Abstract
Building upon the geological cycle theory, this study proposes fault cycles as a critical component of tectonic cyclicity in petroliferous basins. Focusing on reservoir-controlling faults in the southwestern Qaidam Basin, we systematically analyze fault architectures and identify three distinct fault activation episodes: the Lulehe Formation (LLH Fm.), the upper part of the Xiaganchaigou Formation (UXG Fm.), and the Shizigou Formation (SZG Fm.). Three types of fault cycle models are established. These fault cycles correlate with the evolution of regional tectonic stress fields, corresponding to the Cenozoic transition from extensional to compressional stress regimes in the basin. Mechanistic analysis reveals the hierarchical control of fault cycles in hydrocarbon systems: the early cycle governs the proto-basin geometry and low-amplitude structural trap development; the middle cycle affects the source rock distribution; and the late cycle controls trap finalization and hydrocarbon migration. This study proposes a fault cycle-controlled accumulation model, providing a dynamic perspective that shifts from conventional static fault concepts to reveal fault activity periodicity and its critical multi-phase control over hydrocarbon migration and accumulation, essential for exploration in multi-episodic fault provinces.
1. Introduction
In the second volume of his seminal work “Das Antlitz der Erde”, Eduard Suess [1] first proposed the concept of a ‘geological cycle’ through meticulous analysis of stratigraphy and tectonic movements. He demonstrated that the evolution of Earth’s crust follows cyclical patterns rather than linear progression, fundamentally reshaping geological thinking. Subsequent studies expanded this concept to the tectonic cycle [2], which is particularly critical in hydrocarbon systems as they govern basin formation and resource distribution [3,4,5,6]. Fault systems, as dynamic components of the tectonic cycle, exhibit dual roles in hydrocarbon migration; they act as vertical conduits while generating fracture networks that enhance permeability [7,8,9,10,11].
However, current tectonic cycle research predominantly focuses on crustal-scale processes such as orogeny and basin evolution [12], while neglecting the periodic activation of intra-basin fault systems. Despite the pivotal role of faults in controlling hydrocarbon migration and accumulation, analyzing their impact through traditional tectonic cycles faces intrinsic scale mismatches.
In the Qaidam Basin of northwestern China, prevailing research prioritizes fault formation mechanisms, structural styles, and spatial distribution [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. Additionally, research on hydrocarbon accumulation reveals that Liu et al. [22] suggest that the deposition of thick source rocks influences hydrocarbon migration and accumulation; Wang et al. [23] and Zeng et al. [24], based on paleo-structural analysis, propose that paleo-slopes and paleo-uplifts are favorable enrichment zones; Sun et al. [25] considers the extensively developed negative flower structures in the shallow southwestern basin as favorable migration conduits; and Pang et al. [26], Fu et al. [27], and Li et al. [21] indicate that widely developed deep-seated and late-stage strike-slip faults directly control hydrocarbon migration and accumulation. However, studies on fault-activity history remain limited, with insufficient analysis of periodic fault activity’s role in hydrocarbon reservoir formation and inadequate investigation into the coupling relationships between fault activity and hydrocarbon accumulation across different periods.
To resolve this problem between structural characterization and process dynamics, we propose the concept of a “fault cycle”, which characterizes alternating phases of intense activity and relative stability in fault movement. This represents a basin-scale refinement of tectonic cycles. Focusing on Cenozoic fault systems in the southwestern Qaidam Basin, we integrate high-resolution 3D seismic interpretation with quantitative displacement analysis to clarify the characteristics of fault activity in the study area, establish fault cycles patterns correlated with regional tectonic evolution, and elucidate the coupling relationships between fault cycles and key hydrocarbon accumulation processes, including basin formation, trap development, source rock distribution, and hydrocarbon migration.
2. Research Object and Methodology
2.1. Research Object
2.1.1. Location, Stratigraphy, and Tectonic Settings
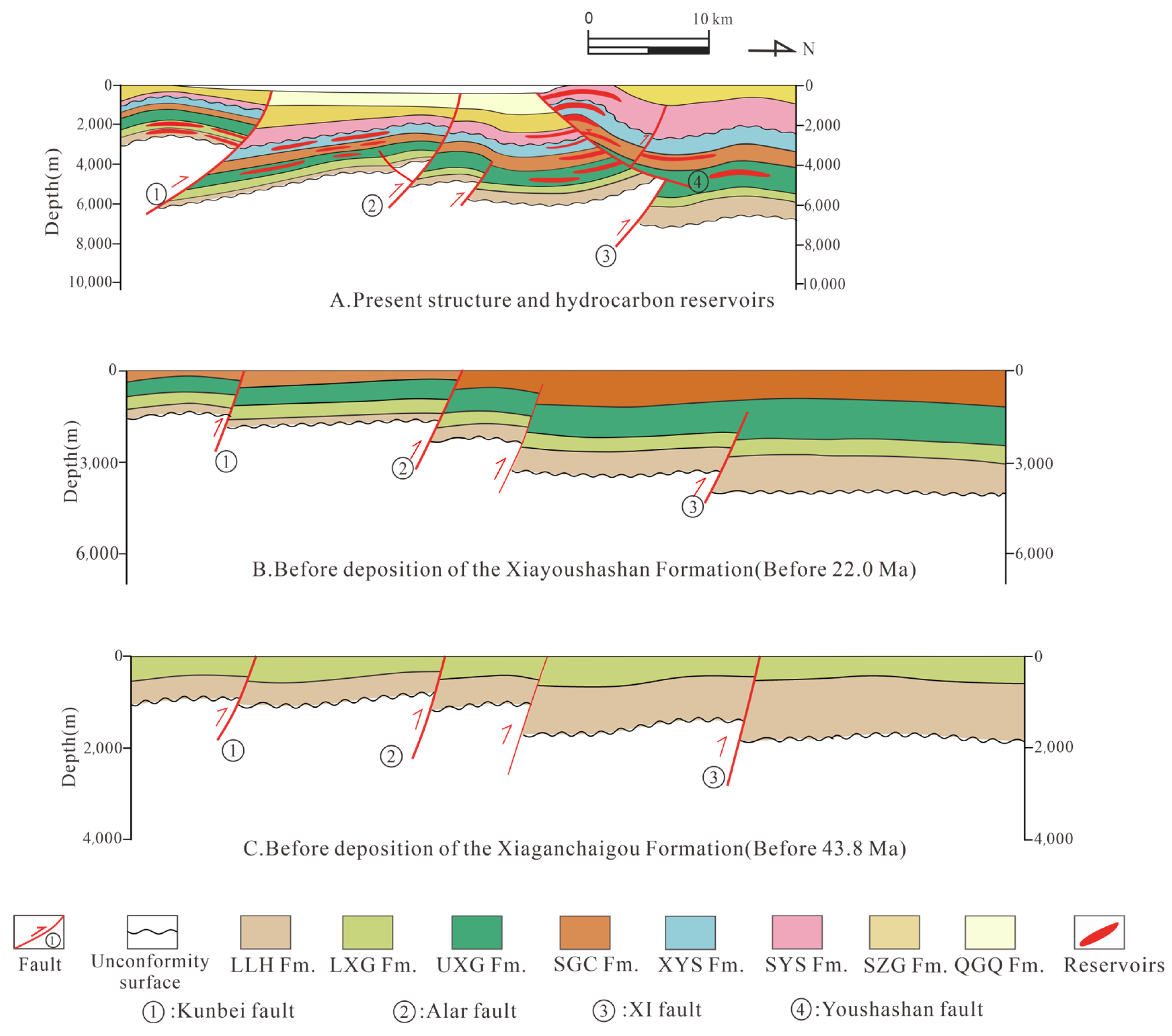
The Qaidam basin, located in the northern part of the Tibetan Plateau, represents a critical Cenozoic intramontane basin; it constitutes China’s principal hydrocarbon province in the northwestern regions. Covering approximately 121,000 km2 with rhomboid geometry bounded by three mountain ranges, it comprises four first-order structural elements: the Western Qaidam Uplift, Southern Altyn Tagh Slope, Yiliping-Sanhu Depression, and Northern Qaidam Uplift (Figure 1A) [28,29,30,31]. The Western Qaidam Uplift, developed under Himalayan tectonic compression, displays a NWW-trending structural framework characterized by alternating uplifts and depressions in an oblique arrangement. This framework is primarily controlled by deep-seated basement faults, all exhibiting reverse faulting characteristics, including the near-EW-oriented Kunbei fault, XIII fault, Altyn fault, and XI fault (Figure 1B).
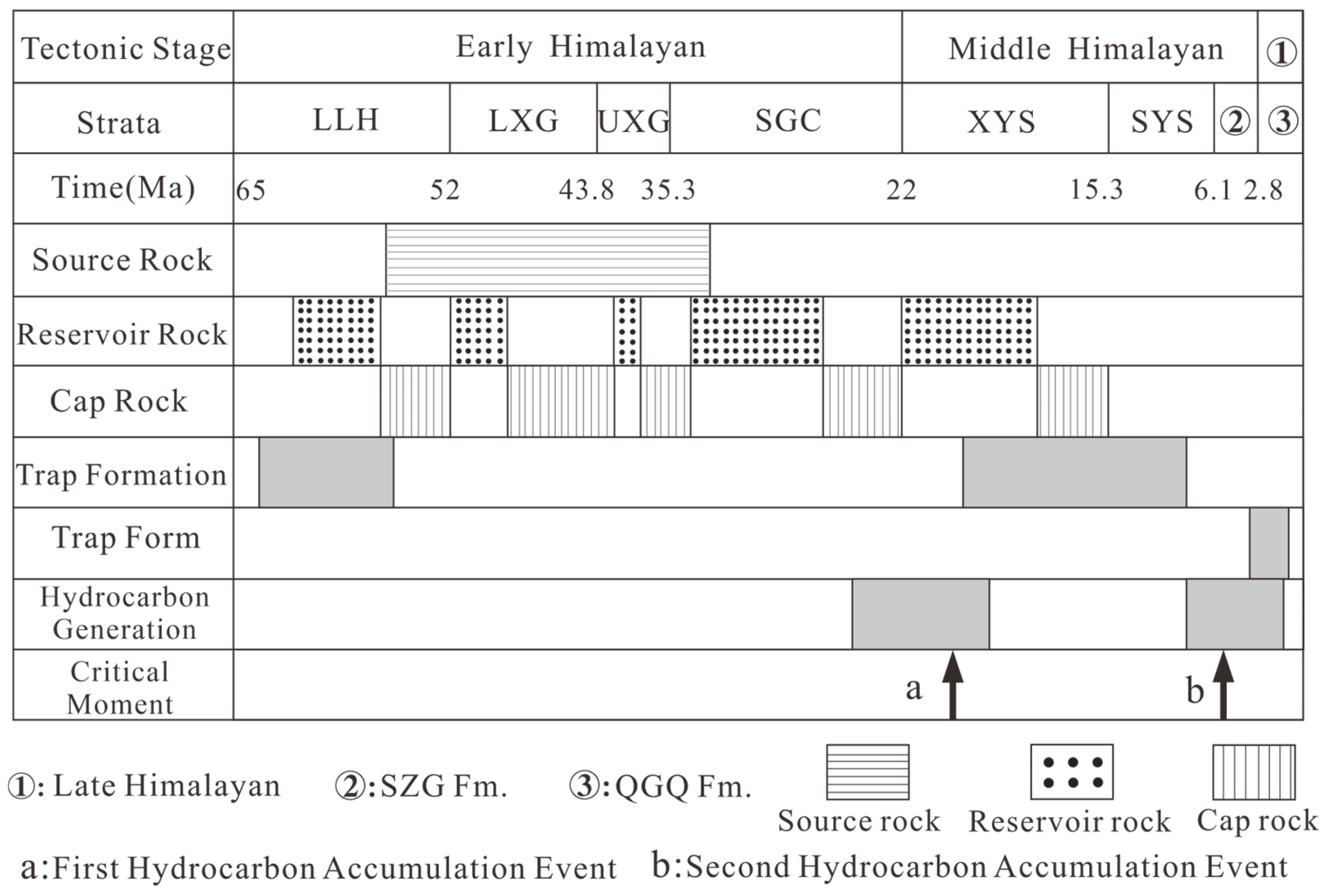
Cenozoic sedimentary sequences, ranging from the Paleocene to the Quaternary, dominate the drilled stratigraphic column in the southwestern Qaidam Basin. Integrated stratigraphic studies and paleontological data demonstrate that the Cenozoic lithostratigraphic units are subdivided from bottom to top into: the Paleocene-Eocene Lulehe Formation (LLH Fm., 63–52 Ma, 0–500 m, conglomerates, sandstones, and mudstones), Xiaganchaigou Formation (lower part: LXG Fm., 350–850 m, mudstones and siltstones with sandstones, and upper part: UXG Fm., 52–35.5 Ma, 750–2700 m, dark gray mudstones and shales with gypsum), Miocene Shangganchaigou Formation (SGC Fm., 35.3–22 Ma, 400–1600 m, gray mudstones and siltstones with sandstones and carbonates), Pliocene Xiayoushashan Formation (XYS Fm., 22–15.3 Ma, 700–2400 m, sandstones and conglomerates with mudstones), Shangyoushashan Formation (SYS Fm., 15.3–8.1 Ma, 450–2250 m, mudstones and siltstones with sandstones and conglomerates), Shizigou Formation (SZG Fm., 8.1–2.8 Ma, 0–1250 m, conglomerates, sandstones, and mudstones), and Quaternary Pleistocene Qigequan Formation (QGQ Fm., 2.8–0 Ma, 0–500 m, conglomerates, sandstones, and mudstones) (Figure 1C) [32,33,34,35,36]. Since the Cenozoic period, the southwestern Qaidam basin has experienced three main tectonic evolutionary phase: (1) the Eocene–Early Oligocene strike-slip stretching stage; (2) the Middle Oligocene–Miocene weak compression stage, and (3) the Pliocene to present intense compression stage, exhibiting progressively intensifying tectonic activity over time (Figure 2) [37].
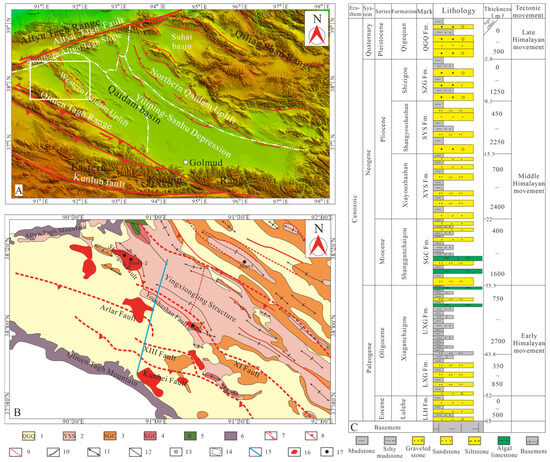
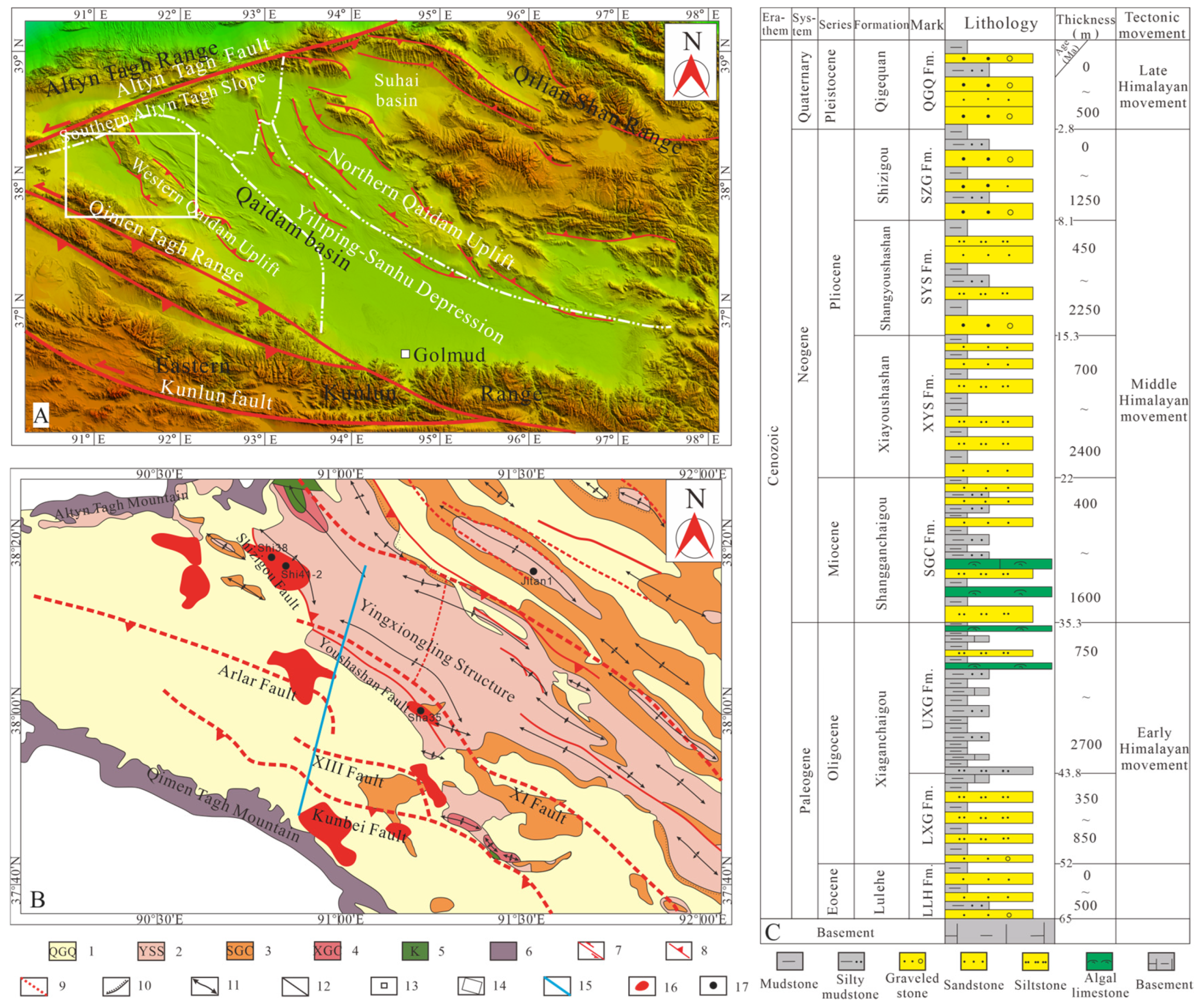

Figure 1.
(A) Digital elevation map (DEM) of the Qaidam basin area (From PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company, Dunhuang, China), (B) Geologic map of the SW Qaidam basin (Revised from Wu et al. [38]). 1: Pleistocene; 2: Pliocene; 3: Miocene; 4: Oligocene; 5: Cretaceous; 6: Pre-Cenozoic; 7: Surficial strike-slip fault; 8: Surficial thrust fault at the surface; 9: Fault along Shangganchaigou Formation; 10: Unconformity; 11: Anticline; 12: Stratigraphic boundary; 13: City; 14: Research area; 15: Seismic section across the southwestern Qaidam; 16: Discovered hydrocarbon reservoirs; 17: well, and (C) Stratigraphic column of the Cenozoic strata in the southwestern Qaidam basin (From Wu et al. [38]).
Figure 1.
(A) Digital elevation map (DEM) of the Qaidam basin area (From PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company, Dunhuang, China), (B) Geologic map of the SW Qaidam basin (Revised from Wu et al. [38]). 1: Pleistocene; 2: Pliocene; 3: Miocene; 4: Oligocene; 5: Cretaceous; 6: Pre-Cenozoic; 7: Surficial strike-slip fault; 8: Surficial thrust fault at the surface; 9: Fault along Shangganchaigou Formation; 10: Unconformity; 11: Anticline; 12: Stratigraphic boundary; 13: City; 14: Research area; 15: Seismic section across the southwestern Qaidam; 16: Discovered hydrocarbon reservoirs; 17: well, and (C) Stratigraphic column of the Cenozoic strata in the southwestern Qaidam basin (From Wu et al. [38]).

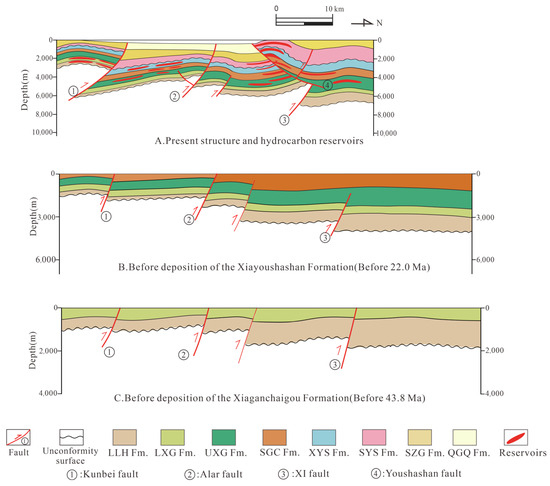
Figure 2.
Tectonic evolution in the southwestern Qaidam basin (stratigraphic abbreviations defined in Section 2.2.1). Modified from Wang et al. [39].
2.1.2. Characteristics of Petroleum Geology and Geochemistry
The Qaidam Basin hosts three distinct petroleum systems: the Jurassic petroleum system along the northern margin, the Paleogene petroleum system in the western depression, and the Quaternary petroleum system in the central-eastern basin [26]. Within the western Paleogene petroleum system, two predominant source rock units have been identified: the UXG Fm., composed of mixed siliciclastic-carbonate deposits, and lacustrine mudstones of the SGC Fm. [40]. The UXG Fm. demonstrates superior hydrocarbon generation potential despite its moderate total organic carbon content (average TOC < 1%, Ro = 0.6–1.2%), which is attributed to its extensive distribution (effective source area: 1.26 × 104 km2; cumulative thickness: 1000 m), hydrogen-rich Type I-II1 kerogen, and elevated carbon conversion efficiency [4,21]. The reservoir systems exhibit significant stratigraphic heterogeneity. Paleogene strata are dominated by saline lacustrine mixed carbonate rocks (e.g., algal-laminated dolomicrite and grainstones), characterized by composite pore networks comprising intergranular pores, dissolution vugs, and tectonic fractures. In contrast, Neogene reservoirs predominantly comprise fan-delta, braided-river delta, and beach-bar sandstone bodies [21,41,42]. Regional sealing is provided by Paleogene gypsum-salt and Neogene thick-bedded mudstone [43]. Structural deformation has generated four trap types: thrust anticlines, fault-nose structures, structural-lithologic combinations, and inversion-drape anticlines [44].
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Data
The dataset, provided by the PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company, comprises core samples, thin sections, fluid inclusion analyses, and post-stack 3D seismic volumes (800 km2 coverage) from the southwestern Qaidam Basin. Fault geometry and displacement were quantified through integrated seismic interpretation, well-to-seismic calibration, and horizon tracking, ensuring stratigraphic consistency and accurate fault throw measurements.
Pre-analysis erosion restoration accounted for tectonic uplift effects on the stratigraphic architecture. The QGQ Formation exhibited extensive erosion, particularly in uplifted zones, while the SZG Formation experienced notable erosion near the Altyn Tagh Mountains and structural highs. The SYS Formation erosion is localized in the Yingxiongling area, and the XYS Formation shows minimal erosion. Erosion thicknesses (Table 1) were restored following Sun’s [45] stratigraphic correlation framework.

Table 1.
Stratal erosion magnitude in different regions of the southwestern Qaidam. Data from Sun [45].
2.2.2. Fault Activity Analysis Method
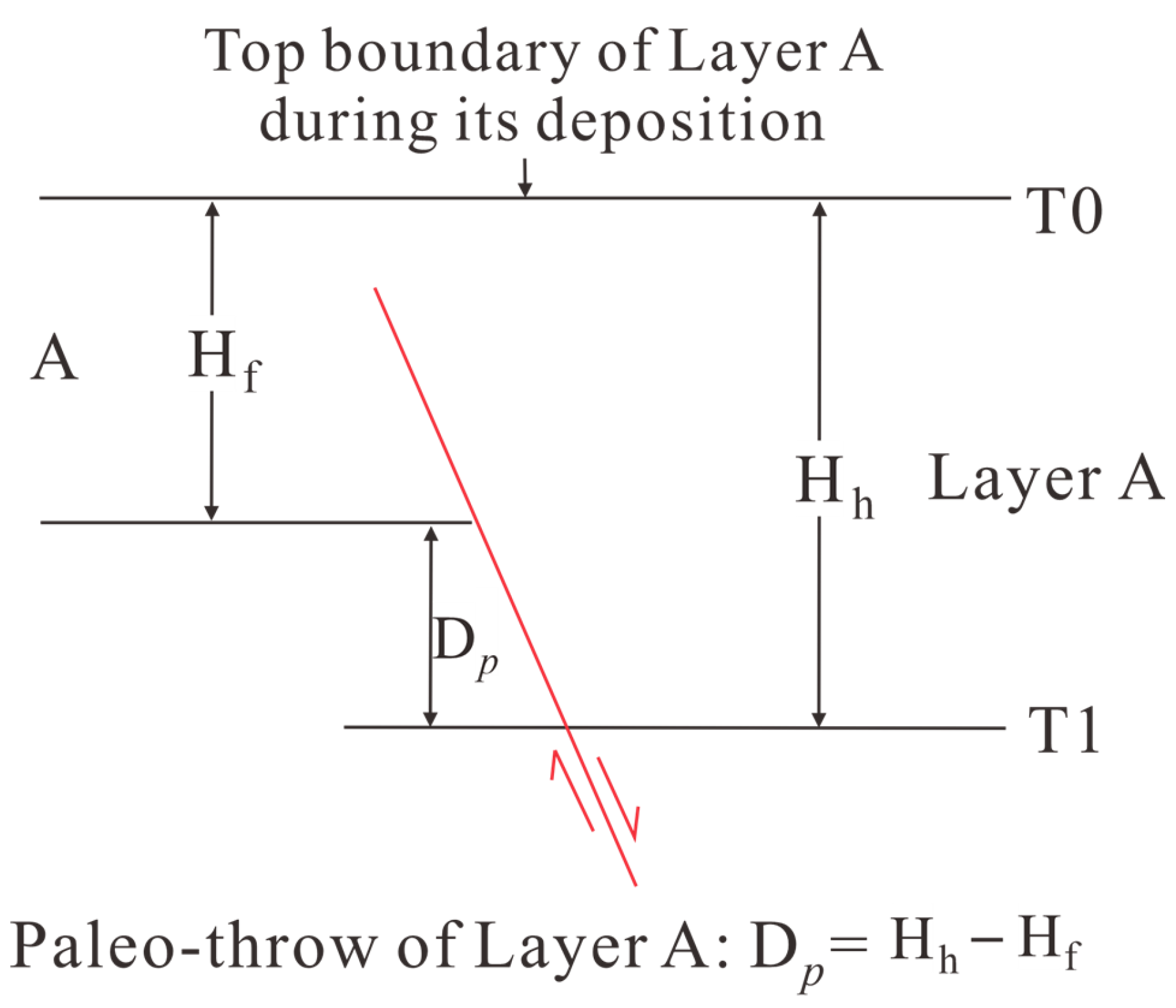
The fault activity rate method was selected to evaluate syndepositional faults in the southwestern Qaidam Basin [39], as it integrates geological time and provides a quantitative measure of activity intensity, overcoming the limitations of the fault growth index (sedimentation rate/erosion dependency) and paleofault displacement methods (lacking geological time constraints). Seismic profiles were used to identify hanging wall and footwall stratigraphic thickness variations across sedimentary periods (Figure 3). Activity rates were calculated by correlating these thickness differences with sedimentation time (Equation (1)).
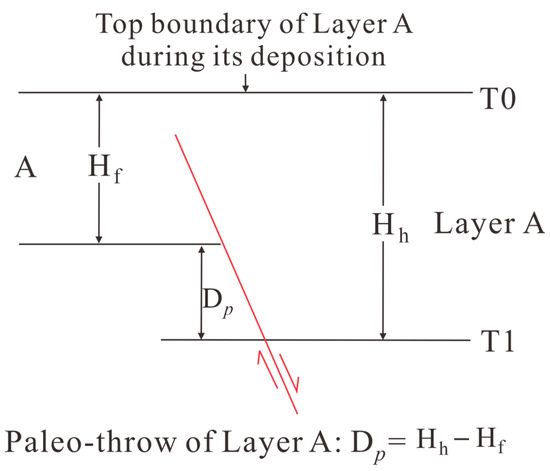
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram illustrating the calculation of paleo-throw (D) across the fault.
The fault slip rate () is calculated by dividing the paleo-throw () by the depositional duration ():
2.2.3. Fault Cycle Division
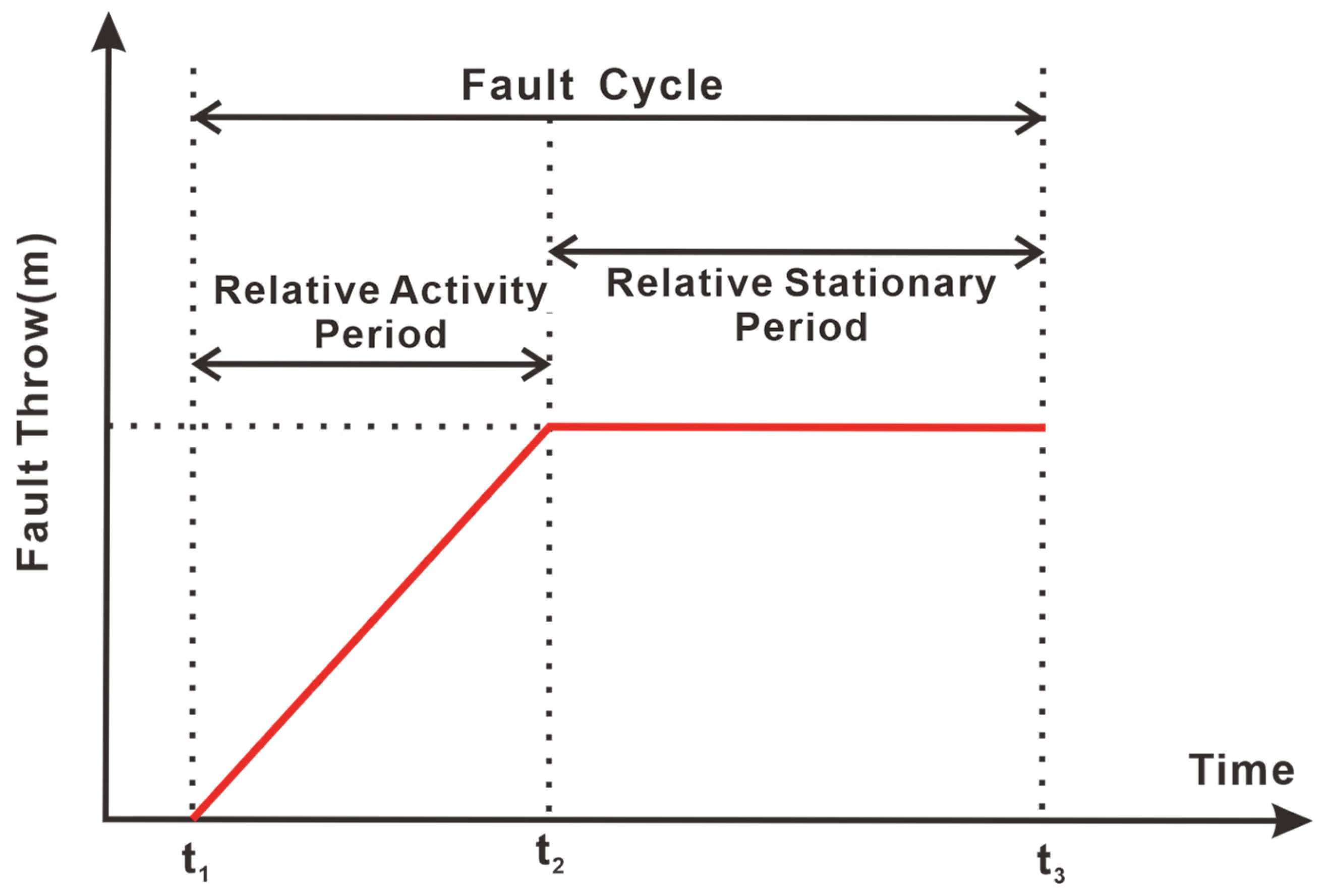
Cyclical geological processes, manifesting in tectonic and sedimentary systems, display periodic alternations between high- and low-intensity phases within a cycle [46]. In this study, we propose the concept of a “fault cycle”, which is based on the periodic nature of the fault activity and its characteristics: (1) intense activity with rapid displacement accumulation; (2) relative stability with reduced displacement rates (Figure 4). Relative stability represents sustained displacement accrual at diminished rates rather than complete quiescence.
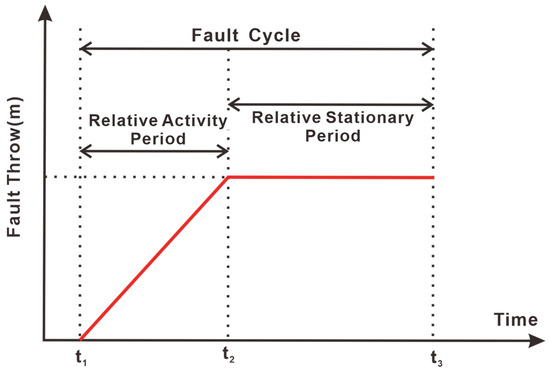
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of fault cycle division.
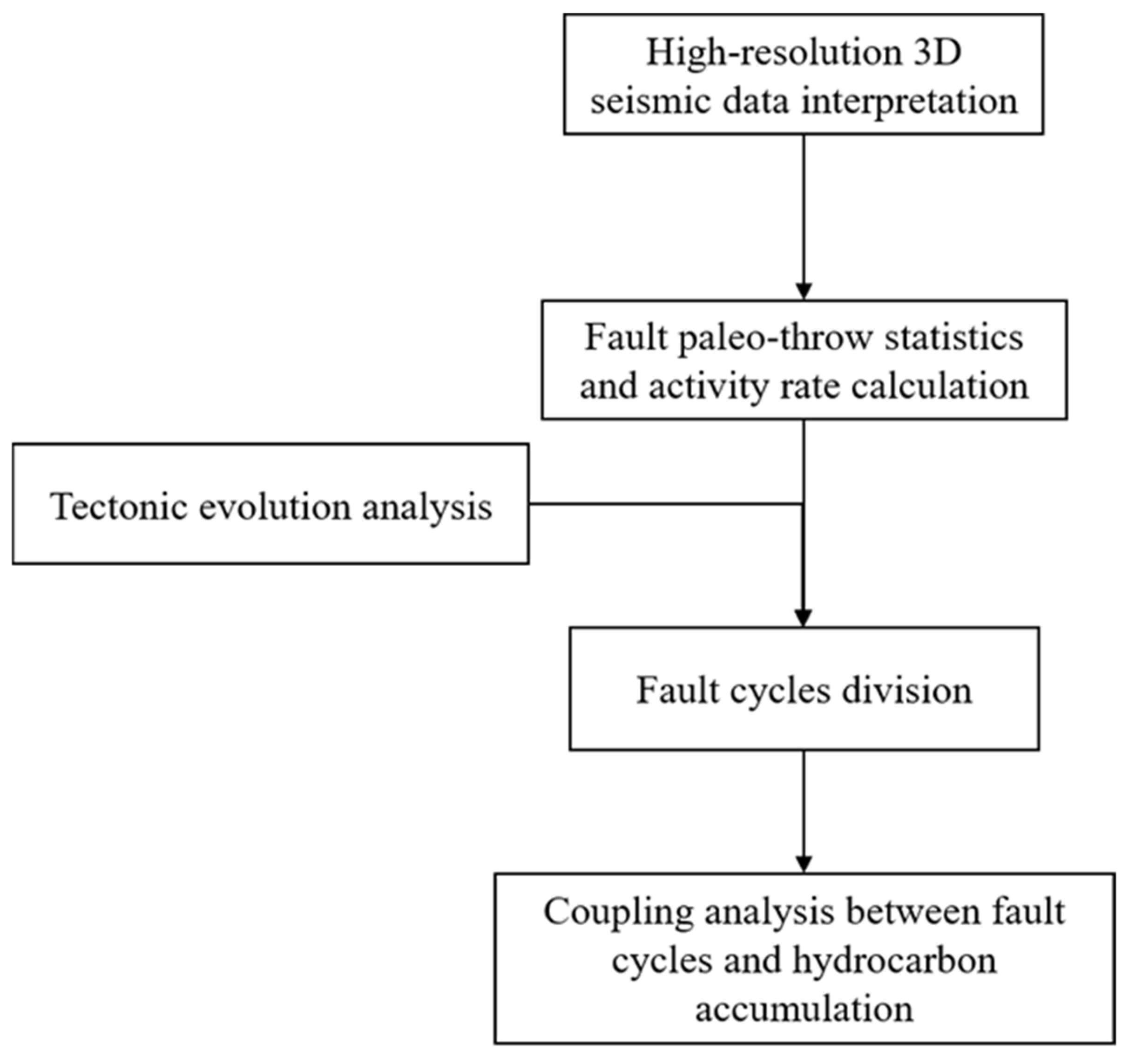
This study first conducts a detailed interpretation of three-dimensional high-resolution seismic data, characterizes the distribution patterns of strata and faults, then counts the ancient drop of faults and calculates the fault activity rate. Secondly, combined with the tectonic evolution analysis of the study area, it classifies the fault cycle mode. Finally, it comprehensively analyzes the fault cycle and oil and gas accumulation. The detailed research workflow is illustrated in Figure 5.
Figure 5.
Research method flowchart.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Fault Development
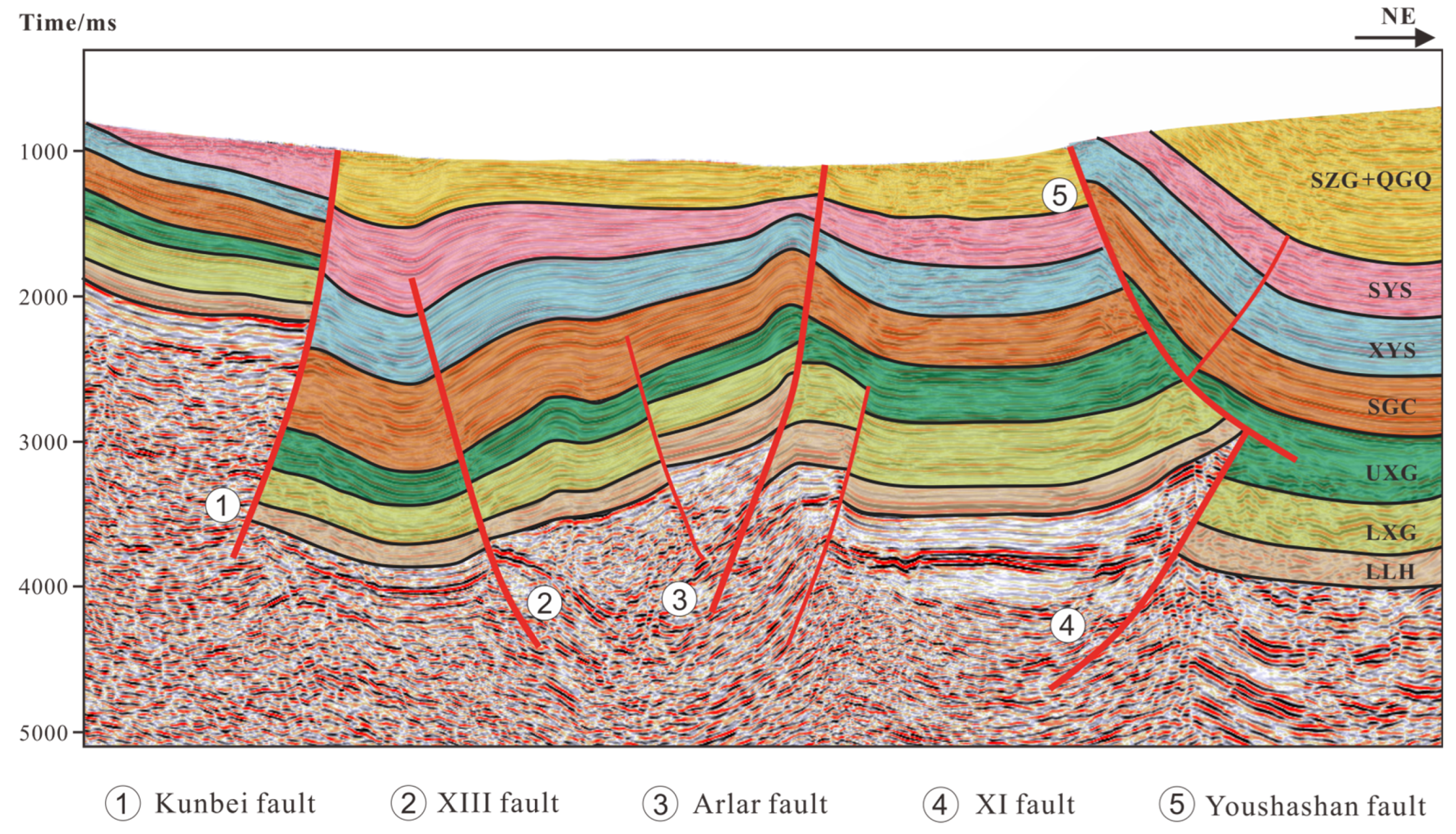
The Tibetan Plateau uplift induced a multistage tectonic stress field in the Qaidam basin, forming a hierarchical fault system dominated by the southwestern Qaidam Uplift structural belt. The early faults that transect the basement are primarily syn-depositional, characterized by steeply dipping fault surfaces. In the Cenozoic strata, the tectonic stress field of the Qaidam basin has undergone a reversal, leading to significant north–south compressional stresses that have facilitated the development of numerous reverse faults. These sustained compressional forces have caused the hanging walls of these faults to move upward along the fault planes, accumulating displacement over time and resulting in steeply inclined fault planes (Figure 6) [47,48].
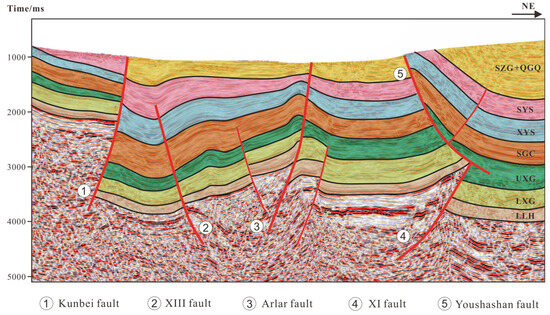
Figure 6.
Seismic reflection profile of the southwestern Qaidam basin. The locations of the profiles can be observed in Figure 1B.
Based on the relationship between the fault development scale and hydrocarbon reservoirs in the study area, five major faults were selected for investigation: the Kunbei fault, XIII fault, Shizigou fault, Youshashan fault, and XI fault (Figure 1B).
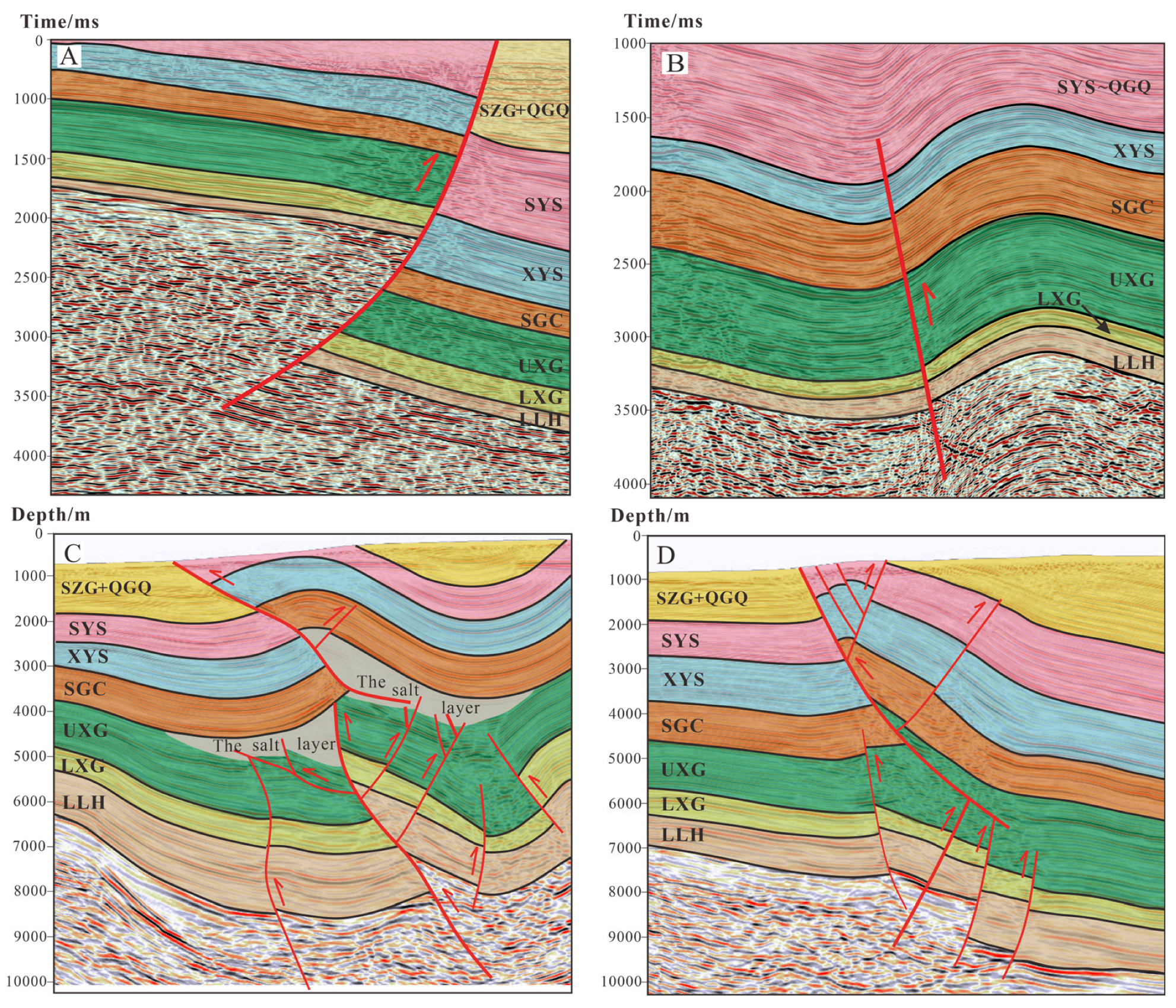
The Kunbei fault, a transtensional thrust fault initiated during the early Cenozoic period, provided a vertical migration pathway for hydrocarbons from the Zhahaquan depression to the Kunbei fault-step zone, controlling the formation of the Kunbei reservoir. This fault exhibits a single-fault geometry in its cross-section (Figure 7A).
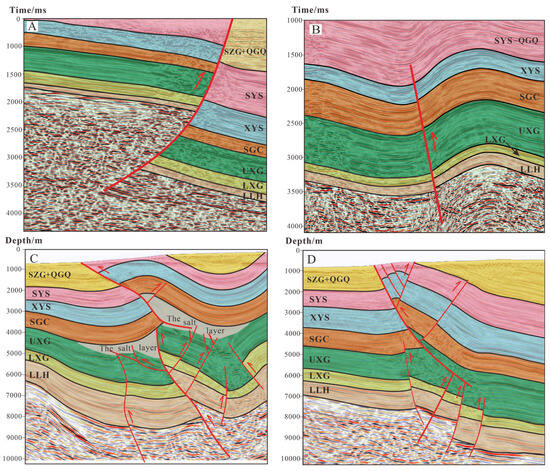
Figure 7.
Seismic profile characteristics. (A) Seismic profile of the Kunbei fault in the Kunbei area; (B) Seismic profile of the XIII fault in the Zhahaquan area; (C) Seismic profile of the Shizigou fault in the Yingxi area; (D) Seismic profile of the Youshashan fault and XI fault in the Yingdong area.
The XIII fault, a deep-seated fault E–W-trending thrust fault, governed the overall tectonic framework of the Zhahaquan area and served as a crucial migration pathway for lithological reservoirs, displaying similar single-fault characteristics in its cross-section (Figure 7B).
The Shizigou and Youshashan faults, developed during Late Cenozoic tectonic activity, have resulted from compressive stresses and the presence of a weak gypsum layer beneath them, leading to detachment deformation and thrust fault characteristics [49]. These two faults controlled the formation of the Yingxi and Yingdong oilfields, both with reserves exceeding 100 million tons. The Shizigou fault displays an antithetic Y-shaped configuration, formed by the main fault and its secondary faults with opposing dip directions (Figure 7C), while the Youshashan fault developed a similar antithetic Y-shaped pattern (Figure 7D).
The XI fault played a crucial role in shaping the tectonic framework of the southwestern Qaidam basin, manifesting as a wedge-shaped intrusion at the termination of the Youshashan fault in seismic profiles, forming a Y-shaped assemblage with associated secondary faults (Figure 7D). The fundamental parameters of these faults are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Structural characteristics of major faults in the southwestern Qaidam Basin.
3.2. Analysis of Fault Activity
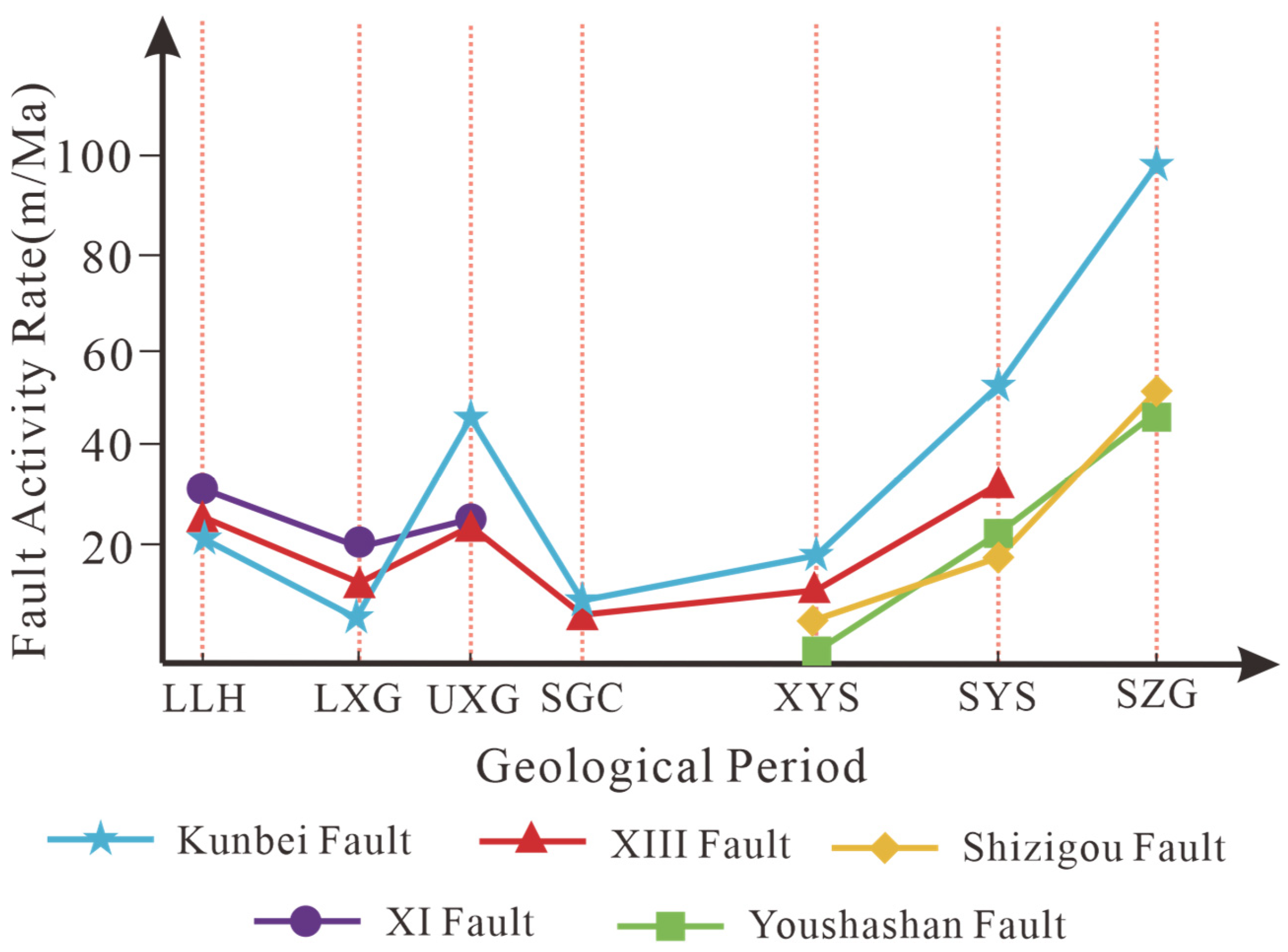
Quantitative statistical results reveal three distinct stages of fault activity in the southwestern Qaidam Basin (Table 3, Figure 8): The first stage initiated during the deposition of the LLH Fm. (65–52 Ma), with activity rates ranging from 21 to 31 m/Ma; The second stage, corresponding to the UXG Fm. (43.8–35.3 Ma), exhibited increased rates of 21–44 m/Ma; The third stage, occurring in the SZG Fm. (8.1–2.8 Ma), reached a peak activity rate of 97.8 m/Ma, driven by the progressively intensifying Himalayan Movement. Based on spatiotemporal evolution characteristics, the faults in the southwestern Qaidam Basin can be classified into three types: the (1) persistent activity type (e.g., Kunbei fault and XIII fault), (2) mid-term termination type (e.g., XI fault), and (3) late-stage activation type (e.g., Shizigou fault and Youshashan fault).

Table 3.
Statistical table of fault throw.
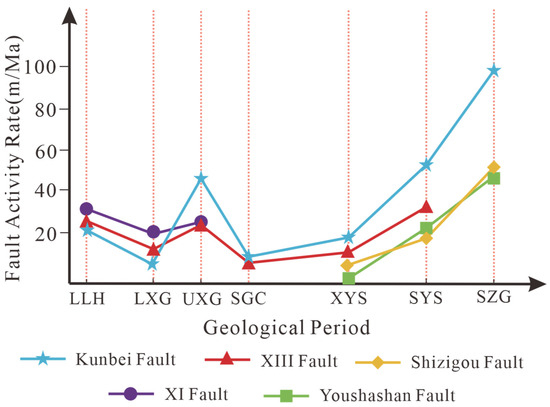
Figure 8.
Statistics of fault activity rates in southwest Qaidam.
Overall, Cenozoic fault activity displays segmented evolutionary patterns, with three phases concentrated in the LLH Fm., UXG Fm., and SZG Fm. Notably, the SZG Fm. stage records peak activity rates exceeding earlier stages by several orders of magnitude.
3.3. Division of Fault Cycles
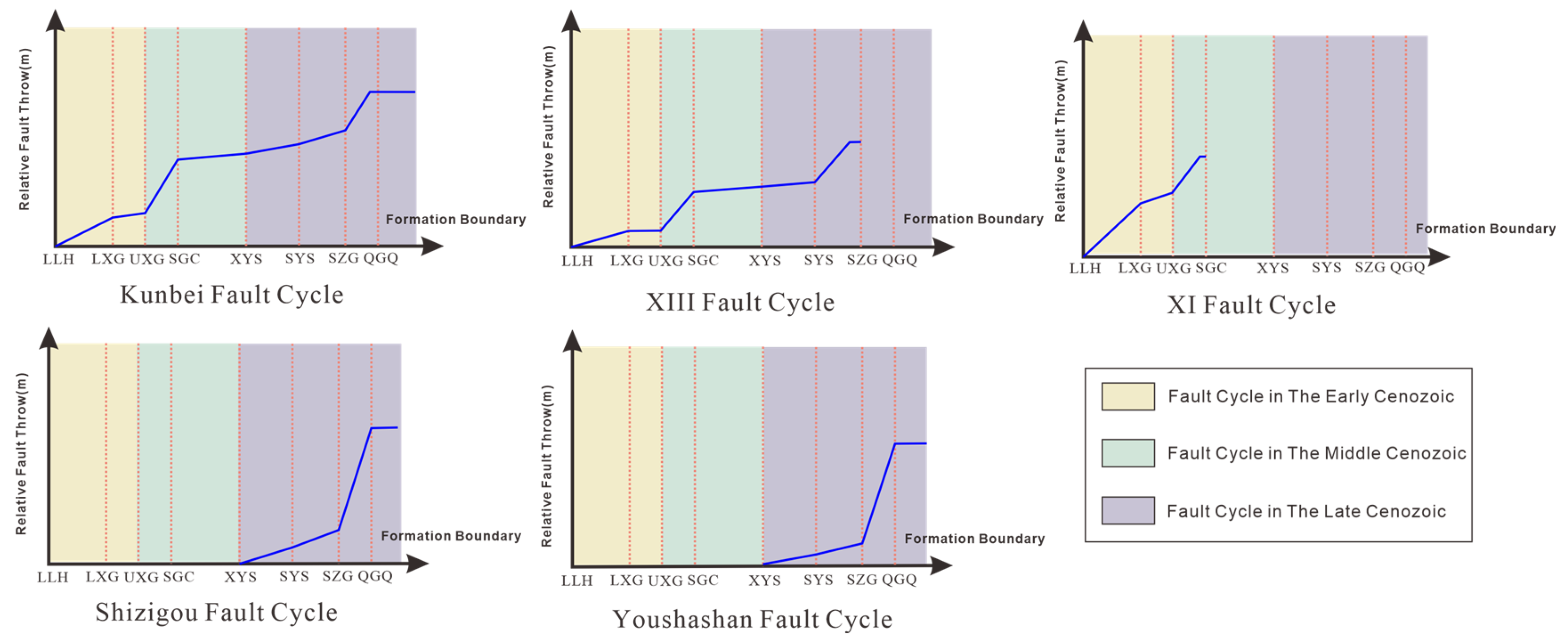
Based on the tectonic evolution and fault activity analysis, the Cenozoic fault cycle in the southwestern Qaidam basin is divided into three stages (Figure 9): the early Cenozoic (65–43.8 Ma), middle Cenozoic (43.8–22 Ma), and late Cenozoic (22 Ma-present). Three distinct fault cycle models are identified: (1) a two-phase fault cycle model for the early to middle Cenozoic (XI fault), (2) a three-phase fault cycle model representing continuous activity from the early to late Cenozoic (Kunbei and XIII faults), and (3) a single-cycle model for late Cenozoic activity (Shizigou and Youshashan faults).
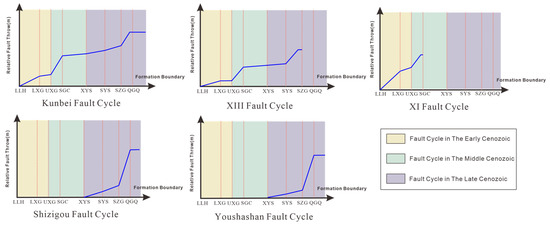
Figure 9.
Fault cycle model classification diagram.
It is worth noting that single-cycle faults are relatively rare in sedimentary basins, with most faults exhibiting multi-cycle superimposed activity patterns.
4. Discussion
4.1. Tectonic Control of Fault Cycle in Southwest Qaidam Basin
The fault cycle in the southwestern Qaidam Basin exhibits synchronous variations with the tectonic stress regime evolution in this region.
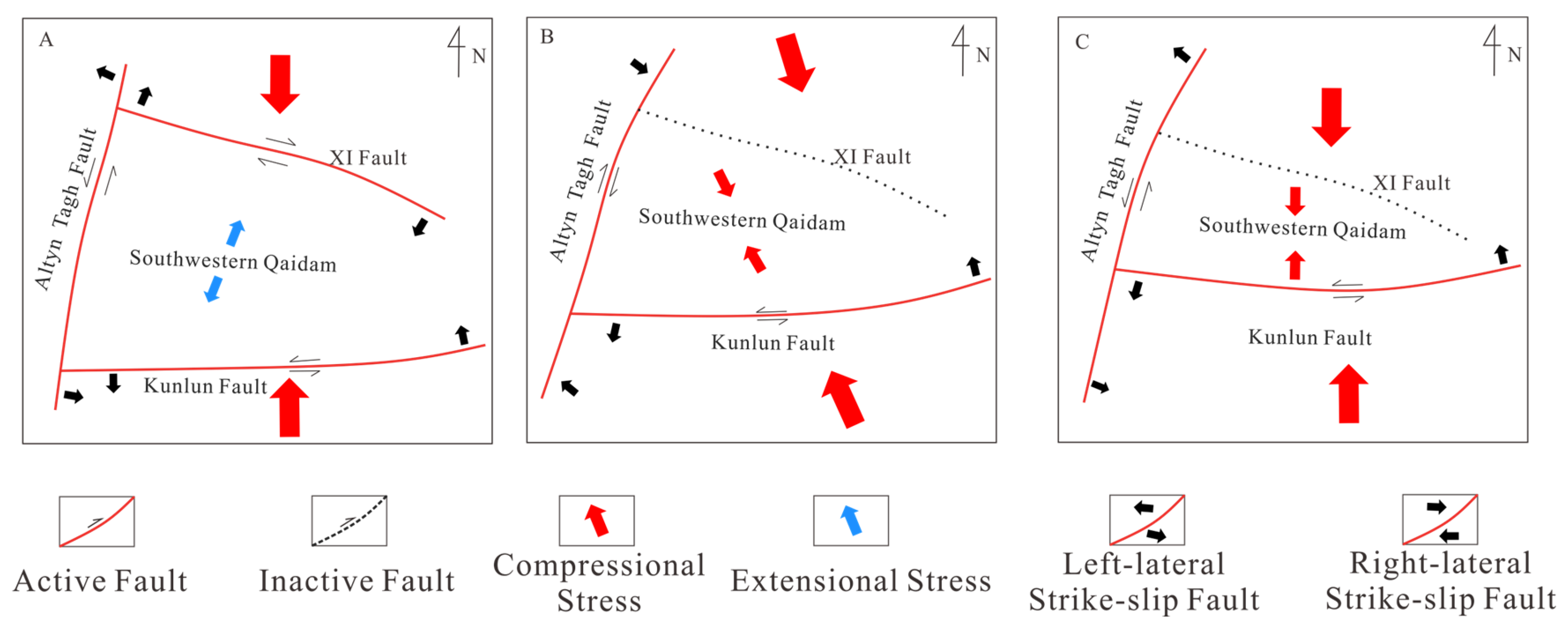
During the Eocene to Early Oligocene period (65–43.8 Ma), the continued northward migration of the Indian Plate triggered subduction and collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates, placing the Tibetan Plateau under a dominantly N–S compressional regime [50]. However, in the southwestern Qaidam Basin, the combined control of structurally heterogeneous faults, including sinistral strike-slip along the Altyn Tagh and East Kunlun faults and dextral strike-slip along the XI fault, facilitated northeastward crustal extrusion and extension (Figure 10A). This tectonic setting corresponds to a strike-slip extensional regime [11,27], during which the first peak of fault activity emerged, with its intensity increasing toward the basin center.
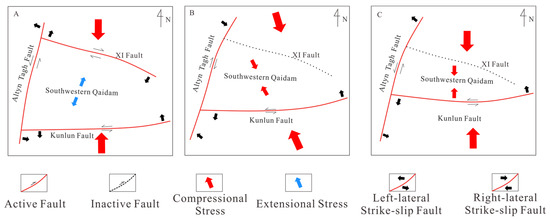
Figure 10.
Schematic diagram of cenozoic tectonic stress field evolution in the southwestern Qaidam basin. (A) Tectonic stress field in the southwestern Qaidam basin (65–48.3 Ma). (B) Tectonic stress field in the southwestern Qaidam basin (48.3–22 Ma). (C) Tectonic stress field in the southwestern Qaidam basin (22 Ma to Present).
During the Late Oligocene to Miocene (43.8–22 Ma), intensified plate collision and northward uplift of the Tibetan Plateau drove a transitional tectonic regime from strike-slip extension to strike-slip compression [51] (Figure 10B). Basin-scale shortening occurred [39], accompanied by a second peak of fault activity. The Kunbei Fault in the basin-margin piedmont zone exhibited higher activity than contemporaneous intra-basin faults, likely linked to the initial uplift of the Kunlun Shan [52,53].
Following the Miocene (After 22 Ma), the tectonic stress field of the Qaidam Basin experienced a fundamental transformation, transitioning to strike-slip-dominated compression (Figure 10C). During this phase, subdued compressional forces resulted in relatively moderate fault activity, with slip rates consistently constrained below 20 m/Ma.
Subsequent to the Late Miocene (After 8.1 Ma), the southwestern Qaidam Basin experienced a third phase of an intense fault cycle, triggered by N–S-oriented compressional stresses. This episode exhibited slip rates an order of magnitude higher than preceding stages, culminating in the formation of late-stage fault systems, including the Shizigou and Youshashan faults.
4.2. Relationship Between Fault Cycle Models and Hydrocarbon Accumulation
Numerous studies have investigated hydrocarbon accumulation events in the southwestern Qaidam Basin (Figure 11) [21,27,40,49,54]. The UXG Fm. saline lacustrine mudstones have been identified as the principal high-quality source rocks governing hydrocarbon generation in the western Qaidam Depression. Cenozoic tectonic intensification in the basin’s southwestern sector facilitated the development of multiple compressional fold structures, comprising early-stage low-amplitude closures (e.g., Qigequan and Yuejin structures) and late-stage structural traps (e.g., Shizigou, Ganchaigou, and Xianshuiquan anticlines). Reservoir fluid inclusion analyses further confirm that two significant oil and gas accumulation events occurred in the southwestern Qaidam region (Figure 12). By correlating fault cycles with hydrocarbon accumulation events in the study area, we find that fault cycles exert distinct and stage-specific control of hydrocarbon migration and accumulation.
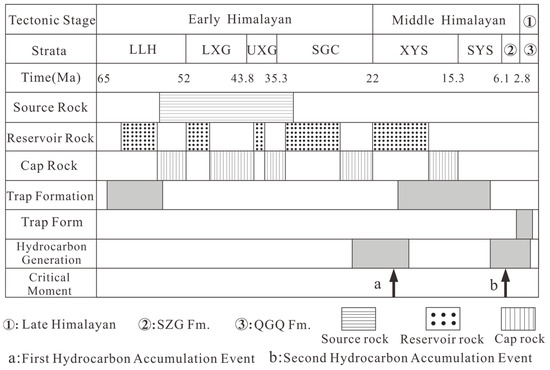
Figure 11.
Hydrocarbon accumulation events in the Southwestern Qaidam basin. Modified from Li [21].
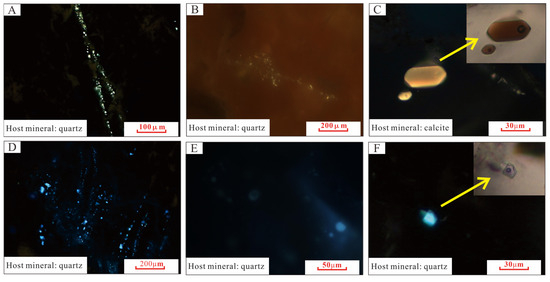
Figure 12.
Analysis of fluid inclusions in the southwestern Qaidam basin (The arrow represents magnification). (A) Well Shi32, 4105.5 m, Yellow fluorescent oil inclusions; (B) Well Zhatan1, 4643.7 m, Hydrocarbon inclusions with a linear distribution exhibit pale yellow fluorescence; (C) Well Shi3-1, 4368 m, Yellow fluorescent oil inclusions; (D) Well Shi32, 4055 m, Blue fluorescent oil inclusions; (E) Well Zha9-3-1, 2400 m, Hydrocarbon inclusions with a planar distribution exhibit blue-white fluorescence; (F) Well Shi41-6-1, 3855 m, Blue fluorescent oil inclusions.
4.2.1. Early Fault Cycle Controls Basin Formation and the Development of Early Traps
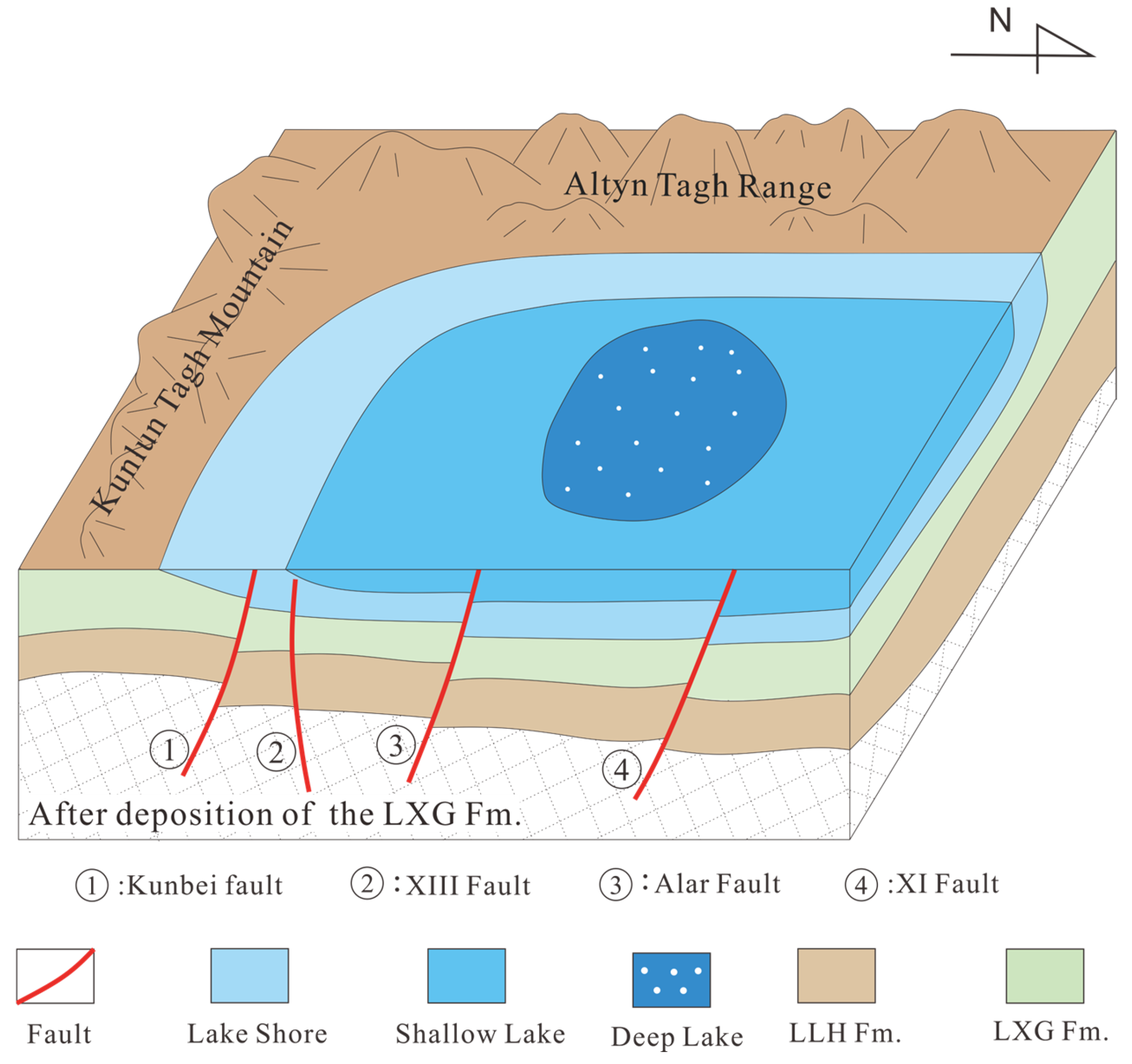
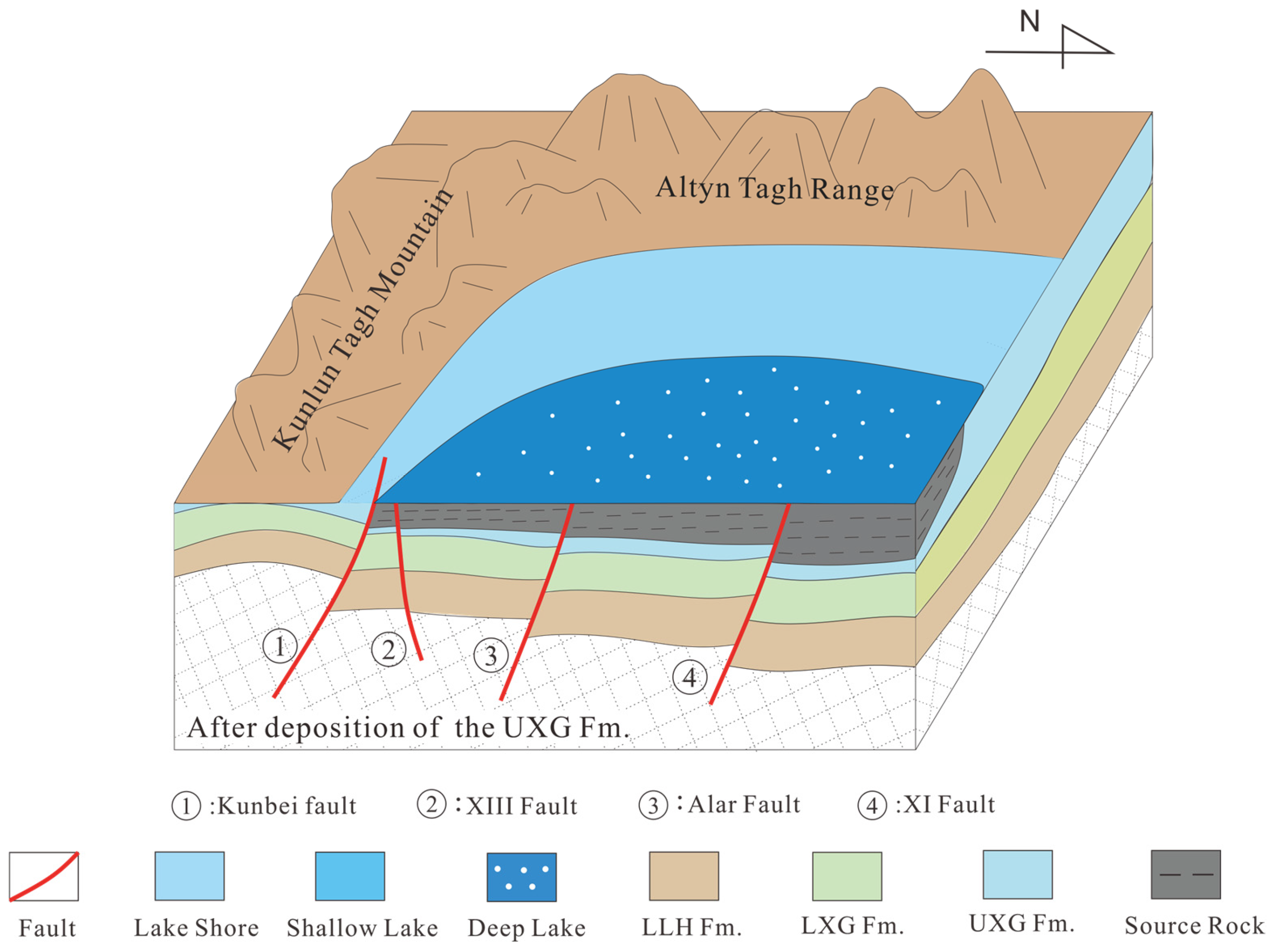
In recent years, significant progress has been made in understanding the Cenozoic evolution of the Qaidam basin, leading to the development of distinct basin evolution models [16,55]. However, increasing evidence suggests that during the early Cenozoic (65–43.8 Ma), the southwestern Qaidam basin may have experienced a phase of weak extension [11,18,27,44,55,56]. Early-activated high-angle faults, such as the Kunbei, XIII, and XI faults, under the influence of regional tectonic stresses, contributed to the formation of a half-graben-like initial basin structure in the southwestern Qaidam basin (Figure 13) [39]. These early faulting cycles also resulted in minor folding and uplift of the strata in the southwestern Qaidam region, causing bending and faulting of the strata near these faults. Consequently, early low-amplitude structural traps were formed within the LLH Fm. and the LXG Fm.
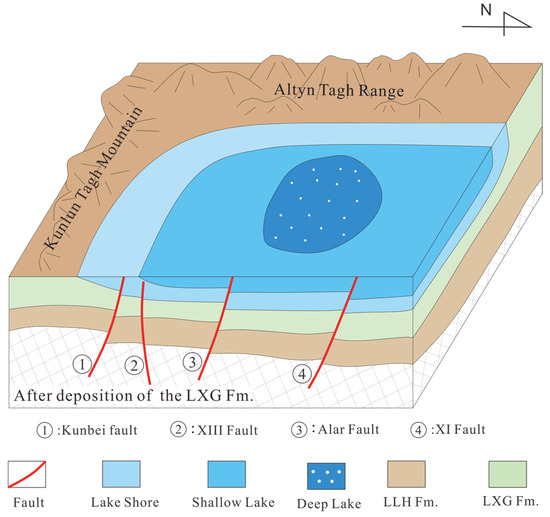
Figure 13.
Schematic diagram of early fault cycle controlling basin formation.
4.2.2. Mid Fault Cycle Controls the Formation and Distribution of High-Quality Source Rocks
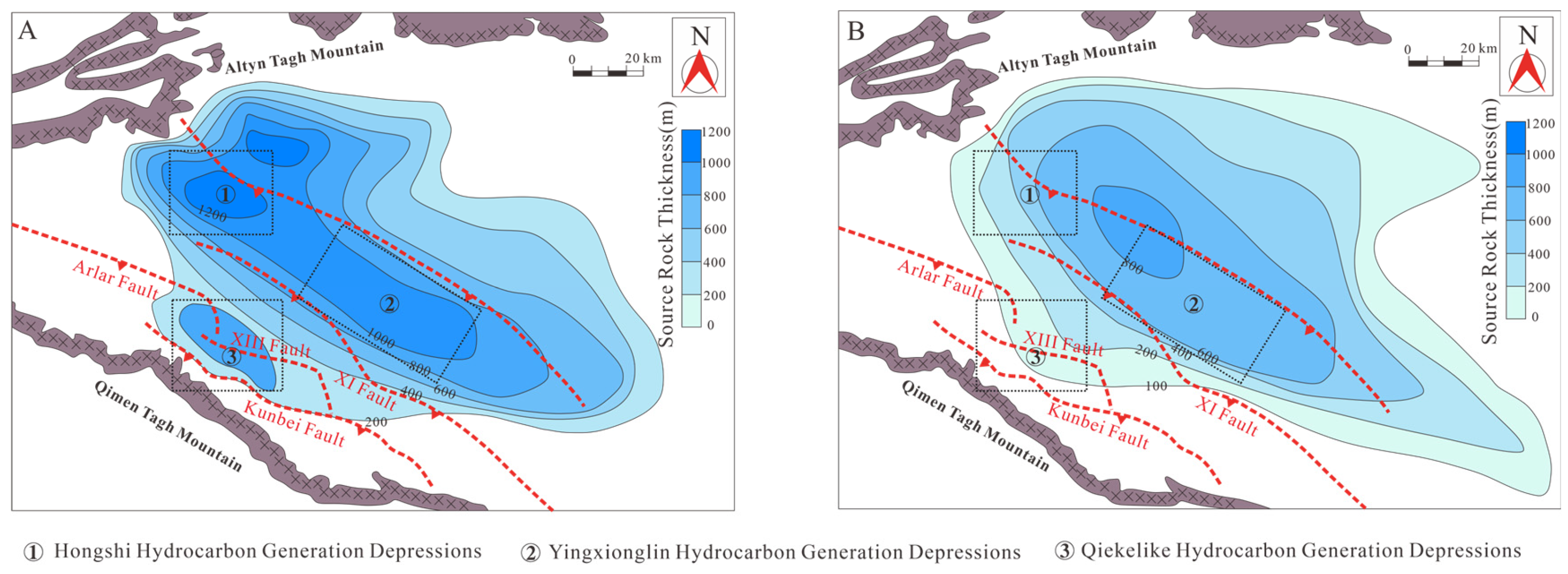
Verified hydrocarbon-generating depressions, including the Hongshi, Yingxiongling, and Qiekelike hydrocarbon generation depressions, exhibit a strong association with fault systems. These depressions are predominantly located along the downthrown sides of major faults [42]. Specifically, the Kunbei fault and XIII fault exert direct control over the formation of the Qiekelike hydrocarbon generation depression, whereas the XI fault governs the development and spatial distribution of the Hongshi and Yingxiongling hydrocarbon generation depressions (Figure 14).
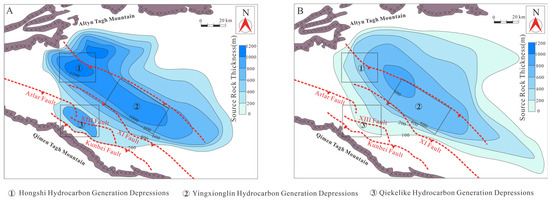
Figure 14.
Thickness distribution of effective source rocks in southwestern Qaidam basin. (A) Sedimentary period of UXG Fm. (B) Sedimentary period of SGC Fm.
The impact of fault cycles on hydrocarbon source rocks in the southwestern Qaidam basin primarily stems from mid-Cenozoic fault activity, which significantly influenced mudstone deposition. Vigorous fault activity induced extensive basin subsidence, particularly peaking during the late Oligocene. This tectonic phase coincided with increased sediment flux [31], facilitating the continuous deposition of thick lacustrine-dark fine-grained mudstones that constitute the primary source rock systems in the southwestern basin (Figure 15).
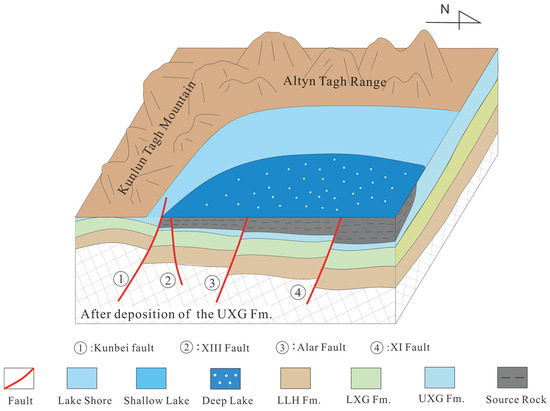
Figure 15.
Schematic diagram of mid fault cycle controlling hydrocarbon source rock deposition.
Fault activity significantly impacts source rock thickness. During the deposition of the UXG Fm. (43.8–35.3 Ma), Kunbei fault, XI fault, and XIII fault, they exhibited normal fault characteristics. Intensive extensional activity amplified stratigraphic displacement between hanging walls and footwalls, thereby increasing the accommodation space favorable for mudstone accumulation. In contrast, reduced fault activity during the SGC Fm. (35.3–22 Ma) diminished displacement magnitudes and accommodation space, resulting in smaller-scale mudstone deposition and, consequently, thinner source rock.
4.2.3. Late Fault Cycle Controls Trap Finalization and Oil–Gas Migration
Numerous structural traps have been identified in the southwestern Qaidam basin, many of which are arranged in linear or clustered patterns along fault zones [51]. This late-stage tectonic activity has not only continued to expand the areas of pre-existing anticline traps, such as those found in the deep structures of Yuejin and Qigequan, but has also generated novel trap configurations, including anticlines, faulted noses, and fault blocks, exemplified by the Youshashan area and shallow traps in Shizigou. These newly formed and expanded traps typically exhibit a NW–SE belt-like distribution pattern [27,56]. By correlating with the formation and stabilization of these traps (Table 4), it is evident that most structural traps in the southwestern Qaidam region were established and stabilized during periods of heightened tectonic activity associated with the later stages of faulting. The late-stage fault cycles demonstrate a critical role in trap genesis and the stabilization of these late-forming structural traps.

Table 4.
The formation and stabilization period of typical structural traps in the southwestern Qaidam basin.
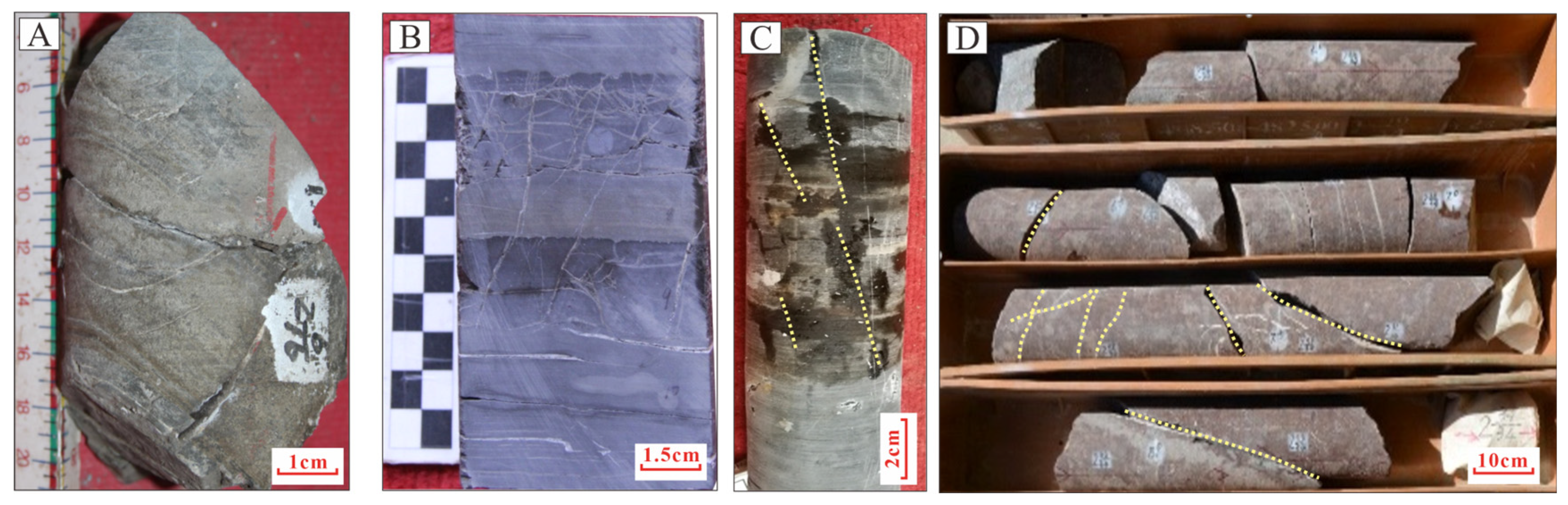
Hydrocarbon migration pathways in the southwestern Qaidam Basin are primarily composed of faults and conductive sand bodies, as evidenced by current drilling data. However, conductive sand bodies exhibit limited influence on hydrocarbon migration due to their restricted lateral continuity, establishing faults as the dominant migration conduits. The Kunbei fault and XIII fault penetrate nearly the entire Cenozoic succession. Later-stage compressional tectonics formed the Shizigou and Youshashan faults, which extend downward into the UXG Fm. These fault systems effectively link deep source rocks with intermediate-to-shallow favorable reservoirs, acting as critical vertical migration pathways. Fault activity also generates tectonic fractures (Figure 16), including vertical opening fractures, horizontal opening fractures, and bedding-parallel slip fractures associated with late-stage reverse faults [18]. These fractures, predominantly clustered near fault zones, enhance pore connectivity and reservoir permeability [19,38]. Hydrocarbon staining within fractures further confirms their role in facilitating fluid migration.
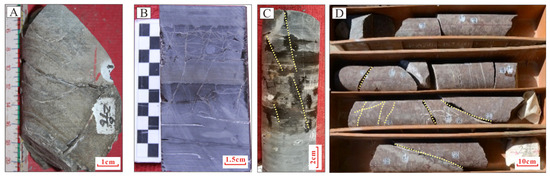
Figure 16.
Fractured core samples from the Qaidam basin (The dashed lines represent cracks). (A) Well Shi38, 3145 m, Oil staining in fractures; (B) Well Shi41-2, 4297 m, high-angle and low-angle fractures; (C) Well Sha35, 2097 m, Oil Traces in Fractures; (D) sWell Jitan1, 4823 m, high-angle and low-angle fractures.
Boiling fluid inclusion evidence in the Qaidam Basin reservoirs indicates pulsed hydrocarbon migration driven by overpressure [51]. Late-stage fault activity induced a sharp increase in fluid potential within the UXG Fm. (source rocks), triggering shallow rock fracturing, seal failure, and volumetric expansion, thereby reducing fluid potential. The resulting fluid potential gradient facilitated rapid hydrocarbon migration from deep high-potential zones to shallow low-potential traps, with hydrocarbons preferentially accumulating in the fault hanging wall.
Temporal correlations between the southwestern Qaidam Basin fault cycle and hydrocarbon charging reveals two distinct phases: During the initial phase (22–18 Ma), weak fault activity and relatively low fluid potential gradients [57] limited vertical migration, confining hydrocarbons near source rocks. The second phase (6.1–5.8 Ma) marked critical reservoir adjustment, coinciding with intensified fault reactivation post–15.3 Ma [22]. Enhanced compressional tectonics generated overpressure-driven hydrocarbon surges, replenishing earlier reservoirs and charging newly formed traps in the Youshashan and Shizigou Formations.
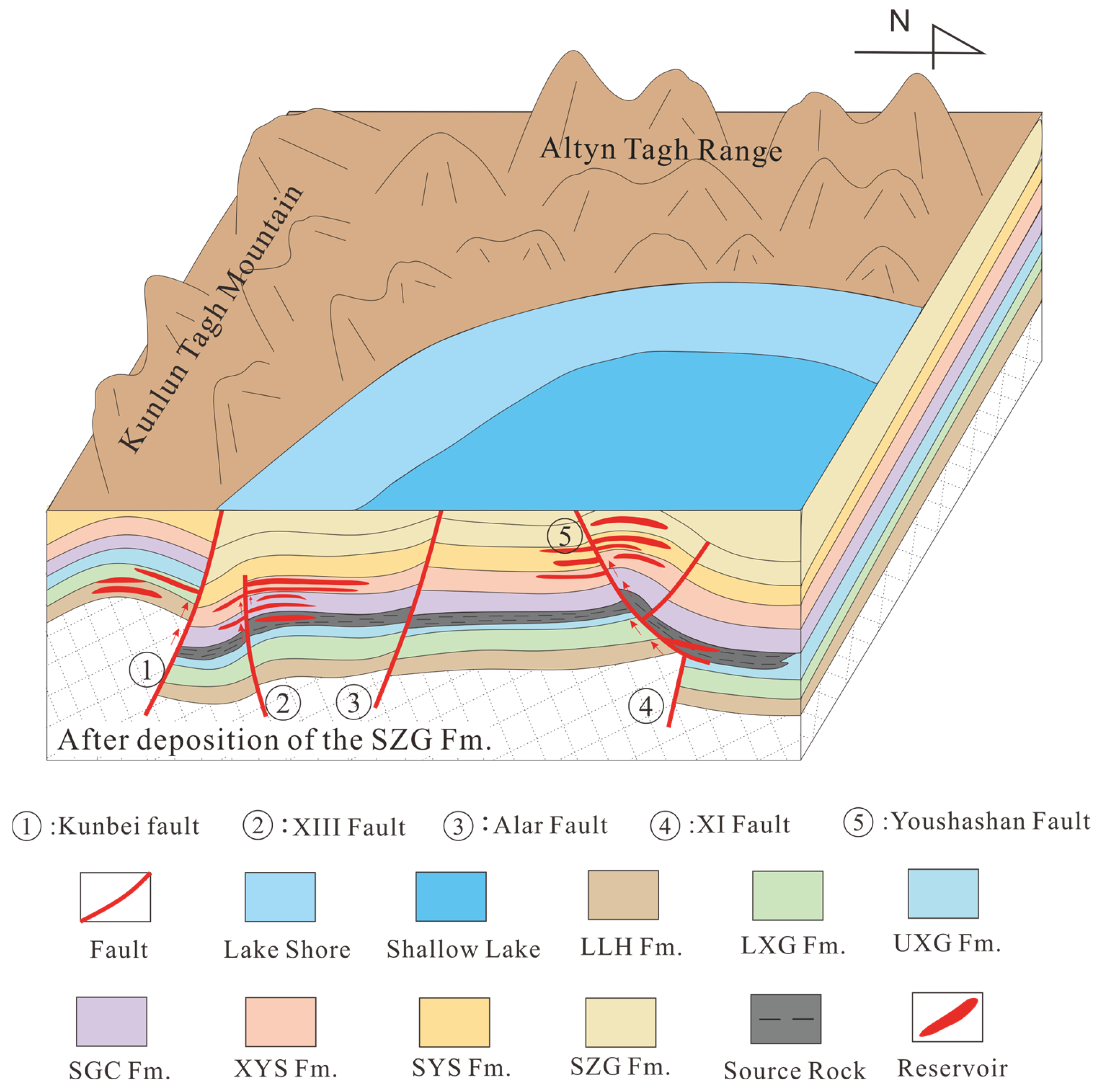
Integrated analysis demonstrates that a late-stage fault cycle governed hydrocarbon accumulation in the southwestern Qaidam Basin, synchronizing with structural trap formation, hydrocarbon generation, and migration histories (Figure 17).
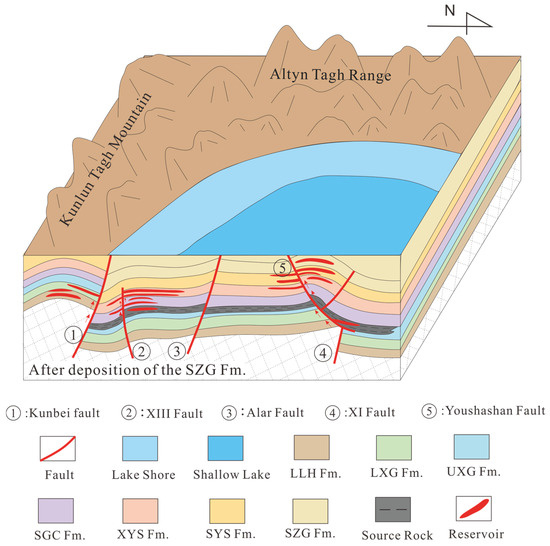
Figure 17.
Schematic diagram of late fault cycle controlling hydrocarbon migration and accumulation.
The conventional fault-controlled hydrocarbon accumulation model typically treats faults as static or long-term stable migration pathways, focusing primarily on the direct influence of fault geometry and sealing capacity on hydrocarbon migration and accumulation, while neglecting the dynamic evolution process of fault activity and its phased control on hydrocarbon accumulation. The fault-cycle-controlled hydrocarbon accumulation model proposed in this study systematically reveals the periodic characteristics of fault activity and its multi-phase control mechanism on hydrocarbon accumulation from a dynamic evolution perspective. This model emphasizes the differential impacts of various fault activity cycle stages on basin tectonic evolution, trap formation, source rock distribution, and hydrocarbon migration, with a particular focus on the dynamic regulatory role of periodic fault activity in hydrocarbon accumulation.
However, this study still has some limitations, particularly regarding the quantitative coupling relationship between fault cycles and hydrocarbon migration dynamics, as well as the differences in migration efficiency between active and quiescent periods. Future research should incorporate numerical simulation and other methods to further deepen the quantitative understanding of hydrocarbon migration under fault cycle influences.
5. Conclusions
This study analyzes the characteristics and activity of the primary reservoir-controlling faults in the southwestern Qaidam basin and investigates the relationship between fault cycles and hydrocarbon accumulation. The following conclusions can be drawn:
- (1)
- Influenced by multi-phase tectonic movements, fault activity in the southwestern Qaidam basin exhibits periodic characteristics, with three distinct periods of intense activity occurring during the LLH Fm., the UXG Fm., and the SZG Fm.
- (2)
- Based on the structural evolution history and fault activity characteristics of the southwestern Qaidam basin, a fault cycle model for this region is established. Fault activity in the southwestern Qaidam basin can be classified into three fault cycle types: early-middle, early-middle-late, and late fault cycles.
- (3)
- The proposed fault-cycle-controlled hydrocarbon accumulation model demonstrates that the dynamic evolution of fault cycles exerts multi-phase control on hydrocarbon accumulation. The early fault cycle primarily controls the basin’s initial morphology and the formation of early traps. The middle fault cycle is crucial for the distribution of high-quality source rocks, while the late fault cycle determines the final configuration of traps and hydrocarbon migration.
This model diverges from traditional static fault analyses by focusing on analyzing fault dynamic activities, thereby providing new insights into hydrocarbon accumulation mechanisms in multi-episodic basins.
Author Contributions
Z.C.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing Original Draft—Review & Editing; Z.L.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision; J.L.: Methodology, Software; F.Z.: Data Curation; Z.F.: Resources, Software; X.M.: Software, Resources. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Third-party data: The availability of these data is restricted. The data were obtained from Qinghai Oilfield Company (PetroChina) and are available from Zhaozhou Chen and Zhen Liu with the permission of Qinghai Oilfield Company (PetroChina).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Fei Zhou was employed by the company PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Suess, E. Das Antlitz der Erde; F. Tempsky: Vienna, Austria, 1909; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.T. A New Class of Faults and their Bearing on Continental Drift. Nature 1965, 207, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.P.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.J. Controls of tectonics on both sedimentary sequences and petroleum systems in Tarim Basin, northwest China. Pet. Sci. 2007, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.X.; Zhang, G.C.; Zhao, Z.G.; Xie, X.X.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, S.L.; Bi, Y.K.; Wang, Y.B. Control of tectonic cycle in South China Sea over hydrocarbon accumulation in the Zengmu Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2016, 21, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Fadul, M.F.; El Dawi, M.G.; Abdel-Fattah, M.I. Seismic interpretation and tectonic regime of Sudanese Rift System: Implications for hydrocarbon exploration in Neem field (Muglad Basin). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 191, 107223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belayouni, H.; Guerrera, F.; Martín-Martín, M.; Tramontana, M.; Bullejos, M. Cenozoic tectono-sedimentary evolution of the onshore-offshore Tunisian Tell: Implications for oil-gas research. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 156, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzocchi, T.; Ringrose, P.S.; Underhill, J.R. Flow through fault systems in high-porosity sandstones. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1998, 127, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.H.; Jin, Z.J. Experimental investigation of episodic oil migration along fault systems. J. Geochem. Explor. 2003, 78–79, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Gao, Z.Q.; Fan, T.L.; Zhang, H.H.; Yuan, Y.X.; Wei, D.; Qi, L.X.; Yun, L.; Karubandika, G.M. Architecture of strike-slip fault zones in the central Tarim Basin and implications for their control on petroleum systems. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 213, 110432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, Y.H.; Chen, C.; Lou, R.; Wang, Q. Fault reactivation in No.4 structural zone and its control on oil and gas accumulation in Nanpu sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2022, 49, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Dai, S.H.; Zhou, Y.J.; Ding, F.F.; Li, M.J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, B.H.; Li, T.; Han, J.N. Fault characteristics and their control on oil and gas accumulation in the southwestern Ordos Basin. Energy Geosci. 2024, 5, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessop, K.; Daczko, N.R.; Piazolo, S. Tectonic cycles of the New England Orogen, eastern Australia: A Review. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 66, 459–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.G.; Wang, X.P. Structural Styles and Stratigraphic Patterns of Syndepositional Faults in a Contractional Setting: Examples from Quaidam Basin, Northwestern China. AAPG Bull. 1993, 77, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Dang, Y.Q.; Zhang, M.; McRivette, M.W.; Burgess, W.P.; Chen, X.H. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Qaidam basin and its surrounding regions (part 2): Wedge tectonics in southern Qaidam basin and the Eastern Kunlun Range. In Special Paper 433: Whence the Mountains? Inquiries into the Evolution of Orogenic Systems: A Volume in Honor of Raymond A. Price; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2007; pp. 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Dang, Y.Q.; Wang, L.C.; Jiang, W.M.; Zhou, S.P.; Chen, X.H.; Gehrels, G.E.; McRivette, M.W. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Qaidam basin and its surrounding regions (Part 1): The southern Qilian Shan-Nan Shan thrust belt and northern Qaidam basin. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2008, 120, 813–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Dang, Y.Q.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.H.; McRivette, M.W. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Qaidam basin and its surrounding regions (part 3): Structural geology, sedimentation, and regional tectonic reconstruction. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2008, 120, 847–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.R.; Fang, X. Cenozoic tectonic development of the Qaidam Basin in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. In Investigations into the Tectonics of the Tibetan Plateau; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.B.; Tang, X.M.; Qi, J.F.; Gong, L.; Yu, F.S.; Wang, T.C. Insight into the Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Qaidam Basin, Northwest China from fracture information. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2012, 101, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xiao, A.C.; Ma, D.D.; Li, H.G.; Xu, B.; Shen, Y.; Mao, L.G. Cenozoic fault systems in southwest Qaidam Basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Geometry, temporal development, and significance for hydrocarbon accumulation. AAPG Bull. 2014, 98, 1213–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, D.W.; Jolivet, M.; Yu, X.J.; Du, W.; Liu, R.C.; Guo, Z.J. Cenozoic structural inversion from transtension to transpression in Yingxiong Range, western Qaidam Basin: New insights into strike-slip superimposition controlled by Altyn Tagh and Eastern Kunlun Faults. Tectonophysics 2018, 723, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zeng, L.B.; Li, W.L.; Zhang, Y.S.; Cai, Z.H. Controls of the Himalayan deformation on hydrocarbon accumulation in the western Qaidam Basin, Northwest China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 174, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Wu, S.T.; Wu, K.Y.; Shen, Y.; Lei, G.; Zhang, B.; Xing, H.T.; Zhang, Q.H.; Li, G.X. Characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation model of Paleogene whole petroleum system in western depression of Qaidam Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.G.; Song, G.Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, S.M.; Wu, Y.X.; Xia, Z.Y.; Shi, Q.; Jia, S.L. Development, sand control mechanism and hydrocarbon accumulation of beach-bar sandstone in a saline lake basin: A case from the Neogene of southwestern Qaidam Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 50, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Tian, J.X.; Zhang, G.Q.; Zhao, J.; Wu, P.; Wang, W. Main types and hydrocarbon exploration direction of the paleo-uplifts in the Qaidam Basin. J. Geomech. 2018, 24, 381–390. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Guo, Z.Q.; Liu, W.H.; Zhang, L.; Tian, J.X.; Zhang, S.S.; Zeng, X. Accumulation mechanism of the Yingdong I field in the Qaidam Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.Q.; Li, Y.X.; Jiang, Z.X. Key geological controls on migration and accumulation for hydrocarbons derived from mature source rocks in Qaidam Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2004, 41, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.T.; Ma, D.D.; Guo, Z.J.; Cheng, F. Strike-slip superimposed Qaidam Basin and its control on oil and gas accumulation, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.D.; Wang, C.S.; Zheng, H.B.; Xiang, F.; Yi, H.S.; Liu, D.Z. Tectonic and sedimentary evolution of basins in the northeast of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and their implication for the northward growth of the Plateau. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 241, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.J.; Yang, Y.C.; Li, J.W.; Yang, C.J.; Dai, T.Y.; Zhao, J.X.; Yi, H.S. Lacustrine tempestite and its geological significance in the Cenozoic study of the Qaidam Basin. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 92, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Liu, J.; Sun, P.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.H.; Zheng, S.J.; Ge, Y. Geochemical features of natural gas in the Qaidam Basin, NW China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 110, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Wang, Y.D.; Song, C.H.; Feng, Y.; Hu, C.H.; Zhong, S.R.; Yang, J.W. Cenozoic sediment flux in the Qaidam Basin, northern Tibetan Plateau, and implications with regional tectonics and climate. Glob. Planet. Change 2017, 155, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.M.; Yang, Z.Y.; Pei, J.L.; Ge, X.H.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, T.S.; Li, W.M.; Yuan, S.H. Magnetostratigraphy of Paleogene sediments from northern Qaidam Basin, China: Implications for tectonic uplift and block rotation in northern Tibetan plateau. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 237, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.M.; Zhang, W.L.; Meng, Q.Q.; Gao, J.P.; Wang, X.M.; King, J.; Song, C.H.; Dai, S.; Miao, Y.F. High-resolution magnetostratigraphy of the Neogene Huaitoutala section in the eastern Qaidam Basin on the NE Tibetan Plateau, Qinghai Province, China and its implication on tectonic uplift of the NE Tibetan Plateau. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 258, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.J.; Xiong, S.F. Magnetostratigraphy of the Dahonggou section, northern Qaidam Basin and its bearing on Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Qilian Shan and Altyn Tagh Fault. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 288, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Appel, E.; Fang, X.M.; Song, C.H.; Cirpka, O. Magnetostratigraphy of deep drilling core SG-1 in the western Qaidam Basin (NE Tibetan Plateau) and its tectonic implications. Quat. Res. 2012, 78, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Ji, J.L.; Zhang, K.X.; Kou, X.H.; Song, B.W.; Wang, C.W. Magnetostratigraphy and Anisotropy of Magnetic Susceptibility of the Lulehe Formation in the Northeastern Qaidam Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2013, 87, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Zhang, D.W.; Yang, S.Y.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.J.; Cui, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.L.; Yi, D.H.; Chang, H.Y. Sedimentary characteristics and genesis of the salt lake with the upper member of the Lower Ganchaigou Formation from Yingxi sag, Qaidam basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 111, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Wang, Q.Q.; Cheng, X.; Feng Cheng Yu, X.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Shen, X.S.; Guo, Z.J. Formation of multi-stage and clustered fractures at 3.6–4.9 km in the Shizigou structure, SW Qaidam basin. J. Struct. Geol. 2023, 169, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Zheng, J.J.; Zhang, W.L.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, X.W.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.H. Cenozoic uplift of the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from the tectonic-sedimentary evolution of the western Qaidam Basin. Geosci. Front. 2012, 3, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Q.; Ma, Y.S.; Liu, W.H.; Wang, L.Q.; Tian, J.X.; Zeng, X.; Ma, F. Main factors controlling the formation of basement hydrocarbon reservoirs in the Qaidam Basin, western China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 149, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.M.; Gao, Z.C.; Li, Y.F.; Wu, F.F.; Wu, J.L.; Wei, G.; Zhang, X.; Gong, H.J.; et al. Effective Reservoir Identification and Controlling Factor Analysis for Mixed Sediments in Saline Lacustrine Basin, Shizigou Area, Qiadam Basin, China. In Proceedings of the AAPG ACE 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 20–23 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.H.; Liu, C.L.; Tian, J.X.; Ran, Y.; Awan, R.S.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, J.K.; Zang, Q.B. Natural Gas Genesis, Source and Accumulation Processes in Northwestern Qaidam Basin, China, Revealed by Integrated 3D Basin Modeling and Geochemical Research. Nat. Resour. Res. 2023, 32, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.S.; Song, G.Y.; Li, S.M.; Long, G.H.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Gong, Q.S.; Xia, Z.Y. Mixed carbonate rocks lithofacies features and reservoirs controlling mechanisms in a saline lacustrine basin in Yingxi area, Qaidam Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.C.; Zhang, N.; Yuan, X.P.; Fan, L.S.; Zhang, B.S. Cenozoic Qaidam basin, China: A stronger tectonic inversed, extensional rifted basin. AAPG Bull. 2001, 85, 715–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Guo, Z.Q.; He, W.Y.; Liu, W.B. Restoration of Eroded Thickness of the Neogene Strata in the Western Qaidam Basin and Its Significance for Oil and Gas Occurrence. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2017, 91, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoso, D.G.C.; Kuchenbecker, M.; Magalhães, A.J.C.; Scherer, C.M.D.S.; Gabaglia, G.P.R.; Strasser, A. Cyclicity in Earth sciences, quo vadis? Essay on cycle concepts in geological thinking and their historical influence on stratigraphic practices. Hist. Geo Space Sci. 2022, 13, 39–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuza, A.V.; Yin, A. Continental deformation accommodated by non-rigid passive bookshelf faulting: An example from the Cenozoic tectonic development of northern Tibet. Tectonophysics 2016, 677, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.S.; Xiao, A.C.; Lin, X.B.; Wang, L.Q.; Chen, H.L. Structural coupling between the Qiman Tagh and the Qaidam Basin, Northern Tibetan Plateau: A perspective from the Yingxiong range by integrating field mapping, seismic imaging, and analogue modeling. Tectonics 2020, 39, e2020TC006287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.D.; Chen, Y.; Xia, X.M.; Wei, X.B.; Wu, Y.X.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. Reservoir formation conditions and key exploration & development technoloiges in the Yingdong Oilfield in western Qaidam Basin. Pet. Res. 2018, 3, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Y.; Xiao, A.C.; Wu, L.; Mao, L.G.; Zhao, H.F.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.Q. Temporal and spatial patterns of Cenozoic deformation across the Qaidam Basin, Northern Tibetan Plateau. Terra Nova 2016, 28, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Tian, J.X.; Wang, B.; Zhou, F.; Wang, C.X.; Cui, H.D.; Zhu, H.H. Cenozoic structural characteristics and petroleum geological significance of the Qaidam Basin. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2023, 41, 879–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, M.; Brunel, M.; Seward, D.; Xu, Z.; Yang, J.; Roger, F.; Tapponnier, P.; Malavieille, J.; Arnaud, N.; Wu, C. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonics of the northern edge of the Tibetan plateau: Fission-track constraints. Tectonophysics 2001, 343, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.K.; Farley, K.A.; Zheng, D.W.; Wang, Z.C.; Duvall, A.R. Early Cenozoic faulting of the northern Tibetan Plateau margin from apatite (U–Th)/He ages. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 296, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhuo, Q.; Lu, X.; Liu, H. Controlling Factors of Hydrocarbon Accumulation and Differential Distribution in the Western Qaidam Basin, Tibet Plateau. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2022, 69, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Marc, J.; Guo, Z.J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.H.; Li, X.Z. Cenozoic evolution of the Qaidam basin and implications for the growth of the northern Tibetan plateau: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 220, 103730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.B.; Tang, X.M.; Wang, T.C.; Gong, L. The influence of fracture cements in tight Paleogene saline lacustrine carbonate reservoirs, western Qaidam Basin, northwest China. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.Z.; Liu, C.L.; Li, P.; Tian, J.X.; Awan, R.S.; Li, H.P.; Feng, D.H.; Wu, Y.P.; Li, G.X.; Zang, Q.B. Distribution, origin and evolution of overpressure in the Paleogene and Neogene in the Western Qaidam Basin, northwestern China. Geol. J. 2024, 59, 2225–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).