Abstract
Anhui Province is located in the superposition area of the “Strategy of the Rise of Central China” and the “Strategy of Integrated Development of the Yangtze River Delta”. Analyzing the high-quality development of Anhui Province is crucial for regional development. This paper proposes a comprehensive evaluation system based on the “New development philosophy”. Then, the information entropy method is applied to measure the high-quality development index (HQDI). The Markov transition probability matrix is used to explore the evolutionary trend of the HQDI. This paper also analyzes the coupling coordination relationships between high-quality development subsystems. Finally, the obstacle factor diagnostic model is adopted to find the factors that impede high-quality development. The result shows that: (1) There exists a significant spatial gradient difference in Anhui Province. The overall spatial distribution of the HQDI shows a pattern of “high in the central and east, low in the north and south”. (2) The “club convergence effect” and the “Matthew effect” of urban high-quality development are observed. (3) Subsystem analysis verified the existence of regional differences. Hefei has the leading position in all development subsystems. (4) The coupling coordination degree of subsystems is relatively low, and the problem of disorder development within Anhui Province is significant. (5) The fixed assets’ investment, the total amount of imports and exports, the GDP, the total urban wastewater treatment and the urban road passenger volume are the main obstacle factors.
1. Introduction
In the past decades, many cities in China have adopted extensive independent modes of development and consumed a large amount of energy and resources, resulting in serious environmental pollution. This leads to problems of labor mobility and urban polarization. Therefore, the issue of unbalanced regional development is severe. For instance, the per capita gross domestic product (GDP) of cities in Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Anhui Provinces in 2020 was compared. This revealed that the per capita GDP in Hefei, Wuhu and Ma’anshan, which are within Anhui Province, ranked only 14th, 15th and 17th among the 40 cities at the prefecture level or above [1,2,3]. The rest of the cities in Anhui Province are at the bottom of the rankings, indicating that the urban economic development level of Anhui Province is among the lowest in the Yangtze River Delta. The comparison of the economic level within Anhui Province reveals an obvious gradient difference and a serious regional development imbalance. For example, Hefei’s GDP exceeded CNY 1 trillion in 2020, which is CNY 919.5 billion higher than that of Huangshan [3]. The per capita GDP of Hefei reached CNY 108,400 in 2020, which is CNY 74,000 higher than that of Fuyang [3]. These facts indicate that Anhui not only has a significant development gap with Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Shanghai but also has a very serious imbalance in its internal economic development. It is imperative to promote the high-quality development of Anhui. Anhui Province is the superposition province of the “Strategy of the Rise of Central China” and the “Strategy of Integrated Development of the Yangtze River Delta”. How to comprehensively solve the problem of unbalanced and insufficient development in Anhui will be an important topic for achieving the overall high-quality development of the Yangtze River Delta and central China.
Therefore, the objective of this paper is to analyze the high-quality development level of the 16 prefecture-level and above cities (abbreviated as cities) in Anhui Province from 2014–2020. The “New development philosophy”, including innovative, coordinated, green, open and shared development, is one of the criteria to evaluate high-quality development in the new era [4]. For the purpose of better identifying high-quality development indicators, this paper adds an economic development dimension to the dimensions of the “New development philosophy”. Thus, a high-quality development index (abbreviated as HQDI) evaluation framework with six dimensions is proposed in this paper. In addition, to comprehensively analyze the HQDI, the information entropy method, Markov transition probability matrix, coupling coordination degree model and obstacle factor diagnostic model are applied. Then, we analyze the HQDI from the perspectives of time series, spatial evolution, level transition and subsystems. To further explore the urban HQDI in Anhui Province, coupling coordination degree analysis and obstacle factor analysis are proposed to construct an analysis framework. This paper reveals the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics, subsystem development process, coupling and coordination degree and main obstacle factors of the urban HQDI in Anhui Province. These facts not only help to analyze the actual level of urban high development but also provide references for improving the high-quality development level and narrowing regional differences in Anhui Province. On the above basis, the research technical framework is as shown in Figure 1.
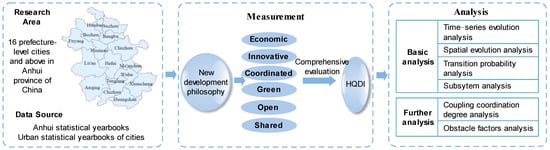
Figure 1.
Research technical framework.
The structure of this paper is organized as follows. Some relevant literature is reviewed in Section 2. A comprehensive evaluation system for measuring the HQDI is built in Section 3. The research methodology is also introduced in Section 3. The results of spatiotemporal evolution, transition characteristics, HQDI of the subsystems, coupling coordination degree and obstacle factors are displayed in Section 4. Then, the research results are discussed in Section 5. Finally, Section 6 presents the conclusions and implications.
2. Literature Review
The construction of the evaluation systems of economic, social and environmental development is the main focus of the existing literature. Narain et al. examined the socioeconomic development level of different states in India from aspects of the agricultural, infrastructural and overall socioeconomic sectors [5]. Ekins et al. proposed a four-capital model, which includes aspects of manufactural capital, natural capital, human capital and social capital to reflect the level of socio-economic development [6]. Kilijoniene et al. constructed a social and economic development indicator calculated by GDP, social infrastructure, labor force quality, unemployment level, incomes of inhabitants, technology and financial and physical resources [7]. Niebel, Shi and Ren proposed an economic growth quality index based on the fundamentals of economic outcomes, social outcomes and ecological outcomes [8]. Jing and Wang established a sustainable development index from aspects of social harmony, economic development and environmental improvement [9]. Liu et al. took green total factor productivity as a substitute indicator of high-quality economic development [10]. Liu and Zhang constructed an indicator system with six dimensions of economic growth, economic structure and innovative development as first-level indicators [11]. Tomal utilized an evaluation system that includes environment, demography, economy, infrastructure, housing and society to measure the local development index of municipalities in Poland [12]. An index system including the dimensions of economic scale, economic structure, economic efficiency and economic welfare was constructed to measure the urban economic development quality [13]. Furthermore, the high-quality development level evaluation system incorporates more aspects of development indicators based on the above studies. Li and Wang measured the high-quality development level from the internal and external aspects. They designed a comprehensive evaluation system that included the dimensions of production, living, ecology and urban connection [14]. Some Chinese researchers constructed a high-quality development evaluation system based on the “New development philosophy”. Gao, Song et al. and Hua et al. selected the indicators from the aspects of economic, innovation, coordinated, shared and open to measure the high-quality development level of China [15,16,17]. Tong et al. incorporated the growth momentum into a high-quality development evaluation system [18]. After the evaluation system construction, researchers mainly adopt the mean square error–TOPSIS method [16], the dynamic quadratic weighted method [18], the back propagation (BP) neural network [19], the information entropy method [20], the entropy–TOPSIS method [11,21], the linear weighted method [22] or the subjective and objective weighted method [23] to measure the level of high-quality development.
Some studies have found significant regional differences in China’s high-quality development level. The overall spatial performance of China’s high-quality development level is “high in the east, flat in the middle and low in the west” [24]. Shi and Zhang found that the urban high-quality development level of China is low and that there are significant convergence characteristics among cities [25]. Nie and Jian measured the inter-provincial high-quality development level and found that the regional difference in the high-quality development index decreased [22]. By measuring the high-quality development index of 10 urban agglomerations in China, Chen and Qing found that China’s urban agglomerations have a gradient of “high in the east and low in the west”, but the difference tends to decrease [21]. Scholars found that the key to promoting the development of low-level cities is to play the radiation-driving role of high-level cities [26]. However, most cities in Anhui Province have a low level of high-quality development, and there are significant spatial differences [27,28].
Scholars have begun to pay attention to the analysis of coupling coordination relationships in high-quality development subsystems. Gan et al. evaluated the coupling coordination degree of urbanization city–industry integration level in Sichuan using a coupling coordination degree model [29]. Some scholars have focused on the coupling coordination degree between economic and social development and environmental pollution [30,31,32]. Some studies have examined the coupling characteristics of ecological environment, science innovation, green finance and high-quality development [33,34,35]. Jin et al. measured the coupling coordination degree of the high-quality development level of prefecture-level cities in Shandong Province [36]. They found that the improvement in the urban coordinated development level was slow, and cities in Shandong Province are still in the primary integration development stage. Hua et al. analyzed the coupling coordination degree of high-quality development in counties of Zhejiang Province. They found that counties in Zhejiang Province have an intermediate coordinated degree [17]. Yuan et al. found that most cities in the eastern coastal areas of China have weak coordination degrees and obvious internal differences [37]. However, there is a lack of measurement of the internal coupling coordination relationships between the high-quality development subsystems.
Intending to promote high-quality development more accurately, scholars have tried to analyze the obstacle factors or influencing factors of high-quality development. The research result of Li et al. suggested that the over-concentration of the population and low energy efficiency are the main obstacles to low-carbon development in the Yangtze River Delta [32]. Chen et al. revealed that the number of full-time university teachers, the number of college students, the per capita living area and the per capita garden space are the main obstacles to high-quality development in the Yellow River basin [38]. Wang et al. analyzed the obstacle factors of 259 cities in China and discovered that a low-carbon economy, society and environment are the main obstacles restricting cities’ low-carbon development quality [39]. Consumer demand, science and technology, fixed asset investment and fiscal expenditure also play essential roles in high-quality economic development [40]. Feng et al. applied the obstacle degree analysis model and found that green development, innovative development and open development are the main obstacles that affect high-quality development in the Yellow River basin [41]. Shi et al. found that the imbalance in innovative development, coordinative development and open development restricts the high-quality development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt [42]. The above studies paid attention to some factors that affect high-quality development but neglected to measure the obstacle degree of subsystems and evaluation indicators.
In summary, these studies focused on the construction of evaluation index systems and the measurement of regional high-quality development levels. However, few studies have adopted the idea of analyzing the high-quality development index from a subsystem perspective. There are also few measurements of the high-quality development level of cities in central China, such as Anhui Province. In addition, the research on the transition probability and coupling coordination degree of subsystems is insufficient. Therefore, further analysis of the obstacle factors represents a breakthrough in improving high-quality development levels.
3. Evaluation System and Methodology
3.1. High-Quality Development Evaluation System
The “New development philosophy” is the theoretical support for achieving high-quality development in China. According to this theory, the realization of high-quality development should focus on the synergistic enhancement of all development dimensions. However, some relevant studies that build evaluation systems based on the “New development philosophy” usually ignore the economic development dimension. These studies incorporate economic indicators into other subsystems or ignore economic development indicators. Therefore, this paper added the economic development dimension to construct the evaluation system HQDI. The theoretical framework of urban high-quality development is shown in Figure 2. The six subsystems have different functions in the process of achieving high-quality development. Thus, this paper selects representative development achievements from each subsystem to construct a complete evaluation framework. Furthermore, concrete indicators are incorporated into the evaluation system to represent the development achievements of each subsystem (Table 1).
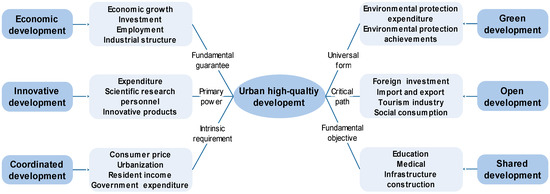
Figure 2.
Theoretical framework of urban high-quality development.

Table 1.
The evaluation system of HQDI.
As shown in Table 1, the HQDI measurement system includes six subsystems: economic development, innovative development, coordinated development, green development, open development and shared development. Considering the scientificity, representativeness and comparability of the evaluation system, 24 indicators are finally included. To reflect the effect of economic operations, GDP, fixed asset investment, number of employees and industrial structure index are selected as economic development indicators. The industrial structure index is calculated by the ratio of value added by the tertiary industry to that of the secondary industry. Then, this paper selects the number of research and development (R&D) personnel, internal expenditure on R&D, number of patents granted and technology fiscal expenditure to reflect the outcome of innovative development. The coordinated development indicators are represented by the general public budget expenditure, consumer price index, urbanization rate of the resident population and disposable income of the rural residents. Environmental protection fiscal expenditure, urban greening coverage area, total urban wastewater treatment and the amount of harmless disposal of domestic waste are selected to represent the green development indicators. Open development indicators are represented by the actual utilization of foreign investment, the total amount of import and export, the value added of the tourism industry and total retail sales of consumer goods. Education fiscal expenditure, medical fiscal expenditure, urban road passenger volume and electricity consumption of the whole society are selected to reflect shared development.
Based on the evaluation system, this paper measures the HQDI of 16 cities in Anhui Province during 2014–2020 (Figure 3). The original data were mainly adopted from the Anhui Statistical Yearbook and the Statistical Yearbooks of Cities.
Figure 3.
Prefecture-level and above cities in Anhui Province.
3.2. Information Entropy Method
The information entropy method is an objective and comprehensive evaluation method for development measurement that is suitable for multi-year evaluation [43]. By using this method, the information entropy in the research data is extracted. After that, the comprehensive evaluation index can be calculated by the weighted method.
Considering the different units and scales of indicators, the research data should be standardized first. The data standardization approach adopted in this paper is shown in Equation (1) [44].
In Equation (1), represents the standardized data of the i-th city and j-th indicator in θ-th year. (θ = 1, 2, 3, …, r; i = 1, 2, 3, …, m; j = 1, 2, 3, …, n), while is the original data. The steps of the information entropy method are as follows [44].
Step 1: the indicator weight is calculated.
Step 2: the information entropy value is calculated. In Equation (3), r and m denote the number of years and the number of cities in the research sample, respectively.
Step 3: the indicator weights are calculated.
Step 4: the comprehensive score is calculated. In Equation (5), represents the HQDI of the i-th city.
3.3. Markov Transition Probability Matrix
To further reflect the transition characteristics of the HQDI, a Markov transition probability matrix is introduced in this paper. The transition probability formula is defined as [22]:
In the above equation, parameter k indicates the level of HQDI. indicates the number of cities that transfer from rank i in year t to rank j in year . indicates the number of cities that rank i in year t. According to Tong et al., Chen and Qing, Nie and Jian, this paper tries to divide the HQDI into 4 levels and focus on the level transition of the HQDI in the next year [18,21,22]. Therefore, this paper takes and .
3.4. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
The coupling degree mainly describes the degree of interaction between subsystems, but it cannot reflect the coordinated development level between subsystems [45]. Further, the coupling coordination degree is a quantitative index to measure the coordination status between subsystems [45]. Therefore, the coupling coordination degree model is applied to study the degree of coordination of six development subsystems. A coupling coordination degree model is as follows [46].
In Equation (6), indicates the HQDI of the n-th subsystem (n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6). C indicates the coupling degree that describes the degree of interaction between subsystems. T indicates the comprehensive evaluation index. represent the weights of each subsystem solved by the information entropy method. D indicates the coupling coordination degree that describes the degree of coordinated development between subsystems. The value of the coupling coordination degree is between 0 and 1; relative studies divide it into 10 states to accurately describe the coordination degree of subsystems (Table 2) [45,47,48]. Therefore, the higher the value of D, the better the degree of coupling and coordination development between subsystems [47].

Table 2.
States distribution of coupling coordination degree.
3.5. Obstacle Factor Diagnostic Model
Obstacle factors can reflect the shortcomings that restrict high-quality development and can be identified by calculating the intensity of the negative impact of each indicator on the whole system [42]. The obstacle factor diagnostic model is utilized to analyze the obstacle factors that affect the high-quality development of cities in Anhui Province. An obstacle factor diagnostic model is as follows [49].
In Equation (10), indicates the deviation of indicators, indicates the standardized values of indicators, indicates the weight of indicator and indicates the obstacle degree (i = 1, 2, 3, …, m; j = 1, 2, 3, …, n). The higher the , the greater the impact of obstacle factors on the high-quality development level and the higher the degree of obstruction.
4. Results
4.1. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Evolution Trend
4.1.1. Time Series Evolution Analysis
The overall HQDI of cities in Anhui Province in 2014, 2016, 2018 and 2020 is displayed in Figure 4 (the full data of the HQDI are presented in Table A1 of Appendix A). (1) The HQDI of Hefei shows a significant growth trend during 2014–2020. It reaches a maximum value of 0.9243 and is much higher than other cities in Anhui Province. The HQDI of Wuhu ranks second in Anhui Province, rising slowly between 0.2245 and 0.3767. (2) The HQDI of the other 14 cities has a slight increasing trend in the range of 0.0428–0.2292. Chizhou, Huaibei, Tongling and Huangshan have low HQDIs. These cities are usually ranked 13th to 16th in Anhui Province. (4) During the research period, Bozhou, Fuyang, Chuzhou, Ma’anshan and Xuancheng rose slightly in the ranking of HQDI. Bengbu, Lu’an and Anqing showed a downward trend in 2020. The rank of the rest of the nine cities remained unchanged. (5) In 2020, the overall HQDI decreased in seven cities, including Bozhou, Bengbu, Fuyang, Huainan, Lu’an, Chizhou and Huangshan. In general, the stratification of the HQDI in Anhui Province is significant.
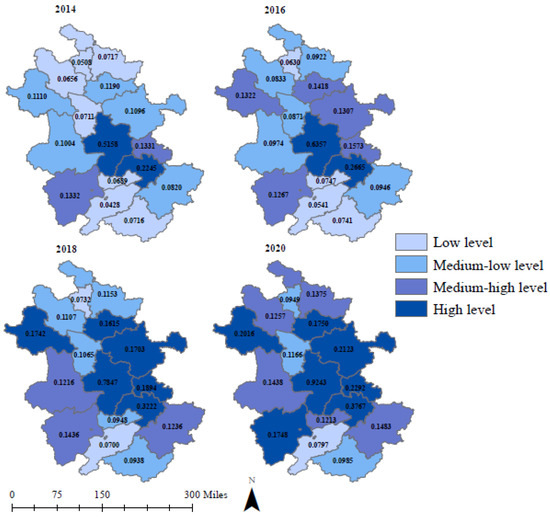
Figure 4.
The HQDI distribution in Anhui Province.
4.1.2. Spatial Evolution Analysis
Drawing on relevant research [21,22], this paper uses the quartile classification method to divide the HQDI into four equal parts, each containing about 25% of the data. To facilitate the division of HQDI levels, two decimal places are reserved for each quartile. Then, the ranges of four HQDI levels are: low level (HQDI < 0.08), medium–low level (0.08 ≤ HQDI < 0.12), medium–high level (0.12 ≤ HQDI < 0.16) and high level (HQDI ≥ 0.16). The resulting spatial characteristic of the HQDI in Anhui Province is shown in Figure 4. (1) In 2014, the spatial characteristics of the HQDI showed that Hefei and Wuhu had a high HQDI level, while Ma’anshan and Anqing had a medium–high HQDI. However, the HQDI of Fuyang, Lu’an, Bengbu, Chuzhou and Xuancheng maintained a medium–low level. Huaibei, Bozhou, Suzhou and Huainan are the northern cities of Anhui Province. Tongling, Chizhou and Huangshan are the southern cities of Anhui Province. Cities in the north and south of Anhui Province had a lower HQDI level. (2) There were two high level cities, five medium–high level cities, five medium–low-level cities and four low level cities in 2016. Compared to 2014, the HQDI level of Fuyang, Bengbu, Chuzhou, Bozhou, Suzhou and Huainan had moved up one level. Specifically, the HQDIs of Huaibei, Tongling, Chizhou and Huangshan are still maintained at a low level. (3) In 2018, the number of high level cities increased to six, including Fuyang, Bengbu, Hefei, Chuzhou, Ma’anshan and Wuhu. Meanwhile, the HQDI of Lu’an and Xuancheng had improved from a medium–low level to a medium–high level. However, Huaibei and Chizhou maintained a low level HQDI in 2018. (4) In 2020, the overall level of the HQDI in Anhui Province improved. And cities in eastern Anhui Province had higher HQDI. There were seven high level cities, five medium–high level cities, three medium–low level cities and one low level city. However, Chizhou always had the lowest HQDI during the research period. Overall, the urban HQDI of Anhui Province showed a pattern of “high in the central and east, low in the north and south”.
4.1.3. Markov Transition Probability Matrix of HQDI
The Markov transition probability matrix calculated in this paper is shown in Table 3. (1) The probability of maintaining the original level after one year is 68.18%, 70.00%, 77.27% and 100% for low level, medium–low level, medium–high level and high level, respectively. The probability on the diagonal is significantly higher than the probability on the off-diagonal. The above results indicate that the HQDI level is stable and that there exists the “club convergence effect” and the “Matthew effect”. (2) The probability of transitioning up a level after one year is 31.82%, 26.67% and 22.73% for the low level, medium–low level and medium–high level, respectively. The probability of transferring up two levels for the low level and medium–low level is 0%. These facts indicate that there is a possibility of leaping across levels. But a leap across two to three levels is almost impossible. (3) The probability of moving from a high level to a medium–high level is 0%. The probability of transferring from a medium–high level to a medium–low level and low level is 0%, too. The probability of transferring from a medium–low level to a low level is 3.33%.

Table 3.
The Markov transition probability matrix in Anhui Province.
4.2. Analysis of HQDI in Subsystems
Figure 5 shows the HQDIs of six subsystems. Despite the overall growth trend of economic HQDI, 14 cities in Anhui Province (except Hefei and Wuhu) showed a downward trend of economic HQDI in 2020. This is mainly caused by a significant employment decrease, weak GDP growth and an unbalanced industrial structure.
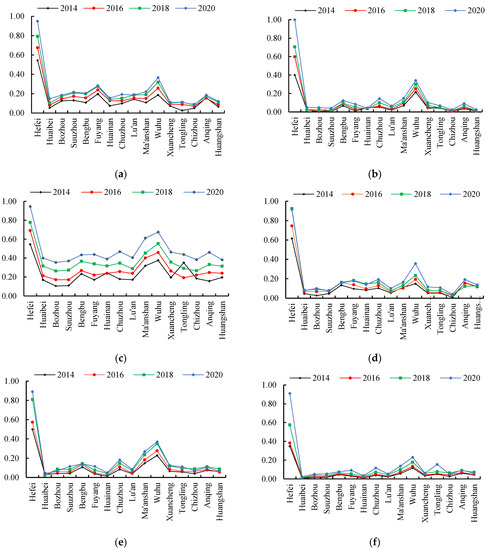
Figure 5.
The HQDI in 6 subsystems: (a) economic subsystem; (b) innovative subsystem; (c) coordinated subsystem; (d) green subsystem; (e) open subsystem; (f) shared subsystem.
The innovative HQDI of Hefei reached 1.0 in 2020 and increased by 150% from 2014 to 2020, while other cities grew slowly. However, the innovative HQDI in Wuhu was only 0.34, second in Anhui Province. The innovative HQDI of the other 14 cities was below 0.15, showing a large gradient. In 2020, Hefei’s internal expenditure on R&D was 2.8 times that of Wuhu, and the number of R&D personnel was 2.5 times that of Wuhu. Meanwhile, the number of patents granted in Hefei was 3.1 times that in Wuhu. Hefei’s technology fiscal expenditure was three times that of Wuhu’s. These facts indicate that there are large internal differences in innovative development.
The coordinated HQDI has a significant growth trend, and the inter-regional differences are smaller than in other development subsystems. However, the coordinated HQDI of Tongling dropped to 0.16 in 2015. The reason for this is that Tongling’s resident population increased by more than double due to the adjustment of the jurisdiction in 2015. Therefore, after 2015, the urbanization rate and the disposable income of the rural residents in Tongling were significantly lowered. In addition, the lack of growth in the coordinated HQDI in Fuyang is mainly due to the urbanization rate reduction in 2020.
Although the overall trend is upward, except for Hefei and Wuhu, there are 14 cities with a green HQDI below 0.2. Thus, the green development in Anhui Province is not effective, and its regional differences cannot be ignored. The reason for this is that environmental protection fiscal expenditure is insufficient and growth is slow. The expansion of green space coverage is not significant. The amount of wastewater treatment and harmless disposal of domestic waste still needs to be improved.
During 2014–2019, the open HQDI in Anhui Province showed an overall increasing trend. However, the tourism industry is one of the sectors most affected by the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. The value added by the tourism industry significantly plummeted and consequently caused the open HQDI of 16 cities in Anhui Province to significantly lower. Also, the actual utilization of foreign investment and the total amount of import and export in Bengbu shrank a lot in 2018. Thus, Bengbu’s open HQDI dropped to 0.14 in 2018. After that, Bengbu’s open HQDI recovered to 0.17 in 2019.
In addition, the shared HQDI displays a large regional difference. Hefei’s shared HQDI increased to 0.91 in 2020, while other cities’ shared HQDIs grew steadily at a lower level below 0.23. By analyzing the reasons behind this, it was found that the education financial expenditure and medical financial expenditure in Hefei increased significantly from 2017 to 2020. In 2020, Hefei’s education financial expenditure was more than 24 times that of Wuhu, and Hefei’s medical financial expenditure was more than 19 times that of Wuhu. These caused a significant gap between the first and second places in the shared HQDIs. Cities with lower shared HQDIs still need to improve their financial expenditures on education and medicine.
The mean value of the HQDI in each subsystem is shown in Figure 6. (1) In most years, coordinated HQDI > economic HQDI > green HQDI > open HQDI > innovative HQDI > shared HQDI. (2) There is an overall increasing trend in the HQDI of the six subsystems. However, the HQDI of the economic, green and open systems slightly decreased in 2020. (3) There are large differences among subsystems. In 2020, the coordinated HQDI was 0.34, 0.33, 0.30, 0.28 and 0.24 times higher than the shared HQDI, innovative HQDI, open HQDI, green HQDI and economic HQDI, respectively. Therefore, the balanced development of each subsystem is an important issue facing Anhui Province.
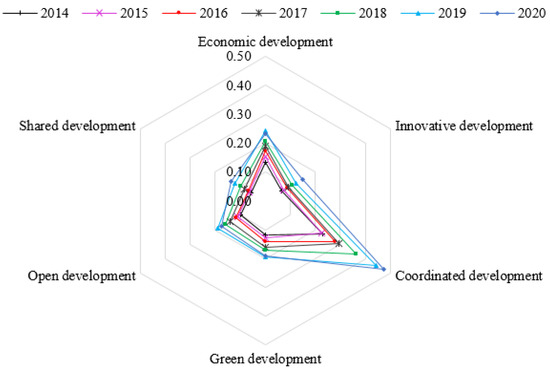
Figure 6.
The average HQDI in 6 subsystems from 2014 to 2020.
4.3. Analysis of Coupling Coordination Degree
To explore the coupling coordination degree (CCD) between subsystems, the CCD was calculated and displayed in Table 4. The CCD of Hefei has gone through a stage of “primary coordinated-intermediate coordinated-good coordinated”. And it upgraded to the “excellent coordination” stage in 2020 with a CCD of 0.97. However, the CCD of the other 15 cities is much lower than that of Hefei. For example, Wuhu’s CCD reached a maximum value of 0.59 in 2020, maintaining a barely coordinated state. Chuzhou, Fuyang, Anqing, Xuancheng, Tongling and Lu’an are currently experiencing the “moderate disorder-mild disorder” stage. Suzhou, Bozhou, Huainan, Huaibei and Chizhou are experiencing the “severe disorder-moderate disorder” stage. Ma’anshan is experiencing the “mild disorder-on the verge of disorder” stage. Huangshan is maintaining a “moderate disorder” state in the current research period.

Table 4.
The coupling coordination degree of 16 cities in Anhui Province.
4.4. Analysis of Obstacle Factors
To further explore the obstacle factors affecting urban high-quality development, this paper used the obstacle factor diagnostic model to analyze the subsystem indicators and the concrete indicators of high-quality development. Table 5 reports the obstacle degree of the six subsystems. The obstacle degree of economic development, green development and shared development shows an increasing trend. In contrast, the obstacle degree of innovative development and open development shows a decreasing trend. However, the obstacle degree of coordinated development shows a mildly fluctuating trend. In addition, innovative development is the biggest obstacle factor to high-quality development during 2014–2020. This is followed by open development, and the third obstacle factor is green development. Economic, shared and coordinated development have relatively small obstacle degrees on high-quality development. Therefore, cities should take the lead in enhancing innovative development. Meanwhile, the levels of open and green development also need to be improved urgently.

Table 5.
Obstacle degree of subsystem indicators in Anhui Province (%).
By calculating the obstacle degree of concrete indicators, the top five concrete obstacle indicators were obtained (Table 6). In 2014, the top five obstacle factors that limited the high-quality development of Anhui Province were fixed asset investment (7.15%), general public budget expenditure (7.04%), total amount of import and export (6.38%), education financial expenditure (5.53%) and GDP (5.30%). In 2017, the top five obstacle indicators that limited high-quality development were fixed asset investment (7.22%), general public budget expenditure (6.82%), total amount of import and export (6.70%), GDP (5.71%), and total urban wastewater treatment (5.58%). In 2020, the top five obstacle indicators that limited the high-quality development of cities in Anhui Province were general public budget expenditure (8.18%), fixed asset investment (6.91%), urban road passenger volume (6.39%), total amount of import and export (5.99%) and GDP (5.17%). Overall, fixed asset investment is the major impediment to high-quality development. It was the first obstacle factor in 2014–2017, and its obstacle degree had an upward trend. Then, it became the secondary obstacle factor in 2018–2020. General public budget expenditure became the largest obstacle factor in 2018, and its obstacle degree increased significantly. The total amount of import and export was the third obstacle factor during 2014–2019. In the process of high-quality development, the opportunities for Yangtze River Delta integration development should be fully utilized. Then, the new development pattern of domestic and international dual cycles will be established. Due to the low level of economic development in Anhui Province, GDP became the fourth obstacle factor during 2015–2018. In the future, economic growth should be regarded as an important task for high-quality development. Total urban wastewater treatment represents the ability to treat industrial and domestic wastewater in cities. It is also one of the main obstacle factors. Cities in Anhui Province should improve their sewage treatment capacities to improve the environment and enhance the effect of green development. The urban road passenger volume indicates the development degree of the urban transportation system. It is a vital indicator of shared development. The obstacle degree of urban road passenger volume increased significantly in 2018–2020. In the process of high-quality development, attention is still needed toward the construction of urban traffic systems.

Table 6.
Obstacle degree of concrete indicators in Anhui Province (%).
5. Discussion
The evaluation of high-quality development has gradually shifted from index evaluation [5,6,7,8,9,10] to index system evaluation [11,12]. The evaluation system is mainly constructed from the combination of high-quality development [13,14] and the “New development philosophy” [15,16,17,18]. Although few existing studies take Anhui Province as a study case, some scholars have paid attention to the measurement of the high-quality development level of cities in the Yangtze River Delta using the entropy–TOPSIS method [11,21], the subjective and objective weighted method [23] and the information entropy method [26]. The above studies found that there is a development gap between Anhui Province and other regions in the Yangtze River Delta. There also exists an obvious unbalanced spatial pattern of “high in the south and low in the north” in Anhui Province [28]. The time series evolution analysis in this paper confirms that the HQDI of most cities in Anhui Province maintains a low level. Also, the considerable spatial gradient differences in HQDI in Anhui Province are discussed by spatial evolution analysis. The above results are consistent with several studies [11,23,27]. In the future, more attention should be paid to the allocation of resources for high-quality development in the low-level cities.
Some scholars have analyzed regional differences by dividing the high-quality development levels. Chen and Qing used the quartile classification method to divide the high-quality development level into four levels. They found that there exists the “club convergence effect” and the “Matthew effect” in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration [21]. This paper also finds that the above two effects exist in Anhui Province. The systematic clustering method was applied to classify the high-quality development level into five levels and found that Hefei and Wuhu are at the medium development level, while Xuancheng, Chuzhou, Fuyang, Lu’an, Chizhou, Bozhou, Anqing, Suzhou, Huainan and Huaibei are at the low development level [23]. Yang et al. divided the high-quality development level of Anhui Province into three categories: Hefei is at the high level, Wuhu is at the medium level, and the other 14 cities are at the low level [27]. Similar to the above studies, central cities such as Hefei and eastern cities such as Bengbu, Chuzhou, Ma’anshan and Wuhu have a high HQDI level. Cities in northern, southern and western Anhui have relatively low HQDIs. The mobility of the HQDI levels across regions is also observed in this paper. Therefore, the risk of downward shifts of medium–low levels exists, but with a low probability. Cities in Anhui Province should consolidate the overall level and try to leap to a higher level while preventing the decline of the HQDI level.
Due to the “strong provincial capital” strategy of Anhui Province [50], Hefei is unique in its high-quality development level [11,50]. We also found that the HQDI of Hefei in all subsystems is significantly higher than in other cities, and the HQDI in Anhui Province presents a single-core model of Hefei alone. Although Wuhu’s HQDI ranks second in six subsystems, it is still significantly lower than Hefei’s HQDI. The HQDI distribution of the subsystems confirms the severity of the spatial gradient differences. Some studies have paid attention to the CCD of high-quality development from different perspectives [17,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. These studies found that the CCD of high-quality development in some cities has not yet reached a high level [17,35,36]. However, there are few studies on the CCD measurement of high-quality development subsystems. Wang and Li pointed out that the balance and coordination of the high-quality development of cities in Anhui Province are relatively low, and the unique situation of Hefei affects its radiation and driving ability [51]. Consistent with the above views, this paper reveals that, except in Hefei, the CCD between subsystems is low. The disorder problem is significant in the other 15 cities in Anhui Province. These will lead to a further widening of the development gap between Hefei and other cities.
The existing research mainly analyzes the obstacle degree or influencing effect on high-quality development, such as population and energy efficiency [32], education and human settlement environment [38], low-carbon development [39], consumption, science and technology, fixed asset investment and fiscal expenditure [40], green, innovative and open development [41] and innovative, coordinative and open development [42]. Consistent with the findings of Feng et al. and Shi et al. [41,42], innovative development is the key to achieving high-quality development. Open and green development is also an important way to achieve high-quality development. Cities in Anhui Province should maintain a high level of economic development, shared development and coordinated development. In the future, improving the level and utilization efficiency of general public budget expenditure and fixed asset investment should become the primary task for cities in Anhui Province. The study by Ren and Zhou also presented the above conclusion [40]. In addition, infrastructure construction and expansion of external circulation should also be given sufficient attention. Meanwhile, maintaining long-term and stable economic growth remains the foundation for achieving high-quality development.
6. Conclusions and Implications
6.1. Conclusions
Based on the “New development philosophy”, this paper adds an economic development dimension and constructs a comprehensive HQDI evaluation system. The information entropy method was used to measure the HQDI of 16 cities in Anhui Province during 2014–2020. The Markov transition probability matrix, coupling coordination degree model and obstacle factor diagnostic model were applied to build a multi-perspective analysis system. Under this system, spatiotemporal evolution characteristics, HQDI level transition trends, subsystem development levels, the coupling coordination degree of subsystems and obstacle factors were analyzed. This paper supplements the existing studies to a certain extent.
According to the results measured in this paper, it is found that: (1) In most years, the HQDIs of cities in Anhui Province have an increasing trend. There are spatial gradient differences among 16 cities in Anhui Province. And the mobility of HQDI levels across regions was observed from 2014 to 2020. (2) The “club convergence effect” and the “Matthew effect” of high-quality development exist in Anhui Province. Upward level transitions and level reductions are possible. Cities in Anhui Province should reduce the risk of reducing their HQDI. (3) The high-quality development of Anhui Province presents a pattern of Hefei being the dominant city. The HQDI of all subsystems in Hefei is significantly higher than that of the other 15 cities. (4) There are also significant differences in the degree of subsystem development. Usually, coordinated HQDI > economic HQDI > green HQDI > open HQDI > innovative HQDI > shared HQDI. (5) The coupling coordination degree of the high-quality development subsystems is low in most cities and shows a disordered state. (6) Innovative development, open development and green development are the main subsystem obstacles. Fixed asset investment, total amount of import and export, GDP, total urban wastewater treatment and urban road passenger volume are the top five obstacle indicators.
6.2. Theoretical and Practical Implications
Based on the above conclusions, the following theoretical and practical implications can be proposed to promote high-quality development in Anhui Province.
(1) A comprehensive quality development evaluation and analysis system should be established and applied. The evaluation system of high-quality development must match China’s development needs in the new era, and building a high-quality development evaluation system based on the “New development philosophy” is a reasonable choice. This will enhance the comparability of high-quality development studies and facilitate governments’ carrying out the evaluation, monitoring and comparison of high-quality development, and then adjusting the development strategy. Meanwhile, measurement and analysis methods are crucial to high-quality development research. Objective measurement methods can evaluate a more accurate high-quality development level, and the Markov transition probability matrix helps to reveal the “club convergence effect” and the “Matthew effect”. The analysis of subsystems and CCD can reflect the development gap between each subsystem and provide a relevant basis for the government to formulate specific policies. Obstacle factor analysis is less frequently applied in current research. By measuring the obstacle degree of development systems and evaluation indicators, the main barriers to high-quality development can be identified.
(2) The graded regional development policies should be formulated in the new era. There are differences in the level of economic development, resource endowment, demographic structure, policy system and business environment of each city. Therefore, governments should promote the coordinated development of various cities in an orderly and differentiated way so that regional development tends towards being balanced.
(3) The rational and efficient flow of regional development factors should be promoted. We should pay more attention to the developmental differences among cities in Anhui Province. The restrictions on resource allocation and factor circulation between cities should be broken. Cooperation and the flow of development factors between cities should be strengthened. Consequently, the quality and efficiency of development can be enhanced. Furthermore, the expansion of regional development imbalances will be avoided. Finally, more coordinated development will be achieved.
(4) Multi-system, balanced high-quality development should be valued. High-quality development is the development of multiple systems achieving steady improvement simultaneously. Few cities have been able to achieve balanced and comprehensive multi-system development. Thus, governments should explore and overcome obstacle factors of high-quality development. Also, the focus point of high-quality development should be identified to realize precise development.
(5) The overall upward leap in the high-quality development level should be promoted. Hefei is the capital city of Anhui Province. It has always taken the leading position in high-quality development and should undertake more development tasks. Its high-quality development advantages and resources can be used to radiate toward neighboring cities. The remaining cities are relatively behind in terms of their high-quality development levels. They should focus on learning from the development experience of advanced cities to achieve high-quality development.
6.3. Limitations and Future Lines of Research
This paper has the following limitations. Due to limitations of the data, we only measured the HQDI of Anhui Province and failed to measure the HQDI of other central provinces in China. Future research should focus on the evaluation and comparison of high-quality development in central China, including Shanxi, Anhui, Jiangxi, Henan, Hubei and Hunan. Additionally, the information entropy method is applied to measure the HQDI in this paper, and the comparative analysis of various measurement methods is not realized. Thus, the comparison and improvement of the measurement methods for high-quality development deserve further research. Finally, the influencing mechanism of obstacle factors on high-quality development is worth further exploring through econometric models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W.; methodology, R.Z.; software, J.X.; validation, X.W.; formal analysis, X.W.; investigation, X.W.; resources, X.W.; data curation, R.Z; writing—original draft preparation, X.W.; writing—review and editing, X.W.; visualization, R.Z. and J.X.; supervision, X.W.; project administration, X.W.; funding acquisition, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project of Anhui Province, China (grant no. AHSKQ2021D96).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
HQDI of 16 cities in Anhui Province.
Table A1.
HQDI of 16 cities in Anhui Province.
| Cities | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hefei | 0.5158 | 0.5538 | 0.6357 | 0.6980 | 0.7847 | 0.8931 | 0.9243 | 0.7150 |
| Huaibei | 0.0509 | 0.0523 | 0.0630 | 0.0673 | 0.0732 | 0.0886 | 0.0949 | 0.0700 |
| Bozhou | 0.0656 | 0.0726 | 0.0833 | 0.0955 | 0.1107 | 0.1370 | 0.1257 | 0.0986 |
| Suzhou | 0.0717 | 0.0791 | 0.0922 | 0.1000 | 0.1153 | 0.1316 | 0.1375 | 0.1039 |
| Bengbu | 0.1191 | 0.1279 | 0.1418 | 0.1505 | 0.1615 | 0.1786 | 0.1750 | 0.1506 |
| Fuyang | 0.1110 | 0.1221 | 0.1322 | 0.1473 | 0.1742 | 0.2090 | 0.2016 | 0.1568 |
| Huainan | 0.0712 | 0.0758 | 0.0871 | 0.0961 | 0.1065 | 0.1194 | 0.1166 | 0.0961 |
| Chuzhou | 0.1096 | 0.1150 | 0.1307 | 0.1443 | 0.1703 | 0.2064 | 0.2123 | 0.1555 |
| Lu’an | 0.1004 | 0.0908 | 0.0974 | 0.1090 | 0.1216 | 0.1450 | 0.1438 | 0.1154 |
| Ma’anshan | 0.1331 | 0.1435 | 0.1573 | 0.1667 | 0.1894 | 0.2133 | 0.2292 | 0.1761 |
| Wuhu | 0.2245 | 0.2411 | 0.2665 | 0.2942 | 0.3222 | 0.3633 | 0.3767 | 0.2984 |
| Xuancheng | 0.0820 | 0.0859 | 0.0946 | 0.1084 | 0.1236 | 0.1475 | 0.1483 | 0.1129 |
| Tongling | 0.0689 | 0.0654 | 0.0747 | 0.0857 | 0.0948 | 0.1125 | 0.1213 | 0.0890 |
| Chizhou | 0.0428 | 0.0475 | 0.0541 | 0.0601 | 0.0700 | 0.0836 | 0.0797 | 0.0625 |
| Anqing | 0.1332 | 0.1228 | 0.1267 | 0.1362 | 0.1436 | 0.1735 | 0.1748 | 0.1444 |
| Huangshan | 0.0716 | 0.0664 | 0.0741 | 0.0842 | 0.0938 | 0.1069 | 0.0985 | 0.0851 |
| Mean | 0.1232 | 0.1289 | 0.1445 | 0.1590 | 0.1785 | 0.2068 | 0.2100 | - |
References
- Jiangsu Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook-2021; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhejiang Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Zhejiang Statistical Yearbook-2021; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Anhui Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Anhui Statistical Yearbook-2021; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bei, J. Study on the “High-Quality Development” Economics. China Polit. Econ. 2018, 1, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narain, P.; Sharma, S.D.; Rai, S.C.; Bhatia, V.K. Statistical evaluation of socio-economic development of different states in India. Indian Soc. Agric. Stat. 2007, 61, 328–335. [Google Scholar]
- Ekins, P.; Dresner, S.; Dahlström, K. The four-capital method of sustainable development evaluation. Eur. Environ. 2008, 18, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilijoniene, A.; Simanaviciene, Z.; Simanavicius, A. The evaluation of social and economic development of the region. Inz. Ekon. Econ. 2010, 21, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Niebel, T. ICT and economic growth—Comparing developing, emerging and developed countries. World Dev. 2018, 104, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wang, J. Sustainable development evaluation of the society–economy–environment in a resource-based city of China: A complex network approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Zhao, L.; An, P. Effect of environmental regulation on high-quality economic development in china—An empirical analysis based on dynamic spatial Durbin model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 54661–54678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, J. Evaluation of the Quality of Economic Development in Anhui Province Based on Entropy-TOPSIS Model. Front. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2022, 4, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomal, M. Evaluation of coupling coordination degree and convergence behaviour of local development: A spatiotemporal analysis of all Polish municipalities over the period 2003–2019. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 71, 102992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Yin, Y.; Kuang, C.; Wen, Z.; Kuang, J. Spatial spillover effect of green innovation on economic development quality in China: Evidence from a panel data of 270 prefecture-level and above cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, H. Comprehensive evaluation of urban high-quality development: A case study of Liaoning province. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 1809–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P. Comprehending, grasping, and promoting high-quality economic development. Econ. Perspect. 2019, 8, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Tao, W.; Shen, Z. Improving high-quality development with environmental regulation and industrial structure in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Jin, X.; Lv, H.; Ye, Y.; Shao, Y. Spatial-temporal pattern evolution and influencing factors of high quality development coupling coordination: Case on counties of Zhejiang Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Chu, C.; Li, Y. Research on the distribution dynamics, regional differences and convergence of China’s high-quality economic development. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2022, 39, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ren, B. Construction, measurement and comprehensive evaluation of China’s high quality development index in the New Era. China Policy Rev. 2019, 14, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, S.; Yan, J. Level Measures and Temporal and Spatial Coupling Analysis of Ecological Environment and High Quality Development in the Yellow River Basin. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 49–57+80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qing, M. Research on the measurement of the high-quality development level of China’s urban agglomerations and its temporal and spatial convergence. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2022, 39, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Jian, X. Measurement of China’s high-quality development and analysis of provincial status. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2020, 37, 26–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Yao, N.; Song, Q.; Chen, J. Quality development level measurement and spatio-temporal difference analysis of Urban Agglomeration in Yangtze River Delta. East China Econ. Manag. 2022, 36, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, S. Study on the measurement of economic high-quality development level in china in the New Era. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2018, 35, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Zhang, B. Measurement and analysis of economic quality development of cities above prefecture level nationwide. Soc. Sci. Res. 2019, 41, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, W. Regional disparity and dynamic evolution of distribution of high-quality urban development in Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2022, 31, 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Dou, Q.; Yao, Y. Measurement on high-quality development level of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomerations. Stat. Decis. 2021, 37, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, D. Spatial and Temporal Differentiation Trends and Attributions of High-Quality Development in the Huaihe Eco-Economic Belt. J. Resour. Ecol. 2023, 14, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Shi, H.; Hu, Y.; Lev, B.; Lan, H. Coupling coordination degree for urbanization city-industry integration level: Sichuan case. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 58, 102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q. Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment—Empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Bai, W.; Jin, Y.; Yu, M.; Ren, J. Measuring coupling coordination between urban economic development and air quality based on the Fuzzy BWM and improved CCD model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, K.; Du, Z.; Han, K. Coupling coordination degree and driving factors of new-type urbanization and low-carbon development in the Yangtze River Delta: Based on nighttime light data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 81636–81657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, G. Identifying network structure characteristics and key factors for the co-evolution between high-quality industrial development and ecological environment. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 25, 6591–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Tan, J.; Liu, D.; Tang, F. Research on the coupling relationship between urban innovation efficiency and economic high-quality development and its temporal and spatial characteristics. J. Stat. Inf. 2021, 36, 104–119. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, J. Coupling and coordination evaluation of regional green finance and high quality development. Stat. Decis. 2021, 37, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhang, B.; Kang, J. Research on the level of high-quality economic development and its coupling and coordination based on the panel data of 17 cities in Shandong Province. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 37, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.; Guo, J.; Zhu, C. Spatial Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Coupling and Coordination of High-Quality Development in Eastern Coastal Areas of China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, W. Evaluation of ecological city and analysis of obstacle factors under the background of high-quality development: Taking cities in the Yellow River Basin as examples. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Yin, S.; Chen, W. Low-carbon development quality of cities in China: Evaluation and obstacle analysis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhou, Z. An Empirical Analysis on the Influencing Factors of Economic Growth in Anhui Province. Int. J. Educ. Humanit. 2022, 2, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X. Measurement of spatio-temporal differences and analysis of the obstacles to high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; He, X.; Peng, K. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of High Quality Development Level in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and Identification of Obstacles. East China Econ. Manag. 2023, 37, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, C.; Cheng, L. Measurement and comparison of high-quality development of world economy. Economist 2020, 32, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, F.; Yuan, X. Evaluation and evolution of provincial high-quality green development in China. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, R. Impact of land use change on coupling coordination degree of regional water-energy-food system: A case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 582–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Min, J. An analysis of coupling between the bearing capacity of the ecological environment and the quality of new urbanization in Chongqing. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 817–828. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Long, H. Spatial pattern and influencing factors of the coordination development of industrialization, informatization, urbanization and agricultural modernization in China: A prefecture level exploratory spatial data analysis. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.; Chen, J.; Tao, F.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M. On the Coupling and Coordination Development between Environment and Economy: A Case Study in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yue, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Spatial-temporal pattern and obstacle factors of urban residents’ quality of life in the Yellow River Basin under the background of high-quality development. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, N. The Evaluation Logic and Spatial Characteristics of Urban High-Quality Development in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Anhui Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2022, 46, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J. Balanced Characteristics and Obstacle Factors of High Quality Green Development in Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 1540–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).