Highlights
What are the main findings?
- Adolescent girls intending to lose weight reported less frequent breakfast consumption and less sleep compared to those not intending to lose weight.
- Adolescent girls intending to lose weight reported more screen time, engaging in muscle toning exercises, vaping, and alcohol use compared to those not intending to lose weight.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- Girls intending to lose weight may benefit from targeted intervention to improve sleep, reduce screen time, and incorporate breakfast into their daily routine.
- While all youths may benefit from programs to reduce vaping and alcohol use, girls intending to lose weight are a priority group as they are at a higher risk of substance abuse.
Abstract
Background: External social influences on body image affect females differently than males, and adolescent girls are more likely to want to change their weight status. Understanding the healthy and unhealthy habits of adolescent girls is vital for developing effective and targeted health promotions and interventions. Methods: Using data from the 2021 Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System (YRBS) survey, this cross-sectional study compares dietary habits, physical activity, vaping, alcohol use, sleep, and screen time in females (9th–12th grades) who intend to lose weight versus those who want to maintain their current weight. Results: The sample consisted of 4362 females, of which 56.7% reported an intent to lose weight. The average BMI percentile was 64.1 compared to 75.4 among those trying to lose weight and 50.1 among those not trying to lose weight. Adolescent girls intending to lose weight also reported less frequent breakfast consumption (OR 0.52; 0.40–0.69), less sleep (OR 0.72; 0.59–0.89), more screen time (OR 1.27; 1.02–1.58), engaging in muscle toning exercises (OR 1.30; 1.07–1.57), vaping (OR 1.22; 1.01–1.47), and alcohol use (OR 1.61; 1.32–1.98) compared to those not intending to lose weight. Conclusions: Adolescent girls trying to lose weight would likely benefit from interventions to help them improve sleep, reduce screen time, improve dietary and exercise habits, and monitor alcohol and vaping use.
1. Introduction
Obesity prevalence reached 22.2% among adolescents aged 12–19, based on the latest National Health Report released in 2021 []. Around 80% of obese adolescents carry it into adulthood, leading to health risks such as metabolic tissue dysfunction, low-grade systemic inflammation, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes [,].
External social influences on body image affect females differently than males []. Weight dissatisfaction is particularly prevalent among girls, ranging from 19.2 to 83.4% among 10–19-year-old girls in an international systematic review []. Perception of body weight plays a role in the motivation to lose weight in young adults, and physically active adolescents have reported a better body perception [,]. However, there is less information regarding physical activity in adolescent girls intending to lose weight. The PA Guidelines for Americans recommend 60 min (1 h) or more of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity daily, including aerobic, muscle-strengthening and bone-strengthening exercise for children and adolescents []. Unfortunately the adherence to these recommendations in adolescents is low, approximately 23.9% adherence overall, and significantly lower for girls at 15.7% [].
The Healthy Eating Index (HEI) score for boys and girls aged 14–18 is 51/100 []. The average vegetable intake for girls that age is less than 1 serving per day. Adhering to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans increases the likelihood of maintaining body weight since it encompasses balance, moderation, variety, and calorie control.
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends that teenagers aged 13 to 18 sleep 8 to 10 h per 24 h regularly to promote optimal health []. There is a consistent association between screen time and sleep in adolescents []. Data from the longitudinal, U.S.-based Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study showed that females recorded about 1 h more average daily app and smartphone use than males []. Coincidentally, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that the percentage of high school students who do not get enough sleep is higher among girls (80%) compared to boys (75%) []. Furthermore, inadequate sleep (including both short duration and poor quality) is associated with overweight and obesity in adolescents []. Adolescents are also susceptible to direct pulmonary injury, addiction, and other health risks from e-cigarettes []. According to the Monitoring the Future survey report, by the National Institute of Health, Institute on Drug Abuse, 27% of 12th grade students had vaped nicotine within the last 12 months in 2022, while 52% of students had used alcohol within the last 12 months in 2022 [].
While there have been some descriptive studies on adolescents’ habits [,,,,], to date, a comprehensive analysis of lifestyle habits among girls intending to lose weight using a representative US sample has been limited [,,].
Understanding the health-related behavior of girls intending to reduce their weight can inform strategies for addressing body weight management in this population. Using a national representative sample, this cross-sectional study compares dietary habits, physical activity, vaping, alcohol use, sleep, and screen time in females (9th–12th grades) who intend to lose weight versus those who want to maintain their current weight. Additionally, this study describes the relationship between actual BMI (using self-reported weight) and weight perception between the two groups of girls (weight loss intent vs. maintaining weight).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
The 2021 Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) is part of a biennial cross-sectional survey conducted by the CDC since 1991 to monitor the prevalence of health risk behaviors among 9th through 12th grade students in public and private schools in the United States. YRBS utilizes a three-stage cluster sample design to generate a representative sample. Each student record was assigned a weighting factor based on student sex, race, ethnicity, and grade to adjust for nonresponse and the oversampling of black and Hispanic students in the sample. The weighted count of students equals the total sample size, and the weighted proportions match the national population proportions.
The 2021 YRBS covered 152 schools, received 17,232 usable questionnaires, and had an overall response rate of 57.5% (72.7% school response rate and 79.1% student response rate) []. Of the 87 questions covered in the questionnaire, only 58 were required, and schools could customize the survey. Question Q67 regarding weight loss was an optional question and was completed by 9273 students, of which 4362 were girls. The test–retest reliability has been shown to be strong for the questions in YRBS []. The institutional review board at the CDC approved the protocol for the YRBS. The YRBS has been described in more detail here []. In addition, the present authors obtained IRB approval at their institution to conduct this secondary data analysis.
2.2. YRBS Measures
The dependent variable, intent to lose weight, was measured as “Which of the following are you trying to do about your weight” (lose weight, gain weight, stay the same weight, I am not trying to do anything about my weight). For the main analyses, this question was dichotomized into (trying to lose weight, not trying to lose weight).
A healthy diet was measured by looking at vegetable intake, fruit intake, breakfast consumption, soda, and milk intake. Dichotomized versions were used for the variables fruit, soda, milk, and breakfast consumption (yes or no regarding 1 or more fruit per day during the past 7 days, 1 or more soda [not including diet soda] per day during the last 7 days, 1 or more glass of milk per day during the previous 7 days, eating breakfast on all 7 days before the survey).
We used two measures to assess physical activity: muscle strengthening (“During the past 7 days, on how many days did you exercise to strengthen or tone your muscles, such as push-ups, sit-ups, or weight lifting?”) and being physically active for 60 min per day (“During the past 7 days, on how many days were you physically active for a total of at least 60 min per day?”). Screen time was measured as time spent in front of a TV, computer, smartphone, or other electronic device watching shows or videos, playing games, accessing the Internet, or using social media on an average school day, not counting time spent doing schoolwork. This variable was dichotomized into spending 3 or more hours per day on screen time (yes, no). Sleep was dichotomized into getting 8 h or more of sleep on an average school night (yes, no). Alcohol use was dichotomized as drinking at least one drink on at least 1 day during the last 30 days before the survey (yes, no). Similarly, vaping was assessed as using electronic vapor products (including e-cigarettes, vapes, vape pens, e-cigars, e-hookahs, hookah pens, and mods) on at least 1 day during the 30 days before the survey. The BMI percentile was available in the YRBS data set and calculated using the 2000 CDC growth charts [].
Body size perception was derived from a question regarding how they view their weight (very underweight, slightly underweight, about the right weight, slightly overweight, very overweight) and comparing it to their BMI percentile (overweight/obese ≥ 85th BMI percentile). Body size perception was then categorized into underestimator (those who perceive themselves lighter than their actual weight), accurate estimator (their weight perception is close to their actual weight classification), and overestimator (their body weight perception is above their actual weight).
2.3. Data Analysis
All variables were weighted to adjust for nonresponse and oversampling. SPSS complex samples were used to account for the YRBS survey design and weighting. Logistic regression was used to assess the association between dietary variables, physical activity variables, sleep, screen time, alcohol intake, vaping, BMI percentile, and weight loss intent. The fit of the model was assessed by examining ROC curves (AUC = 0.78), which indicated a good fit and good discrimination between groups.
To assess whether associations differed among girls with good versus poor body perception, we conducted analyses stratified by body size perception.
SPSS v29 was used for all statistical analyses (IBM Corp. Released 2023. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 29.0.2.0 Armonk, NY, USA: IBM Corp). Statistical significance was determined at the 5% level (2-sided).
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
The mean BMI percentile among the girls in our sample was 64.2 (95% CI 62.4–65.9). In total, 55.5% (95% CI 53.6–57.4) wanted to lose weight. This intent was the highest among girls of Hispanic (66.3%) or multiple-Hispanic descent (59.9%) and lowest among girls of Asian descent (50.5%) or ‘Other’ descent (50.0%) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of adolescent girls by weight loss intent status (2021 YRBS).
3.2. Weight Loss Intent and Lifestyle Behaviors
Results from the weighted logistic regression models are presented in Table 2 and were adjusted for race/ethnicity, grade level, BMI percentile, vegetable consumption, muscle strengthening, sleep, screen time, alcohol intake, and vaping. Girls trying to lose weight were more likely to report engaging in muscle-strengthening exercises (OR 1.30, 95% CI 1.07–1.57), spending 3 h or more per day using screens (OR 1.27; 1.02–1.58), drinking alcohol (OR 1.61; 1.32–1.98), and vaping (OR 1.22; 1.01–1.47). Girls trying to lose weight were less likely to report eating breakfast daily (OR 0.52; 0.40–0.69), eating other vegetables (not including potatoes, salad, or carrots) (OR 0.78; 0.67–0.90), and getting 8 h of sleep (OR 0.72; 0.59–0.89) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Adjusted odds ratios for lifestyle behaviors associated with weight loss intent among adolescent girls (2021 YRBS).
3.3. Weight Loss Intent and BMI
A large proportion of girls within the normal weight category indicated an intent to lose weight despite being within the normal BMI percentile (43.4%). The intent to lose weight was the highest among obese girls (87.8%). (Figure 1) As previously shown in Table 1, Hispanic and multiple-Hispanic girls were more likely to want to lose weight when considering the entire sample of girls. When considering girls within normal weight only, this body size dissatisfaction was the largest among white girls and girls of Asian descent (47.5% and 45.7%, respectively).
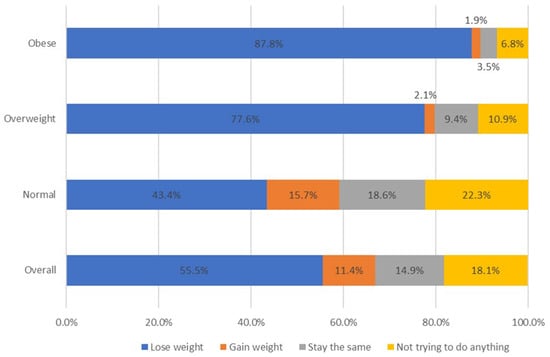
Figure 1.
Proportion of adolescent girls reporting weight loss intent by BMI percentile categories (Normal Weight, Overweight, Obese) in the 2021 YRBS Survey: BMI, Body Mass Index. Normal weight BMI% < 85, overweight BMI% 85–<95, obese BMI% ≥ 95.
4. Discussion
This study examined the associations between sleep, screen time, physical activity, dietary-related variables, alcohol, vaping, and weight loss intent among adolescent girls. The relationship between BMI percentile and weight loss intent is also described. We found that girls intending to lose weight were associated with several unhealthy lifestyle behaviors. Girls intending to lose weight were more likely to report skipping breakfast, more screen time, and less sleep. Furthermore, a weight loss intent was associated with a higher consumption of alcohol and vaping use. The only healthy lifestyle behavior associated with weight loss intent was muscle-strengthening exercises. Due to the cross-sectional nature of the data, we cannot know if girls engaging in these unhealthy lifestyle activities are more likely to develop an intent to lose weight or if girls intending to lose weight are more likely to develop listed unhealthy lifestyle habits. Lastly, we found that weight-loss intent was most common among obese girls. However, many girls within a normal BMI range also reported an intent to lose weight.
4.1. Physical Activity
There were no differences in following the PA recommendation of 60 min. per day among the groups. Our results show that girls trying to lose weight were more likely to do strength training 1–3 times per week. These results were similar to data from the 2017 YRBS []. Engaging in muscle-strengthening activities can increase body weight, making it harder to fit the slim female ideal often seen in the media. Therefore, it is possible that girls who engage in strength training do so with the intention of losing weight, rather than the training itself leading to weight loss.
Physical activity can help regulate body weight [] and dramatically lower the risk of many chronic illnesses []. Promoting increased physical activity levels could improve health in all adolescents regardless of weight loss intent. Conversely, the correlation between weight loss intent and muscle-strengthening exercise should be studied further to identify potential needs to improve body image among girls in sports. Low energy availability is highly prevalent among female athletes, up to 90% in some sports like ballet []. It is crucial to ensure proper food intake in these girls because under-fueling in sports can not only reduce sports performance but also impair immune function, bone health, cardiovascular health, and menstrual function [].
4.2. Diet
In the present study, those trying to lose weight were less likely to eat other vegetables than those who were not trying to lose weight. Other vegetables refer to any vegetable, excluding potatoes, carrots, and salad greens. The YRBS survey only includes questions on the frequency of consumption of fruits and vegetables, and it does not specify the amounts. Although we did not see any significant differences in the consumption frequency of fruits and vegetables, aside from other vegetables, we could not explore a difference in the portion sizes of fruits and vegetables consumed.
Intervention studies targeting increased vegetable intake in this group can improve eating behaviors. However, as previously stated, the frequency of fruit and vegetable intake was low across this population, indicating that both groups of girls would benefit from increasing fruit and vegetable consumption. Adolescents have limited freedom to choose their diet as they follow their family’s eating habits and grocery shopping. In this context, school cafeterias could play a pivotal role in offering healthier options to provide opportunities to increase intake.
Our results indicate that skipping breakfast was correlated with a desire to lose weight, confirming results from a previous study []. Skipping breakfast has also been positively associated with obesity [] and negative body image [] in girls. The association between breakfast and weight can also be attributed to other factors, such as sleep deprivation. According to data from Project EAT (Eating and Activity in Teens and Young Adults) [], those who went to bed after 12:30 a.m. were more likely to skip breakfast.
A crossover study using block randomization of breakfast type in children showed that low-glycemic index foods eaten at breakfast had a significant impact on food intake at lunch []. Consuming breakfast increases satiety and contributes to higher fiber intake in adolescent girls []. Common barriers expressed by adolescents to have breakfast are lack of time and not being hungry []. This could be associated with eating late, which is usually associated with being awake late at night. Early school start times are also a likely contributor to poor breakfast habits and delaying school start time has been shown to improve breakfast consumption among highschoolers []. Insufficient sleep changes melatonin levels that in turn affects energy homeostasis related to the melanocortin system in the hypothalamus []. Additionally, sleeping duration regulates ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates appetite and feeding behavior [].
Given the health consequences of skipping breakfast, providing adolescents with strategies to incorporate breakfast in their daily routine is paramount. An environment conducive to healthy food choices is key to implementing effective behavioral changes. An example is to provide incentives for participation in the school breakfast program, offering high-quality nutrients and breakfast options that are low in saturated fat and sugar. Education is only one aspect of health promotion. A more comprehensive approach needs to be applied to change health behaviors.
4.3. Sleep and Screen Time
Sleep is another lifestyle factor affecting body weight. Adolescents are chronically sleep-deprived []. The percentage of high school students who do not get enough sleep is higher among girls (80%) []. Regularly sleeping fewer than the recommended hours is associated with attention, behavior, and learning problems []. In the present study, girls trying to lose weight were less likely to sleep 8 h or more. Lack of sleep in adolescents affects their cognitive functioning and mental health. A recent review on sleep deprivation reported associations between sleepiness and subjective perception of depression, anxiety, and antisocial behavior []. Improvements in sleep need to be addressed in all adolescents, but specific strategies could be tailored to girls trying to lose weight.
Screen time also affects sleep []. The percentage of girls spending more than 3 h on screen time was high overall, and it was higher in those girls who intend to lose weight (81%) versus those who do not (75%). These results are consistent with reported data on screen time and body weight dissatisfaction [], and girls who want to lose weight are more likely to spend more than 3 h per day using screens (not counting school work). Consistently, girls with higher than median screen time over a two-year period rated their body image lower than girls with below median screen time screen []. These studies showed the negative role of screen time on body image. The association between screen time and suicidality was 4.67% mediated by overweight/obesity (observed only in female adolescents) and 9.66% mediated by self-perceived overweight (both male and females) []. There is likely a bidirectional association between screen time and weight loss intent. Reducing social media use has been shown to improve body satisfaction in adolescents []. Therefore, limiting screen time in girls may be highly important to improve mental health and body image. A 7-month school-based intervention using social cognitive theory reduced screen time in overweight and obese adolescent girls []. Results from a meta-analysis showed that interventions targeting screen time are effective in reducing total screen time and television time in children and adolescents []. Hence, the implementation of these interventions in this group of girls is possible and warranted.
4.4. Vaping and Alcohol Use
Preventing primary use in teens and young adults is the most important step that can be taken to reduce the long-term complications of nicotine exposure []. In the present analysis, girls who intend to lose weight are more likely to vape. Consistent with our results, Mohapatra et al. reported in their recent systematic review that the high rates of vaping seemed to correlate with increased weight concerns, particularly among females. Girls facing body image pressures may see vaping as a weight loss or weight control strategy [].
Alcohol intake was higher in females intending to lose weight in this sample. These results are consistent with those from the COMPASS, which is a longitudinal cohort study of secondary school students (Grades 9–12) in Canada []. Restrictive eating behavior has also been associated with binge drinking [], suggesting that girls intending to lose weight may be more prone alcohol consumption. Risky behaviors, such as vaping and drinking alcohol, may be used as coping mechanisms []. Therefore, this group may benefit from increased support from school counselors to address mental health and prevent addictive behaviors.
Overall, vaping and alcohol are public health issues that need to be addressed in youth and understanding motivation can help to better target prevention strategies. Existing campaigns, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) Real Cost Campaign [], have been shown to influence youth beliefs related to vaping and can be useful tools to help students avoid or quit vaping []. Tackling one of the potential factors triggering these addictive behaviors can be a cost-effective measure. Thus, offering programs targeting girls promoting healthier strategies to manage and accept their body weight is an appropriate preventative measure.
4.5. BMI and Weight Loss Intent
Despite having a normal BMI, more than half of these girls are actively trying to change their weight—revealing a significant degree of body image dissatisfaction. Notably, 43% are attempting to lose weight, while 16% are striving to gain weight.
This corresponds well with previous years of YRBS. Approximately 80% of the girls within BMI of 85–95% intend to lose weight in our sample; this is consistent with another representative sample of American adolescents where 86.9% of the ones in the overweight category reported that they intend to lose weight [].
Culture impacts body image perception. Additionally, the immediate environment, such as family and friends, plays a role in how adolescents perceive themselves. A recent study reported that frequent negative familial weight talk was associated with higher weight bias internalization across gender in non-Hispanic White 10–15-year-old children living in MA []. In the present analysis, weight loss intent was the highest among white girls and girls of Asian descent. Similarly, according to data from The Ningbo Youth Risk Behavior Survey, self-perception of overweight and obesity was positively associated with lower-calorie diets and increased levels of PA in Chinese adolescents []. This information can be used to specifically target more vulnerable girls and develop culturally appropriate programs for these groups.
4.6. Limitations
The general limitations of the 2021 YRBS survey were previously reported []. Limitations specific to this study are outlined below. Given the cross-sectional nature of the YRBS, it is impossible to determine the temporal directionality of associations or assess the directionality of correlations. Future studies should use a longitudinal design to establish cause-and-effect relationships. Nevertheless, cross-sectional research can help identify subpopulations that may be more vulnerable and help provide targeted interventions. As mentioned earlier, the YRBS survey includes questions on the frequency of food consumption, not specific amounts. This limited our analyses and we were unable to assess portion sizes. All questions in YRBS were assessed through self-reports, which can lead to overestimation or underestimation of the variables measured. The 2021 survey was conducted during COVID-19, which may have influenced dietary behaviors and access to food. Despite any limitations COVID-19 might have introduced, it will be useful to have these results recorded in the literature so comparisons can be made as future versions of the YRBS are administered.
5. Conclusions
School interventions may focus on offering healthier lunch options and providing breakfast programs, emphasizing high-quality nutrients that can enhance eating habits among all youth. Parents and caregivers should limit screen time to promote better sleep patterns, improve mental health, and foster positive body image. Programs designed to prevent substance abuse among youth should specifically target girls who are attempting to lose weight, as they are at a higher risk.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.F., M.C.C., J.V. and A.J.P.; methodology and formal analysis, E.F.; writing—original draft preparation, E.F. and M.C.C.; writing—review and editing, M.C.C., A.J.P. and J.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The YRBS was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Worcester State University 2425-0001, 7 October 2024.
Informed Consent Statement
As this study involved secondary analysis of existing data, the requirement for informed consent was waived.
Data Availability Statement
The data can be downloaded from https://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/data/yrbs/data.htm/, accessed on 11 May 2025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| YRBS | Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
References
- Stierman, B.; Afful, J.; Carroll, M.D.; Chen, T.-C.; Davy, O.; Fink, S.; Fryar, C.D.; Gu, Q.; Hales, C.M.; Hughes, J.P.; et al. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017-March 2020 Prepandemic Data Files-Development of Files and Prevalence Estimates for Selected Health Outcomes. Natl. Health Stat. Rep. 2021, 158, 15610–15620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, M.C.; Andersen, C.J. Assessment of Dietary Patterns Represents a Potential, Yet Variable, Measure of Inflammatory Status: A Review and Update. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 3102870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, M.; Llewellyn, A.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Predicting Adult Obesity from Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toselli, S.; Zaccagni, L.; Rinaldo, N.; Mauro, M.; Grigoletto, A.; Maietta Latessa, P.; Marini, S. Body Image Perception in High School Students: The Relationship with Gender, Weight Status, and Physical Activity. Children 2023, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, M.C.S.; Assumpção, D.D.; Barros, M.B.D.A.; Mattei, J.; Barros Filho, A.D.A. Prevalence of Body Weight Dissatisfaction among Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2023, 41, e2021204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wharton, C.M.; Adams, T.; Hampl, J.S. Weight Loss Practices and Body Weight Perceptions Among US College Students. J. Am. Coll. Health 2008, 56, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualdi-Russo, E.; Rinaldo, N.; Zaccagni, L. Physical Activity and Body Image Perception in Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piercy, K.L.; Troiano, R.P.; Ballard, R.M.; Carlson, S.A.; Fulton, J.E.; Galuska, D.A.; George, S.M.; Olson, R.D. The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. JAMA 2018, 320, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, S.L.; Jones, S.E.; Merlo, C.L.; Sliwa, S.A.; Lee, S.M.; Cornett, K.; Brener, N.D.; Chen, T.J.; Ashley, C.L.; Park, S. Dietary and Physical Activity Behaviors in 2021 and Changes from 2019 to 2021 Among High School Students—Youth Risk Behavior Survey, United States, 2021. MMWR Suppl. 2023, 72, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Food and Nutrition Service, Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion. Average Healthy Eating Index-2020 Scores for the U.S. Population—Total Ages 2 and Older and by Age Groups, WWEIA, NHANES 2017–2018; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Food and Nutrition Service: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2023.
- Paruthi, S.; Brooks, L.J.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Hall, W.A.; Kotagal, S.; Lloyd, R.M.; Malow, B.A.; Maski, K.; Nichols, C.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Consensus Statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine on the Recommended Amount of Sleep for Healthy Children: Methodology and Discussion. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 1549–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, L.; Guan, S. Screen Time and Sleep among School-Aged Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Literature Review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2015, 21, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.D.; Linkersdörfer, J.; Toda-Thorne, K.; Sullivan, R.M.; Cummins, K.M.; Tomko, R.L.; Allen, N.B.; Bagot, K.S.; Baker, F.C.; Fuemmeler, B.F.; et al. Passively Sensing Smartphone Use in Teens with Rates of Use by Sex and across Operating Systems. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Youth Risk Behavior Survey Data Summary & Trends Report for Dietary. Physical Activity, and Sleep Behaviors: 2013–2023; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2024.
- Fatima, Y.; Doi, S.A.R.; Mamun, A.A. Sleep Quality and Obesity in Young Subjects: A Meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, D.L.; Kass, A.P.; Chiel, L.E.; Boyer, E.W.; Casey, A.M.H. A Review of Toxic Effects of Electronic Cigarettes/Vaping in Adolescents and Young Adults. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miech, R.A.; Johnston, L.D.; Patrick, M.E.; O’Malley, P.M.; Bachman, J.G.; Schulenberg, J.E. Monitoring the Future National Survey Results on Drug Use, 1975–2022: Secondary School Students; Monitoring the Future Monograph Series; University of Michigan, Institute for Social Research: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie, R.P.; Lutsey, P.L.; Widome, R.; Laska, M.N.; Larson, N.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Sleep Indices and Eating Behaviours in Young Adults: Findings from Project EAT. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 21, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, J.M.; Weinstein, S.; Alsamman, S.; Lee, C.M.; Dooley, E.E.; Ganson, K.T.; Testa, A.; Gooding, H.C.; Kiss, O.; Baker, F.C.; et al. Association of Physical Activity and Screen Time with Cardiovascular Disease Risk in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.; Ranjit, N.; Kelder, S.H.; Gill, M.; Hoelscher, D.M. Intention to Lose Weight and Use of Electronic Cigarettes among Adolescents. Prev. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, K.M.; Patte, K.A.; Leatherdale, S.T. Examining Predictors of Breakfast Skipping and Breakfast Program Use Among Secondary School Students in the COMPASS Study. J. Sch. Health 2018, 88, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.D. Energy Balance-Related Factors Associating with Adolescent Weight Loss Intent: Evidence from the 2017 National Youth Risk Behavior Survey. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordeleau, M.; Gilbert, J.-A.; Alméras, N.; Monthuy-Blanc, J.; Gagnon, J.; Mathieu, M.-È.; Drapeau, V. Body Image and Health-Related Behaviors among Fitspirit Participants. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpofu, J.J.; Underwood, J.M.; Thornton, J.E.; Brener, N.D.; Rico, A.; Kilmer, G.; Harris, W.A.; Leon-Nguyen, M.; Chyen, D.; Lim, C.; et al. Overview and Methods for the Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System—United States, 2021. MMWR Suppl. 2023, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brener, N.; Kann, L.; Mcmanus, T.; Kinchen, S.; Sundberg, E.; Ross, J. Reliability of the 1999 Youth Risk Behavior Survey Questionnaire. J. Adolesc. Health 2002, 31, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczmarski, R.J.; Ogden, C.L.; Guo, S.S.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M.; Flegal, K.M.; Mei, Z.; Wei, R.; Curtin, L.R.; Roche, A.F.; Johnson, C.L. 2000 CDC Growth Charts for the United States: Methods and Development. Vital Health Stat. 11 2002, 246, 1–190. [Google Scholar]
- Chaput, J.-P.; Klingenberg, L.; Rosenkilde, M.; Gilbert, J.-A.; Tremblay, A.; Sjödin, A. Physical Activity Plays an Important Role in Body Weight Regulation. J. Obes. 2011, 2011, 360257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.; Durstine, J.L. Physical Activity, Exercise, and Chronic Diseases: A Brief Review. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2019, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagim, A.R.; Fields, J.; Magee, M.K.; Kerksick, C.M.; Jones, M.T. Contributing Factors to Low Energy Availability in Female Athletes: A Narrative Review of Energy Availability, Training Demands, Nutrition Barriers, Body Image, and Disordered Eating. Nutrients 2022, 14, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Niu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Duo, B.; Effah, C.Y.; Guan, L. The Effect of Breakfast on Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1222536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ayed, H.; Yaich, S.; Ben Jemaa, M.; Ben Hmida, M.; Trigui, M.; Jedidi, J.; Sboui, I.; Karray, R.; Feki, H.; Mejdoub, Y.; et al. What Are the Correlates of Body Image Distortion and Dissatisfaction among School-Adolescents? Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2021, 33, 20180279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.M.; Henry, C.J.K.; Simonite, V. Low Glycemic Index Breakfasts and Reduced Food Intake in Preadolescent Children. Pediatrics 2003, 112, e414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewski-Fruer, J.K.; Seall, C.; Tolfrey, K. Breakfast Consumption Suppresses Appetite but Does Not Increase Daily Energy Intake or Physical Activity Energy Expenditure When Compared with Breakfast Omission in Adolescent Girls Who Habitually Skip Breakfast: A 7-Day Randomised Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widome, R.; Erickson, D.J.; Laska, M.N.; Berger, A.T.; Lenk, K.M.; Iber, C.; Kilian, G.; Lammert, S.; Wahlstrom, K.L. Impact of Delaying High School Start Times on Weight and Related Behaviors—The START Study. Prev. Med. 2023, 172, 107548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahluwalia, M.K. Chrononutrition—When We Eat Is of the Essence in Tackling Obesity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovetkina, A.; Nadir, R.; Fung, J.N.M.; Nadjarpour, A.; Beddoe, B. The Physiological Role of Ghrelin in the Regulation of Energy and Glucose Homeostasis. Cureus 2020, 12, e7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J.; Adolescent Sleep Working Group; Committee on Adolescence; Au, R.; Carskadon, M.; Millman, R.; Wolfson, A.; Braverman, P.K.; Adelman, W.P.; Breuner, C.C.; et al. Insufficient Sleep in Adolescents and Young Adults: An Update on Causes and Consequences. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e921–e932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson-Urbain, W.; Servot, S.; Godbout, R.; Montplaisir, J.-Y.; Touchette, E. La somnolence chez les adolescents: Étiologie et conséquences multiples. L’Encéphale 2023, 49, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priftis, N.; Panagiotakos, D. Screen Time and Its Health Consequences in Children and Adolescents. Children 2023, 10, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrafnkelsdottir, S.M.; Brychta, R.J.; Rognvaldsdottir, V.; Chen, K.Y.; Johannsson, E.; Guðmundsdottir, S.L.; Arngrimsson, S.A. Screen Time and Body Image in Icelandic Adolescents: Sex-Specific Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, M. Mediation of the Association between Screen Time and Suicidality by Overweight/Obesity and Perceived Overweight: Results from the Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System of the United States. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1287021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, H.; Davis, C.G.; Mahboob, W.; Perry, S.; Adams, A.; Goldfield, G.S. Reducing Social Media Use Improves Appearance and Weight Esteem in Youth with Emotional Distress. Psychol. Pop. Media 2024, 13, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherniya, M.; Mostafavi Darani, F.; Sharma, M.; Maracy, M.R.; Allipour Birgani, R.; Ranjbar, G.; Taghipour, A.; Safraian, M.; Keshavarz, S.A. Assessment of the Efficacy of Physical Activity Level and Lifestyle Behavior Interventions Applying Social Cognitive Theory for Overweight and Obese Girl Adolescents. J. Res. Health Sci. 2018, 18, e00409. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Tang, X.; Peng, X.; Hao, G.; Luo, S.; Liang, X. Effect of Screen Time Intervention on Obesity among Children and Adolescent: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies. Prev. Med. 2022, 157, 107014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohapatra, S.; Wisidagama, S.; Schifano, F. Exploring Vaping Patterns and Weight Management-Related Concerns among Adolescents and Young Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patte, K.A.; Leatherdale, S.T. A Cross-Sectional Analysis Examining the Association between Dieting Behaviours and Alcohol Use among Secondary School Students in the COMPASS Study. J. Public Health 2016, 39, fdw034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leatherdale, S.T. An Examination of the Co-Occurrence of Modifiable Risk Factors Associated with Chronic Disease among Youth in the COMPASS Study. Cancer Causes Control 2015, 26, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, K.E.; Connell, A.M. The Role of Substance Use Coping in Linking Depression and Alcohol Use from Late Adolescence through Early Adulthood. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2021, 29, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, S.; Mahoney, C.; Murray, M.P.; Benoza, G. “The Real Cost”: Reaching At-Risk Youth in a Fragmented Media Environment. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 56, S49–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMonegle, A.; Bennett, M.; Speer, J.L.; O’Brien, E.K.; Pitzer, L.; Jaarsma, A.; Nguyen Zarndt, A.; Duke, J. Evaluating the Real Cost Digital and Social Media Campaign: Longitudinal Effects of Campaign Exposure on E-Cigarette Beliefs. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2024, 26, S19–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinami, L.; Houle-Johnson, S.A.; Demissie, Z.; Santosa, S.; Fulton, J.E. Meeting Fruit and Vegetable Consumption and Physical Activity Recommendations among Adolescents Intending to Lose Weight. Prev. Med. Rep. 2019, 13, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancaño, K.M.; Puhl, R.; Skeer, M.; Eliasziw, M.; Must, A. Negative Familial Weight Talk and Weight Bias Internalization in a US Sample of Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2024, 19, e13108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Wu, Z.; Liang, J. Secular Trends in the Prevalence of Meeting 24-Hour Movement Guidelines among U.S. Adolescents: Evidence from NHANES 2007–2016. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1362718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).