Abstract
High- and very high-resolution (HR, VHR) remote sensing (RS) images can provide comprehensive and intricate spatial information for land cover classification, which is particularly crucial when analyzing complex built-up environments. However, the application of HR and VHR images to large-scale and detailed land cover mapping is always constrained by the intricacy of land cover classification models, the exorbitant cost of collecting training samples, and geographical changes or acquisition conditions. To overcome this limitation, we propose an unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) with contrastive learning-based discriminative feature augmentation (CLDFA) for RS image classification. In detail, our method first utilizes contrastive learning (CL) through a memory bank in order to memorize sample features and improve model performance, where the approach employs an end-to-end Siamese network and incorporates dynamic pseudo-label assignment and class-balancing strategies for adaptive domain joint learning. By transferring classification models trained on a source domain (SD) to an unlabeled target domain (TD), our proposed UDA method enables large-scale land cover mapping. We conducted experiments using a massive five billion-pixels dataset as the SD and tested the HR and VHR RS images of five typical Chinese cities as the TD and applied the method on the completely unlabeled world view 3 (WV3) image of Urumqi city. The experimental results demonstrate that our method excels in large-scale HR and VHR RS image classification tasks, highlighting the advantages of semantic segmentation based on end-to-end deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs).
1. Introduction
With the rapid advancement of remote sensing (RS) technology, high- and very high-resolution (HR, VHR) RS images have emerged as a rich source of spatial information, offering comprehensive and detailed evidence for land cover classification. Consequently, the processing and the learning of RS image information have garnered significant attention in the realm of intelligent interpretation [1]. As a viable scheme for RS image interpretation, the essence of spectral image classification lies in categorizing individual pixels within an image into distinct classes based on predefined rules or algorithms, utilizing spectral brightness, spatial structural features, or other pertinent information extracted from various spectral bands [2]. RS image classification techniques are widely applied in various fields such as land use/land cover map updating [3,4], agricultural monitoring [5,6], forest resource monitoring [7,8], natural disaster assessment [9,10], urban planning and management [11,12], and environmental and hydrological monitoring [13,14].
In the early stages of land use/land cover applications, RS image classification has primarily focused on classification and recognition based on pixel or object–spatial units. However, due to the complex structures and patterns present in HR and VHR images, the application of HR and VHR images in large-scale land cover classification has been limited [15]. In the past decade, deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) have emerged as a solution which offers higher efficiency and better feature representation capabilities when compared with traditional classification methods. However, most DCNNs, as well as their variants, rely heavily on the volume and quality of training data, which in turn affects the model’s generalizability [16]. To overcome these challenges, numerous densely labeled land cover datasets, with spatial resolutions ranging from sub-meter to meter (0.05–10 m), have been released, such as ISPRS Potsdam and ISPRS Vaihingen [17], Zurich Summer [18], RIT-18 [19], and Zeebruges [20]. Conversely, existing large-scale datasets, encompassing coverage areas exceeding 1000 km2 and featuring wide geographical distributions, typically provide annotations for only about 10 classes. Moreover, these datasets lack the inclusion of detailed urban functional categories, which are crucial for comprehensive land cover analysis. Noteworthy examples of such large-scale datasets include SpaceNet [21], DeepGlobe [22], MiniFrance [23], Gaofen Image Dataset (GID) [24], and LandCoverNet [25]. However, the current existing large-scale datasets are limited in terms of the number of categories. For instance, while some datasets have sufficient volume and data diversity, their incomplete land cover category systems prevent them from fully bridging the gap between algorithmic research and practical applications. To address the data dependency issue, the current widely used methods utilize domain adaptation (DA) techniques. In general, DA involves joint training using data from both source and target domains, allowing the transfer of rich knowledge from the source domain (SD) to serve the target domain (TD), thereby addressing the limited categories or insufficient data volume in classification tasks. Its core feature lies in the ability to utilize related but differently classified SD data to supplement the TD data, resulting in more comprehensive and reliable classification results for the target application, better meeting practical application requirements. Furthermore, DA is extensively employed as a means by which to address the issue of model performance degradation or failure arising from dissimilar distributions of characteristics between the SD and TD. When tackling cross-domain problems, the DA method proves advantageous by effectively acquiring invariant image structure and content information between the SD and TD, as opposed to training the TD model directly using labeled data from the SD. This approach enables the acquisition of more resilient and broadly applicable deep feature representations.
This paper proposes an unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) with contrastive learning (CL)-based discriminative feature augmentation (CLDFA) for RS image classification. In detail, the method employs CL within a Siamese network framework to enhance feature representation capabilities. The key innovations of this method are as follows: (1) CL-based discriminative feature augmentation effectively improves the feature representation capability of the model; (2) by joining the memory bank one can effectively store and use the features of previous learning to achieve better generalizability; (3) use of a dynamic pseudo-label strategy and an end-to-end DCNN allows one to fully mine image semantic information so as to achieve high-quality cross-domain remote sensing image classification. The proposed method, with its focus on CL and memory bank behavior, aims to overcome the limitations of previous approaches. Experimental results demonstrate the excellent performance of this method in the task at hand. It effectively alleviates the generalization challenges under static labels through sample CL, thereby improving the accuracy and consistency of prediction results. It has important significance for solving cross-domain problems in large-scale HR and VHR image classification tasks.
2. Related Works
2.1. DCNNs for RS Image Classification
In recent years, DCNNs have been widely applied and extensively studied in RS image classification tasks [26]. Early researchers have focused on designing classical DCNN architectures and establishing a series of benchmark datasets as the foundation for subsequent algorithm evaluations [27,28]. However, due to the data dependency of DCNN labels, many DCNN-based classification methods have struggled to adapt to real-world applications [29]. Subsequently, researchers from both domestic and international domains have explored various methods by which to optimize the DCNN model itself. Representative works include the introduction of global attention mechanisms to enhance feature representation capabilities [30,31], the design of multi-resolution fusion allows for the achievement of fine-grained integration [32,33] and alleviates the dependency on annotated data while improving classification performance.
However, the cross-domain applicability of DCNN models remains a major challenge. To overcome this challenge, some early researchers designed different DCNNs based on adversarial learning to reduce the differences between the SD and TD and enhance the transfer learning capability of DCNNs in new tasks [34,35]. Current research has primarily focused on exploring deep-feature mining in DCNNs. For instance, spatial attention mechanisms are employed to enhance the multi-scale semantic extraction capability of DCNNs, further improving classification accuracy [36,37]. As DCNN architectures continue to evolve, optimizing various details gradually elevates their application effectiveness to new heights. Consequently, DCNNs have become the preferred tool for RS image classification and analysis.
2.2. UDA for RS Image Classification
DA involves the process of adapting models across domains in order to develop machine learning models capable of generalizing to the TD and effectively handling distribution discrepancies between domains [38]. In comparison with supervised and semi-supervised DA approaches, UDA eliminates the need to label the target sample set. This eliminates the costs associated with data labeling and substantially enhances learning performance in various applications [39]. UDA techniques have become important tools for cross-domain classification of RS images. Traditional transfer learning (TL) methods face challenges when dealing with partially labeled TD, limiting their applicability in RS tasks. As a special case of TL, UDA focuses on eliminating domain differences within the realm of unsupervised learning [40]. Early works have primarily adopted statistical methods, such as the maximum mean discrepancy (MMD), to match the feature distributions between the SD and TD [41]. However, these methods overlook the complex and deep semantic features present in image content. Subsequently, researchers began utilizing adversarial learning to generate similar distributions, adjusting the feature distributions of the SD and TD to achieve consistency [42]. This idea is widely used in various UDA classification networks.
Owing to its proven superior performance when handling the domain shift problem, UDA methods have also been widely used in RS image classification tasks. Different from conventional images, RS images are affected by factors such as illumination conditions, observation angles and different sensors, and the classification target is usually a subcategory set of geological class rather than a simple annotation, which puts forward higher requirements for the generalizability of a UDA model. Therefore, some studies based on UDA have begun to try to use DCNNs to extract multi-scale semantic features, so that richer visual information can be used to better align the features of the SD and the TD [43,44].
However, as RS image classification increasingly focuses on HR and VHR images as well as multi-sensor data, relying solely on distribution alignment is insufficient to meet the demands of RS image classification. Subsequent works have begun utilizing deep structures, such as convolutional autoencoders to extract multi-level image patterns [45,46], and employing techniques like joint classification based on pseudo-labels to provide richer feature representation support for UDA classification [47,48].
2.3. CL in RS Image Processing
CL has emerged as a hot topic in the field of machine learning in recent years and has also gained attention in the domain of RS image processing. Its fundamental idea is to learn the intrinsic structure and features of the data by comparing the differences between data samples [49].
Acquiring samples for RS image classification can present difficulties, with category sample distributions often exhibiting imbalance. This necessitates the optimization of limited sample information during model training. CL has shown promise in addressing such challenges through skillful utilization of relational information between samples [50,51]. Specifically, CL constructs relative representations that encode the affinity between embedded samples within a joint embedding space [52]. This enables effective demarcation of classification boundaries even under limited supervised signals. When applied to RS tasks, CL techniques have been shown to outperform traditional supervised approaches, achieving comparable or improved results using smaller labeled datasets [53,54].
Additionally, category boundaries in RS images are frequently indistinct and blurred. Relying solely on label information makes efficient classification difficult. Through the augmentation of differences between samples, CL can more clearly define classification criteria, facilitating the learning of characteristic features in challenging samples. This is highly significant for RS image classification [55,56].
Furthermore, RS images are prone to concept drift across differing time periods and locations [57]. However, CL emphasizes relative relationships between samples and is less susceptible to concept drift effects. This confers superior generalization abilities in scenarios where RS image polymorphism is pronounced.
In this study, the CL method was introduced to bolster the model’s feature representation capacity and enhance classification performance and generalization by leveraging CL’s strengths in constructing sample relative relations.
3. Method
To address the limited generalizability of deep models across diverse data domains and meet the demands of large-scale land cover classification using HR and VHR RS images, this study presents a novel UDA approach. The proposed methodology leverages CL to enhance feature representation capabilities and employs DA to learn the distribution of unlabeled data and mitigate domain shifts. In this section, we provide an overview of the CLDFA framework, followed by a detailed exposition of its key constituents: the Siamese network, the memory bank, and the dynamic pseudo-label assignment mechanism.
3.1. Network Structure
As a hybrid RS image classification model combining the memory bank [58] and UNet [59], CLDFA follows the well-established framework of UNet. The UNet architecture specifically incorporates skip connections between corresponding encoding and decoding stages through feature maps, thus preserving more original information from the input images and integrating it into the decoding process. This design approach helps compensate for information loss in the encoding path, which is crucial for satellite image classification that heavily relies on spectral information.
The overall framework of the CLDFA method is illustrated in Figure 1. The CLDFA method incorporates three key modules: the Siamese network, memory bank, and dynamic pseudo-label assignment. By employing a Siamese network, the CLDFA method aims to collect more reliable pseudo-labels. The Siamese network architecture consists of branch networks that generate feature maps for TD images. These feature maps capture essential visual information and serve as a foundation for subsequent processing stages. The Siamese network enables the CLDFA method to calculate a joint classification loss, which is weighted by pixel order of magnitude by the combination of the pseudo-label and the ground truth (GT) from SD. This approach helps mitigate the issues associated with inaccurate pseudo-labels and prevents the model from being overly influenced by easily classified samples. The memory bank serves as a repository for accumulating knowledge about the visual characteristics of different classes over time. By leveraging the stored features during the classification phase, the model can make more informed predictions. The memory bank enhances the model’s ability to distinguish between different features and contributes to improved classification accuracy. The dynamic pseudo-label assignment addresses the dynamic nature of the target domain and the need for accurate pseudo-labels. This component assigns pseudo-labels to high-confidence pixels within the TD image based on their feature similarity to the SD image.
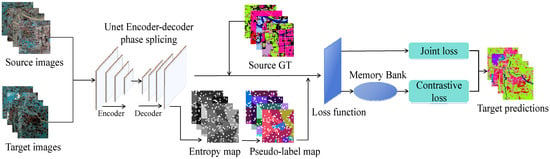
Figure 1.
Approach workflow for CLDFA.
3.2. Siamese Network
To enable DA in DCNNs, capturing the feature distribution of the TD is essential. In this study, the CLDFA method is employed, which utilizes pseudo-labeling to adapt the model through the collection of reliable pixel-level samples from the TD. Compared with difference-based and adversarial-based DA methods, the pseudo-labeling approach does not require explicit alignment of the feature spaces between the SD and TD, allowing for greater flexibility when addressing the complexities of real-world scenarios. To avoid erroneous pseudo-labels and the misguidance of simple samples during the training process, CLDFA adopts a Siamese network [60] to collect pseudo-labels. The sample quantity dynamically increases with training iterations, and a joint classification loss is calculated, weighted by the combination of pseudo-labels and true values from the SD.
Due to the limited number of pseudo-labels during the initial iterative training, the sample quantity is small, raising concerns about the uniformity of sample selection. To ensure effective parameter updates throughout the training iterations, the two branches of the Siamese network share the same architecture and parameters, enabling the network to learn information from both distributions simultaneously.
3.3. Memory Bank
CL plays an increasingly significant role in visual representation learning. Memory banks, as an important CL technique, are widely applied in visual representation learning [58,61]. Memory bank is a queryable table structure that can store and manage the learned feature representations of a model. For each incoming sample, the model first extracts its feature representation, which is then stored in the memory bank. Through the memory bank, the model can compare the features of new incoming samples. It can retrieve the features of other samples stored in the memory bank and calculate the similarity between them and the current sample’s feature representation. This enables the comparison between samples and facilitates the learning of more distinctive and unique feature representations.
By memorizing the feature representations of training samples in the memory bank, the model can better separate the feature space of the samples. This helps enhance the model’s ability to extract and differentiate sample features, leading to improved self-supervised learning (SSL) outcomes.
3.4. Dynamic Pseudo-Label Assignment
Traditional methods for collecting pseudo-labels often rely on fixed sample proportions based on empirical thresholds. However, this approach can lead to erroneous pseudo-labels that misguide the training process, and the impact of such errors tends to worsen with training iterations. In this study, a different approach is adopted, one in which pseudo-labels are dynamically assigned to varying numbers of samples during different training periods. Shannon entropy [62] is employed to quantify pixel confidence, where the information entropy is inversely proportional to the classification confidence. The formula for calculating the information entropy of the TD is as follows:
where represents the value at pixel , denotes the total number of classes, and represents the feature mapping of the TD. The entropy map, , is sorted in ascending order, and the top pixels are selected. The calculation formula for is as follows:
where represents the current training epoch, denotes the total number of epochs, indicates the proportion of selected pixels to all pixels at the end of training, and can control the overall size of pseudo-labels. The initial value of is related to the scale and quality of the target data. For cities with large data volumes and high quality, the range can be larger, while for cities that are more difficult to classify, the initial value of can be smaller in order to control the number of selected samples. This strategy can avoid the negative impact on classification of selecting a large number of pseudo-labels when the error rate of the initial model may be relatively high. This design approach primarily addresses the initial limitation of the pseudo-label generation network in adapting to the TD, resulting in the generation of reliable pseudo-labels for only a small number of pixels. As the network gradually learns the distribution of the TD, it becomes capable of making reliable predictions for an increasing number of pixels.
The class probability vector of the pixel located at can be obtained by applying the softmax function, as follows:
In Formula (3), represents the feature vector of the pixel located at , and is the th element of the vector, indicating the likelihood of the pixel belonging to class . Based on this, the assignment of pseudo-labels can be determined as follows:
where .
3.5. Loss Function
This study employed a combined approach of joint classification loss with pseudo-labels and CL loss to optimize the model’s performance and to achieve better training results. The joint classification loss with pseudo-labels refers to the training of the model using pseudo-labels generated by the model itself in the absence of true labels. By minimizing this loss, the model learns how to better predict the class of samples. The CL loss aims to teach the model how to differentiate between different samples. By minimizing the CL loss, the model learns how to map similar samples to nearby feature space and different samples to distant feature space.
3.5.1. Joint Loss Function with Pseudo-Labels
We adopted a dynamic pseudo-label assignment strategy to mitigate distribution bias caused by class imbalance. We calculated the ratio between the number of pixels in each class in the SD dataset and the total number of labeled pixels. Let represent the ratio for class , and the weight for that class is set as follows:
Based on this, the loss function for the TD branch can be computed as follows:
where represents the cross-entropy loss function, denotes the pseudo-label of the th selected pixel from the SD dataset, and represents the class probability vector for that pixel. is calculated by applying class-balanced weighting to all SD pixels . The joint classification loss function for the Siamese network is given by the following:
3.5.2. Contrastive Loss
The CL loss in this study is computed using normalized temperature-scaled cross-entropy loss (NT-Xent). After storing the sample features in the memory bank, the cosine similarity between the current sample feature and all of the sample features in the memory bank is calculated. Based on the similarity, a probability distribution is computed, and then the CL loss is computed using the cross-entropy loss function, as follows:
where and represents the number of samples in a batch. Due to the computation of the dual-branch loss function of NT-Xent, there are samples in total, where and represent a positive pair, and the denominator represents the negative pairs. denotes the similarity between samples and and is the temperature parameter.
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Datasets
The experimental SD dataset used in this study is the five billion-pixels [63] HR land cover dataset. The five billion pixels dataset is a reorganized and expanded version of the previously constructed GID land cover dataset, aiming to bridge the gap between GID and practical application requirements. It consists of 150 HR multispectral images captured by the Chinese HR imaging satellite (GF-2). The images have a resolution of 6800 × 7200 pixels and a spatial resolution of 4 m. Benefiting from the HR and wide field of view of the GF-2 satellite, the five billion pixels dataset provides more detailed surface information.
The dataset was constructed through a carefully designed multi-round annotation process, with the category system adjusted according to national standards, ensuring fine-grained and rigorous annotation quality. Compared with GID, the five billion pixels dataset has significant advantages in terms of a more comprehensive and reasonable category system, wider coverage area, and broader distribution range. It provides robust data support for HR RS image understanding tasks.
The TD dataset used in this study follows the DPA [63] method and focuses on five representative mega-cities in China: Beijing, Chengdu, Guangzhou, Shanghai, and Wuhan. These cities exhibit variations in geographical location, climatic conditions, and urban development levels, reflecting the generalization performance of the classification method in diverse real-world scenarios. The sources, acquisition times, and quantities of the images for these five cities are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Information sheet on the RS images of five cities.
Due to the large area of the five target cities, it is difficult to carry out intensive global labeling. Therefore, two 1000 × 1000-pixel sub-regions of the target image of each city are selected for intensive labeling in order to facilitate later precision verification calculation. Sample city labels are shown in Figure 2.
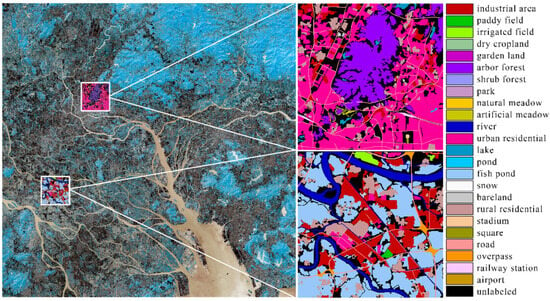
Figure 2.
Regional labels display of cities (taking Guangzhou as an example).
4.2. Implementation Details
4.2.1. Training Settings
The operating environment of this experiment is as follows: Ubuntu 22.04 system, i9-13900k CPU, NVIDIA RTX A6000 GPU, 128 GB RAM. The CLDFA method used in this experiment is implemented based on PyTorch 1.13.1. The model was trained using the Stochastic gradient descent (SGD) optimizer with a momentum term of 0.9 and weight decay factor of 1 × 10−5. This method improves upon the standard momentum approach by incorporating both momentum and Nesterov momentum for parameter updates during the optimization process. The initial learning rate was set to 0.005, and a poly decay strategy was employed.
During training, both the SD and the TD images were cropped into 1000 × 1000-pixel patches for batch input to the network. The experiments were conducted in an environment with eight data loader threads, and the batch size was set to four. The maximum number of training epochs was set to 120.
4.2.2. Evaluation Index
In addition to overall classification accuracy (OA), this study employed the mean intersection over union (MIoU) and average F1 score as evaluation metrics. The calculation of these two metrics is based on a confusion matrix. For each class, IOU is defined as the intersection over union ratio between the predicted values and the GT, as follows:
The F1 score for each class is computed as follows:
where MIoU represents the average IoU across all classes, while the average F1 score represents the average F1 score across all classes.
5. Results and Analysis
5.1. Classification Performance of CLDFA on Public Datasets
The experimental results section compares the CLDFA method proposed in this study with other mainstream UDA methods in terms of their differences and advantages from multiple perspectives. As shown in Table 2, the baseline method (DS-only), using only the SD for training, achieves the lowest performance across all three metrics, demonstrating the difficulty of achieving good cross-domain classification performance without DA. AdaptSeg [64] and CLAN [65], which align the feature space through adversarial learning, as well as AdvEnt [66] and FADA [67], which utilize pseudo-label learning and joint adversarial loss, improve the accuracy and IoU of the TD to some extent, with FADA, incorporating pseudo-labels, showing better results. The DPA method effectively alleviates the negative impact of label generalization difficulties by introducing a multi-objective dynamic pseudo-label assignment strategy. The CLDFA method, based on the DPA method, enhances feature representation capability through CL and introduces a memory bank to store sample features for effective classification and generalization. The experimental results demonstrate significant improvements of CLDFA over single-objective or static label methods in all evaluation metrics. In particular, it surpasses mainstream UDA methods by over 10 percentage points in terms of IoU, validating the advantages of dynamic multi-objective strategies and CL in UDA tasks.

Table 2.
Accuracy comparison of various mainstream UDA methods and the CLDFA method in the five cities.
The performance differences of the CLDFA method when classifying the five cities are closely related to the data collection and attribute characteristics of these urban images. The data presented in Table 3 indicate that CLDFA outperforms, in terms of classification accuracy, in Beijing, Chengdu, and Guangzhou. This can be attributed to the quality assurance of images in these three cities. Beijing utilizes homogenous and HR ST-2 imagery, which avoids the deep learning challenges associated with the fusing of multi-source images. Chengdu, despite using multi-temporal PS imagery, compensates for the limitations in image resolution with a large sample size. While Guangzhou has a smaller sample size, its higher data resolution and developed urban structure, which is relatively simpler, contribute to improved image quality and classification performance. In contrast, Shanghai and Wuhan utilize multi-source low-resolution imagery, coupled with the complex urban structure of these older industrial cities, making it challenging for deep learning to extract urban features. This, to some extent, increases the classification difficulty for CLDFA in these two cities.

Table 3.
Classification accuracy of the CLDFA method in the five cities.
Due to the significant scale of these cities, conducting global pixel-level annotations is challenging. Therefore, this study employed region-level annotations for validating the classification accuracy. Figure 3 displays the classification results and GT for selected regions in the five cities, columns a to c correspond to original image, predicted result and GT value, rows I to V correspond to Beijing, Chengdu, Guangzhou, Shanghai and Wuhan, respectively.
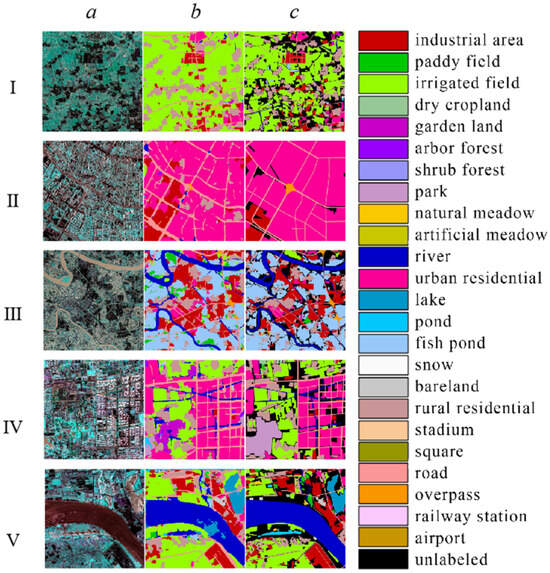
Figure 3.
Examples of the classification results for the five cities.
As shown in Figure 4, rows I to IV show different regions of the examples in the corresponding five cities. The first column of each city is the original image, the second column is the classification result, and the third column is the superimposed graph of the classification result and the original image. For example, in Beijing, columns a to c correspond to original image, classification result, superimposed graph of the classification result and the original image.
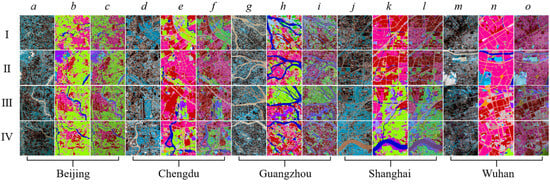
Figure 4.
Example classification results for some regional sites from public datasets for five cities.
Given the non-uniform distribution of region annotations and urban features, there may be missing or scarce analogies within certain regions. Consequently, the experimental results do not showcase the accuracy of each individual class but focus on the analysis of region-level annotated data.
5.2. Classification Application of CLDFA in Urumqi
In this study, the CLDFA method was applied to unsupervised land cover classification in Urumqi city using world view 3 (WV3) imagery. The region of the WV3 image is nwLat = 43.903000, nwLong = 87.448303, seLat = 43.802090, and seLong = 87.597397. In the experiment, we selected the near-infrared and RGB bands from the image for classification.
As shown in Figure 5, column a is the legend for the CLDFA classification results, column b is the CLDFA classification results, column c is the 1 m resolution land cover map of Urumqi city, column d is the legend of the land cover map. By comparing the CLDFA classification results with the 1 m resolution land cover map [15], we found that CLDFA can achieve fine-grained land cover classification, especially in areas with dense buildings and artificial vegetation.
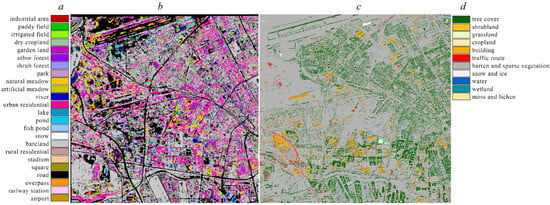
Figure 5.
Classification results of CLDFA (column b) and 1 m resolution land cover map (column c) for part of the new city district of Urumqi city. (column a is the legend of Classification results of CLDFA, column d is the legend of 1 m resolution land cover map).
As shown in Figure 6, columns a to d correspond to original image, original images of the region examples, classification results of the region examples, overlays of the classification results and original images of the region examples, rows I to VI show different regions of the examples.
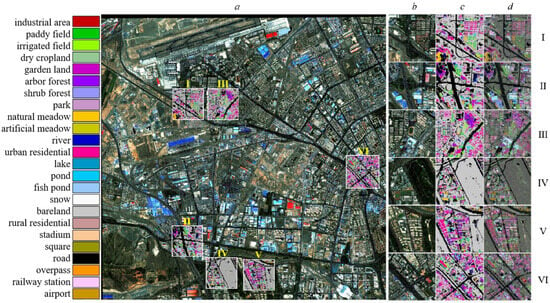
Figure 6.
Classification detail map of some areas from part of the new city district of Urumqi.
Based on the final classification results, the CLDFA method demonstrates impressive performance on WV3 imagery with a spatial resolution of 0.5 m. The overall classification granularity is detailed, although there are instances of misclassification between bare land and road classes. However, the delineation of various land cover features in different regions is relatively accurate. The misclassification issue may be influenced by the large number of classes present. Considering the classification application in Urumqi city, the CLDFA method exhibits stable performance across different categories, indicating its strong adaptability to complex and diverse datasets.
6. Conclusions
In this study, we propose a UDA classification method that enhances feature discrimination using memory bank. This method inherits the dynamic pseudo-labeling algorithm advantage of the DPA method, enabling effective CL of sample features, which is of significant importance when addressing the domain shift issue in urban classification tasks. This method improves the model’s ability to establish pairing relationships between the SD and TD in order to mitigate the impact of insufficient label annotations.
Experimental results of the CLDFA on several urban datasets demonstrate its capability to achieve overall classification accuracy while effectively identifying details within different urban structures. The results from various cities further confirm the validity of the dynamic multi-objective learning strategy, which allows for better adaptation to complex and diverse data features instead of forcibly unifying the feature space like traditional methods, enhances the generalization ability. The main contribution of this research lies in the utilization of memory bank technology, which effectively enhances feature extraction and classification capabilities. Sample CL effectively mitigates the challenges of generalization under static labels, thereby improving the accuracy and consistency of prediction results. This provides an efficient solution for large-scale or cross-domain image classification tasks.
The performance of the CLDFA method is somewhat dependent on the quality of the image data and may not be suitable for data with poor pixelation or high attribute noise. Moreover, the universal learning framework itself is prone to overfitting to specific tasks. Future work should focus on how to extract more general urban detail representation capabilities from deep features.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.X. and A.S.; funding acquisition, A.S.; investigation, R.X., E.L., E.Z. and W.L.; methodology, R.X. and A.S.; project administration, A.S.; supervision, A.S.; visualization, R.X. and A.S.; writing—original draft, R.X.; writing—review and editing, R.X. and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 42071424, 42371389), the Western Young Scholars Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences under grant number 2022-XBQNXZ-001, and the Tianshan Talent Development Program under grant number 2022TSYCCX0006.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Wuhan University for developing and sharing the five billion pixels dataset and SinoLC-1, the first 1 m resolution national-scale land-cover map of China. We are also grateful to Tong et al. for providing the prototype DPA method and test dataset used to evaluate our proposed approach. The authors would also like to thank the editors and reviewers for their valuable comments, which helped us to improve the quality of our paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Funding statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Bi, H.; Xu, F.; Wei, Z.; Xue, Y.; Xu, Z. An active deep learning approach for minimally supervised POLSAR image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9378–9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, C. A survey of remote sensing image classification based on CNNs. Big Earth Data 2019, 3, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, R.J. Texture analysis and classification of ERS SAR images for map updating of urban areas in the Netherlands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, C.; Bruzzone, L.; Fernández-Prieto, D. A novel approach to the unsupervised update of land-cover maps by classification of time series of multispectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4259–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Bao, Y.; Wang, J.; Chu, H.; Zhao, N.; He, Y.; Liu, Y. Crop row segmentation and detection in paddy fields based on treble-classification Otsu and double-dimensional clustering method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, R.; Milioto, A.; Lottes, P.; Stachniss, C.; Bennewitz, M.; Schultz, T. Gradient and log-based active learning for semantic segmentation of crop and weed for agricultural robots. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 1350–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, S.; Kamruzzaman, M.M. Study on modeling method of forest tree image recognition based on CCD and theodolite. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 159067–159076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wen, Z.; Lilong, Y.; Xin, T. Research progress of remote sensing classification and change monitoring on forest types. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2019, 34, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Sahar, L.; Muthukumar, S.; French, S.P. Using aerial imagery and gis in automated building footprint extraction and shape recognition for earthquake risk assessment of urban inventories. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3511–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, L.; Jiao, L.; Dong, Y.; Li, X. Stacked Fisher autoencoder for SAR change detection. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 96, 106971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Chen, C.; Fang, L.; Khoshelham, K.; Shen, G. MS-RRFSegNet: Multiscale regional relation feature segmentation network for semantic segmentation of urban scene point clouds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8301–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, D.; Yao, R. Multistage fusion and multi-source attention network for multi-modal remote sensing image segmentation. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2021, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Fu, H.; Li, D.; Altan, O.; Cheng, T. Remote sensing monitoring of multi-scale watersheds impermeability for urban hydrological evaluation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Fu, R.; Li, D.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y.; Jia, K.; Hicks, B.J. Remote sensing big data for water environment monitoring: Current status, challenges, and future prospects. Earth Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, W.; Cheng, M.; Hu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H. SinoLC-1: The first 1-meter resolution national-scale land-cover map of China created with the deep learning framework and open-access data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2023, 15, 4749–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.-S.; Hu, J.; Hu, F.; Shi, B.; Bai, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X. Aid: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottensteiner, F.; Sohn, G.; Gerke, M.; Sohn, G. ISPRS semantic labeling contest. ISPRS 2014, 1, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Volpi, M.; Ferrari, V. Semantic segmentation of urban scenes by learning local class interactions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kemker, R.; Salvaggio, C.; Kanan, C. Algorithms for semantic segmentation of multispectral remote sensing imagery using deep learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, D.; Volpi, M.; Kellenberger, B.; Tuia, D. Land cover mapping at very high resolution with rotation equivariant cnns: Towards small yet accurate models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Etten, A.; Lindenbaum, D.; Bacastow, T.M. Spacenet: A remote sensing dataset and challenge series. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.01232. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, I.; Koperski, K.; Lindenbaum, D.; Pang, G.; Huang, J.; Basu, S.; Hughes, F.; Tuia, D.; Raskar, R. Deepglobe 2018: A challenge to parse the earth through satellite images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 172–181. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Navarro, J.; Le Saux, B.; Boulch, A.; Audebert, N.; Lef, S. Semi-supervised semantic segmentation in earth observation: The minifrance suite, dataset analysis and multi-task network study. Mach. Learn. 2021, 111, 3125–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.-Y.; Xia, G.-S.; Lu, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, S.; You, S.; Zhang, L. Land-cover classification with high-resolution remote sensing images using transferable deep models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemohammad, H.; Booth, K. Landcovernet: A global benchmark land cover classification training dataset. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.03111. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L. Remote Sensing Image Classification Methods Based on CNN: Challenge and Trends. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning (CONF-SPML), Stanford, CA, USA, 14 November 2021; pp. 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, L.; Li, J. Remote sensing image classification based on convolutional neural networks with two-fold sparse regularization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Q.; Cheng, B.; Cao, L.; Yang, H. Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification Based on Object Relationship Reasoning CNN. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8000305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; You, Y.; Meng, G. Multi-Scale Context-Aware R-Cnn for Few-Shot Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2022—2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 1908–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Long, Y.; Li, D.; Wei, C.; Tang, G.; Liu, J. High-resolution remote sensing image retrieval based on CNNs from a dimensional perspective. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Li, N.; Liu, S.; Li, G. Attpool: Towards hierarchical feature representation in graph convolutional networks via attention mechanism. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6480–6489. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, X.; Fang, X.; Lin, S. Multi-stream hybrid architecture based on cross-level fusion strategy for fine-grained crop species recognition in precision agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 185, 106134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Tu, W.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.; He, B.; Wang, C.; Shi, T.; Li, Q. A hierarchical approach for fine-grained urban villages recognition fusing remote and social sensing data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 106, 102661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmardi, M.; Tasdizen, T. Domain adaptation for biomedical image segmentation using adversarial training. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 554–558. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Ouyang, W.; Li, W.; Xu, D. Collaborative and adversarial network for unsupervised domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3801–3809. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yin, F. Multi-scale spatial attention-guided monocular depth estimation with semantic enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 8811–8822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Yao, L.; Qin, J.; Lu, N.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, C. Multi-scale attention integrated hierarchical networks for high-resolution building footprint extraction. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 109, 102768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, W. Deep visual domain adaptation: A survey. Neurocomputing 2018, 312, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganin, Y.; Lempitsky, V. Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 1180–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Oza, P.; Sindagi, V.A.; Sharmini, V.V.; Patel, V.M. Unsupervised domain adaptation of object detectors: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 46, 4018–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbel, M.; Korba, A.; Salim, A.; Gretton, A. Maximum mean discrepancy gradient flow. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; He, G.; Li, J.; Liao, Y.; Gryllias, K.; Li, W. Domain adversarial transfer network for cross-domain fault diagnosis of rotary machinery. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 8702–8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, Y.; Wu, J.; Long, C. CMFST: Class-based Multi-scale Fusion Self-training for Adapting Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 China Automation Congress (CAC), Xiamen, China, 25–27 November 2022; pp. 3982–3987. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, C.; Zhang, L. Multi-Scale Depth-Aware Unsupervised Domain Adaption in Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Gold Coast, Australia, 18–23 June 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, G. Depth-wise separable convolutions and multi-level pooling for an efficient spatial CNN-based steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 15, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, W.; Zhou, D.; Dai, Y.; Fang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. MLDA-Net: Multi-level dual attention-based network for self-supervised monocular depth estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4691–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, L.; Long, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Ma, F. Fedtrinet: A pseudo labeling method with three players for federated semi-supervised learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–18 December 2021; pp. 715–724. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Lou, J.; Xiong, L.; Shahabi, C. Semifed: Semi-supervised federated learning with consistency and pseudo-labeling. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.09412. [Google Scholar]
- Le-Khac, P.H.; Healy, G.; Smeaton, A.F. Contrastive representation learning: A framework and review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193907–193934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Han, K.; Wei, X.S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. Contrastive learning based hybrid networks for long-tailed image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 943–952. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y. Few-shot classification with contrastive learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 293–309. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Xie, P. Contrastive self-supervised learning for graph classification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 10824–10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, P.; Qiu, X. KNN-contrastive learning for out-of-domain intent classification. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 5129–5141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Huang, J.; Han, X. Transformer-based unsupervised contrastive learning for histopathological image classification. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 81, 102559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Shi, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, L. Hyperspectral imagery classification based on contrastive learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5521213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciortan, M.; Dupuis, R.; Peel, T. A framework using contrastive learning for classification with noisy labels. Data 2021, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žliobaitė, I.; Pechenizkiy, M.; Gama, J. An overview of concept drift applications. In Big Data Analysis: New Algorithms for a New Society; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 91–114. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, I.; Sabater, A.; Ferstl, D.; Montesano, L.; Murillo, A.C. Semi-supervised semantic segmentation with pixel-level contrastive learning from a class-wise memory bank. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 8219–8228. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III. pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.K.; Harandi, M.; Nock, R.; Hartley, R. Siamese networks: The tale of two manifolds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3046–3055. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoo, S. Contrastive learning with large memory bank and negative embedding subtraction for accurate copy detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.04323. [Google Scholar]
- Lesne, A. Shannon entropy: A rigorous notion at the crossroads between probability, information theory, dynamical systems and statistical physics. Math. Struct. Comput. Sci. 2014, 24, e240311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.Y.; Xia, G.S.; Zhu, X.X. Enabling country-scale land cover mapping with meter-resolution satellite imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 196, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; Xie, G.S.; Yao, Y.; Huang, X.; Tang, Z. Classification constrained discriminator for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), London, UK, 6–10 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, L.; Guan, T.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y. Taking a closer look at domain shift: Category-level adversaries for semantics consistent domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2507–2516. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, T.H.; Jain, H.; Bucher, M.; Cord, M.; Pérez, P. Advent: Adversarial entropy minimization for domain adaptation in semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2517–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Shen, T.; Zhang, W.; Duan, L.Y.; Mei, T. Classes matter: A fine-grained adversarial approach to cross-domain semantic segmentation. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 642–659. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).