Abstract
This study aims to investigate the effects of exercise on depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors and identify the optimal exercise prescription for this population. Searches were conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Embase, Scopus, CNKI, and Wanfang Data up to 7 January 2024. A meta-analysis was performed to calculate the standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval. Thirteen studies were included in this meta-analysis. Exercise significantly alleviated depression (SMD, −0.54; p = 0.002) and anxiety (SMD, −0.66; p = 0.0002) in lung cancer survivors. Subgroup analyses showed that aerobic exercise, exercise conducted >3 times per week, <60 min per session, and ≥180 min per week, were more effective in alleviating depression and anxiety, particularly in middle-aged individuals. In conclusion, exercise alleviates depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors, particularly those who are middle-aged, and aerobic exercise may be the most effective intervention. This meta-analysis provides clinicians with evidence to recommend that lung cancer survivors engage in exercise more than three times per week, with each session lasting less than 60 min, aiming to achieve a total of 180 min per week by increasing the frequency of exercise.
1. Introduction
Lung cancer is the most prevalent form of cancer, significantly contributing to the escalating global public health burden [1,2,3]. In recent years, cancer-related deaths, totaling 2,397,700, have increased by 21.6%, with lung cancer ranking among the top five cancers with the highest mortality rates [3]. Lung cancer survivors commonly exhibit clinical symptoms such as hemoptysis, chest pain, fatigue, and weight loss [4,5]. Notably, these clinical symptoms often lead to emotional issues, including depression and anxiety [6], frequently adding an additional burden onto survivors during the treatment process. However, depression and anxiety are frequently overlooked in clinical assessments. Additionally, studies have shown that over 40% of all lung cancer survivors experience psychological distress, representing one of the highest prevalence rates among all cancers [7]. Emotional distress can reduce adherence to subsequent adjuvant therapies and impair survivors’ quality of life [8]. Moreover, it is negatively correlated with the survival rates of cancer survivors [9]. Therefore, prompt intervention, as recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network [10], should be applied when necessary. A longitudinal study conducted in early adulthood indicated that high levels of anxiety may elevate the risk of cancer-related mortality [11]. Consequently, the negative impact of depression and anxiety must be thoroughly considered when devising treatment plans for lung cancer survivors.
Exercise, as a non-pharmacological intervention, has been proven to benefit individuals with depression and anxiety [12], as evidenced by recent studies [13,14]. For example, He et al. [14] showed positive effects of exercise interventions on depressive symptoms across various age groups. Recently, a network meta-analysis further demonstrated the equivalence of aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, and mind–body exercises in alleviating depressive symptoms in people over 65 years of age [15]. Additionally, a previous study demonstrated that 20 weeks of resistance exercise significantly reduced depressive symptoms in people with Parkinson’s disease [16]. Furthermore, evidence indicates that exercise can alleviate both depression and anxiety in people with breast cancer [17]. Moreover, one recent review concluded that aerobic exercise is the most effective mode for improving anxiety symptoms [18].
Despite these benefits of exercise, considerable debate persists regarding the effectiveness of exercise for depression and anxiety in individuals with lung cancer, including optimal exercise dosage. For example, an 8-week exercise intervention incorporating both Baduanjin and resistance exercise was shown to significantly alleviate depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors [19]. Conversely, Temel et al. [20] demonstrated that a structured exercise regimen for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer did not lead to improvements in depression or anxiety. In addition, it was found that 6 weeks of multidimensional exercise did not significantly improve depressive symptoms, although anxiety scores were reduced [21]. Furthermore, a meta-analysis indicated that exercise has the potential to improve depression and anxiety in individuals with advanced lung cancer [22]. However, that meta-analysis included only two studies related to depression and anxiety, and the assessment measures were not distinctly categorized. Consequently, the current study builds upon this foundation by further distinguishing between depression and anxiety.
Moreover, a recent meta-analysis conducted by Su et al. [23] demonstrated that exercise interventions may reduce depression and anxiety levels in lung cancer survivors. However, that study did not focus on specific exercise moderators, leaving it uncertain how these individuals should exercise. Therefore, the current study was conducted to investigate the effects of exercise on depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors and identify the optimal exercise prescription for this population.
2. Materials and Methods
This meta-analysis adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, and the protocol was registered on PROSPERO with the registration number CRD42024500407.
2.1. Search Strategy
A comprehensive search was performed across 7 databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Embase, Scopus, China National Knowledge Internet (CNKI), and Wanfang Data, up to 7 January 2024. The initial search included the following specific keywords and MESH terms: exercise, cancer, depression, and anxiety. Additionally, the reference lists of all identified reviews were hand-searched. Two authors (CZ and XT) independently completed the process using a standardized form. In cases of disagreement between the two authors, a third author (LY) joined the discussion until a consensus was reached.
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
The following criteria were considered: (1) randomized controlled trial (RCT) design; (2) lung cancer survivors as subjects; (3) the presence of both an intervention group and a control group; and (4) inclusion of a metric for depression or anxiety outcomes.
The exclusion criteria included (1) duplicate publications; (2) conference papers; (3) incomplete data reporting; (4) acute exercise interventions; and (5) animal studies.
2.3. Data Extraction
Two authors (C.Z. and X.T.) independently extracted data, focusing on: (1) study details, such as the first author’s last name and the year of publication; (2) specifics of the intervention, including type of intervention, frequency, intervention duration, and session duration; (3) participant information, such as sample size, gender, and age; and (4) treatment outcomes. In cases where the results were incomplete, the corresponding authors were contacted via email for further information.
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
The methodological quality of the included studies was assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias criteria [24], mainly from 7 aspects: random sequence generation (selection bias), allocation concealment (selection bias), blinding of participants, personnel (performance bias), outcome-blind assessment (detection bias), incomplete result data (loss bias), selective reporting (report bias), and other biases. The assessment of methodological quality was independently conducted by two authors (C.Z. and X.T.), with any disagreements being discussed and resolved through consensus with a third author (L.Y.).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
A meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager software (version 5.4). Changes in mean and standard deviation (SD) were calculated for depression and anxiety. For studies reporting the standard error (SE) or 95% confidence interval (CI), SD was derived through conversion [25,26]. Data were pooled using either fixed-effects or random-effects models to determine the standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% CI. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic [27], with values of 0%, 25%, 50%, and 75% interpreted as indicating no, low, moderate, and high heterogeneity. Where heterogeneity was high (I2 > 60%), subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis were performed to explain the results [28]. Funnel plots were used to scrutinize potential publication bias. The significance level was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
As illustrated in Figure 1, 7422 records were identified, consisting of 7270 articles from English databases and 152 from Chinese databases. After removing duplicates, 4787 studies remained. Following the screening of titles and abstracts, 4735 studies were deemed ineligible for inclusion, leaving 52 articles selected for full-text assessment. A total of 39 studies were excluded after a full-text review of these 52 studies, for the following reasons: (1) lack of data (n = 15); (2) absence of a control group (n = 10); (3) study protocols (n = 5); (4) no outcome indicators (n = 5); and (5) conference papers (n = 4). Ultimately, 13 studies [19,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] investigating the effects of exercise on depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors were included in the meta-analysis.
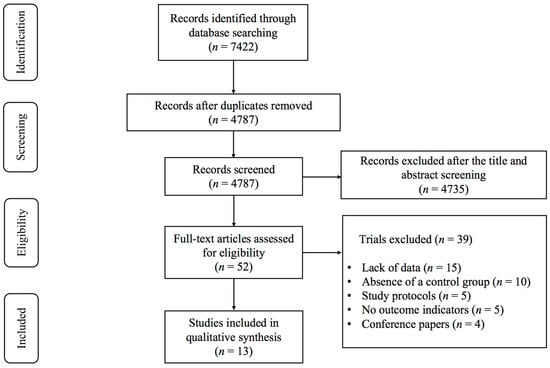
Figure 1.
PRISMA flowchart of study selection.
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
The primary characteristics of the interventions and participants are presented in Table S1. A total of 449 participants across 15 exercise intervention groups and 441 participants across 13 control groups were included in the studies. The participants’ mean age ranged from 48.1 to 68.0 years. Participants in seven studies [19,33,34,35,36,37,39] were included, with a mean age of 45–60 years, while participants in another six studies [29,30,31,32,38,40] were included, with a mean age of ≥60 years. Interventions specified aerobic exercise [29,30,33,34,35,37,39,40], combined exercise [19,31,38,40], and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) [36]. The total duration of intervention ranged from 4 to 12 weeks, the frequency of intervention per week was 2 to 14 times, and the minutes of intervention per session ranged from 15 to 90 min. In terms of results, 12 studies addressed depression, while 12 studies examined anxiety.
3.3. Meta-Analysis Results
Compared with the control group, exercise had a positive effect on alleviating depression (SMD, −0.54; 95% CI, −0.88 to −0.20, p = 0.002, I2 = 77%, Figure 2) and anxiety (SMD, −0.66; 95% CI, −1.00 to −0.32, p = 0.0002, I2 = 81%, Figure 3) in lung cancer survivors.
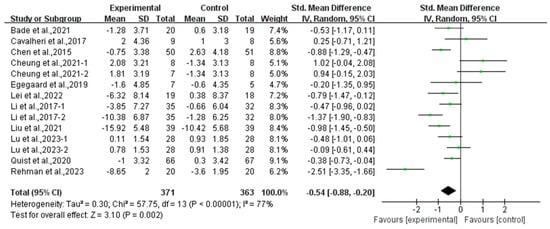
Figure 2.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of exercise on depression in lung cancer survivors.
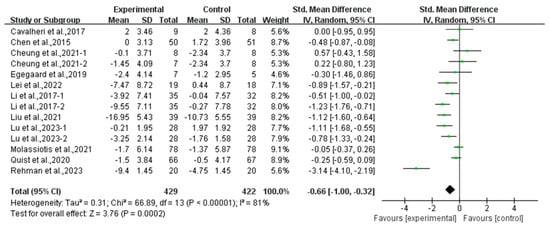
Figure 3.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of exercise on anxiety in lung cancer survivors.
3.4. Subgroup Analysis
3.4.1. Effects of Various Exercise Moderators on Depression in Lung Cancer Survivors
Subgroup analysis showed that aerobic exercise (SMD, −0.77; 95% CI, −1.25 to −0.28, p = 0.002, I2 = 82%) significantly alleviated depression, while combined exercise had no significant effect on depression (SMD, −0.11; 95% CI, −0.73 to 0.52, p = 0.74, I2 = 68%, Figure 4) in lung cancer survivors.
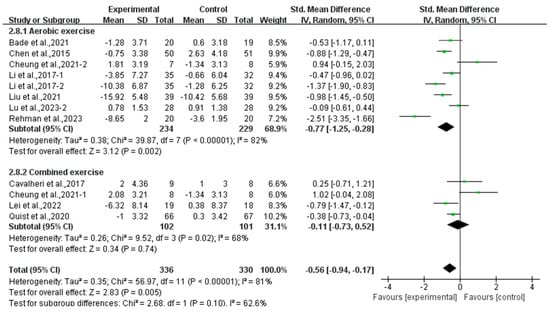
Figure 4.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of types of intervention on depression in lung cancer survivors.
In addition, a subgroup analysis based on intervention frequency revealed that exercise conducted >3 times per week significantly alleviated depression (SMD, −0.78; 95% CI, −1.37 to −0.19, p = 0.009, I2 = 81%), while exercise conducted for ≤3 times per week had no significant effect on depression (SMD, −0.29; 95% CI, −0.79 to 0.21, p = 0.26, I2 = 80%, Figure 5) in lung cancer survivors.
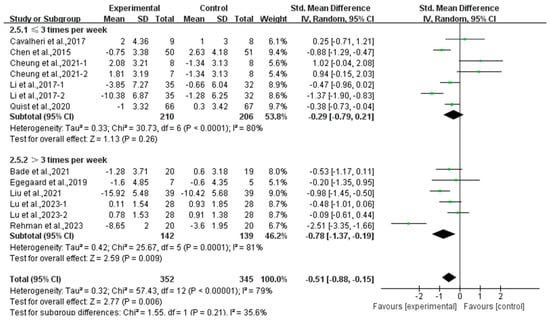
Figure 5.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of frequency of exercise on depression in lung cancer survivors.
Furthermore, analyzing the subgroup by session duration, exercise lasting <60 min per session significantly alleviated depression (SMD, −0.85; 95% CI, −1.23 to −0.46, p < 0.0001, I2 = 75%), while exercise lasting ≥60 min per session had no significant effect on depression (SMD, 0.35; 95% CI, −0.43 to 1.13, p = 0.38, I2 = 73%, Figure 6) in lung cancer survivors.
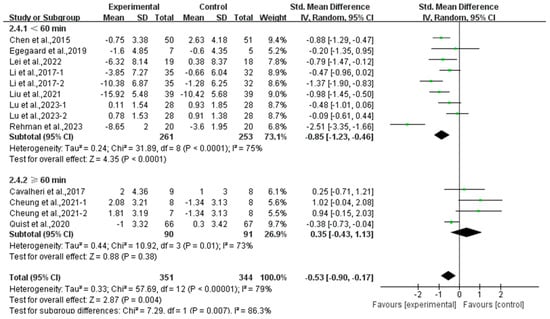
Figure 6.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of duration of exercise per session on depression in lung cancer survivors.
Moreover, a subgroup analysis according to weekly time found that exercise conducted for ≥180 min per week significantly alleviated depression (SMD, −0.41; 95% CI, −0.76 to −0.07, p = 0.02, I2 = 55%), while exercise conducted for <180 min per week had no significant effect on depression (SMD, −0.57; 95% CI, −1.28 to 0.13, p = 0.11, I2 = 86%, Figure 7) in lung cancer survivors.
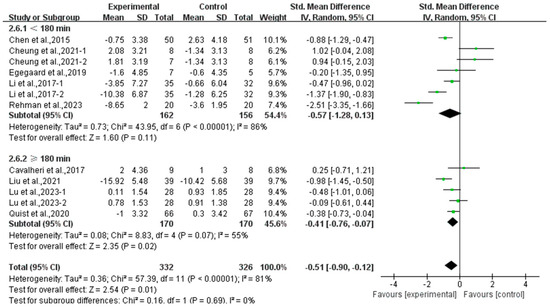
Figure 7.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of duration of exercise per week on depression in lung cancer survivors.
Finally, exercise significantly alleviated depression in middle-aged lung cancer survivors (SMD, −0.90; 95% CI, −1.38 to −0.42, p = 0.0002, I2 = 80%), while exercise had no significant effect on depression in elderly lung cancer survivors (SMD, −0.12; 95% CI, −0.60 to 0.35, p = 0.61, I2 = 70%, Figure 8).
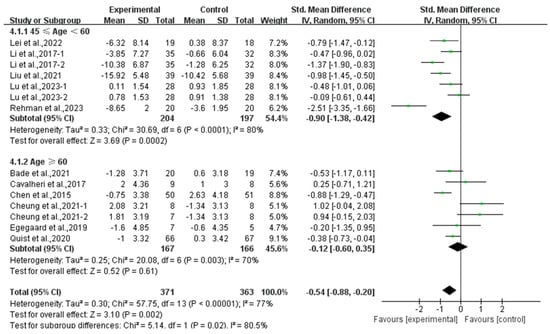
Figure 8.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of exercise on depression in middle-aged and elderly lung cancer survivors.
3.4.2. Effects of Various Exercise Moderators on Anxiety in Lung Cancer Survivors
Subgroup analysis showed that aerobic exercise significantly alleviated anxiety (SMD, −0.84; 95% CI, −1.34 to −0.34, p = 0.0009, I2 = 87%), while combined exercise had no significant effect on anxiety (SMD, −0.24; 95% CI, −0.73 to 0.26, p = 0.35, I2 = 52%, Figure 9) in lung cancer survivors.
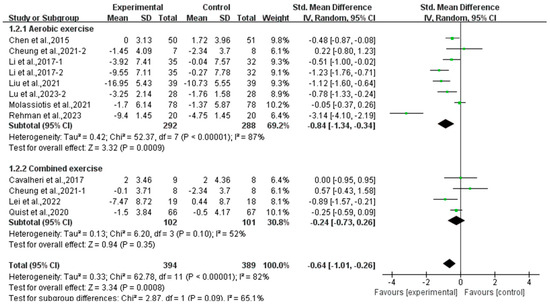
Figure 9.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of types of intervention on anxiety in lung cancer survivors.
In addition, a subgroup analysis based on intervention frequency revealed that exercise conducted ≤3 times per week (SMD, −0.37; 95% CI, −0.73 to −0.01, p = 0.05, I2 = 63%) and >3 times per week (SMD, −1.04; 95% CI, −1.75 to −0.34, p = 0.004, I2 = 89%, Figure 10) significantly alleviated anxiety in lung cancer survivors, with exercise conducted >3 times per week showing a better effect.
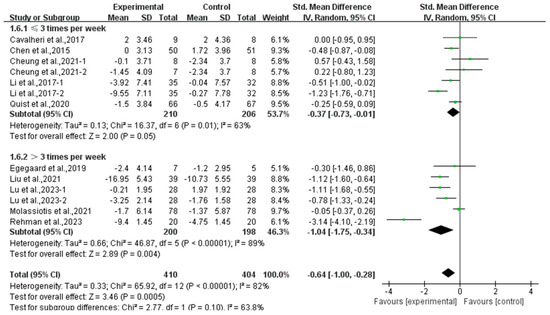
Figure 10.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of frequency of exercise on anxiety in lung cancer survivors.
Furthermore, analyzing the subgroup by session duration, exercise lasting <60 min per session significantly alleviated anxiety (SMD, −1.01; 95% CI, −1.40 to −0.62, p < 0.00001, I2 = 75%), while exercise lasting ≥60 min per session had no significant effect on anxiety (SMD, −0.12; 95% CI, −0.41 to 0.18, p = 0.44, I2 = 0%, Figure 11) in lung cancer survivors.
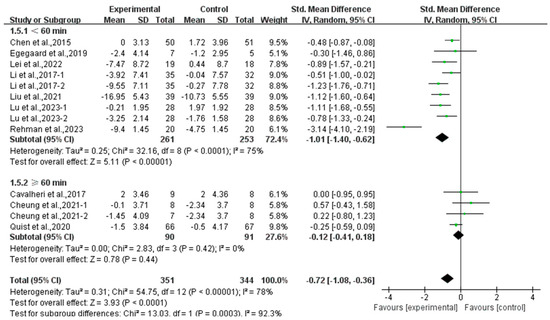
Figure 11.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of duration of exercise per session on anxiety in lung cancer survivors.
Moreover, a subgroup analysis according to weekly time found that exercise conducted for <180 min per week (SMD, −0.62; 95% CI, −1.18 to −0.05, p = 0.03, I2 = 86%) and ≥180 min per week significantly alleviated anxiety (SMD, −0.69; 95% CI, −1.13 to −0.25, p = 0.002, I2 = 71%, Figure 12) in lung cancer survivors, with exercise conducted for ≥180 min per week showing a better effect.
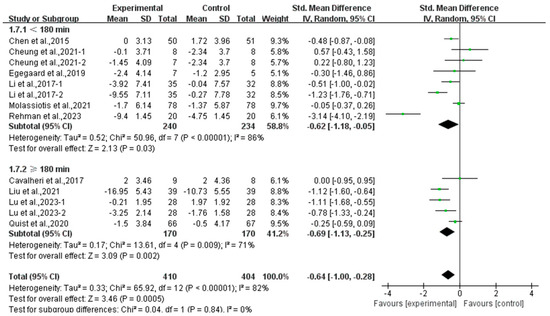
Figure 12.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of duration of exercise per week on anxiety in lung cancer survivors.
Finally, exercise significantly alleviated anxiety in middle-aged (SMD, −1.03; 95% CI, −1.53 to −0.53, p < 0.0001, I2 = 86%) and elderly lung cancer survivors (SMD, −0.25; 95% CI, −0.48 to −0.02, p = 0.04, I2 = 0%, Figure 13), with a more pronounced effect observed in middle-aged lung cancer survivors.
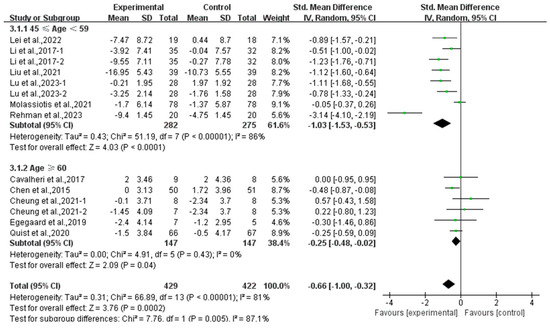
Figure 13.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of exercise on anxiety in middle-aged and elderly lung cancer survivors.
3.5. Risk of Bias
This study employed the Cochrane risk of bias criteria for quality assessment, which is based on six factors: selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, reporting bias, and other biases. The quality of the included studies was classified into three levels based on the criteria: low risk, high risk, and unclear (Figure S1).
3.6. Publication Bias
Funnel plots were visually inspected to assess publication bias, revealing asymmetry for both depression (Figure S2) and anxiety (Figure S3). Egger’s test indicated that small sample size did not significantly influence the combined effect sizes for depression (p = 0.439) or anxiety (p = 0.336, Table S2).
3.7. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis to explore the effects of exercise on depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors. Thirteen studies were included and the findings indicated that exercise significantly alleviated depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors. Subgroup analyses showed that aerobic exercise, exercise conducted >3 times per week, <60 min per session, and ≥180 min per week were more effective in alleviating depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors, particularly in middle-aged individuals.
4.2. Effects of Exercise on Depression and Anxiety in Lung Cancer Survivors
It is widely recognized that exercise can serve as an effective complement or alternative to both pharmacological and psychological therapies [14,41,42,43]. As a non-invasive and non-pharmacological intervention, exercise has been shown to effectively alleviate depressive symptoms, as evidenced by previous studies [44,45]. A meta-analysis by Singh et al. [46] showed that physical activity is particularly effective in alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety in adults. In addition, a systematic review also indicated that exercise can alleviate depression in lung cancer survivors [47]. Furthermore, in an observational study of 8098 adults, individuals who exercised regularly exhibited a lower risk of being diagnosed with an anxiety disorder compared to those who were sedentary [48].
Both qualitative and quantitative studies have illustrated the benefits of exercise on depression and anxiety. Although clear causal mechanisms were not uncovered, the trends observed in the data are valuable for generating hypotheses. The beneficial effects of exercise on depression and anxiety are likely to be attributable to a combination of various neurophysiological and psychological mechanisms. Current research has identified several potential physiological mechanisms, including the regulation of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis activity, enhanced monoamine system function, promotion of new neuronal growth in the hippocampus, reduction of systemic inflammation, and increased levels of opioids and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) [49,50,51].
Dysfunction within the HPA axis has been linked to a range of symptoms, including disorders of the sympathetic nervous system, hyperarousal, and mental illness such as depression and anxiety [52,53]. Animal studies found that 6 weeks of voluntary wheel running regulated HPA axis activity [54,55]. Additionally, exercise can increase levels of β-endorphins [56,57], vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) [58,59], BDNF [60], and serotonin (5-HT) [61]. β-endorphins facilitate the generation of new neurons in the dentate gyrus [62], while 5-HT has been shown to enhance cellular proliferation and neurogenesis in this region among adults [63]. VEGF [58] and BDNF [64] are acknowledged for their roles in supporting neuronal survival. Therefore, the therapeutic effects of exercise on depression and anxiety may be linked to its potential to enhance neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus through these mechanisms [51].
Furthermore, the pathology of depression and anxiety is associated with abnormalities in the function of monoamines in the brain [49]. Numerous studies have found that exercise can increase the availability of central monoamines, such as dopamine [65], norepinephrine [66], and 5-HT [67], thereby regulating depression and anxiety. Concurrently, it helps lower the levels of inflammatory factors like interleukin-17 (IL-17) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) [68]. Moreover, exercise plays a vital role in increasing endogenous opioid activity in the central and peripheral nervous system [56], thereby further supporting mental health. In addition to physiological mechanisms, psychosocial factors, such as self-efficacy, are recognized as playing a crucial role [49]. Numerous studies have suggested that the enhancement of self-efficacy through exercise may alleviate negative emotions such as depression and anxiety [69].
Conversely, Cavalheri et al. [31] discovered that anxiety and depression did not demonstrate improvements following exercise. This may be attributed to a sample size of fewer than 30 participants and the relatively low baseline scores for depression and anxiety. A recent review by Bartley et al. [70] indicated that aerobic exercise is ineffective in alleviating anxiety, which contradicts the findings of the current study. However, it is worth noting that the population included in Bartley et al.’s study was not specifically subdivided, unlike the population of lung cancer survivors in this study. There is considerable debate in the existing research, which may be attributed to discrepancies in the characteristics of the research subjects, as well as the physical condition, rehabilitation capacity, and recovery potential of patients across different age groups. Moreover, the type of exercise and the duration of the intervention may result in disparate outcomes with respect to depression.
4.3. Effects of Various Exercise Moderators on Depression and Anxiety in Lung Cancer Survivors
In order to determine the optimal exercise prescription for lung cancer survivors, we conducted subgroup analyses based on the type of intervention, session duration, frequency, weekly time, and participants’ age.
Through subgroup analysis of type of intervention, we found that only aerobic exercise exhibited positive effects in alleviating depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors, aligning with the results of a previous study [71] showing that there was a negative correlation between aerobic exercise and depression and anxiety in cancer survivors. Additionally, a meta-analysis indicated that Tai Chi and Qigong, as forms of aerobic exercise, can help regulate depression levels in cancer survivors [72]. Meanwhile, a recent review has demonstrated that aerobic exercise has a significant effect on alleviating anxiety symptoms [73].
Numerous observational studies have shown a negative correlation between exercise, especially aerobic exercise, and anxiety symptoms [18,74,75]. Its effectiveness in alleviating depression and anxiety may be attributed to its ease of implementation and widespread feasibility. Cancer survivors typically exhibit significantly lower levels of physical functioning compared with the general population [76]. Aerobic exercise is characterized by lower intensity compared with combined exercise. Furthermore, aerobic exercise may be more tolerable for cancer survivors, and it has been established that aerobic exercise is both safe and effective [77]. Notably, a meta-analysis examining the effects of HIIT on depression and anxiety reported no significant improvements [78]. Paolucci et al. [79] found that HIIT resulted in elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), along with increased perceived stress. In contrast, moderate-intensity continuous aerobic exercise did not induce such effects. Resistance exercise is often associated with mild muscle pain and falls experienced by participants [15], which may contribute to the lack of significant effects from combined exercise.
It is noteworthy that exercise conducted more than three times per week significantly alleviated depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors, which is consistent with previous studies [80,81], and the intervention effect was enhanced with a higher exercise frequency. This phenomenon may be attributed to the moderating effect of exercise frequency on endogenous opioids, with studies showing that regular exercise four times a week enhances endorphin release [82]. Other studies have shown that exercising more than three times a week can significantly improve depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors [39]. Additionally, Temel et al. [20] suggested that exercising twice a week does not significantly improve depression and anxiety. Thus, exercise more than three times per week may produce more favorable outcomes in terms of depression and anxiety.
In addition, a subgroup analysis of session duration revealed that exercise lasting <60 min per session was more effective in alleviating depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors, which is in agreement with the results of Rethorst et al. [83], showing that durations of 45 to 59 min produced greater antidepressant benefits than longer bouts of activity. A previous study showed that extended exercise sessions exceeding 60 min may lead to considerable muscle fatigue and increased concentrations of lactic acid [84]. It has been demonstrated that lung cancer survivors typically exhibit lower exercise tolerance [85], which may hinder their ability to engage in prolonged exercise during each session.
Considering only the frequency and session duration is insufficient to account for the influence of other variables. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that individuals engage in 150–300 min of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week [86]. Therefore, we combined frequency and session duration to calculate the weekly time. Our subgroup analysis showed that exercise lasting ≥180 min per week was more effective in alleviating depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors. This finding is consistent with previous studies [87,88,89], suggesting that increasing the frequency of interventions may necessitate a reduction in the duration of individual sessions while ensuring that the total exercise volume is remains at a minimum of 180 min per week. This dose–response relationship may be more effective in alleviating depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors, ensuring both safety and improved outcomes.
Finally, this study indicated that exercise had a more pronounced effect on alleviating depression and anxiety in middle-aged lung cancer survivors. However, as individuals age, several factors come into play that can influence the efficacy of exercise interventions. Firstly, lower tolerance for exercise becomes more prevalent among older adults, which may limit their ability to engage in intense or prolonged physical activities [90]. This decline in exercise tolerance can be attributed to age-related changes in muscle mass, cardiovascular efficiency, and overall physical strength. Secondly, increased susceptibility to fatigue is another challenge faced by older lung cancer survivors. Fatigue is a common side effect of both the disease itself and its treatment, and it can exacerbate the physical and mental strain experienced by these individuals [91]. Lastly, decreased adherence to exercise among older adults can also undermine the benefits of exercise interventions. This may be due to various factors, including lack of social support, mobility limitations, or simply a shift in priorities as individuals prioritize other aspects of their health and daily living [92].
4.4. Limitations of This Study
This study has the following limitations. Firstly, the results of this study should be interpreted with caution due to the potential risk of bias. The trials evaluated were at a high risk of performance bias because blinding participants in exercise interventions is not feasible unless a more rigorously controlled comparison design is employed to assess the effects of the intervention. Secondly, some of the studies that were included did not report the intensity of exercise interventions, thus limiting the understanding of how exercise intensity influences depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors. Lastly, given the limited number of studies on exercise interventions and the absence of resistance exercise among the exercise modalities, further research is necessary to address these gaps.
5. Conclusions
Exercise alleviated depression and anxiety in lung cancer survivors, particularly those who are middle-aged, and aerobic exercise may be the most effective intervention. To alleviate depression and anxiety, this meta-analysis provides clinicians with evidence to recommend that lung cancer survivors engage in exercise more than three times per week, with each session lasting less than 60 min, aiming to achieve a total of 180 min per week by increasing the frequency of exercise.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/curroncol32060304/s1, Figure S1: Results of Cochrane risk of bias tool; Figure S2: Funnel plot (depression); Figure S3: Funnel plot (anxiety); Figure S4: Sensitivity analyses results (depression); Figure S5: Sensitivity analyses results (anxiety); Table S1: Characteristics of studies included in this meta-analysis; Table S2: Results of Egger’s test.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Z., X.T. and L.Y.; methodology, C.Z., X.T. and Y.L.; software, C.Z. and X.T.; validation, B.L. and Y.Z.; formal analysis, C.Z. and X.T.; investigation, C.Z., X.T., B.L., Y.Z. and G.L.; resources, L.Y.; data curation, B.L. and Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Z. and X.T.; writing—review and editing, C.Z., X.T., B.L., Y.Z., G.L., Y.L. and L.Y.; visualization, C.Z. and X.T.; supervision, L.Y.; project administration, L.Y.; funding acquisition, L.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Humanities and Social Science Fund of Ministry of Education of China, grant number 24YJC890065.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Evaluation and Meta-Analyses |
| CNKI | China National Knowledge Internet |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SE | Standard error |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| SMD | Standardized mean difference |
| HIIT | High-intensity interval training |
| HPA | Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| 5-HT | Serotonin |
| IL-17 | Interleukin-17 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocarnik, J.M.; Compton, K.; Dean, F.E.; Fu, W.; Gaw, B.L.; Harvey, J.D.; Henrikson, H.J.; Lu, D.; Pennini, A.; Xu, R.; et al. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived with Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years for 29 Cancer Groups from 2010 to 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 420–444. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, W.; Long, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yin, P.; Zhou, M. National and subnational trends in cancer burden in China, 2005–20: An analysis of national mortality surveillance data. Lancet. Public Health 2023, 8, e943–e955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corner, J.; Hopkinson, J.; Fitzsimmons, D.; Barclay, S.; Muers, M. Is late diagnosis of lung cancer inevitable? Interview study of patients’ recollections of symptoms before diagnosis. Thorax 2005, 60, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Shi, Q.; Williams, L.A.; Mao, L.; Cleeland, C.S.; Komaki, R.R.; Mobley, G.M.; Liao, Z. Inflammatory cytokines are associated with the development of symptom burden in patients with NSCLC undergoing concurrent chemoradiation therapy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, P.; Stephens, R.J. Depression in patients with lung cancer: Prevalence and risk factors derived from quality-of-life data. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabora, J.; BrintzenhofeSzoc, K.; Curbow, B.; Hooker, C.; Piantadosi, S. The prevalence of psychological distress by cancer site. Psycho-Oncology 2001, 10, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMatteo, M.R.; Lepper, H.S.; Croghan, T.W. Depression is a risk factor for noncompliance with medical treatment: Meta-analysis of the effects of anxiety and depression on patient adherence. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.W.; Levy, A.R.; Rosberger, Z.; Edgar, L. Psychological distress and cancer survival: A follow-up 10 years after diagnosis. Psychosom. Med. 2003, 65, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J. NCCN practice guidelines for the management of psychosocial distress. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Oncology 1999, 13, 113–147. [Google Scholar]
- Tolmunen, T.; Lehto, S.M.; Julkunen, J.; Hintikka, J.; Kauhanen, J. Trait anxiety and somatic concerns associate with increased mortality risk: A 23-year follow-up in aging men. Ann. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, M.A.; Guerra de Andrade, L.H. Guerra de Andrade, Physical activity and mental health: The association between exercise and mood. Clinics 2005, 60, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noetel, M.; Sanders, T.; Gallardo-Gómez, D.; Taylor, P.; Del Pozo Cruz, B.; van den Hoek, D.; Smith, J.J.; Mahoney, J.; Spathis, J.; Moresi, M.; et al. Effect of exercise for depression: Systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2024, 384, e075847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.X.; Turner, D.; Generaal, E.; Bos, D.; Ikram, M.K.; Ikram, M.A.; Cuijpers, P.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. Exercise interventions for the prevention of depression: A systematic review of meta-analyses. BMC Public. Health 2020, 20, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.J.; Areerob, P.; Hennessy, D.; Gonçalves-Bradley, D.C.; Mesagno, C.; Grace, F. Aerobic, resistance, and mind-body exercise are equivalent to mitigate symptoms of depression in older adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. F1000Research 2020, 9, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, T.A.; Ferreira-Moraes, R.; Alves, W.M.G.D.C.; Alves, T.G.G.; Pimentel, C.P.; Sousa, E.C.; Abrahin, O.; Cortinhas-Alves, E.A. Resistance training reduces depressive symptoms in elderly people with Parkinson disease: A controlled randomized study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehnert, A.; Veers, S.; Howaldt, D.; Braumann, K.M.; Koch, U.; Schulz, K.H. Effects of a physical exercise rehabilitation group program on anxiety, depression, body image, and health-related quality of life among breast cancer patients. Onkologie 2011, 34, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Gao, W. The effects of physical exercise on anxiety symptoms of college students: A meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1136900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Yang, J.; Dong, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Hou, X.; Bai, Z. An exercise prescription for patients with lung cancer improves the quality of life, depression, and anxiety. Front. Public. Health 2022, 10, 1050471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, J.S.; Greer, J.A.; Goldberg, S.; Vogel, P.D.; Sullivan, M.; Pirl, W.F.; Lynch, T.J.; Christiani, D.C.; Smith, M.R. A structured exercise program for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quist, M.; Adamsen, L.; Rørth, M.; Laursen, J.H.; Christensen, K.B.; Langer, S.W. The Impact of a Multidimensional Exercise Intervention on Physical and Functional Capacity, Anxiety, and Depression in Patients with Advanced-Stage Lung Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peddle-McIntyre, C.J.; Singh, F.; Thomas, R.; Newton, R.U.; Galvão, D.A.; Cavalheri, V. Exercise training for advanced lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2, Cd012685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xiao, Q.; Zhai, J.; Kong, Z.; Li, X. Effects of exercise interventions on anxiety and depression in patients with lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trails. J. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2025, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Xi, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Tao, X.; Lv, Y.; Hou, X.; Yu, L. Effects of exercise in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public. Health 2024, 12, 1387658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, K.; Zhang, S.; Tao, X.; Li, G.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. A systematic review and meta-analysis on effects of aerobic exercise in people with Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. Effects of exercise on cancer-related fatigue in breast cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Life 2024, 14, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Sun, T.; Yu, L. Effects of acute ingestion of caffeine capsules on muscle strength and muscle endurance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, B.C.; Gan, G.; Li, F.; Lu, L.; Tanoue, L.; Silvestri, G.A.; Irwin, M.L. Randomized trial of physical activity on quality of life and lung cancer biomarkers in patients with advanced stage lung cancer: A pilot study. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Tsai, C.M.; Wu, Y.C.; Lin, K.C.; Lin, C.C. Randomised controlled trial on the effectiveness of home-based walking exercise on anxiety, depression and cancer-related symptoms in patients with lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheri, V.; Jenkins, S.; Cecins, N.; Gain, K.; Phillips, M.J.; Sanders, L.H.; Hill, K. Exercise training for people following curative intent treatment for non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized controlled trial. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2017, 21, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egegaard, T.; Rohold, J.; Lillelund, C.; Persson, G.; Quist, M. Pre-radiotherapy daily exercise training in non-small cell lung cancer: A feasibility study. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2019, 24, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Jiao, H. Application of eight-section brocade in postoperative rehabilitation of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Chin. Nurs. Res. 2017, 31, 3755–3759. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Yang, J.; Yao, F. Effects of the Baduanjin Exercise on Quality of Life and Fatigue in Lung Cancer. Yunnan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Medica 2021, 42, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.B.; Ma, R.C.; Yin, Y.Y.; Song, C.Y.; Yang, T.T.; Xie, J. Clinical Indicators of Effects of Yoga Breathing Exercises on Patients with Lung Cancer After Surgical Resection: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cancer Nurs. 2024, 47, E151–E158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.B.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, X.; Ma, R.C.; Yin, Y.Y.; Song, C.Y.; Yang, T.T.; Xie, J. Effects of Preoperative High-Intensity Interval Training Combined with Team Empowerment Education in Lung Cancer Patients with Surgery: A Quasi-experimental Trial. Cancer Nurs. 2023, 47, E368–E375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molassiotis, A.; Vu, D.V.; Ching, S.S.Y. The Effectiveness of Qigong in Managing a Cluster of Symptoms (Breathlessness-Fatigue-Anxiety) in Patients with Lung Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 15347354211008253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quist, M.; Langer, S.W.; Lillelund, C.; Winther, L.; Laursen, J.H.; Christensen, K.B.; Rørth, M.; Adamsen, L. Effects of an exercise intervention for patients with advanced inoperable lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy: A randomized clinical trial. Lung Cancer 2020, 145, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Ahmad, U.; Waseem, M.; Ali, B.; Tariq, M.I. Effects of Exercise Training in Patients with Lung Cancer during Chemotherapy Treatment. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 30, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, D.S.T.; Takemura, N.; Lam, T.C.; Ho, J.C.M.; Deng, W.; Smith, R.; Yan, Y.; Lee, A.W.M.; Lin, C.C. Feasibility of Aerobic Exercise and Tai-Chi Interventions in Advanced Lung Cancer Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 15347354211033352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, G.M.; Dwan, K.; Greig, C.A.; Lawlor, D.A.; Rimer, J.; Waugh, F.R.; McMurdo, M.; Mead, G.E. Exercise for depression. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 9, Cd004366. [Google Scholar]
- Rimer, J.; Dwan, K.; Lawlor, D.A.; Greig, C.A.; McMurdo, M.; Morley, W.; Mead, G.E. Exercise for depression. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 7, Cd004366. [Google Scholar]
- Recchia, F.; Leung, C.K.; Chin, E.C.; Fong, D.Y.; Montero, D.; Cheng, C.P.; Yau, S.Y.; Siu, P.M. Comparative effectiveness of exercise, antidepressants and their combination in treating non-severe depression: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, M.P.; Jacob, M.L.; Suveg, C.; Dishman, R.K.; O’Connor, P.J. Feasibility of exercise training for the short-term treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: A randomized controlled trial. Psychother. Psychosom. 2012, 81, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, M.; Wall, A.; Nyberg, J.; Adiels, M.; Lundin, K.; Bergh, Y.; Eggertsen, R.; Danielsson, L.; Kuhn, H.G.; Westerlund, M.; et al. Effects of exercise on symptoms of anxiety in primary care patients: A randomized controlled trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 297, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Olds, T.; Curtis, R.; Dumuid, D.; Virgara, R.; Watson, A.; Szeto, K.; O’Connor, E.; Ferguson, T.; Eglitis, E.; et al. Effectiveness of physical activity interventions for improving depression, anxiety and distress: An overview of systematic reviews. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravier, F.E.; Smondack, P.; Prieur, G.; Medrinal, C.; Combret, Y.; Muir, J.F.; Baste, J.M.; Cuvelier, A.; Boujibar, F.; Bonnevie, T. Effects of exercise training in people with non-small cell lung cancer before lung resection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 2022, 77, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Heianza, Y.; Manson, J.E.; Franco, O.H.; Qi, L. Association of Cardiovascular Health with Life Expectancy Free of Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes, Cancer, and Dementia in UK Adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2023, 183, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.; Shivakumar, G. Effects of exercise and physical activity on anxiety. Front. Psychiatry 2013, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosse, A.L.; Sheets, E.S.; Lett, H.S.; Blumenthal, J.A. Exercise and the treatment of clinical depression in adults: Recent findings and future directions. Sports Med. 2002, 32, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, C.; Olson, A.K.; Pinel, J.P.; Lam, R.W.; Christie, B.R. Antidepressant effects of exercise: Evidence for an adult-neurogenesis hypothesis? J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2006, 31, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Penninx, B.W.; Beekman, A.T.; Bandinelli, S.; Corsi, A.M.; Bremmer, M.; Hoogendijk, W.J.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L. Late-life depressive symptoms are associated with both hyperactivity and hypoactivity of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2007, 15, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kloet, E.R.; Joëls, M.; Holsboer, F. Stress and the brain: From adaptation to disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campeau, S.; Nyhuis, T.J.; Sasse, S.K.; Kryskow, E.M.; Herlihy, L.; Masini, C.V.; Babb, J.A.; Greenwood, B.N.; Fleshner, M.; Day, H.E. Hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis responses to low-intensity stressors are reduced after voluntary wheel running in rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2010, 22, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranahan, A.M.; Lee, K.; Mattson, M.P. Central mechanisms of HPA axis regulation by voluntary exercise. Neuromol. Med. 2008, 10, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.A.; Gates, W.K.; Maksud, M.G.; Morgan, W.P. Increases in plasma beta-endorphin/beta-lipotropin immunoreactivity after treadmill running in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1982, 52, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambert, S.R.; Garthwaite, T.L.; Pontzer, C.H.; Cook, E.E.; Tristani, F.E.; Duthie, E.H.; Martinson, D.R.; Hagen, T.C.; McCarty, D.J. Running elevates plasma beta-endorphin immunoreactivity and ACTH in untrained human subjects. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1981, 168, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabel, K.; Fabel, K.; Tam, B.; Kaufer, D.; Baiker, A.; Simmons, N.; Kuo, C.J.; Palmer, T.D. VEGF is necessary for exercise-induced adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schobersberger, W.; Hobisch-Hagen, P.; Fries, D.; Wiedermann, F.; Rieder-Scharinger, J.; Villiger, B.; Frey, W.; Herold, M.; Fuchs, D.; Jelkmann, W. Increase in immune activation, vascular endothelial growth factor and erythropoietin after an ultramarathon run at moderate altitude. Immunobiology 2000, 201, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeper, S.A.; Gómez-Pinilla, F.; Choi, J.; Cotman, C.W. Physical activity increases mRNA for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor in rat brain. Brain Res. 1996, 726, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouloff, F.; Laude, D.; Elghozi, J.L. Physical exercise: Evidence for differential consequences of tryptophan on 5-HT synthesis and metabolism in central serotonergic cell bodies and terminals. J. Neural Transm. 1989, 78, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, A.I.; Thorlin, T.; Bull, C.; Zarnegar, P.; Ekman, R.; Terenius, L.; Eriksson, P.S. Mu- and delta-opioid receptor antagonists decrease proliferation and increase neurogenesis in cultures of rat adult hippocampal progenitors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Singh, R.H.; Dey, P.K. Exercise training: Significance of regional alterations in serotonin metabolism of rat brain in relation to antidepressant effect of exercise. Physiol. Behav. 1992, 52, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairanen, M.; Lucas, G.; Ernfors, P.; Castrén, M.; Castrén, E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and antidepressant drugs have different but coordinated effects on neuronal turnover, proliferation, and survival in the adult dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastioli, G.; Arnold, J.C.; Mancini, M.; Mar, A.C.; Gamallo-Lana, B.; Saadipour, K.; Chao, M.V.; Rice, M.E. Voluntary Exercise Boosts Striatal Dopamine Release: Evidence for the Necessary and Sufficient Role of BDNF. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 4725–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wei, R.; Lu, Y. Effect of a Nurse-Led Exercise Program on Depression in Elderly Patients with Diabetes: A Retrospective Study. Actas Esp. Psiquiatr. 2024, 52, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, S.; Barzegari, A.; Shariatzadeh, M.; Vatandoust, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Mahdinia, E.; Neghabi, F.; Rajabpour, A.; Sadat Aleahmad, A.; Sadat Balaghati, F.; et al. Voluntary physical activity increases maternal care and reduces anxiety- and depression-related behaviours during the postpartum period in mice. Brain Res. 2022, 1784, 147880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calapai, M.; Puzzo, L.; Bova, G.; Vecchio, D.A.; Blandino, R.; Barbagallo, A.; Ammendolia, I.; Cardia, L.; Calapai, F.; Currò, M.; et al. Effects of Physical Exercise and Motor Activity on Depression and Anxiety in Post-Mastectomy Pain Syndrome. Life 2024, 14, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.Y.; Han, S.S.; Zhang, Y.S.; Ye, Y.P.; Xu, C.Y. Effect of physical exercise on negative emotions in Chinese university students: The mediating effect of self-efficacy. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, C.A.; Hay, M.; Bloch, M.H. Meta-analysis: Aerobic exercise for the treatment of anxiety disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 45, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segar, M.L.; Katch, V.L.; Roth, R.S.; Garcia, A.W.; Portner, T.I.; Glickman, S.G.; Haslanger, S.; Wilkins, E.G. The effect of aerobic exercise on self-esteem and depressive and anxiety symptoms among breast cancer survivors. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 1998, 25, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wayne, P.M.; Lee, M.S.; Novakowski, J.; Osypiuk, K.; Ligibel, J.; Carlson, L.E.; Song, R. Tai Chi and Qigong for cancer-related symptoms and quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cancer Surviv. 2018, 12, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishwarya, S.; Kumar, P. Aerobic Exercise Versus Plyometrics in Reducing Anxiety Levels in College Students with Mild Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Cureus 2024, 16, e70165. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza Moura, A.M.; Lamego, M.K.; Paes, F.; Ferreira Rocha, N.B.; Simoes-Silva, V.; Rocha, S.A.; de Sá Filho, A.S.; Rimes, R.; Manochio, J.; Budde, H.; et al. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Anxiety Disorders: A Systematic Review. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 14, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBouthillier, D.M.; Asmundson, G.J. A Single Bout of Aerobic Exercise Reduces Anxiety Sensitivity But Not Intolerance of Uncertainty or Distress Tolerance: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 2015, 44, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters-Stone, K.M.; Horak, F.; Jacobs, P.G.; Trubowitz, P.; Dieckmann, N.F.; Stoyles, S.; Faithfull, S. Falls, Functioning, and Disability Among Women with Persistent Symptoms of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2604–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.M.; Thomas, S.M.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Douglas, P.S.; Yu, A.F.; Rusch, V.; Huang, J.; Capaci, C.; Harrison, J.N.; Stoeckel, K.J.; et al. Effects and tolerability of exercise therapy modality on cardiorespiratory fitness in lung cancer: A randomized controlled trial. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Gaia, J.W.P.; Schuch, F.B.; Ferreira, R.W.; Souza, E.L.; Ferreira, V.M.S.; Pires, D.A. Effects of high-intensity interval training on depressive and anxiety symptoms in healthy individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2024, 34, e14618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, E.M.; Loukov, D.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Heisz, J.J. Exercise reduces depression and inflammation but intensity matters. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 133, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Tao, X.; Hou, X.; Du, L.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. The effect of exercise on flow-mediated dilation in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1347399. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhen, K.; Su, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. The Effect of Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Function in People with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.; Lin, A.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, H.; Sun, C.; Yang, H. Effects of health qigong exercise on sleep and life quality in patients with drug abuse. Hong Kong J. Occup. Ther. 2023, 36, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rethorst, C.D.; Wipfli, B.M.; Landers, D.M. The antidepressive effects of exercise: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izci-Balserak, B.; Zhu, B.; Wang, H.; Bronas, U.G.; Gooneratne, N.S. Independent associations between sleep duration, gamma gap, and cognitive function among older adults: Results from the NHANES 2013–2014. Geriatr. Nurs. 2022, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barğı, G.; Baytok, E.; Çelik, Z.; Türk, M.Ş.; Çelik, A.; Kurul, İ.C.; Boşnak Güçlü, M. Exercise capacity, muscle strength, dyspnea, physical activity, and quality of life in preoperative patients with lung cancer. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 2621–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tao, X.; Lei, B.; Hou, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, L. Effects of exercise on post-stroke cognitive function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2024, 31, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; You, Q.; Hou, X.; Zhang, S.; Du, L.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. The effect of exercise on cognitive function in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 2908–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Hou, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, L. The effect of exercise on balance function in stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 4751–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, A.; Okwose, N.; Scragg, J.; Eggett, C.; Luke, P.; Bandali, A.; Velicki, R.; Greaves, L.; MacGowan, G.A.; Jakovljevic, D.G. The effect of age on mechanisms of exercise tolerance: Reduced arteriovenous oxygen difference causes lower oxygen consumption in older people. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 149, 111340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, K.; Hladkowicz, E.; Dorrance, K.; Bryson, G.L.; Forster, A.J.; Gagné, S.; Huang, A.; Lalu, M.M.; Lavallée, L.T.; Saunders, C.; et al. Barriers and facilitators to participation in exercise prehabilitation before cancer surgery for older adults with frailty: A qualitative study. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picorelli, A.M.; Pereira, L.S.; Pereira, D.S.; Felício, D.; Sherrington, C. Adherence to exercise programs for older people is influenced by program characteristics and personal factors: A systematic review. J. Physiother. 2014, 60, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).