Abstract
In this article, both numerical and experimental investigations were carried out on the durability of hemp concrete. For this, an accelerated aging process was performed using cycles of immersion, freezing and drying. Then, an experimental campaign was enabled to determine heat and mass transfer properties, as well as the microstructure for both aged and reference materials. Observations using a digital microscope showed the appearance of cracks at the interfaces and an increase of the porosity of about 6%. These microstructural modifications imply a non-negligible evolution of heat and mass transfer properties. Thus, a numerical model for the prediction of heat and mass transfer was developed. The prediction of physical phenomena was computed using both aged and reference material properties. It highlights the aging effects on the behaviour of the hemp concrete. The numerical simulation results showed significant discrepancies between the predicted relative humidity values for the two configurations (aged and reference) of about 18% and a maximum phase shift of 40 min, due to the amplification of the mass transfer kinetics after aging. Nevertheless, few deviations in temperature values were found. Thus, after aging, sensible heat fluxes were overestimated compared to the reference case, unlike latent heat fluxes, where an underestimation was shown.
1. Introduction
Climate change has been observed over recent decades. This phenomenon is related to gas emissions, particularly those from the building sector. Several regulations have been proposed to reduce the environmental impact of construction, by increasing building energy efficiency [1,2,3]. In France, the thermal regulations (RT2012 and RE2020) prescribe the construction of building envelopes with low air tightness [4]. As a consequence, the moisture content in indoor climates increases, which can lead to moisture disorders such as mould growth [5,6] or low air quality [7].
To avoid these disorders, the choice of construction material is essential. Among the available materials, the hygroscopic and bio-based ones [8,9,10,11,12,13], such as hemp concrete, have interesting advantages from an energetic and environmental point of view [14]. Indeed, this new, low energy-consuming material is mainly formulated from biomass (animal or vegetal). It constitutes an essential solution to reducing the environmental impact, by absorbing CO2, and the energetic impact, due to its promising thermal and hygric properties [8,9,13], which, consequently, ensures better comfort inside the living environment. Thus, several studies have been carried out to investigate the behaviour of such material, regarding heat and mass transfer [8,15]. Recent studies have been aimed at integrating the hysteresis effects on the moisture content, to accurately predict the hygrothermal behaviour of hemp concrete [16,17,18,19]. More precisely [17,18], results showed that the predictions are very sensitive to the model input parameters, such as the moisture capacity, main adsorption and desorption curves, and the vapour diffusion resistance factor. In [13], it was also demonstrated that the reliability of the model depends on the microstructure of the hemp concrete. The morphological variations (due to swelling and shrinking) impact the structure of the material. Therefore, the hygrothermal behaviour of the material is strongly influenced by these phenomena [10,20,21]. Additional studies highlighted, through experimental campaigns, the aging and time evolution of the material’s thermophysical and microstructural properties [22,23,24].
Thus, there is a strong relation between the aging phenomena of the material, the modification of the material properties and the heat and mass transfer in the materials. Few experimental studies have investigated the effect of aging on the heat and mass transfer properties of hemp concrete. In addition, no numerical investigations have taken account of this effect on the predictions of the model. The objectives of this article are twofold. First, the aging effects were investigated using an experimental campaign to estimate the modification of the material properties. Then, a numerical model was developed to analyse the prediction of the physical phenomena considering aged and reference material properties.
2. Basis of the Model
The modelling of coupled heat, air and moisture transfers in the building envelope is based on the establishment of the mass and energy conservation equations. In this case, these equations are defined as a function of the transfer potentials that overcome the problems of discontinuity encountered during the study of multilayer envelopes, namely: temperature and vapour pressure. The main assumptions are summarised below:
- The different phases are in thermodynamic equilibrium at any point of the porous medium;
- The solid medium is homogeneous, isotropic, non-deformable and unreactive;
- Heat transfer by radiation is negligible compared to the other modes;
- The liquid phase consists of pure water;
- The gaseous phase obeys the law of perfect gases, consisting of water vapour and dry air;
- The hysteresis and chemical reaction between phases are not considered;
- The evolution of the water content, as a function of temperature, is neglected;
- The evolution of the thermal conductivity, as a function of temperature and humidity, is neglected;
- The transfer due to gravity is negligible compared to the other modes;
- The total pressure is considered to be constant.
2.1. Mass Conservation Equations
Moisture mass and energy balances are given by the following equations:
where is the phase change rate, is the flux density of the liquid and vapour phase, respectively, is the heat flux density, is the heat capacity of the material, is the water content (l: liquid and v: vapour) and is the dry density.
2.1.1. Liquid Transfer
In the case of partially saturated porous materials, mass transfer mainly occurs in two forms simultaneously: liquid and vapour transfer. For clarity, each phase is treated separately. Transfer of the liquid phase is governed by a capillary pressure gradient obtained by the application of Darcy’s law. The mass flux density of the liquid phase is then expressed by Equation (4):
Since a local equilibrium between the gaseous and liquid phases has been assumed, Kelvin’s law is, therefore, applicable. This law is used to express the capillary pressure gradient as a combination of vapour pressure and temperature gradient and is given by Equation (5):
As the saturating vapour pressure depends on temperature, the temperature gradient appears in the term , in addition to the vapour pressure gradient, as shown in Equation (6):
where is the capillary pressure, [J/(mol·K)] is the gas constant, is the relative humidity, [K] is the temperature, [Pa] is the water vapour pressure, [Kg/mol] the water molar mass, [Kg/m3] is the water density and [Kg/(m·s·Pa)] is the hydraulic conductivity.
By introducing Equation (6) into Equation (4):
In order to simplify this:
where is the coefficient of liquid phase transfer, governed by a water vapour pressure gradient, and is the coefficient of liquid phase governed by a temperature gradient.
2.1.2. Vapour Transfer
The transfer of the vapour phase is a diffusive process under a vapour pressure gradient, governed by Fick’s law. The mass vapour flux density is given by Equation (9):
where [kg/(m².s)] is the vapour mass flux density and [kg/(m·s·Pa)] is the water vapour permeability.
Finally, by adding Equations (1) and (2) and introducing the global moisture flux ( obtained after the additivity of the liquid and vapour mass fluxes, the mass balance equation becomes:
where is the moisture storage capacity of the material.
2.1.3. Energy Transfer
In partially saturated porous media, heat transfer occurs in three forms: conduction (expressed by Fourier’s law), convection through liquid and vapour fluxes, and the transfer of latent heat due to phase changes. The density of the heat flux is expressed as follows [25]:
where
From Equation (12), the density of the heat flow becomes:
where is the latent heat of evaporation, are the mass enthalpies of liquid and vapour water, respectively, is the mass heat capacity, is the reference temperature and is the thermal conductivity of the material.
By introducing the expressions of liquid (8) and vapour (9) flux densities into the relationship (13), the heat flux density becomes:
Finally, introducing Equation (14) into the energy conservation balance equation gives:
where is the coefficient of heat transfer by conduction, due to temperature gradient which is the coefficient of heat transfer by convection due to the vapour pressure gradient.
Finally, the EDP system translating the hygrothermal behaviour prediction model is as follows:
Boundary conditions are of great importance in numerical simulation, in order to have a more accurate prediction close to realistic cases in terms of air flow at the material boundary. In this case, the boundary conditions chosen were of the imposed flow type. The heat flux (q) and the mass flux (g) are evaluated at the air/material interfaces as follows [26]:
where is the convective heat transfer coefficient, is the convective mass transfer coefficient calculated by the Lewis method, and is the vapour diffusion resistance, expressed in (m). The latter expresses the thickness of air of the same resistance as the material. is the thickness of the studied sample, and is the water vapour diffusion resistance factor.
2.2. Model Validation
To be able to use the developed model in a faithful way, it is essential to carry out a validation of the model based either on a comparison of the numerical results with experimental results, or with an analytical solution. In this case, the validation consisted of comparing the numerical simulation results obtained by the developed model with other reference results defined in the European standard EN 15026 (AFNOR 2008). The test proposed by the standard consists of studying a very thick homogeneous material (20 m semi-infinite wall) and reproducing the temperature and water content profiles after 7, 30 and 365 days. The initial and boundary conditions adopted are of the Dirichlet type and are given in Figure 1:
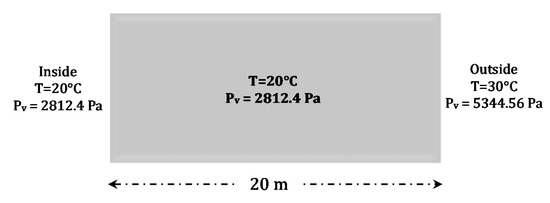
Figure 1.
Initial and boundary conditions of the model.
The input parameters for this material are summarised below (EN 15026).
The thermal conductivity as a function of water content is given by Equation (19):
The hydraulic conductivity is also given as a function of water content as follows:
Concerning water vapour permeability, it is given by the following expression:
The adsorption isotherm and the moisture storage capacity are given by the expressions (22) and (23), respectively:
Given the complexity and the strongly coupled nature of the partial differential equations describing the phenomena of heat, air and moisture transfer, the resolution was carried out by the finite element method, using the Comsol Multiphysics simulation environment. This software is a powerful simulation code for solving a variety of research and engineering problems, including the treatment of multiphysical problems where several phenomena are involved simultaneously, such as the coupled transfer of heat and moisture. The temperature and water content profiles obtained by the developed model have been compared with those of the literature (EN 15026 standard). The results are presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
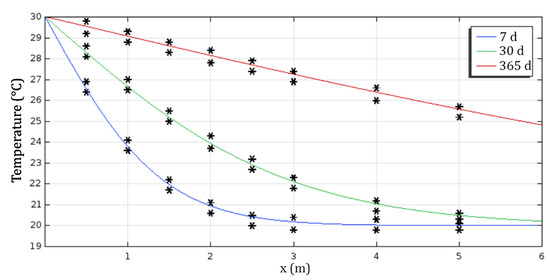
Figure 2.
Comparison of the temperature profiles obtained numerically (continuous lines) with those of the EN 15026 standard (asterisks).
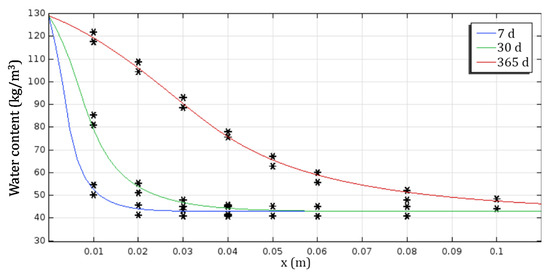
Figure 3.
Comparison of the water content profiles obtained numerically (continuous lines) with those of the EN 15026 standard (asterisks).
These results clearly show that the developed model allows perfect reproduction of the temperature and water content profiles proposed by the EN 15026 standard, with good accuracy. In addition, satisfying the standard result means that the numerical results correspond to the standard results with a tolerance of 2.5%.
Based on these results, it can be concluded that, on the one hand, the proposed model is able to finely predict the hygrothermal behaviour of this type of material proposed by the standard and, on the other hand, that the Comsol Multiphysics environment is reliable and can be used for future simulations. The model developed and implemented in Comsol was then used to numerically study the effect of material ageing on its hygrothermal behaviour.
3. Materials and Methods
The material considered in this study is hemp concrete. It comprises hemp shives with air lime and hydraulic binders and has been elaborated in the laboratory according to professional recommendations (see Table 1). After formulation, samples were conserved in their moulds for four days, in a climate chamber at a temperature of 20 °C and a relative humidity of 50%. Then, the moulds were disassembled to allow drying of the samples. From this moment on, mass monitoring was carried out for a period of 24 h, in order to obtain the drying kinetics. Investigations were started after sample mass stabilisation, which corresponds to a mass variation of less than 0.1%.

Table 1.
Standard proportion of lime binder, hemp shives and water, by mass, for concrete.
The aim of the experimental campaign was to obtain the model input parameters of aged and reference materials. Thus, the importance of aging phenomena on the prediction of the physical phenomena was investigated. It is important to underline the fact that the type of accelerated aging that needs to be chosen mainly depends on the climatic conditions of the city where the material is to be used. For example, for regions with a mild climate, such as coastal zones, less-severe accelerated aging was chosen. This protocol consists in applying a succession of humidification and drying cycles at 85% and 20% relative humidity, respectively. The temperature was kept constant at 30 °C and the duration of the test was 8 months. Despite the long duration of this type of aging, we did not observe significant changes in the properties of the material after aging. These results are in line with the literature where authors have concluded that microstructural changes are not sufficient to lead to modifications in material properties during the first months of aging [27,28].
However, for harsh climates, where the climatic conditions are variable (e.g., Canada), another type of accelerated aging was used in the laboratory to characterise the extreme degradation case of these materials. The latter consisted of applying successive 48 h wetting cycles, followed by a freezing phase at −18 °C, over 24 h. It ended with drying in a climatic chamber at 50 °C, for 72 h. As illustrated in Figure 4, the entire design lasted 42 days. This protocol reflects the extreme degradation that hemp concrete can undergo after several years of use under harsh conditions.
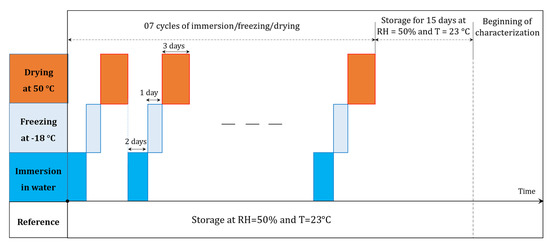
Figure 4.
Accelerated aging protocol (immersion/freezing/drying).
Other samples, denoted as reference materials, were stored in a climatic chamber at T = 23 °C and RH = 50%. At the end of the aging process, the samples were stored in this chamber so that all materials (aged and reference) had the same thermal and mass equilibrium state before characterisation.
Concerning the characterisation procedure, the specific heat capacity was measured by using the Calorimeter Calvet® device, which is based on a static measurement method. The thermal conductivity was characterised by the λ-Meter Ep500e® device, based on the guarded hot-plate method according to the standards EN 12667 [29] and EN 12664 [30]. The adsorption isotherm curves were evaluated according to a gravimetric experimental approach, using the ProUmid device. The moisture storage capacity (Cm) was deduced directly from the slope of the water sorption isotherm curve. Finally, the water vapour permeability was measured by using the Gravitest® device, which is based on the cup method according to the standard NF-EN-12572 [31]. More information on the characterisation methods can be found in these studies [9,12,32].
The results of the characterisation of aged and reference materials are presented in Table 2. The sorption curves and moisture capacity of both materials are given in Figure 5a,b. The material properties correspond to the model inputs. As noted in Table 2, the results highlight the impact of aging on the material properties. Modifications of the microstructure have been observed. An increase of 6% of the total porosity was noted after aging. Indeed, the hygrothermal variations that occurred during the aging process led to swelling and shrinking of the hemp shives. Furthermore, the freezing cycles modified the morphology of the material. As a consequence, remarkable differences between the macroscopic properties were observed.

Table 2.
Aged and reference properties used to feed the numerical model.
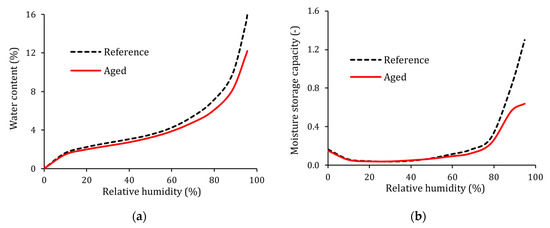
Figure 5.
(a) Adsorption isotherm and (b) moisture storage capacity of aged and reference hemp concrete.
The water vapour adsorption isotherms and moisture storage capacities of aged and reference hemp concrete are shown in Figure 5a,b, respectively.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Aging Effects on the Prediction of Heat and Mass Transfer in Hemp Concrete
Using the properties for both the aged and reference materials, the predictions for heat and mass transfer were computed using the model presented in Section 2. Two configurations were considered, isothermal and non-isothermal, inspired by the Nordtest protocol [33,34].
4.1.1. Isothermal Case
The isothermal case is illustrated in Figure 6. The temperature was set as a constant while the relative humidity varied with time. A sample of 20 cm of hemp concrete was submitted to a moisture flux on one face for 72 h. The other material faces were assumed to be adiabatic and impermeable, to ensure a unidirectional transfer. The total pressure was assumed to be constant in this case. The initial and boundary conditions are given in Figure 6.
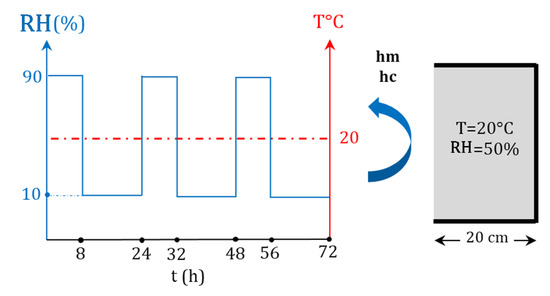
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram showing the climatic conditions applied in the isothermal case.
The relative humidity profile for both materials is presented in Figure 7. Based on the results, the hygrothermal behaviour of the aged material is different from the reference one. Discrepancies of 12% and 9% are observed at t = 1100 min and t = 1430 min, respectively. Those differences are probably related to the modification of the microstructure and material properties of the aged material, as shown in Figure 8.
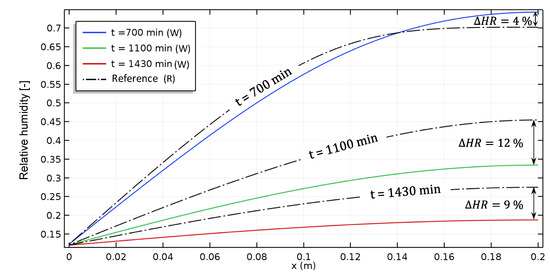
Figure 7.
Isothermal case: Relative humidity profiles of aged (W) and reference (R) hemp concrete: (discontinuous line: reference material and continuous line: aged material).

Figure 8.
Photograph showing the effect of aging on the microstructure of hemp concrete: (a) reference hemp concrete; (b) aged hemp concrete.
Indeed, the modification of the microstructure of hemp concrete after aging implies changes in the total porosity and pore size distribution, which modifies the physical parameters related to transfers within the material. As a result, significant changes in the hygric and thermal properties of the material have occurred (Figure 5, Figure 8, and Table 2), hence the discrepancies observed.
Furthermore, the kinetics of mass transfer are faster in the aged material. As can be seen in Figure 9, during the humidification process, the relative humidity in the aged material is higher than the reference one. The amplitude is also higher. However, during the drying phase, the relative humidity becomes lower and reaches the defined boundary condition faster. In addition, a small offset in the dynamics was also noticed between the two materials. The maximal offset reached 24 min. This faster kinetic is due to the increase of the vapour permeability of the aged material, leading to a reduction of the vapour diffusion resistance.
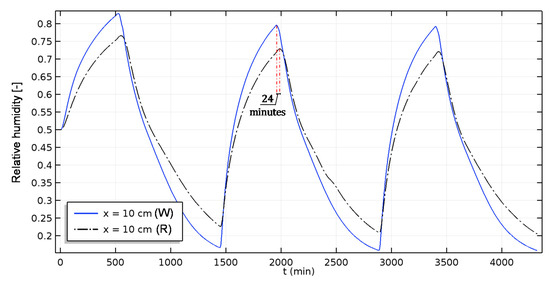
Figure 9.
Isothermal case: Evolution of the relative humidity of aged and reference hemp concrete (W: Weathered; R: Reference).
The temperature evolution of both materials is given in Figure 10. The difference in the predictions is very small. Indeed, the boundary conditions consider a constant time temperature. The temperature variations in the materials are mainly due to the coupling effects through the latent heat transfer. The small discrepancies observed arise from the difference in the vapour permeability for both materials.
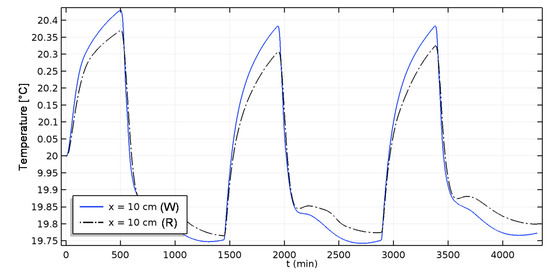
Figure 10.
Isothermal case: Temperature evolution of aged and reference hemp concrete (W: Weathered; R: Reference).
4.1.2. Non-Isothermal Case
For this second case study, the material was submitted to time-varying boundary conditions, as shown in Figure 11. The sample was exposed to an increase of both temperature and relative humidity at 80% and 20 °C for 8 h. Then, after 16 h, the temperature and relative humidity decreased to 0.1 and 5 °C, respectively. The initial conditions were 20 °C and RH = 0.5.
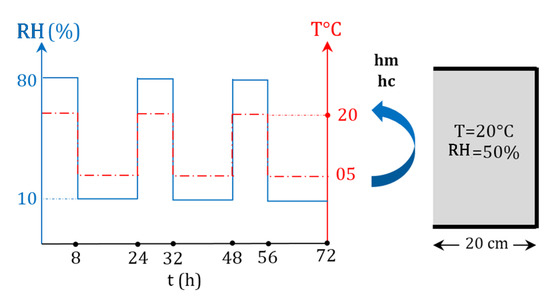
Figure 11.
Dynamic climatic conditions applied in the non-isothermal case.
Figure 12 and Figure 13 give the time and space variation of temperature in both aged and reference materials. The difference between both predictions is less than 1 °C.
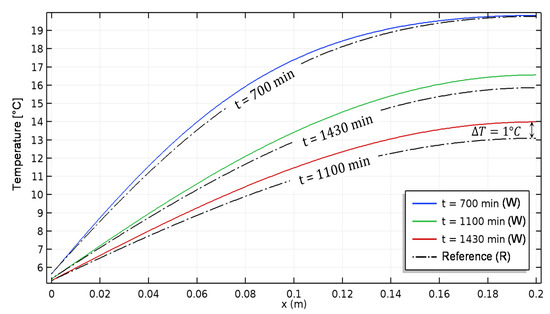
Figure 12.
Non-isothermal case: Temperature profiles of aged and reference hemp concrete (W: Weathered; R: Reference).
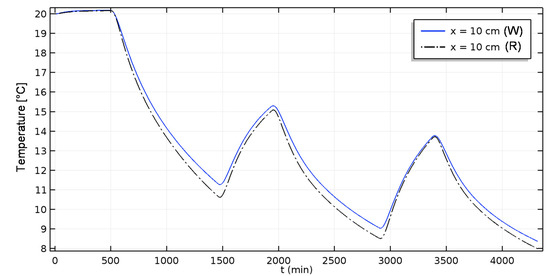
Figure 13.
Non-isothermal case: Temperature evolution of aged and reference hemp concrete over time (W: Weathered; R: Reference).
However, during the drying process, the heat transfer occurs faster in the aged material, due to a diminution of its thermal conductivity. During the humidification, the predictions almost overlapped between the two materials. During this phase, the mass transfer influences heat transfer through latent phenomena. Since the aged material has higher vapour permeability, there is probably compensation between sensible and latent heat flux.
Figure 14 shows the profiles of relative humidity in both materials. The difference reaches 18% at t = 1430 min. As for the previous isothermal case, faster mass transfer occurs in the aged material due to higher vapour permeability.
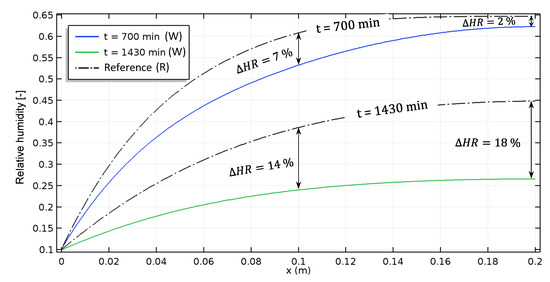
Figure 14.
Non-isothermal case: Relative humidity profiles of aged and reference hemp concrete (W: Weathered; R: Reference).
In Figure 15, an offset of 40 min can be observed in the dynamic mass transfer. This difference in the kinetics of mass transfer leads to non-negligible discrepancies in the prediction of the physical phenomena. Moreover, those discrepancies are higher for this case than for the non-isothermal one. Indeed, the model considers the effect of mass transfer under temperature gradient: the so-called “thermo-diffusion effect” [35,36,37].
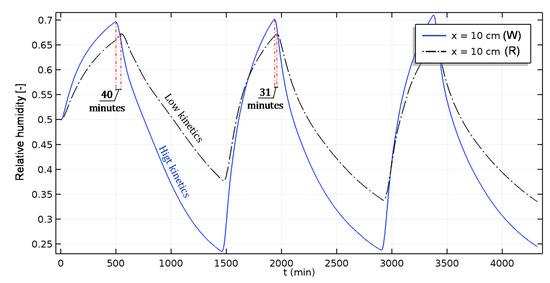
Figure 15.
Non-isothermal case: Evolution of the relative humidity of aged and reference hemp concrete (W: Weathered; R: Reference).
4.2. Impact of Aging on the Energy Efficiency Assessment at the Wall Scale
It is important to remember that these accelerated aging tests do not simulate the real case to which the materials are subjected over time. However, they allow simulation of the extreme degradation case of these materials.
Additional, one-dimensional simulations were performed to evaluate the impact of material aging effects on the energy efficiency assessment. A wall of 20 cm thickness, built with hemp concrete, was submitted to climatic variations in the city of La Rochelle, France. The outside boundary conditions are given in Figure 16. The internal temperature and relative humidity were set, as illustrated in Figure 16. A slight increase in both fields occurred during the summer period. The initial condition was T = 20 °C and RH = 0.5. The investigations were carried out for one year in both configurations. The first one assumed a reference material, with standard material properties. The second one considered a wall with aged material properties.
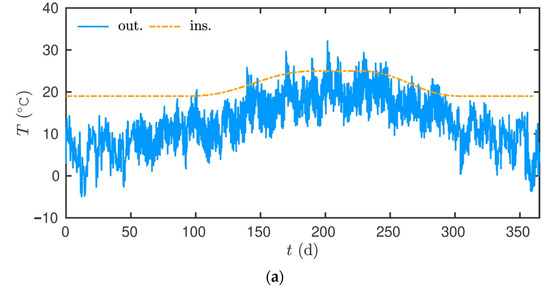
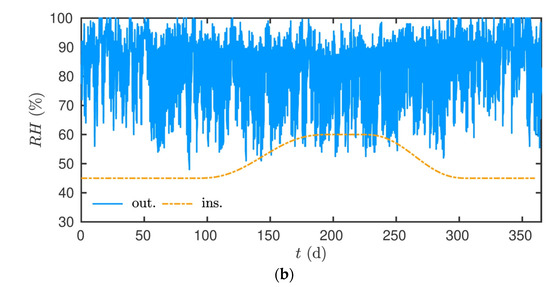
Figure 16.
Inside and outside boundary conditions applied to the studied wall: (a) Temperature; (b) Relative humidity.
The impact on the energy efficiency was evaluated through the computation of the inside heat flux jq, the monthly conduction loads E and the inside moisture flux jm of the studied wall, in order to evaluate the behaviour of hemp concrete in an extreme degradation case.
Figure 17a–c shows the time evolution of the latent, sensible and total heat flux, respectively. In addition, Figure 18a gives the probability density function of the difference of heat flux between both configurations. The sensible heat flux is overestimated by the simulation considering the reference material properties. Inversely, the latent heat flux is underestimated for the same configuration. These results are consistent with the previous ones and the modification of the macroscopic material properties, particularly the vapour permeability and the thermal conductivity. The primer is higher, while the latter is lower, for the aged material. One can remark that the sensible flux has a higher magnitude than the latent one for both configurations. Thus, the total flux is higher in the reference configuration. As a consequence, the conduction loads are lower in the case of aged material, as illustrated in Figure 18b. In other words, the thermal efficiency is improved with aged materials.
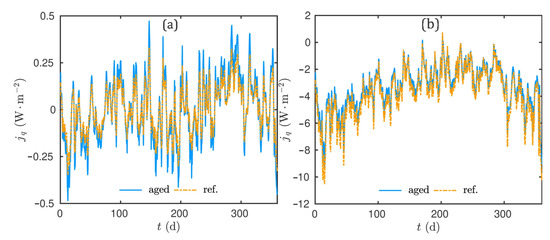
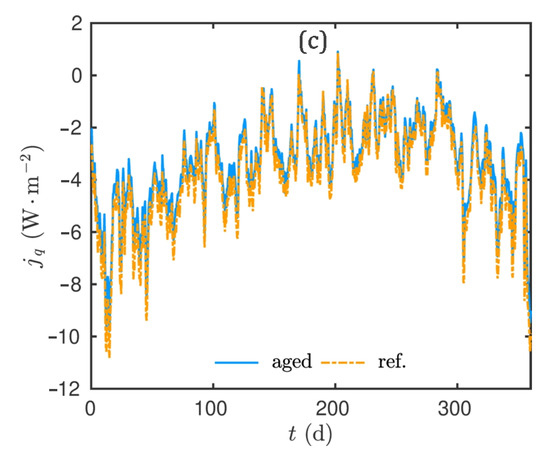
Figure 17.
Time evolution of the (a) latent, (b) sensible and (c) total heat flux inside the wall.
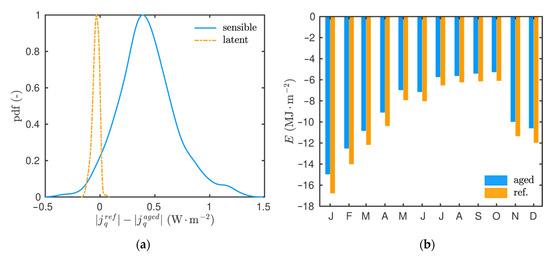
Figure 18.
(a) Probability density function of the difference of heat flux between both configurations and (b) monthly conduction loads.
Figure 19b compares both configurations. For most of the occurrences, the difference between the moisture flux in both configurations is negative. Thus, the magnitude of the moisture flux is higher for the aged material. Consequently, more moisture is released by the wall to the inside air zone in the case of aged material. This is mainly due to a modification of the sorption cure and vapour permeability transfer by the aging phenomena.
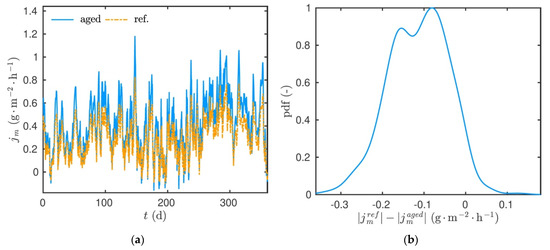
Figure 19.
(a) Time evolution of the moisture flux and (b) density function of the difference of moisture flux between both configurations.
In fact, these results only concern this type of accelerated aging (immersion/gel/drying). A different type of aging can give rise to different results. It is important to note that the physical model considers the aging effects through the macroscopic material properties. The aging phenomena induces a modification of the microstructure of the material through the phenomena of (i) swelling and shrinking of the fibres, (ii) the deterioration of the interface fibres/binders and (iii) the leaching of pore solution ions [20]. These modifications impact the macroscopic properties, such as vapour permeability, sorption curves and thermal conductivity, and are determined using an experimental campaign. The modified macroscopic properties were used in the model so that the aging effects on the prediction of heat and mass transfer could be investigated. At no point does the model include a prediction of the degradation of the microstructure.
5. Conclusions
This study presents an experimental and numerical investigation of the aging effects on the hygrothermal behaviour of hemp concrete. For this, samples were submitted to several cycles of wetting, drying and freezing. Then, an experimental campaign was undertaken to determine the transfer properties of both aged and reference materials. In addition, a model to predict the phenomena of heat and mass transfer in the material was proposed and validated using results from the literature. To investigate the aging effects on the model predictions, the model inputs were defined according to the properties of both materials. The investigations led to the following conclusions:
- According to the experimental results, the aging protocol had a significant impact on the microstructure of the hemp concrete. Observations made using a digital microscope highlighted important cracks at the interface between the hemp shives and the binder. Those cracks were induced by swelling and shrinking of the hemp shives due to their sensitivity to heat and mass variations. Moreover, an overall increase of the porosity (by 6%) was observed for the aged material. The modifications of the microscopic properties led to a 39% increase of the vapour permeability and 11% of the thermal conductivity. In addition, significant differences were noted on the sorption curve and moisture capacity.
- According to the numerical investigations, a validated model was proposed, based on a normative comparison. For both cases, isothermal and non-isothermal, the aging effects modified the predictions of the heat and mass transfer, compared to the reference material. In the isothermal case, the difference reached 12% between the relative humidity profiles. In the second case, those differences were increased by 6%, highlighting the coupling effects between heat and mass transfer. Furthermore, the sensible heat flux was overestimated by the simulation considering the properties of the reference material. As for the latent heat flux, it was underestimated for the same configuration. Consequently, the conduction loads were lower in the case of aged materials. In other words, thermal efficiency is improved with aged materials.
Lastly, these results highlight the importance of aging effects on the hygrothermal behaviour of hemp concrete, using experimental and numerical investigations. Given the aggressiveness of the accelerated aging protocol applied in this study, it is important to note that this protocol reflects the extreme degradation case that hemp concrete can undergo after several years of use in harsh climates.
Author Contributions
F.B. (Ferhat Benmahiddine): investigation, methodology, validation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. R.B.: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, validation. J.B.: validation, writing—review and editing, visualisation. F.B. (Fares Bennai): validation, writing—review and editing, visualisation. A.T.: supervision, validation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data used to produce the results of the study are available from the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
The Region and European Union have supported the project under the “CPER-FEDER Bâtiment durable Axis 2 MADUR Project: High-performance building materials with low environmental impact, sustainable and resilient” within the framework of the “Operational Program FEDER/FSE 2015–2020” and Energy saving certificate program of the Ministry of Ecological and Solidarity Transition “SmartReno support” 2019–2021.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Z. Life cycle carbon emissions of two residential buildings in China: Comparison and uncertainty analysis of different assessment methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 122037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.; Li, X.; Cai, W.; Zuo, J.; Jia, F.; Wei, H. Exploring the impact of urbanization on urban building carbon emissions in China: Evidence from a provincial panel data model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 56, 102068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, S.; Luo, L.; Liao, L. A building information modeling-based carbon emission measurement system for prefabricated residential buildings during the materialization phase. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministère de la Cohésion des Territoires et des Relations avec les Collectivités Térritorailes. Available online: https://www.cohesion-territoires.gouv.fr/rt2012 (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Gradeci, K.; Labonnote, N.; Time, B.; Köhler, J. Mould growth criteria and design avoidance approaches in wood-based materials—A systematic review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Guernouti, S.; Woloszyn, M.; Buhe, C. Factors governing the development of moisture disorders for integration into building performance simulation. J. Build. Eng. 2015, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Belarbi, R. Development of an Analytical Method for Simultaneous Heat and Moisture Transfer in Building Materials Utilising Transfer Function Method. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. ASCE 2005, 17, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.D.; Samri, L.; Rahim, M.; Douzane, O.; Promis, G.; Langlet, T. Effect of Temperature-dependent Sorption Characteristics on the Hygrothermal Behavior of a Hemp Concrete Building. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2016, 78, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Bennai, F.; Issaadi, N.; Abahri, K.; Belarbi, R.; Tahakourt, A. Experimental characterization of thermal and hygric properties of hemp concrete with consideration of the material age evolution. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 54, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennai, F.; El Hachem, C.; Abahri, K.; Belarbi, R. Microscopic hydric characterization of hemp concrete by X-ray microtomography and digital volume correlation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abahri, K.; El Hachem, C.; Bennai, F.; Ngoc, T.; Belarbi, R. Prediction of Hemp Concrete Morphological Deformation by X-ray Tomography. Am. Concr. Inst. ACI Spec. Publ. 2017, 320, 616–625. [Google Scholar]
- Benmahiddine, F.; Cherif, R.; Bennai, F.; Belarbi, R.; Tahakourt, A.; Abahri, K. Effect of flax shives content and size on the hygrothermal and mechanical properties of flax concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennai, F.; Abahri, K.; Belarbi, R. Contribution to the Modelling of Coupled Heat and Mass Transfers on 3D Real Structure of Heterogeneous Building Materials: Application to Hemp Concrete. Transp. Porous Media 2020, 133, 333–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, J.; Sonebi, M.; Taylor, S.; Amziane, S. The effect of a polyacrylic acid viscosity modifying agent on the mechanical, thermal and transport properties of hemp and rapeseed straw concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantine, G.; Maalouf, C.; Moussa, T.; Polidori, G. Experimental and numerical investigations of thermal performance of a Hemp Lime external building insulation. Build. Environ. 2018, 131, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rémond, R.; Almeida, G.; Perré, P. The gripped-box model: A simple and robust formulation of sorption hysteresis for lignocellulosic materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 170, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aït Oumeziane, Y.; Bart, M.; Moissette, S.; Lanos, C. Hysteretic Behaviour and Moisture Buffering of Hemp Concrete. Transp. Porous Media 2014, 103, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelievre, D.; Colinart, T.; Glouannec, P. Hygrothermal behavior of bio-based building materials including hysteresis effects: Experimental and numerical analyses. Energy Build. 2014, 84, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Busser, T.; Colinart, T.; Dutykh, D. Critical assessment of a new mathematical model for hysteresis effects on heat and mass transfer in porous building material. Int. J. Sci 2020, 151, 106275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benmahiddine, F.; Bennai, F.; Cherif, R.; Belarbi, R.; Tahakourt, A.; ABAHRI, K. Experimental investigation on the influence of immersion/drying cycles on the hygrothermal and mechanical properties of hemp concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 101758, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennai, F.; El Hachem, C.; Abahri, K.; Belarbi, R. Influence of hydric solicitations on the morphological behavior of hemp concrete. Rilem Tech. Lett. 2019, 4, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arizzi, A.; Viles, H.; Martín-Sanchez, I.; Cultrone, G. Predicting the long-term durability of hemp–lime renders in inland and coastal areas using Mediterranean, Tropical and Semi-arid climatic simulations. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassoni, E.; Manzi, S.; Motori, A.; Montecchi, M.; Canti, M. Experimental study on the physical-mechanical durability of innovative hemp-based composites for the building industry. Energy Build. 2015, 104, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabannes, M.; Garcia-Diaz, E.; Clerc, L.; Bénézet, J.C. Studying the hardening and mechanical performances of rice husk and hemp-based building materials cured under natural and accelerated carbonation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 94, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remki, B.; Abahri, K.; Tahlaiti, M.; Belarbi, R. Hygrothermal transfer in wood drying under the atmospheric pressure gradient. Int. J. Sci. 2012, 57, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroukhi, M.Y.; Abahri, K.; Belarbi, R.; Limam, K. Integration of a hygrothermal transfer model for envelope in a building energy simulation model: Experimental validation of a HAM–BES co-simulation approach. Heat Mass Transf. Und Stoffuebertragung 2017, 53, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannoy, G.; Marceau, S.; Glé, P.; Gourlay, E.; Guéguen-Minerbe, M.; Amziane, S.; Farcas, F. Durability of hemp concretes exposed to accelerated environmental aging. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, S.; Glé, P.; Guéguen-Minerbe, M.; Gourlay, E.; Moscardelli, S.; Nour, I.; Amziane, S. Influence of accelerated aging on the properties of hemp concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NFEN12667. Performance Thermique des Matériaux et Produits Pour le Bâtiment—Détermination de la Résistance Thermique Par la Méthode de la Plaque Chaude Gardée et la Méthode Fluxmétrique—Produits de Haute et Moyenne Résistance Thermique; Afnor Editions: Seine-Saint-Denis, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- NFEN12664. Performance Thermique des Matériaux et Produits Pour le Bâtiment—Détermination de la Résistance Thermique Par la Méthode de la Plaque Chaude Gardée et la Méthode Fluxmétrique—Produits Secs et Humides de Moyenne et Basse Résistance Thermique; Afnor Editions: Seine-Saint-Denis, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- European Standard ISO 12572. Building Materials—Determination of Water Vapor Transmission Properties; (ISO/DIS 12572:1997) PrEN ISO 12572 1997; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Issaadi, N.; Nouviaire, A.; Belarbi, R.; Aït-Mokhtar, A. Moisture characterization of cementitious material properties: Assessment of water vapor sorption isotherm and permeability variation with ages. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 83, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, C.; Peuhkuri, R.; Time, B.; Gustavsen, A.; Ojanen, T.; Ahonen, J.; Svennberg, K.; Harderup, L.-E.; Arfvidsson, J. Moisture Buffering of Building Materials; Technical University of Denmark, Department of Civil Engineering: Lyngby, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rode, C.; Peuhkuri, R.; Time, B.; Svennberg, K.; Ojanen, T. Moisture Buffer Value of Building Materials. J. Astm. Int. 2006, 4, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belarbi, R.; Qin, M.; Aït-Mokhtar, A.; Nilsson, L.O. Experimental and theoretical investigation of non-isothermal transfer in hygroscopic building materials. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 2154–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Belarbi, R.; Ait-Mokhtar, A.; Nilsson, L.-O. Nonisothermal moisture transport in hygroscopic building materials: Modeling for the determination of moisture transport coefficients. Transp. Porous Media 2008, 72, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, A.; Belarbi, R.; Abahri, K.; Qin, M. Assessment of temperature gradient effects on moisture transfer through thermogradient coefficient. Build. Simul. 2012, 5, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).