Comparison of Microwave Sensitivity and Performance of Asphalt Mastic with Various Steel Slag Powders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
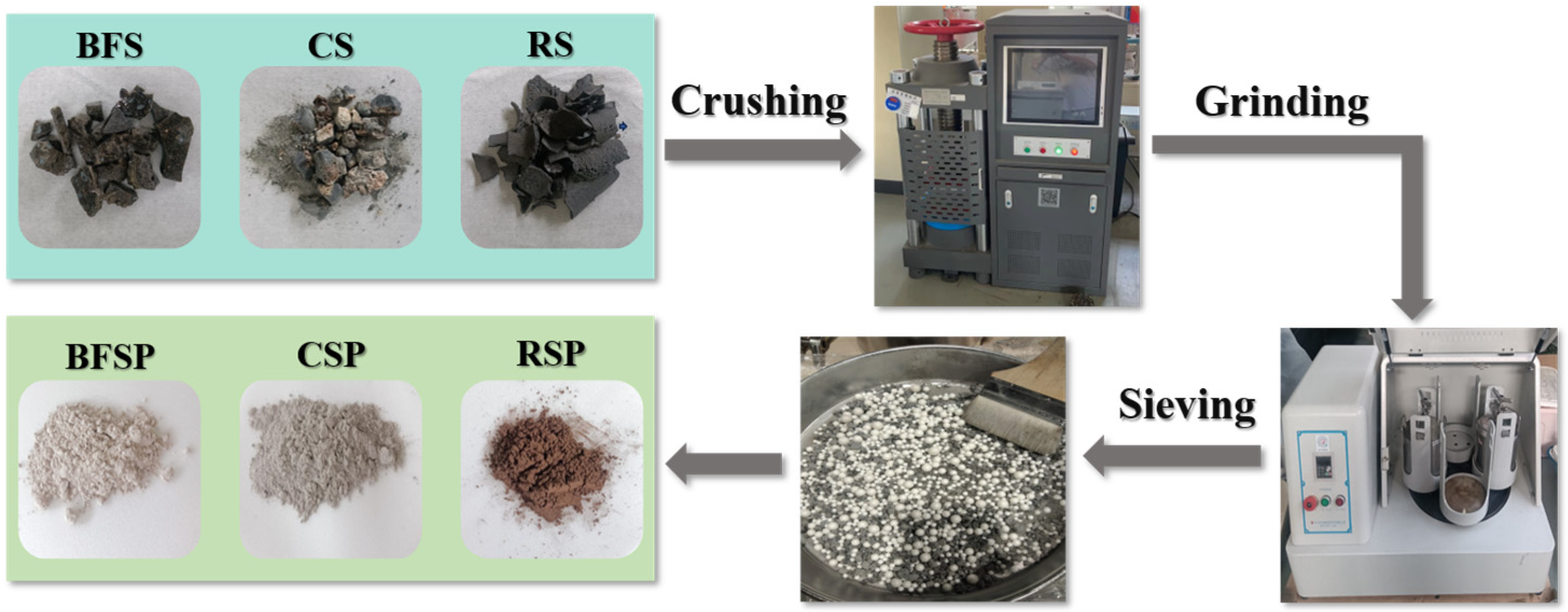
2.1.1. Steel Slag and Limestone Powders
2.1.2. Asphalt
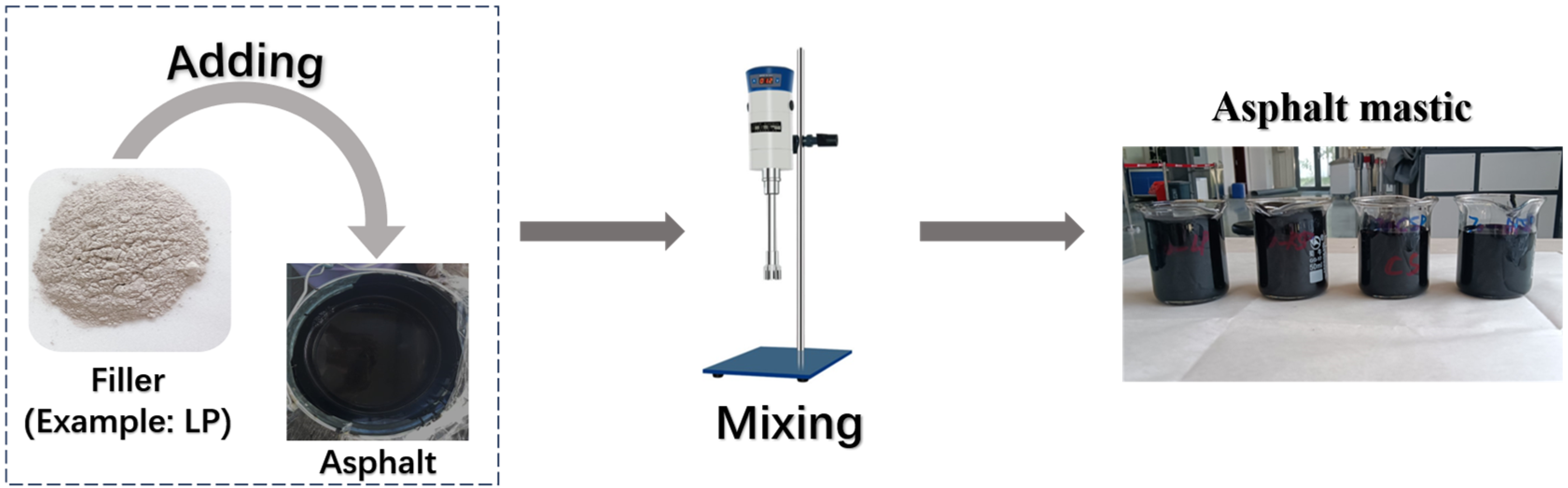
2.2. Preparation of Asphalt Mastics with Different Fillers
2.3. Test Methods for Properties of Steel Slag and Limestone Powders
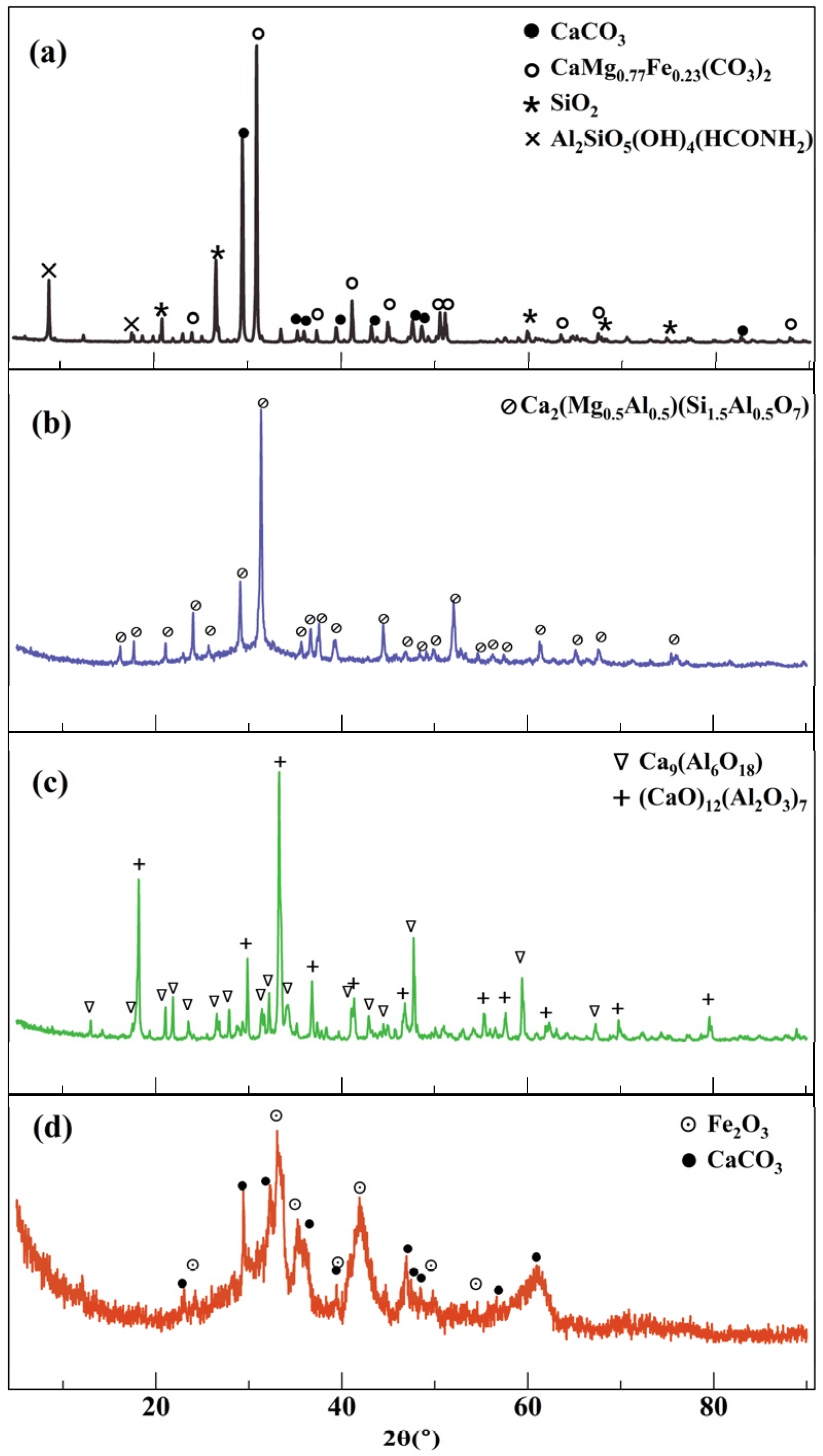
2.3.1. XRD Test
2.3.2. XRF Test
2.3.3. Electromagnetic Performance Test
2.4. Test Methods for Performance of Asphalt Mastics
2.4.1. Microwave Heating Test
2.4.2. DSR Test
2.4.3. BBR Test
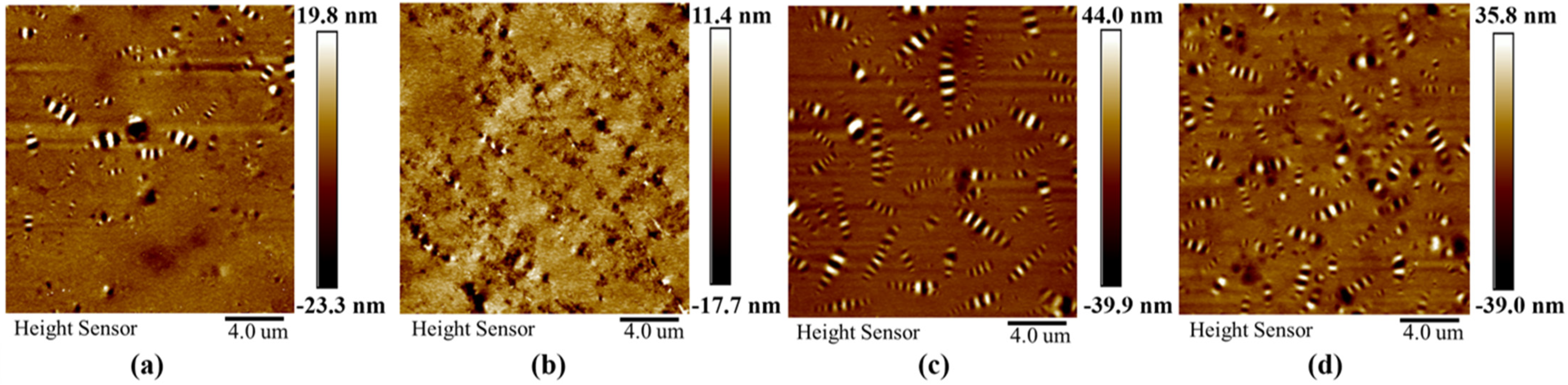
2.4.4. AFM Test
3. Properties of Steel Slag and Limestone Powders
3.1. Chemical Composition
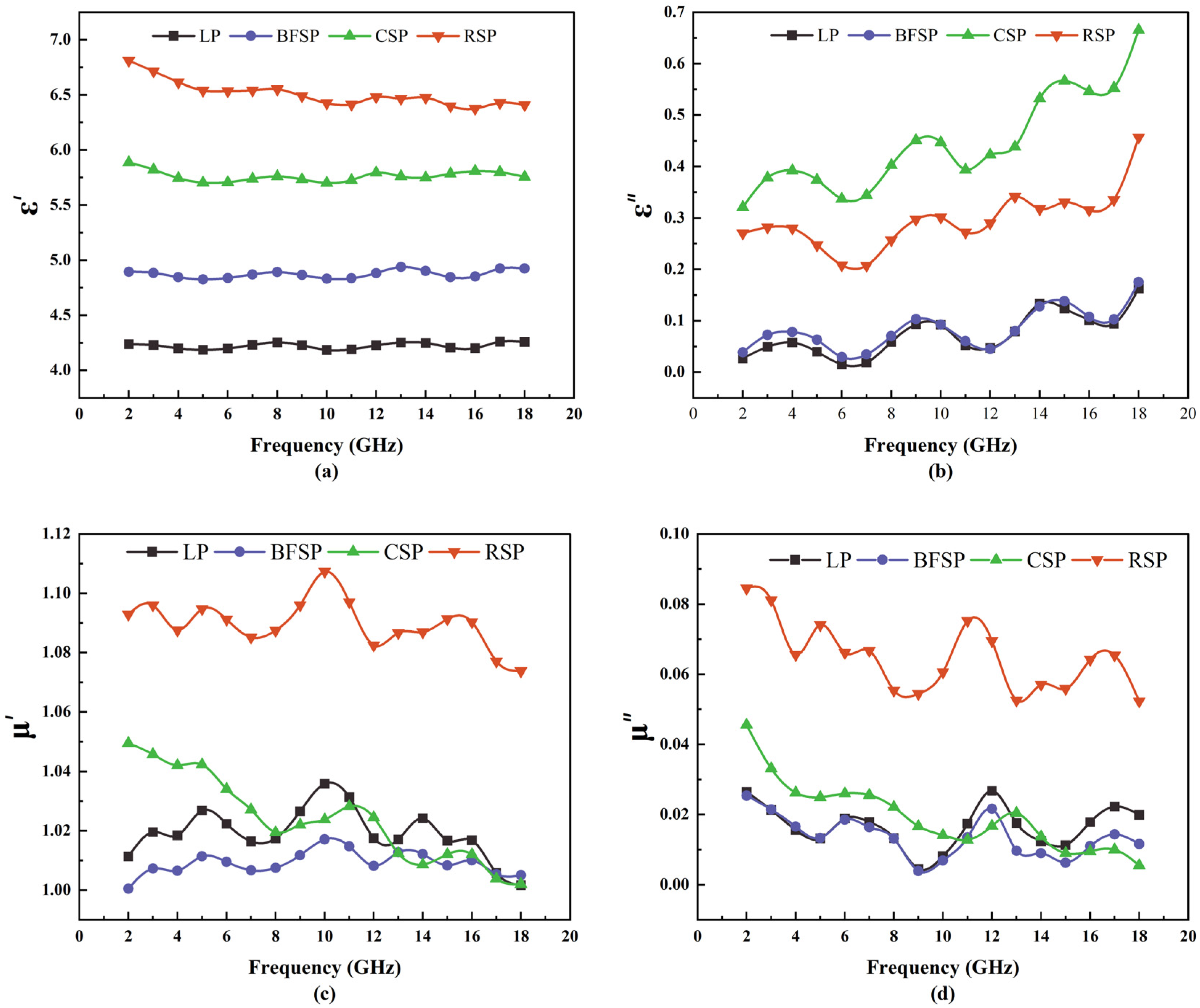
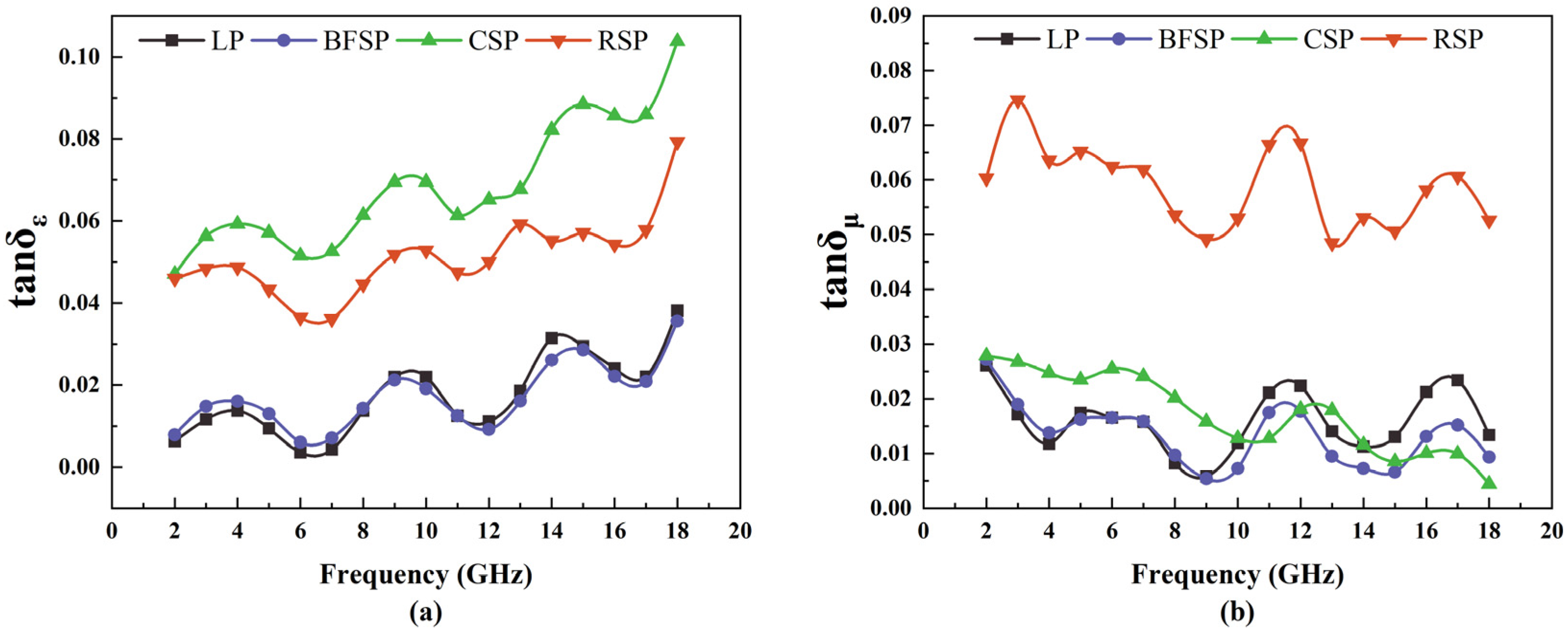
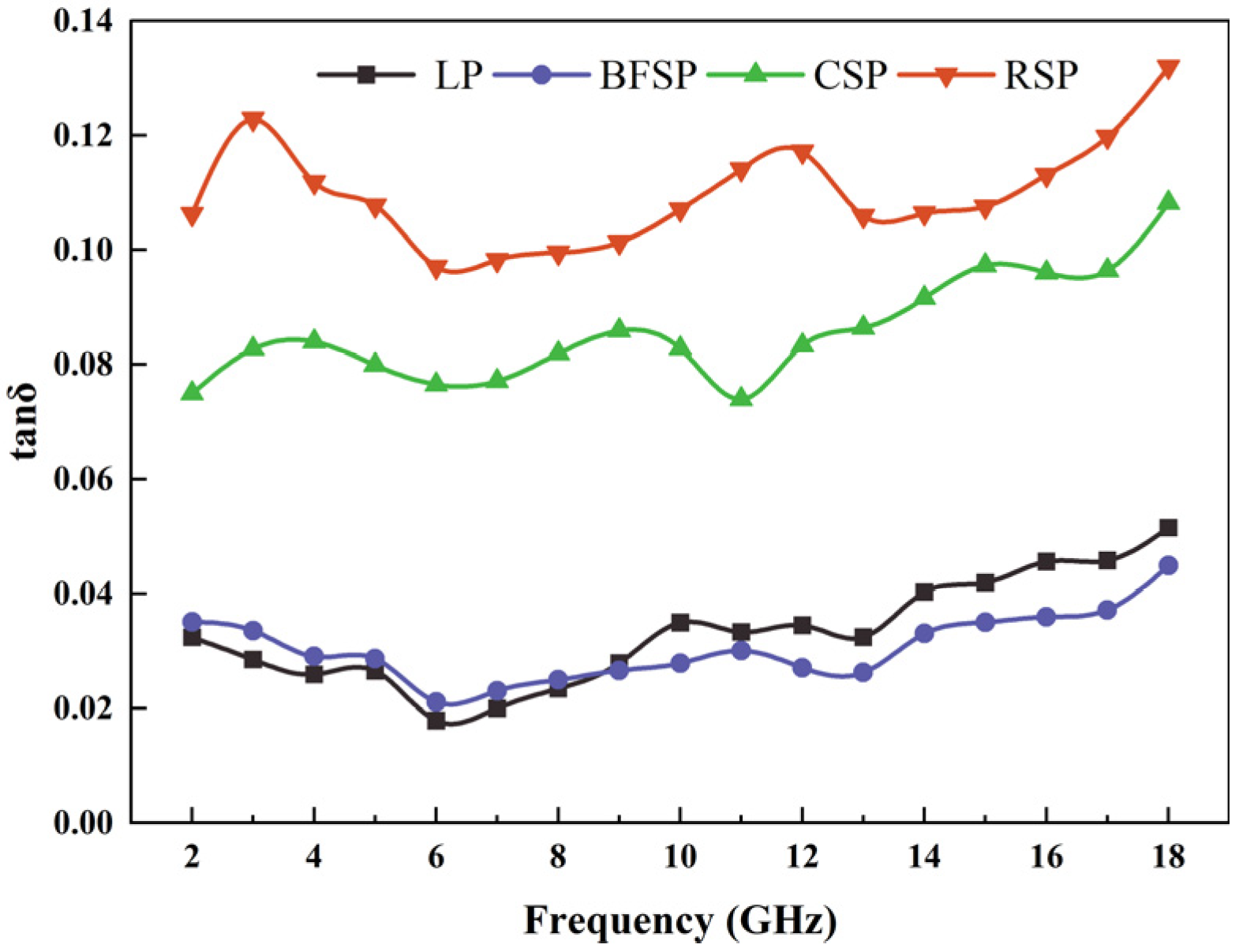
3.2. Microwave Absorption Property
4. Microwave Sensitivity of Asphalt Mastics with Different Fillers
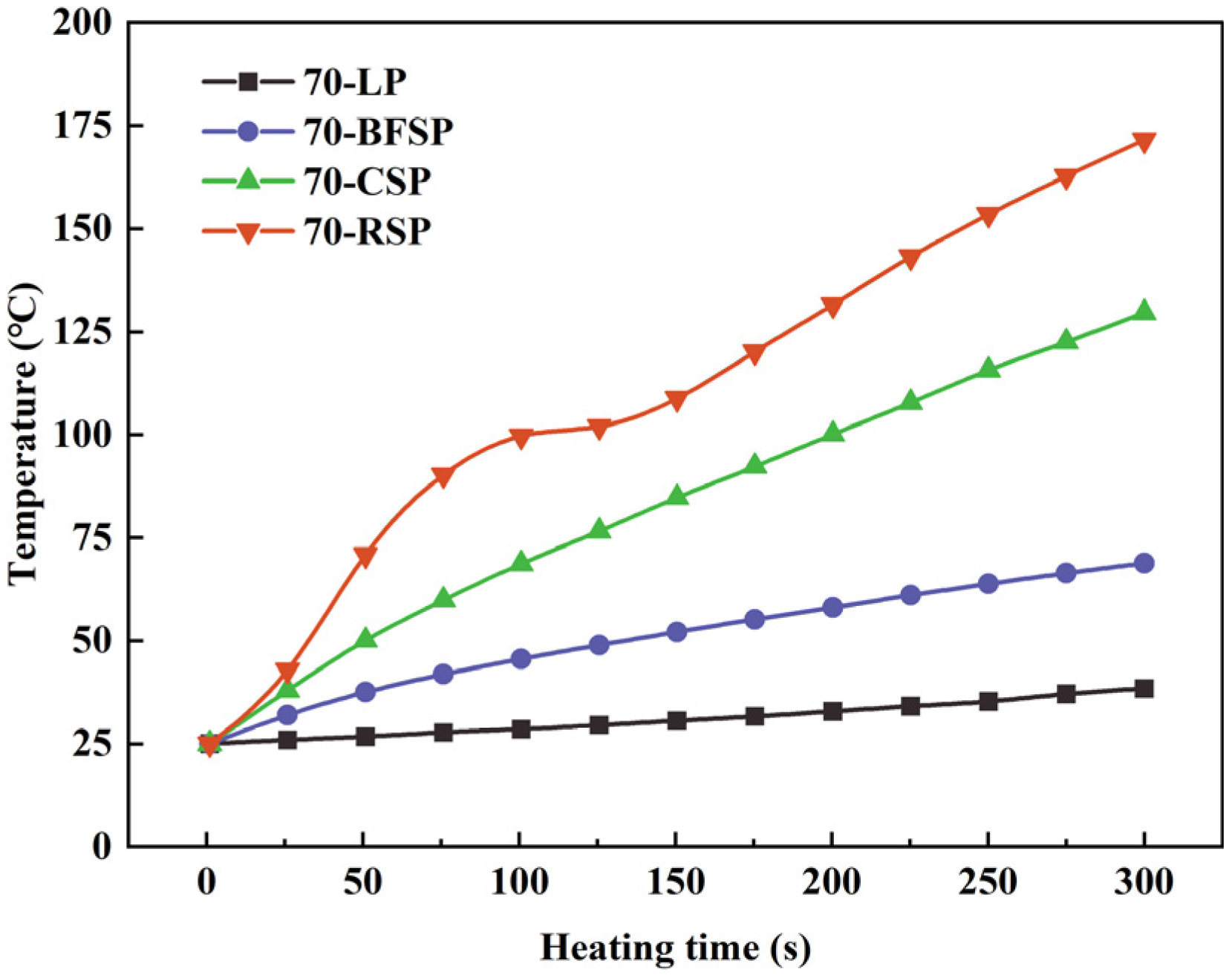
4.1. Heating Curve
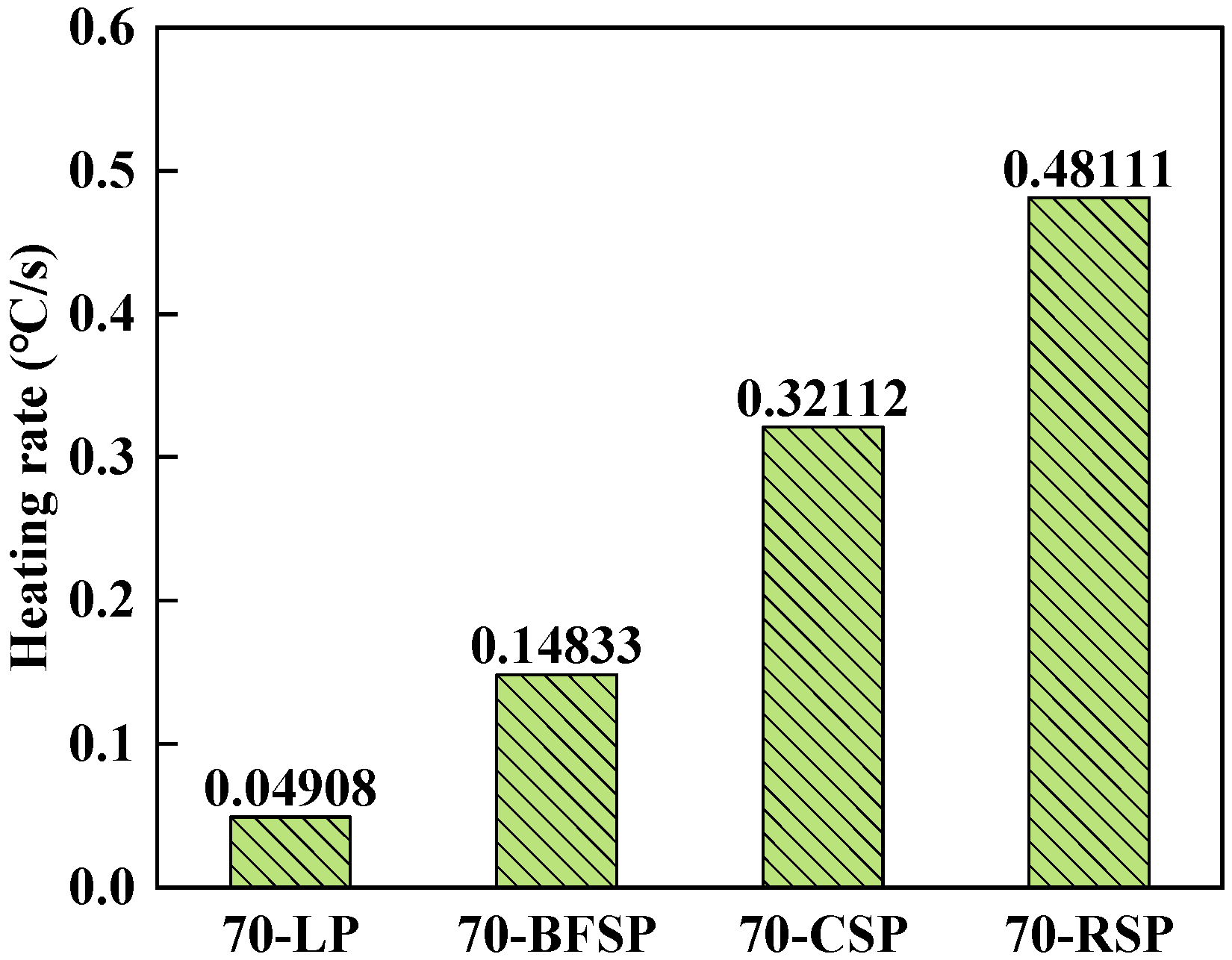
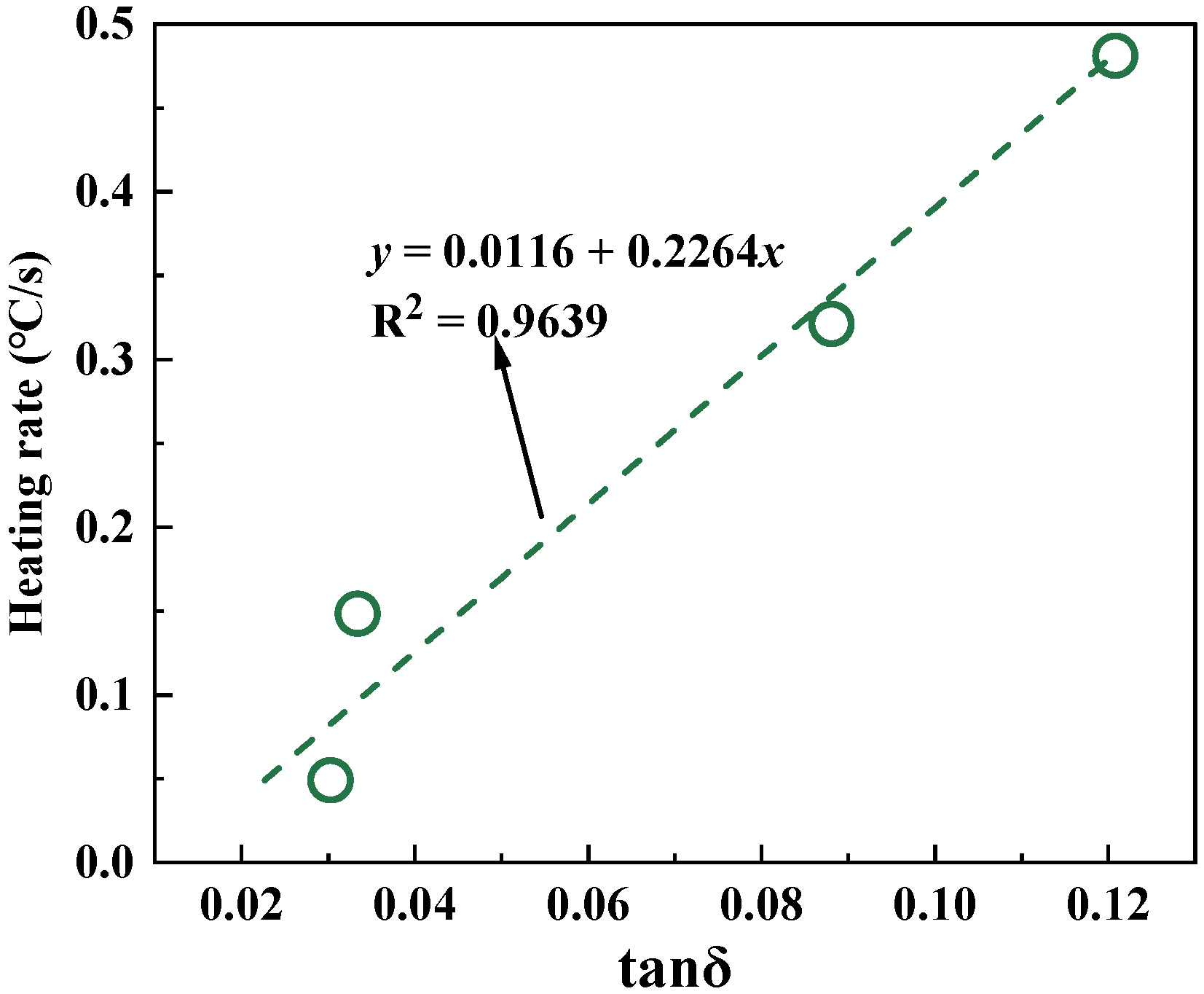
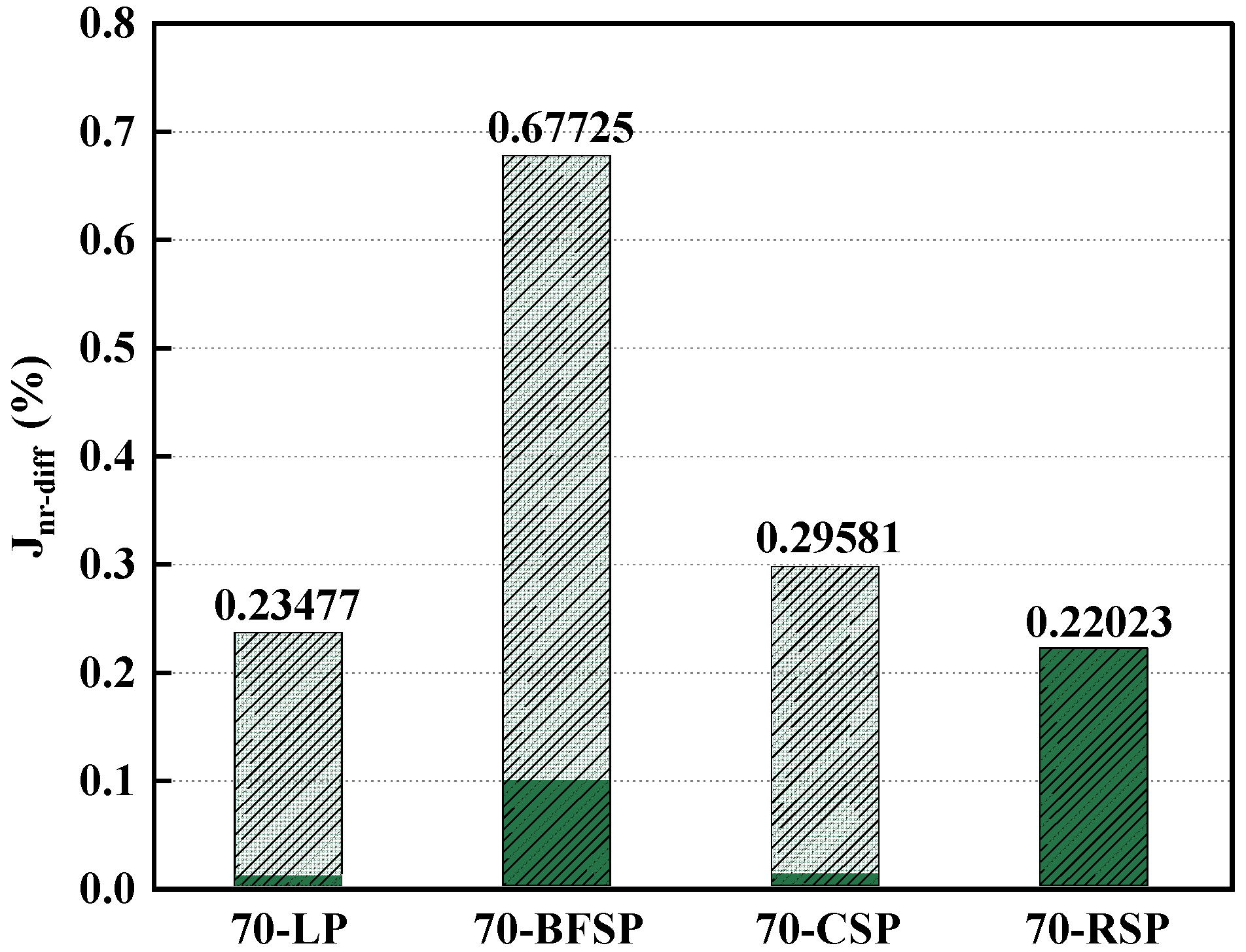
4.2. Heating Rate
5. Performance of Asphalt Mastics with Different Fillers
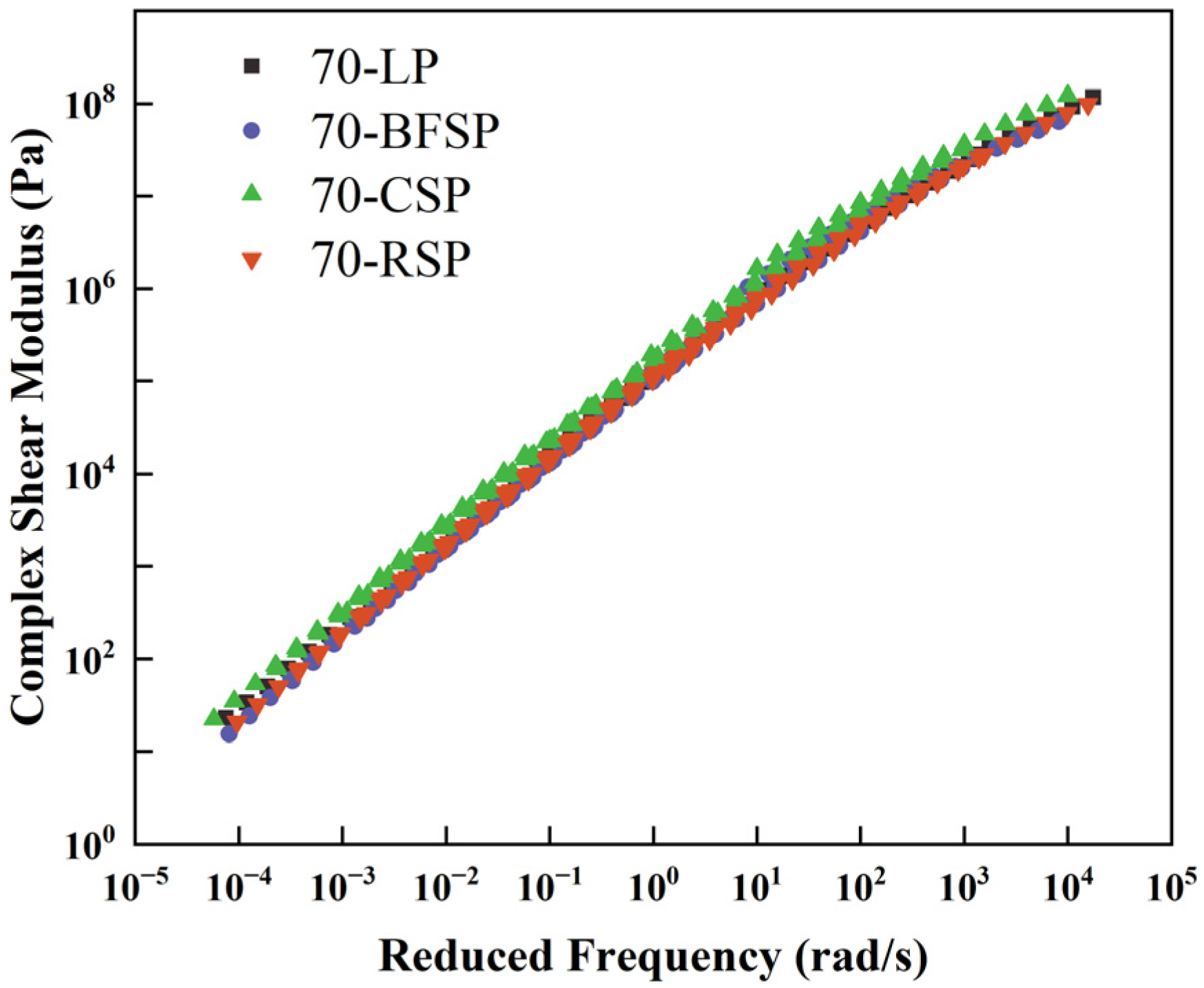
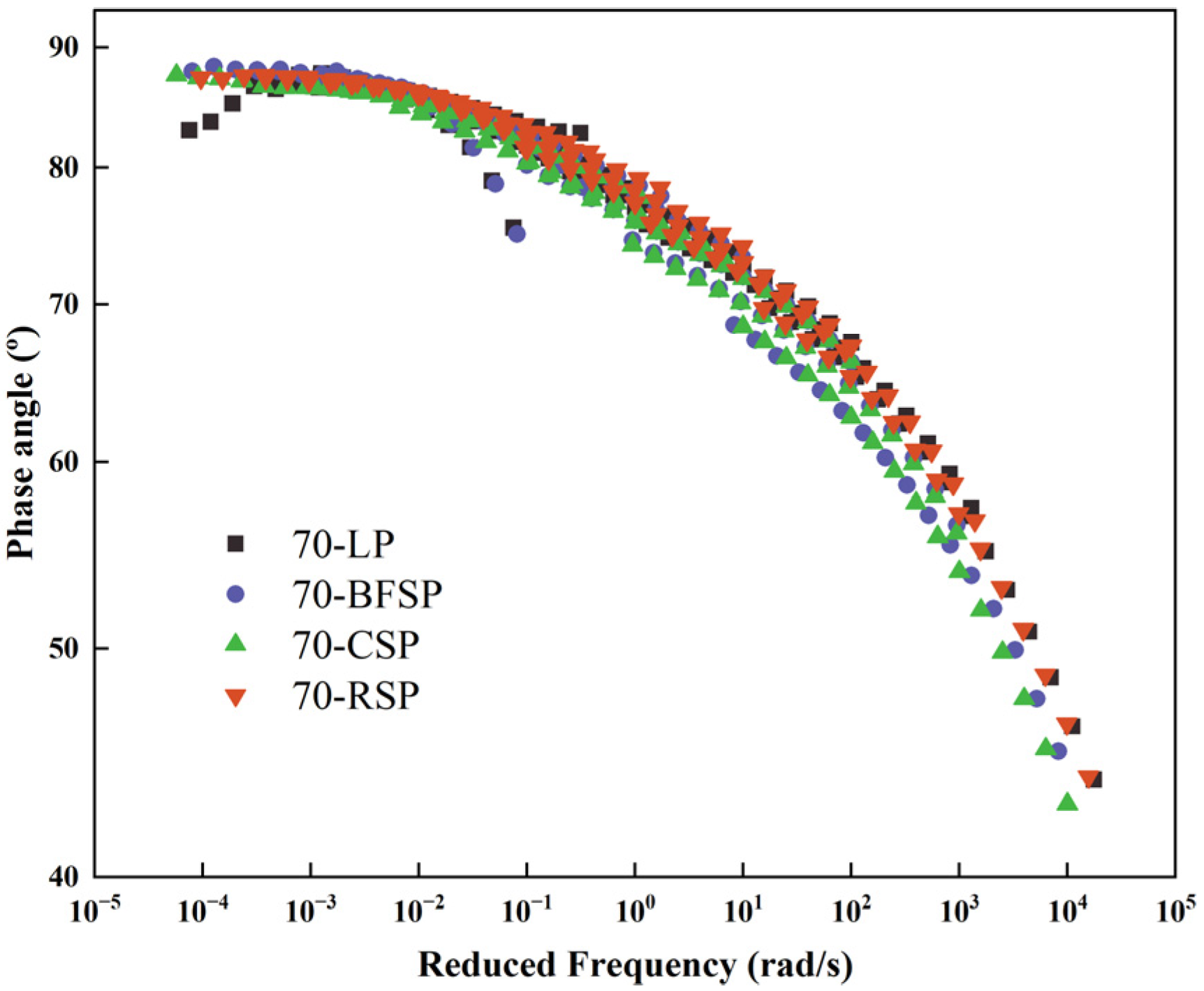
5.1. Viscoelastic Characteristics
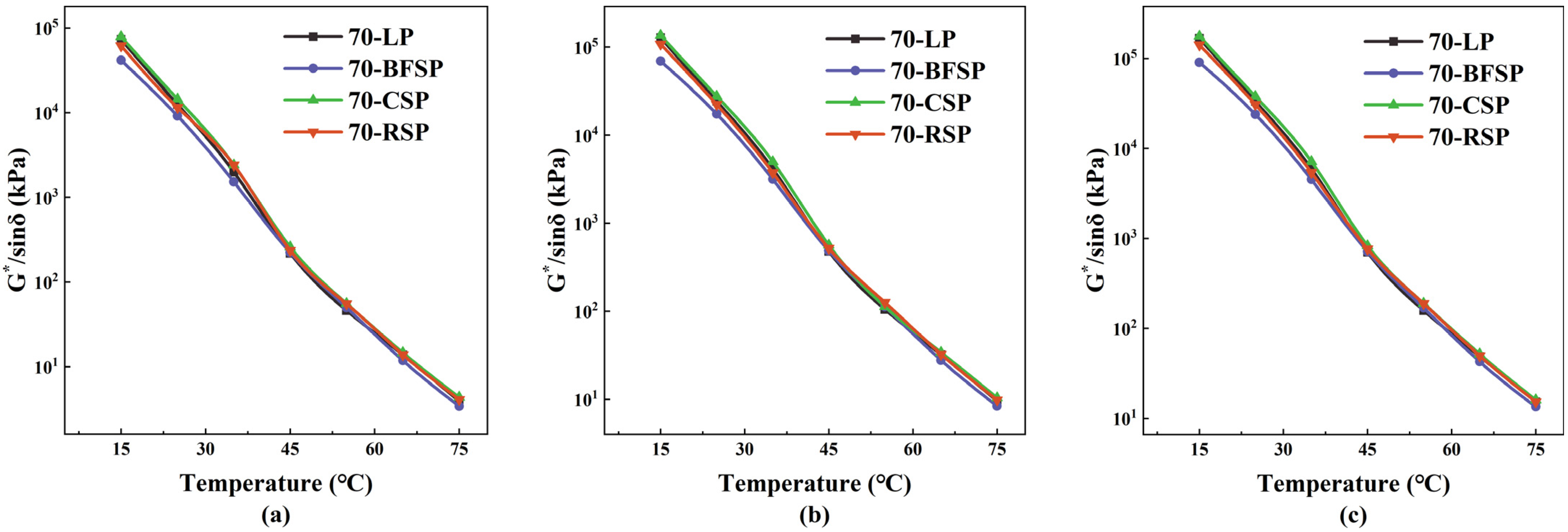
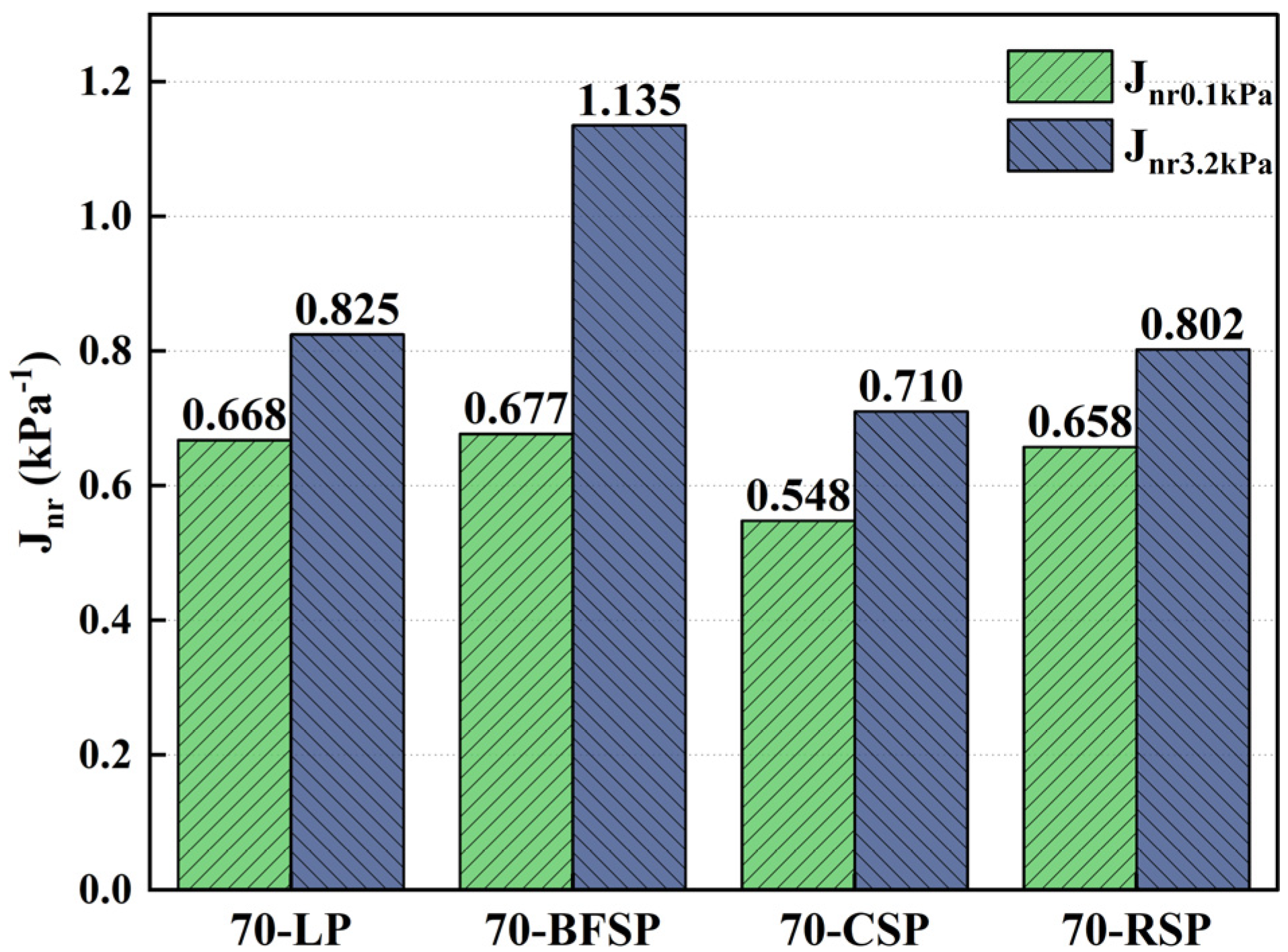
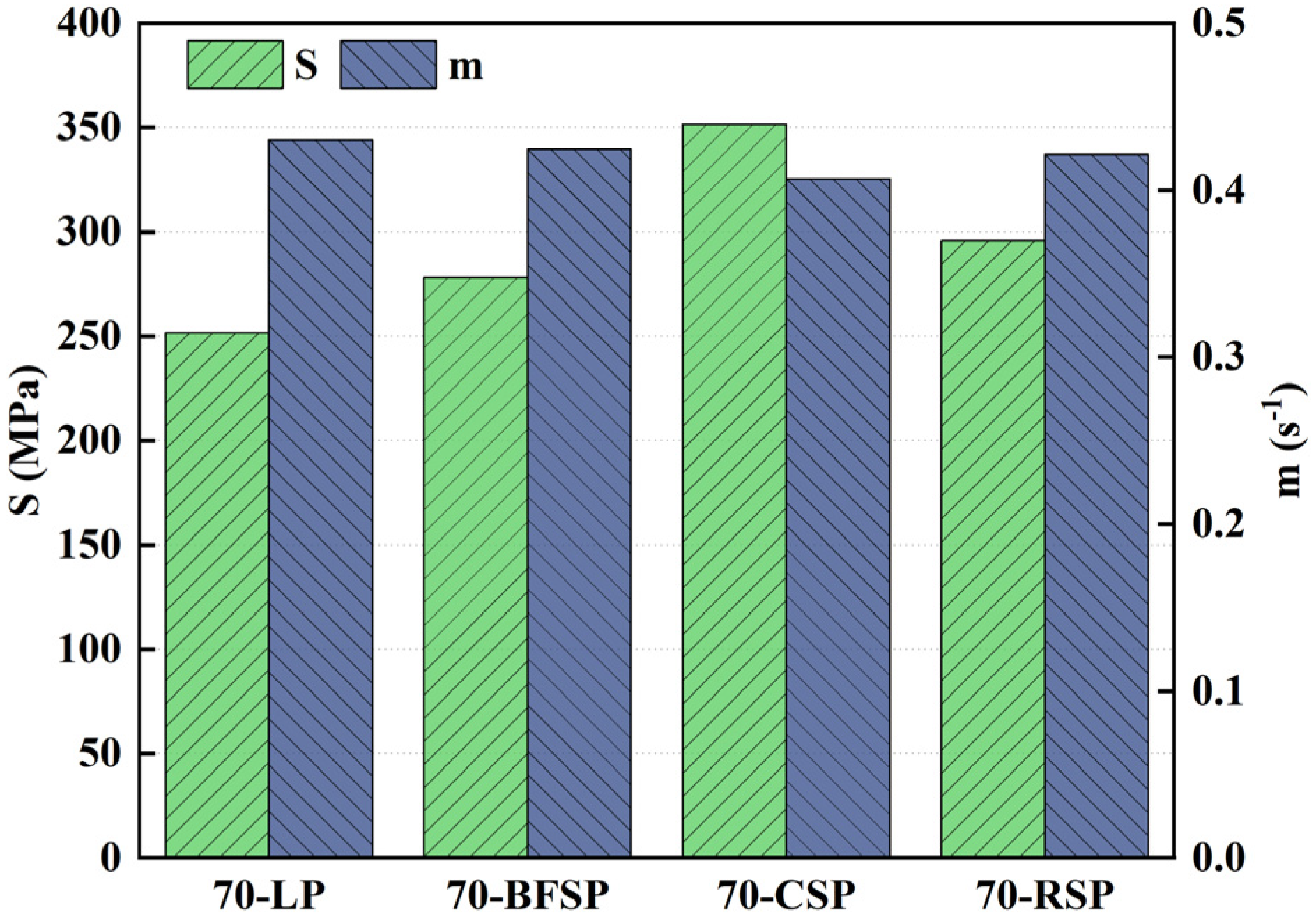
5.2. Resistance to Rutting
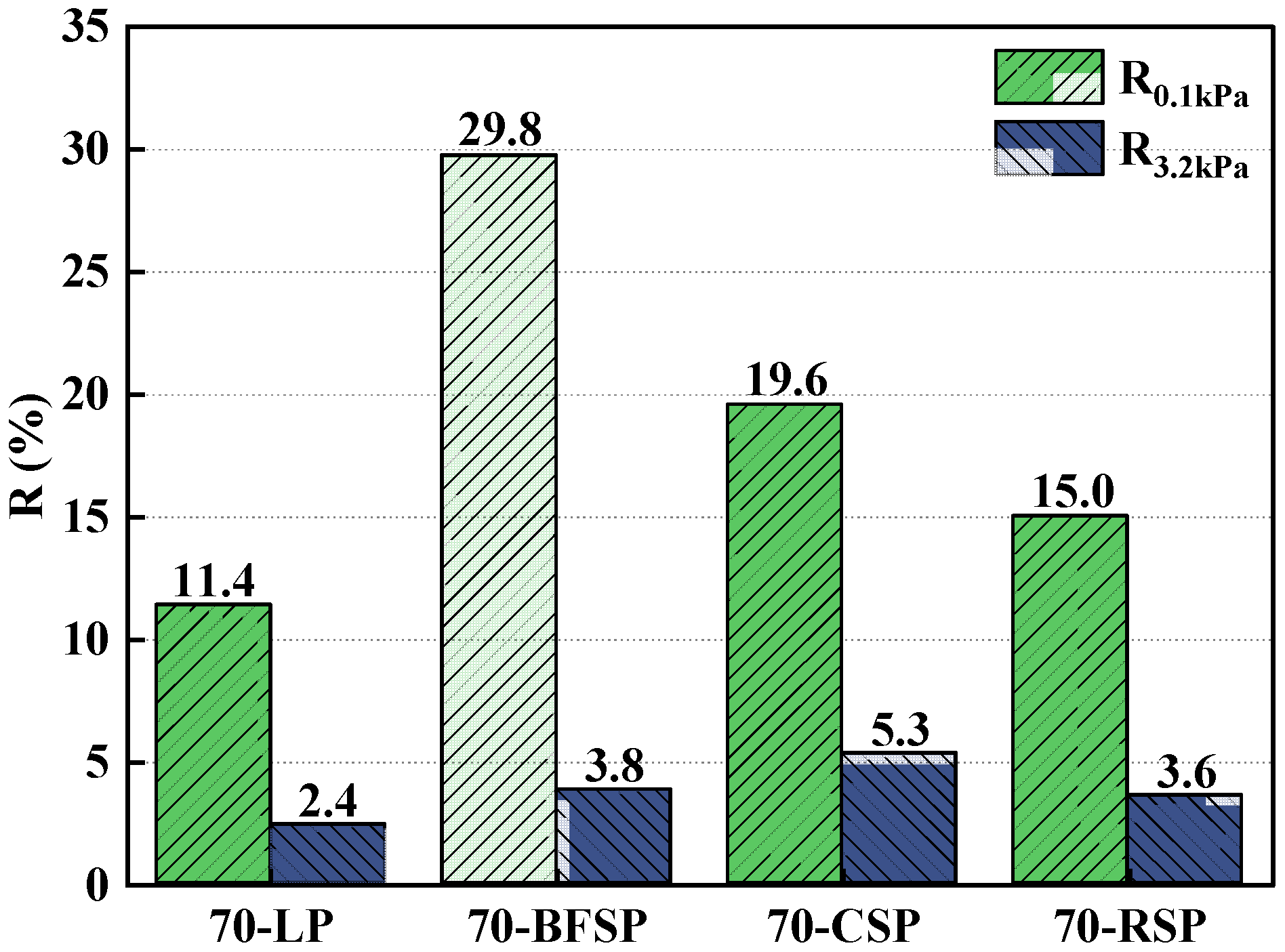
5.3. Low-Temperature Crack Resistance
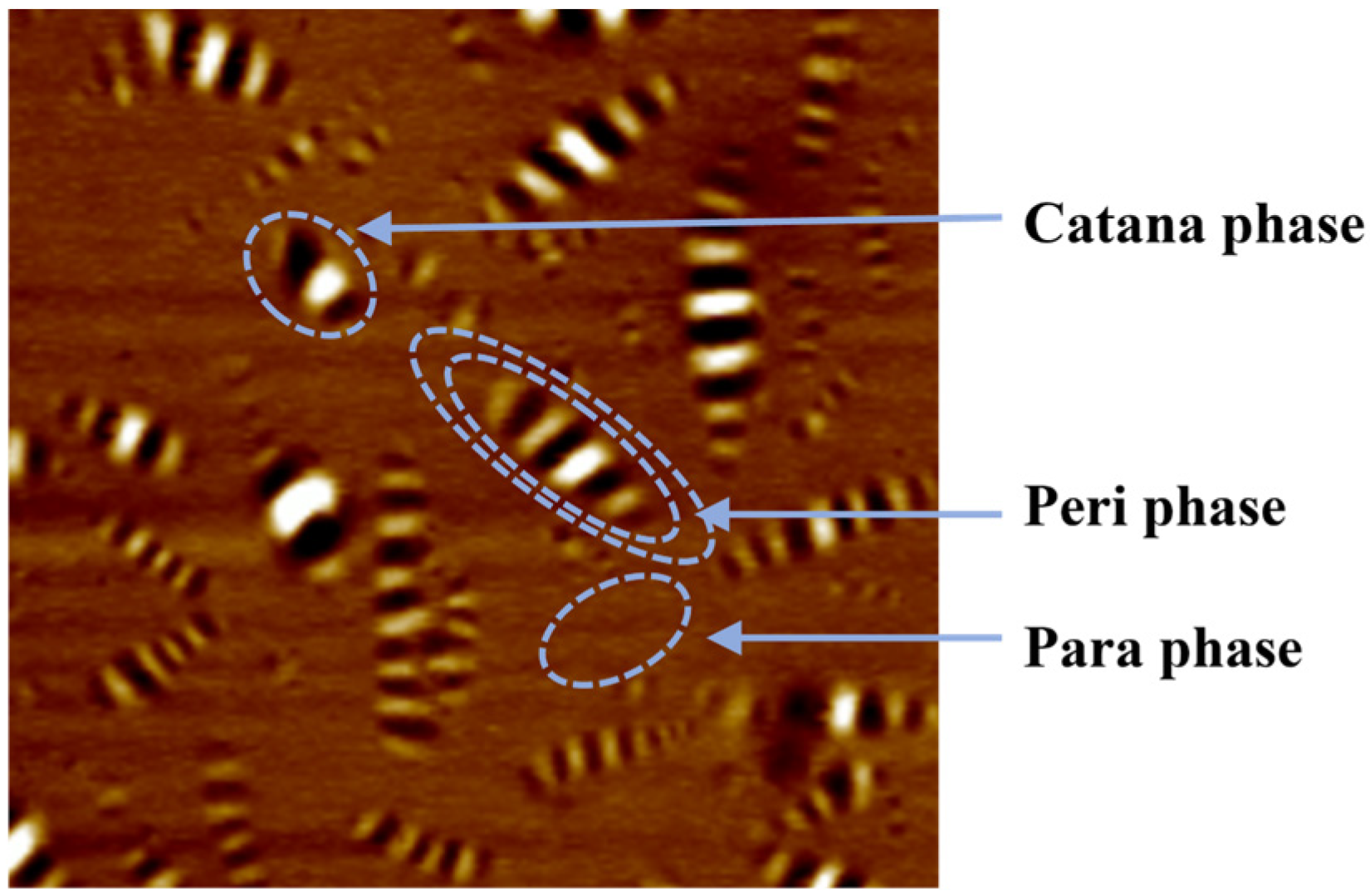
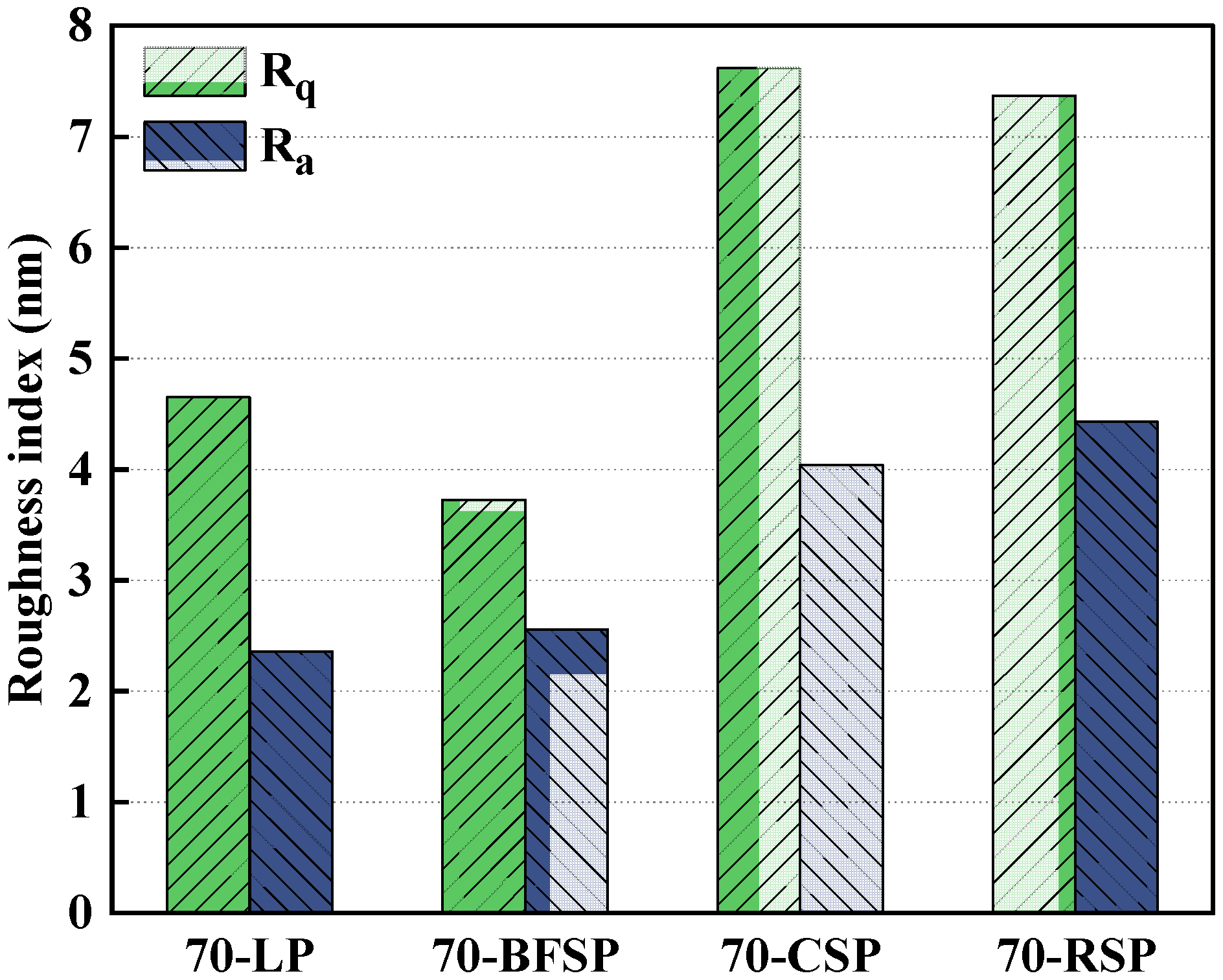
6. Microscopic Mechanism of Steel Slag Powder Impacting Asphalt Mastic Performance
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- The chemical compositions of BFSP, CSP, RSP, and LP are similar. RSP has the strongest ability to convert microwave energy into thermal energy. CSP has a good dielectric loss ability, but its magnetic loss ability is poor. Both LP and BFSP have worse dielectric and magnetic loss properties. However, the dielectric loss ability of BFSP is higher than that of LP in the low-frequency range.
- (2)
- Steel slag powder can improve the microwave sensitivity of asphalt mastic, especially RSP and CSP. There is a good linear relationship between the electromagnetic property of fillers and the microwave sensitivity of corresponding asphalt mastics.
- (3)
- BFSP and RSP have little influence on the stiffness of asphalt mastic, and CSP improves the stiffness of asphalt mastic. RSP would not destroy the elastic properties of asphalt mastic, while BFSP and CSP can improve the elastic properties of asphalt mastic.
- (4)
- Steel slag powders have an adverse effect on the low-temperature cracking resistance of asphalt mastic, but the creep strength and creep rate of asphalt mastic with steel slag powder are within a reasonable range.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BFSP | blast furnace slag powder |
| CSP | converter slag powder |
| RSP | refined slag powder |
| LP | limestone powder |
| XRD | X-ray diffractometer |
| XRF | X-ray fluorescence |
| AFM | atomic force microscope |
| DSR | dynamic shear rheometer |
| BBR | bending beam rheometer |
| BFS | blast furnace slag |
| CS | converter slag |
| RS | refined slag |
| MSCR | the multiple stress creep recovery |
| 70-LP | asphalt mastic with limestone powder |
| 70-BFSP | asphalt mastic with blast furnace slag powder |
| 70-CSP | asphalt mastic with converter slag powder |
| 70-RSP | asphalt mastic with refined slag powder |
| S | the creep strength |
| m | the creep rate (m) |
References
- Guo, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, M. Steel slag in China: Treatment, recycling, and management. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Zhou, W.; Lyu, X.; Liu, X.; Su, H.; Li, C.; Wang, H. Comprehensive utilization of steel slag: A review. Powder Technol. 2023, 422, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y. Sustainable Utilization of Steel Slag from Traditional Industry and Agriculture to Catalysis. Sustain. Sci. 2020, 12, 9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Xu, G.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Wan, Y.; Chen, H. An Overview of Utilization of Steel Slag. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, A.; Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, J. Mechanism of asphalt concrete reinforced with industrially recycled steel slag from the perspectives of adhesion and skeleton. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 424, 135899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qian, J.; Zhang, H.; Nan, X.; Chen, G.; Li, X. Exploring skid resistance over time: Steel slag as a pavement aggregate—Comparative study and morphological analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 464, 142779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Cui, P.; Ma, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L. Enhancement mechanism of asphalt mixture skeleton structures due to morphological characteristics of steel slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 432, 136703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wang, L. Study on mesoscopic model of low-temperature cracking of steel slag asphalt mixture based on random aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 364, 129974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, İ. A review of steel slag usage in construction industry for sustainable development. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 19, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liu, L.; Feng, Y. Evaluation of steel slag powder as filler in hot-mix asphalt mixtures. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2018, 7, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Leng, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, F.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Cai, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, N.; et al. Innovative use of industrially produced steel slag powders in asphalt mixture to replace mineral fillers. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 131124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos-Varas, M.; Movilla-Quesada, D.; Raposeiras, A.C.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Vega-Zamanillo, Á.; Cumian-Benavides, M. Use of Hydrated Ladle Furnace Slag as a filler substitute in asphalt mastics: Rheological analysis of filler/bitumen interaction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 332, 127370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, B.; Xie, J.; Xiao, Y. Effects of steel slag fillers on the rheological properties of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, X.; Guo, Y.; Yue, M.; Yue, J. Investigating the differences between steel slag and natural limestone in asphalt mixes in terms of microscopic mechanism, fatigue behavior and microwave-induced healing performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, J.; del Val, M.A.; Contreras, V.; Páez, A. Heating asphalt mixtures with microwaves to promote self-healing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 42, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulisano, F.; Gallego, J. Microwave heating of asphalt paving materials: Principles, current status and next steps. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 121993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Jiang, X.; Leng, Z. Sustainable microwave-heating healing asphalt concrete fabricated with waste microwave-sensitive fillers. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, S. Improving microwave absorption efficiency of asphalt mixture by enriching Fe3O4 on the surface of steel slag particles. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, H.; Shu, B.; Li, Y.; Gu, D.; Gao, Y.; Chen, A.; Feng, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; et al. Microwave heating mechanism and self-healing performance of asphalt mixture with basalt and limestone aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wan, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q. Investigation on the temperature distribution characteristics of steel slag asphalt mixture under different microwave heating and cooling methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 425, 136004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Guan, B.; Zhao, H.; He, Z.; Ding, D.; Gai, W. Microwave self-healing characteristics of the internal voids in steel slag asphalt mixture subjected to salt-freeze-thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T. Microwave heating uniformity, road performance and internal void characteristics of steel slag asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 353, 129155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Sha, A.; Barbieri, D.M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F. Microwave heating properties of steel slag asphalt mixture using a coupled electromagnetic and heat transfer model. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 291, 123248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sha, T.; Xiong, Y.; Cai, Y.; Yue, J.; Wang, H. Potential contribution of steel slag fillers to asphalt mastic in terms of microwave heating efficiency, electromagnetic mechanisms and fatigue durability. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2240471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG 3432-2024; Test Methods of Aggregates for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transport: Beijing, China, 2024.
- AASHTO T350-19; Standard Method of Test for Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Test of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- AASHTO T313-19; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Flexural Creep Stiffness of Asphalt Binder Using the Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Luo, M.; Chen, C.; Li, T. Experimental Study on the Influence of Temperature and Loading Frequency on Dynamic Modulus of Asphalt Mixture. Open J. Transp. Technol. 2019, 8, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.; Castorena, C. Implications of physico–chemical interactions in asphalt mastics on asphalt microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 94, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Fan, Z.; Yang, X.; Hao, L.; Lu, G.; Fini, E.H.; Wang, D. Recycling waste fiber-reinforced polymer composites for low-carbon asphalt concrete: The effects of recycled glass fibers on the durability of bituminous composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 223, 138692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, S.; Jiang, J.; Kan, J.; Tu, M. Analysis of asphalt microscopic and force curves under water-temperature coupling with AFM. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Technical Indexes | BFSP | CSP | RSP | LP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent density (g/cm3) | 3.023 | 3.203 | 3.651 | 2.807 |
| Hydrophilic coefficient | 0.85 | 1.06 | 0.74 | 0.81 |
| Heat invariability | No color change | |||
| Technical Indexes | Unit | 70# Asphalt |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 5 s, 100 g) | 0.1 mm | 67 |
| Penetration Index (PI) | / | −0.37 |
| Ductility (10 °C) | cm | 34 |
| Ductility (15 °C) | cm | >100 |
| Softening Point (TR&B) | °C | 48.0 |
| Solubility | % | 99.84 |
| Flash Point | °C | 268 |
| Density (15 °C) | g/cm3 | 1.036 |
| Fillers | LP | BFSP | CSP | RSP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass ratio | 1.000:1 | 1.077:1 | 1.141:1 | 1.301:1 |
| Filler Type | CaO | MgO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LP | 59.77% | 17.87% | 14.85% | 4.34% | 1.43% | 0.06% |
| BFSP | 32.12% | 11.91% | 33.18% | 18.64% | 0.57% | 0.41% |
| CSP | 58.21% | 2.43% | 2.67% | 30.75% | 0.94% | 0.07% |
| RSP | 38.82% | 6.02% | 14.88% | 2.85% | 26.01% | 5.20% |
| Asphalt Mastics | Fitting Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 70-LP | y = 0.043x + 24.54 | 0.9898 |
| 70-BFSP | y = 0.137x + 30.38 | 0.9820 |
| 70-CSP | y = 0.336x + 32.52 | 0.9925 |
| 70-RSP | y = 0.441x + 44.35 | 0.9628 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, Z.; Yu, W.; Jiang, M.; Miao, Y. Comparison of Microwave Sensitivity and Performance of Asphalt Mastic with Various Steel Slag Powders. Materials 2025, 18, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061348
Geng Z, Yu W, Jiang M, Miao Y. Comparison of Microwave Sensitivity and Performance of Asphalt Mastic with Various Steel Slag Powders. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061348
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Zeyu, Weixiao Yu, Min Jiang, and Yinghao Miao. 2025. "Comparison of Microwave Sensitivity and Performance of Asphalt Mastic with Various Steel Slag Powders" Materials 18, no. 6: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061348
APA StyleGeng, Z., Yu, W., Jiang, M., & Miao, Y. (2025). Comparison of Microwave Sensitivity and Performance of Asphalt Mastic with Various Steel Slag Powders. Materials, 18(6), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061348






