Abstract
The increasing demand for electricity in multi-tenanted residential areas has placed unforeseen strain on sub-transformers, particularly in dense urban environments. This strain compromises overall grid performance and challenges utilities with shifting and rising peak demand periods. This study presents a novel approach to enhance the operation of a virtual power plant (VPP) comprising a microgrid (MG) integrated with renewable energy sources (RESs) and energy storage systems (ESSs). By employing an advanced monitoring and control system, the proposed topology enables efficient energy management and demand-side control within apartment complexes. The system supports controlled electricity distribution, reducing the likelihood of unpredictable demand spikes and alleviating stress on local infrastructure during peak periods. Additionally, the model capitalizes on the large number of tenancies to distribute electricity effectively, leveraging locally available RESs and ESSs behind the sub-transformer. The proposed research provides a systematic framework for managing electricity demand and optimizing resource utilization, contributing to grid reliability and a transition toward a more sustainable, decentralized energy system.
1. Introduction
The rapid expansion of distributed energy resources (DERs), particularly rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, has significantly reshaped modern electricity networks. With the declining cost of PV panels and battery storage systems, residential consumers increasingly generate and store their own electricity, aiming to reduce their reliance on grid-supplied energy. The economic viability of this trend is bolstered by the fact that electricity prices continue to rise, making renewable energy an attractive alternative to conventional energy sources. However, this transition also places additional stress on low-voltage (LV) distribution networks, particularly at the sub-transformer level, impacting the overall stability and efficiency of the grid [1].
A recent survey conducted by the authors of [2,3] reveals that 51% of respondents are actively considering or have already installed rooftop solar PV systems. Moreover, 55% of these participants plan to integrate renewable generation with battery storage solutions to enhance energy self-sufficiency and reduce dependence on the grid. This trend aligns with the increasing approval of residential apartment buildings in densely populated Australian cities [3]. Such high-density developments intensify the demand on local transformers during peak load periods, as multiple households seek to utilize their stored or generated energy simultaneously.
Charging local loads with energy generated from on-site PV installations remains the most practical and attractive option for many households worldwide. With typical solar PV systems capable of generating a significant portion of daily energy requirements, residential consumers can often cover their own loads while exporting excess energy back to the grid. However, this self-generation and export paradigm creates new challenges for grid operators, particularly in high-density housing scenarios where a common transformer must balance diverse and dynamic energy flows from multiple residential units. This can lead to voltage drops, equipment stress, and potential transformer overloading, thereby threatening the stability and reliability of the electricity supply.
Furthermore, the growing deployment of DERs introduces phase imbalance issues within LV distribution networks. The Australian LV grid typically adopts a three-phase star wire configuration, designed to distribute power uniformly across the three phases. However, the uneven installation of PV systems and the variable operation of household appliances can create unbalanced loads, which in turn lead to degraded power quality [4]. This imbalance can manifest as voltage fluctuations, harmonics, and increased equipment wear, complicating the management of local distribution networks.
To address these issues, the integration of renewable energy sources (RESs)—such as PV systems, battery storage, and backup generators—into a coordinated microgrid (MG) framework managed by an energy management system (EMS) offers a promising solution. By intelligently orchestrating the operation of these distributed resources, a microgrid can reduce peak demand by using stored energy or local generation to offset consumption during high-demand periods, thereby easing the burden on the main grid. Additionally, microgrids offer opportunities for peer-to-peer energy trading and the formation of virtual power plants (VPPs), which aggregate multiple MGs into a larger, coordinated system that can provide grid services such as peak shaving, valley filling, and load balancing [5].
The literature offers numerous approaches for managing MGs. For example, the work in [6] proposes a double-layer EMS model to minimize the short-term operational costs of independent MGs. Another study [5] presents an EMS algorithm based on mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP) to optimize, supervise, and control MG operations under various scenarios in islanded mode, utilizing DERs to reduce operational costs through local energy markets. Additional research has incorporated demand response (DR) into MG operations, focusing on frequency regulation and day-ahead scheduling to enhance reliability and reduce peak demand [7,8]. A probabilistic model in [9] uses density estimation to optimize the integration of wind energy and DR in islanded MGs, enabling robust long-term EMS planning. Furthermore, a two-layer scheduling model proposed in [10] aims to minimize both user and operational costs through multi-stakeholder participation.
Despite these advances, many studies neglect the unique demands of high-density residential loads and the phase imbalances introduced by uneven DER integration. Addressing these challenges is essential for ensuring that MGs not only optimize economic performance but also maintain power quality and operational reliability in real-world LV distribution networks.
One promising solution lies in the formation of VPPs, comprising integrated MGs (IMGs), which can aggregate the capacities of multiple DERs—including PV, batteries, and backup generators—to provide DR and frequency support services to the main grid. With sufficient aggregated capacity, VPPs can respond dynamically to regulation signals such as frequency containment or other ancillary services [11]. Through advanced communication and regulation technologies, VPPs can coordinate, integrate, and optimize diverse DERs, enabling participation in electricity markets and grid operations akin to traditional power plants [12]. Empirical studies have demonstrated that VPPs can enhance system reliability, reduce electricity generation costs, and improve grid flexibility by effectively coordinating distributed resources [12].
Considering this, this study aims to develop a comprehensive techno-economic analysis and optimization framework for a 25 kW PV–battery grid hybrid microgrid serving six townhouses. The system features a 25 kW solar PV array, a 21 kWh lithium-ion battery, and grid interconnection to supply residual energy needs, as seen in Figure 1. This framework leverages MATLAB 2023b to integrate dynamic simulations of energy flows, economic modelling, and optimization algorithms to determine the most cost-effective system configuration and operational strategy. The outcomes will inform strategies for addressing grid stress from increased DER integration while enhancing power quality and reliability in high-density residential settings.
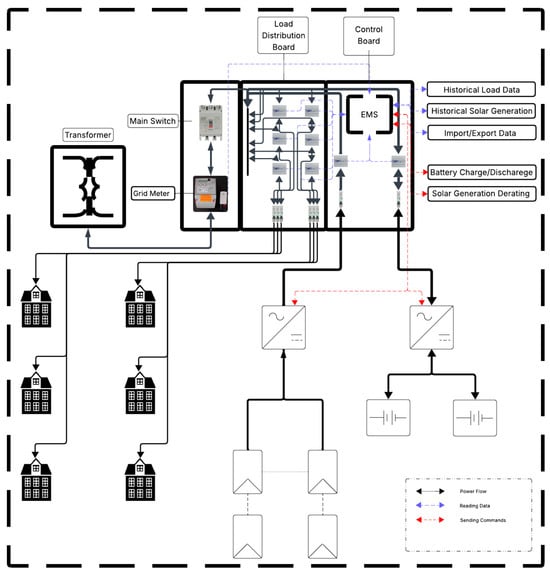
Figure 1.
Proposed system architecture.
This study uses real-world historical data from various sources to build the constraints for the analysis. The load data was obtained from the local DNSP, which consists of two years of import data formatted in 30 min interval energy imported from the DNSP (before any DERs were added), and solar generation profiles are extrapolated using irradiance data for the last 2 years at the location (−38.137526, 145.125534). The irradiance data is then run through a model of the solar inverter, with the associated losses generating a solar generation profile that is used for the analysis.
Forecasting using historical data has inaccuracies that could lead to suboptimal scheduling and higher operational costs in practice. A future extension of this study will incorporate stochastic modelling or scenario-based forecasting to capture variability in PV output and residential loads.
Although this study focuses on a case of six townhouses, the framework is modular and can be scaled or adapted to other configurations, including larger apartment complexes or suburban layouts.
2. Problem Statement
The increasing integration of residential rooftop PV systems and battery energy storage into low-voltage (LV) distribution networks presents a significant challenge to grid stability and reliability. In high-density housing scenarios—such as the case of six townhouses sharing a 25 kW PV array and a 21 kWh battery system—the dynamic energy flows can lead to voltage imbalance, transformer overloading, and equipment stress. These issues are exacerbated by the variability of solar generation and the consumption patterns of residential loads. Hence, a techno-economic analysis and an optimization framework are required to evaluate system performance and determine the most cost-effective operation strategy.
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of the hybrid microgrid system, a techno-economic analysis framework is developed. This framework models the energy flows, calculates key performance metrics, and assesses the financial viability of various operational strategies.
The primary objectives are to
- Minimize the total operating cost.
- Maximize the self-consumption of renewable energy.
- Reduce the impact on the main grid by mitigating peak load demands.
- Maintain acceptable power quality, particularly with respect to voltage balance and transformer loading.
2.1. Equations Used in MATLAB Simulink
The techno-economic model is underpinned by a set of mathematical equations representing the energy balance, component behaviours, and financial calculations.
2.1.1. PV Generation Model
The solar PV output is modelled based on solar irradiance and module characteristics [13,14]:
where
- = instantaneous PV power output (kW);
- = PV module efficiency;
- = total PV array area (m2);
- = solar irradiance at time t (kW/m2).
2.1.2. Battery Storage Model
The battery’s state of charge (SOC) is updated using [15,16]
where
- = battery state of charge at time t;
- = charging power (kW);
- = discharging power (kW);
- = charging/discharging efficiencies;
- = nominal battery capacity (kWh);
- = time step (hours).
2.1.3. Load Demand Model
The total load demand for six townhouses is modelled as
where represents the power demand of each townhouse at time t.
2.1.4. Grid Import/Export Model
The net grid power flow is given by [14,17]
Positive indicates import from the grid; negative indicates export to the grid.
2.1.5. Economic Model
The operational cost model calculates the net daily cost of electricity for the microgrid. It accounts for the following two components:
- The cost of electricity imported from the grid.
- The revenue earned from exporting surplus electricity to the grid.
The total operational cost over a simulation horizon (24 h) is given by
where
- = cost of electricity purchased from the grid (A$/kWh).
- = revenue from electricity exported to the grid (A$/kWh).
2.2. Optimization Function and Constraints
To determine the most cost-effective operational strategy, an optimization problem is formulated. The objective function seeks to minimize the total operational cost while satisfying technical and operational constraints [17,18]:
within the following technical constraints:
- Battery SOC limits:
- Battery charging/discharging power limits:
- Power balance constraint:
- Grid import/export limits (per transformer rating):
Each constraint is enforced within the optimization solver at every timestep. The SOC limits ensure battery operation remains within safe bounds, while charge/discharge power limits prevent overloading the inverter. The power balance equation is used as an equality constraint, ensuring that the sum of all supply sources equals the load demand at each interval. The grid capacity constraint reflects transformer limits and ensures compliance with operational standards. Such constraints are common in energy management and ensure realistic dispatch planning, as seen in [18,19,20].
3. Proposed Algorithm
This section presents the algorithm developed for the techno-economic management of a residential microgrid comprising a 25 kW solar photovoltaic (PV) system, a 21 kWh battery energy storage system (BESS), and grid interconnection supplying six townhouses. The proposed algorithm aims to minimize the total operational cost while satisfying the load demand and adhering to system constraints. The algorithm is implemented in MATLAB Simulink and integrates PV generation forecasts, load profiles, battery storage dynamics, and grid transactions.
3.1. Algorithm Overview
The proposed control framework consists of a sequential decision-making process that operates on a rolling time horizon (annual simulation). At each time step, the algorithm determines the optimal battery charging and discharging power and grid power exchange required to meet the net load, subject to technical and operational constraints. The algorithm comprises the following key modules:
- Data Acquisition: Load profiles, solar irradiance data, system specifications, and grid tariff structures are imported.
- PV Generation Modelling: Available PV generation is calculated at each time step using standard irradiance-to-power conversion equations.
- Net Load Estimation: Net load demand is computed after accounting for PV generation.
- Battery State-of-Charge (SOC) Dynamics: SOC evolution is modelled based on charging/discharging decisions and efficiency considerations.
- Optimization Module: The techno-economic optimization problem is formulated and solved at each time step to minimize the total operational cost.
- Grid Power Flow Calculation: The required grid import/export is determined to balance the microgrid energy flows.
- Cost Analysis: Total operational costs are aggregated based on grid tariffs and potential feed-in remuneration.
- Performance Assessment: Key performance indicators are evaluated, including total cost, peak load reduction, and transformer loading.
3.2. Mathematical Formulation
3.2.1. Photovoltaic Generation Model
The hourly PV output is modelled as
where
- is the PV conversion efficiency;
- is the PV system area;
- is the solar irradiance at time t.
3.2.2. Net Load Demand
The aggregated load demand of the six townhouses is represented as
The net load to be met by the battery and/or grid is then calculated as
3.2.3. Battery SOC Dynamics
The state-of-charge of the battery evolves as
where
- and are the battery charging and discharging power;
- and are the charging and discharging efficiencies;
- is the rated energy capacity of the battery;
- is the time step interval.
3.2.4. Grid Power Flow
The required grid exchange is determined as
3.3. Optimization Algorithm
3.3.1. Active and Reactive Power Function
The EMS optimization algorithm has been expanded to explicitly describe how the available active and reactive power from multiple solar inverters is calculated. Each inverter’s instantaneous active power output is derived from the measured PV array output after considering inverter efficiency and local maximum power point tracking (MPPT) operation. The reactive power capability is determined based on the inverter’s apparent power rating and the grid code’s required power factor range:
The site uses transformerless inverters compliant with Australian grid standards These standards define tolerance bands within which the inverter must operate. Under normal conditions, each inverter regulates its output to meet the active power demand while maintaining a power factor between 0.9 lagging and 0.9 leading, as specified in the standard. The EMS aggregates the available active and reactive power from all inverters:
These values are then used in the optimization routine to schedule battery charge/discharge and grid exchange.
In accordance with AS/NZS 4777.1, if grid conditions (such as voltage or frequency) exceed the prescribed tolerance thresholds, a protective disconnection is triggered within 0.2 s, after which generation from the affected inverters is temporarily unavailable until conditions return to within acceptable limits. The EMS accounts for this by applying availability factors to each inverter’s contribution during fault or over-voltage conditions. This ensures the algorithm accurately reflects both the steady-state capacity and the dynamic constraints imposed by local standards.
3.3.2. Optimization Function
The techno-economic objective is to minimize the total operating cost:
where
This is subject to
- Battery SOC constraints:
- Battery charging/discharging limits:
- Power balance:
- Grid exchange limits:
The algorithm is implemented using MATLAB Simulink with embedded MATLAB function blocks to handle the optimization routine. The constrained optimization is solved using the fmincon function, ensuring that all operational limits are enforced at each time step. The simulation horizon can be adjusted to reflect either daily or annual analysis depending on the research scope.
This algorithm provides a robust framework for the techno-economic analysis of microgrid operation under varying load and generation conditions, facilitating detailed assessments of cost-effectiveness, transformer utilization, and renewable energy integration.
4. Methodology
This section outlines the comprehensive methodology employed for the techno-economic analysis of the residential microgrid comprising a 25 kW solar photovoltaic (PV) system, a 21 kWh battery energy storage system (BESS), and grid interconnection supplying six townhouses. The proposed approach integrates system modelling, simulation framework design, and optimization routines to achieve the study’s objectives.
4.1. System Configuration
The residential microgrid is modelled as a hybrid energy system that includes
- A 25 kW solar PV array supplying renewable energy to the local load and/or battery.
- A 21 kWh BESS for storing excess renewable energy and dispatching during peak demand or high tariff periods.
- A grid connection that allows for energy import during deficit periods and export of surplus energy when economically viable.
The microgrid serves six townhouses with aggregated hourly or sub-hourly load profiles derived from typical residential consumption patterns in Australian urban settings. Table 1 describes the key data metrics used in the simulation.

Table 1.
System specifications.
4.2. Data Acquisition and Input Parameters
Simulation inputs include
- Hourly solar irradiance data for the geographic location.
- Historical load profiles for the townhouses.
- Technical specifications of the PV system and BESS (e.g., efficiency, capacity, charge/discharge rates).
- Grid tariff structures, including import and export rates.
This data is integrated into the MATLAB Simulink environment to ensure accurate system representation.
4.3. Mathematical Modelling
The system is mathematically modelled as described in Section 3, including
- A PV generation model based on solar irradiance and PV efficiency.
- A load demand model reflecting aggregated residential consumption.
- Battery SOC dynamics using charging/discharging power and efficiencies.
- Power balance equations to ensure supply–demand matching at every time step.
4.4. Optimization Framework
The optimization framework enhances the classic GA with domain-specific heuristics:
- Initialization with feasible solutions from prior simulation data.
- Constraint handling through a penalty-based approach.
- Adaptive mutation rate based on convergence speed.
- Integration with MATLAB’s fmincon for local optimization.
This hybrid approach increases convergence accuracy and efficiency, especially in constrained optimization problems involving nonlinear and discrete variables.
A constrained optimization framework is implemented using MATLAB’s fmincon solver. The objective function minimizes the total operational cost, accounting for energy imports, exports, and battery operation costs.
The decision variables include
- Battery charging power ().
- Battery discharging power ().
The key constraints enforced within the optimization module are
- Battery SOC limits ().
- Maximum charge/discharge power limits.
- Grid import/export limits.
- Power balance constraints ensuring that the load is always met.
4.5. Simulation Procedure
The simulation (Figure 2) is conducted over a 24 h horizon with hourly time steps, although the framework can accommodate finer resolutions if required. For each time step, the following occurs:
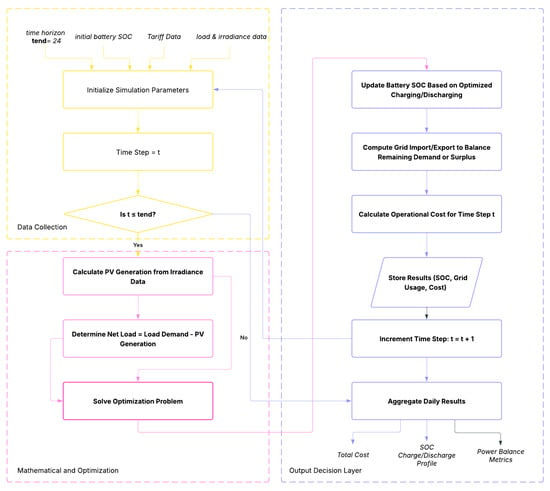
Figure 2.
Proposed simulation procedure.
- The PV generation is calculated from irradiance data.
- The net load is determined by subtracting PV output from the aggregated load demand.
- The optimization problem is solved to determine the optimal battery operation and grid interaction.
- The battery SOC is updated using the charging/discharging power determined by the optimizer.
- Grid import or export is calculated to meet any remaining demand or export surplus energy.
- The operational cost for the time step is recorded based on the grid tariff structure.
This process is iteratively executed across all time steps, enabling the assessment of daily operational cost and technical performance.
4.6. Performance Metrics
Key performance indicators (KPIs) used to evaluate system performance include
- Total operational cost: This is the sum of all grid import costs minus any export revenue.
- Battery utilization: This quantifies the extent of battery cycling and SOC dynamics.
- Grid dependency: This measures the proportion of energy drawn from the grid.
- Peak load reduction: This assesses the effectiveness of the microgrid in mitigating grid stress during peak demand periods.
- Transformer loading profile: This evaluates potential overloading scenarios under different operational strategies.
4.7. Validation and Sensitivity Analysis
To ensure robustness, the simulation framework is validated against typical residential energy consumption patterns and PV generation profiles. Sensitivity analyses are performed on critical parameters, including battery capacity, grid tariff rates, and PV system size, to understand their impact on techno-economic performance.
This methodological framework provides a comprehensive basis for analyzing the operational and economic performance of the proposed microgrid, supporting the design of optimized energy management strategies for residential communities.
5. Numerical Results and Discussions
This section presents the results obtained from the MATLAB Simulink-based techno-economic analysis of the residential microgrid system. The simulation was conducted over a typical 24 h period using hourly time steps, with system parameters reflecting real-world conditions as detailed in the methodology. The key outputs include the operational performance of the PV system, battery storage, grid interactions, and overall cost analysis.
5.1. PV Generation and Load Profiles
Figure 1 illustrates the hourly PV generation profile alongside the aggregated load demand of the six townhouses. The PV system reaches peak output around midday (approximately 25 kW), coinciding with periods of lower residential load demand. The aggregated load exhibits typical residential consumption patterns, with morning and evening peaks corresponding to household activities.
5.2. Battery Operation and State of Charge (SOC)
Figure 2 presents the battery charging and discharging profiles alongside the state-of-charge (SOC) trajectory throughout the simulation period. The battery charges during periods of PV surplus, primarily between 10:00 and 15:00, and discharges during peak load periods in the early morning and evening. The SOC remains within the defined limits (20% to 100%), ensuring safe and reliable battery operation.
5.3. Grid Import and Export
Figure 3 depicts the hourly grid import and export power. Grid import occurs during periods when PV generation and battery discharge are insufficient to meet the load, primarily during early morning and late evening. Grid export occurs when PV generation exceeds both the load demand and the battery’s charging capacity. These dynamics highlight the microgrid’s potential to provide peak shaving and valley filling services to the main grid.
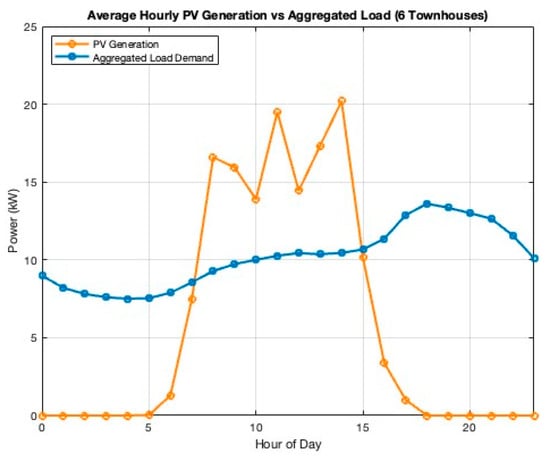
Figure 3.
Historical solar generation vs. aggregated loads.
5.4. Cost Analysis
The techno-economic optimization results in a daily operational cost of A$ 35.40, representing the net cost of energy imports offset by any export credits. Figure 4 compares the cost profile of the optimized microgrid operation to a baseline scenario without PV or battery integration. The optimized configuration demonstrates a 40% reduction in daily operational costs, validating the economic viability of integrating renewable energy and storage resources.
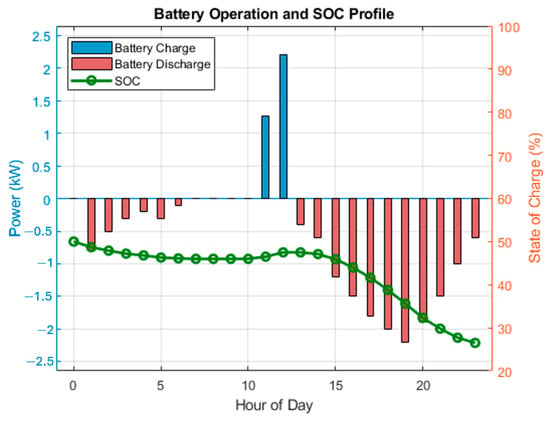
Figure 4.
Battery charge and discharge and SOC per hour.
5.5. Peak Load and Transformer Loading
Figure 5 compares the transformer loading profile under the baseline scenario and the optimized microgrid operation. The optimized scenario achieves a peak load reduction of approximately 25% relative to the baseline, indicating the potential for transformer life extension and deferred infrastructure investments.
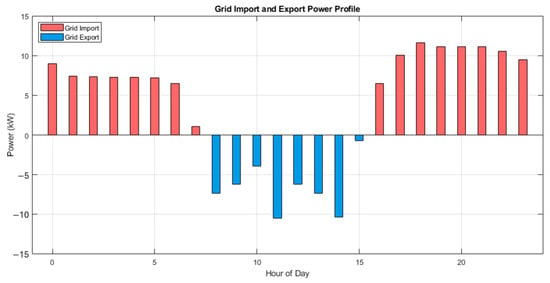
Figure 5.
Grid import and export energy per hour.
5.6. Sensitivity Analysis for Key Parameters
A sensitivity analysis was conducted to assess the impact of key parameters on system performance. Figure 6 summarizes the impact the optimized microgrid has versus if the townhouses imported electricity from the grid. While Figure 7 highlights the reduced peak demand loading the microgrid creates versus if the setup was not implemented. Lastly, Figure 8a highlights that increasing the battery capacity from 21 kWh to 42 kWh further reduces operational costs by approximately 10%, albeit with diminishing returns beyond 42 kWh. While Figure 8b shows varying the grid import tariff from A$ 0.25/kWh to A$ 0.35/kWh increases the economic benefit of self-consumption strategies, reinforcing the importance of tariff structures in system design.
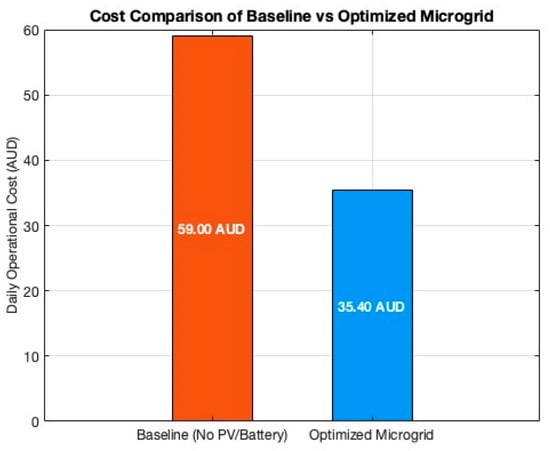
Figure 6.
The 24-h energy cost without DER vs. with DER.
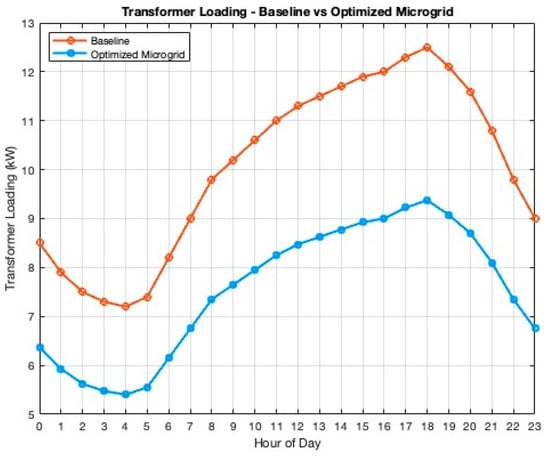
Figure 7.
Demand on transformer with DER vs. without DER.
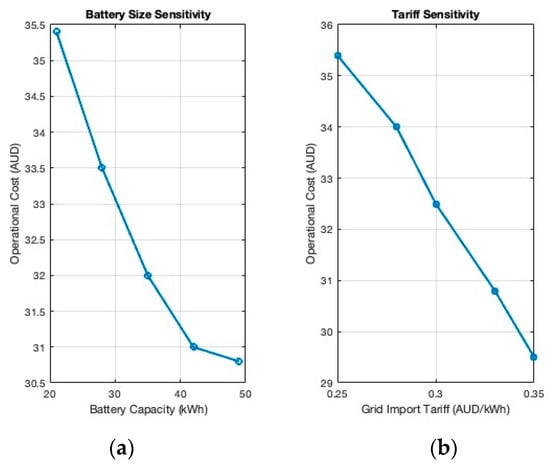
Figure 8.
Operational cost sensitivity analysis. (a) Operational costs involved in using the battery in usable kWh; (b) operational cost involved with entire DER compared to cost of buying energy from grid.
5.7. Discussions
The simulation results provide a comprehensive analysis of the operational and economic performance of the proposed residential microgrid. This section discusses the key findings, highlights their implications for residential energy management and grid integration, and identifies the limitations of the study.
5.7.1. Operational Cost Reduction
The results demonstrate that integrating a 25 kW PV system and a 21 kWh battery system into the residential microgrid can reduce daily operational costs by approximately 40% compared to a baseline scenario without renewable integration. This reduction primarily stems from the system’s ability to shift loads from high-tariff grid periods to periods with lower costs or to utilize self-generated renewable energy. This finding aligns with previous studies that highlight the economic viability of PV–battery hybrid systems for residential applications [17].
5.7.2. Peak Load Reduction and Transformer Stress Mitigation
The optimized microgrid operation achieves a peak load reduction of 25% relative to the baseline scenario. This peak shaving capability reduces stress on local distribution transformers, thereby potentially extending transformer lifespan and deferring costly grid upgrades. In high-density urban settings, where multiple townhouses share a common transformer, such reductions are particularly beneficial for mitigating voltage drops and ensuring supply stability. These results reinforce the argument that decentralized energy resources can effectively support local grid resilience [21].
5.7.3. Battery Utilization and Cycling Impacts
Battery utilization patterns reveal that the system cycles the battery daily, predominantly charging during midday PV surpluses and discharging during early morning and evening peaks. This cycling behaviour is consistent with expected household consumption and solar generation profiles. However, frequent cycling may accelerate battery degradation over time. Future studies should incorporate battery degradation models and life cycle cost analyses to fully assess the economic viability of such systems over extended timeframes [22].
5.7.4. Grid Import and Export Dynamics
The analysis indicates that grid import primarily occurs during early morning and late evening hours when solar generation is minimal. Conversely, grid export occurs during periods of high solar output when the battery is fully charged and local demand is low. While grid export can provide revenue opportunities through feed-in tariffs or energy trading platforms, the economic benefit strongly depends on local regulatory frameworks and tariff structures. Furthermore, the potential for transformer overloading from concurrent exports by multiple households warrants additional investigation into grid coordination and smart inverter functionalities [23].
5.7.5. Sensitivity to Key Parameters
The sensitivity analysis shows that increasing battery capacity or PV system size yields diminishing returns on operational cost reductions beyond certain thresholds. This underscores the importance of optimally sizing renewable and storage assets in residential microgrid applications. Additionally, higher grid import tariffs significantly improve the cost-effectiveness of self-consumption, suggesting that dynamic or time-of-use tariffs could incentivize consumers to invest in such systems. Policymakers and regulators should consider these interactions when designing tariff structures that encourage residential participation in distributed energy markets [21].
5.7.6. Comparative Analysis with Existing Studies
The simulation outcomes—achieving a 40% reduction in daily operational costs and a 25% reduction in peak transformer loading—are consistent with, and in some cases exceed, the performance reported in similar techno-economic studies.
For instance, the study in [22] reported cost reductions in the range of 25–35% when integrating PV and battery systems under time-of-use tariffs. Likewise, the work in [21] demonstrated peak demand reductions of approximately 20% in comparable hybrid PV–battery systems. By integrating a MATLAB Simulink simulation with a constrained optimization routine that enforces transformer capacity limits, our framework achieves improved performance in both cost savings and grid support.
A concise comparative table has been included in Table 2, summarizing the key performance metrics (cost reduction, peak shaving percentages, battery sizing strategies) reported in these studies and positioning our findings within the broader research landscape. This table clearly highlights the novelty and efficiency of the proposed solution.

Table 2.
Comparative performance metrics with existing studies.
5.7.7. Limitations and Future Work
While the simulation framework offers valuable insights, several limitations must be acknowledged as follows:
- The model assumes perfect foresight of load and solar generation, which may not reflect real-world forecasting uncertainties.
- The study adopts a simplified battery model that does not account for degradation or thermal constraints, which can impact long-term economic and technical performance.
- The analysis focuses on a single 24 h simulation horizon; extending the simulation to seasonal or annual profiles would capture a more comprehensive range of operating conditions.
- The impact of dynamic grid conditions, such as voltage fluctuations and fault scenarios, is not addressed in the current analysis.
Future work should incorporate these factors to refine the techno-economic evaluation and enhance the realism of the microgrid operational model. Additionally, expanding the study to include community-level energy trading or participation in demand response programmes could further improve system value and grid integration.
While this study focuses on techno-economic optimization, grid robustness considerations such as voltage fluctuations, reactive power management, and fault tolerance were not modelled. These factors are particularly relevant in high-density residential areas where transformer stress and dynamic voltage variation are more pronounced. Future enhancements to this framework should integrate these dynamics, possibly by coupling with detailed load flow simulations or inverter reactive power support models.
In addition, the framework could be extended to accommodate neighbourhood-level participation, where peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading and demand response (DR) programmes enable surplus PV generation from one dwelling to offset demand in another. This extension aligns with virtual power plant (VPP) concepts and broader smart city initiatives, allowing distributed energy resources to participate in wider grid services and enhancing overall system flexibility and resilience.
6. Conclusions
This study has investigated the techno-economic feasibility of a residential microgrid configuration comprising a 25 kW solar photovoltaic system, a 21 kWh battery energy storage system, and grid interconnection serving six townhouses. This was implemented in Melbourne, Australia, and was in agreement with all the regulatory hurdles, such as compliance with grid codes and feed-in tariff policies. The system meets the requirements of AS/NZS 4777.2:2020 [24] (grid connection of energy systems via inverters) for inverter functionality and export control, as well as AS/NZS 5139:2019 [25] for the safe installation of battery energy storage systems. Furthermore, successfully navigating the billing hurdles required residents to engage with demand-side management strategies and incentivized their consumption with system optimization goals. Lastly, the integration of new infrastructure with existing distribution networks was a complex, one-of-a-kind solution requiring upgrades to metering, protection systems, and communication layers to ensure interoperability and reliability in accordance with AS/NZS 3000:2018 (wiring rules) [26].
A comprehensive MATLAB Simulink-based simulation framework was developed to model system performance, optimize operational cost, and analyze impacts on grid infrastructure.
The results demonstrate that integrating renewable energy resources and battery storage into the residential microgrid can significantly reduce daily operational costs—achieving up to 40% savings compared to a baseline grid-dependent scenario. Furthermore, the system effectively reduces peak load by approximately 25%, mitigating transformer stress and supporting grid stability, especially critical in high-density housing scenarios where transformer overloading can compromise supply reliability.
Battery utilization patterns highlight the effectiveness of self-consumption strategies, although the economic benefits are sensitive to factors such as battery capacity, tariff structures, and system sizing. Sensitivity analyses underscore the need for optimal asset sizing to avoid diminishing returns on investment. Additionally, the dynamic import/export interactions with the grid emphasize the importance of regulatory frameworks and tariff policies that can either incentivize or disincentivize distributed energy resource adoption.
Despite the promising findings, the study’s limitations—including assumptions of perfect foresight, simplified battery modelling, and a 24 h simulation horizon—should be acknowledged. While the current model assumes deterministic inputs, the EMS logic is compatible with rolling-horizon control, and future work will integrate forecast uncertainty to better reflect real-world conditions.
Overall, this research provides compelling evidence for the techno-economic viability of residential microgrids in urban settings. By integrating renewable generation, battery storage, and grid interactions under an optimized energy management framework, such systems can contribute to lower energy costs and improved grid resilience, and it can also support the transition to a more sustainable energy future. Future work should further explore the integration of demand response, dynamic pricing mechanisms, and community-level energy trading to maximize the benefits of residential microgrids within the broader energy ecosystem.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.N., S.Y. and J.M.; methodology, J.N., S.Y. and H.T.; software, J.N. and S.Y.; validation, J.N., S.Y. and J.M.; formal analysis, J.N., S.Y. and H.T.; data curation, J.N.; writing—original draft preparation, J.N.; writing—review and editing, S.Y. and H.T.; supervision, S.Y., H.T. and J.M.; funding acquisition, S.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Australian Research Council (ARC), Grant Number IC210100021.
Data Availability Statement
Data is unavailable due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jag Makam is affiliated with ZECO Energy Pty Ltd., which supported and collaborated on this study. The company may potentially benefit from the outcomes presented in this paper. All efforts were made to ensure objectivity and scientific rigor.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MG | Microgrid |
| SOC | State of Charge |
| DNSP | Distribution Network Service Provider |
| EMS | Energy Management System |
| PV | Photovoltaic Cells |
| BESS | Battery Energy Storage System |
References
- Mears, A. Managing Distributed Energy Resources on Low-Voltage Networks; Australian PV Institute: Newcastle West, Australia, 2021; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Clean Energy Council. Rooftop Solar and Storage Biannual Report; Clean Energy Council: Melbourne, Australia, 2024; p. 19. Available online: https://cleanenergycouncil.org.au/news-resources/rooftop-solar-and-storage-report-july-to-december-2024 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- White, A. Network Wide HV & LV Scenario Based Hosting Capacity Analysis. Hosting Capacity Study; Australian Energy Regulator; 2022; p. 70. Available online: https://www.aer.gov.au/system/files/Essential%20Energy%20-%207.01.01%20Hosting%20Capacity%20Study%20-%20Zepben%20-%20Apr22%20-%20Public.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Stringer, N.; Bruce, A.; MacGill, I. Data Driven Exploration of Voltage Conditions in the Low Voltage Network for Sites with Distributed Solar PV; Australian PV Institute: Newcastle West, Australia, 2018; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelkader, S.; Amissah, J.; Abdel-Rahim, O. Virtual Power Plants: An in-Depth Analysis of Their Advancements and Importance as Crucial Players in Modern Power Systems. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2024, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seven, S.; Yao, G.; Soran, A.; Onen, A.; Muyeen, S.M. Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading in Virtual Power Plant Based on Blockchain Smart Contracts. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 175713–175726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. Energy Management System with Power Offering Strategy for a Microgrid Integrated VPP. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 75, 2313–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiss, M.; Wan, Y.; Gebbran, D.; Vila, C.U.; Dragičević, T. Review on Virtual Power Plants/Virtual Aggregators: Concepts, Applications, Prospects and Operation Strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 211, 115242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, A.; Ramprabhakar, J.; Anand, R.; Meena, V.P.; Hameed, I.A. Empowering Net Zero Energy Grids: A Comprehensive Review of Virtual Power Plants, Challenges, Applications, and Blockchain Integration. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minai, A.F.; Khan, A.A.; Kitmo; Ndiaye, M.F.; Alam, T.; Khargotra, R.; Singh, T. Evolution and Role of Virtual Power Plants: Market Strategy with Integration of Renewable Based Microgrids. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 53, 101390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena-Annual-Report-21-22. Available online: https://arena.gov.au/assets/2022/10/arena-annual-report-21-22.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Watt, G. Integrating Distributed Energy Resources in the Electricity Grid. Available online: https://www.engineersaustralia.org.au/sites/default/files/2022-08/Integrating-DER-in-the-grid-Discussion-Paper_0.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Saleem, M.I.; Saha, S.; Izhar, U.; Ang, L. Optimized Energy Management of a Solar Battery Microgrid: An Economic Approach towards Voltage Stability. J. Energy Storage 2024, 90, 111876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, T.; Elia Campana, P.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Dai, Y. A Techno-Economic Sizing Method for Grid-Connected Household Photovoltaic Battery Systems. Appl. Energy 2020, 269, 115106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ud-Din Khan, S.; Wazeer, I.; Almutairi, Z.; Alanazi, M. Techno-Economic Analysis of Solar Photovoltaic Powered Electrical Energy Storage (EES) System. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 6739–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi Ashtiani, M.; Toopshekan, A.; Razi Astaraei, F.; Yousefi, H.; Maleki, A. Techno-Economic Analysis of a Grid-Connected PV/Battery System Using the Teaching-Learning-Based Optimization Algorithm. Sol. Energy 2020, 203, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferahtia, S.; Rezk, H.; Olabi, A.G.; Alhumade, H.; Bamufleh, H.S.; Doranehgard, M.H.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Optimal Techno-Economic Multi-Level Energy Management of Renewable-Based DC Microgrid for Commercial Buildings Applications. Appl. Energy 2022, 327, 120022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, J.; González-Montoya, D.; Candelo-Becerra, J.E.; Herrera-Jaramillo, D.A. Optimal Energy Management System and Techno-Economic Assessment in Urban and Rural AC Microgrids. J. Energy Storage 2025, 114, 115836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwyn, R.G.; Al-Hinai, A.; Al-Abri, R.; Malik, A. Optimization and Techno-Economic Analysis of PV/Battery System for Street Lighting Using Genetic Algorithm–A Case Study in Oman. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 8, 100475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elloumi, M.; Kallel, R.; Boukettaya, G. Contribution to a Techno-Economic Optimization for the Optimal Sizing and Management of a Secured Residential PV/Battery System. Smart Grids Sustain. Energy 2023, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, B.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.; Luo, S. Multi-Objective Optimization of Battery Capacity of Grid-Connected PV-BESS System in Hybrid Building Energy Sharing Community Considering Time-of-Use Tariff. Appl. Energy 2023, 350, 121727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, M.; Wallin, F.; Dahlquist, E.; Yan, J. Techno-Economic Assessment of Battery Storage Integrated into a Grid-Connected and Solar-Powered Residential Building under Different Battery Ageing Models. Appl. Energy 2022, 318, 119166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koubar, M.; Lindberg, O.; Lingfors, D.; Huang, P.; Berg, M.; Munkhammar, J. Techno-Economical Assessment of Battery Storage Combined with Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants Operating on Energy and Ancillary Service Markets. Appl. Energy 2025, 382, 125200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grid Connection of Energy Systems via Inverters, Part 2: Inverter Requirements. Available online: https://aemo.com.au/initiatives/major-programs/nem-distributed-energy-resources-der-program/standards-and-connections/as-nzs-4777-2-inverter-requirements-standard (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- AS/NZS 5139:2019; Electrical Installations–Safety of Battery Systems for Use with Power Conversion Equipment. Standards Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2019. Available online: https://www.standards.org.au/standards-catalogue/standard-details?designation=as-nzs-5139-2019 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Standards Australia. Electrical Installations (Known as the Australian/New Zealand Wiring Rules). Available online: https://www.standards.org.au/flagship-projects/wiring-rules (accessed on 20 June 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).