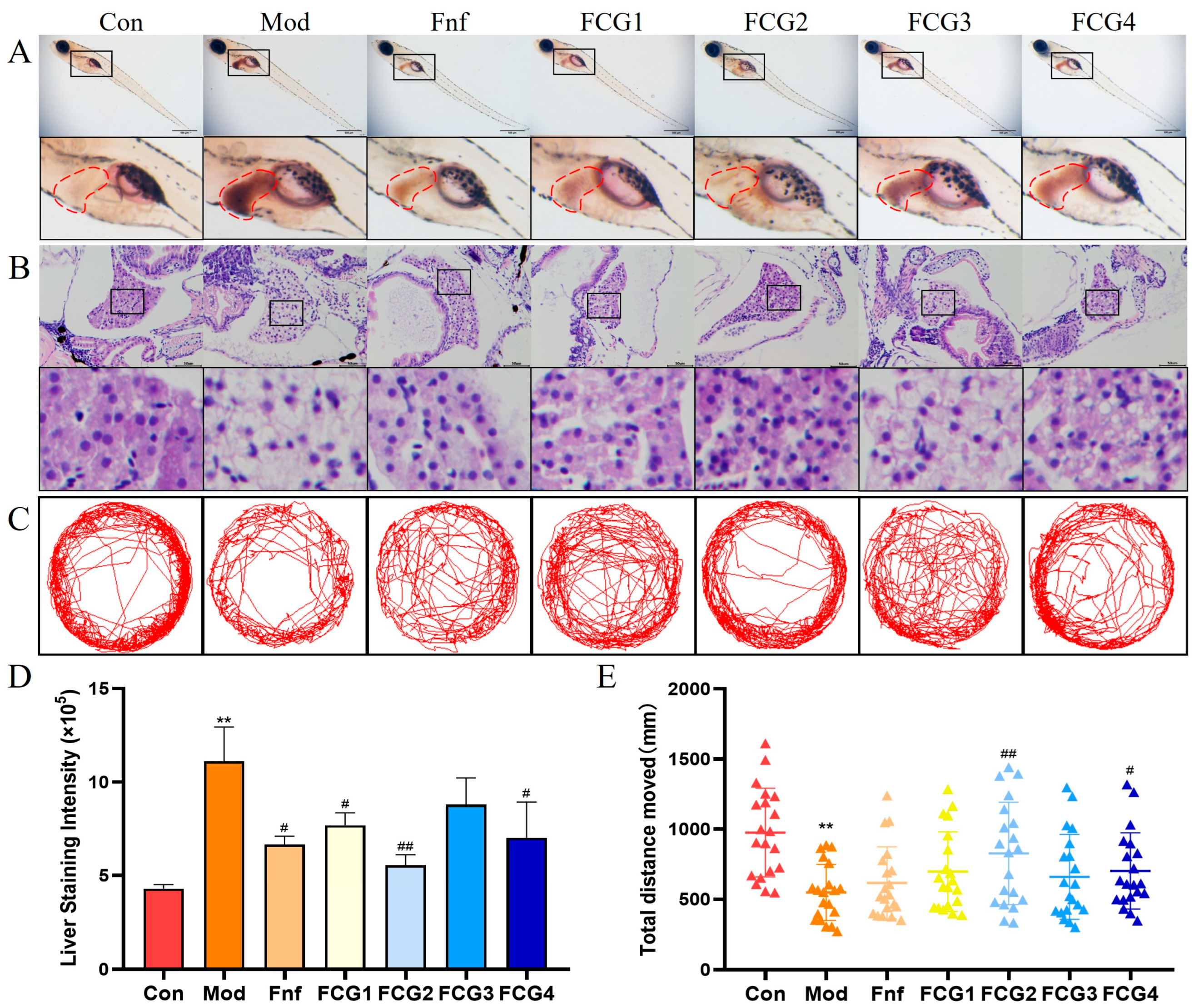
3.6. Effect of FCGs on Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in MASLD Zebrafish
3.7. Effect of FCGs on Hepatic Tissue Injury in MASLD Zebrafish
3.8. Effect of FCGs on Behavioral Indicators of MASLD Zebrafish
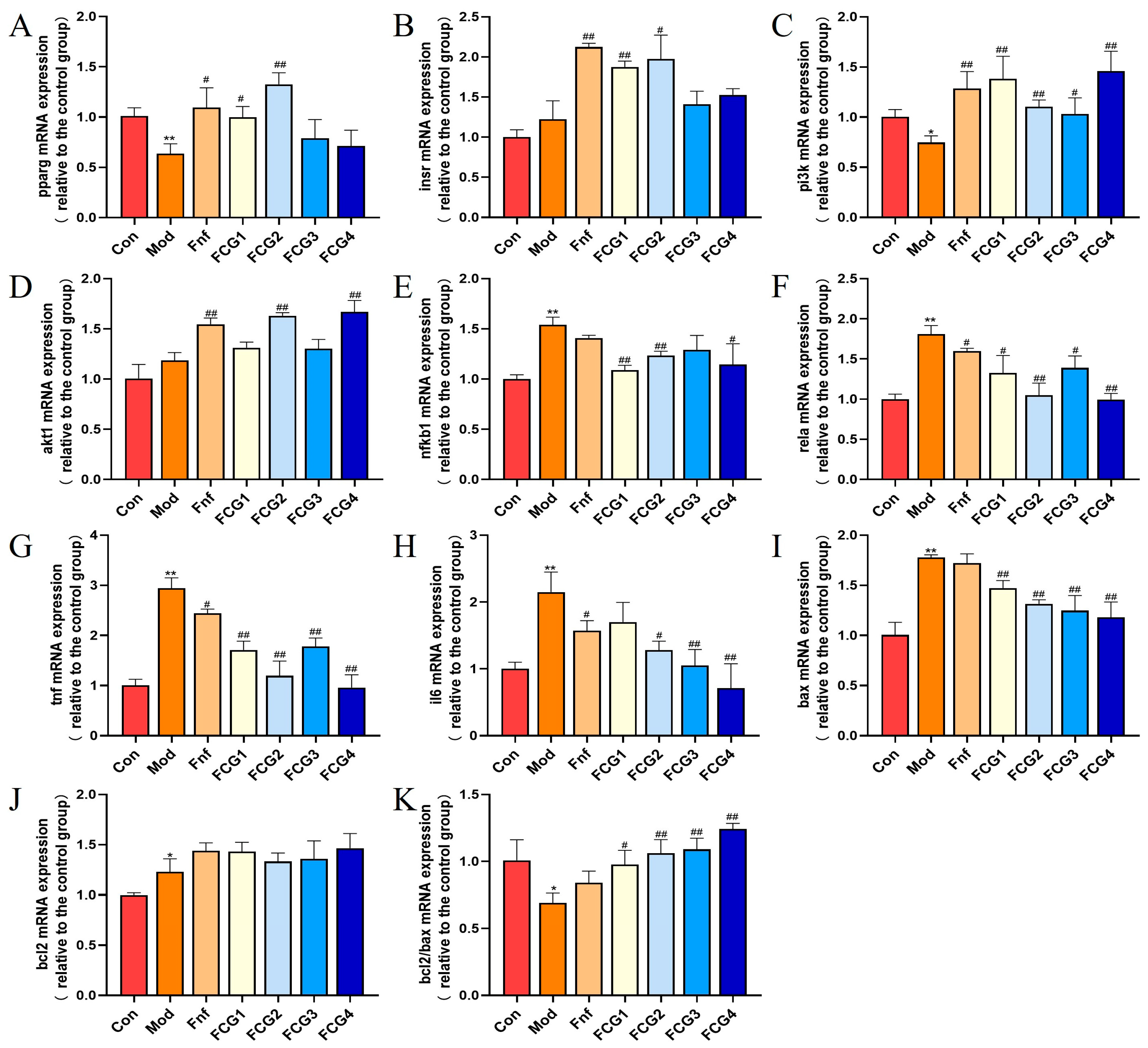
3.9. Effect of FCGs on mRNA Expression Levels in MASLD Zebrafish
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MASLD | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| FCGs | flavone C-glycosides |
| TG | triglyceride |
| TC | total cholesterol |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL-C | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| PPI | protein-protein interaction |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
References
- Wong, V.W.-S.; Ekstedt, M.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Hagström, H. Changing Epidemiology, Global Trends and Implications for Outcomes of NAFLD. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A Systematic Review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Multiple Parallel Hits Hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, F.-Y.; Zhu, Y.Z. Roles of the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 192, 106786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yu, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Shen, P. Apigenin, a Modulator of PPARγ, Attenuates HFD-Induced NAFLD by Regulating Hepatocyte Lipid Metabolism and Oxidative Stress via Nrf2 Activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 136, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushi, R.; Hirota, Y.; Ogawa, W. Insulin Resistance and Exaggerated Insulin Sensitivity Triggered by Single-Gene Mutations in the Insulin Signaling Pathway. Diabetol. Int. 2021, 12, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, D. Current Studies on Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, e1863429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.-L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.-Q.; Li, Z.-H. Alpinetin Improved High Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) through Improving Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Response and Lipid Metabolism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondylis, V.; Kumari, S.; Vlantis, K.; Pasparakis, M. The Interplay of IKK, NF-κB and RIPK1 Signaling in the Regulation of Cell Death, Tissue Homeostasis and Inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, R.M.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Castro, R.E.; Solá, S.; Costa, A.; Moura, M.C.; Camilo, M.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.P. Apoptosis and Bcl-2 Expression in the Livers of Patients with Steatohepatitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 18, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wang, L.; Evans, P.C.; Xu, S. NAFLD and NASH: Etiology, Targets and Emerging Therapies. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, S.J. Resmetirom: First Approval. Drugs 2024, 84, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K. Resmetirom Proves Positive for NASH with Liver Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisnovali, N.F.; Haney, C.; Goedeke, L. RezdiffraTM (Resmetirom): A THR-β Agonist for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 45, 1081–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Li, Q.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, Y.; Fang, M.; Yu, Z.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Gao, Y.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the Treatment of NAFLD: A Promising Drug Potentilla Discolor Bunge. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3529–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, L. Mechanism of Natural Drugs on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 3030–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.-C.; Jeong, Y.H.; Cho, W.-K.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Ma, J.Y. Inhibitory Effects of Dianthi Herba Ethanolic Extract on Inflammatory and Nociceptive Responses in Murine Macrophages and Mouse Models of Abdominal Writhing and Ear Edema. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 211, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Dang, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, S.; Lv, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, G. Preparative Isolation of Maltol Glycoside from Dianthus Superbus and Its Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Vitro. R. Soc. Chem. Adv. 2022, 12, 5031–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kletter, C. Traditional Mongolian Medicine—A Potential for Drug Discovery. Sci. Pharm. 2008, 76, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, G.S.; Nile, A.S.; Kwon, Y.D.; Enkhtaivan, G.; Nile, S.H. Utilization of Dianthus Superbus L. and Its Bioactive Compounds for Antioxidant, Anti-Influenza and Toxicological Effects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; Jin, H.-G.; Kim, H.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.; Lee, Y.; Kang, D. Dianthus Superbus Improves Glomerular Fibrosis and Renal Dysfunction in Diabetic Nephropathy Model. Nutrients 2019, 11, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Gupta, V.K.; Jiang, Y. New Insights on Bioactivities and Biosynthesis of Flavonoid Glycosides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.C.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Silva, A.M.S. Plant Flavonoids: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Wier, B.; Koek, G.H.; Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R.M.M. The Potential of Flavonoids in the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 834–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Jin, L.; Qin, X.; He, B. Natural Flavonoids: Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1005312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Dang, J.; Li, G. Impact of Preparative Isolation of C-Glycosylflavones Derived from Dianthus Superbus on In Vitro Glucose Metabolism. Molecules 2024, 29, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Mao, T.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X.; Sun, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, L.; et al. Protective Effects and Mechanisms of Yinchen Linggui Zhugan Decoction in HFD-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rats Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 908128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Gong, L.; Wang, C.; Hu, N.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Dai, X.; Li, Y. Radix Polygoni Multiflori and Its Main Component Emodin Attenuate Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Zebrafish by Regulation of AMPK Signaling Pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, C.-Q.; Fan, Y.-Q.; Xie, Y.-S.; Yin, Z.-F.; Xu, Z.-J.; Zhang, H.-L.; Cao, J.-T.; Han, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Optimizing Methods for the Study of Intravascular Lipid Metabolism in Zebrafish. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1871–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Zhang, J.-P. Comparative Study of Different Diets-Induced NAFLD Models of Zebrafish. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Hou, M.; Luo, R.; He, J.; Lin, F.; Xia, X.; Li, P.; He, C.; He, P.; et al. Danggui Shaoyao San Ameliorates the Lipid Metabolism via the PPAR Signaling Pathway in a Danio Rerio (Zebrafish) Model of Hyperlipidemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroslawa, K.; Wojciech, C. Flavone C-glycosides from Bryonia alba and B. dioica. Phytochemistry 1995, 39, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, L.; Férézou, J.P.; Tinoco, L.W.; Kaiser, C.R.; Costa, S.S. Flavonoids from Mimosa xanthocentra (Leguminosae: Mimosoideae) and molecular modeling studies for isovitexin-2″-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside rotamers. Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 5, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.H.; Yen, M.H.; Chung, M.I.; Lin, C.N. A flavone C-glycoside and an aromatic glucoside from Gentiana species. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obmann, A.; Werner, I.; Presser, A.; Zehl, M.; Swoboda, Z.; Purevsuren, S.; Narantuya, S.; Kletter, C.; Glasl, S. Flavonoid C- and O-glycosides from the Mongolian medicinal plant Dianthus versicolor Fisch. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.; Figueredo, C.; Rinella, M.E. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Identification and Management of High-Risk Patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zang, E.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-C.; Niu, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, M.-H. Dianthi Herba: A Comprehensive Review of Its Botany, Traditional Use, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Capanoglu, E.; Jassbi, A.R.; Miron, A. Advance on the Flavonoid C-Glycosides and Health Benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56 (Suppl. 1), S29–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willebrords, J.; Pereira, I.V.A.; Maes, M.; Crespo Yanguas, S.; Colle, I.; Van Den Bossche, B.; Da Silva, T.C.; de Oliveira, C.P.M.S.; Andraus, W.; Alves, V.A.; et al. Strategies, Models and Biomarkers in Experimental Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Research. Prog. Lipid Res. 2015, 59, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölttä-Vuori, M.; Salo, V.T.V.; Nyberg, L.; Brackmann, C.; Enejder, A.; Panula, P.; Ikonen, E. Zebrafish: Gaining Popularity in Lipid Research. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Miller, S.R.; Ober, E.A.; Sadler, K.C. Making It New Again: Insight Into Liver Development, Regeneration, and Disease From Zebrafish Research. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 124, 161–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-M.; Ni, X.-X.; Xu, Q.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.-Y.; Hua, J. Regulation of Lipid-Induced Macrophage Polarization through Modulating Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma Activity Affects Hepatic Lipid Metabolism via a Toll-like Receptor 4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 1998–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyni, G.L.; Sasidharan, K.; Francis, S.K.; Das, A.A.; Nair, M.S.; Raghu, K.G. Licarin B from Myristica Fragrans Improves Insulin Sensitivity via PPARγ and Activation of GLUT4 in the IRS-1/PI3K/AKT Pathway in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. R. Soc. Chem. Adv. 2016, 6, 79859–79870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, S.S.; Weigert, C.; Lehmann, R. Divergent Roles of IRS (Insulin Receptor Substrate) 1 and 2 in Liver and Skeletal Muscle. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1827–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Madiraju, A.K.; Gassaway, B.M.; Marcel, M.; Nasiri, A.R.; Butrico, G.; Marcucci, M.J.; Zhang, D.; Abulizi, A.; Zhang, X.-M.; et al. Insulin Receptor Thr1160 Phosphorylation Mediates Lipid-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4361–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Xu, N.; Meng, Q.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; Xu, F.; Li, Y. VEGFB Ameliorates Insulin Resistance in NAFLD via the PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Kawada, N.; Japan Study Group of NAFLD (JSG-NAFLD). The Role of Insulin Resistance and Diabetes in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoleri, D.; Titchenell, P.M. Resolving the Paradox of Hepatic Insulin Resistance. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvandová, M.; Majzúnová, M.; Dovinová, I. The Role of PPARγ in Cardiovascular Diseases. Physiol. Res. 2016, 65 (Suppl. 3), S343–S363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. NF-κB in the Liver—Linking Injury, Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, P.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Zheng, W.; Sun, W. Hesperetin Ameliorates Hepatic Oxidative Stress and Inflammation via the PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-ARE Pathway in Oleic Acid-Induced HepG2 Cells and a Rat Model of High-Fat Diet-Induced NAFLD. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3898–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsova, P.; Gores, G.J. Death Receptor-Mediated Cell Death and Proinflammatory Signaling in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Yamazaki, M.; Shibata, T.; Nirei, K.; Takahashi, H.; Kaneko, T.; Fujisawa, M.; Higuchi, T.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Apoptosis and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.P.; Li, J.H.; He, S.Y.; Li, P.; Zhong, X.L. Roles of Fas/Fasl, Bcl-2/Bax, and Caspase-8 in Rat Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Pathogenesis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 3991–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | ACATCAGCATGGCTTCTGCT | GAAGTCCTCTCGGGGAAAGC |
| pparg | TCACTCTCCGCTGATATGGTG | TTGGGTCATTCTGTGTTGGGT |
| insr | TCATCTTCCGCGTCTATGGC | CTGTGGAGGCCGATTTCCTT |
| pi3k | TGTGAAGCACTCAAGCAGTCA | ATCACCGAGGCAGAAAGACG |
| akt1 | AAGAGGGGATCACAGACGGA | GTCCTGGTTGTAGAACGGCA |
| nfkb1 | AGGCCAAAGACACTGTTCGG | GGAAAGGTTGTGGGGTCCAT |
| rela | CCCGCCATTAGGGTTCACAA | CTCGTGTGGGTGTGGCTTAT |
| tnf | CAAATCACCACACCTTCAGCTTC | CACACCGCCAACCCATTTCA |
| il6 | TAAATCCGCATGGACTCGCA | CGGTCCTCTTGGGGTCTTTC |
| bcl2 | TTCTAACCGTGGCCGAAGAG | ATCTACCTGGGACGCCATCT |
| bax | TACTTTGCCTGTCGCCTTGT | AGCGAGGAAAACTCCGACTG |
| Proteins | Compound | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Binding Residues |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPARγ | FCG1 | −5.4 | TYR-63 |
| FCG2 | −5.3 | MET-22 ILE-37 | |
| FCG3 | −5.9 | ASN-8 LEU-47 MET-22 | |
| FCG4 | −6.0 | TYR-63 GLY-62 VAL-60 ASP-58 ASN-46 ARG-47 | |
| INSR | FCG1 | −7.2 | LEU-1002 HIS-1081 SER-1086 |
| FCG2 | −6.7 | ALA-1080 ASP-1083 | |
| FCG3 | −6.9 | ASP-1083 SER-1086 ARG-1089 GLU-1096 | |
| FCG4 | −8.1 | ASP-1083 LYS-1085 | |
| PI3K | FCG1 | −9.9 | GLN-291 LYS-298 ASP-654 HIS-658 ARG-849 |
| FCG2 | −8.5 | GLU-852 ARG-849 GLN-846 GLU-880 ASP-788 ARG-690 ARG-277 | |
| FCG3 | −9.5 | LYS-298 PRO-866 GLY-868 | |
| FCG4 | −10.4 | LYS-298 GLN-291 PRO-866 ARG-849 HIS-658 LEU-657 ASP-654 | |
| AKT1 | FCG1 | −7.6 | ARG-15 |
| FCG2 | −7.2 | GLU-32 ARG-328 ASP-325 ASN-324 | |
| FCG3 | −8.6 | LYS-276 ASN-279 GLU-85 | |
| FCG4 | −7.8 | ARG-346 GLY-345 LEU-347 PRO-348 | |
| NF-κB1 | FCG1 | −7.1 | ASN-219 GLN-435 |
| FCG2 | −7.2 | GLN-439 GLN-435 ASN-257 ASP-261 | |
| FCG3 | −8.6 | ASP-316 ASN-394 VAL-312 ASN-352 SER-351 TRP-318 ASN-310 ASP-271 | |
| FCG4 | −8.2 | LYS-299 GLN-435 LYS-431 ASN-257 | |
| RELA | FCG1 | −7.9 | LYS-140 GLU-182 ARG-85 |
| FCG2 | −6.8 | TYR-25 | |
| FCG3 | −7.8 | LYS-122 ARG-132 ASN-42 | |
| FCG4 | −7.3 | GLU-133 SER-63 ARG-85 | |
| TNF | FCG1 | −8.0 | GLU-110 GLY-108 GLU-107 LYS-103 PRO-102 ASP-104 |
| FCG2 | −8.6 | GLU-107 PRO-102 LYS-112 | |
| FCG3 | −9.6 | GLU-116 CYS-101 PRO-100 SER-99 | |
| FCG4 | −8.2 | GLU-107 GLY-108 GLY-68 LYS-112 | |
| IL6 | FCG1 | −7.3 | ASP-160 LYS-46 ARG-104 GLN-159 |
| FCG2 | −7.0 | ASP-140 ASN-144 GLU-93 | |
| FCG3 | −6.8 | ASN-144 LYS-66 | |
| FCG4 | −7.6 | LYS-46 GLN-156 ARG-104 | |
| BAX | FCG1 | −8.0 | ASN-104 LEU-47 PRO-130 |
| FCG2 | −6.9 | LEU-47 ALA-42 GIN-28 GLU-41 | |
| FCG3 | −6.5 | ASP-98 ASP-102 MET-99 GLN-52 LYS-57 | |
| FCG4 | −7.0 | ALA-35 ASN-104 | |
| BCL-2 | FCG1 | −8.3 | PRO-163 GLY-162 SER-75 |
| FCG2 | −9.2 | ASP-62 ARG-66 ARG-26 ARG-68 LYS-22 | |
| FCG3 | −9.1 | TYR-67 TYR-161 ARG-66 ARG-26 ARG-68 ARG-65 | |
| FCG4 | −9.3 | PRO-163 GLU-119 ARG-66 ARG-26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, M.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, J.; Li, G. Flavone C-Glycosides from Dianthus superbus L. Attenuate Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) via Multi-Pathway Regulations. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152456
Chu M, Tong Y, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Dang J, Li G. Flavone C-Glycosides from Dianthus superbus L. Attenuate Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) via Multi-Pathway Regulations. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152456
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Ming, Yingying Tong, Lei Zhang, Yu Zhang, Jun Dang, and Gang Li. 2025. "Flavone C-Glycosides from Dianthus superbus L. Attenuate Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) via Multi-Pathway Regulations" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152456
APA StyleChu, M., Tong, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, Y., Dang, J., & Li, G. (2025). Flavone C-Glycosides from Dianthus superbus L. Attenuate Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) via Multi-Pathway Regulations. Nutrients, 17(15), 2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152456







