Abstract
The vegetation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (QTP), China, is diverse and sensitive to climate change. Because of extensive grassland degradation in the QTP, several ecological restoration projects, which affect the livestock population, have been implemented in the QTP. Although many studies have reported the impacts of climate change on vegetation in the QTP, our knowledge on the impacts of both climate change and livestock on vegetation remains very limited. Here, we investigated the impacts of climate change and livestock population on vegetation growth by using the annual maximum normalized difference vegetation index (NDVImax) and growing-season climate data from 1981 to 2019. We analyzed the relationship between NDVImax and climate and livestock population using the modified Mann-Kendall trend Test and Pearson correlation analysis. For the entire QTP, NDVImax had a two-phase trend, with a slow rise during 1981–2000 and a rapid rise during 2000–2019. Overall, NDVImax in the QTP increased and decreased in 63.7% and 6.7% of the area in 2000–2019. In areas with significant changes in NDVImax, it was strongly correlated with relative humidity and vapor pressure. The small positive trend in NDVImax during 1981–2000 was influenced by warmer and wetter climate, and the overgrazing by a large population of livestock slowed down the rate of increase in NDVImax. Livestock population for Qinghai and Tibet in recent years has been lower than in the 1980s.The warmer and wetter climate and substantial drops in the livestock population contributed to large recovery in vegetation during 2001–2019. Vegetation degradation in Qinghai during 1981–2000 and central-northern Tibet during 2000–2019 was driven mainly by drier and hotter climatic. Although 63.7% of the area in the QTP became greener, the vegetation degradation in central-northern Tibet should not be ignored and more measures should be taken to alleviate the impact of warming and drying climate. Our findings provide a better understanding of the factors that drove changes in vegetation in the QTP.
1. Introduction
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (QTP), China, has an average elevation of 4500 m, and is known as the roof and third pole of the world [1]. Its climate is characterized as arid, cold, windy, anoxic, sunny, and has large swings in daily air temperature [2]. The unique climate and geographical environment of the QTP have fostered diverse ecosystem types, including forests, shrubs, alpine grasslands, alpine meadows, and alpine desert. Studies have shown that air temperature in the QTP has increased twice the global average, and precipitation has significantly increased since 1982 [3,4]. The changes in climate on the QTP have altered the atmosphere and hydrological cycles and thus has reshaped the local environment [4]. As an indicator of climate change, vegetation plays a pivotal role in linking the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere at the regional scale and across Asia [5,6]. Studying the impact of climate change on the vegetation of the QTP will help advance our understanding of changes in QTP vegetation under a warming climate and provide information that is vital to sustainable development [5,7].
NDVI is highly correlated with vegetation leaf area index, greenness, and productivity [8]. Spaceborne time series NDVI images are vital for monitoring the dynamics of vegetation at large spatial scales [9,10,11,12]. This index has been extensively used and applied at regional to global scales. Many scholars have used NDVI to study the response of vegetation to climate change in the QTP at different time scales and resolutions. Several studies have reported changes in vegetation in the QTP before 2013, and these studies have greatly contributed to monitoring vegetation in the QTP [3,5,6,13,14,15]. However, these studies do not reflect the latest dynamics of vegetation change in the QTP. Chen [7] studied the characteristics of vegetation change during 2000–2019 and its correlation with climate factors, but they did not conduct in-depth study on the impact of the livestock population on vegetation changes.
The vastness of the QTP means that climate change and its impacts on vegetation growth vary from place to place. Therefore, it is necessary to study the difference in the spatial response of vegetation to climate change. Some previous studies used average NDVI (NDVIavg) to represent the growth status of vegetation, such as mean annual NDVI, [5] and mean annual growing season NDVI [7], seasonal average NDVI [11], and some others used the annual maximum NDVI (NDVImax) [16,17]. Both NDVIavg and NDVImax have been widely used. NDVIavg reflects the average state, while NDVImax is associated with peak greenness during the growing season [18]. Piao [19] reported that the grassland above-ground biomass was well correlated with the NDVImax.
Terrestrial ecosystems of the QTP are particularly sensitive to climate change during the growing season [20,21,22], and it is also an important time for biomass accumulation. Thus, climatic conditions during the growing season directly affect biomass accumulation and NDVImax. In previous research, air temperature and precipitation were the main climate variables studied for their effects on vegetation growth [6,13,15,23], while atmospheric water conditions have been rarely considered. According to Ding [24], atmospheric aridity affects grassland productivity in the QTP because plants close their stomata to prevent water loss when they are water stressed, which inhibits photosynthesis, carbon assimilation, and growth. Yuan [25] showed that increased atmospheric vapor pressure deficit reduced global vegetation growth.
In addition to climate change, the impact of livestock production (e.g., livestock population, types, grazing management, and policies) cannot be ignored. Overgrazing is widely considered to be a key factor affecting the structure, productivity, and nutritional value of natural grassland vegetation, as well as the main driver of grassland degradation [3,26,27]. The livestock population determines grazing intensity and whether it is overgrazed to some extent. Many researchers have used livestock population or the grazing pressure index to analyze the impact of anthropogenic activities on grassland productivity in the QTP and found that changes in livestock population affect vegetation productivity and grassland yield [3,28]. However, a better understanding of the impact of the latest livestock population on vegetation changes in the QTP is needed.
We found from our literature review that information on the spatial-temporal responses of vegetation to climate change during the growing season and livestock population in the QTP was very limited and outdated, which indicates that there is a knowledge gap. To address this gap, here, we aimed to analyze the spatiotemporal vegetation dynamics and its response to climate changes and livestock population in the QTP from 1981 to 2019. We used NDVImax as an index of vegetation greenness and we used relative humidity and vapor pressure as indicators of atmospheric water conditions to address the following questions: (1) What are the spatiotemporal changes of NDVImax in the QTP from 1981 to 2019? (2) How does NDVImax respond to climate change (temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, and vapor pressure) in the QTP during 1981–2019? (3) How does NDVImax respond to both climate change and livestock number changes in the QTP during 1981–2019? This study will shed new insight that helps us to better understand those factors that drove the vegetation changes in the QTP.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
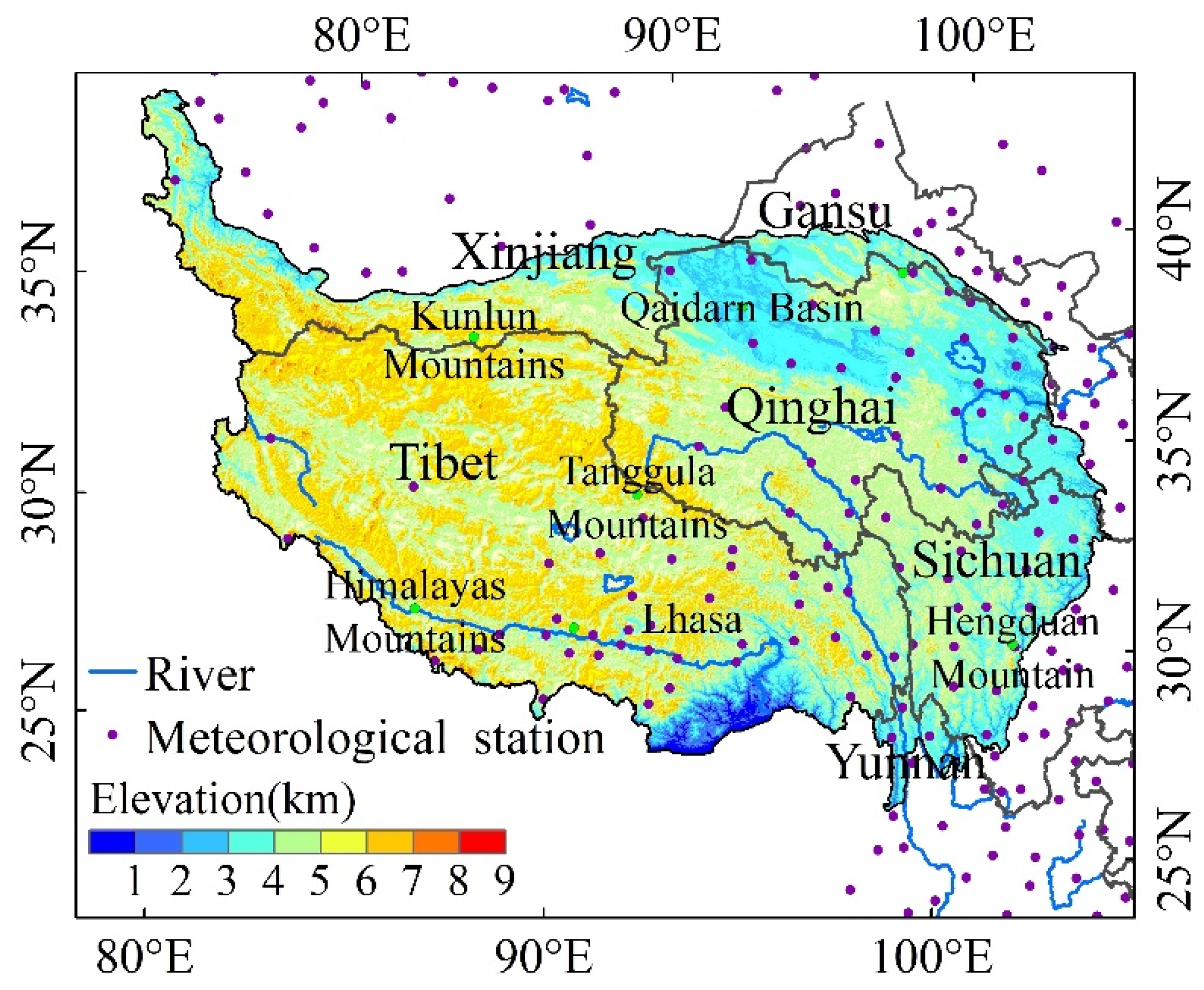
The QTP extends from the southern Himalayas in the south to the northern Qilian Mountains in the north, the Pamirs and Karakoram Mountains in the west, and the Hengduan Mountain and the Loess Plateau in the east [29], and covers all of China’s Tibet, most of Qinghai, and some areas in Gansu, Xinjiang, and the Western Sichuan Plateau, with a total area of 2.58 million square kilometers (Figure 1). The average elevation of Tibet is 4736 m, which is higher than Qinghai’s average of 4034 m. The Tibet pastoral area and Qinghai pastoral area are two of the four largest pastoral areas in China. The central and eastern QTP is the source of many large rivers, such as the Yangtze River, Yellow River, Lancang River, Mekong River, Yarlung Zangbo River, and Indus River. The QTP has dense river networks, abundant water resources, and is known as Asia’s Water Tower. The growing season for vegetation in the QTP is from May to September, and vegetation often reaches its maximum biomass in July or August.The precipitation in the QTP gradually decreases from southeast to northwest. Precipitation in summer (from June to August) accounts for as much as 40–60% of the annual precipitation in most areas of the QTP [30].
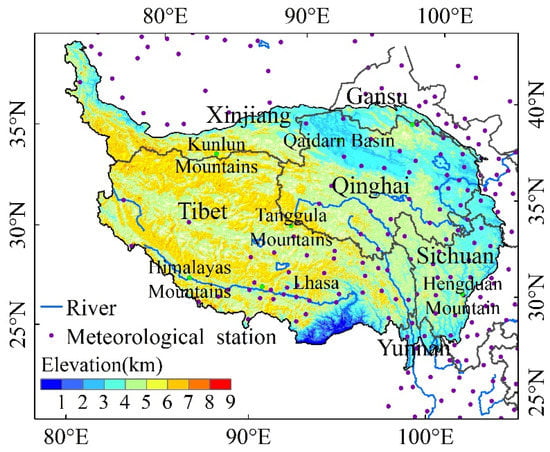
Figure 1.
Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and geographical locations of 117 weather stations in the QTP and its surrounding area, China.
2.2. Datasets and Preprocessing
2.2.1. NDVI Data from AVHRR and MODIS
Two data sources, the third generation GIMMS NDVI from the AVHRR sensors and the MOD13A2 from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS), were used to create time series NDVI from 1981–2019. According to Du [31] and Zhang [14], NDVI values of the two data sources were highly correlated in the QTP, and they both reflect vegetation dynamics. In addition, Zhao [32] found that the two data sources responded to all climatic variables and had the same trend. Therefore, it is credible to analyze the trend of changes in vegetation and its correlation with climatic variables using the time series NDVI images from the two data sources. We constructed time series NDVI from 1981 to 2000 using GIMMS 3 g NDVI with a spatial resolution of 8 km and constructed the NDVI dataset from 2001 to 2019 using MOD13A2 with a resolution of 1 km. We resampled the MOD13A2 images to 8 km to match the GIMMS 3 g NDVI spatial resolution.
We used the maximum value compositing (MVC) method to calculate NDVImax because it can eliminate the influence of clouds on the vegetation index. Time series NDVImax images during 1981–2019 were created using the Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform, which includes widely used geospatial datasets, has massive computational capabilities, and provides numerous algorithms [33].
2.2.2. Meteorological Data
The monthly average air temperature, monthly precipitation, relative humidity, and monthly average vapor pressure were collected from 117 standard weather stations in the QTP and its surrounding area during 1981–2019, which were provided by the Meteorological Data Sharing Service System of China (http://data.cma.cn/, accessed on 17 October 2021). Those data were interpolated using the Thin Plate Spline (TPS) method to obtain the spatial distribution of climate variables over the QTP with a spatial resolution of 8 km.
The monthly average temperature, monthly average precipitation, monthly average relative humidity, and monthly average vapor pressure during the annual growing season was calculated using the interpolated meteorological data from May to September of each year.
2.2.3. Livestock Data
Tibet and Qinghai are the main part of the QTP. The livestock population in Tibet and Qinghai from 1980 to 2019 were provided by the National Bureau of Statistics of China (http://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=E0103, accessed on 17 October 2021), and included the number of large livestock (e.g., cattle, horses, camels) and small livestock (e.g., goats and sheep).
The GIMMS 3 g NDVI and MOD13A2 covered different time periods, so we divided the entire research period into two stages: 1981–2000 and 2001–2019. In the subsequent data processing and analysis of this paper, we divided the NDVI data, meteorological data, and livestock population according to these two periods.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Modified Mann-Kendall Test
The Modified Mann–Kendall (MK) test [34] was used to analyze the interannual trends of climate variables and NDVImax at the pixel level. In many situations, the observed time series data are autocorrelated and this autocorrelation will result in misinterpretation of trend tests results when using the MK trend test [35]. The modified MK trend Test method as described by Yue [34] was able to eliminate the influence of sequence correlation on the trend test, and it has been shown to be as powerful as the original MK trend test when applied to uncorrelated sequences [36].
When the rates of NDVImax and climate variables were significantly greater than 0 at a level of p < 0.05, they were considered a significant increase, and when the rates of NDVImax and climate variables were significantly less than 0 at a level of p < 0.05, they were considered a significant decrease. In other cases, the rate was insignificant.
2.3.2. Linear Regression
We used linear regression to calculate the trends in NDVImax, climate variables, and livestock population at the regional scale. The specific calculation formula can be found in the papers of Huang [6] and Chen [7].
2.3.3. Pearson Correlation Analysis
Pearson correlation analysis was used to calculate the relationships between NDVImax and monthly temperature, monthly precipitation, monthly relative humidity, and monthly vapor pressure. The Person correlation analysis was proposed by Karl Pearson, [37] and the Pearson correlation coefficient r is often used to measure the strength of correlation between two variables.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of NDVImax during 1981–2019
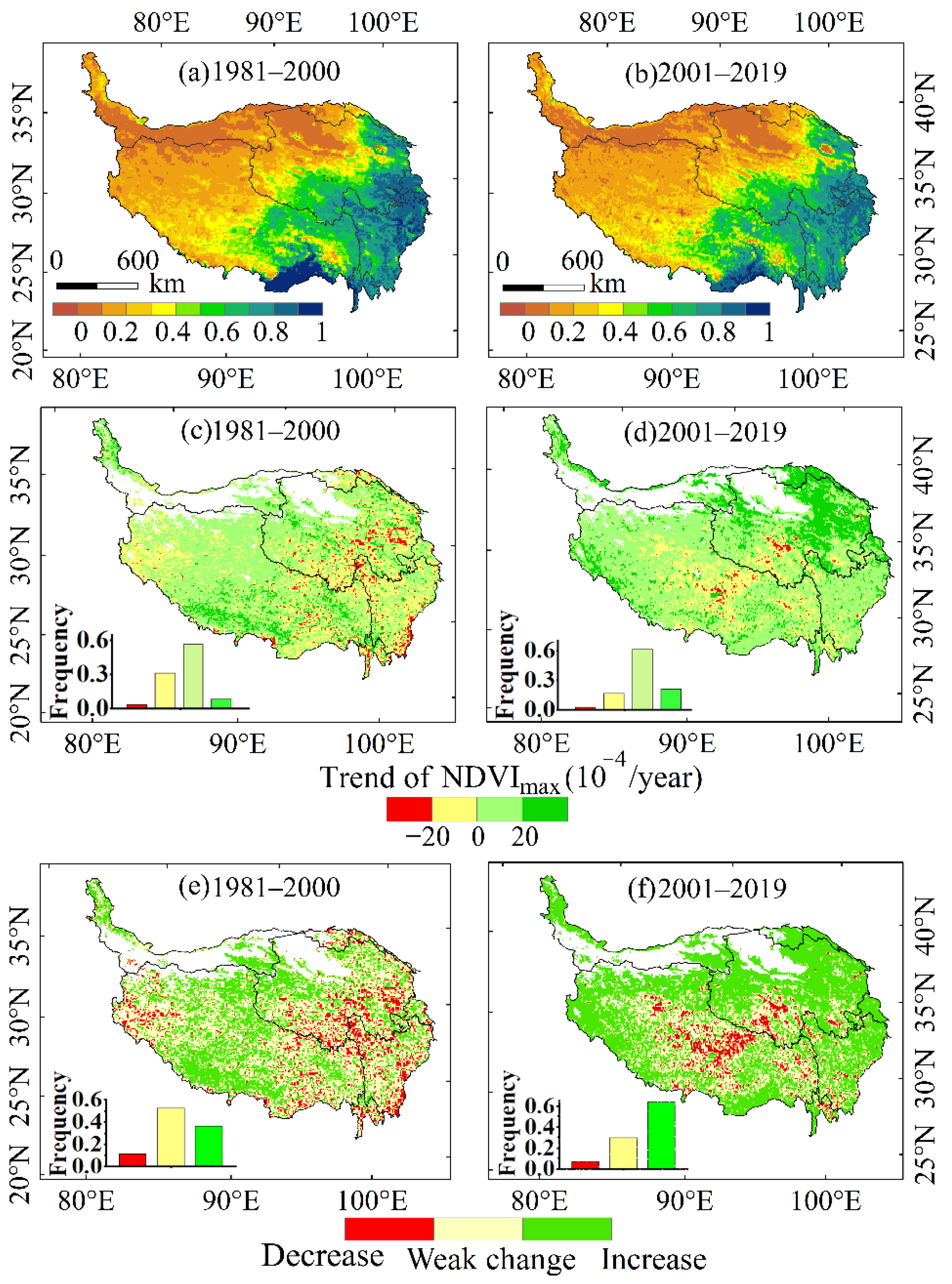
The spatial distribution of the average NDVImax from 1981–2000 and 2001–2019 was shown in Figure 2a,b, respectively. The trends in NDVImax and their significance during 1981–2000 and 2001–2019 were calculated using the modified MK Test method as described by Yue [34]. The results are shown in Figure 2c–f.
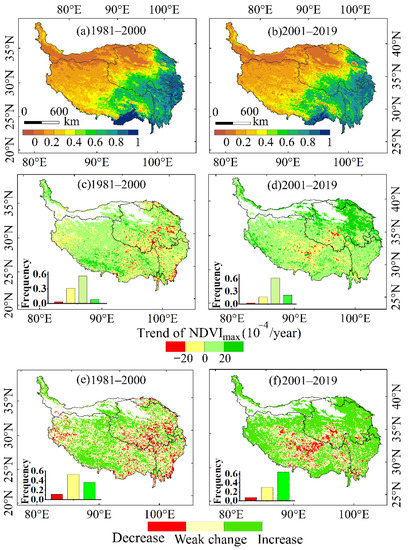
Figure 2.
The spatial distribution of NDVImax (a). 1981–2000; (b). 2000–2019, the trend of NDVImax (c). 1981–2000; (d). 2000–2019, and the significance of trends (e). 1981–2000; (f). 2000–2019.
The average NDVImax values had a negative trend from southeast to northwest (Figure 2a,b). The southeastern and middle eastern QTP had higher NDVI values, and the corresponding vegetation types there are forest, shrub, and meadow. In the west and northwest, especially in the Qaidam Basin and Kunlun Mountains, the NDVI values were relatively small, and the area is classified as alpine desert. In the subsequent analysis, we masked out the pixels with a perennial mean of NDVImax less than 0.1 to exclude sparse vegetation areas and the influence of water bodies and shadows.
The vegetation dynamics in the QTP during the two periods had different spatial characteristics. As shown in Figure 2c,e, the negative trends in NDVImax during the first period were in eastern QTP, central and southern Qinghai, the junction of Qinghai, Sichuan, and Tibet, and in the vicinity of Hengduan Mountain and northwestern Tibet. In 1981–2000, NDVImax increased mainly in central Tibet, at the junction of Qinghai, Tibet, and Xinjiang. In 2001–2019, NDVImax in most areas of the QTP had a positive trend, such as in central and northern Tibet, the western Sichuan plateau, and the southern and western parts of Tibet Figure 2d,f. North-central Qinghai had the highest positive trend in NDVImax, which was greater than 0.002 yr−1.
Area with greenness increased significantly, from 36.3% in 1981–2000 to 63.7% in 2000–2019. The area with negative trends in NDVImax became smaller, from 11.3% in 1981–2000 to 6.7% in 2001–2019. During 2001–2019, there were still some areas with a negative trend in NDVImax, which were found in central-northern Tibet and southern Qinghai.
In eastern Qinghai and the Western Sichuan Plateau, degraded vegetation had a positive trend in NDVImax after 2000. Figure 1 and Figure 2f showed that areas with decreased NDVImax during 2001–2019 were located at a higher altitude than in 1981–2000. According to Li [38], alpine grasslands at higher elevations in the QTP have been found to be more sensitive to climate variability than those at lower elevations.
3.2. The Relationships between NDVImax and Climate Changes during 1981–2019
3.2.1. Interannual Trend of Climate Variables during 1981–2019
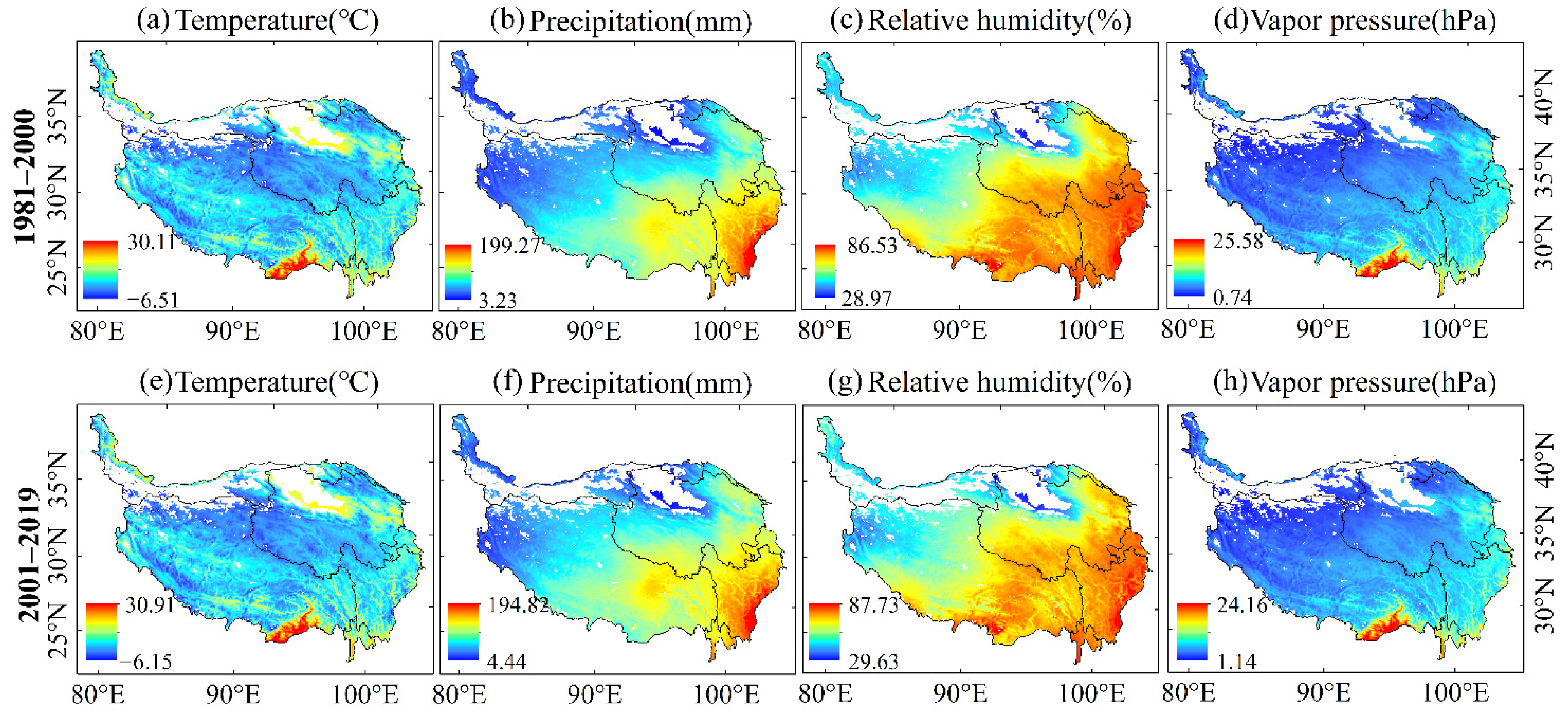
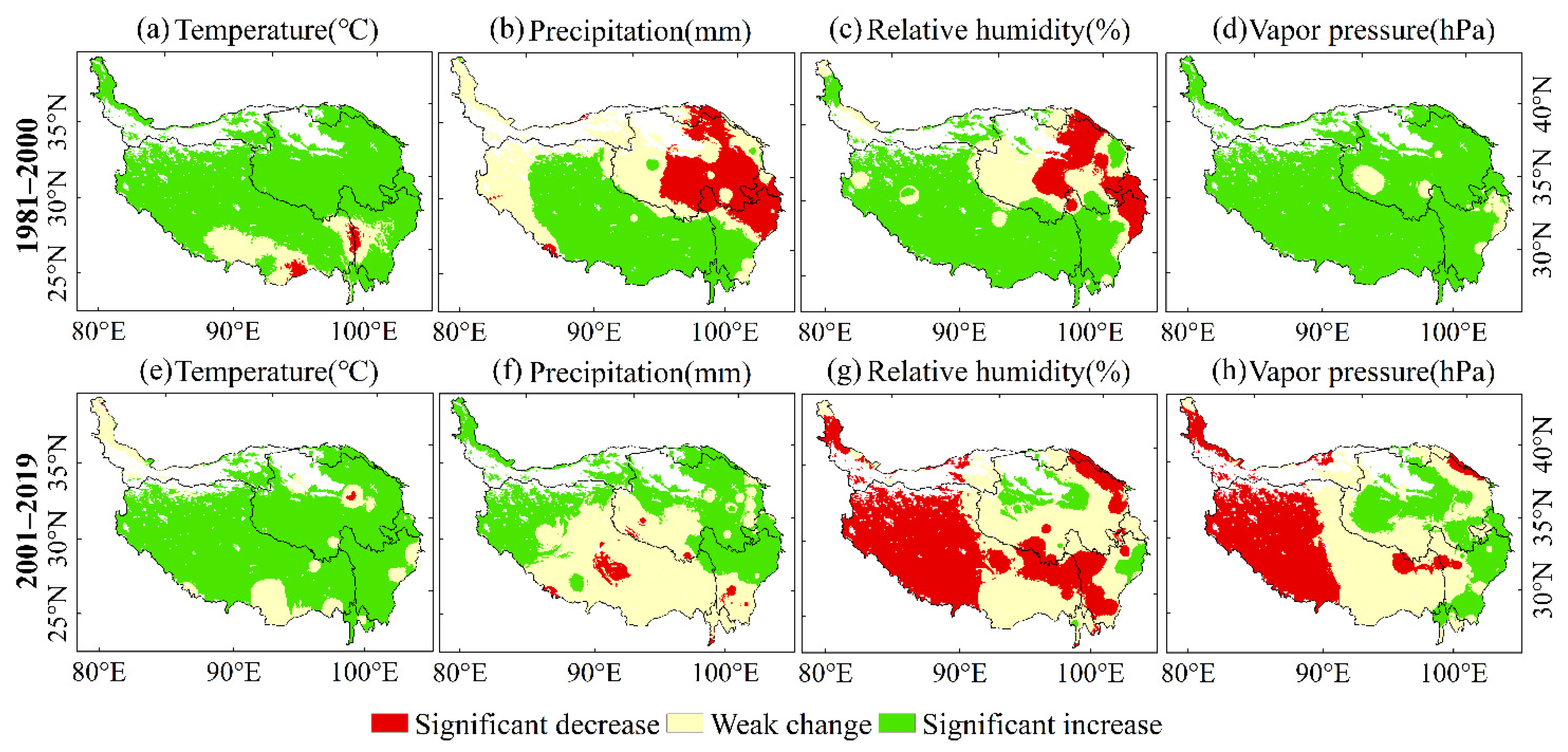
We calculated monthly average temperature, monthly average precipitation, monthly average relative humidity, and monthly average vapor pressure of the annual growing season during 1981 to 2000 and 2001–2019. The results are shown in Figure 3. We calculated the trend and their significance for climatic variables during 1981–2000 and 2001–2019. The results are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively.
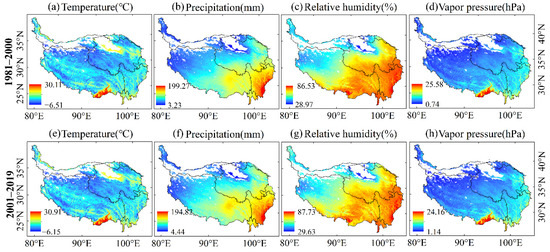
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of climatic variables in growing season during 1981–2000 and 2001–2019.
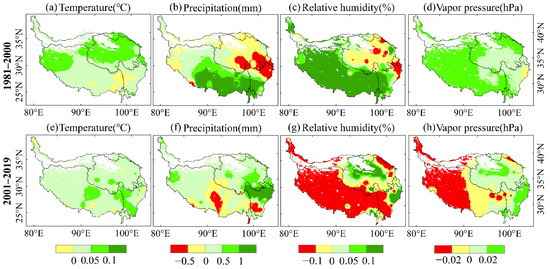
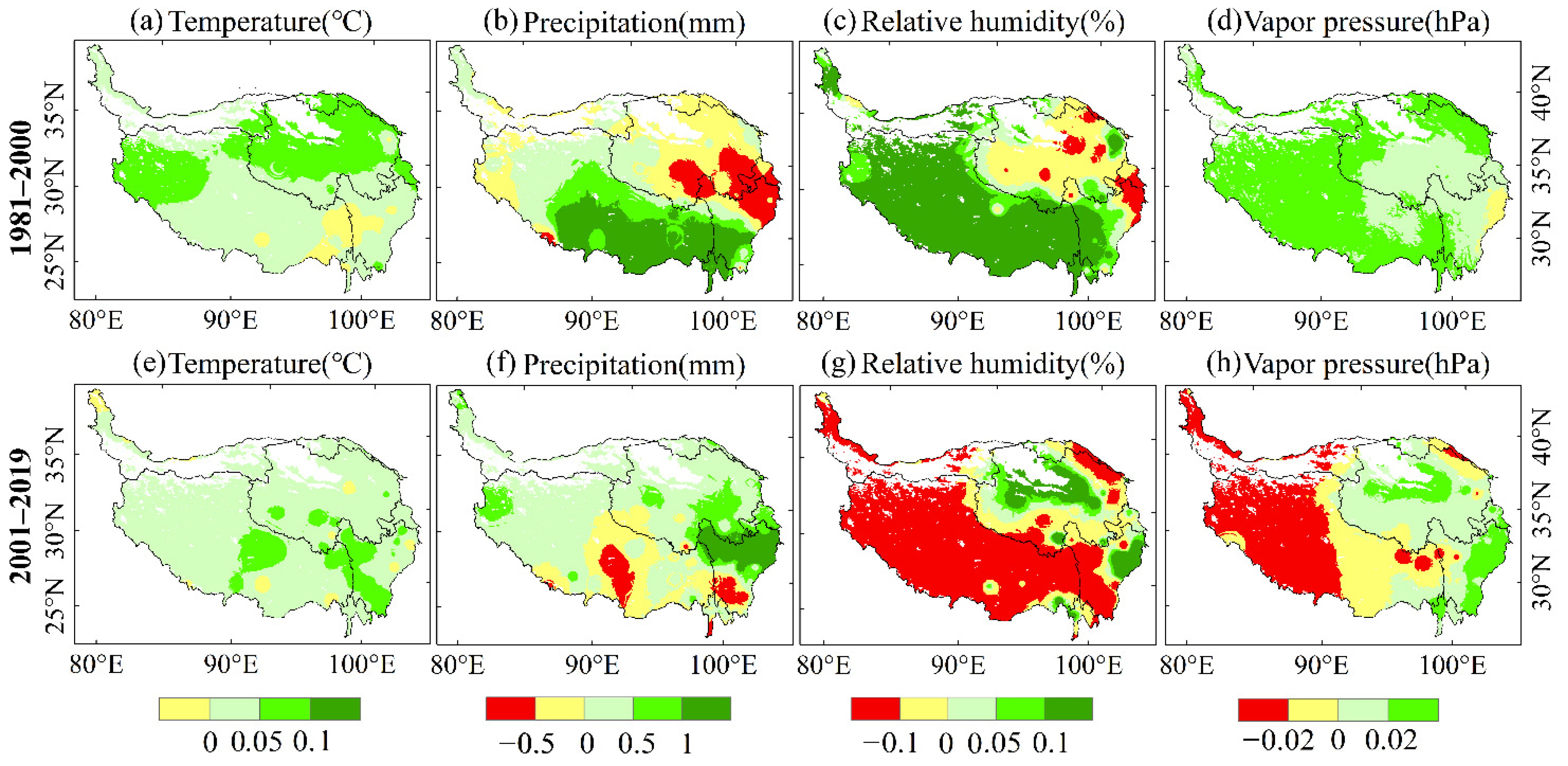
Figure 4.
Trends of climatic variables from 1981 to 2000 (a–d) and from 2001 to 2019 (e–h) in the QTP using the modified MK test.
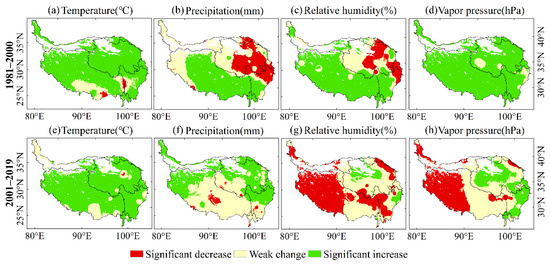
Figure 5.
Significance of the trends in climatic variables from 1981 to 2000 (a–d) and from 2001 to 2019 (e–h) in the QTP using the modified MK test.
Figure 3 shows that the four climatic variables have strong spatial differences. Among them, both precipitation and relative humidity gradually increased from northwest to southeast. We also found that the distribution of NDVImax was highly consistent with the distribution of precipitation and relative humidity in the QTP at regional scale (Figure 3). Our finding agree with Fang [39] and Shi [40], in that precipitation and vegetation cover were positively correlated in the QTP.
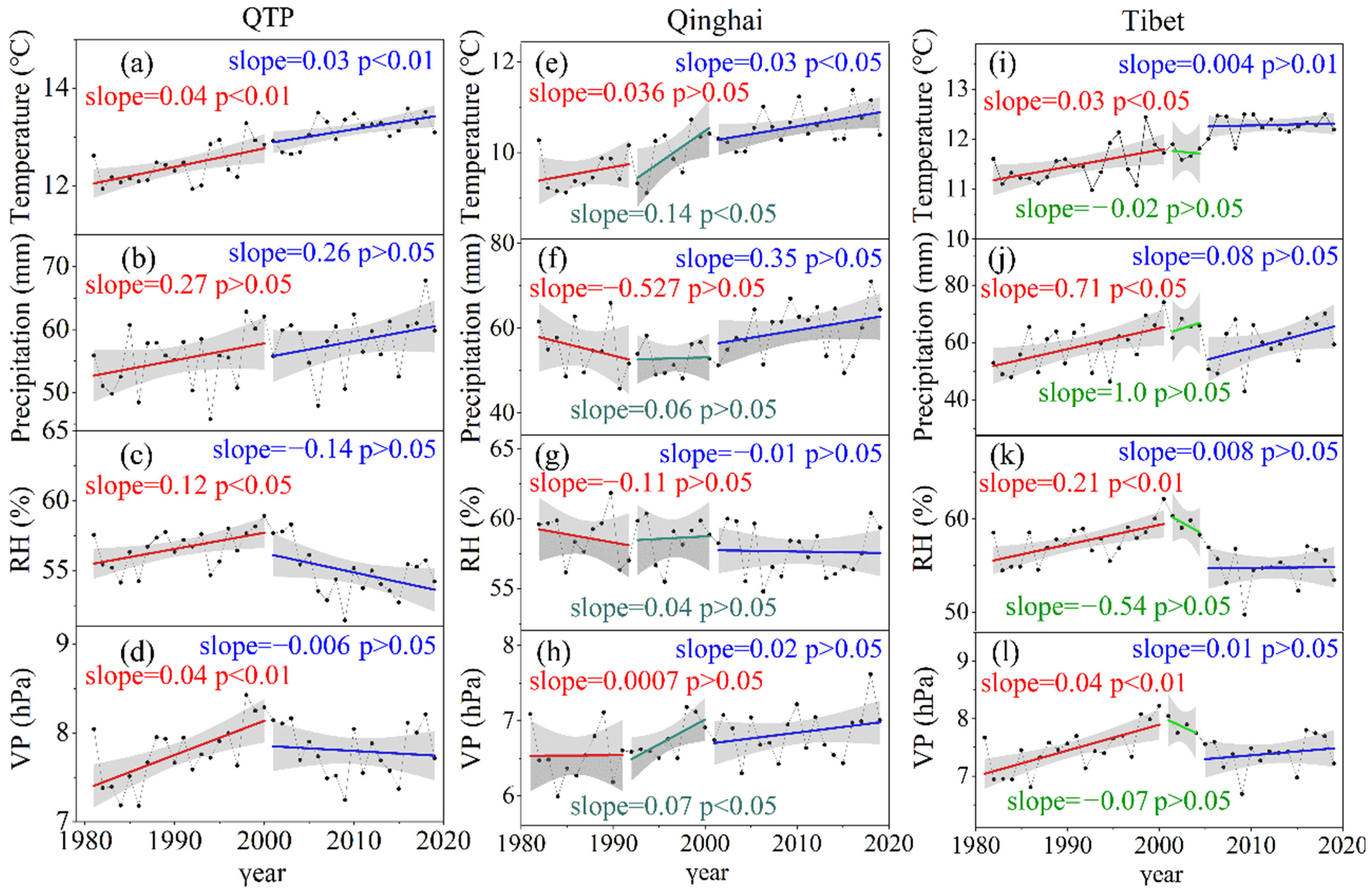
From 1981 to 2000, the average temperature in most areas of the QTP had a significant positive trend (Figure 4a and Figure 5a). The temperature in the northern QTP rose rapidly, which ranged from 0.05 to 0.1 °C (Figure 4a). Both precipitation and relative humidity had obvious spatial differences during 1981–2000, with some areas showing an obvious positive trend, and some areas showing an obvious negative trend. Precipitation in Tibet had a positive trend during 1981–2000 (Figure 5b), especially in the southern QTP where the annual increase rate was 0.5–1.5 mm (Figure 4b), while precipitation in the eastern QTP had a significant negative trend. The relative humidity in most of Tibet had a positive trend, with an annual rate of increase of 0.1–0.2%, while most areas in Qinghai had a negative trend with an annual rate of decrease of less than 0.1%. The vapor pressure of the QTP increased significantly from 1981 to 2000, especially in Tibet, at a rate of 0–0.2 hPa/year.
From 2001 to 2019, the temperature in the QTP maintained a significant upward trend, with an average annual temperature increase of 0–0.15 °C. There was no obvious change in precipitation in the central and southern QTP. The precipitation in northern and eastern QTP significantly increased. The relative humidity of the southern and western QTP from 2001 to 2019 had a significant downward trend, including almost all areas of Tibet and western Sichuan, with a decrease of 0.1–0.8%. Only a few areas in the northern QTP increased by 0.1–0.2%. The vapor pressure in western Tibet had a negative trend, which ranged from 0.02 to 0.22 hPa, while the vapor pressure increased in central Qinghai and western Sichuan, which ranged from 0.02 to 0.2 hPa.
Regionally, the temperature increased, and precipitation decreased in Qinghai during the first period, which indicated that there was a warming and drying trend that would not have been conducive to vegetation growth. Meanwhile, all the four climatic variables, temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, and vapor pressure, in Tibet increased, which signaled a trend in warming and humidification from 1981 to 2000. This trend of climate change is more beneficial to vegetation productivity, because a certain range of increased temperature and precipitation can increase photosynthesis and growth [6,41]. From 2000 to 2019, temperature, precipitation, and vapor pressure in most of Qinghai had a positive trend. Thus, it can be inferred that evaporation decreased because of the trend in relative humidity, and that the change in climate in Qinghai from 2000 to 2019 was beneficial to vegetation growth. During 2001–2019, the temperature in Tibet increased significantly, while the precipitation in most areas of Tibet did not significantly change. Meanwhile, considering that the relative humidity in this area decreased significantly, it can be inferred that the evaporation increased. The climate change in some areas of Tibet during the second stage may inhibit the productivity and growth of vegetation.
3.2.2. Correlation between NDVImax and Climatic Variables
Figure 2a,b and Figure 3 show that the distribution of NDVImax was consistent with the water conditions of the QTP, especially precipitation and relative humidity. The southeastern QTP had a suitable temperature, sufficient precipitation, and high NDVImax, whereas the northwestern QTP had a relatively low temperature, less precipitation, and a low NDVImax.
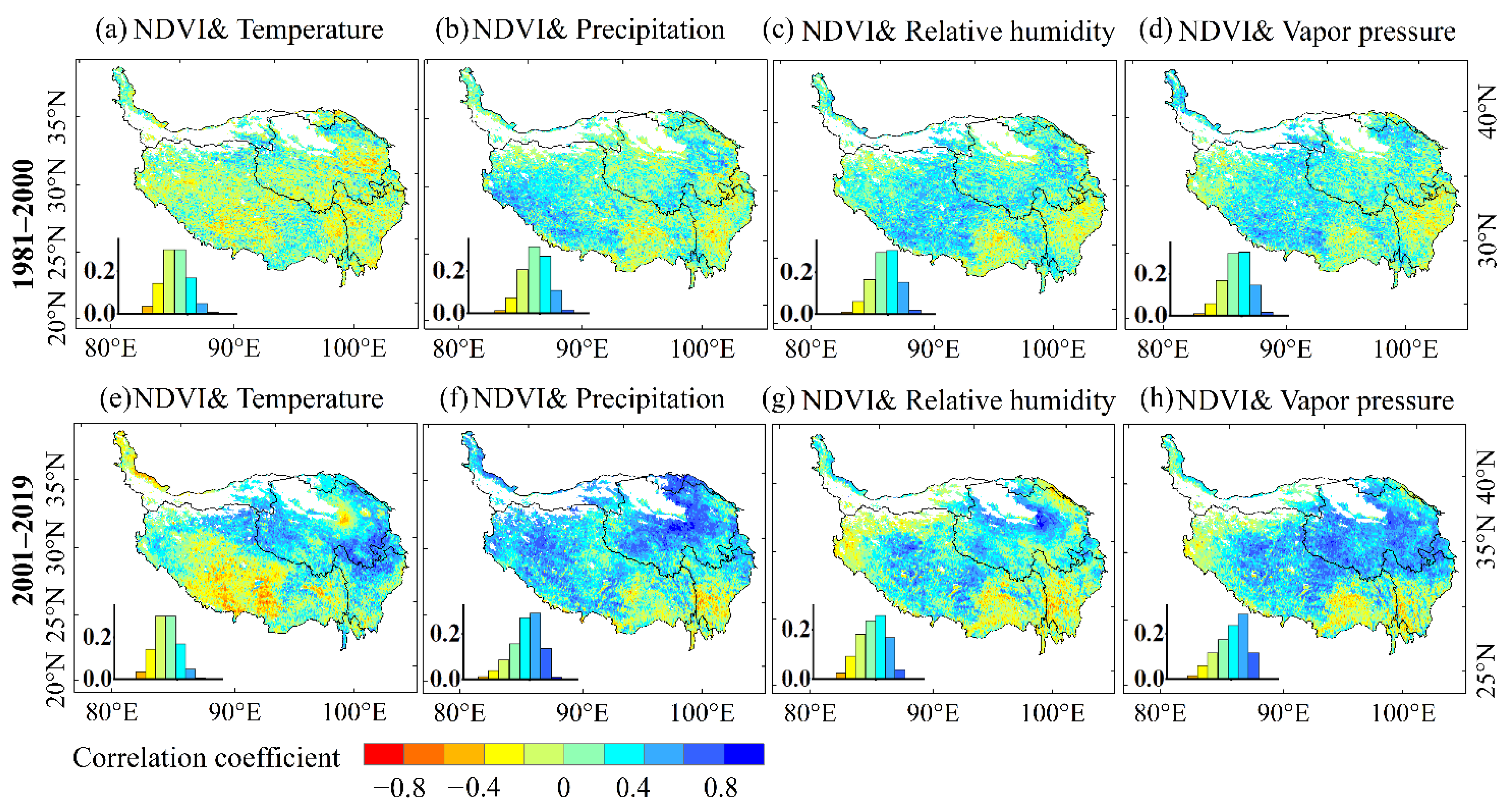
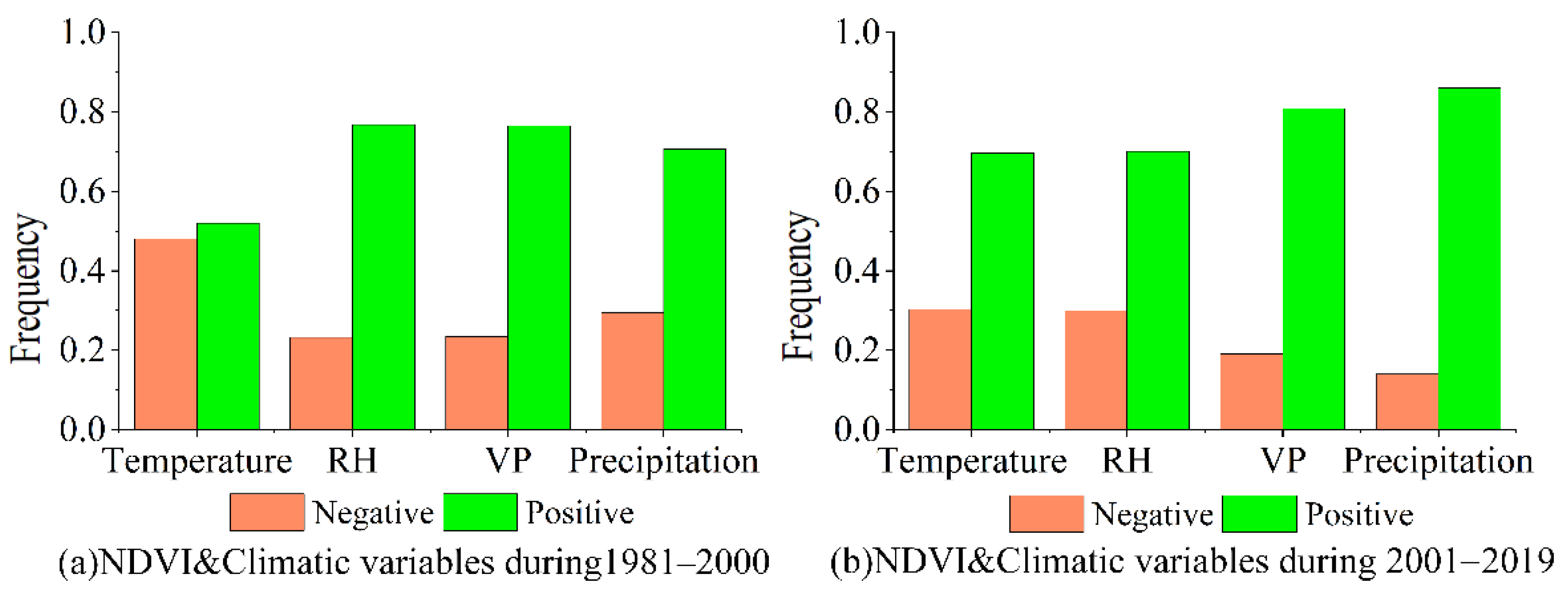
The spatial distributions of the correlation between NDVImax and climatic variables during the growing season were computed and are shown in Figure 6. The frequency of the correlations between NDVImax and the four climatic variables are shown in Figure 7.
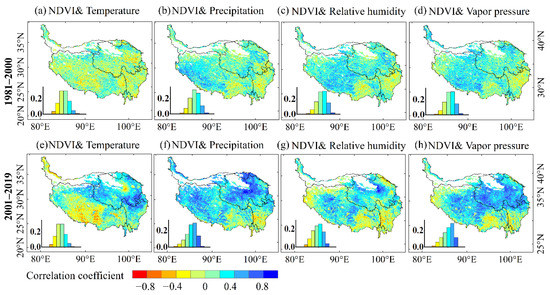
Figure 6.
Spatial distributions of correlation coefficient between NDVImax and climatic variables in growing season.
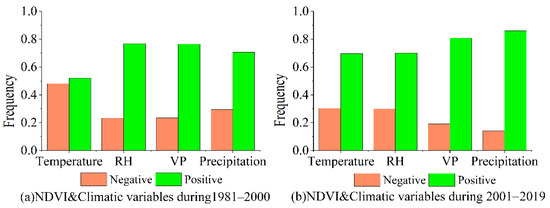
Figure 7.
The frequency of correlations between NDVImax and the four climatic variables (RH is relative humidity; VP is vapor pressure).
As is shown in Figure 6, the correlation between NDVImax and the four climatic variables could vary among the different stages and places in the QTP. Overall, NDVImax and the four climatic variables mainly had a positive correlation (Figure 7). The correlation between NDVImax and climate variables in 2001–2019 was stronger than in 1981–2000 (Figure 6), which may indicate that the vegetation change in 2001–2019 was more affected by climate change than in 1981–2000. The two data sources of NDVI may also lead to differences in the correlation between NDVI and climatic variables. From 2000 to 2019, the eastern QTP had a positive correlation between temperature and NDVImax, especially at the junction of Qinghai and Sichuan, where the correlation coefficient was greater than 0.8. But in most areas of Tibet, temperature and NDVImax were negatively correlated (Figure 6e). The reason for the negative correlation may be that when precipitation in those areas decreased (Figure 4b and Figure 5b), increased temperature (Figure 4a and Figure 5a) can exacerbate drought and inhibit vegetation activity.
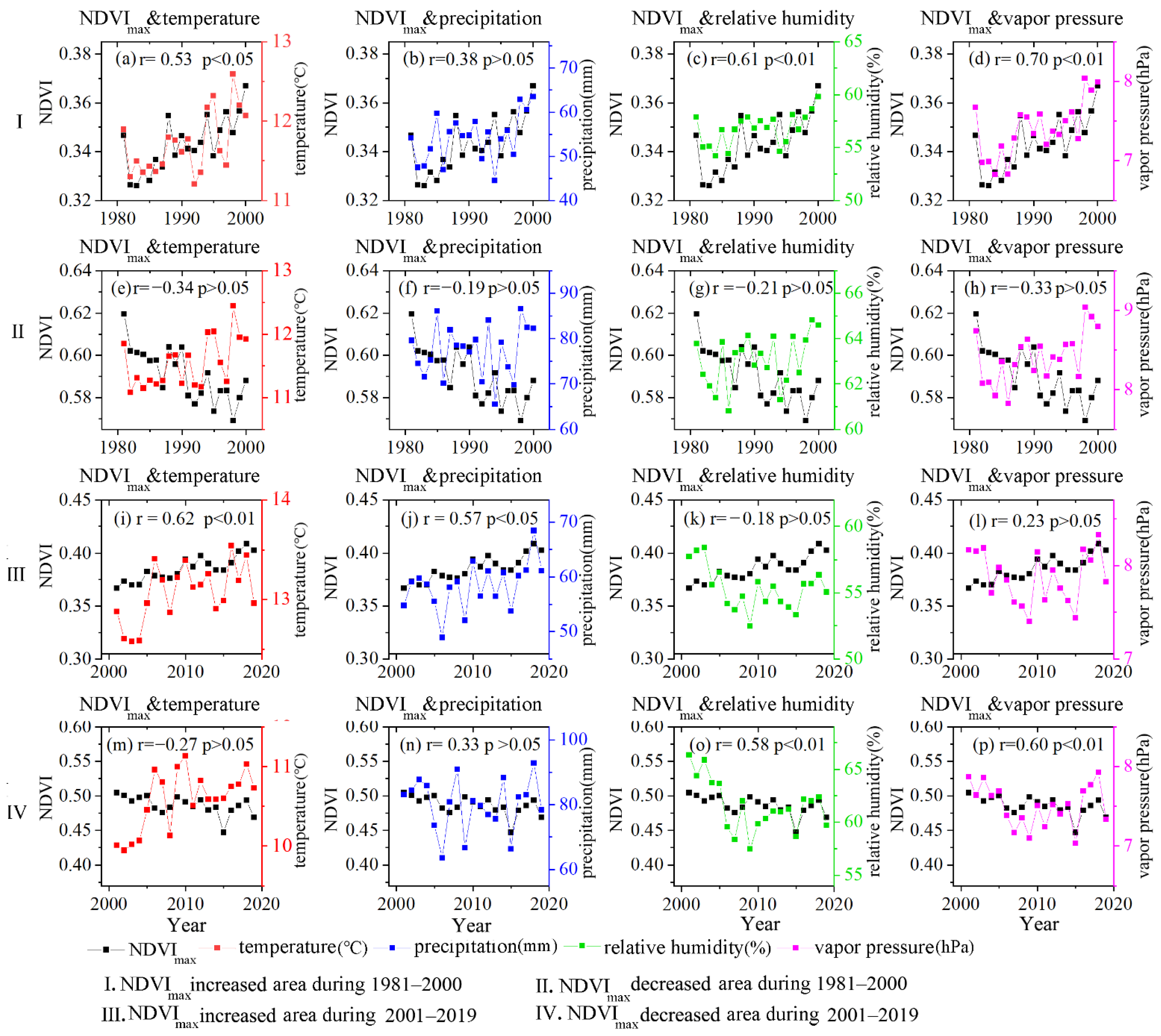
To further analyze the relationship between NDVImax and climate in areas with significant changes in NDVImax, those areas where vegetation significantly increased or decreased were extracted, and annual average NDVImax of those areas and the corresponding monthly average temperature, monthly average precipitation, and monthly average relative humidity, and monthly average vapor pressure were calculated and counted. The correlation between annual average NDVImax and the four climate variables in areas with significant changes in NDVImax was analyzed separately, and the results are shown in Figure 8.
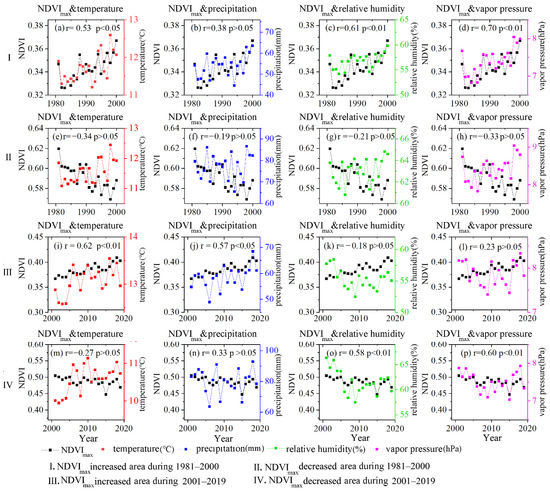
Figure 8.
Correlation between the annual NDVImax and climatic variables in areas with significant changes in NDVImax.
As shown in Figure 8, the NDVImax in areas with increased NDVImax during 1981–2000 (I), NDVImax in areas with increased NDVImax area during 2001–2019 (III), and NDVImax in areas with decreased NDVImax during 2001–2019 (IV) show a strong correlation with the climatic variables. NDVImax in areas with decreased NDVImax during 1981–2000 (II) show a weak correlation with climatic variables. The correlation coefficients between the NDVImax and the temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, and vapor pressure in the areas with increased vegetation during 1981–2000 were 0.53 (p < 0.05), 0.38 (p > 0.05), 0.61, and 0.70 (p < 0.01) (Figure 8a–d). Thus, vegetation growth during the first period was significantly related to vapor pressure, followed by relative humidity and temperature. In areas with decreases in vegetation, the correlation coefficients between NDVImax and four climatic variables were small, −0.34, −0.19, −0.21, and −0.33, respectively. Although NDVImax showed a weak correlation with climatic variables in areas with decreases in vegetation during the first period, there were obvious spatial differences (Figure 2e and Figure 6a–d). For example, in areas with vegetation degradation of northwestern Tibet, there was a strong positive correlation between NDVImax and precipitation. But in areas with vegetation degradation near Tanggula Mountains, NDVImax showed a weak correlation with the four climate variables.
NDVImax and temperature in the areas with increased NDVImax during the second period had the strongest correlation, with a correlation coefficient of 0.62 (p < 0.01) (Figure 8i), followed by precipitation, with a correlation coefficient of 0.57 (Figure 8j). In areas with decreased NDVImax during the second period, NDVImax was correlated with relative humidity and vapor pressure, with correlation coefficients of 0.58 and 0.60, respectively (Figure 8o,p).
3.3. The Relationships between NDVImax, Climate and Livestock Population at the Regional Scale
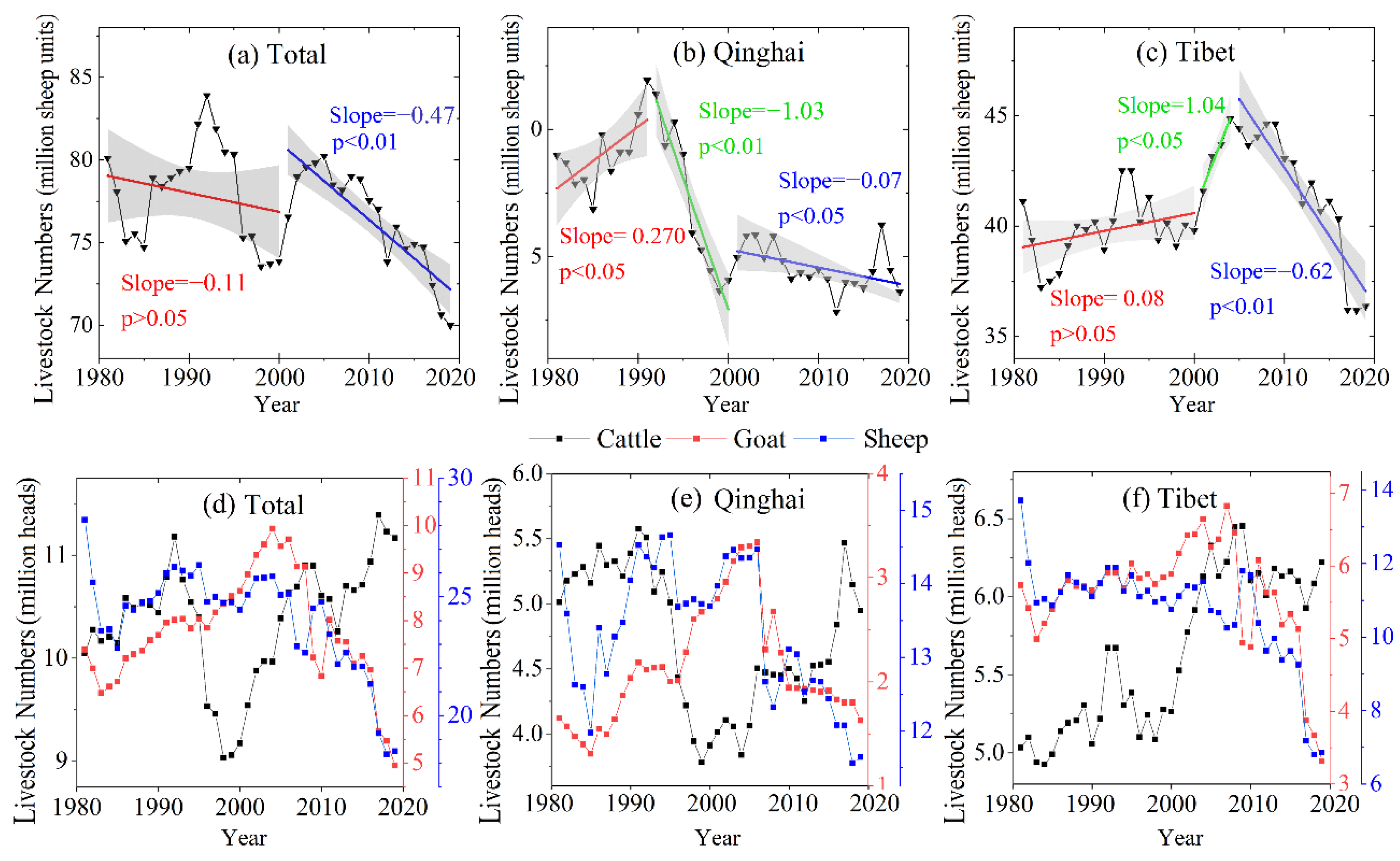
Due to the differences in livestock population, climate change, and vegetation, it is necessary to analyze the two provinces separately. In this section, we analyzed the impact of livestock population and climate change on NDVImax at the regional scale. Interannual variations of NDVImax were shown in Figure 9. According to Chen [3] and Fan [28], large livestock (such as cattle and horses) was converted to four sheep units. Then, we calculated the livestock population in Qinghai, Tibet, and total numbers, and then analyzed the trends in the livestock population. The results are shown in Figure 10a–c. Detailed results for cattle, goat, and sheep are shown Figure 10d–f. The interannual change in climate in the QTP, Qinghai, and Tibet during the growing period from 1981 to 2019 were counted and analyzed using the interpolation results of the climate variables. The results are shown in Figure 11a–l).
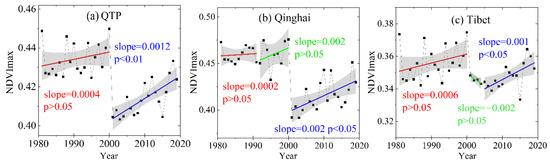
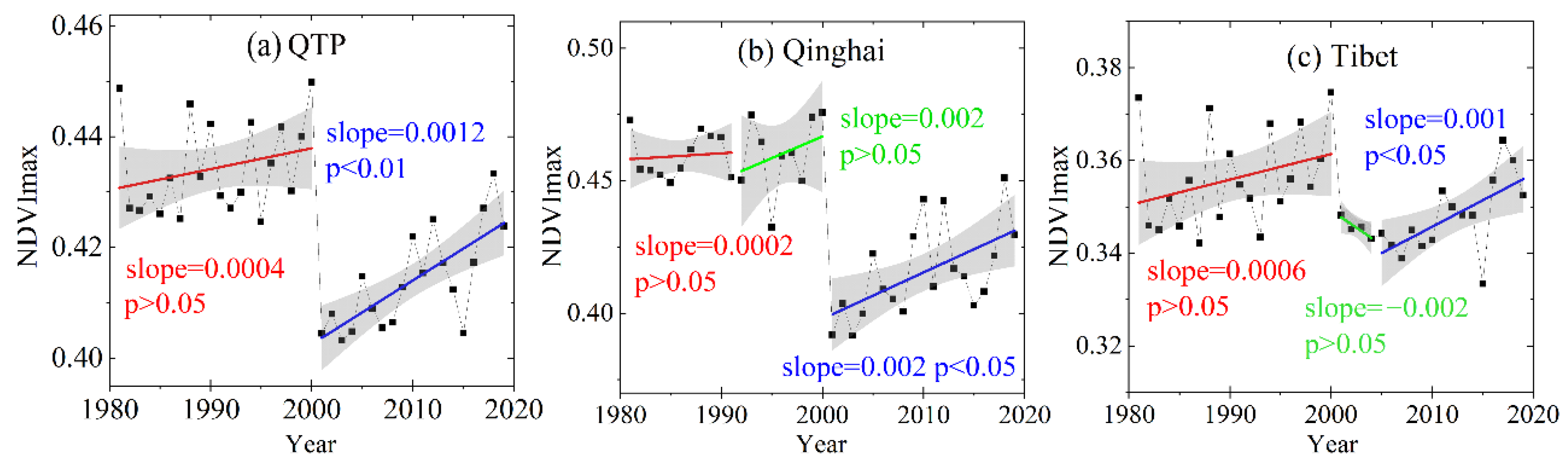
Figure 9.
Interannual variations of NDVImax in the QTP (a), Qinghai (b), and Tibet (c).
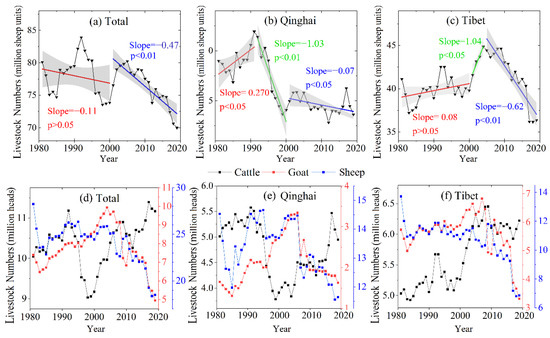
Figure 10.
The trends in livestock population and by livestock type in the QTP, Qinghai, and Tibet.
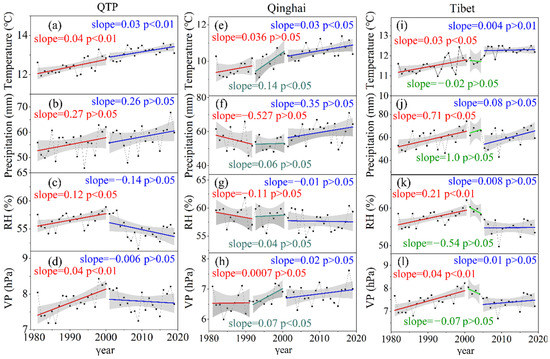
Figure 11.
Trends for the climate variables during the growing period for 1981–2019 ((a–d) QTP; (e–h) Qinghai; (i–l) Tibet; RH is relative humidity; VP is vapor pressure).
NDVImax, total livestock population, and interannual chases in climate in the Tibetan Plateau were divided into two periods, 1981–2000 and 2001–2019, respectively. It can be seen from Figure 10 that the changes of the livestock population in both Qinghai and Tibet generally occurred during three periods: 1981–1991, 1991–2000, and 2000–2019 for Qinghai, and 1981–2000, 2000–2004, and 2005–2019 in Tibet. To analyze the impact of livestock population on NDVImax, the interannual variations of NDVImax, trends in the livestock population, and interannual climate trends in Qinghai and Tibet were divided into three periods.
As shown in Figure 9a, there was a significant difference in the average NDVImax in the QTP during the two stages, which was caused by the different NDVI sources. NDVImax had a non-significant trend during the first stage, with an annual growth rate of 0.0004 yr−1 (p > 0.05), but NDVImax had a significant positive trend of about 0.0012 yr−1 (p < 0.01) during 2001–2019. Overall, the changes in livestock population in the QTP between 1981 and 2000 were not conducive to vegetation growth (Figure 10a). Although the livestock population decreased starting in 1991, the disturbed alpine vegetation can take many years to recover [42,43]. Therefore, the positive influence of warmer and wetter climate (Figure 11a–d) should be the main reason why the NDVImax did not decrease during 1981–2000 (Figure 10a). From 2001 to 2019, the livestock population in the QTP decreased at a rate of 0.07 million sheep units/year (p < 0.01) (Figure 11a). The decrease in the livestock population helped reduce the grazing pressure over the QTP. Simultaneously, the climate conditions became warmer and wetter (Figure 11a–d), and vegetation had a positive trend in NDVImax during this period (Figure 10a). In addition, NDVImax in the QTP peaked in 2018 (Figure 9a) with a peak in precipitation (Figure 11b), but other climatic factors did not significantly change. The simultaneous peak in NDVImax and precipitation indicated that under a constant temperature, higher precipitation can promote vegetation growth and be the driving force of changes in vegetation.
As shown in Figure 9b, NDVImax in Qinghai changed little from 1981 to 1991, and it had a non-significant positive trend from 1992 to 2000 with a rate of 0.002 yr−1 (p > 0.05). From 2000 to 2019, NDVImax in Qinghai increased significantly at a rate of 0.002 yr−1 (p < 0.05). From 1981 to 1991, the livestock population in Qinghai increased significantly and peaked in 1991 (Figure 10b). During this period, temperature increased, and precipitation decreased (Figure 11e,f). Changes in weather conditions and livestock population are not beneficial to vegetation growth. However, there was no obvious change in NDVImax (Figure 9b), which may be due to the better elasticity of the vegetation ecosystem in this area, and this change was within its tolerance. From 1992 to 2000, the livestock population in Qinghai decreased significantly at a rate of 1.03 million sheep units/year (p < 0.01) (Figure 10b). During this period, the temperature and the precipitation increased (Figure 11e,f). Thus, the increase of NDVImax between 1992 and 2000 in Qinghai can be explained by the positive trend in temperature and precipitation and stark decreases in the livestock population.
From 2000 to 2019, the livestock population in Qinghai maintained a downward trend (p < 0.05) (Figure 10a). During this period, both temperature and precipitation increased (Figure 11a,b). Both the changes of livestock population and weather conditions in Qinghai from 2000 to 2019 contributed to the increase of NDVImax.
As shown in Figure 9c, NDVImax in Tibet had a positive trend from 1981 to 2000, with a rate of 0.0006 yr−1 (p > 0.05). From 2000 to 2004, NDVImax decreased at a rate of 0.002 yr−1 (p > 0.05). From 2005 to 2019, NDVImax increased at a rate of 0.001 yr−1 (p < 0.05). During 1981–2000, the livestock population in Tibet increased slowly at a rate of 0.08 million sheep units/year (Figure 10c), and temperature and precipitation increased significantly (p < 0.05) (Figure 11i,j). Thus, vegetation has favored changes in climate during this period and could have been a driving force of the positive trends in NDVImax (Figure 9d). Considering that the climate during 2001–2004 did not change significantly, the rapid increase in livestock population in Tibet at a rate of 1.039 million sheep units/year (Figure 10c) was the driving force of negative NDVImax trends (Figure 9c). From 2005 to 2019, the livestock population in Tibet decreased rapidly at a rate of 0.622 million sheep units/year (p < 0.05) (Figure 11b), and temperature and precipitation increased (Figure 11e,f). Due to decreased livestock population and favorable climate conditions, NDVImax during this period increased significantly at a rate of 0.001 yr−1 (p < 0.05).
It can be seen from Figure 10a–c that the livestock population for Qinghai and Tibet in recent years has been lower than in the 1980s. Overall, the control of the livestock population was beneficial to vegetation recovery.
4. Discussion
4.1. Interannual Trends of NDVI in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau
As an indicator of vegetation greenness, NDVI has been widely used to assess vegetation dynamics [9,10,11,12] MOD13A2 and GIMMS-NDVI have been the most widely used source of NDVI data. In previous studies on vegetation dynamics in the QTP, nearly all used average NDVI (NDVIavg) to represent the overall level of vegetation growth. For example, Zhang [5] used annual mean NDVI, and Chen [7] used averaged NDVI in the growing season.
Zhang [5] used annual NDVIavg derived from GIMMS and non-parametric rank-based MK test to analyze the interannual trends of vegetation change in the QTP and found that 26.4% of the pixels increased and 5.58% decreased significantly during 1981–2000. Using mean annual growing season NDVI from MOD13A2 and a univariate linear regression to determine the trend, Chen [7] found that NDVIavg in the growing season had a significant increase (0.0011 yr−1) during 2000–2019. They found that approximately 79.29% of the pixels had a greening trend and the greener area was mainly concentrated in northern QTP, especially in the northeast. Areas with a negative trend in greenness accounted for 20.71% of the area, which were mainly concentrated in the central plateau and north Tibet.
Here, we used NDVImax to represent the peak of vegetation greenness. Although our findings were basically consistent with previous studies, growth rate of NDVI and the areas where NDVImax changed were moderately different. Our results show that the annual NDVImax increased at a rate of 0.0012 yr−1 during 2000–2019, which is little higher than the growth rate of NDVIavg in the conclusion of Chen [7]. The difference in vegetation status represented by maximum NDVI and average NDVI may be the reason for the difference in the growth rate between them [16]. We found that annual NDVImax during 1981–2000 increased for 36.3% of the area in the QTP, and 11.3% of the area had a significant decrease in NDVImax (p < 0.05). Annual NDVImax during 2001–2019 showed that 63.7% of the vegetation became significantly greener and 6.7% of the QTP area had a significant decrease in NDVImax. The changed area of NDVImax during 1981–2000 in our results is larger than the results of Zhang [5]. The changed area of NDVImax during 2001–2019 is smaller than that of Chen [7]. The difference between our study and other studies is likely caused by different change detection methods (e.g., non-parametric rank-based MK test, modified Mann–Kendall test, and univariate linear regression). The linear regression method uses the least squares method to fit the linear model and determines the trend according to the slope of the fitted line [5]. The MK test is suitable for trend analysis of non-normally distributed hydrometeorological data and climatic time series [35]. Yue [34] proposed the modified MK test using effective sample size to eliminate the influence of serial correlation in time series. Therefore, the difference in these algorithms may lead to different results for the same climate data. In the future, perhaps we should compare the effectiveness of the different change detection methods in the QTP.
4.2. The Effects of Climate Change on the Interannual Trends of NDVI
Several studies evaluated the interannual trend of the climate variables [5,7]. Zhang [5] collected from meteorological stations and the non-parametric rank-based MK test to analyze trends of climate in QTP. They found that the temperature had a positive trend from 1981 to 2013, and that the annual rainfall in Tibet from 1981 to 2000 also had a positive trend, while the rainfall in Qinghai from 1981 to 2000 had a negative trend, which was consistent with our results. Chen [7] collected temperature data from the MOD11A2 product, calculated a moist coefficient to represent water availability, applied univariate linear regression to calculate the trends of climate change in the growing season, and calculated the correlation between vegetation and climatic factors in the QTP during 2000–2019. They found that the northeast, mid-east, and western edges of the plateau became cooler and wetter, while the southwest, mid-west, and southeast became warmer and drier. However, we found that from 2001 to 2019, nearly all of the QTP had increased temperature. The difference in these findings may be due to the use of different meteorological data and different trend analysis methods.
In terms of the correlation between NDVI and climate variables, Chen [7] showed that vegetation in northern QTP was mainly negatively correlated with temperature, while in the southern QTP there was a positive correlation. However, we found that NDVI in most areas of the QTP during 2000–2019, especially Qinghai and western Sichuan, was mainly positively correlated with temperature, while central-northern Tibet was negatively correlated with temperature. Our results were consistent with Zhou [44], who used GIMMS-NDVI data and temperature obtained from the China National Meteorological Information Center to investigate the relationship between alpine grassland vegetation and temperature from 1982 to 2006 over the QTP. They found that NDVImax was negatively correlated with temperature in areas with severe degradation, while NDVImax was mainly positively correlated with temperature in areas with greener vegetation. Both Zhou [44] and we used meteorological data from weather Station, while Chen [7] used MOD11A2 product. The different sources of meteorological data may be the reason why our results of the correlation analysis are similar with Zhou [44] but different with Chen [7].
In terms of the impact of climate on vegetation, our results agreed with Huang [6] who collected precipitation and temperature datasets from the Chinese Meteorological Data Service and used linear regression and the sequential MK method to detect trends. Their results showed that the climate in the arid regions across Tibet from 2000 to 2011 did not promote grassland growth and the effects of climate and human activities on vegetation varied with location and time period.
As shown in Figure 8, in areas where NDVImax changed significantly, relative humidity and vapor pressure had a strong correlation with NDVImax. Considering that relative humidity and vapor pressure both represent atmospheric moisture to some extent, our results indicated that atmospheric water content has a great influence on the vegetation growth in the QTP, which was consistent with the conclusions of Ding [24] and Yuan [45], whose research showed atmospheric water content affects vegetation growth.
4.3. The Effects of Livestock Management on the Interannual Trends of NDVImax
To strengthen the ecological protection of the QTP, the Chinese government adopted a series of measures in recent decades. Since 2003, the Chinese government has implemented the Grazing Withdrawal Program (GWP) in Tibet and other pastoral provinces to restore and improve vegetation conditions. Since then, many fencing projects have been implemented in the QTP to restore and protect the degraded grasslands. By 2012, the area of fenced land in northern QTP had reached 3.32 million hectares [46]. In these areas, grazing prohibition, no grazing, or grazing rotation policies were implemented. Since 2011, eight provinces and regions, including Tibet, Qinghai, Sichuan, Xinjiang, and Gansu, have implemented the Ecological Subsidy and Award System. These subsidies and rewards mainly include grazing prohibition subsidies, grass-livestock balance rewards, pasture seed subsidies, livestock seed subsidies, and production subsidies.
The size of the livestock population is the key to effective alpine grassland management in the QTP [3]. Many studies have found that these ecological protection measures have significantly reduced the livestock population, relieved the grazing pressure on grasslands, and contributed to the ecological restoration of pastures [3,46]. Here, we found that the livestock population in Tibet and Qinghai has decreased since 2004, which was after the implementation of the GWP. Li [47] conducted a short term field experiment (4–5 years) to quantify the impact of different grazing management regimes and found that fencing was the most suitable grazing management regime for QTP alpine meadows. Through meta-analyses and questionnaire-based surveys, Sun [48] reported that fences were effective in promoting aboveground vegetation growth for up to four years in degraded alpine meadows and for up to eight years in the alpine steppes of the QTP. Our results also show that the reduction in the livestock population had a positive impact on vegetation restoration. Since 2003, adverse effects of overgrazing on vegetation have been gradually curbed and the contribution of climate change to grassland degradation exceeds the impact of overgrazing in the QTP.
In terms of the impact of climate and livestock population on vegetation changes, our results were consistent with those of Lehnert [49]. Based on the precipitation data provided by the Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission (TRMM, 3B42) from 2000 to 2013 and temperature from the ERA-Interim reanalysis data, Lehnert [49] used linear multi-temporal correlation analysis methods to study the effects of climate change and livestock population on vegetation coverage. They found that the vegetation cover has increased since the year 2000 in north-eastern QTP due to an increase in precipitation, and that vegetation cover declined in central-western QTP due to rising temperature and declining precipitation. They concluded that climate variability, rather than overgrazing, was the primary cause for large-scale changes in vegetation in the QTP since the new millennium. However, vegetation change includes not only vegetation degradation, but also vegetation greenness. We found that both climate change and the decline in the livestock population were beneficial to vegetation greening. Future studies are needed to determine which factor contributed more to vegetation greening.
5. Conclusions
The annual growth rate of NDVImax during 2000–2019 had a significant positive trend with an annual growth rate of 0.0012 yr−1 (p < 0.01). From 1981 to 2000, 11.3% of the QTP area had a decrease in NDVImax, mainly in the central and eastern of QTP. From 2000 to 2019, 63.7% of the QTP area became greener and 6.7% of the QTP area had a decrease in NDVImax. These areas with a decrease in NDVImax were mainly located in central-northern Tibet and southern Qinghai.
We also found a strong correlation between NDVImax and vapor pressure in areas with significant changes in NDVImax, which indicated that atmospheric water content greatly impacted vegetation growth in the QTP. The reasons for NDVImax changing differed between the periods and for different places. Positive trends in average NDVImax in Tibet from 1981 to 2000 was mainly due to favorable climate change that vegetation found to be favorable. Vegetation degradation in large areas of Qinghai from 1981 to 2000 and central-northern Tibet during 2000–2019 was mainly affected by a drier and hotter climate, considering that the negative impact caused by the increase in livestock population was weakened or offset by later livestock management. Overall, significant reductions in the livestock population and favorable changes in climate during 2000–2019 contributed to vegetation restoration of the entire QTP.
Author Contributions
E.L. conceived of the idea, analyzed the data, wrote and revised the manuscript. X.X. contributed to the design of the research, commented and revised the manuscript. H.S. contributed to analysis of the results and revised the manuscript. X.Y. contributed to analysis of the results. Y.Z. and Y.Y. performed the computations. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was supported in part by the China Scholarship Council (201908510014), the Key Project of Education Department of Sichuan Province of China (Natural Science) (Grant No.16ZA0087), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81961128002), and the U.S. National Science Foundation (1911955).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
GIMMS NDVI and MOD13A2 data is available on Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform (https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog, accessed on 17 October 2021). Meteorological Data can be in-quired through the website for the Meteorological Data Sharing Service System of China (http://data.cma.cn/, accessed on 17 October 2021).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IJmker, J.; Stauch, G.; Pötsch, S.; Diekmann, B.; Wünnemann, B.; Lehmkuhl, F. Dry periods on the NE Tibetan Plateau during the late Quaternary. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2012, 346, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Cui, M.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y. Altitude and temperature dependence of change in the spring vegetation green-up date from 1982 to 2006 in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Tao, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C. The impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on alpine grassland over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189–190, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, H.; Qin, J.; Lin, C.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: A review. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 112, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chang, J.; Xu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiang, S.; Duan, Z. The response of lake area and vegetation cover variations to climate change over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during the past 30 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zu, J.; Zhang, J. The influences of climate change and human activities on vegetation dynamics in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Yan, F.; Lu, Q. Spatiotemporal Variation of Vegetation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Influence of Climatic Factors and Human Activities on Vegetation Trend (2000–2019). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, H.; Vijay, P.; Daniel, R.; Brandt, M.; Michael, B.; Jerry, H.; David, W. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index as an Estimator for Abundance and Quality of Avian Herbivore Forage in Arctic Alaska. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1234. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Julien, Y. Global trends in NDVI-derived parameters obtained from GIMMS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 4267–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, D.; Guo, H.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y. Moisture-induced greening of the South Asia over the past three decades. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 4995–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.; Venevsky, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, M. NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and its response to climate changes at Amur-Heilongjiang River Basin from 1982 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Wei, J.; Pei, J.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, F.; Li, F.; Ye, J. Impacts of climate change and human activities on grassland vegetation variation in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Ma, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, S.; Xu, J.; Long, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Z. The impacts of climate change and human activities on alpine vegetation and permafrost in the Qinghai-Tibet Engineering Corridor. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gang, C.; An, R.; Li, J. Vegetation dynamics and its driving forces from climate change and human activities in the Three-River Source Region, China from 1982 to 2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, L.; Yan, J.; Qu, R. Vegetation net primary productivity and its response to climate change during 2001–2008 in the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Du, L.T.; Hou, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Gong, F. Spatiotemporal variations of NDVI in terrestrial ecosystems in China from 1982–2012. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 1885–1896. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Fan, K.; Zhou, L. Satellite observations of El Niño impacts on Eurasian spring vegetation greenness during the period 1982–2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, G.J.; Epstein, H.E.; Walker, D.A. Spatial heterogeneity of tundra vegetation response to recent temperature changes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Fang, J.; He, J.; Xiao, Y. Spatial distribution of grassland biomass in China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2004, 28, 491. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Piao, S.; Chen, X.; An, S.; Fu, Y.H.; Wang, S.; Cong, N.; Janssens, I.A. Strong impacts of daily minimum temperature on the green-up date and summer greenness of the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3057–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Yi, G.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, X.; Miao, J.; Bie, X. Interannual variation in the start of vegetation growing season and its response to climate change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau derived from MODIS data during 2001 to 2016. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 48506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Air Temperature and Precipitation on Soil Moisture on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during the 2015 Growing Season. Adv. Meteorol. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, N.; Shen, M.; Yang, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Piao, S. Varying responses of vegetation activity to climate changes on the Tibetan Plateau grassland. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Peng, S.; Wang, T.; Piao, S. Increasingly important role of atmospheric aridity on Tibetan alpine grasslands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 2852–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zheng, Y.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Lombardozzi, D.; Wang, Y.; Ryu, Y.; Chen, G.; Dong, W.; Hu, Z. Increased atmospheric vapor pressure deficit reduces global vegetation growth. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, x1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kemp, D.R.; Guodong, H.; Xiangyang, H.; Michalk, D.L.; Fujiang, H.; Jianping, W.; Yingjun, Z. Innovative grassland management systems for environmental and livelihood benefits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8369–8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, X.; Wu, J.; Gong, X.; Lang, X.; Wang, C.; Song, S.; Ahmad, A.A. Effects of long term fencing on biomass, coverage, density, biodiversity and nutritional values of vegetation community in an alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 130, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Harris, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, R. Assessment of effects of climate change and grazing activity on grassland yield in the Three Rivers Headwaters Region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, F.; Li, H.; Hu, Q. Responses of vegetation greening and land surface temperature variations to global warming on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, 2001–2016. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.W.; Zhang, B.P.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, S. TRMM-data-based spatial and seasonal patterns of precipitation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 999–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Shu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y. Comparison of GIMMS and MODIS normalized vegetation index composite data for Qing-Hai-Tibet Plateau. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 533–544. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z. Temporal and spatial variation analysis of vegetation on the Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2013. Temporal Spat. Var. Anal. Veg. Tibet. Plateau 2017, 42, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, Z. Mapping cropping intensity in China using time series Landsat and Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Wang, C. The Mann-Kendall test modified by effective sample size to detect trend in serially correlated hydrological series. Water Resour. Manag. 2004, 18, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, G.C. The modified Mann-Kendall test: On the performance of three variance correction approaches. Bragantia 2013, 72, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cohen, I. Pearson Correlation Coefficient; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Zu, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, M.; Paudel, B. Increasing sensitivity of alpine grasslands to climate variability along an elevational gradient on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Piao, S.; Tang, Z.; Peng, C.; Ji, W. Interannual variability in net primary production and precipitation. Science 2001, 293, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ma, W.; Liang, C.; Flynn, D.; Schmid, B.; Fang, J.; He, J.S. Field-based observations of regional-scale, temporal variation in net primary production in Tibetan alpine grasslands. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 16843–16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, K.W.; Gao, J.B.; Wu, S.H.; Hou, W. Research progress on the response processes of vegetation activity to climate change. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Gu, S.; Zhou, X. Stability of alpine meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Shang, Z.; Gao, J.; Boone, R.B. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 287, 106684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.S.; Gao, H.F.; Zhang, T.; Ma, Y.Z. Relationship between vegetation index and ground surface temperature on the Tibetan Plateau alpine grassland. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2015, 37, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Xiao, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zou, Z.; Qin, Y. Open surface water mapping algorithms: A comparison of water-related spectral indices and sensors. Water 2017, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Song, C.; Fang, Y.; Wurst, S.; Wu, J. Grazing exclusion to recover degraded alpine pastures needs scientific assessments across the northern Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Cao, W.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Shi, S. Effects of grazing regime on vegetation structure, productivity, soil quality, carbon and nitrogen storage of alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, M.; Fu, B.; Kemp, D.; Zhao, W.; Liu, G.; Han, G.; Wilkes, A.; Lu, X.; Chen, Y. Reconsidering the efficiency of grazing exclusion using fences on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, L.W.; Wesche, K.; Trachte, K.; Reudenbach, C.; Bendix, J. Climate variability rather than overstocking causes recent large scale cover changes of Tibetan pastures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).