A Novel Bromophenol Derivative BOS-102 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human A549 Lung Cancer Cells via ROS-Mediated PI3K/Akt and the MAPK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. BOS-102 Inhibits Cell Proliferation
2.2. BOS-102 Inhibits Colony Formation
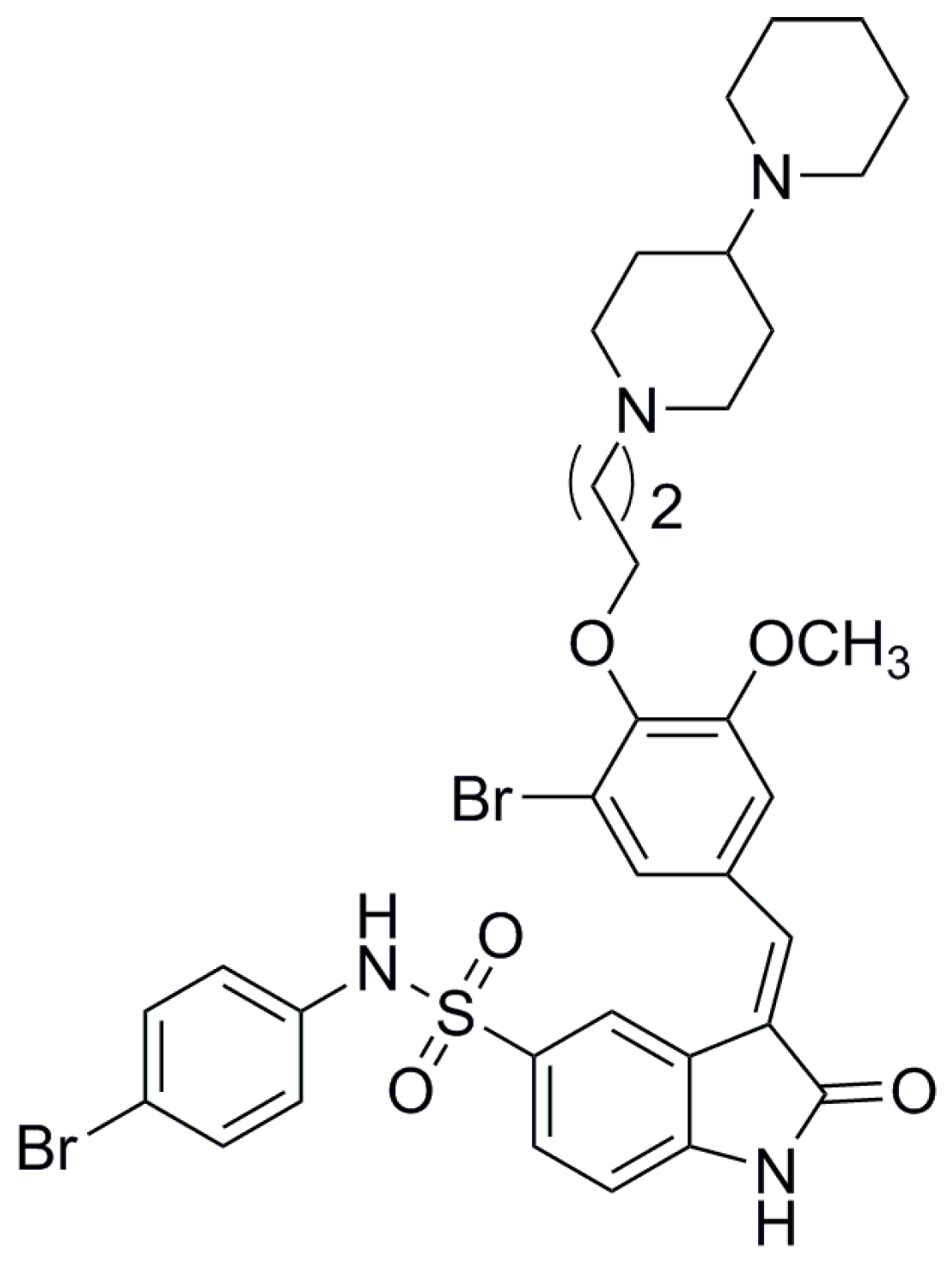
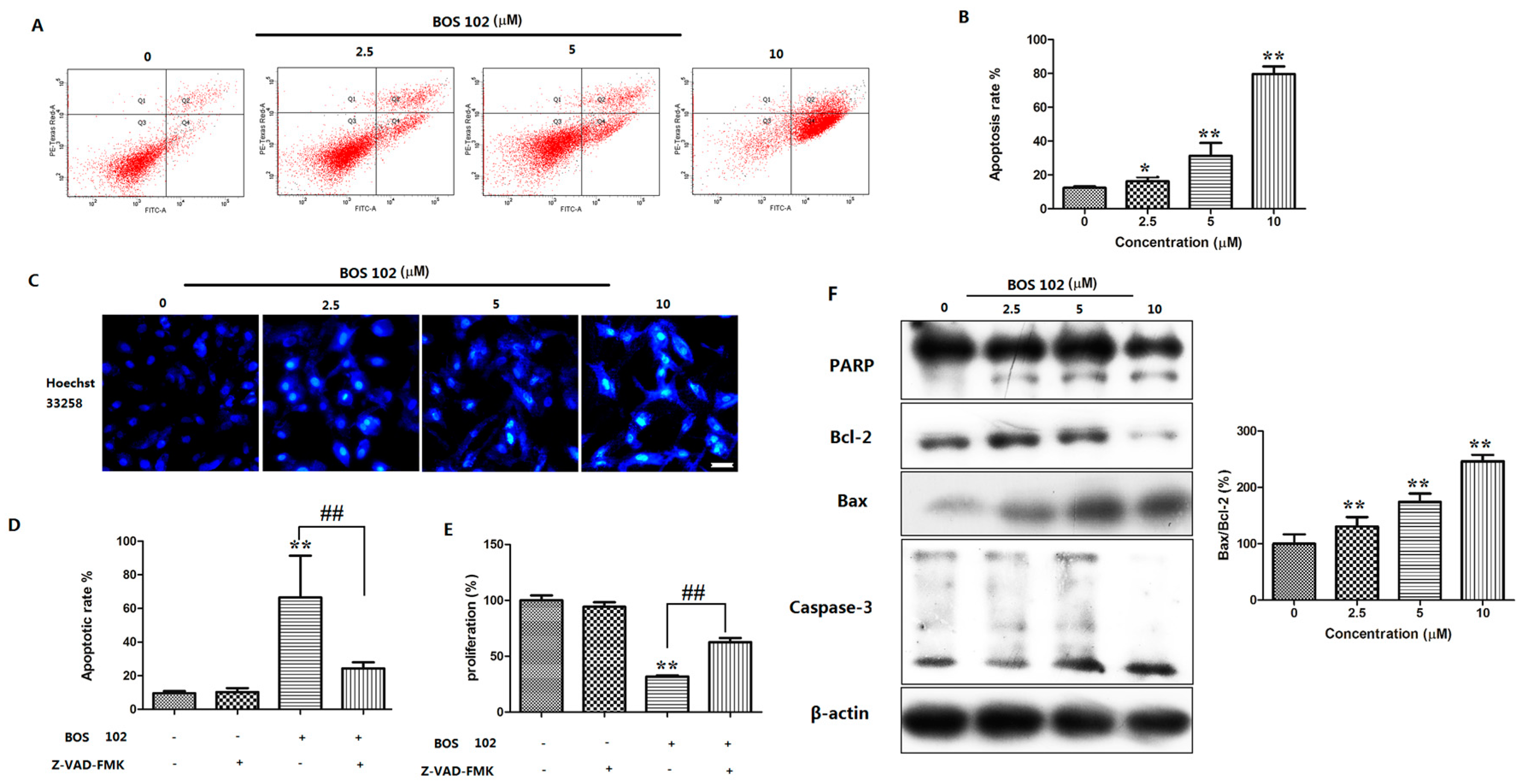
2.3. BOS-102 Induces A549 Apoptosis
2.4. Effect of BOS-102 on the Expression of Apoptosis-Related Proteins
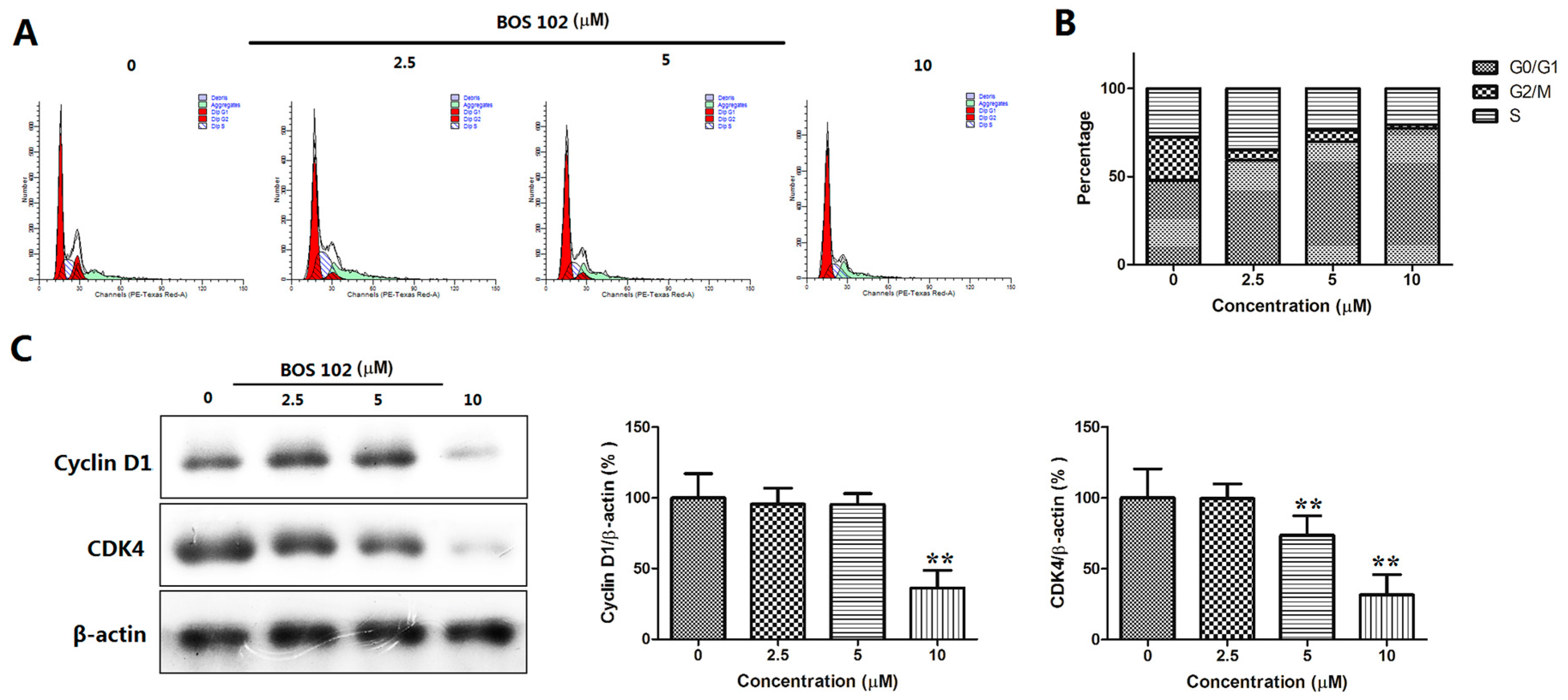
2.5. BOS-102 Induces G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Down-Regulates Cyclin D1 and CDK4 in A549 Cells
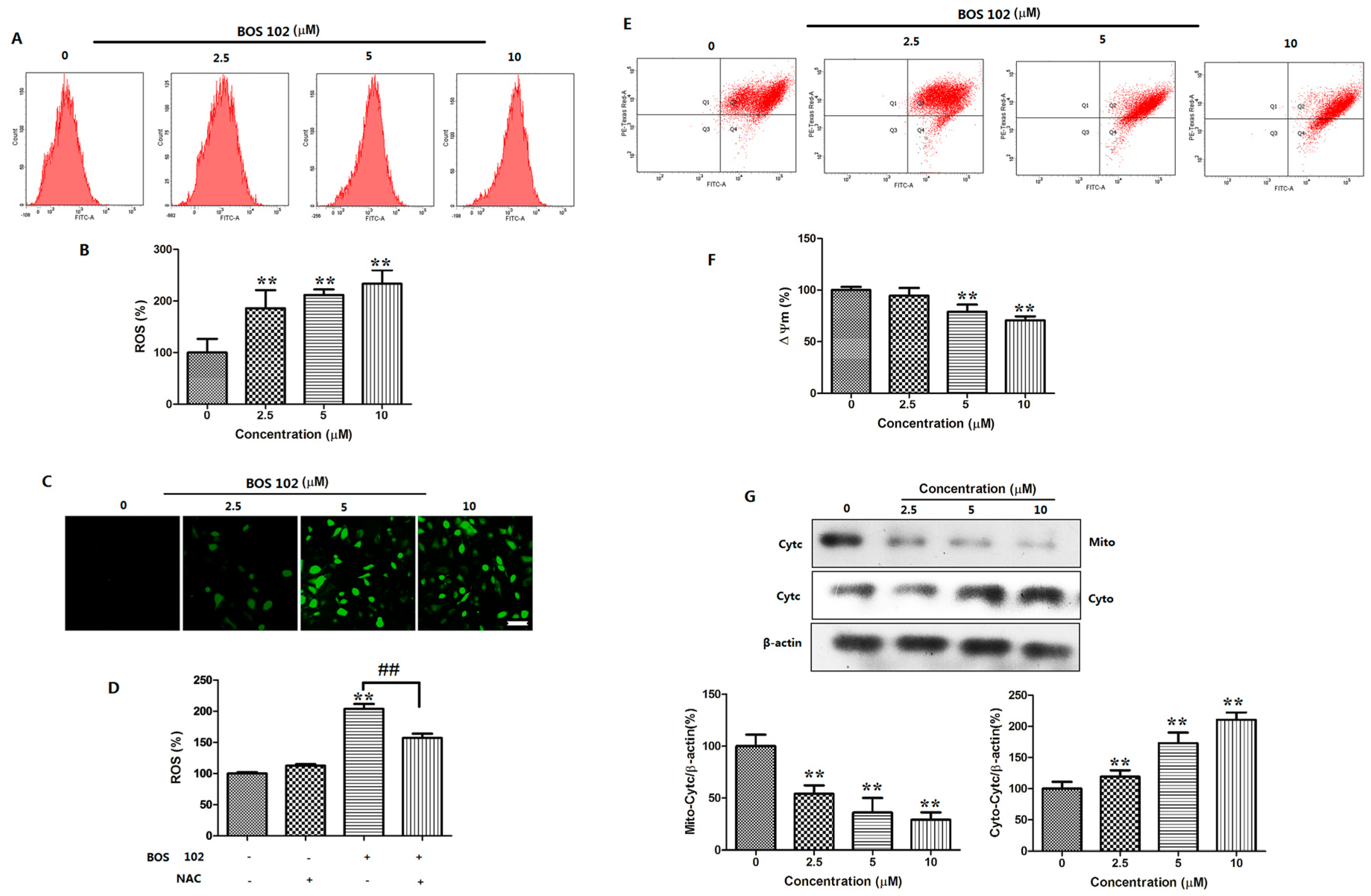
2.6. BOS-102 Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunctionin in A549 Cells
2.7. BOS-102 Induces ROS Generation in A549 Cells
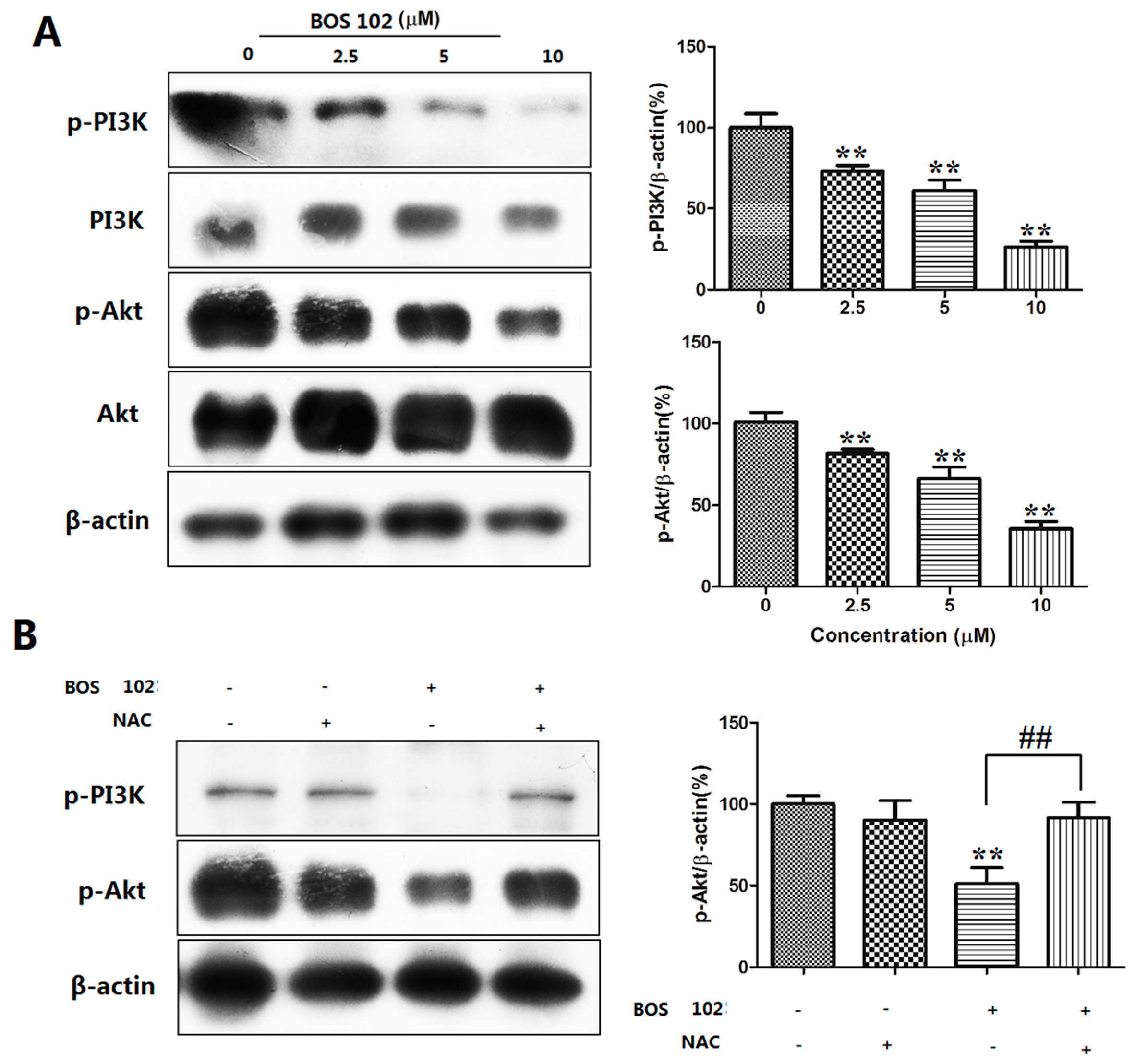
2.8. BOS-102 Suppresses the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
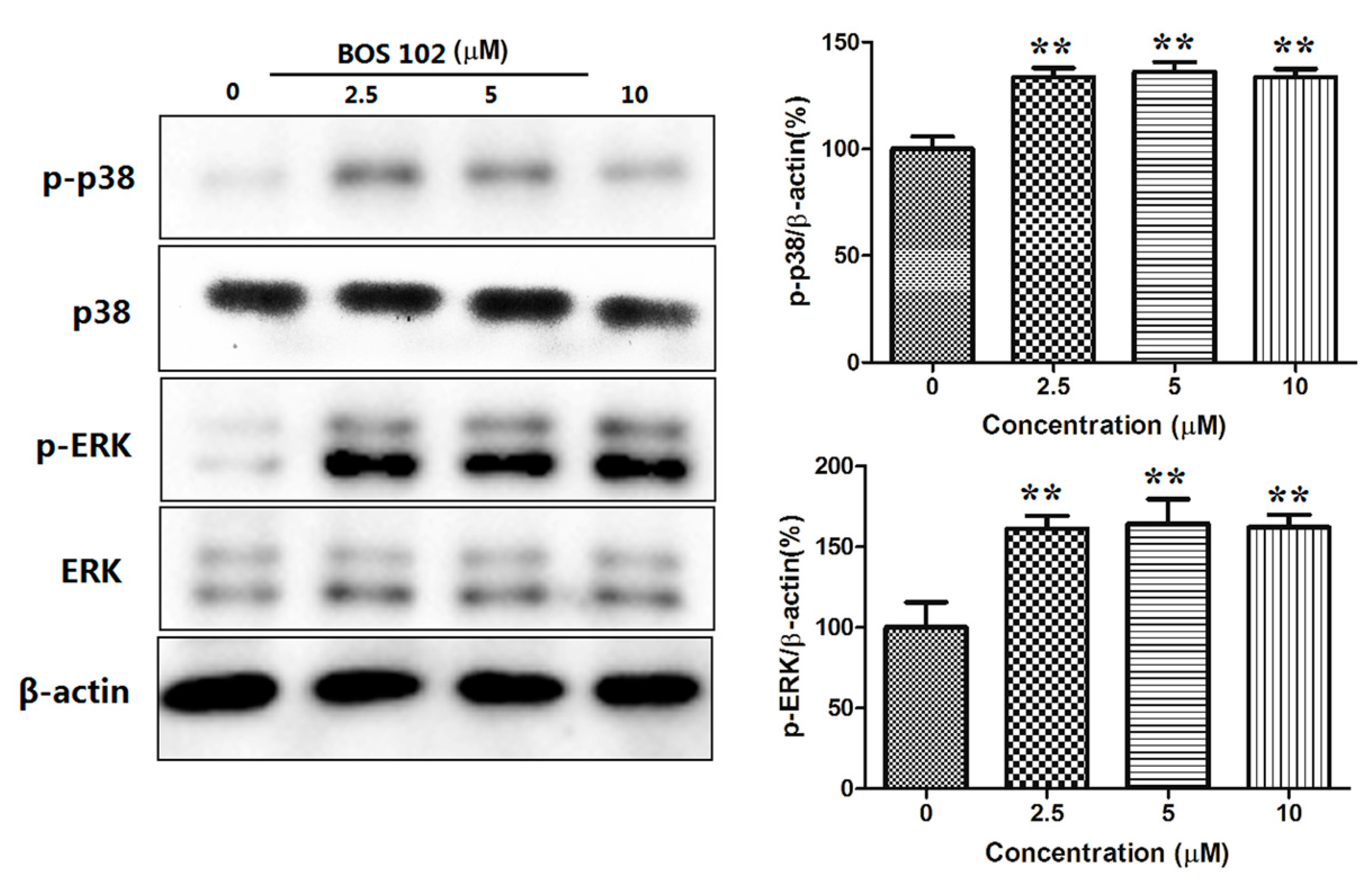
2.9. BOS-102 Activates the P38/ERK Signaling Pathway
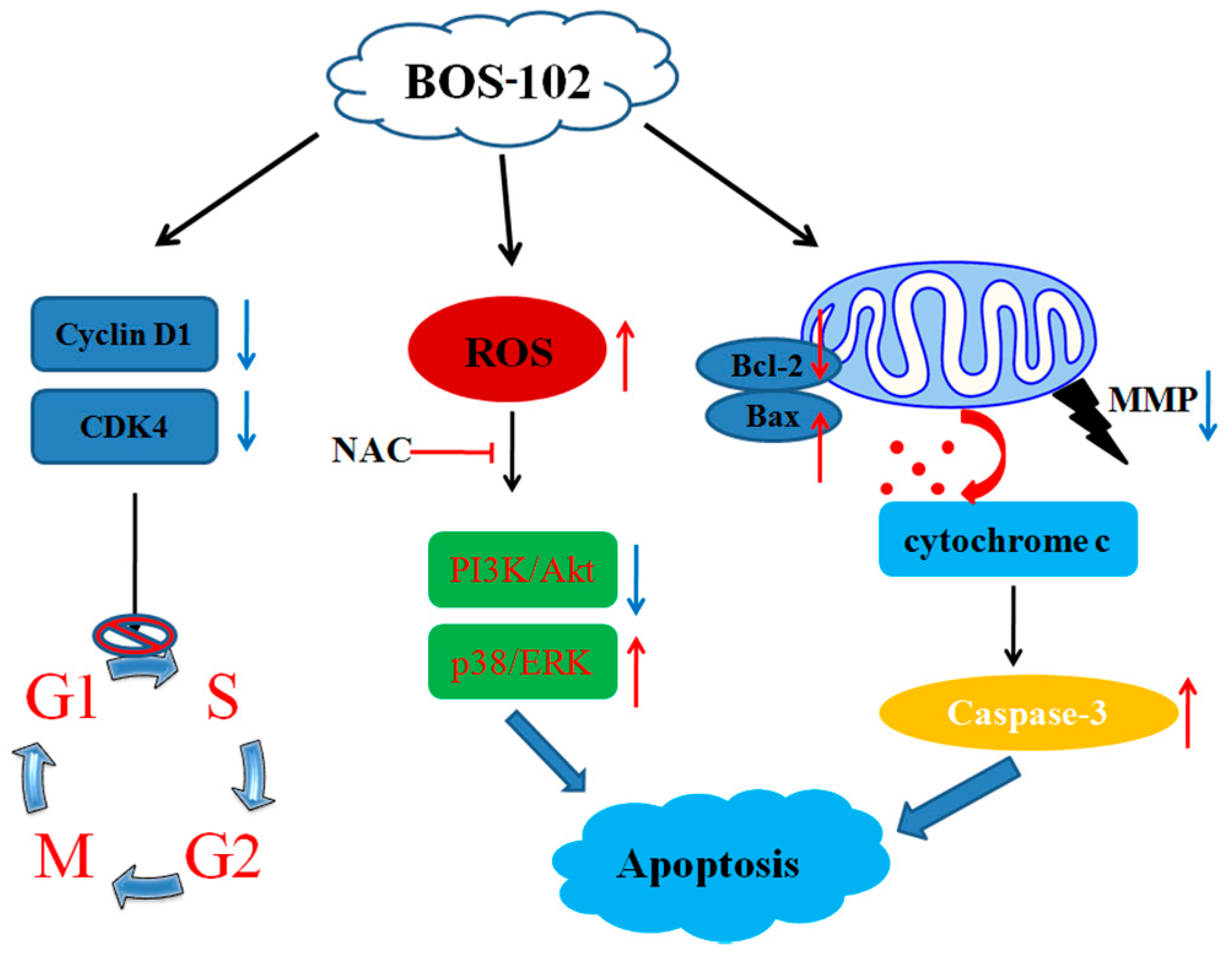
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Test
4.4. Colony Forming Assay
4.5. Assays for Apoptosis
4.6. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Cell Cycle
4.7. Morphological Analysis of Apoptosis
4.8. ROS Determination
4.9. Analysis of the MMP
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Travis, W.D.; Rusch, V.W. Lung cancer—Major changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhu, J.; Ding, K. Inhibition of cathepsin S induces autophagy and apoptosis in human glioblastoma cell lines through ROS-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and JNK signaling pathways. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 228, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleury, C.; Mignotte, B.; Vayssiere, J.L. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling. Biochimie 2002, 84, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainaut, P.; Plymoth, A. Targeting the hallmarks of cancer: Towards a rational approach to next-generation cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Youn, H.; Kang, C.; Youn, B. Inflammation-induced radioresistance is mediated by ROS-dependent inactivation of protein phosphatase 1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Qin, B.; Qi, X.; Mao, J.; Wu, D. Isoalantolactone induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells via ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway and downregulation of SIRT1. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, Q.; Lu, N. LYG-202 exerts antitumor effect on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 1253–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romashkova, J.A.; Makarov, S.S. NF-kappa B is a target of AKT in anti-apoptotic PDGF signalling. Nature 1999, 401, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Chu, B.Z.; Liu, F.; Li, B.; Gao, C.M.; Li, L.L.; Sun, Q.S.; Shen, Z.F.; Jiang, Y.Y. New benzimidazole acridine derivative induces human colon cancer cell apoptosis in vitro via the ROS-JNK signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, H.; Wartenberg, M.; Hescheler, J. Reactive oxygen species as intracellular messengers during cell growth and differentiation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2001, 11, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki, Y.W.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Shin, I.C.; Koh, H.C. JNK and p38 MAPK regulate oxidative stress and the inflammatory response in chlorpyrifos-induced apoptosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 218, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Jiang, B.; Wu, N.; Li, X.Q.; Wang, B.C.; Luo, J.; Yang, M.; Jin, S.H.; Shi, D.Y. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel bromophenol derivatives incorporating indolin-2-one moiety as potential anticancer agents. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 806–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Hansen, P.E.; Lin, X.K. Bromophenols in Marine Algae and Their Bioactivities. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1273–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oztaskin, N.; Cetinkaya, Y.; Taslimi, P.; Goksu, S.; Gulcin, I. Antioxidant and acetylcholinesterase inhibition properties of novel bromophenol derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 60, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-J.; Guo, C.-L.; Li, X.-Q.; Wang, S.-Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.-J.; et al. Discovery of Novel Bromophenol Hybrids as Potential Anticancer Agents through the Ros-Mediated Apoptotic Pathway: Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Luo, J.; Jiang, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Fu, C.; Li, J.; Shi, D. Marine bromophenol bis (2,3-dibromo-4,5-dihydroxy-phenyl)-methane inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via modulating beta1-integrin/FAK signaling. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1010–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Chi, G.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Moon, S.K.; Nam, S.W.; Kim, W.J.; Yoo, Y.H.; Choi, Y.H. Induction of apoptosis and autophagy by sodium selenite in A549 human lung carcinoma cells through generation of reactive oxygen species. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 212, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treite, F.; Kohler, L.; Mosch, B.; Pietzsch, J. Cell cycle regulating kinase Cdk4 as a potential target for tumour visualisation in vivo. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, S325. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, J.H.; Hsu, L.S.; Huang, H.C.; Lin, C.L.; Pan, M.H.; Hong, H.M.; Chen, W.J. 1-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)-3-phenyl-1,3-propanedione Induces G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Autophagy in HeLa Cervical Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.P.; Guo, C.L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Lv, Y.B.; Lv, F.X.; Lu, Z.X. Fengycin inhibits the growth of the human lung cancer cell line 95D through reactive oxygen species production and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2013, 24, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhao, Q.L.; Wu, L.H.; Jawaid, P.; Jiao, Y.F.; Kadowaki, M.; Kondo, T. Isofraxidin, a potent reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger, protects human leukemia cells from radiation-induced apoptosis via ROS/mitochondria pathway in p53-independent manner. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Won, Y.S.; Park, K.H.; Lee, M.K.; Tachibana, H.; Yamada, K.; Seo, K.I. Celastrol inhibits growth and induces apoptotic cell death in melanoma cells via the activation ROS-dependent mitochondrial pathway and the suppression of PI3K/AKT signaling. Apoptosis 2012, 17, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, W.; Liu, W.; Gao, X. The ERK/eIF4F/Bcl-XL pathway mediates SGP-2 induced osteosarcoma cells apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2014, 352, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhunapantula, S.V.; Mosca, P.J.; Robertson, G.P. The Akt signaling pathway: An emerging therapeutic target in malignant melanoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 1032–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.G.; Dickens, M.; Raingeaud, J.; Davis, R.J.; Greenberg, M.E. Opposing Effects of Erk and Jnk-P38 Map Kinases on Apoptosis. Science 1995, 270, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Hsiao, M.; Chang, J.L.; Yang, S.F.; Tseng, T.H.; Cheng, C.W.; Chow, J.M.; Lin, K.H.; Lin, Y.W.; Liu, C.C.; et al. Quercetin induces mitochondrial-derived apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-mediated ERK activation in HL-60 leukemia cells and xenograft. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Luo, J.D.; Chu, S.Z.; Chen, L.J.; Xu, L.N.; Zang, H.J.; Alnemah, M.M.; Ma, J.; Fan, S.Q. CGP57380 enhances efficacy of RAD001 in non-small cell lung cancer through abrogating mTOR inhibition-induced phosphorylation of eIF4E and activating mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27787–27801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, C.-L.; Wang, L.-J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, X.-Q.; Jiang, B.; Luo, J.; Guo, S.-J.; Wu, N.; Shi, D.-Y. A Novel Bromophenol Derivative BOS-102 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human A549 Lung Cancer Cells via ROS-Mediated PI3K/Akt and the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020043
Guo C-L, Wang L-J, Zhao Y, Liu H, Li X-Q, Jiang B, Luo J, Guo S-J, Wu N, Shi D-Y. A Novel Bromophenol Derivative BOS-102 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human A549 Lung Cancer Cells via ROS-Mediated PI3K/Akt and the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(2):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020043
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Chuan-Long, Li-Jun Wang, Yue Zhao, Hua Liu, Xiang-Qian Li, Bo Jiang, Jiao Luo, Shu-Ju Guo, Ning Wu, and Da-Yong Shi. 2018. "A Novel Bromophenol Derivative BOS-102 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human A549 Lung Cancer Cells via ROS-Mediated PI3K/Akt and the MAPK Signaling Pathway" Marine Drugs 16, no. 2: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020043
APA StyleGuo, C.-L., Wang, L.-J., Zhao, Y., Liu, H., Li, X.-Q., Jiang, B., Luo, J., Guo, S.-J., Wu, N., & Shi, D.-Y. (2018). A Novel Bromophenol Derivative BOS-102 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human A549 Lung Cancer Cells via ROS-Mediated PI3K/Akt and the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs, 16(2), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020043





