RNAi-Mediated Silencing of Chitin Synthase 1 (CHS1) Disrupts Molting and Growth in Monochamus alternatus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Feeding Conditions
2.2. Gene Cloning
2.3. Bioinformatics Characterization of MalCHS1 in M. alternatus
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. RNAi of MalCHS1
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bioinformatics Analysis of MalCHS1 in M. alternatus
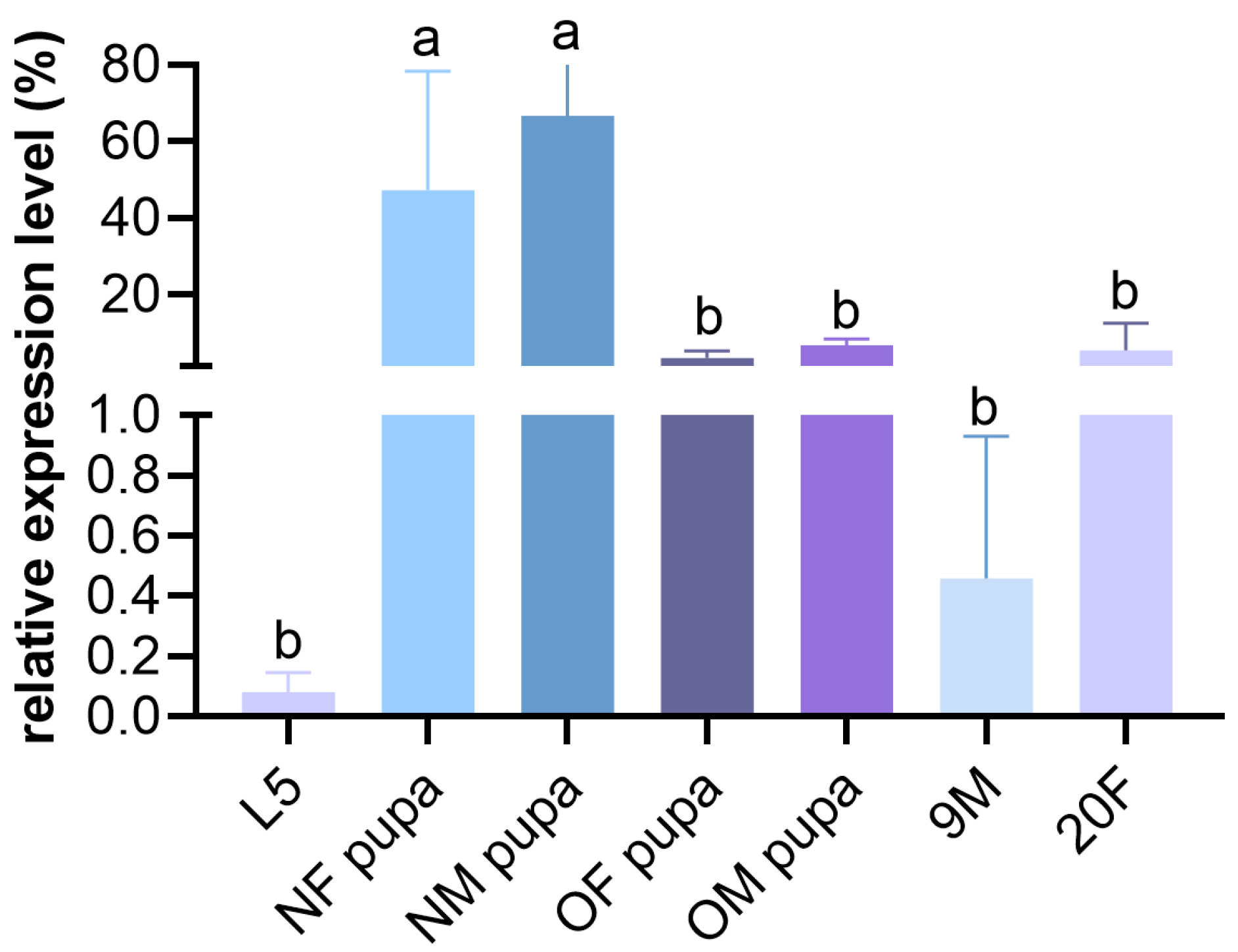
3.2. The Developmental Stage-Specific Expression of the MalCHS1 Gene
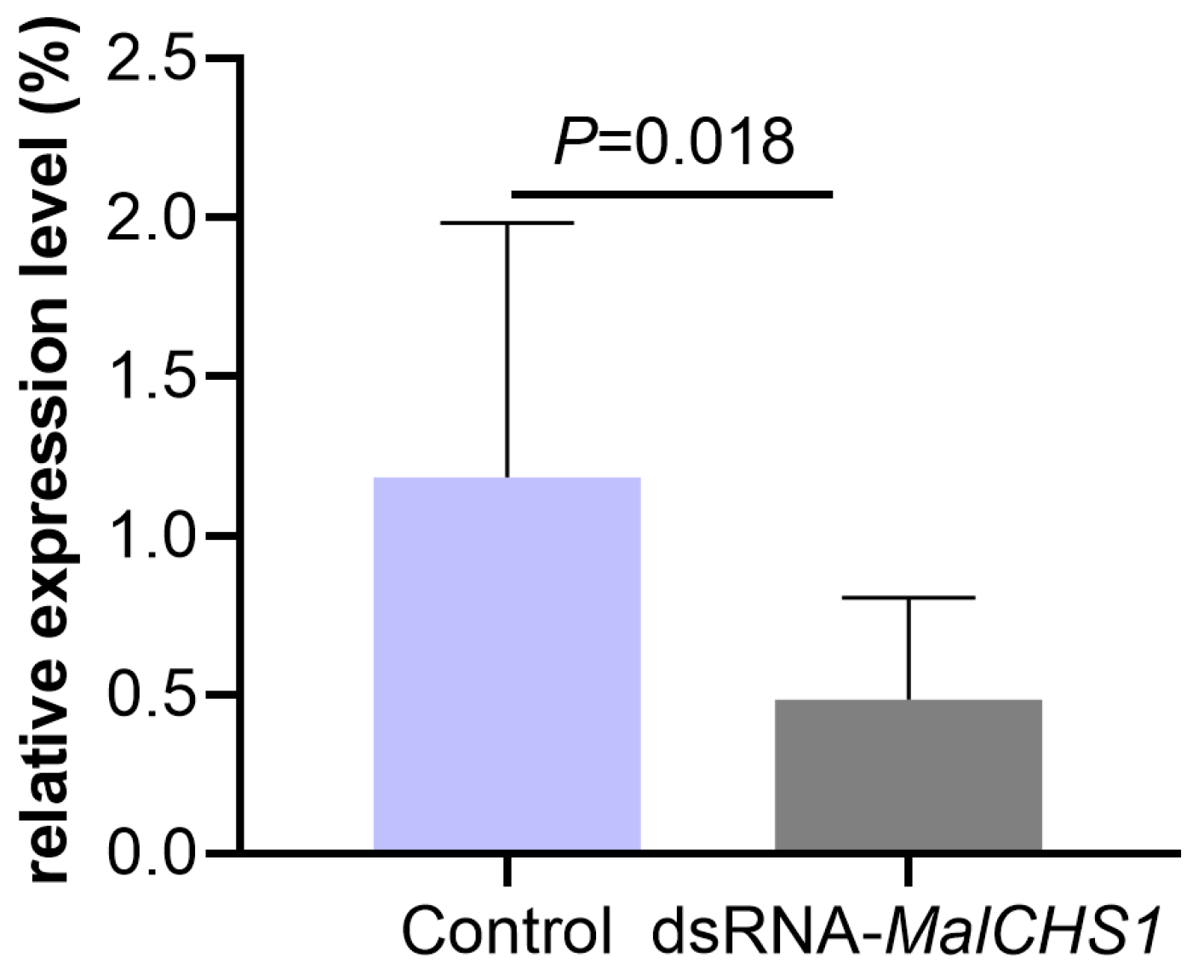
3.3. Changes in MalCHS1 Gene Expression in M. alternatus After RNAi
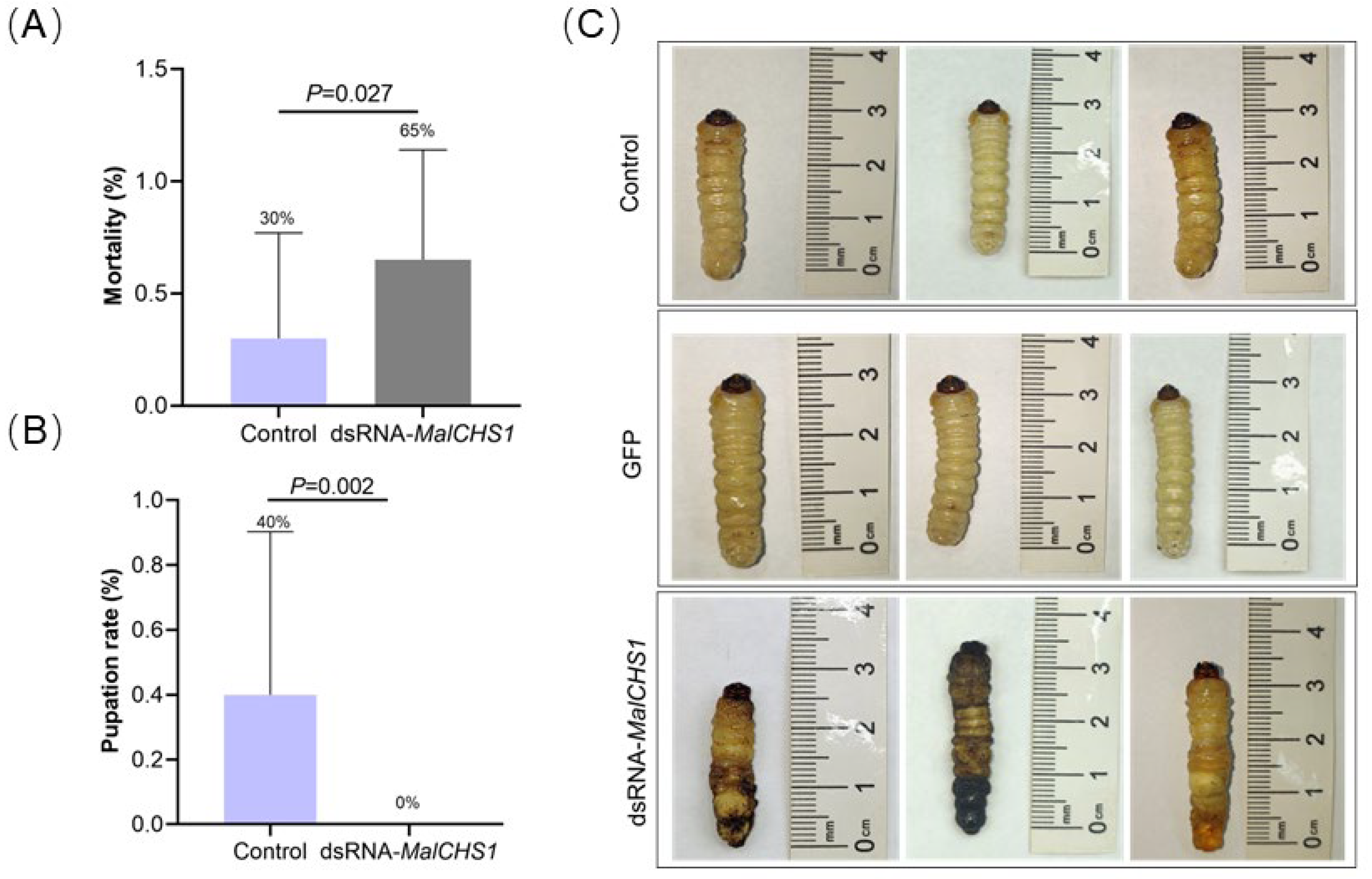
3.4. Phenotypic Changes in M. alternatus Larvae After RNAi
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Qiao, H.; He, X.; Tan, J.; Hao, D. Comparative transcriptome analysis of the heat stress response in Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.G. Pine Wilt Disease in China. In Pine Wilt Disease; Zhao, B.G., Futai, K., Sutherland, J.R., Takeuchi, Y., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, Y.; Futai, K. Assessing the role of asymptomatic infected trees in pine wilt disease spread in Japan—Insights from tree health monitoring. Forests 2025, 16, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linit, M.J. Nemtaode-vector relationships in the pine wilt disease system. J. Nematol. 1988, 20, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.Q.; Yuan, W.M.; Tian, X.J.; Fan, B.; Fang, X.; Ye, J.R.; Ding, X.L. Specific and Functional Diversity of Endophytic Bacteria from Pine Wood Nematode Bursaphelenchus Xylophilus with Different Virulence. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, M.; Shi, H.; Yi, T.; Xu, G.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, R. Algorithm for Detecting Trees Affected by Pine Wilt Disease in Complex Scenes Based on CNN-Transformer. Forests 2025, 16, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, J.; Yan, J.; Fang, G. Economic Loss of Pine Wood Nematode Disease in Mainland China from 1998 to 2017. Forests 2020, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, W.; Lamont, B.A.O.; Liu, Y.; Wei, P.; Xue, W.; Xiong, Z.; Tang, L.; Wang, Y.A.O.; Wang, P.; et al. Modeling the distribution of pine wilt disease in China using the ensemble models MaxEnt and CLIMEX. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhou, C.; Yang, W.J.; Jin, D.C.; Long, G.Y. Molecular cloning, expression, and functional analysis of the chitin synthase 1 gene and its two alternative splicing variants in the white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Merzendorfer, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Muthukrishnan, S. Biosynthesis, Turnover, and Functions of Chitin in Insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzendorfer, H. The cellular basis of chitin synthesis in fungi and insects: Common principles and differences. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.D.; Wang, Z.B.; Wang, L.X.; Zhao, P.; Yun, C.H.; Bai, L. Structure, catalysis, chitin transport, and selective inhibition of chitin synthase. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellam, R.L.; Eisemann, C. Chitin is only a minor component of the peritrophic matrix from larvae of Lucilia cuprina. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 30, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, G.Y.; Song, Q.S.; Stanley, D.; Wei, S.J.; Zhu, J.Y. Genomic and transcriptomic analyses of chitin metabolism enzymes in Tenebrio molitor. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 111, e21950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakane, Y.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Kramer, K.J.; Specht, C.A.; Tomoyasu, Y.; Lorenzen, M.D.; Kanost, M.; Beeman, R.W. The Tribolium chitin synthase genes TcCHS1 and TcCHS2 are specialized for synthesis of epidermal cuticle and midgut peritrophic matrix. Insect Mol. Biol. 2005, 14, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimoch, L.; Merzendorfer, H. Immunolocalization of chitin synthase in the tobacco hornworm. Cell Tissue Res. 2002, 308, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakane, Y.; Hogenkamp, D.G.; Zhu, Y.C.; Kramer, K.J.; Specht, C.A.; Beeman, R.W.; Kanost, M.R.; Muthukrishnan, S. Characterization of two chitin synthase genes of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum, and alternate exon usage in one of the genes during development. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzendorfer, H.; Zimoch, L. Chitin metabolism in insects: Structure, function and regulation of chitin synthases and chitinases. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 4393–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.G.; Michel, K.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Siegfried, B.D.; Hunter, W.B.; Smagghe, G.; Zhu, K.Y.; Douglas, A.E. Towards the elements of successful insect RNAi. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyre, B.R.; Rieske, L.K. Using RNAi to silence heat shock protein has congeneric effects in North America’s Dendroctonus bark beetles. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 520, 120367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyre, B.R.; Bentz, B.J.; Rieske, L.K. Susceptibility of mountain pine beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins) to gene silencing through RNAi provides potential as a novel management tool. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 473, 118322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Wang, X.; Ding, Q.; Said, F.; Gao, X.; Desneux, N.; Song, D. RNAi-Mediated Knockdown of Chitin Synthase 1 (CHS1) Gene Causes Mortality and Decreased Longevity and Fecundity in Aphis gossypii. Insects 2020, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Kato, D.; Kamiya, K.; Minakuchi, C.; Miura, K. Chitin synthase 1 gene is crucial to antifungal host defense of the model beetle, Tribolium castaneum. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 143, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.H.; Mu, L.L.; Jin, L.; Anjum, A.A.; Li, G.Q. RNAi for chitin synthase 1 rather than 2 causes growth delay and molting defect in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 178, 104934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjunan, N.; Thiruvengadam, V.; Sushil, S.N. Nanoparticle-mediated dsRNA delivery for precision insect pest control: A comprehensive review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, M.A.; Bonifácio, L.; Inácio, M.L.; Mota, M.; Boa, E. Pine wilt disease: A global threat to forestry. Plant Pathol. 2024, 73, 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychlik, W. OLIGO 7 primer analysis software. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 402, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.M. Comparing Group Means: T-Tests and One-Way ANOVA Using STATA, SAS, R, and SPSS [Working Paper]. Indiana University, Center for Statistical and Mathematical Computing. 2009. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2022/19735 (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandapani, R.K.; Gurusamy, D.; Duan, J.J.; Palli, S.R. RNAi for management of Asian long-horned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis: Identification of target genes. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 93, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.W.; Khan, M.M.; Song, F.; Wu, L.; He, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y. RNA Interference-Based Silencing of the Chitin Synthase 1 Gene for Reproductive and Developmental Disruptions in Panonychus citri. Insects 2020, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Sun, M.; Du, P.; Niu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Guo, H. Protective roles of chitin synthase gene 1 in Nilaparvata lugens against Cordyceps javanica and insecticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2025, 209, 106324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yin, H.; Sun, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhou, D.; Shen, B. Physiological characterization of chitin synthase A responsible for the biosynthesis of cuticle chitin in Culex pipiens pallens (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sui, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Lu, L.; You, M.; Xie, C.; Li, B.; Ni, Z.; Liang, R. Plant-mediated RNAi of grain aphid CHS1 gene confers common wheat resistance against aphids. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2754–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Aksoy, E.; Çalışkan, M.E.; Bakhsh, A. Transgenic potato lines expressing hairpin RNAi construct of molting-associated EcR gene exhibit enhanced resistance against Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata, Say). Transgenic Res. 2019, 28, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, E.; Santos, D.; Mingels, L.; Verdonckt, T.W.; Broeck, J.V. RNA Interference in Insects: Protecting Beneficials and Controlling Pests. Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joga, M.R.; Mogilicherla, K.; Smagghe, G.; Roy, A. RNA Interference-Based Forest Protection Products (FPPs) Against Wood-Boring Coleopterans: Hope or Hype? Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 733608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singewar, K.; Fladung, M. Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) technology to control forest insect pests and fungal pathogens: Challenges and opportunities. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2023, 23, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.A.O.; Ren, B.Y.; Shen, J.A.O. Nanoparticle-mediated double-stranded RNA delivery system: A promising approach for sustainable pest management. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, J.; Howard, J.D.; Brown, S.; Portwood, D.E.; Kilby, P.M.; Dickman, M.J. Strategies for the production of dsRNA biocontrols as alternatives to chemical pesticides. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 980592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| PCR | MalCHS1-F | CAAAGTATGGGAATGAACAG |
| MalCHS1-R | TCTTTCTGTGTCTGATCTTC | |
| RT-qPCR | MalCHS1-F | CAAACTTAACGCCAACCCTG |
| MalCHS1-R | TTTCTCTGGGCCACATTGTT | |
| β-actin-F | GTTGCCCTCGACTTCGAACA | |
| β-actin-R | ACGGATATCAACGTCGCACT | |
| RNAi | T7 promoter | TAATACGACTCACTATAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, W.; Li, T.; Weng, M.; Guo, W.; Xin, F.; Yu, W.; Wu, S.; Guo, Y. RNAi-Mediated Silencing of Chitin Synthase 1 (CHS1) Disrupts Molting and Growth in Monochamus alternatus. Forests 2025, 16, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060922
Ye W, Li T, Weng M, Guo W, Xin F, Yu W, Wu S, Guo Y. RNAi-Mediated Silencing of Chitin Synthase 1 (CHS1) Disrupts Molting and Growth in Monochamus alternatus. Forests. 2025; 16(6):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060922
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Wanlin, Tong Li, Mingqing Weng, Wenchi Guo, Feiyi Xin, Wei Yu, Songqing Wu, and Yajie Guo. 2025. "RNAi-Mediated Silencing of Chitin Synthase 1 (CHS1) Disrupts Molting and Growth in Monochamus alternatus" Forests 16, no. 6: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060922
APA StyleYe, W., Li, T., Weng, M., Guo, W., Xin, F., Yu, W., Wu, S., & Guo, Y. (2025). RNAi-Mediated Silencing of Chitin Synthase 1 (CHS1) Disrupts Molting and Growth in Monochamus alternatus. Forests, 16(6), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060922





