Abstract
An underground aqueduct is usually a canal built in the subsurface to transfer water from a starting point to a distant location. Systems of underground aqueducts have been applied by ancient civilizations to manage different aspects of water supply. This research reviews underground aqueducts from the prehistoric period to modern times to assess the potential of achieving sustainable development of water distribution in the sectors of agriculture and urban management, and provides valuable insights into various types of ancient underground systems and tunnels. The review illustrates how these old structures are a testament of ancient people’s ability to manage water resources using sustainable tools such as aqueducts, where the functionality works by using, besides gravity, only “natural” engineering tools like inverted siphons. The study sheds new light on human’s capability to collect and use water in the past. In addition, it critically analyzes numerous examples of ancient/historic/pre-industrial underground water supply systems that appear to have remained sustainable up until recent times. The sustainability of several underground structures is examined, correlated to their sound construction and regular maintenance. Moreover, several lessons can be learned from the analysis of ancient hydraulic works, particularly now, as many periodically hydrologic crises have occurred recently, overwhelmingly impacted by climate change and/or over-exploitation and degradation of available water resources.
1. Introduction
Traditional underground hydro-technologies were constructed mainly for the exploitation of groundwater in arid areas. These technologies presented major achievements in this scientific field throughout the millennia [1]. In fact, it is difficult to investigate past underground structures and prove their sustainability. However, an example described by Barghouth and Al-Sa’ed [2] presented an overview on the sustainability of ancient water supply systems in Jerusalem from the Chalcolithic period (ca 4500–3200 BC) to the present. Archaeological evidence and landscape settings showed that the ancient water resources management in Jerusalem were based on underground hydro-structures. Sustainable water supply facilities were erected, consisting mainly of well-developed aqueducts or other similar underground hydro-structures, in order to supply the town and their agricultural developments, showing that irrigated agriculture was practiced for many centuries in this region.
This analysis of ancient hydro-technology works provides valuable insight into the most significant underground systems: aqueducts of various types, qanats and associated hydraulic structures like cisterns, sewage systems, etc., and moreover, how they functioned. Open or tunneled aqueducts providing transport from water sources to inhabited settlings are always the most important part of the hydraulic system. Qanats consist of tunnels and various types of inclined galleries with or without shafts, transferring ground and/or surface water from an aquifer and/or a spring, usually located in a mountain ridge or at its foothills, to the lowlands, sometimes several kilometers away, for various uses of the conveyed water [3] (All the engineering works going from underground aqueducts to drainage tunnels and shafts/wells, down to the final function of water collection (cisterns, tanks), belong to type A in the classification of artificial cavities, adopted at the international level by the Commission on Artificial Cavities of the International Union of Speleology). Cisterns are among the terminal devices of the hydraulic system intended for water storage.
Several examples from all over the world are reviewed with emphasis on durability of their applied technologies. The general features of aqueducts, qanats, associated hydraulic structures and their sustainability are preliminarily described below in Section 1. The chosen samples of hydro-technology are centered around the territories of Egypt, Middle East and the Mediterranean (plus three samples of exceptional qanat structures located in Peru, Tarim and Kerala and two samples of very specific underground aqueducts in Cuba and Japan). They are listed chronologically in the order of their construction. The article ends with general considerations about sustainability and final remarks. As a whole, this review paper is organized in eight sections as follows: (a) the first section is introductory; (b) the second describes prehistoric times from ca 3200 to 1000 BC; (c) the third deals with the historical times until 330 AD; (d) the fourth refers to medieval times until ca 1400 AD (e); the fifth to early and mid-modern times until ca 1900 AD; (f) the sixth to the contemporary time; (g) the seventh discusses emerging trends, future issues and challenges on sustainability; and (h) the eighth provides concluding remarks.
1.1. Aqueducts
Aqueducts of various types were largely used by the ancient Egyptians, Greek, Roman and Persian civilizations in order to provide water for cities, irrigating crops, drinking and for other household purposes [4]. Their simplest version of an aqueduct is consisted ditches directly cut in to the ground surface. Like the opened aqueducts, underground aqueducts are built at a lower level of the water source and can run for several kilometers because the hydraulic system controls the flow, transportation and the delivery of the water without using any other energy supply, just simply by using gravity.
Romans built magnificent hydro-structures mainly for water supply to urban areas, heavily influenced by Hellenic philosophy, and water supply sanitary engineering. They subsequently applied these earlier hydro-techniques on a larger scale by constructing infrastructures serving synchronically a great number of users and employing the advantages of their building methods using concrete-based walls and vaulted roofing [5]. These aqueducts are among the most well-known and widespread types of monuments found in Rome, and a large number of them are, like the Aqua Appia aqueduct, almost entirely underground, which protected their water supply from both enemies and pollution.
In fact, every urban settlement needs an adequate supply of drinkable water in order to exist, therefore, as a common policy in the Republic and the Empire, several town, village or hamlet had its own aqueduct, wells, or cisterns bringing precious water from far away sources, at first to the public fountains and, later, to every house. In some cases, even the most remote and isolated Roman settlements, especially those located in arid or semi-arid areas, fulfilled their water demand by constructing such hydro-structures, including direct abstraction from rivers and lakes, transport by elaborated engineering works like aqueducts to the site, and cisterns for collecting surface or rainwater [6,7].
1.2. Qanats
Qanats are traditional water-related technologies that exist throughout much of the Middle East, extending into North Africa, Spain, Central and South Asia, as far as Peru and Japan. In the Middle East they are called Qanat or Falaj, in Mediterranean Foggara or Khettara, in Central Asia Karez (all words generated from the Arabic or Persian languages), in Spain Socavón or Galería, in Peru Puquío and in Japan Manbo [8,9].
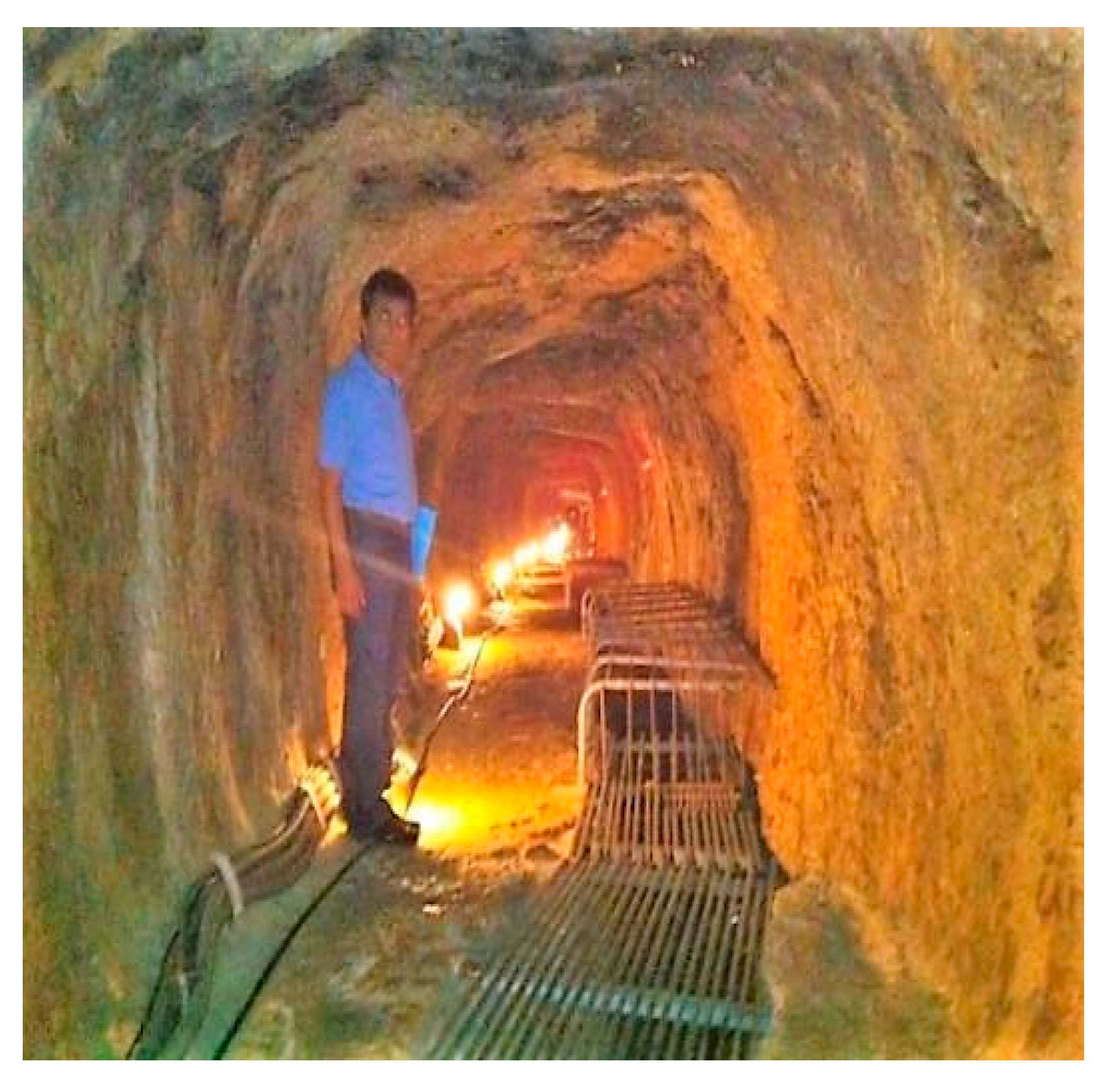
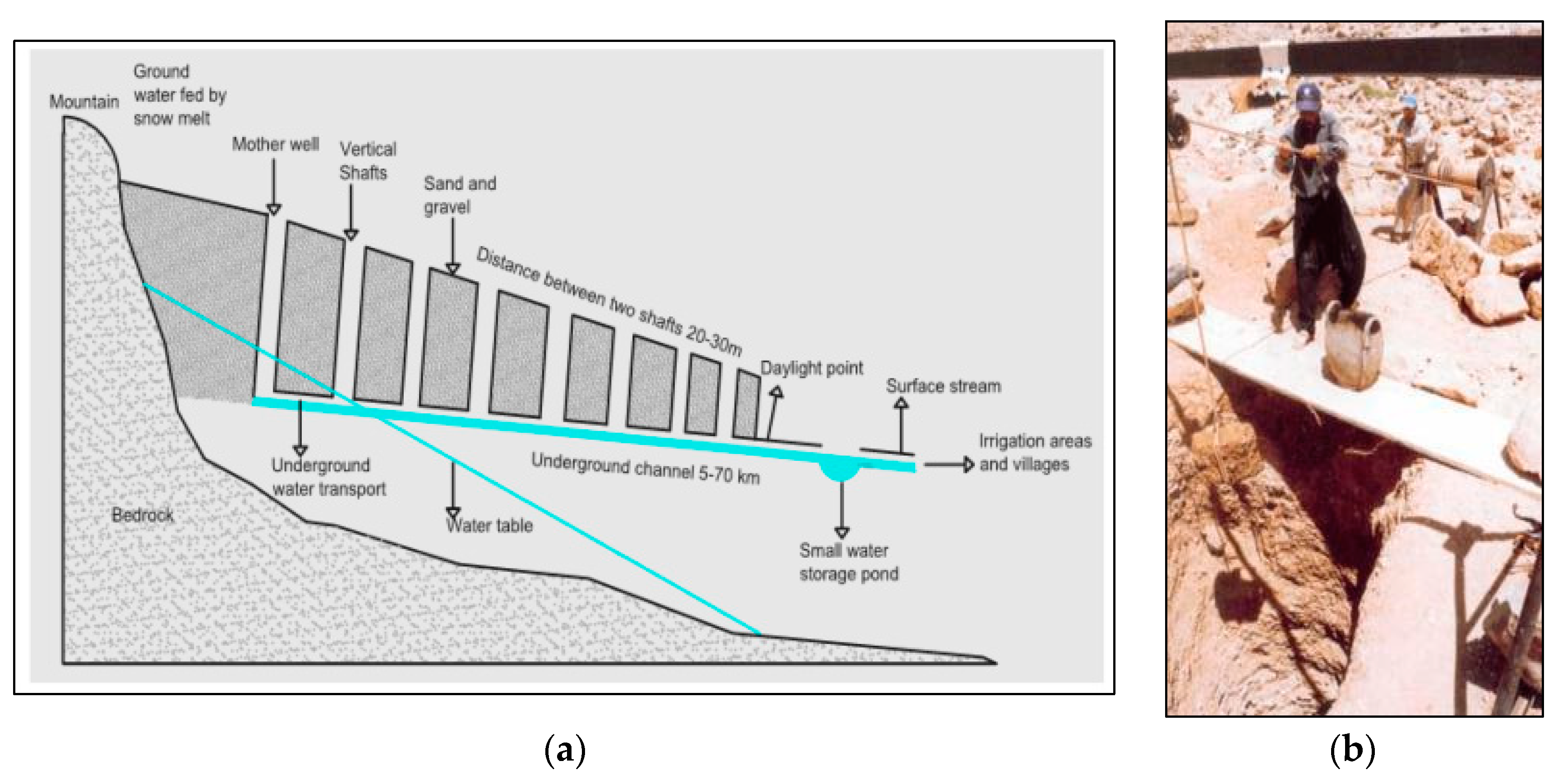
The qanats consist of large underground passageways excavated into the ground used for collecting groundwater, transporting it to lower elevation areas and delivering it to the surface, usually in plains with low water availability. While they appear relatively simple, these tunnels can extend for several kilometers and require accurate planning, construction and maintenance [10]. The qanat tunnel is excavated from the base outlet upwards into the area of the water source, where the mother well is located, and, along the tunnel itinerary, vertical shafts are dug every 20 m to 200 m to provide ventilation and access for the immediate removal of pollutions and for cleaning. The slope of the underground tunnel has to be around 2 to 5 m per 1000 m in order to allow continuous water flow from the source into the farm or city, while at the same time, minimize the erosion of its inner surface [11,12] (Figure 1a,b). The structural dimensions of the tunnels, such as the depth of vertical shafts and the length, can vary depending on the depth of aquifers, the topography of the relief and the geographical and geological conditions of the area.
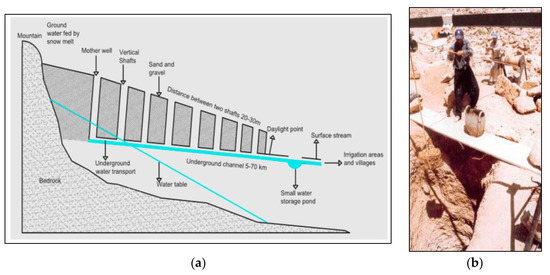
Figure 1.
Qanat system: (a) sketch of a qanat transporting water from upland to lowland areas [19]; (b) cleaning of a 1500-year-old qanat in Syria [20].
Even though amongst scholars the origin of these structures is still a disputable topic, most probably qanats have been in operation in mining since 2800 years ago, in the Iranian Plateau [13].
When looking at a qanat, the system should be considered as a whole. Qanats were and are part of a sophisticated system of management, ownership, distribution and social cooperation: all elements that eventually allowed the entire system to operate through more than two millennia [13,14,15]. Unlike other hydraulic structures, shareholders managed the qanat locally, with maintenance carried out by mutual cooperation, making decentralization of power and economy an inherent character of the qanat technology [12].
The qanat construction involves a variety of expertise and different types of knowledge, which makes qanat engineering a collective knowledge developed through time [14,15]. Botany is needed to locate the position of the first main well, called the mother well, which can be detected by the presence of phreatophytes (plants with a deep root system) or other signs. Furthermore, as qanats are often extended structures that, where their underground itinerary, might pass through variable geological conditions, and a sound scientific understanding of the geology, hydrogeology and the soil of the area is necessary. This understanding involves mathematics, geometry, knowledge of materials, architectural planning and many engineering techniques. In that way, the network of aquifers and qanats influenced the morphogenesis of cities, villages and farms. It also affects the social structures of the local communities, cities, public buildings and institutions, such as temples, schools and bazaars [16,17,18].
In the world, until 50 years ago were still functioning around 100,000 qanat systems that by now have been reduced by half: 65% of them are located in East Iran, 20% in Afghanistan and the remaining 15% in other countries.
In the following chapters, other than the classic qanats, several significant cases of qanat-like aqueducts of different periods are considered: the Peisistratus aqueduct of Athens in ca 540–530 BC, the aqueducts and utility tunnels implemented during Roman times in Italy, Spain and Athens (Hadrian aqueduct, ca 2nd century AD); the 16th AD aqueduct of Pylos (Greece); the 19th century Alvear Aqueduct at Havana (Cuba); and the early 20th century in India.
1.3. Associated Hydraulic Structures
These underground tunnels are usually associated alongside other types of hydraulic structures which allow for water access, distribution and preservation. Cisterns are quite widespread and were found far and wide in both the Middle East and in Mediterranean regions ever since prehistoric times, and in most of the ancient cities and villages of Iran, water reservoirs (‘ab-anbars’) were part of the whole qanat system entering the city or the village. In addition, in case of altitude difference, underground watermills were sometimes built to employ the qanat’s water force, and usually watermill owners paid the qanat owners rent which was used for maintenance of the qanat itself. Indeed, all these technical and social aspects should arguably be considered when discussing the sustainability of a whole qanat or qanat-like system.
1.4. Sustainability
At present, water sustainability issues are much more complicated than what was found in ancient times. As changes became more and more accelerated, adaptations could not evolve overnight and these changes took time. Three major historical eras can be identified as benchmarks for the historical progress in underground hydro-technology: (a) prehistoric to medieval times (ca 3200 BC–ca 1400 AD); (b) early and mid-modern times (ca 1400–1900); (c) contemporary times (1901–present).
A comprehensive review of the history of underground hydro-technologies is undertaken herein, with a focus on sustainability. Water use sustainability refers to a use of water that supports the capability by part of human society to endure and flourish into the indefinite future without undermining the integrity of the present ecological systems and/or the hydrological cycle that depend on it [21,22,23]. Then, sustainability of water resources involves the availability of freshwater supply throughout periods of climate change and global warming, extreme events (i.e., droughts and floods), population growth and the legacy of needed supplies left behind for our future generations [21]. One of the most significant aspects regarding the sustainability of underground water supply systems is that many of them are—totally or partially—still functioning ever since 300 BC right up until the present, e.g., the qanat systems in Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, China, the UAE, Oman, Iraq, Egypt, Algeria, Morocco, Spain, Portugal, Peru and Syria (Figure 1b).
2. Underground Hydro-Technologies in Prehistoric Times (3200 BC–1000 BC)
2.1. Ancient Egypt
In dynastic Egypt, the state administration was in charge of the water supply from beginning to end, and samples of aqueducts for conveying surface or underground water were various, located in agricultural, urban or religious contexts. The most ancient implementations were simply shaped open canals where water moved by gravity: in oases and desert areas, they were used for the conveyance of groundwater or springs to the surface for irrigation and drinking purposes. Later on, in religious sites, they were excavated between the Nile river and the pyramids, apparently for ritual use [24].
Most impressive is the use of aqueducts in the monuments built by the Pharaohs (3100–332 BC), who, since priests were a highly influencing caste, favored the harvest of the Nile and use of rainwater for their temples and palaces for several uses (among which to bathe the king’s statues). Nile water was carried through gateways and aqueducts, and clean rainwater from the pyramid sides (Each of the largest Kuphu and Kafre pyramids could collect more than 1000 tons of rainwater per year) was held within stone walls. Both kinds of water were finally released through underground aqueducts and stored in groups of cisterns.
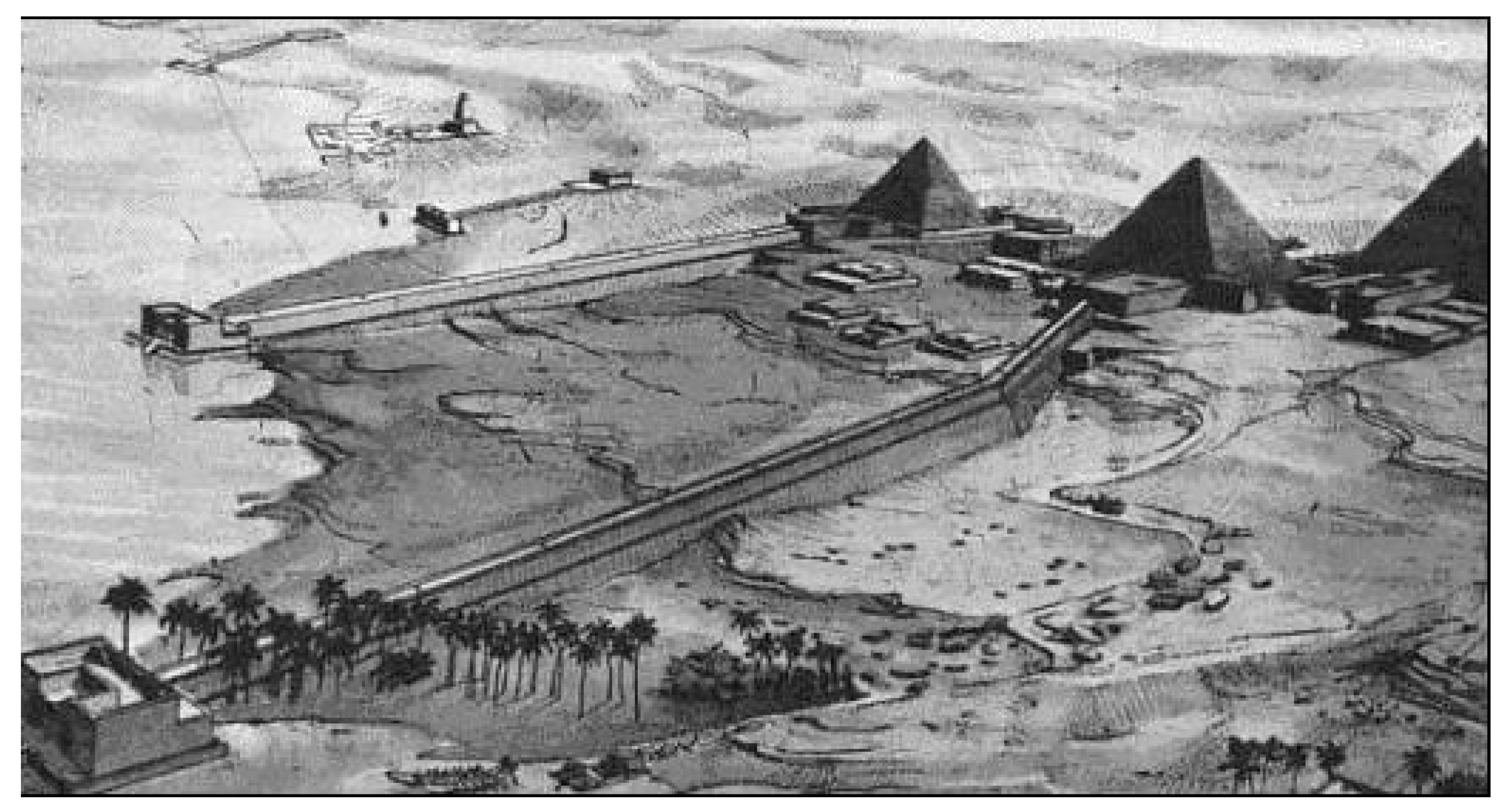
The entire surface of the Giza plateau, made mostly of limestone, was modified for such a water harvesting functionality. Aqueducts transporting the water from the Nile to the base of Menkaure and Khafre pyramids of the Giza pyramid site (ca 2500 BC) are shown in Figure 2. Two ducts connected the bed of the Nile to the base of the pyramids via gateways made of huge stone leaves regulating the water delivery; under the pyramids there were natural and artificial openings, including shafts and square, circular and vadose-shaped water ducts (Figure 3), which led to several chambers, among which was a huge underground cave the length of a football field. The ducts were built lower than the Nile water surface so that the massive chamber that was located underneath would fill up with water [24].

Figure 2.
Reconstruction showing two causeways and aqueducts connecting the Nile with the Menkaure and Khafre pyramids of the Giza complex (ca 2500 BC). The third causeway stretches from the Kuphu pyramid out of view on the right side of the figure (view to W) [24].
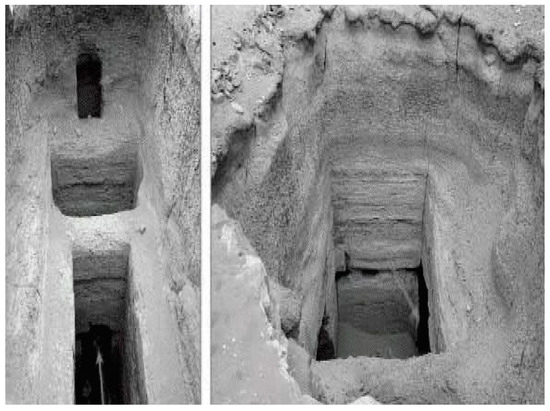

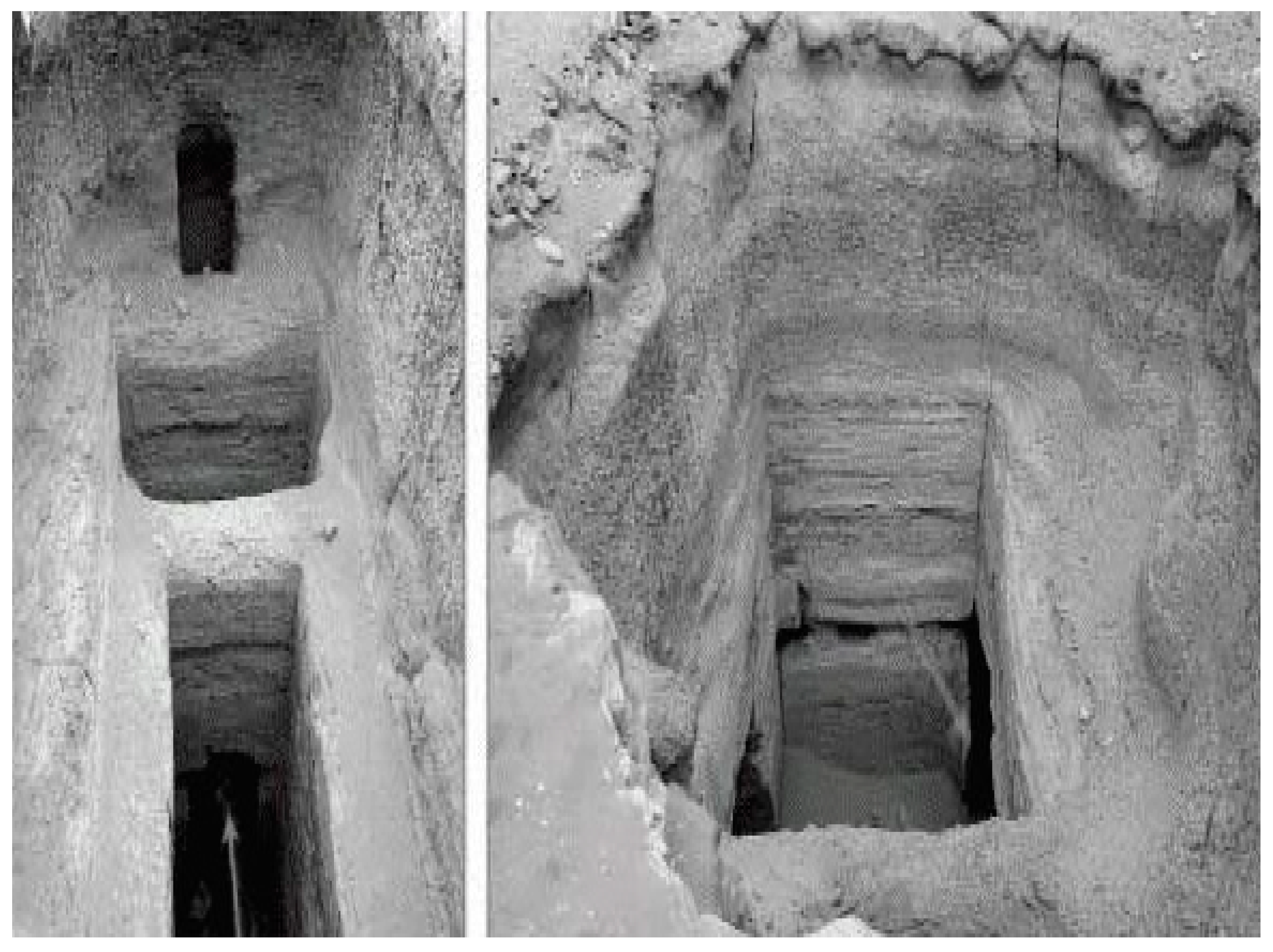
Figure 3.
Deep holes in the Giza pyramids site, with arrows pointing to their connection to underground horizontal passageways [24].
Similar hydraulic implementations are found in several subsequent Egyptian temples (Figure 4a,b), like the Dendera temple, one of the most magnificent and best preserved temples of Egypt built around 350 BC in Upper Egypt by the last of the native pharaohs [24], and the Edfu temple, built in 237 BC in Lower Egypt during the Hellenistic period by Ptolemy III, where an 1 km long aqueduct (or tunnel) was constructed to deliver Nile water beyond the great hypostyle hall into a well (called “Nile Chamber”) where the priests could collect holy water (Several temple sites are located on the river bank of the Nile, so that, during floods, even in absence of aqueducts, the rise of water level can provide by itself the direct entrance of river water to the underneath aqueduct of the temple (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
The Nile: (a) view from a temple bordering the river bank of the Nile (photo by M. Salgot); (b) walls of a temple located near the river bank of the Nile, where the mark of the water level raise during the river floods coincides with a passage allowing the direct water flow to the underneath temple’s aqueduct [24].
At the start of the Ptolemaic dynastic period (ca 305–30 BC), Ptolemy I, after the making of the newly founded Alexandria, the capital town, built from the Nile a 30 km long waterway that, every year, when the Nile floods from June to September, carried this water to the city and filled such an abundance of these cisterns that the water provision could be utilized for an entire year for drinking and watering gardens [25]. This is why, from that moment until the end of the XIX century, and almost a millennium earlier than Byzantium (see Section 4.1), Alexandria became famously known as “city of cisterns.”
After the death of Cleopatra and the colonization of Egypt (ca 30 BC), the Romans took care of the richest granary of the empire and renovated the hydraulic works that inherited the Hellenistic hydraulic tradition, among which were Alexandria’s aqueducts and cisterns (Figure 5).

Figure 5.
El-Nabih Roman cistern beneath Alexandria (Egypt), supported by a three-floor structure. In Alexandria, so far more than hundred ancient cisterns have been identified [25].
2.2. Minoan and Mycenaean Civilizations
The Minoan civilization (ca 3200–1100 BC) of Crete arose independently and with mutual commercial and cultural influences as with the Egyptian and Near East cultures. Here, since the Early Bronze Age, the complex relief in the region promoted the development of pioneering underground technologies for transporting water to settlements and palaces.
The first palaces along with the aqueducts of Knossos in Crete were constructed during the Middle Minoan period (2100–1500 BC), when water was carried by gravity using structures partly built underground with sections of open or covered channels of various dimension and length, and included closed terracotta pipes (Figure 6). Analogue terracotta pipes in underground sections have also been found in other Minoan settlements such as Tilissos and Gournia. Increasing water demand and frequent earthquakes may have caused the local decline of aquifer levels, making it necessary to transport water from longer distances [26]. It was out of necessity that the first Knossos aqueducts carrying water from the Mavrokolymbos spring emerged a distant 0.7 km away from the southwestern hills and moreover, in later time, carried water even further stretching from the Archanes springs located 10 km from the south.
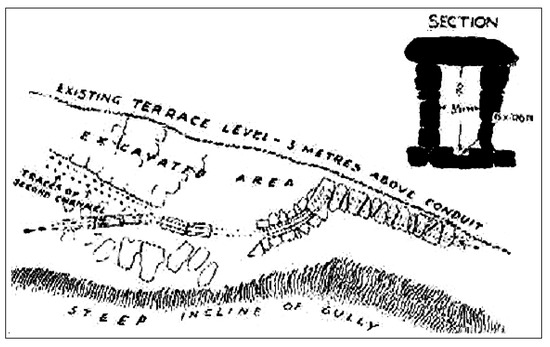
Figure 6.
Plan of the excavation of a partial segment of the Minoan aqueduct in the SW surroundings of the Knossos palace and section of the aqueduct [27].
The same kind of hydraulic techniques were developed during the Mycenaean period (ca 1600–1100 BC). One great example of the use of tunnels for drainage purposes is the 2.2 km long Akraifnio drainage tunnel, constructed by the Mycenaeans in ca 1300 BC in order to drain the Kopais Lake and use the drained land for agriculture. At first, 16 vertical shafts were dug along the axis of the planned itinerary and then, through these shafts, a tunnel 1.8 m high and 1.5 m wide was excavated [27,28].
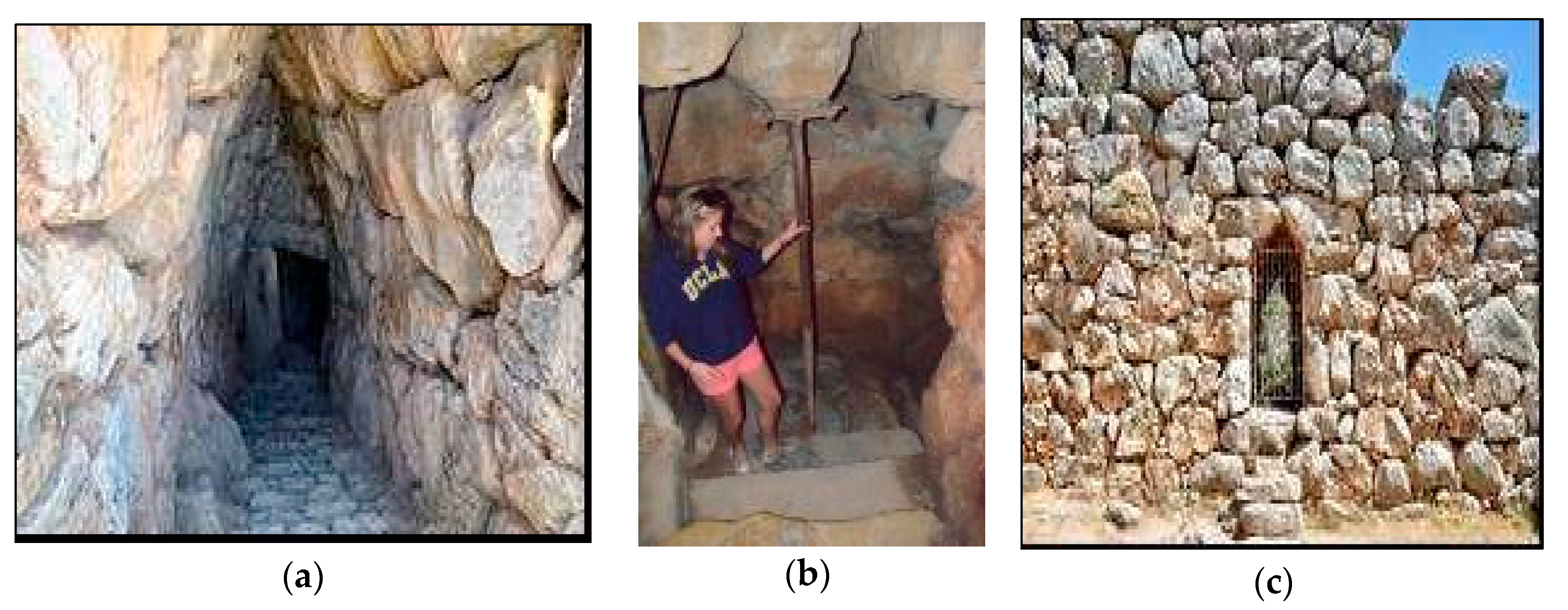
In 1225 BC, in Mycenae itself (ca 1350–1200 BC), being one of the major cities of the Mycenaean civilization, was built a water supply system, based on an underground cistern. This represented a highly impressive engineering feat in which it allowed the citadel to have an unlimited and secure water supply. This cistern was located 18 m below the surface inside the northeastern part of the citadel and was supplied through underground pipes from a nearby natural spring (Perseia Fountain) located outside [29]. Access to the cistern was provided from inside the walls by a steep tunneled passage made of 99 steps paved with stones and was large enough for two people standing side by side with the ability to move easily (Figure 7a,b). Access from outside the citadel was provided by a secondary door that was opened from the external wall neighboring the tunnel entrance (Figure 7c).
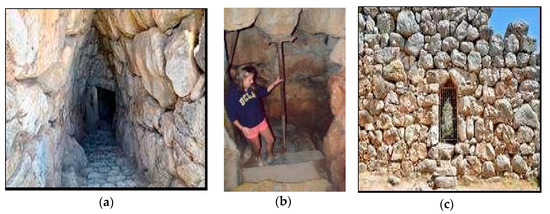
Figure 7.
(a) Steep passage-tunnel to the water cistern; (b) interior steps with scale; (c) secondary entrance through the external northern wall neighboring the cistern (photos by A. N. Angelakis) [30].
3. Underground Hydro-Technologies in Historical Times (1000 BC–330 AD)
3.1. Assyrian and Achaemenid Aqueducts and Qanats
The first complex long-distance canals for water transportation were built by the Assyrian Empire (ca 900 BC), including underground tunnels several kilometers long that for that time could be considered a significant engineering achievement.
Under Assyrian rule, in 800 BC in Babylon was constructed a series of sophisticated and extensive canals, and the town of Nineveh (modern-day northern Iraq) was fed by 18 water canals dated to ca 600 BC, among which was one 65 km long (https://www.ancient.eu/jerusalem/). However, most significant Assyrian hydraulic implementation has been the introduction of the first documented proto-type of qanat, dated to ca 7th century BC, intended for depleting the groundwater level for mining purposes. Subsequently, such hydro-technology was successfully applied for the catchment and gravity transport by underground galleries of groundwater from distant aquifers to agricultural and urban complexes. In that way, qanat systems spread in the entire Middle East, mostly in the Iranian plateau where they still represent the main water resource of towns and villages located in very arid environments. Its technical aspect is described in Section 1.2.
The building of aqueducts and qanats continued and blossomed under Achaemenid rulers. They gave to the aqueduct builders and their heirs a major incentive by allowing them to keep the earnings from newly built aqueducts for five generations. Consequently, many new settlements were founded and the preexisting ones expanded. When, during ca 550–331 BC, the Persian Empire spread from the Indus to the Nile, the building of aqueducts was further diffused from Mesopotamia westward to the Mediterranean coast and southward into parts of Egypt.
3.2. Archaic, Classical and Hellenistic Greece
Underground aqueduct-like qanats, made of gently sloping and artificial underground galleries, and which bringing spring or groundwater from mountainous water-rich aquifers to lowlands located sometimes several kilometers away, were known in Europe since early antiquity [1,31].
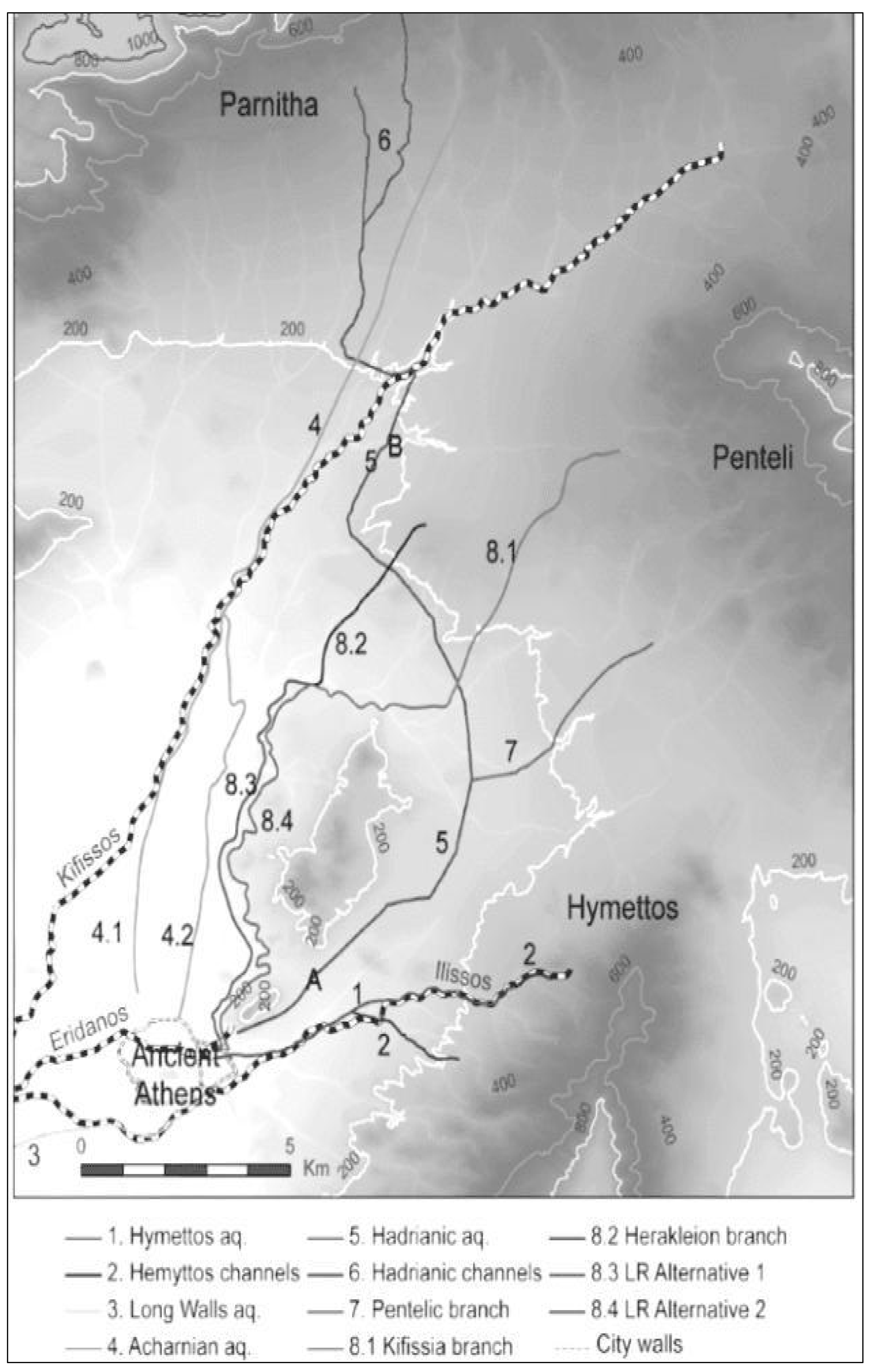
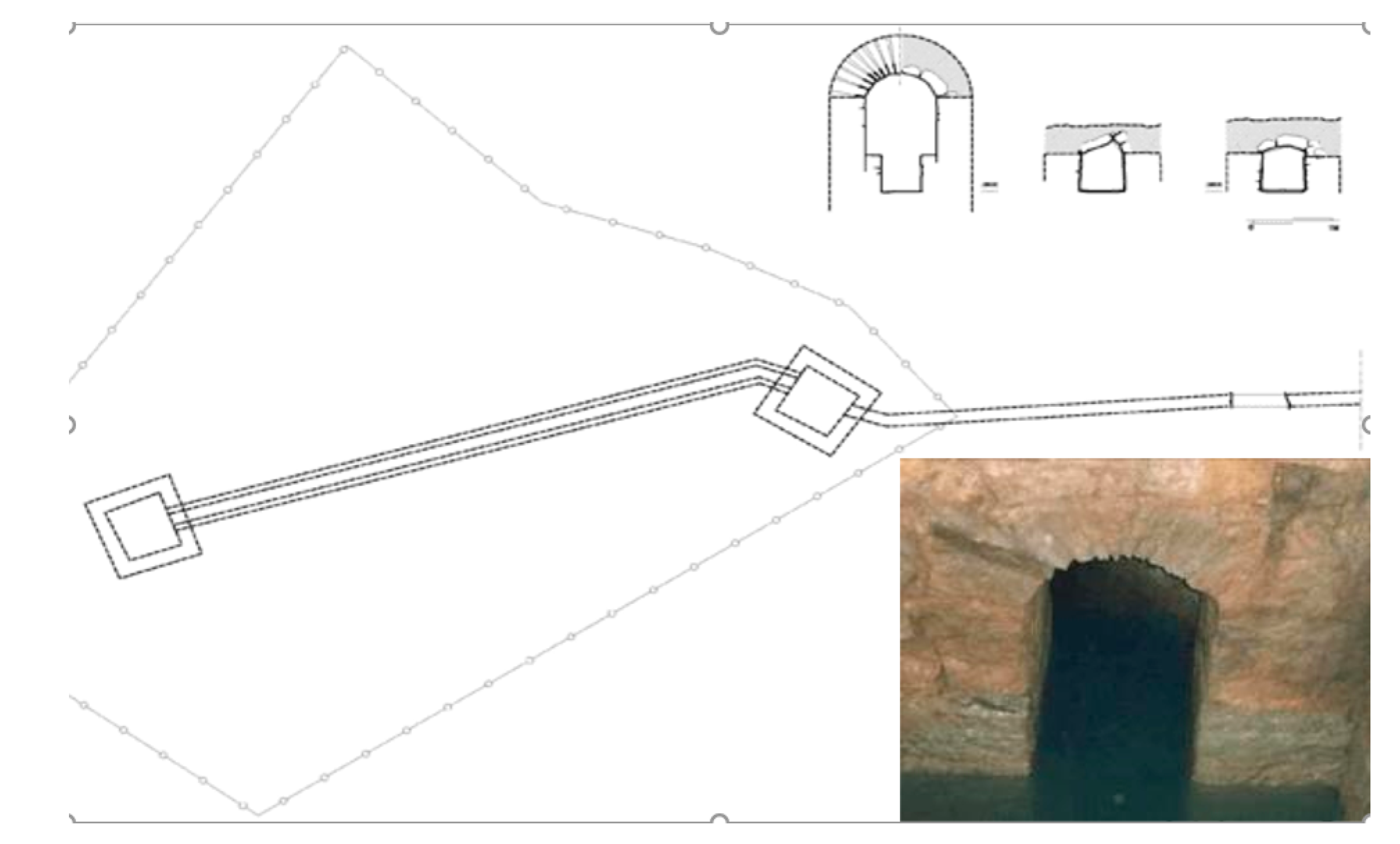
Ancient Hellas had well-constructed Classical and Hellenistic aqueducts (IV–I BC) that were restored and reused in Roman times as both water supply or sewage systems, and in some cases, they are still in use today [32,33]. Of the several aqueducts that were built in order to bring water to the city of Athens (Figure 8), the main one was the so-called Peisistratos aqueduct (Figure 8, #1, 2), probably constructed during the decade from 540 to 530 BC. It was built to enable water transport from the foothills of the Hymettos mountain to the center of the city, near the Acropolis [34]. It is estimated to be up to 10 km long (including the final sector) and built using two techniques: most of it as a tunnel carved 14 m below the surface and probably with shafts [33], and the rest as a canal, either carved into the rock or made from stone masonry, with a depth of 1.30–1.50 m and a width of 0.65 m [34]. At the bottom of both tunnel and canal, there was a pipe made of ceramic sections (Figure 9a,b).
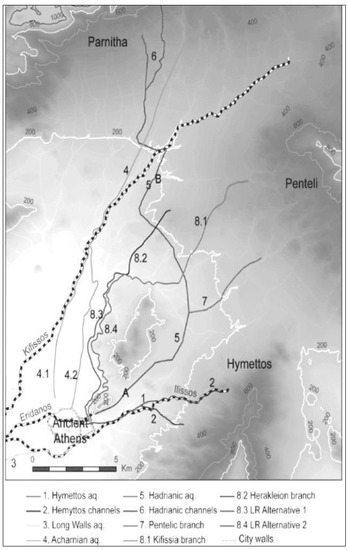
Figure 8.
Probable routes of the ancient aqueducts in the basin of Athens [33] with the Peisitrateian marked with numbers 1 and 2.

Figure 9.
Peisistratian aqueduct: (a) branch of clay modular pipes near the Syntagma metro station in Athens (lids are missing); (b) contemporary mid-19th century terminal open pond in the National Garden, fed by continuous water flow from the Peisistratian aqueduct (photos by G. Antoniou).
Large stretches of the Peisistratian aqueduct were found during excavations for the construction of the Athens metropolitan subway, and parts of it are exhibited inside the metro stations of Syntagma and Evangelismos. The pipe modules have their ends appropriately shaped so that each could be tightly fitted into the next; they have elliptic openings in their upper part with ceramic lids (missing today), for cleaning and maintenance (Figure 9) and an extended distribution network of clay pipes reach fountains at its ends. (From 1875 to date, the aqueduct has been used to irrigate the National Garden of Athens (Figure 9b). The main features of the 12 other underground qanat-like aqueducts of ancient Greece are described elsewhere [1].
Concerning the Aegean region, one of the earliest underground aqueducts documented is the Eupalinos tunnel, or Eupalinian aqueduct (in Greek “Efpalinion orygma”, named after the engineer who built it), in the island of Samos. It represents the longest tunnel and oldest aqueduct in Greece since Hellenistic times and one of the greatest engineering achievements of ancient times. The tunnel, presumably completed between ca 550 and 530 BC, during the tyranny of Polycrates, was in operation until the ca 5th century AD [35].
It is a 1036 m long tunnel with about a 4 m2 cross section, built to serve as an aqueduct, supplying fresh water from an inland spring to the ancient capital of Samos, which today is called Pythagoreion (Figure 10). The tunnel was excavated during 10 years and remained in operation until the 5th century AD, after which it was abandoned and, ultimately, forgotten. The tunnel crossed Mount Kastro, consisting of solid limestone, and was excavated from both ends (amfistomon, “having two openings”, as Herodotus, History, Γ, 60 mentions) [1]. Today, it is very common that tunnels are constructed simultaneously from both its openings, to reduce construction time and, inevitably, cost. Today high-tech geodetic means and techniques like global positioning systems and laser rays are used to ensure that the two fronts will meet each other precisely. One of the greatest achievements of Eupalinos’ (Eupalinus of Megara) engineering, is that he did such job using the simple means available at that time, showing however the presence of good knowledge of geometry and geodesy [36]. A question still exists: why did Eupalinos construct the tunnel instead of an open conduit along the periphery of the hill? The question remains open and still requires justification [1].
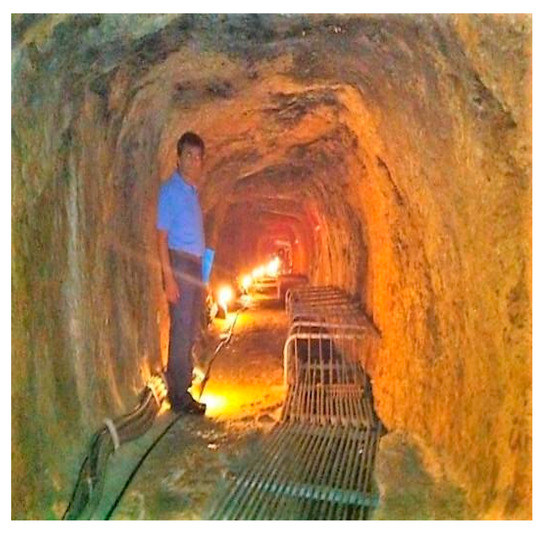

Figure 10.
Eupalinian aqueduct in the Aegian island of Samos (with permission of Prof. K. Voudouris).
3.3. Roman Aqueducts and Cisterns
Romans built magnificent hydro-structures heavily influenced by Hellenic philosophy. They subsequently applied these earlier hydro-techniques on a larger scale mainly to urban areas for water supply and sanitary engineering, constructing infrastructures that served a great number of users at the same time and employed the advantages of their building methods using concrete-based walls and vaulted roofing [5].
Concerning aqueducts (see Section 1.3), according to the historical sources, among the 11 aqueducts that supplied the city of Rome, the first to reach the urban area was Aqua Appia in 312 BC, thanks to the work of the censor Appio Claudio Cieco. Its overall length is about 16 km and for safety reasons it was developed entirely underground into the outskirts of Rome for safety reasons. At diverse time intervals, other aqueducts followed, until the most recent Aqua Alexandrina in 226 AD. All of them are the object of wide literature [32,33,37,38,39]. These aqueducts brought a huge amount of water to Rome, with the highest volume coming from the Anio Novus, transporting more than 2200 L/s of water [40]. In the case of Rome, the hydraulic works were developed over volcanic rocks, but the same techniques were used by the Romans to build similar structures in other areas, even with more complex hydrogeological settings.
Referring to later imperial times, Sextus Julius Frontinus, in 97 AD, was Currator Aquarum in Rome. He was in charge of the management of the aqueducts of the city and the distribution of their water within the city.
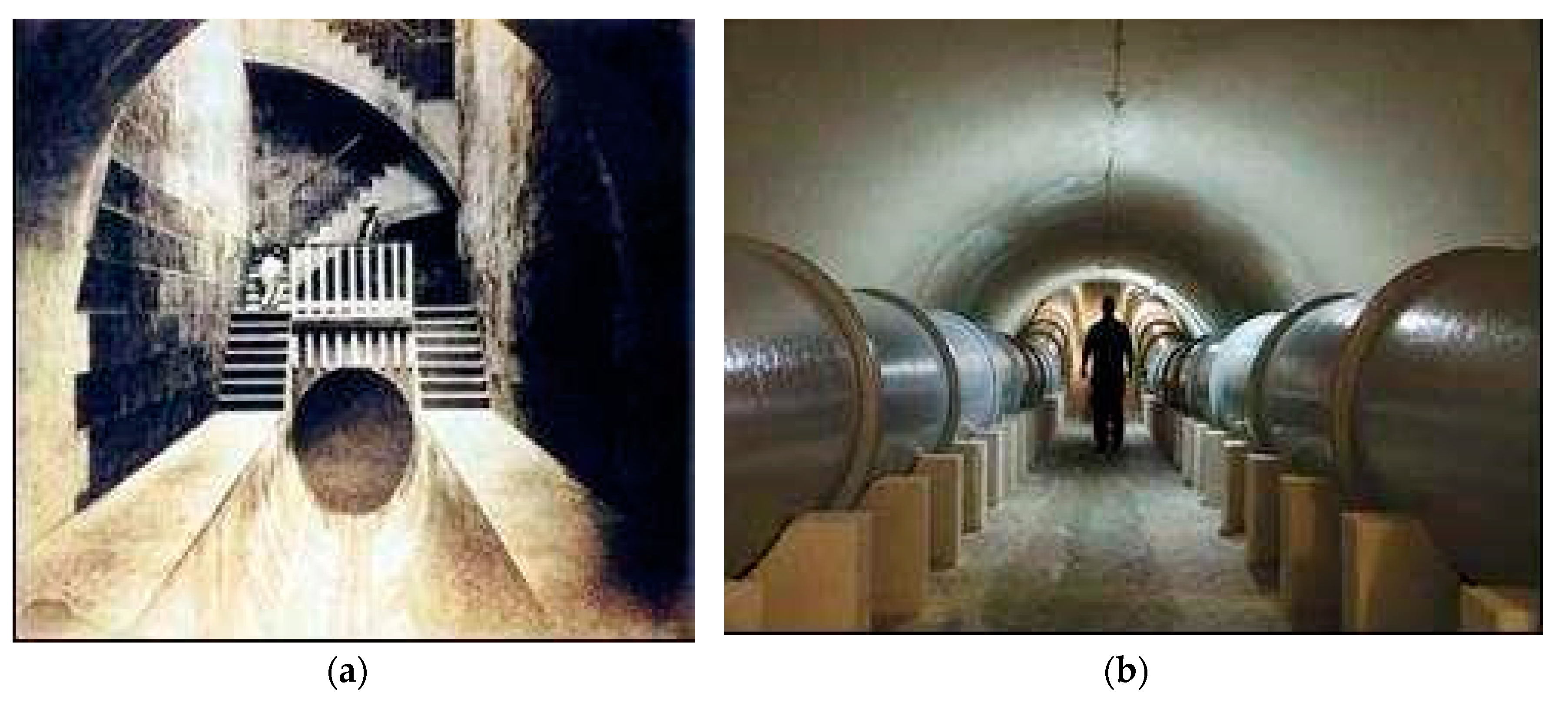
Underground engineering was crucial for the protection of the water system from both pollution and enemy incursions in Rome as well as in other Italian and European sites [41,42]. In particular, they developed qanat-type technologies in the construction of utility tunnels for the water supply of urban sewage systems [43], like the grandiose urban sewerage system of the sewers of Rome, with ducts characterized of a large cross-section and still in operation, and several lesser but similar implementations found in present in Luxembourg, Croatia, Portugal, Germany, Italy, Greece and Spain [1,6,44,45,46,47,48,49].
The need for underground public works in order to facilitate good living conditions in communities has existed for millennia. Utility services have been placed underground in order to achieve limited visual impact and more protection against vandalism, adverse climatic conditions, and natural disasters [43]. Use of utility tunnels dates back to the engineers of the Roman Empire, who try to apply the tunnels for the sewerage systems (Figure 11). An example of this technology can be found in the current sewers of Rome, with a huge cross-section still in use today. However, such undersurface structures were ignored during the Middle Ages and revived only later in the mid-19th century (1855), after the project of Haussman (a great admirer of Roman engineers) to reform the urban utility structures of Paris was finally approved [50].

Figure 11.
Utility tunnel used for the sewage system of Chelva (Valencia, Spain), built during Roman times [43].
In the ancient city of Rhodes [of which the town plan was possibly designed by Hippodamus of Miletus (498–408 BC)], during the Roman Hellenistic period was realized an aqueduct based on an underground network of galleries built with limestone rocks and dry-stone masonry down to a depth of 70 m. It consists of four major tunnels of variable length, with wells (shafts) and stairs’ accesses at intermediate distances ranging from 50 to 60 m (Figure 12).

Figure 12.
Roman underground aqueduct in the Aegean island of Rhodes, Greece: (a) part of the underground tunnel; (b) aligned shafts at the ground surface (photos by A. N. Angelakis).
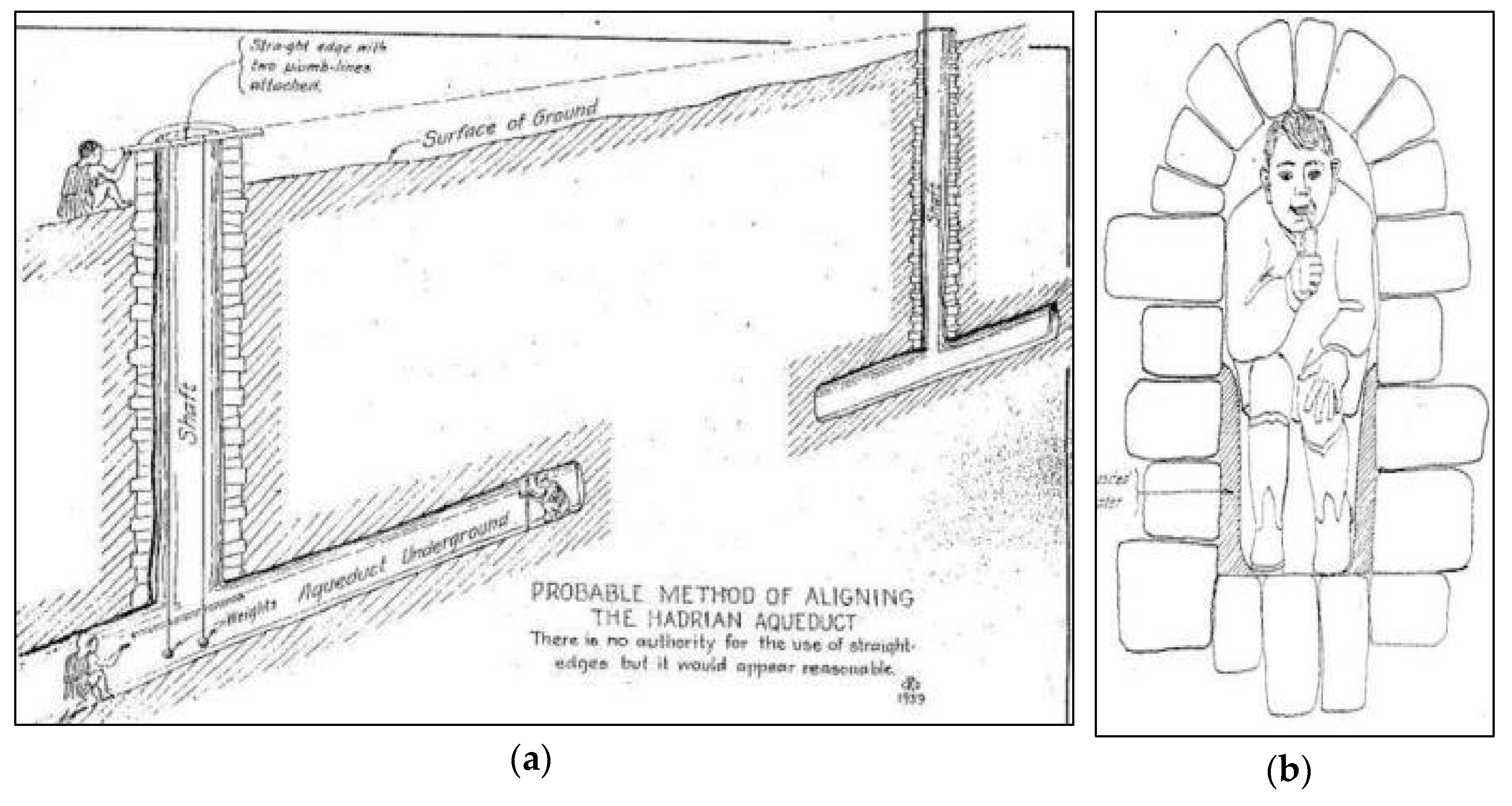
One of the most important hydraulic works of the Roman imperial period is the Hadrian Aqueduct, built in Athens during ca 2nd century AD and is still functional today. Its construction was started in 125 AD by the Roman Emperor Hadrian and completed in 140 AD by his successor [51] mostly for the improvement of the water supply for the ancient city, and then to provide water to the new Roman-neighborhood near the Olympeion Sanctuary [32]. The 25 km long tunnel was constructed from the foothills of Mount Parnitha, had secondary branches as the one on the region of Mount Pendelikon (Figure 8, #5–7), and was instilled with 465 wells (shafts) approximately 35–50 m apart (Figure 13a,b). Water was transported by gravity until the foothills of Lycabettus, where it was stored in a stone-built terminal cistern of about 500 m3 [25], which originally might have been larger considering the architectural reconstruction of the building. Significant parts of the tunnels are located at depths greater than 20 m, and thus, besides the original spring waters, it could receive groundwater from aquifers along its route (Figure 8) as well as through its side branches.
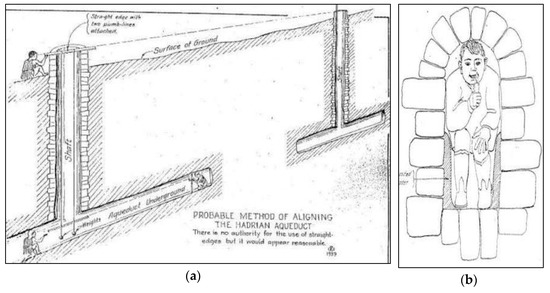
Figure 13.
Hadrian aqueduct of Athens: (a) method of tunnel alignment; (b) cross section of a narrow sector of the tunnel, at the limit of the working possibility [49].
The Hadrian Aqueduct and its end-of-the-pipe cistern operated properly only for a few centuries, until the Ottoman Empire, when the cistern collapsed and the Athenians turned to the alternate construction of wells of private domestic wells (In the late 1700s the aqueduct was decommissioned and the stones of the ruined terminal cistern were used for the fortification of Athens by the tyrannical Ottoman governor Hatzi-Ali Haseki [50]. During late Ottoman rule, some sections of the aqueduct were repaired for feeding few fountains and irrigating the vineyards of the city center.).
Only after 1847, under the newly established Kingdom of Greece, the aqueduct started to be repaired, cleaned and progressively exploited. By the end of ca 19th century AD, several underground sectors were reactivated and the terminal cistern rebuilt (Figure 14a,b). As a result, starting from 1930, the population of the Chalandri suburb of Athens was collecting clean fresh water from the aqueduct shafts once again.
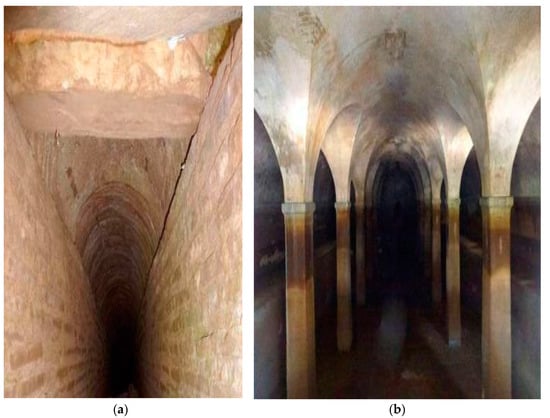

Figure 14.
Parts of the Hadrian aqueduct: (a) underground tunnel near Acharnes, 10 km north of Athens at the foot of the Parnitha mountain; (b) terminal cistern, rebuilt during the 1870s (Photos by G. Antoniou).
All over the empire, in order to preserve the highest amount of runoff, the surface-running water caught by canal systems was stored in underground cisterns [52,53]. Cisterns had an average size of around 10 m by height and 3– per 5 m by plan (Figure 15a), typically bell-shaped or, less frequently, cone-shaped. They housed a central square opening on the upper rock above the cisterns to collect water, and then a hollow at the bottom for the settling of impurities and periodical cleaning. Furthermore, they were usually coated with plaster to make them waterproof.
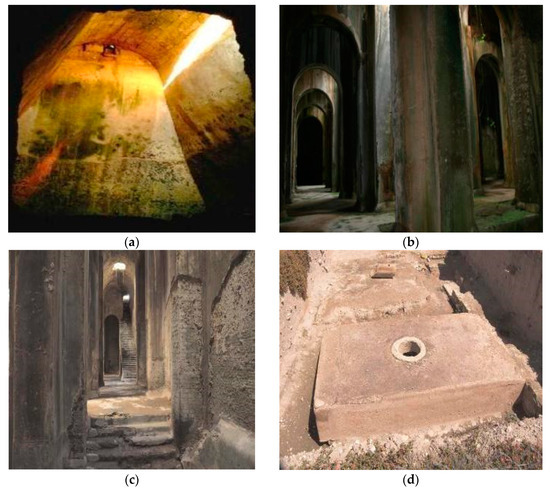

Figure 15.
Roman cisterns in Mediterranean region: (a) common cistern at Grottaglie, Apulia; (b) large cistern Piscina Mirabilis at Bacoli, Campania; (c) cistern located above Piscina Mirabilis; (d) square stone cover of the cistern at Ilici, Spain [56].
In the Mediterranean region, one of the largest Roman cisterns is the Piscina Mirabilis (Figure 15b) located in Bacoli (Phlegrean Fields, Southern Italy) [54], where the water supply system was the ancient aqueduct Serino, dating back to 33–2 BC, and its floor plan size of 27 m by 72 m and depth of 15 m corresponds to a capacity of 10,700 m3 [55]. Other remarkable Roman cisterns are the smaller cistern located above Piscina Mirabilis (Figure 15c) and the one of Ilici (now Elx, in Spain, 125 BC) (Figure 15d) [56].
During the Late Roman period, possibly under inspiration of the Middle East technology, one of the earliest samples of a qanat-like aqueduct system was introduced in a distant oasis of Egypt. Discovered in 1905 at Ain Umm Dabadib, in the Kharga Oasis of the Western Desert, it consists of seven twisting and turning underground aqueducts developing for total 14.3 km and conveying by gravity the water of the wadis and ephemeral aquifers to agricultural fields. One of these ducts is a tunnel around 3 km long carved into solid sandstone at a depth of 40 m, with sectioning starting from 0.6 m width by 1.5 m height and ending with 1.5 by 0.75 m, and the gallery itinerary provided access holes and air vents every few meters for maintenance and clearing from sand fills. In 1905, it was still supplying around 2 L/s and is working, undamaged, until now [24].
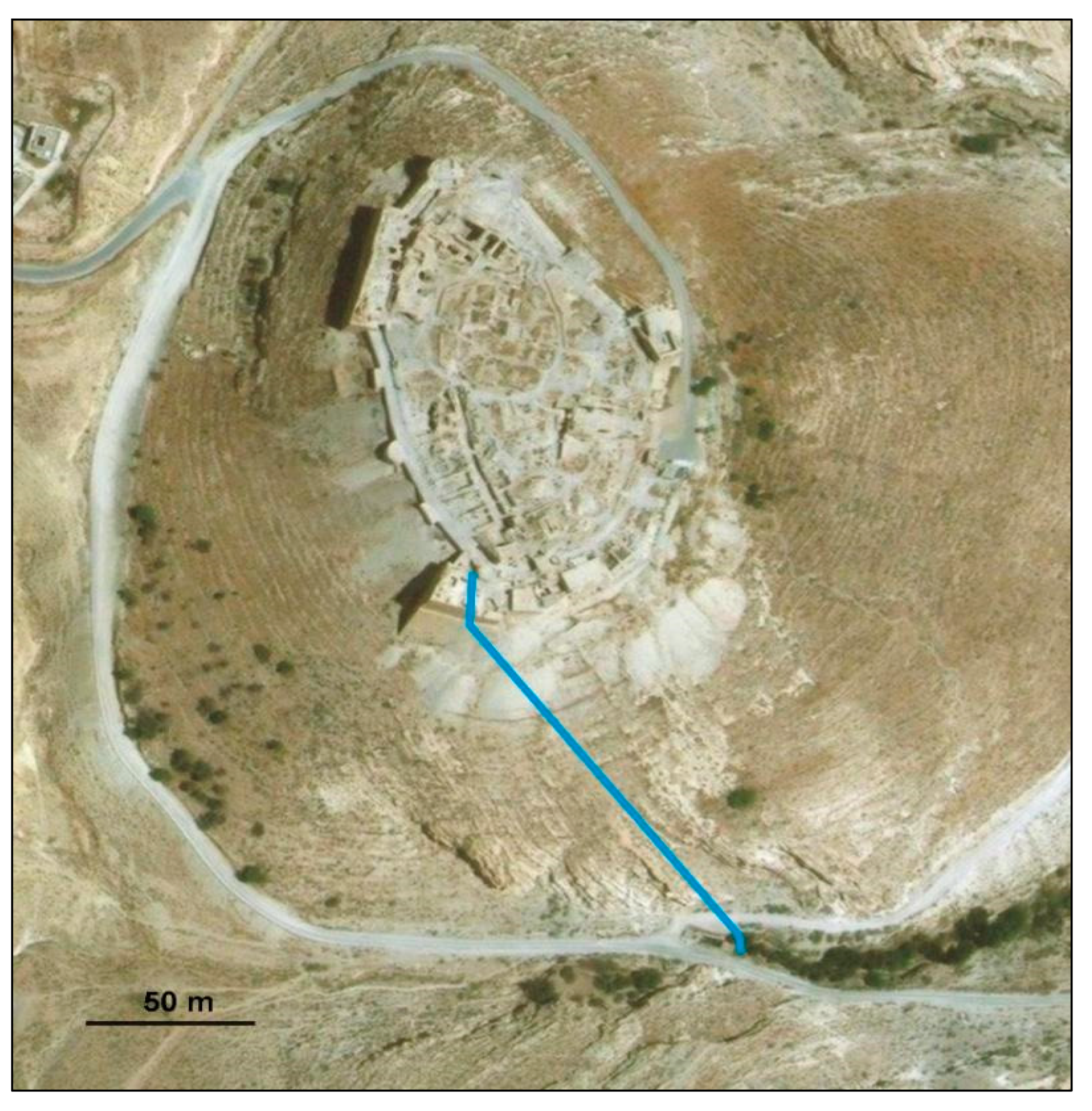
3.4. Petra
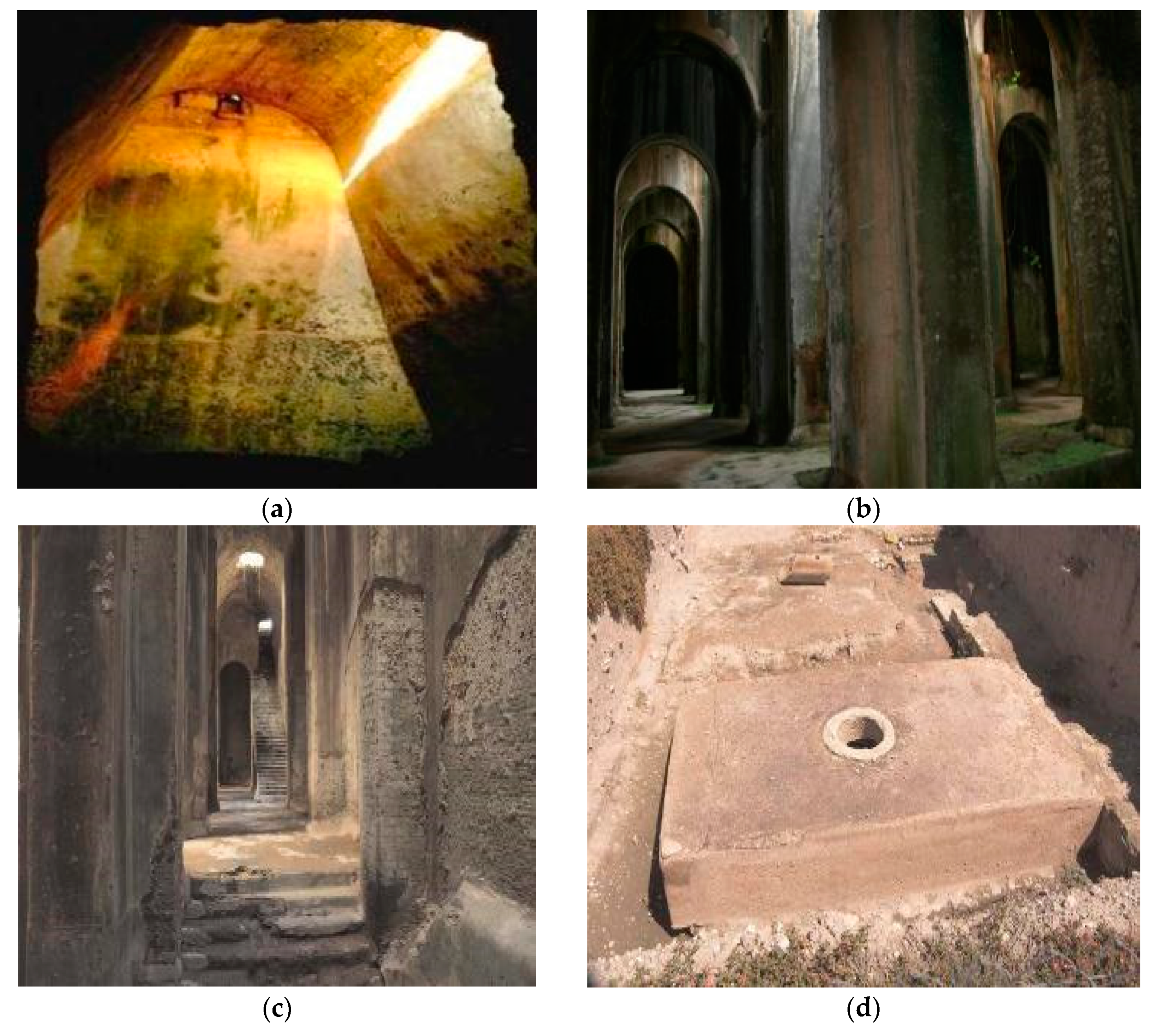
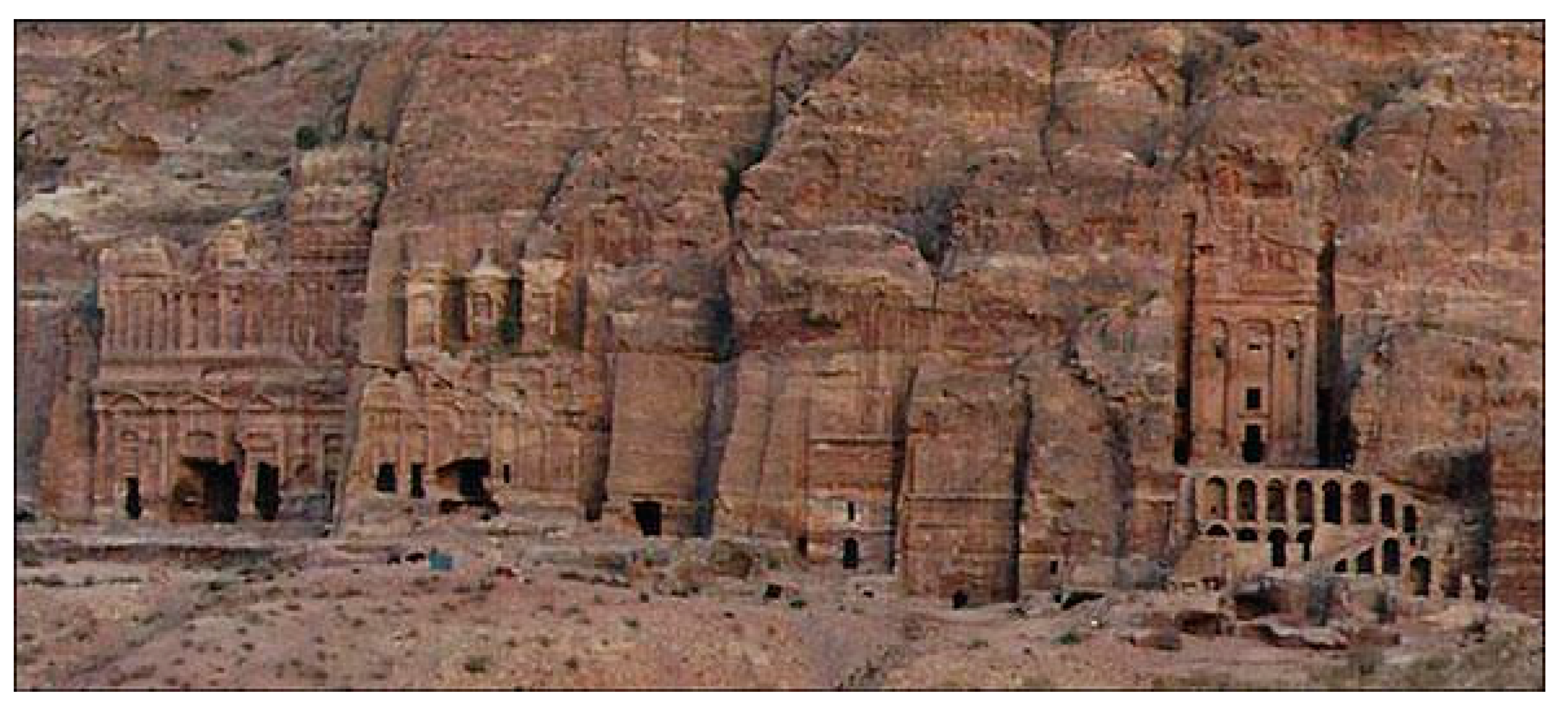
Most significant for its unique hydraulic engineering system is the complex of urban cave buildings discovered in 1812 AD in the hot desert region of Petra (present Jordan) (Figure 16). Its construction started in the ca 3rd century BC under the Nabataeans, blossomed under the Roman Empire as its main center of the regional trade route (with population peaking to 20,000 inhabitants), and then faded during the ca 4th century AD. The architectural complex fulfills the function of a rich urban trade town as well as the function of rain-water harvesting system. The investigated hydrological structures were supposed to serve the purpose of controlling the impact of wadis’ flash floods and of water harvesting in order to cope with prolonged drought conditions [57,58,59].

Figure 16.
Carved cave structures in the Petra city, endowed with subsurface water storage function [57]. Note the keyhole shapes at the tomb entrances and the whitish effect of salt-laden water wicking into sandstone from the upper ground [59].
4. Underground Hydro-Technologies in Medieval Times (ca 330–1400 AD)
4.1. Byzantium
The majority of aqueducts built in Medieval times followed the same paths and used the same structures that were previously built and used by past civilizations (For example, the analysis at national level of the Italian underground aqueducts [43] pointed out that during the Byzantine-Medieval period of ca 7th-14th century AD very few aqueducts were built anew, whilst the greatest majority were the result of Greek and Roman works predating the 6th century AD). In fact, in many different civilizations, knowledge from the past was kept alive and helped to plan and realize new hydraulic works in different environmental and political situations.
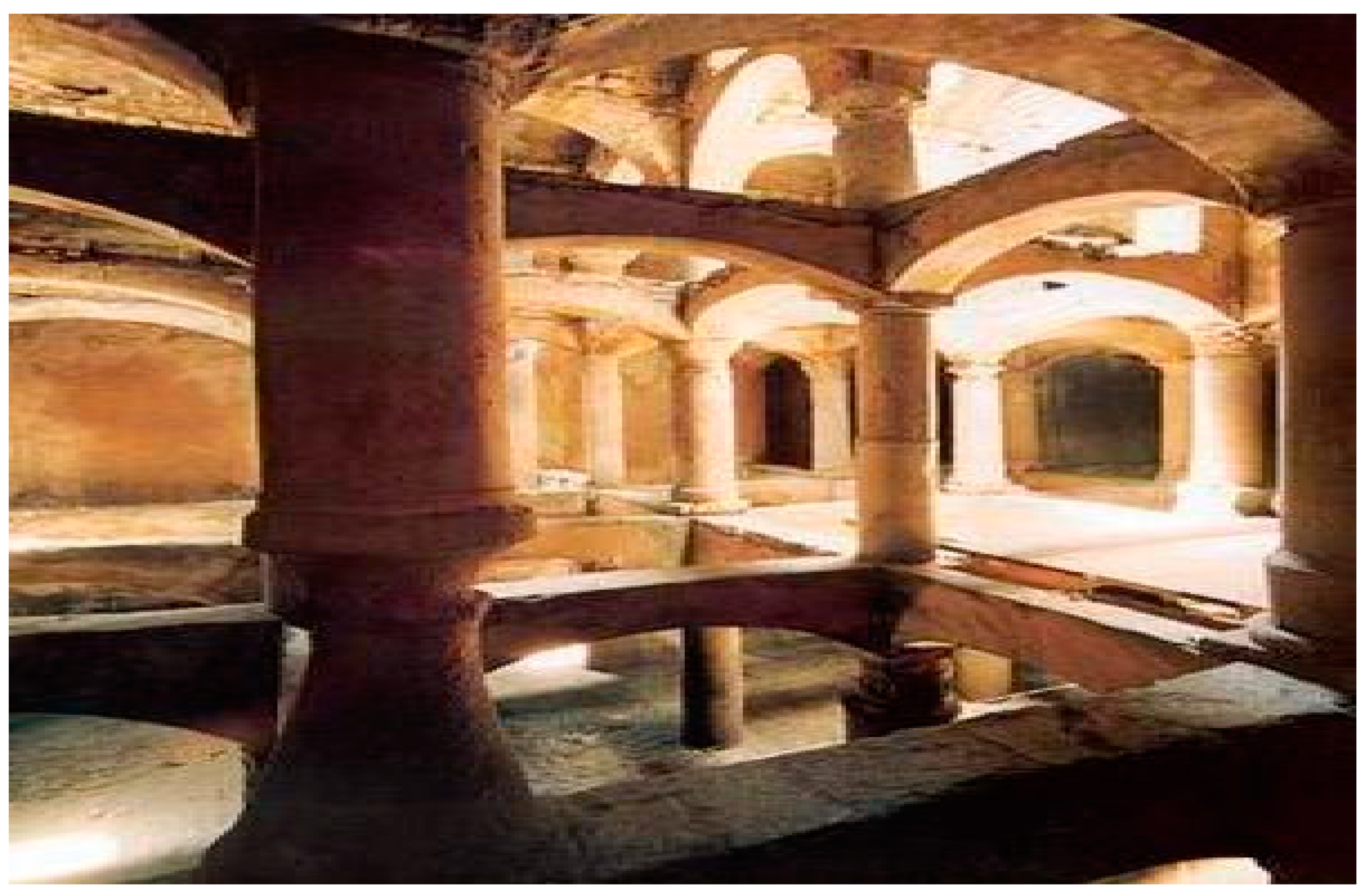
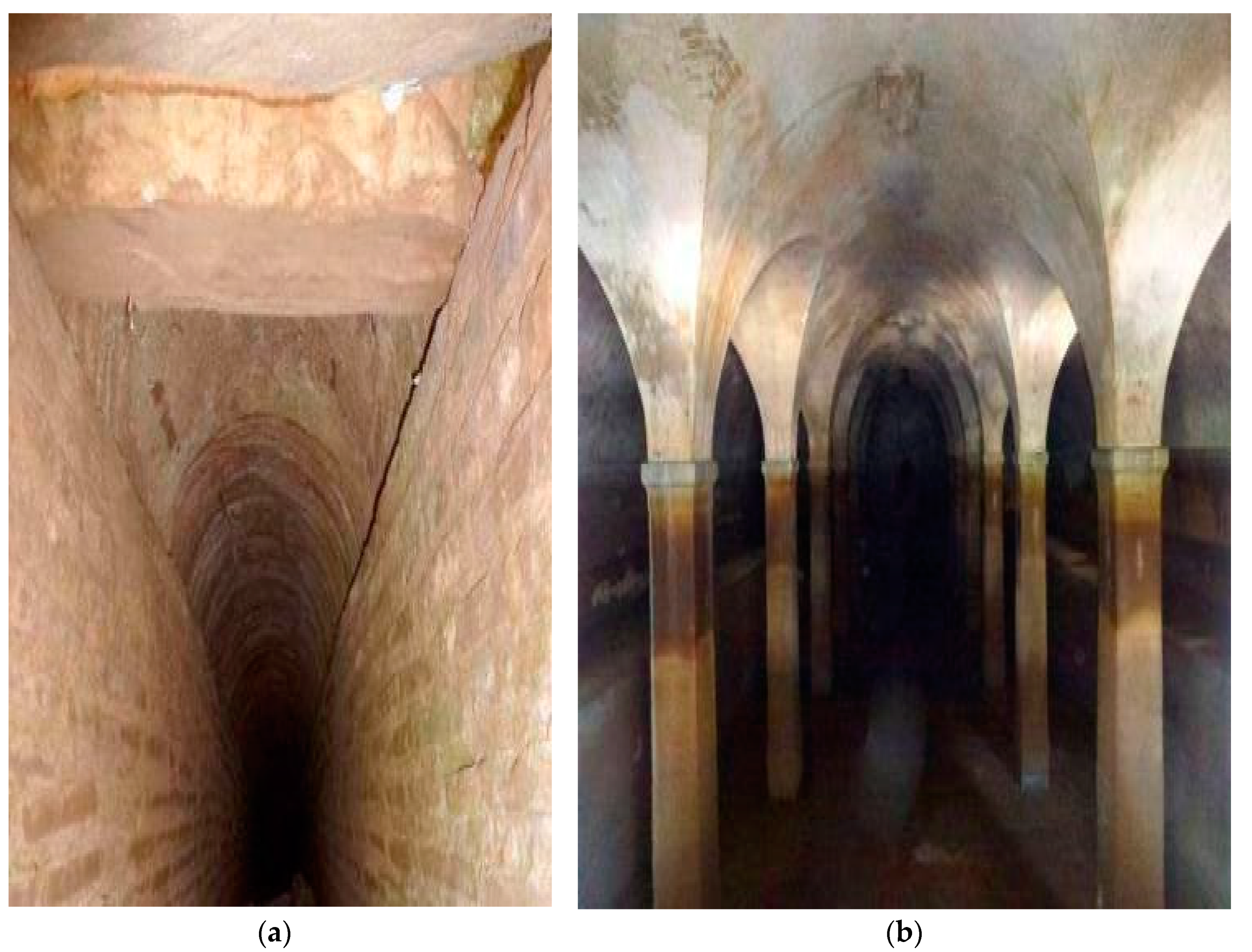
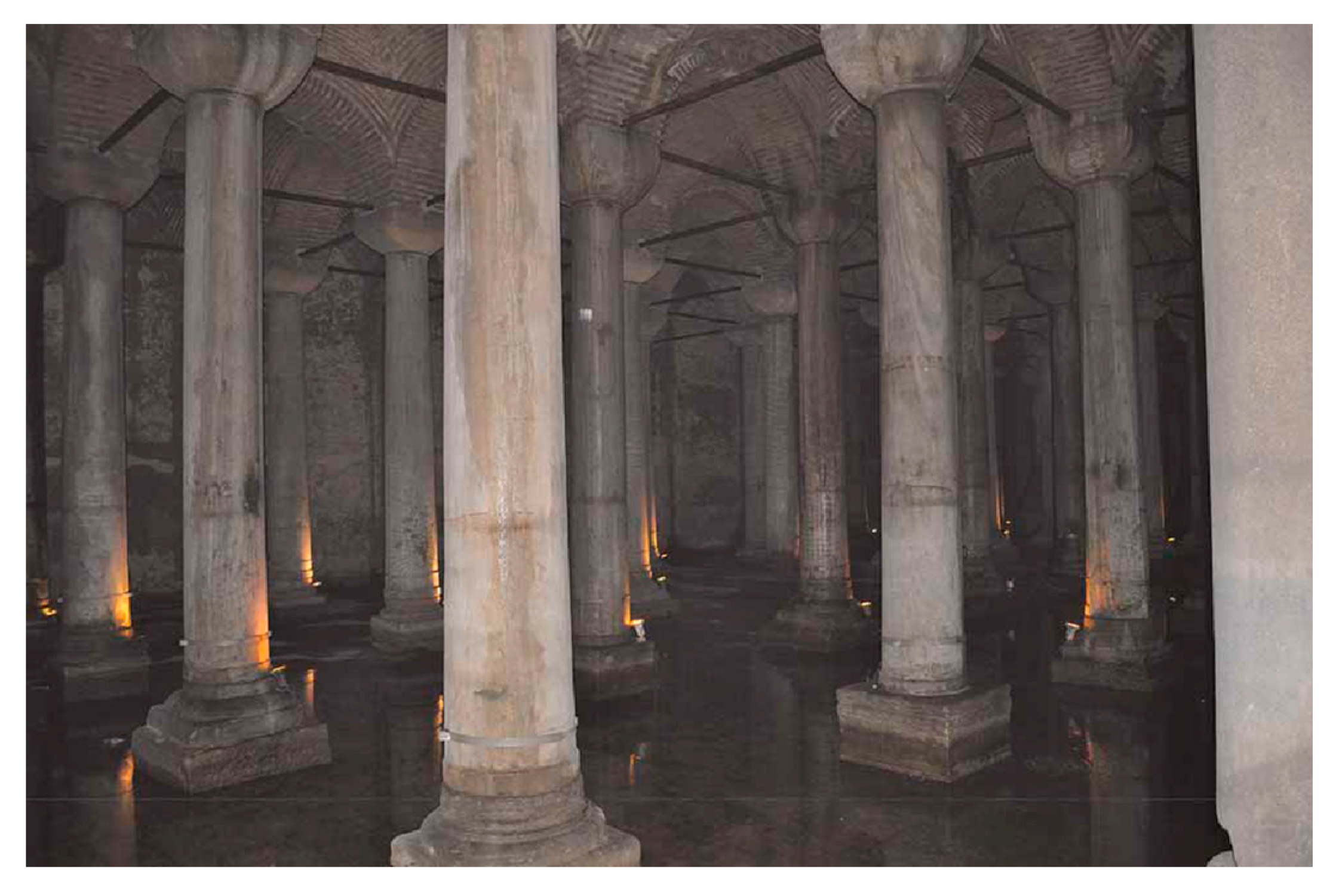
An example is the hundreds of cisterns that were successively built, and renovated and that memorialized in the town of Constantinople-Byzantium-Istanbul. The most famous and majestic among them is the Basilica Cistern, an underground hydro-structure located 150 m southwest of the Hagia Sophia on the historical peninsula of Sarayburnu, built in the 6th century during the reign of Byzantine Emperor Justinian I and continuously operative. It has the size of an underground cathedral, with a chamber of 138 by 65 m (about 9800 m2) that can hold 80,000 m3 of water (Figure 17) [56], and its ceiling is supported by a forest of 336 marble columns, each 9 m high, arranged in 12 rows of 28 columns with mutual distance of 5 m. The capitals of the columns are mainly in Ionic and Corinthian styles with engraved motives, with the exception of a few in Doric style with no engravings. This famous underground hydro-structure is still operating today [56].

Figure 17.
Basilica cistern at Istanbul, Turkey [56].
4.2. Crusaders
Another example of Medieval transmission of past knowledge of underground water structures is the Shobak Castle in Jordan (Figure 18), also called Crac de Montréal. This structure is famously known as the Great Crusader’s castle, as described by the Arab chronicler Fadhel [60]. The monumental fortress, built in 1115 by Baldwin I of Jerusalem, is literally an architectural archive spanning at least 1600 years, covering the Roman-Byzantine, Crusader-Ayyubid, Mamluk and Ottoman periods. For centuries, especially from the 12th to the 16th AD, it played a key role in controlling and connecting land communication, placed at a vital crossroad for the entire Mediterranean Near East, where Great Syria met Arabia and Egypt.
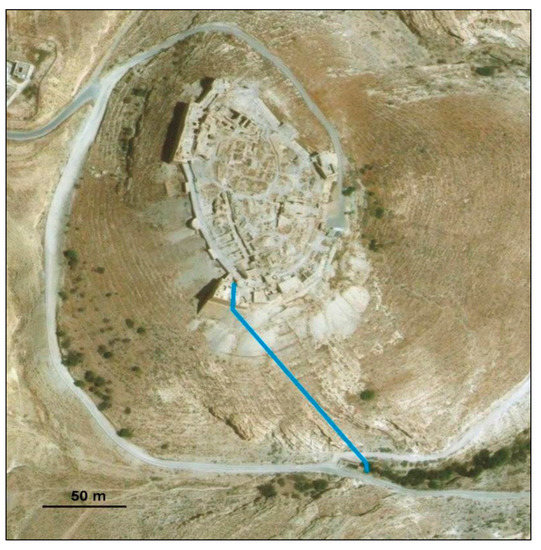

Figure 18.
Shobak castle and itinerary of the subterranean spring. The subterranean spring is reached from inside the SW corner of the walls through a tunnel 50 m deep, and Ain Al Ragaye emerges at the foothills 170 m south [60].
The fortress was built in a carbonate rock mass consisting of alternating layers of calcarenites and grey-blackish flint, each 15–20 cm thick. From inside the southwestern sector of the castle was excavated a steep gradient tunnel of 375 steps down to a depth of 50 m, leading to a cistern fed by a natural subterranean spring. The subterranean spring will emerge beyond the fortress walls from the foothills 170 m south, which explains why it was and is called Ain al Ragaye, meaning “the chameleon”, likely referring to its changeable aspect before and after the emergence, as the homonymous camouflaging reptile. The tunnel was realized following a helical section that, with a significant height drop in a small space [61], allowed to reach the spring from the fortified structure, probably for defensive reasons during sieges. As in other underground hydraulic works excavated in carbonate rocks affected by karst processes [46], it is likely that some of the sections at the Shobak tunnel were due to natural dissolution of carbonates and then included in the tunnel. The excavations of this fortified site greatly illustrate the capabilities of water search and collection in an arid environment, moreover in extreme conditions as it might have been a siege or a military occupation, capabilities certainly inherited from past experiences in nearby sites and/or from previous civilizations.
4.3. Puquios of Nazca (Peru)
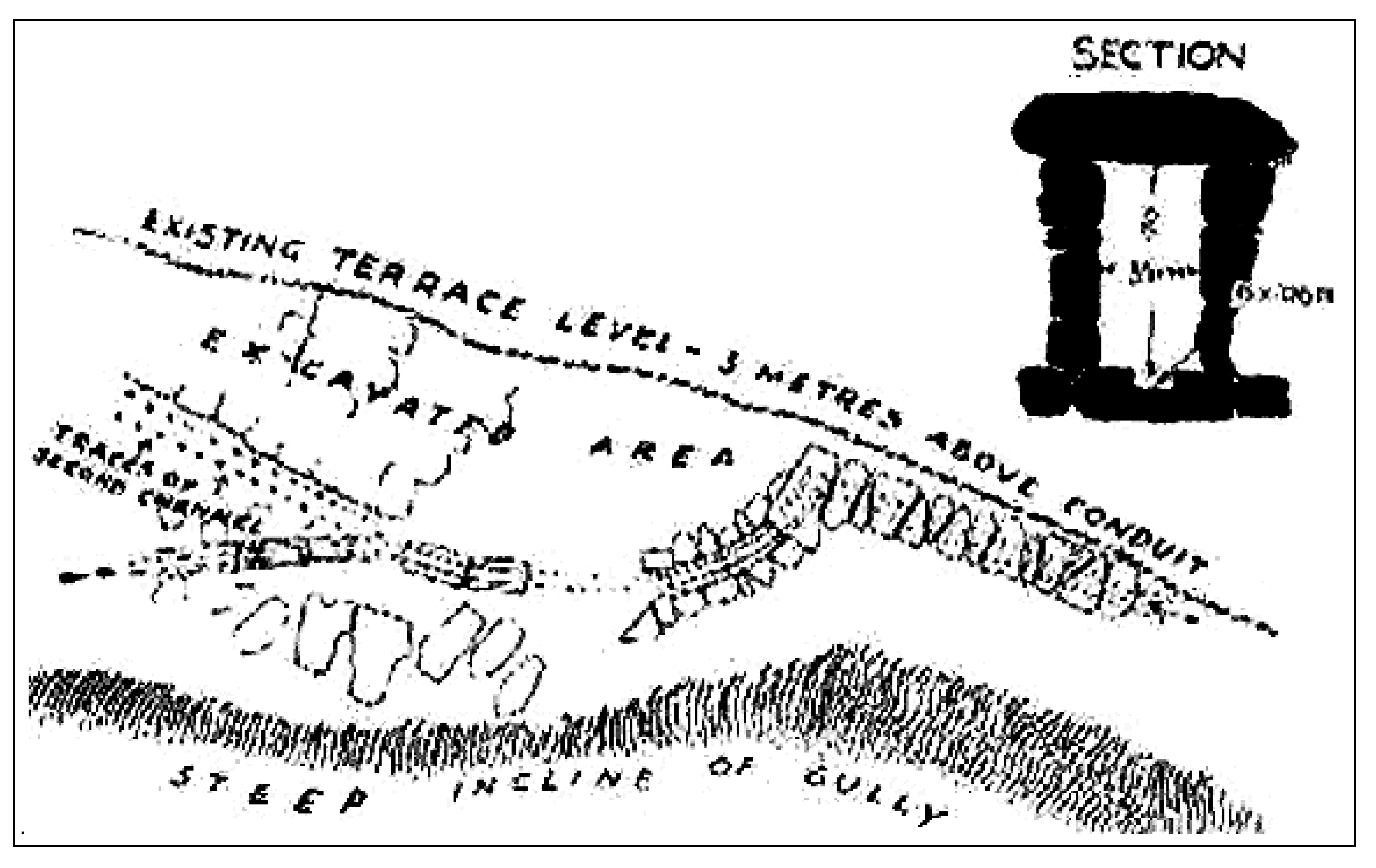
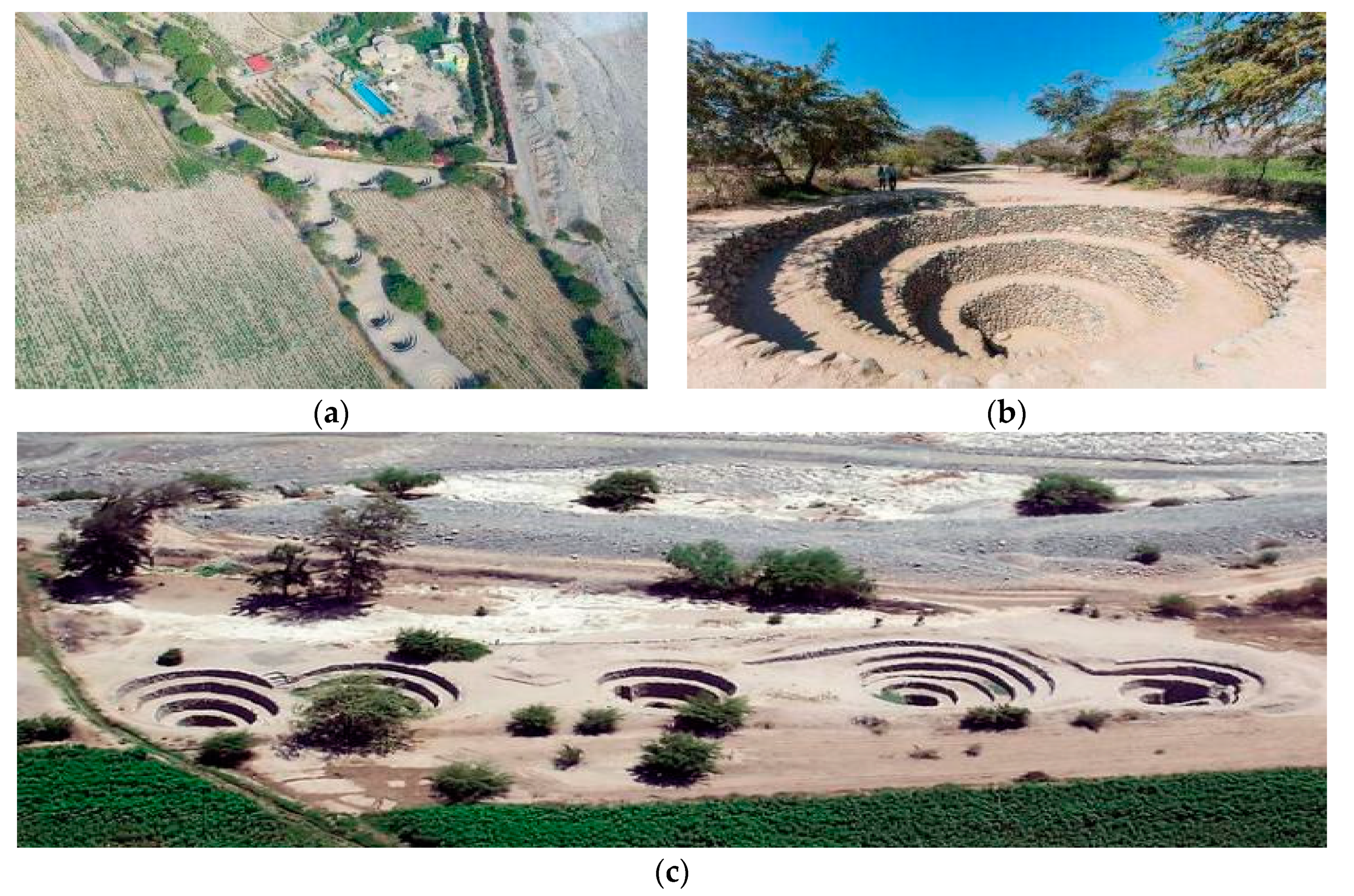
The following medieval hydraulic structure on our list is located at the antipodes, on the Pacific coast of Peru, and deserves mention by being a quite peculiar qanat-type aqueduct, product of the Nazca civilization. The Nazca civilization is without a doubt one of the most enigmatic ancient cultures of the Americas. It developed in the southern coast of Peru between ca 100 BC and 800 AD, in the intermittent drainage of the valleys of the Rio Grande and Ica river basins, i.e., one of the driest and most arid deserts on the planet [62]. Here has been designed and implemented an underground waterwork known as puquio: basically a qanat-type tunnel gathering groundwater from a dry riverbed and transporting it by gravity to houses and agricultural fields (Figure 19a–c) [63].
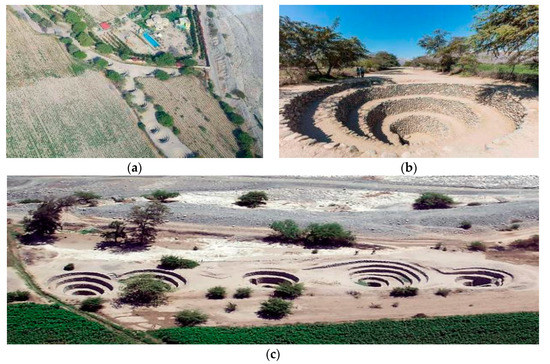
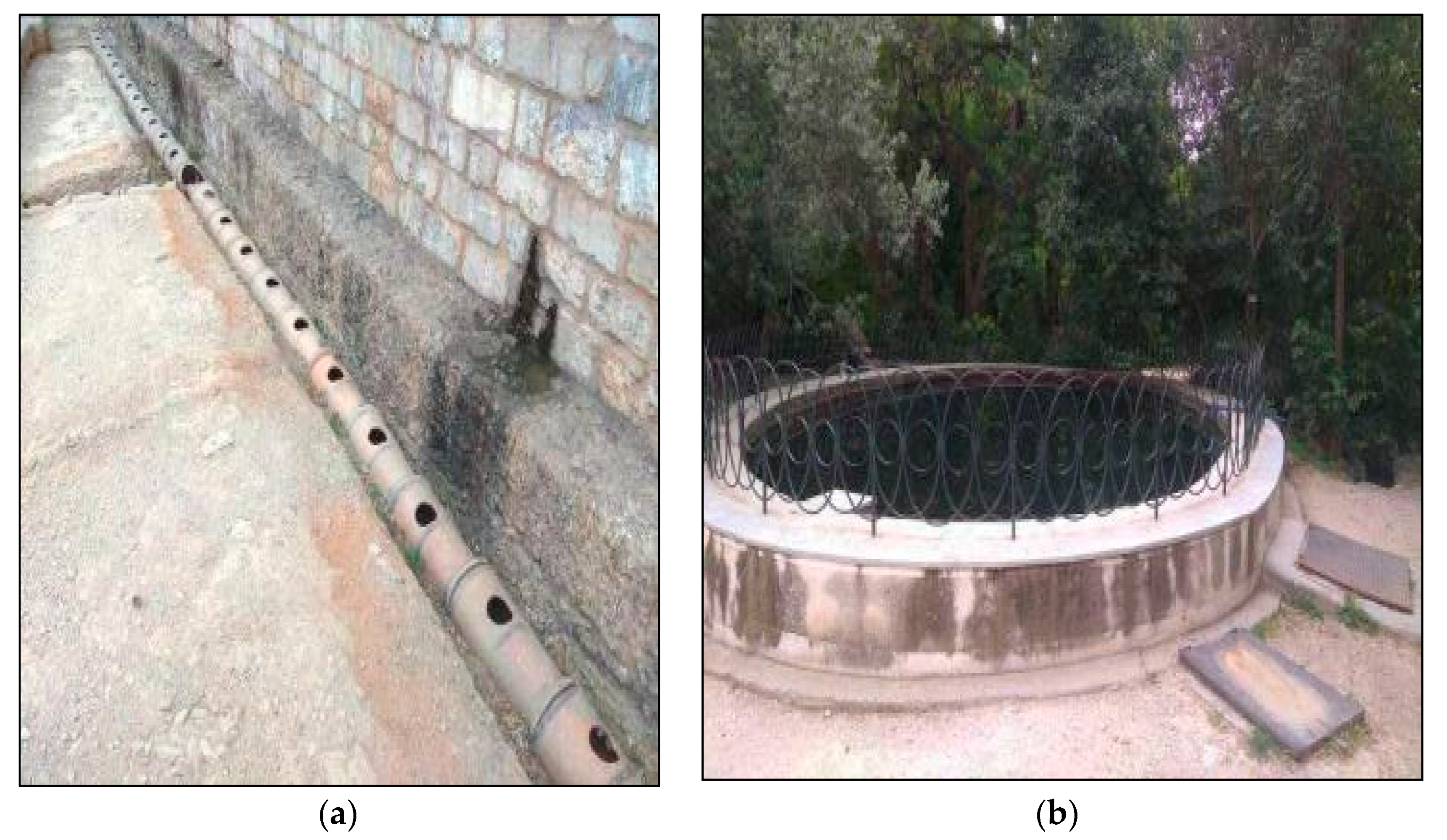
Figure 19.
System of puquios (qanat-like aqueduct with spiraling shaft) at Cantalloc (Southern Peru, Nazca culture, ca 2nd–7th century AD): (a) aerial view of the central part of the system; (b) ground level photo of a well 8–10 m deep, with scale [64]; (c) the first five (right-to-left) mother wells of the line, fed by the water table of the paralleling dry riverbed (view to N) [62].
In the Nasca region, there have been 46 such systems documented, of which 32 (70%) still are in use today [65,66]. Among them, the most famous is the Cantalloc (Cantayo) puquio, located 4 km east of the town of Nazca, dated to ca 2nd–7th century AD, and made of a gallery 350 m long provided of 22 spiraling 8–10 m deep shafts and then ending as an open canal surrounded by fields (Figure 18). Similar structures are built along the Taruga and Las Trancas seasonal streams, located respectively 10 and 17 km south of Nazca [67,68,69]. The building material, besides a few Huarango trunks for roofing, is mainly stone: small- and medium-sized alluvial rounded boulders from the river bed. Such a spiraling stepped conical shape is required for stabilizing the walls of wells, due to the kind of building material and the seismic character of the region, and for easing access to obtain the water.
4.4. Karez of Central Asia
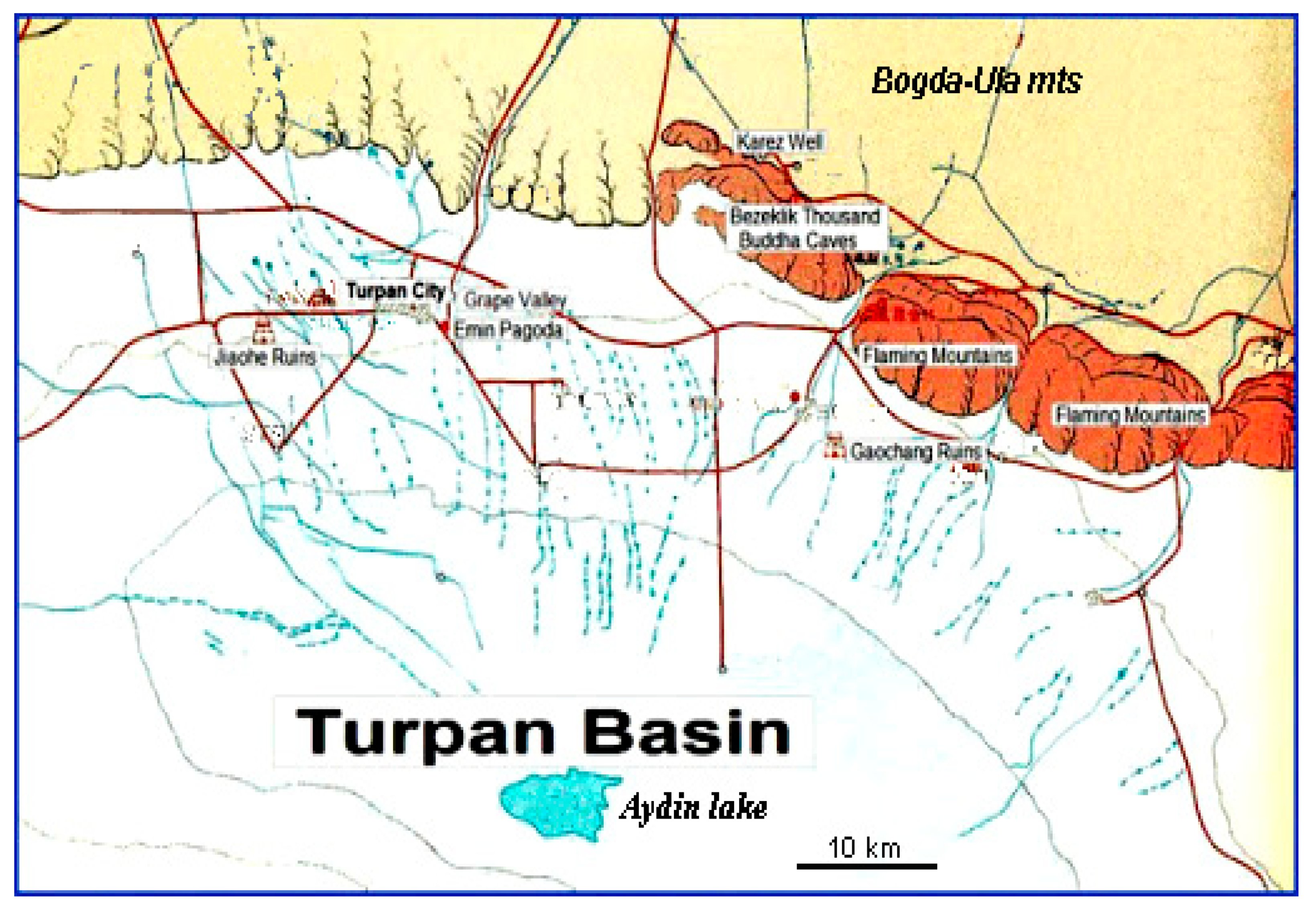
Karez (in Persian, an earlier version of the word qanat) is the name given in Central Asia to a subterranean water works intended for the resurgence of aquifer water to the ground surface. Its implementations are found in the arid contexts of Central Asia from the ca 7th century AD to present times. However, where the karez structures of East Central Asia (Turpan basin) are synonymous of real qanats consisting of artificial tunnels several km long and shafts, the karez of West Central Asia (Uzbekistan, South Kazakhstan) consist of relatively short lines of wells between which the water transport happens by infiltration and micro-artesian piezometric pressure [4].
The karez of the Turpan basin (Tarim, Xingjiang, China) are systems of classic qanat structures spanning for 50–60 km between the upper pre-mountain zone (900 m asl) of the Bogda-Ula mountains to the north and the second deepest depression of the world (Aydin lake, −154 m asl) to the south (Figure 20 and Figure 21). During the rainy season, the water flows from the mountain to the plain where it infiltrates the ground and recharges the local aquifer systems.
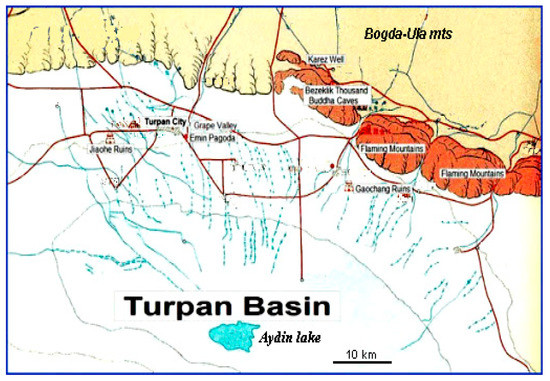
Figure 20.
Karez lines (in blue) of the Turpan basin, distributed along the southern slopes of the Bogda-Ula mountains. In the last 50 years, the number of karez active systems decreased from 1000 to 480 [70].

Figure 21.
Scale model of the entire karez system of the Turpan basin, from the piedmonts of the Bogda-Ula mountains in the north to the colonized plain 20–50 km far in the south [70].
Referring to archaeological data and oral accounts, the appearance of karez in the Turpan basin dates back to the import of the qanat technology from Middle East, in two waves: the first wave during the Uyghurian Huihe dynasty (790–1755 AD) and the second after 1755 AD during the Qing Chinese dynasty.
The typical Turpan karez system consists of a sloping underground gallery averaging 3–5 km in length (max up to 25 km) between an aquifer and the terminal resurgence, along which are vertically dug around 1500 wells averaging depth of 20 m. (decreasing from more than 100 m. on the hill sides to 2–3 m in the valley bottom) and mutual distance of 25 (decreasing from 70–30 to 20–10 m).
In 1950, such systems were in number of 1084 (with the total development of the lines counting over 5000 km and the total depth of the wells 3000 km) and provided a total water discharge of 700 million m3, enough for watering 24,000 ha of farmland. In 2003, the number of systems more than halved to 446 and the water discharge diminished by four times to 170 million m3, enough to support just 8800 h of farmland. The contraction of the total number of karez systems has been caused by the general drop of the aquifers’ water table that followed excessive water subtraction; and the decrease of functionality could not be inverted in spite of the additional drilling of around 5000 deeper wells.
In spite of the fact that the Turpan karez system represents a very sustainable way of water harvesting, under present conditions it is sentenced to dry out in a short time. Its restoration can only be implemented by considering the total hydrological system of the depression (precipitation, evaporation, infiltration, water table) and respecting sustainable values of groundwater subtraction [70].
5. Underground Hydro-Technologies in Early- and Mid-Modern Times (ca 1400–1900 AD)
Here, we focus on three most sustainable underground aqueducts during early- and mid-modern times.
A quite characteristic example of an underground water supply structure, which sustains its functionality up until the present, is the original section of the 18 km long Ottoman aqueduct of Pylos (Peloponnese, Greece), built in the 1630s [71] as a military structure that provided water to the Niokastro (New-Navarino) castle located 43 m asl above the entrance of the bay. An initial subterranean conduit (Figure 22) (constructed underground, probably for safety and hygienic reasons) conveys the water of Chandrinos spring to the following 18 km long surface aqueduct. Due to its importance, sound construction and regular maintenance, it keeps functioning even now. The local farmers have opened several holes along its path to irrigate their crops and named it “suyelo”, a name deriving from the Turkish term su yolu (water path) [71].
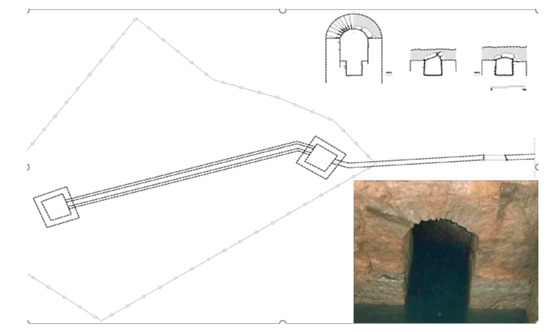
Figure 22.
The aqueduct of Pylos at the Chandrinos spring. Top: the mid-19th c. square wells connected with an arched gallery under a protective coverage of concrete. Right bottom: the opening of the arched gallery [71].
At the original Pylos aqueduct, in the mid-19th century the preexisting turbes (small domed spring water catching construction) was replaced by an improved—and definitely sustainable—water-catching underground structure made of a tunnel and two terminal tanks (Figure 22) from where, until the early 20th century, water was pumped into a modern pipeline supplying the town of Pylos.
Another remarkable evidence of underground hydraulic structure of this period is the aqueduct “Madonna della Stella” in the territory of Gravina in Apulia, southern Italy (Figure 23a,b) [72]. The building of the aqueduct is attributed to the Orsini family that governed this section of Apulia at that time [73]. Its construction started in 1743 and was accomplished between 1743 and 1778, result of the reconstruction of a preexisting viaduct of which the existence was first documented by historical sources in 1686 but postulated dating back to the Roman period [74,75]. Over 3500 m long, it is one of the best preserved underground man-made structures for collection and transport of water resources in southern Italy, draining the waters issuing at the contact between Plio-Pleistocene calcarenites and the overlying clays, with clear differences in permeability [45]. A number of inspection wells go down to a system of underground galleries developing at different heights. Close to the town, a spectacular bridge-canal was built across the torrent, in order to send the waters with pressure to the fountains located in town [72].

Figure 23.
(a) The bridge carrying water to the town of Gravina in Puglia (on the left side of the gorge), after a 3.5 km-long course of the underground aqueduct “Madonna della stella”; (b) view of a segment of the underground aqueduct [72].
In Anatolia, under Ottoman rule, the construction of nomads’ cisterns increased significantly. Koyuncu et al. [76] refers that just in Antalya (Anatolia, present Turkey) around 110 cisterns of nomadic type have been documented, presenting different construction techniques: cisterns with wells, cistern-wells with staircases, cisterns with gable roofs, with vaulted/cupola, fed by spring or short aqueducts; etc. Most of these cisterns are today still in use, mainly in order to supply water for the livestock [77].
A special type of circular shaped cistern emerged during the 16th and 17th century in rural areas of the southwestern Anatolia regions, originally built for military purposes by the Ottoman Army [56]. Their standard type is built on a superstructure about 7 m in diameter, 1–2 m high and covered by a domed roof with height about one third of the diameter, and a substructure a few meters in depth with stairs that descend to the cistern bottom (Figure 24) [56].

Figure 24.
Ottoman cistern built for military purposes in Bodrum, Turkey [56].
6. Underground Hydro-Technologies in Contemporary Times (1900 AD–Present)
In this section, we provided four underground hydro-technologies in contemporary times with respect to their importance.
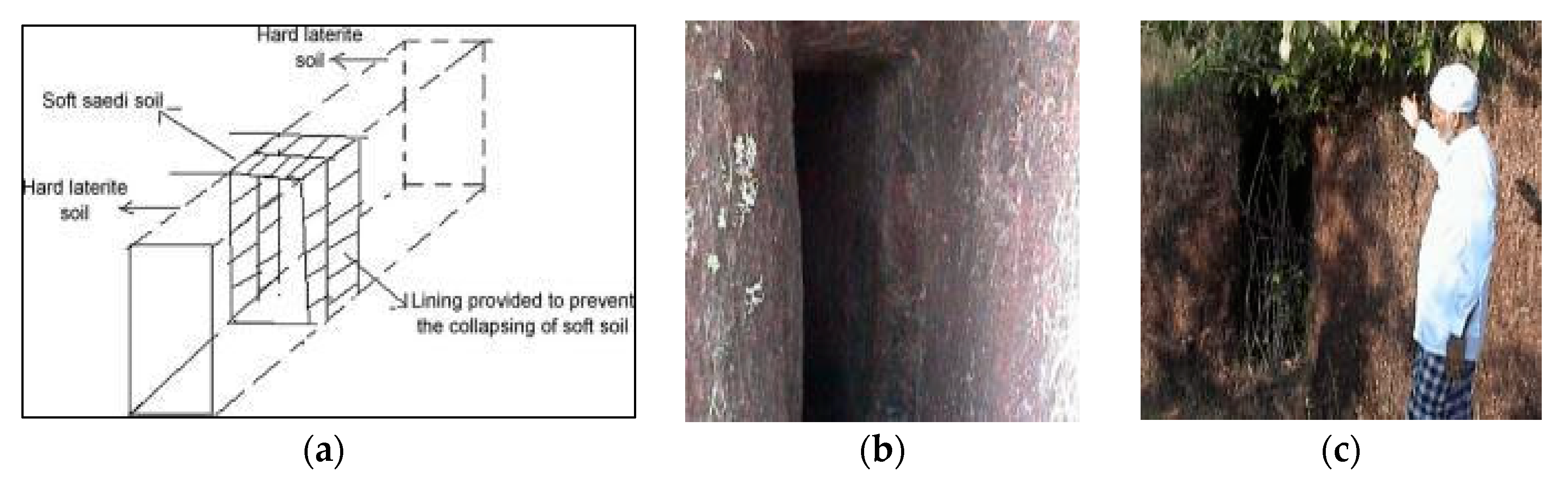
A contemporary example of underground aqueducts is the Indian qanat-like surangam, a Dravidian word for tunnel [78]. The building of these tunnel-well structures is documented in the early 1920s in South India, but their tradition could be older, by some authors attributed to their diffusion from the Arabs of the Malabar coast during the 17th AD, but most probably of autochthonous origin from Maharashtra, due to their exceptional insertion in a wet tropical context and the relatively short length of the tunnels (Figure 25a–c). The tunnels range from 3 to 150 m in length (averaging 25 m), about 2 m in height and 0.75 m in width, usually with rectangular cross-section. Short bamboos and shafts are sometimes used in small and long segments respectively.

Figure 25.
Tunnel wells: (a) structure; (b) entrance; (c) in operation [78].
These tunnels are still in operation being that farmers and small holders are highly dependent on the surangams for the supply of their water requirements. However, many efforts are needed in order to sustain and revive these traditional water harvesting structures. In fact, surangams are inserted in a very humid environment and water fed by percolation from the walls, which makes walls vulnerable to collapse, plants and animals spreading into the cavities and, as a whole, sustainability problems more redicent. But the main threat is an excessive drainage from the aquifer system during the monsoon season, driving to waste and lowering of the water table, which can decrease to zero in case the raining season is too short. This explains why the total number of surangam, formerly counted at 5000, is today progressively decreasing [78].
One impressive underground aqueduct in use today is the Alvear Aqueduct. It was built in the early 1900s by Spanish military engineers to address the water shortage in Havana, Cuba (Figure 26a,b). The size of the canal is 2.4 m depth and approximately 2 m width, its slope is 1/5000, its discharge 1.67 m3/s and can be increased up to two times [79].
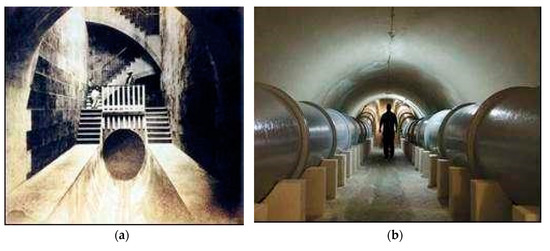
Figure 26.
Alvear aqueduct at Havana, Cuba: (a) in 1927; (b) in 2012 [79].
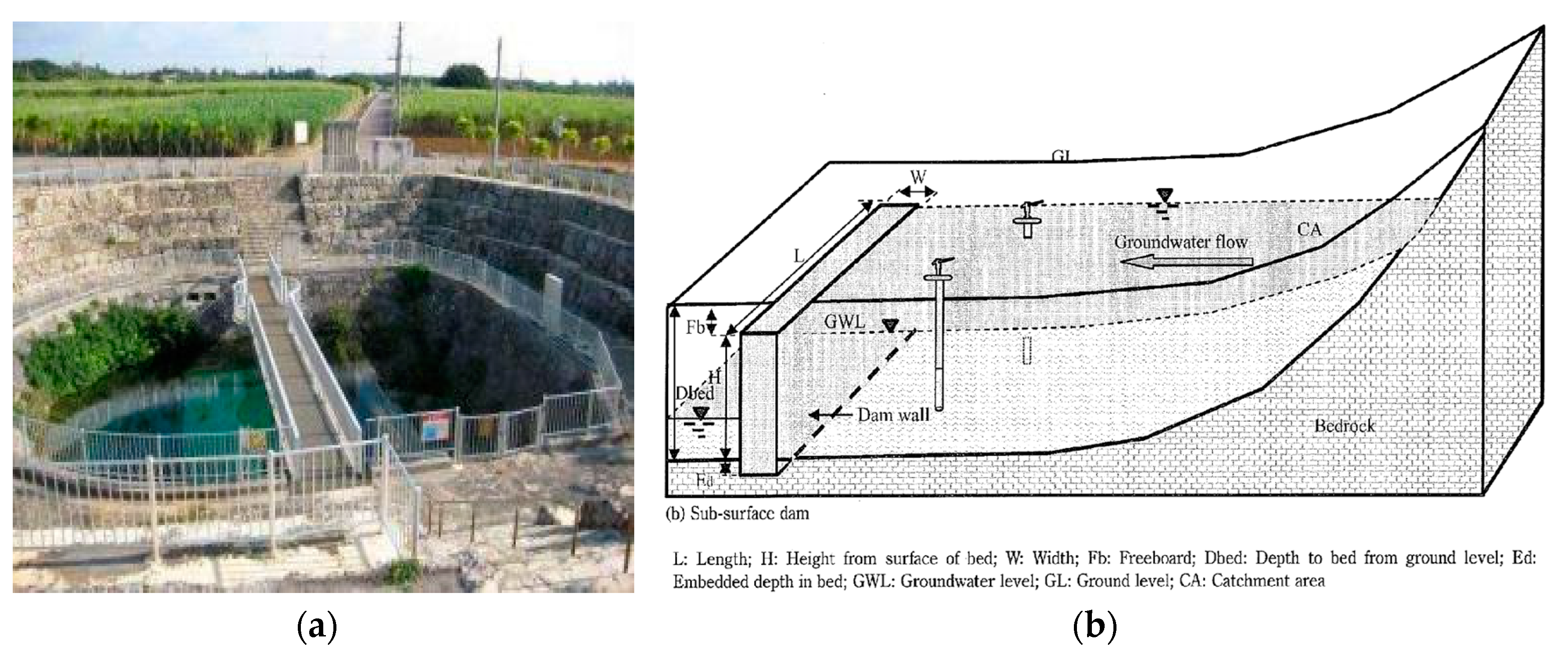
Building an underground dam can be considered as an option to overcome the problems of overexploitation of water through deep wells, which could cause the decline of the water table and make its extraction not financially sustainable. In fact, underground dams block the flow and, in that way, improve groundwater storage in the aquifer (Figure 27a). They can also divert the flow below the ground level [80] and feed neighboring aquifers as well as prevent marine intrusion, after all expanding water resources [81]. There is some evidence of using underground dams in Roman times in Sardinia [46] and North Africa [82] and also during the 18th century in Arizona [81]. However, the real development of subsurface water dams began during the 20th century, especially in its last few decades [81]. Famous is the Fukuzato Underground Dam, located in Okinawa, Japan (Figure 27b), with a dam wall of a length of 1790 m and a height of 27 m. The retained water is pumped by using more than 80 wells for the irrigation of sugarcane fields above the dam [83,84] and can also act as additional sustainable water resources for urban development.
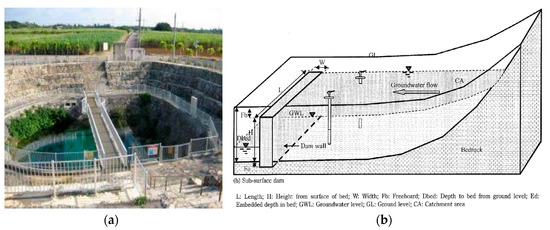
Figure 27.
Underground dams: (a) Fukuzato underground dam [85]; (b) general sketch of an underground dam [84].
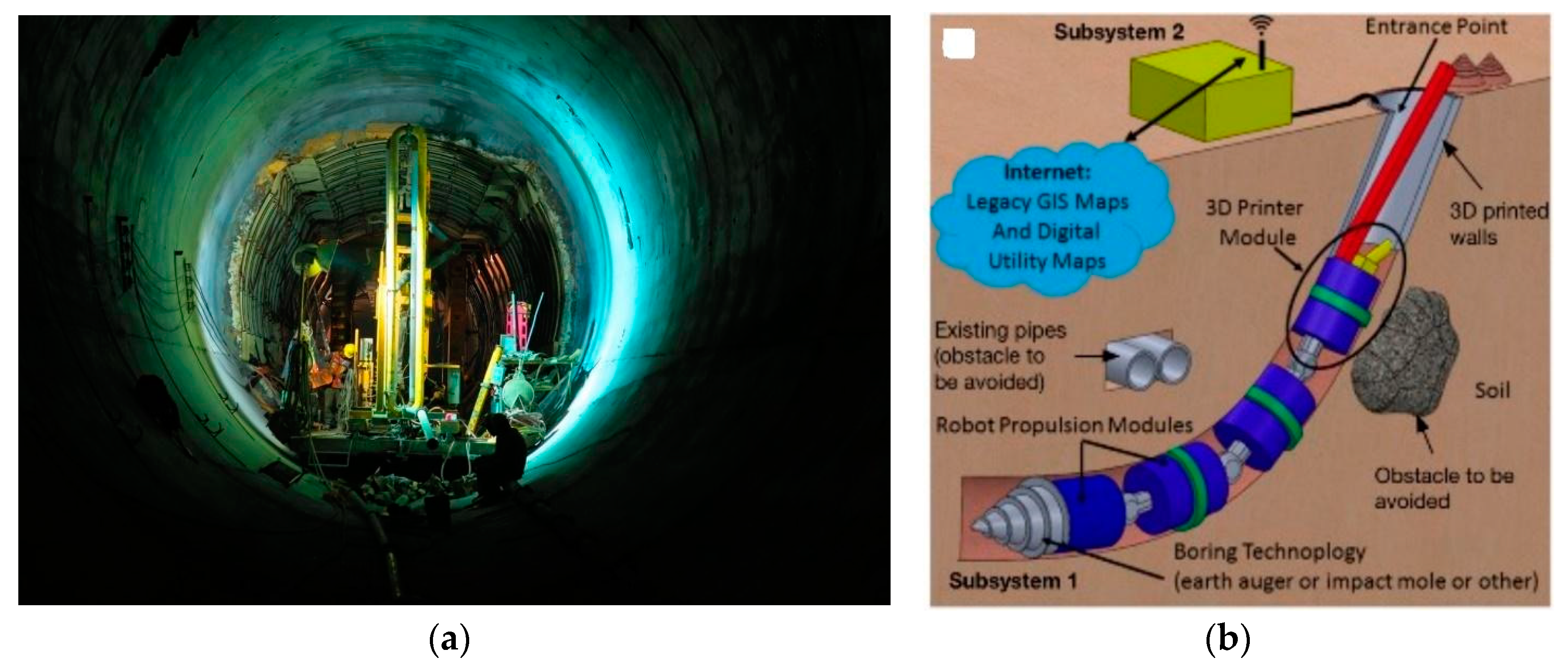
We conclude our review of historical aqueducts with the case of a modern implementation intended for the experimenting the use and sustainability of new building technologies. In the 1980s, the European Union (EU) financed a great research project on municipal engineering involving Italian, Spanish and French companies (Eureka EU 40) [43]. The goal was to develop a utility tunnel for the future use, and its major achievement was employing a robot for installing and repairing the utility tunnel, being that the size of the space required for a robot was much smaller than that the one needed for human workers. The implementation was cost efficient and reduced the initial costs in the utility tunnel cross-section. However, the working conditions inside the tunnel were difficult and eventually increased the maintenance charge. Although nowadays this new method looks like science fiction, perhaps in the near future urban engineering will adopt solutions which would include drilling robots (Figure 28a,b). These technologies follow trenchless technologies for installation of underground infrastructures systems, as these have become more prevalent over the past 10–20 years. These robots are a part of the roBot for Autonomous unDerGround trenchless opERations, mapping and navigation (BADGER) project. The goal of the project is the design and development of the BADGER, an autonomous underground robotic system that can drill, maneuver, localize, map and navigate in the underground space, equipped with tools for constructing horizontal and vertical networks of stable bores and pipelines. The proposed robotic system will enable the execution of tasks that cut across different application domains of high societal and economic impact, including trenchless constructions, cabling and pipe installations, geotechnical investigations, large-scale irrigation installations, search and rescue operations, remote science and exploration, and defense applications [85]. The underground robot consists of a number of modules united by mechanical couplings that give to it flexibility and mobility, i.e., a mechatronic system that allows the drill-head to move and turn in all directions and at all angles with maximum maneuverability, meaning, the robot can turn and maneuver in open and closed angles, whenever needed [85].
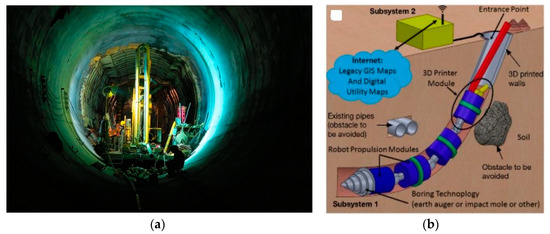
Figure 28.
(a) Modern tools to build a water tunnel; (b) future generation of drilling robots [86].
Sustainability of underground infrastructure plays a key role to support not only present but also future urban demands. The remaining challenge is utilizing sustainable methods that do not induce adverse consequences. Besides the technical aspects, municipal engineers should do their best to establish sustainable urban underground infrastructures through good and ethical governance [43].
7. Emerging Trends and Future Issues and Challenges on Sustainability
Social, hydrogeological and geotechnical aspects make the operation of underground aqueducts throughout the centuries possible, up until the present [86]. An important number of underground aqueducts are still in operation, particularly in Iran, where 37,000 active qanats have been registered [87]. The lessons that can be learned from older aqueducts should be employed to improve the efficiency of present and future structures. The material used for the construction of the underground aqueducts can be replaced/boosted using new materials for refurbishing the old aqueduct projects. This can be considered an improvement to the stability of underground facilities [86]. However, any improvement in relation to this aspect must be properly studied and examined, because the efficiency cannot be considered as the mere goal for any technological improvement. In addition, other sustainable-related criteria, which allow for endurability of the whole system, the existing ownership, management regimes, and social, cultural and economic interdependencies, are of utmost importance.
Nowadays, modern techniques represent an advanced reliable assessment of the geotechnical situations by evaluating losses occurred, failures mechanisms and weak formations. In addition, employing physical models (i.e., small-scale facilities) and computer simulations can help engineers to have quantitative monitoring, especially during operation processes, to minimize unpredictable risks. Besides these quantitative assessments, the qualitative understanding of each specific context is very important. Accessing or transporting water is not purely a technical problem, and involves a variety of sciences, disciplines and technologies [12].
Application of any new technology means interacting within the existing social and managerial system of water. For example, during World War II, many qanats were replaced by deep wells, introduced to Iran by the Allied Armies. The premises of this introduction were multiple. As scheduled, it was more efficient (more water is obtained faster) to get water from a deep well than from a qanat. The deep wells were a separate matter from topography and soil conditions. They could be built with fewer constraints and without using local materials or local labor. However, they might result in degrading water sources and emptying the aquifers. Notably, the change from qanats to deep wells represented a complete shift in the management of the territory. It was a shift from a collective legal act in qanat’s cooperative managerial system, to exploitation according to individual interest [88].
Governments and stakeholders could have a crucial role by giving financial aid for the dredging of qanat systems, supervision of digging new wells and groundwater exploitation, compilation of rules concerning renovation and conservation of qanat systems as sustainable hydro-structures for water resources management. Such endeavors will guarantee the life of these ancient underground hydro-technologies [89].
Most of the ancient underground aqueducts were built to deal with water-related challenges such as dry climate, droughts, floods, water shortage, etc. Therefore, the problems regarding global warming, climate change and water crisis may shape future trends in sustainability of aqueduct technology. There would be many ways to develop and maintain ancient underground aqueducts if applicable solutions to repair and fix their stability problems could be found, and the sustainability of these structures would be worthy for our future generations [86].
8. Conclusions
Sustainable use of water resources seems to have its roots in many ancient civilizations, as evidenced by their advanced technological water achievements, indicating the use of sophisticated management technologies such as underground aqueducts. Using these aqueducts was the only way to collect and convey water to populated or irrigated areas, since at that time drilling or pumping was not possible.
A brief historical development of underground hydro-structures from prehistoric times up to the present has been presented. These unique structures have allowed humans to live in arid and semi-arid regions for over 5000 years. These hydraulic structures certainly provide evidence of social, political, and economic conditions, and most likely their durability and sustainability, of the various periods of human history.
Due to their importance throughout history, such structures were not only well built and therefore durable, but also had regular maintenance even many centuries after their original construction. In addition, several of the underground aqueducts, besides the typical conveyance of spring water, passed through known aquifers, which increased by abstraction of their supplying capabilities. The combination of these factors contributed thoroughly to the accumulation of sustainable characteristics of the underground aqueducts. Moreover, the given protection, since they were underground, increased their ability for continuous operation through centuries.
Currently, even though there are numerous engines and industrial products to support water supply, engineers typically consider the useful period of hydro-structures is approximately 40–50 years, based upon economic and environmental considerations. It is difficult to infer the design principles of ancient people in terms of durability of structures. Nevertheless, it is notable that several ancient hydraulic works, such as underground aqueducts, have been operating for very long periods, sometimes until present (For example, as mentioned in Section 3.2, the Peisistratean aqueduct in Athens has been in operation since the 6th century BC. In addition, the case of the Hadrian’s aqueduct in Athens, which supplied the modern city for over 100 years, only relying on regular repairs, is a remarkable example of an ancient sustainable underground aqueduct well exploited by 19th and 20th century engineers [49]). There are also some investigations claiming that underground aqueducts, and particularly qanat systems employed in historical times, have a potential to serve as models for sustainable water supply systems today [3,4,12,44,90,91,92] (The forthcoming project of the Athenian Water Supply and Sewerage Company (EYDAP), to use water from the Peisistratian aqueduct of the 6th century BC to irrigates the National Garden since mid-19th century and thereafter the 2nd century AD Hadrian’s underground aqueduct to irrigate parks and gardens in Athens, is a sound evidence of the sustainability of such structures.)
Overusing groundwater resources to supply water, due to increasing demand of population especially in arid and semi-arid regions, results in deterioration of aquifers, as well as environmental issues including land degradation and water quality problems [73,93,94,95]. Unfortunately, nowadays, most of the societies in arid and semi-arid regions tend to abandon the historic underground aqueducts, particularly in favor of modern technologies [96]. However, some of these ancient underground aqueducts (e.g., qanats) are gravity-flow- and environment-friendly and can be still usable in regions facing water shortages [2]). One of the advantages of qanats is their equity, for which multiple stakeholders can have access to the same amount of water. They can also serve for sustainability of ecosystems against urban infrastructure proposals [97]. Therefore, considering global warming and inequity to access water resources resulting in a water crisis, ancient aqueducts and particularly qanats should be taken into account and viewed as lessons to be learnt about how to find successful solutions for sustainability and resiliency of water management in the future. Protection, revitalization and reconsideration of historic and utilizable water acquisition systems as smart technologies and social friendly solutions would help for the sustainable usage of water sources [97].
Although there are some attempts by governments and NGOs to protect ancient aqueducts as heritage monuments, many actions are still needed to increase the knowledge and awareness of local societies on the importance of historic water structures, their sustainable values and the need to safeguard them in facing different challenges of modernization. Most of the antique underground aqueducts are not only physical buildings, but also social lifestyle and cultural frames, which have remained a memento on our planet for future generations.
In conclusion, the study of ancient underground aqueducts represents definitely an exciting challenge that may open new lights toward the capability of man to collect water in the past and, more generally, to work toward a sustainable use of our natural resources [98]. Further, since we periodically experience hydrologic crises, often related to over-exploitation and degradation of water resources, and climate changes as well, several lessons may be learned from the analysis of ancient hydraulic works [99]. Water supply management is an extremely delicate matter, and deficiencies in such an issue have always been a recipe for disaster, because of the direct and cyclic nature of the routes of transmission of waterborne disease [100].
The traditional underground hydro-technologies should be taken into account, not only as ancient artifacts, but also as potential models and structures for sustainable water management for the present and leaning toward the future. A crucial factor in sustaining historical underground aqueducts depends on placing a premium on ancient approaches and methods that have shown to be functional and successful, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions [56]. The traditional aqueducts were built based on easy control, simplicity, and required uncomplicated operation. These characteristics have made them more sustainable. It is notable that the design and operation of some of them were enormously successful, analyzing these systems even by today’s standards. It is worth mentioning that the fundamental concepts of the environmental conservation and protection of energy and mass did not exist at the time, but these ancient systems were already built for the acquisition of sustainability of our water resources.
The looming water crisis across the world should be faced by using ancient knowledge and technologies inherited from history, in addition to modern day achievements [101,102,103,104], to deal with water scarcity, especially in developing countries. The use of qanats and cisterns can be implemented nowadays, especially where these systems are lacking, in order to strive for the sustainability of water resources [56].
Author Contributions
M.V. wrote about qanats, cisterns, Cantalloc aqueducts, Alvear aqueduct, tunnel wells, underground dams, drilling robots, and revised and edited the manuscript. A.T.A. wrote about Egyptian aqueducts in ancient times and reviewed the manuscript. G.P.A. wrote about Greek hydro-structures. R.S. wrote about karez in medieval times, added historical information all along the manuscript, and revised and edited the manuscript. M.P. wrote about Roman hydro-technologies and reviewed the manuscript. M.S. wrote about Spanish and South American structures and revised the manuscript. N.S.B. wrote about qanats and reviewed the manuscript. A.N.A. had the original idea, prepared the original draft of the manuscript, and revised and edited it. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
A portion of the material presented in this paper has been submitted and will be presented in the 6th IWA International Symposium on Water, Wastewater and Environment in Ancient Civilizations: Traditions and Culture 24 & 25 March 2021 at Bogazici University and 26 March 2021 at the Theological School of Halki, island of Heybeliada, Istanbul, Turkey, wwetc2020.eap.gr/. We greatly acknowledge Cynthia Lynn Hann for her considerable contribution of English grammatical and fluidity improvement in the development of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Voudouris, K.; Christodoulakos, Y.; Stiakakis, M.; Angelakis, A.N. Hydrogeological Characteristics of Hellenic Aqueducts-like qanats. Water 2013, 5, 1326–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barghouth, J.M.; Al-Sa`ed, R.M.Y. Sustainability of Ancient Water Supply Facilities in Jerusalem. Sustainability 2009, 1, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Mays, L.W.; De Feo, G.; Salgot, M.; Laureano, P.; Drusiani, R. Topics and Challenges on Water History. In Global Trends & Challenges in Water Science, Research and Management: A compendium of hot topics and features from IWA Specialist Groups, 2nd ed.; Li, H., Ed.; IWA: London, UK, 2016; pp. 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wessels, J.I.; Weingartner, H.; Eslamian, S.; Angelakis, A.N. Underground Aqueducts: Past, Present, and Future Trends. In Underground Aqueducts Handbook; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 491–509. [Google Scholar]
- De Feo, G.; Laureano, P.; Mays, L.W.; Angelakis, A.N. Water Supply Management Technologies in the Greek and Roman Civilizations. In Evolution of Water Supply throughout Millennia; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012; pp. 351–382. [Google Scholar]
- Weingartner, H. Water Supply by qanats: A Contribution to Water Shortage in Mediterranean Areas. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Kos Island, Greece, 5–7 September 2007; pp. 1555–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M.; Marangella, A.; Maranò, P.; Sammarco, M.; Sannicola, G. Collecting, transporting and storing water in karst settings of southern Italy: Some lessons learned from ancient hydraulic systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 13, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.T. Water Quality for Irrigation and Drinking Water Use of Aflaj in Oman. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 15, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, M. “Aqueduct”. Ancient History Encyclopedia, 1 September 2012. Available online: https://www.ancient.eu/aqueduct/ (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Beaumont, P. Qanat systems in Iran. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1971, 16, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goblot, H. Les Qanats, une Technique D’acquisition de l’eau/English: Qanat a Technique for Obtaining Water; Ecole des Hautes en Sciences Sociales: Paris, France, 1979; p. 236. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdi, S.; Asghar, A.; Khaneiki, M.L. Qanat Knowledge: Construction and Maintenance; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- English, P.W. The origin and spread of qanats in the Old World. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 1968, 112, 170–181. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Taiee, T.M. Kahrezes (Qanats) A ground water harvesting technology in arid and semi-arid regions. In Proceedings of the 3rd IWA Specialized Conference on “Water and Wastewater Technologies in Ancient Civilizations”, Istanbul, Turkey, 22–24 March 2012; pp. 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M.; Abbasnejad, A.; Abbasnejad, B.; Derakhshani, R.; Hemmati, S.A. Qanat is not a hazard. Rebuttal to Qanat hazard in Iranian urban areas: Explanation and remedies. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1306. [Google Scholar]
- English, P.W. City and Village in Iran: Settlement and Economy in the Kirman Basin; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Bonine, M.E. The morphogenesis of Iranian cities. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1979, 69, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonine, M.E. From qanat to kort: Traditional irrigation terminology and practices in central Iran. Br. Inst. Persian Stud. 1982, 20, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himat, A.; Dogan, S. Ancient karez systems as a sustainable tool for irrigation and water supply in rural Afghanistan. Int. J. Ecosyst. Ecol. Sci. 2017, 7, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Wessels, J. Reviving ancient water tunnels in the desert—Digging for gold? J. Mt. Sci. 2005, 2, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, L.W. Lessons from the ancients on water resources sustainability. In Ancient Water Technologies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 217–239. [Google Scholar]
- Gleick, P.H. The World’s Water, The Biennial Report on Freshwater Resources; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gleick, P.H.; Loh, P.; Gomez, S.; Morrison, J. California Water 2020: A Sustainable Vision; Pacific Institute for Studies in Development, Environment and Security: Oakland, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.T.; Elsanabary, M.H. The water supply history of underground aqueducts in Egypt. In Underground Aqueducts Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsoyiannis, D.; Zarkadoulas, N.; Angelakis, A.N.; Tchobanoglous, G. Urban water management in Ancient Greece: Legacies and lessons. ASCE J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2008, 134, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, K.; Tsatsanifos, C.; Yannopoulos, S.; Angelakis, A.N. Evolution of Underground Aqueducts in the Hellenic World. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 16, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A. The Palace of Minos at Knossos: A Comparative Account of the Successive Stages of the Early Cretan Civilization as Illustrated by the Discoveries; Macmillan and Co.: London, UK, 1921; Reprinted by Biblo and Tannen: New York, NY, USA, 1962; Volume 1–4, pp. 1921–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Tsatsanifos, C. Ancient Greek Geotechnical Successes. In Proceedings of the during the ISSMGE European Members Meeting during the XIV ECSMGE, Madrid, Spain, 20–24 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cistern of Ancient Mycenae. Mikinai—Mikines—Mykenai. 2020. Available online: https://www.showcaves.com/english/gr/subterranea/Mycenae.html (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Nordin, J.P. The Ancient City of Mycenae. 2004. Available online: https://theplaka.com/mycenae/index.htm (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Margat, J.; Van der Gun, J. Groundwater around the World: A Geographic Synopsis; CRC Press/Balkema: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2013; p. 343. [Google Scholar]
- Pappas, A. Water Supply of Ancient Athens (Η Ύδρευσις των Αρχαίων Αθηνών). Ελεύθερη Σκέψις; University Microfilm International: Athens, Greece, 1999. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Chiotis, D.E.; Chioti, E.L. Water supply of Athens in the antiquity. In Evolution of Water Supply through the Millennia; IWA: London, UK, 2012; pp. 407–442. [Google Scholar]
- Valipour, M. Assessment of important factors for water resources management in European agriculture. J. Water Resour. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 4, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, K.; Valipour, M.; Kaiafa, A.; Zheng, X.Y.; Kumar, R.; Zanier, K.; Kolokytha, E.; Angelakis, A. Evolution of water wells focusing on Balkan and Asian civilizations. Water Supply 2019, 19, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Urban Water Engineering and Management in ancient Greek times. In The Encyclopedia of Water Science; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 999–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, J.H. The Aqueducts of Ancient Rome; Kessinger Publishing: Oxford, UK, 1876. [Google Scholar]
- Kastenbein, T.R. Archeologia Dell’Acqua: La Cultura Idraulica nel Mondo Classico; Longanesi & C.: Milano, Italy, 1993; p. 278. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, C.R. The walls and aqueducts of Rome in the early middle ages. J. Roman Stud. 1998, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, D.R. The volume of water delivered by the four great aqueducts of Rome. In Papers of the British School at Rome; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1979; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Delle Rose, M.; Giuri, F.; Guastella, P.; Parise, M.; Sammarco, M. Aspetti archeologici e condizioni geologico-morfologiche degli antichi acquedotti pugliesi. L’esempio dell’acquedotto del Triglio nell’area tarantina. Opera Ipogea 2006, 1–2, 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- De Marco, M.; Guastella, P.; Marangella, A.; Parise, M. L’antico acquedotto romano del Saturo-Leporano (Taranto, Puglia). Opera Ipogea 2008, 1–2, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Cano-Hurtado, J.J.; Canto-Perello, J. Sustainable development of urban underground space for utilities. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 1999, 14, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, T. The Aqueducts of Ancient Rome; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Judson, S.; Kahane, A. Underground drainageways in southern Etruria and northern Latium. In Papers of the British School at Rome; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1963; Volume 31, pp. 74–99. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, A.T. Roman Aqueducts and Water Supply; Bloomsbury Publishing PLC: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M.; Galeazzi, C.; Germani, C.; Bixio, R.; Del Prete, S.; Sammarco, M. The map of ancient underground aqueducts in Italy: Updating of the project, and future perspectives. In Proceedings of the International Congress in Artificial Cavities “Hypogea 2015”, Rome, Italy, 11–17 March 2015; pp. 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M.; Sammarco, M. The historical use of water resources in karst. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gausmann, R. Water for Athens; Gennadius Library: Athens, Greece, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Curiel-Esparza, J.; Canto-Perello, J.; Calvo, M.A. Establishing sustainable strategies in urban underground engineering. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2004, 10, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlos, J. Pictorial Dictionary of Ancient Athens; Hacker Art Books: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Hekimoglou, E. Ydatini Istoriografia (Υδάτινη Ιστοριογραφία) EYDAP; University Microfilm International: Athens, Greece, 2014. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Maranò, P. Il Problema Acqua a Grottaglie: Sistemi di Raccolta Dell’Acqua Piovana. Bachelor’s Thesis, Faculty of Architecture, University of Florence, Florence, Italy, 2005–2006. [Google Scholar]
- De Feo, G.; De Gisi, S.; Malvano, C.; De Biase, O. The greatest water reservoirs in the ancient Roman world and the “Piscina Mirabilis” in Misenum. In Proceedings of the International Water Association Specialty Conference, 2nd International Symposium on “Water and wastewater technologies in ancient civilizations”, Bari, Italy, 28–30 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M.; Marangella, A.; Maranò, P.; Sammarco, M.; Sannicola, G. Ancient Hydraulic Systems for Collection, Transport, and Storage of Water in Karst Settings of Southern Italy. In Proceedings of the IWA Specialized Conference on Water & Wastewater, Istanbul, Turkey, 22–24 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mays, L.W. Use of cisterns during antiquity in the Mediterranean region for water resources sustainability. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 14, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaff, S.A.; Sim, S.C.; Efzan, M.E. A review of underground building towards thermal energy efficiency and sustainable development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 692–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milstein, M. “Lost City” of Petra Still Has Secrets to Reveal. Nationalgeo-graphic. Available online: http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/archaeology/lost-city-petra/ (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Paradise, D.T. The PETRA PROJECT, University of Arkansas, Department of Geosciences. 2013. Available online: http://geosciences.uark.edu/217.php (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Shama, A. Le livre des deux jardins. Histoire des deux règnes, celui de Nour ed-Din et celui de Salah ed-Din (sec. XIII), Recueil dés histories dés croisades, Historiens orientaux, tomo IV; Hachette Livre BnF: Paris, France, 1898. [Google Scholar]
- Burri, E.; Germani, C.; Mancini, M.; Nucciotti, M.; Parise, M.; Vannini, G. Ain al Ragaye: A tunnel for exploitation of natural spring in Shawbak Castle (Jordan). Opera Ipogea 2009, 1, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, H.; Proulx, D.A. The Nasca; Blackwell Publishing: Malden, MA, USA; Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Klimczak, N. Solved: The Mystery of the Spiraling Holes in the Nasca Region of Peru. Ancient Origins, 13th April 2016. Available online: https://www.ancient-origins.net/news-history-archaeology/solved-mystery-spiraling-holes-nasca-region-peru-005704 (accessed on 15 September 2019).
- Delso, D. Cantalloc Subterranean Aqueducts, Nazca, Peru. 2015. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acueductos_subterr%C3%A1neos_de_Cantalloc,_Nazca,_Per%C3%BA,_2015-07-29,_DD_01.JPG (accessed on 15 September 2019).
- Barnes, M. Dating of Nazca aqueducts. Nature 1992, 359, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, W. Under the skin of Nazca. Nature 1992, 358, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, P.; Dorn, R. Archaeology New Chronometric Dates for the Puquios of Nasca, Peru Latin American Antiquity; Society for American Archaeology: Lima, Peru, 1995; Volume 6, pp. 56–69. [Google Scholar]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Following the Ancient Nasca Puquios from Space, In Satellite Remote Sensing: A new tool for Archaeology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 269–290. [Google Scholar]
- Proulx, D.A.; Rickenbach, J. Nasca Puquios and Aqueducts. University of Massachusetts. Available online: people.umass.edu/~proulx/online_pubs/Zurich_Puquios_revised_small.pdf (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- Mächtle, B.; Hecht, S.; Manke, N.; Kromer, B.; Lindauer, S.; Li, C.S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Bubenzer, O. The age and origin of Karez systems of Silk Road oases around Turpan, Xinjiang, PR of China. In Socio-Environmental Dynamics along the Historical Silk Road; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 359–378. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniou, G.P. The Architecture and Evolution of the Aqueduct of Pylos—Navarino. In Proceedings of the 3rd IWA Specialized Conference on Water and Wastewater Technologies in Ancient Civilizations, Istanbul, Turkey, 22–24 March 2012; pp. 410–419. [Google Scholar]
- Bixio, R.; Parise, M.; Saj, S.; Traverso, M. L’acquedotto sotterraneo di Gravina in Puglia “Sant’Angelo-Fontane della Stella”. Opera Ipogea 2007, 9, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Nardone, D. Gli Orsini di Roma nel fondo di Gravina (1388–1816). Tip. Attolini; Archivo Storico Capitolino, Gravina in Puglia: Roma, Italy, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Perron, F. Feudi e feudatari napoletani della prima metà del cinquecento, Archivio Storico per le Province Napoletane, XVI; Archivo Storico Capitolino: Roma, Italy, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Emetere, M.E.; Valipour, M. Comparative assessment of ground and satellite aerosol observations over Lagos-Nigeria. Croat. Meteorol. J. 2018, 53, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Koyuncu, I.; Altinbas, M.; Aydin, A.F.; Guclu, S.; Turken, T.; Ecis, R.; Yildiz, A.; Tutuncu, H. Nomad cisterns in Antalya. In Proceedings of the 3rd IWA Specialized Conference on Water and Wastewater Technologies in Ancient Civilizations, Istanbul, Turkey, 22–24 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ozis, U. Outlook on ancient cisterns in Anatolia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rain Water Cistern Systems; University of Hawaii: Manoa, Turkey, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Balooni, K.; Kalro, A.H.; Kamalamma, A.G. Sustainability of tunnel wells in a changing agrarian context: A case study from South India. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portuondo, M.M. Una Obra maestra: El acueducto Albear de La Habana. Technol. Cult. 2005, 46, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goran, H.; Nilsson, A.K. Ground Water Dams for Rural-Water Supplies in Developing Countries. Ground Water 1986, 24, 497–506. [Google Scholar]
- Zarkesh, M.M.K.; Ata, D.; Jamshidi, A. Performance of Underground Dams as a Solution for Sustainable Management of Drought. J. Biourbanism 2012, 1, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, S. A History of Dams; Peter Davies: London, UK, 1971; pp. 25–49. [Google Scholar]
- Nishigaki, M.; Kankam-Yeboah, K.; Komatsu, M. Underground dam technology in some parts of the world. J. Groundw. Hydrol. 2004, 46, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, S.; Tsuchihara, T.; Yoshimoto, S.; Imaizumi, M. Sustainable use of groundwater with underground dams. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2011, 45, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, Á. A Small, Autonomous, Subterranean Robot for Urban Environments. 2018. Available online: https://blog.ferrovial.com/en/2018/08/subterranean-robot-urban/ (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Chiotis, E.D.; Marinos, P.G. Geological aspects on the sustainability of ancient aqueducts of Athens. Bull. Geol. Soci. Greece 2012, 46, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megdiche-Kharrat, F.; Ragala, R.; Moussa, M. Promoting a sustainable traditional technique of aquifer water acquisition common to arid lands: A case study of Ghassem Abad qanat in Yazd Province (Iran). Water Supply 2019, 19, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaan Bensi, N. The qanat System: A Reflection on the Heritage of the Extraction of Hidden Waters. In Adaptive Strategies for Water Heritage; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Motiee, H.; Mcbean, E.; Semsar, A.; Gharabaghi, B.; Ghomashchi, V. Assessment of the contributions of traditional qanats in sustainable water resources management. Int. J. Water Res. Dev. 2006, 22, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, P. Qanats on the varamin plain. Iran. Trans. Inst. Br. Geograph. 1968, 45, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, F.; Saleh Mafakheri, M. qanat water supply systems: A revisit of sustainability perspectives. Environ. Syst. Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonnier, J.; Hopper, K. The Qanāt: A multidisciplinary and diachronic approach to the study of groundwater catchment systems in archaeology. Water Hist. 2018, 10, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannopoulos, S.I.; Lyberatos, G.; Theodossiou, N.; Li, W.; Valipour, M.; Tamburrino, A.; Angelakis, A.N. Evolution of water lifting devices (pumps) over the centuries worldwide. Water 2015, 7, 5031–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, S.; Davari, A.; Reyhani, M.N. Iranian Qanāts: An Ancient and Sustainable Water Resources Utilization. In Underground Aqueducts Handbook; Taylor and Francis, CRC Group: Abingdon, UK, 2017; Volume 9, pp. 123–150. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri, K.; Taheri, M.; Parise, M. Impact of intensive groundwater exploitation on an unprotected covered karst aquifer: A case study in Kermanshah Province, western Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megdiche-Kharrat, F.; Moussa, M.; Rejeb, H. Aflaj Water Management in Oman: The Case of Falaj Al-Khatmeen in Birkat Al-Mouz, Wilayat Nizwa. In Water and Land Security in Drylands; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Megdiche-Kharrat, F.; Ragala, R.; Moussa, M. The aqueducts of the Sultanate of Oman. Sustainable water-supplying systems irrigating oases cities. In Underground Aqueducts Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- Laureano, P. Water Atlas: Traditional Knowledge to Combat Desertification; Bollati Boringhieri: Torino, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Castellani, V.; Dragoni, W. Italian tunnels in antiquity. Tunn. Tunn. 1991, 23, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Pike, E.B. Drinking water supply-a backward look into the future. Environmentalist 1999, 19, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M. Global experience on irrigation management under different scenarios. J. Water Land Dev. 2017, 32, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M. How do different factors impact agricultural water management? Open Agric. 2016, 1, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M.; Saeed, F.; Saeed, S.; Islam, M.N.; Ismail, M.; Klutse, N.A.B.; Siddiqui, M.H. Projected change in temperature and precipitation over Africa from CMIP6. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M.; Saeed, S.; Saeed, F.; Islam, M.N.; Ismail, M. Projections of Precipitation and Temperature over the South Asian Countries in CMIP6. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 297–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).