Assessment of Nonnucleoside Inhibitors Binding to HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Using HYDE Scoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global HIV & AIDS statistics. Available online: http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet (accessed on 27 March 2019).
- World Health Organization. HIV/AIDS Fact Sheet. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs360/en/ (accessed on 27 March 2019).
- Wainberg, M.A.; Zaharatos, G.J.; Brenner, B.G. Development of antiretroviral drug resistance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, K.M.; Burch, B.D.; Soriano-Sarabia, N.; Margolis, D.M. Prospects for treatment of latent HIV. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 93, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shattock, R.J.; Warren, M.; McCormack, S.; Hankins, C.A. AIDS. Turning the tide against HIV. Science 2011, 333, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bec, G.; Meyer, B.; Gerard, M.A.; Steger, J.; Fauster, K.; Wolff, P.; Burnouf, D.; Micura, R.; Dumas, P.; Ennifar, E. Thermodynamics of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in action elucidates the mechanism of action of non-nucleoside inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9743–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, P.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Fang, Z.; De Clercq, E.; Liu, X. HIV-1 NNRTIs: Structural diversity, pharmacophore similarity, and implications for drug design. Med. Res. Rev. 2013, 33 (Suppl. 1), E1–E72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulup, S.K.; Huang, D.S.; Wong, H.L.; Georg, G.I. Identification of the metabolic profile of the α-tubulin-binding natural product (−)-pironetin. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1484–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Liu, X. Anti-HIV drug discovery and development: Current innovations and future trends. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 59, 2849–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhan, P.; De Clercq, E.; Liu, X. Strategies for the design of HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Lessons from the development of seven representative paradigms. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3595–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahungu, T.; Owen, A. Current progress in the pharmacogenetics of infectious disease therapy. In Genetics and Evolution of Infectious Disease, 2nd ed.; Tibayrenc, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.A.; Li, J.F.; Morris, L.; Martinson, N.; Gray, G.; McIntyre, J.; Heneine, W. Emergence of drug-resistant HIV-1 after intrapartum administration of single-dose nevirapine is substantially underestimated. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V.A.; Brun-Vezinet, F.; Clotet, B.; Conway, B.; D’Aquila, R.T.; Demeter, L.M.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Pillay, D.; Schapiro, J.M.; Telenti, A.; et al. Drug resistance mutations in HIV-1. Top. HIV Med. 2003, 11, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Lehman, D.A.; Wamalwa, D.C.; McCoy, C.O.; Matsen, F.A.; Langat, A.; Chohan, B.H.; Benki-Nugent, S.; Custers-Allen, R.; Bushman, F.D.; John-Stewart, G.C.; et al. Low-frequency nevirapine resistance at multiple sites may predict treatment failure in infants on nevirapine-based treatment. JAIDS J. Acquired Immune Defic. Syndr. 2012, 60, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulco, P.P.; McNicholl, I.R. Etravirine and rilpivirine: Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors with activity against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains resistant to previous nonnucleoside agents. Pharmacotherapy 2009, 29, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usach, I.; Melis, V.; Peris, J.E. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: A review on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2013, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Clark, A.D.; Lewi, P.J.; Heeres, J.; de Jonge, M.R.; Koymans, L.M.H.; Vinkers, H.M.; Daeyaert, F.; Ludovici, D.W.; Kukla, M.J.; et al. Roles of conformational and positional adaptability in structure-based design of TMC125-R165335 (etravirine) and related non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors that are highly potent and effective against wild-type and drug-resistant HIV-1 variants. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 2550–2560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Non-nucleosite RT inhibitors. Available online: http://www.aidsmap.com/Non-nucleoside-RT-inhibitors/page/1729428/ (accessed on 27 March 2019).
- Steegen, K.; Bronze, M.; Papathanasopoulos, M.A.; van Zyl, G.; Goedhals, D.; Variava, E.; MacLeod, W.; Sanne, I.; Stevens, W.S.; Carmona, S. HIV-1 antiretroviral drug resistance patterns in patients failing NNRTI-based treatment: Results from a national survey in South Africa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyrer, C.; Pozniak, A. HIV drug resistance—An emerging threat to epidemic control. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1605–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Fang, Z.; Huang, B.; Lu, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Huo, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Z.; Meng, Q.; et al. Structure-based optimization of thiophene [3,2-d]pyrimidine derivatives as potent HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors with improved potency against resistance-associated variants. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4424–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhan, P.; Li, D.; De Clercq, E.; Liu, X. Recent advances in DAPYs and related analogues as HIV-1 NNRTIs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansdon, E.B.; Brendza, K.M.; Hung, M.; Wang, R.; Mukund, S.; Jin, D.; Birkus, G.; Kutty, N.; Liu, X. Crystal structures of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with etravirine (TMC125) and rilpivirine (TMC278): Implications for drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4295–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, P.A.; Lewi, P.J.; Arnold, E.; Daeyaert, F.; de Jonge, M.; Heeres, J.; Koymans, L.; Vinkers, M.; Guillemont, J.; Pasquier, E.; et al. In search of a novel anti-HIV drug: Multidisciplinary coordination in the discovery of 4-[[4-[[4-[(1E)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl]amino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino] benzonitrile (R278474, rilpivirine). J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludovici, D.W.; De Corte, B.L.; Kukla, M.J.; Ye, H.; Ho, C.Y.; Lichtenstein, M.A.; Kavash, R.W.; Andries, K.; de Bethune, M.P.; Azijn, H.; et al. Evolution of anti-HIV drug candidates. Part 3: Diarylpyrimidine (DAPY) analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 2235–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.M.; Cahn, P.; Grinsztejn, B.; Lazzarin, A.; Mills, A.; Saag, M.; Supparatpinyo, K.; Walmsley, S.; Crauwels, H.; Rimsky, L.T.; et al. Rilpivirine versus efavirenz with tenofovir and emtricitabine in treatment-naive adults infected with HIV-1 (ECHO): A phase 3 randomised double-blind active-controlled trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.J.; Andrade-Villanueva, J.; Clotet, B.; Fourie, J.; Johnson, M.A.; Ruxrungtham, K.; Wu, H.; Zorrilla, C.; Crauwels, H.; Rimsky, L.T.; et al. Rilpivirine versus efavirenz with two background nucleoside or nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors in treatment-naive adults infected with HIV-1 (THRIVE): A phase 3, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.T.; Colby-Germinario, S.P.; Asahchop, E.L.; Oliveira, M.; McCallum, M.; Schader, S.M.; Han, Y.; Quan, Y.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Wainberg, M.A. Effect of mutations at position E138 in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and their interactions with the M184I mutation on defining patterns of resistance to nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors rilpivirine and etravirine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3100–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xu, H.T.; Asahchop, E.L.; Oliveira, M.; Quashie, P.K.; Quan, Y.; Brenner, B.G.; Wainberg, M.A. Compensation by the E138K mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase for deficits in viral replication capacity and enzyme processivity associated with the M184I/V mutations. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11300–11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.T.; Feng, M.; Falgueyret, J.P.; Tawa, P.; Witmer, M.; DiStefano, D.; Li, Y.; Burch, J.; Sachs, N.; Lu, M.; et al. In vitro characterization of MK-1439, a novel HIV-1 nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novič, M.; Tibaut, T.; Anderlub, M.; Borišek, J.; Tomašić, T. The Comparison of Docking Search Algorithms and Scoring Functions: An Overview and Case Studies. In Methods and Algorithms for Molecular Docking-Based Drug Design and Discovery; Dastmalchi, S., Hamzeh-Mivehroud, M., Sokouti, B., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 99–127. [Google Scholar]
- Paneth, A.; Płonka, W.; Paneth, P. What do docking and QSAR tell us about the design of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase nonnucleoside inhibitors? J. Mol. Model. 2017, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzemińska, A.; Świderek, K.; Paneth, P. Theoretical studies of energetics and binding isotope effects of binding a triazole-based inhibitor to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. PCCP 2016, 18, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SCIGRESS; Fujitsu Limited: Tokyo, Japan, 2016.
- ADMEWORKS ModelBuilder; Fujitsu Kyushu Systems, Limited: Fukuoka, Japan, 2014.
- Mercader, A.G.; Duchowicz, P.R.; Fernández, F.M.; Castro, E.A. Advances in the replacement and enhanced replacement method in QSAR and QSPR theories. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, N.; Lange, G.; Hindle, S.; Klein, R.; Rarey, M. A consistent description of HYdrogen bond and Dehydration energies in protein–ligand complexes: Methods behind the HYDE scoring function. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeadIT 2.1.0; BioSolveIT GmbH: St. Augustin, Germany, 2012.
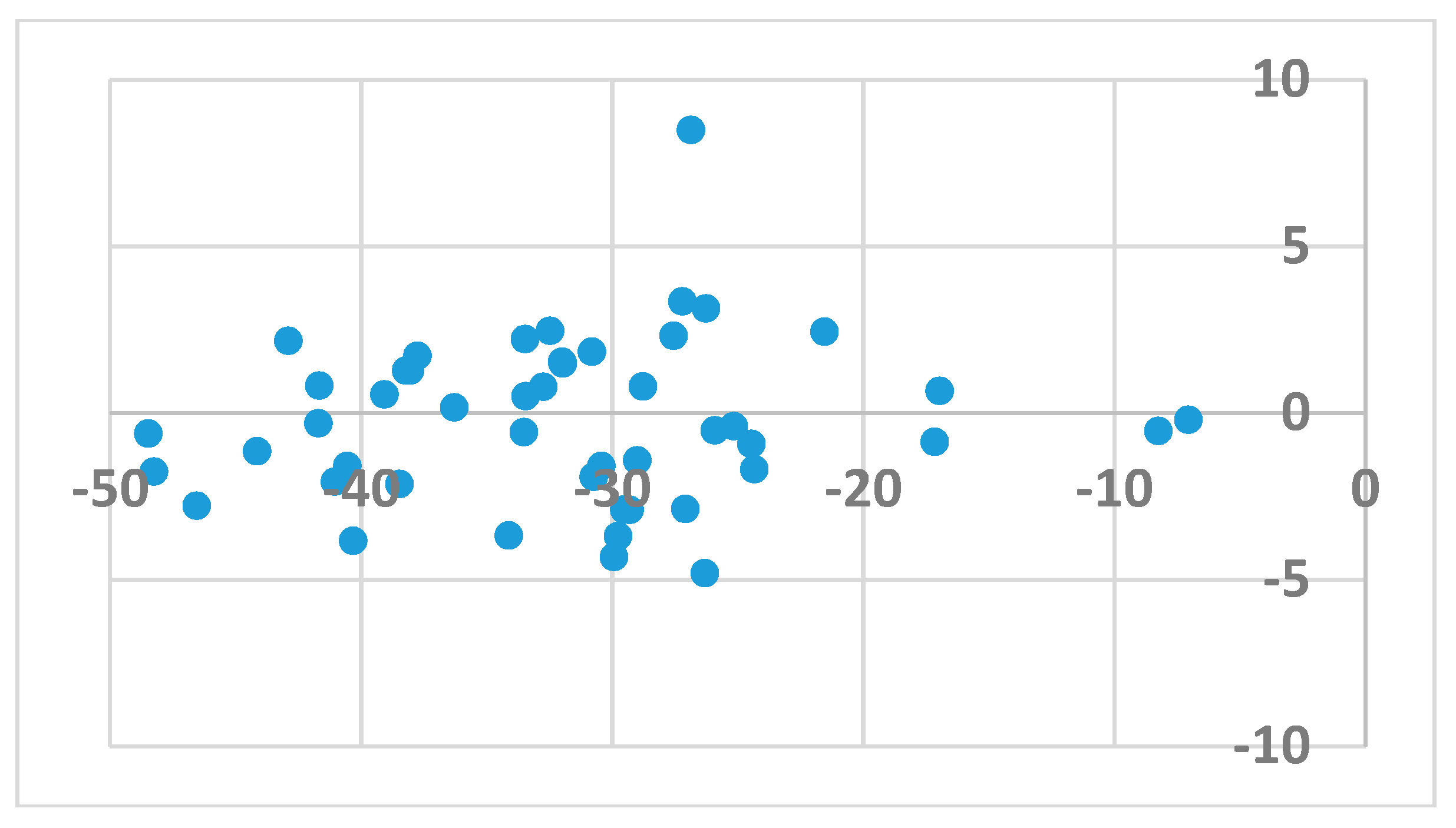
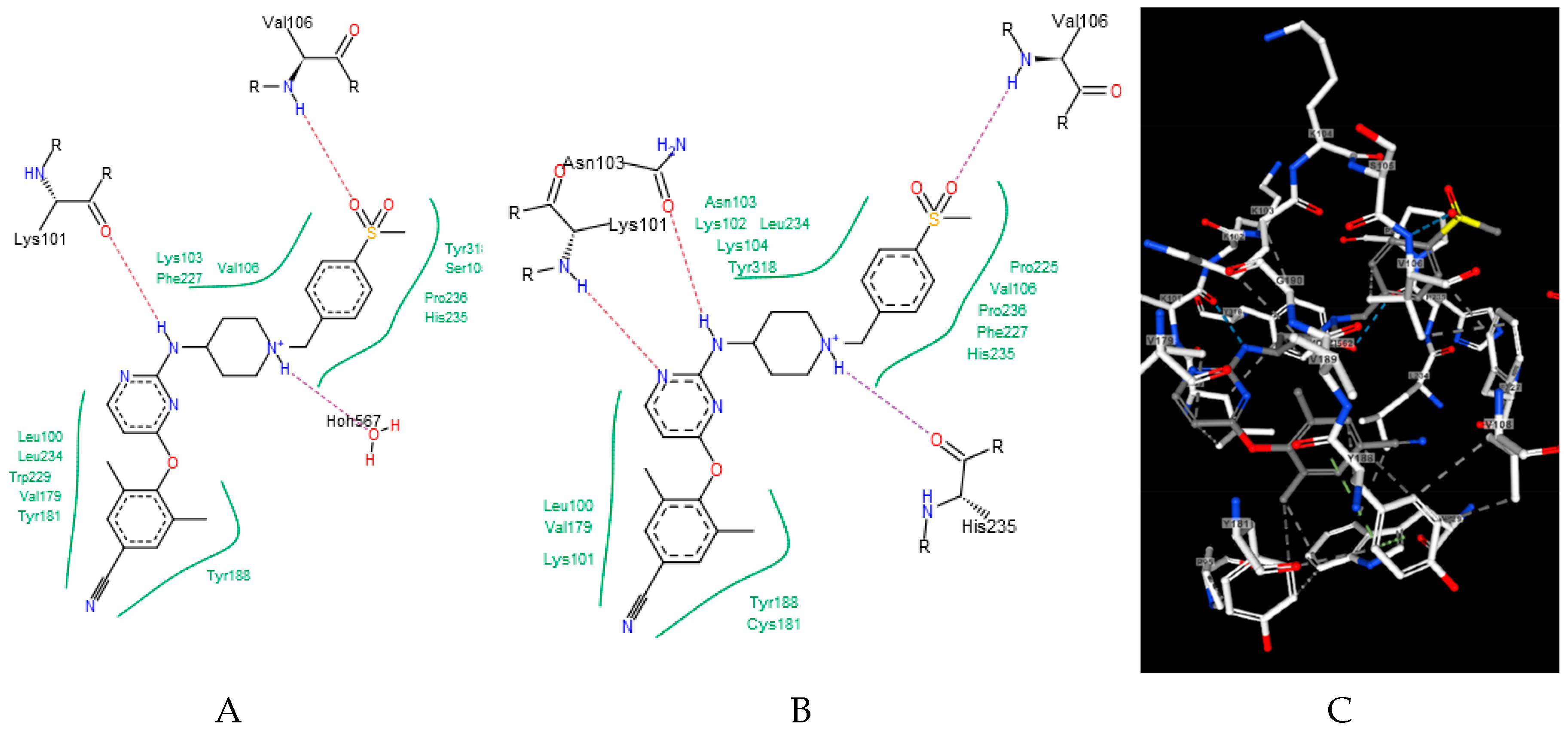
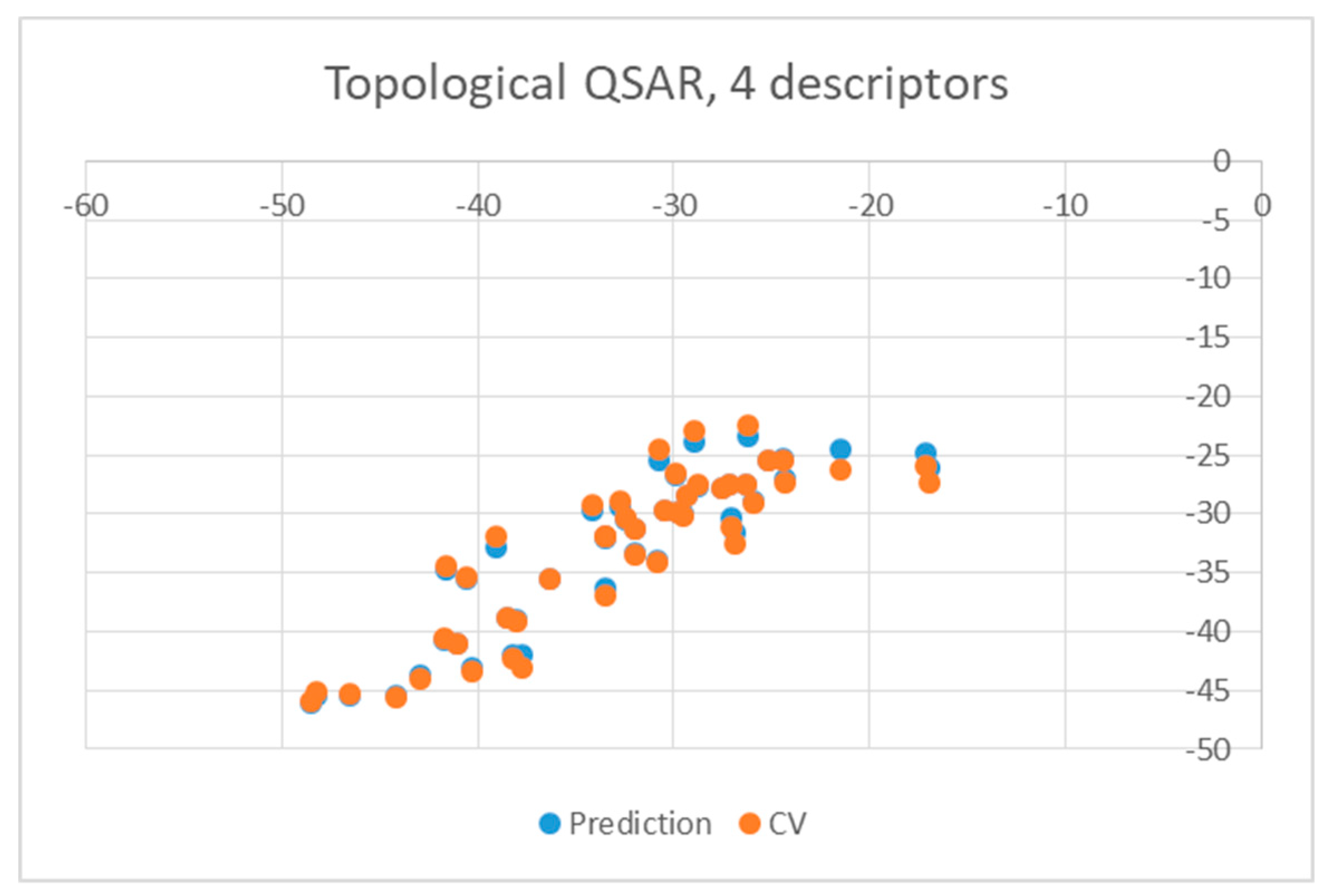
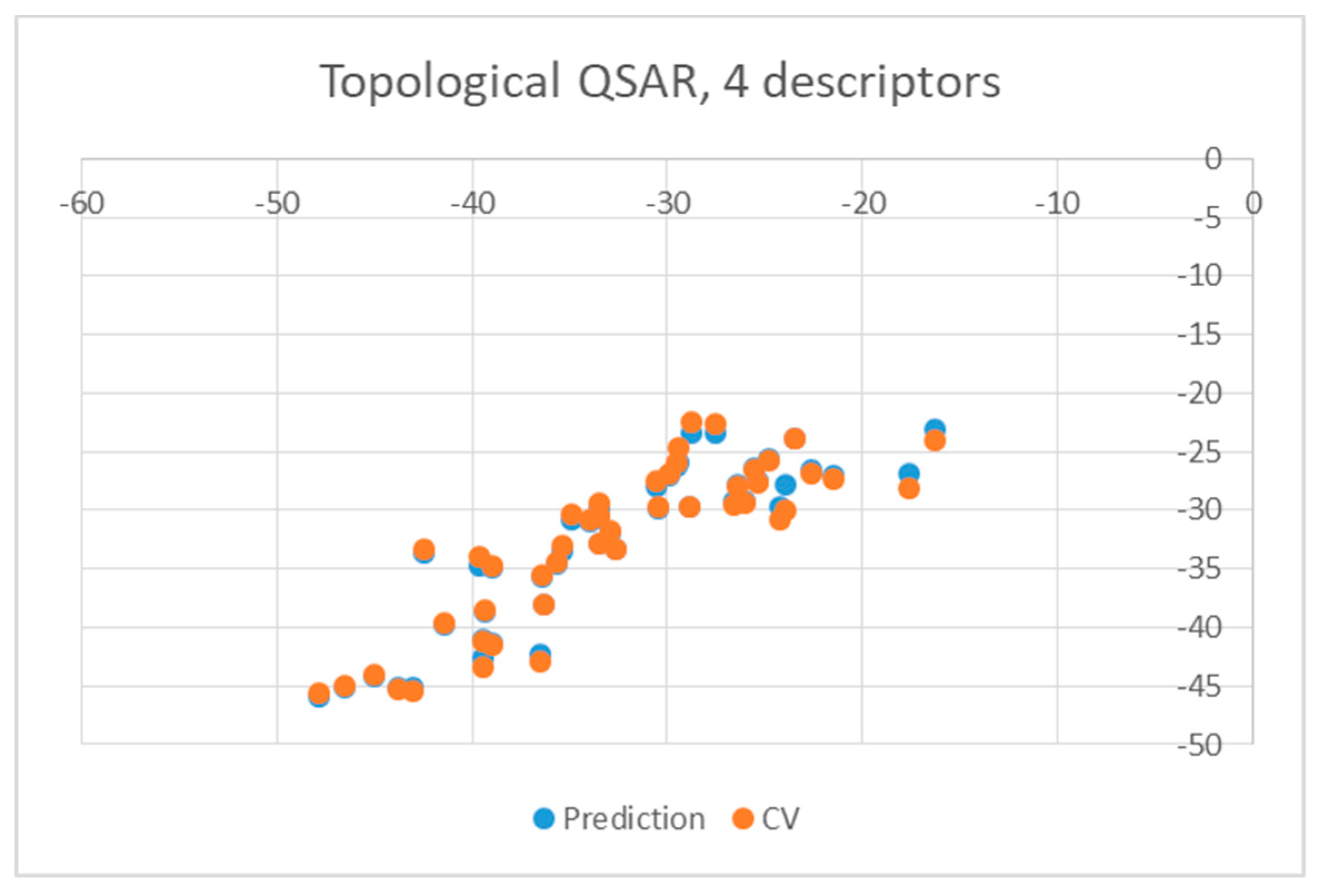
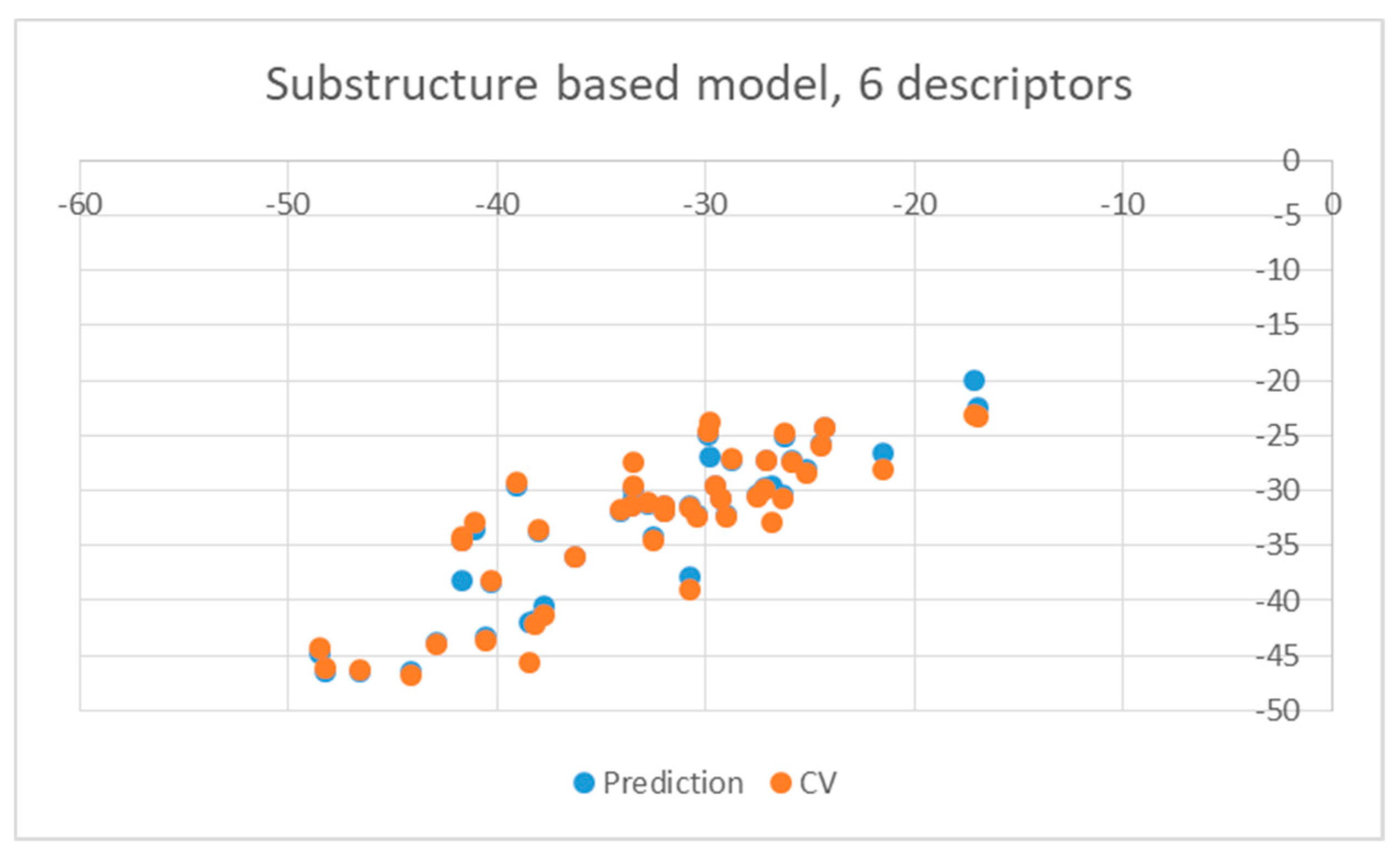
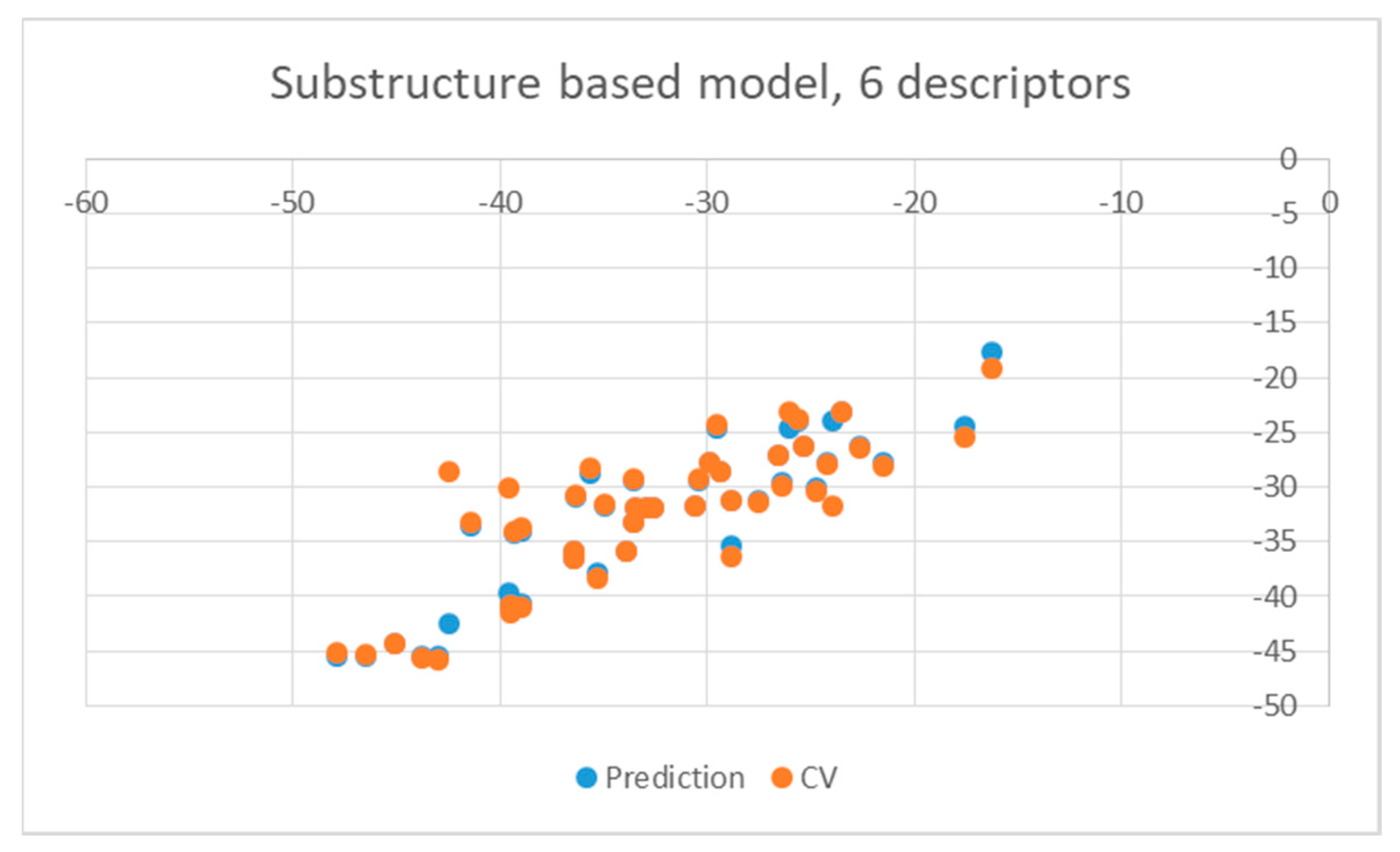
| Ligand | wt | Mutants | Ligand | wt | Mutants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1BT | −34.1152 | −30.4307 | HBY | −38.4728 | −36.3343 |
| 5DV | −36.2861 | −36.4489 | IL5 | −17.1507 | −16.2802 |
| ETR | −29.5144 | −26.6089 | IB1 | −28.9966 | −27.5694 |
| AAP | −27.0837 | −24.194 | IET | −28.7788 | −29.569 |
| AC | −8.23919 | −7.69253 | JLJ | −33.4534 | −33.9484 |
| ADB | −24.4548 | −23.5214 | KBT | −32.7463 | −33.5286 |
| BML | −41.6980 | −41.3882 | KRL | −16.9556 | −17.6174 |
| CXD | −29.3032 | −26.394 | KRP | −27.2074 | −30.5539 |
| DIZ | −26.8585 | −35.3463 | KRV | −25.1656 | −24.7641 |
| EFZ | −33.4729 | −35.689 | MRX | −24.3403 | −22.6474 |
| EUR | −30.4311 | −28.8389 | NNB | −31.9689 | −33.4506 |
| FPT | −27.5513 | −29.8596 | NNC | −30.8118 | −32.6434 |
| FTC | −26.3065 | −21.4942 | NNI | −33.5227 | −32.9436 |
| G73 | −32.4751 | −34.9394 | NVE | −37.7553 | −39.4643 |
| GFA | −38.0480 | −39.3134 | NVP | −25.9061 | −25.3768 |
| GWB | −38.2004 | −39.4685 | RPV | −7.04157 | −6.83753 |
| GWE | −39.0764 | −39.6241 | TNK | −31.9944 | −33.5303 |
| GWI | −21.5385 | −23.9688 | TT1 | −41.0422 | −38.9757 |
| GWJ | −26.2591 | −29.3954 | UCL | −40.5484 | −38.9499 |
| H12 | −44.1400 | −42.9899 | UDR | −40.3172 | −36.4783 |
| H16 | −48.2483 | −46.4841 | WHU | −29.9227 | −45.0533 |
| H18 | −48.4723 | −47.8513 | YKN | −30.7327 | −25.5981 |
| H20 | −46.5444 | −43.7552 | ZZE | −29.7661 | −28.8066 |
| HBQ | −41.6605 | −42.4763 | QO9 | −7.04157 | −6.83753 |
| Descriptor | Normalized Coefficient (wt) | Normalized Coefficient (mutants) |
|---|---|---|
| carbonyl count/MW | 0.4412 | 0.4152 |
| hydrophobic dipole2 | 0.5324 | 0.4130 |
| ln (Nitrogen count) | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 1.0/all bond count | 0.7695 | 0.8702 |
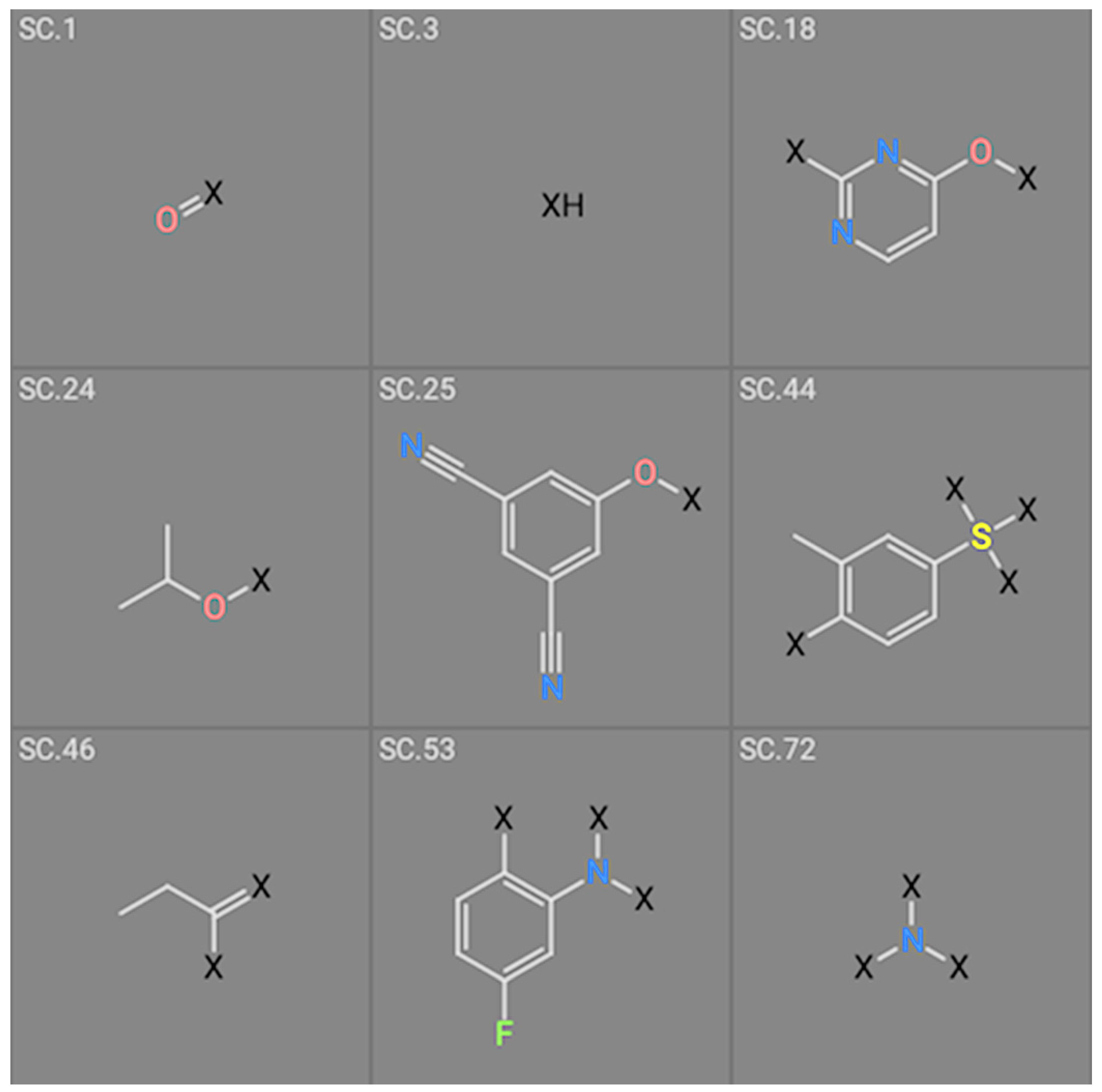
| Structure # | Coefficient wt | Coefficient Mutants |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.84922 | Not used |
| 3 | −4.12649 | −4.15675 |
| 18 | 1.58811 | Not used |
| 24 | −2.07260 | Not used |
| 25 | 3.688460 | 3.63206 |
| 44 | Not used | −1.39970 |
| 46 | Not used | 1.13761 |
| 53 | Not used | −2.04931 |
| 72 | 5.30721 | 5.31799 |
 |  |  |
| 1BT | EFZ | TT1 |
 |  | 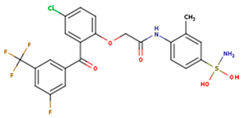 |
| JLJ | GWB | GWE |
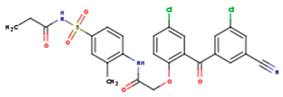 | 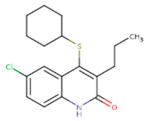 | 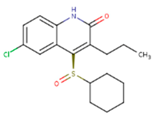 |
| GWI | H16 | H18 |
 |  |  |
| IB1 | WHU | EUR |
 |  |  |
| GWJ | I15 | IET |
 |  |  |
| KR1 | KRP | KRV |
 |  |  |
| NNI | 65B | NVP |
 |  |  |
| TNK | MRX | UC1 |
 |  |  |
| ETR(T27) | HBQ | ADB |
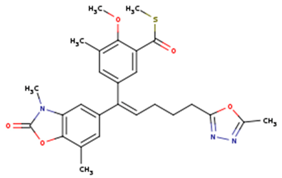 | 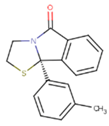 | 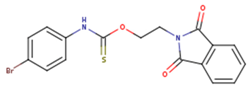 |
| UDR | BM1 | NNB |
 | 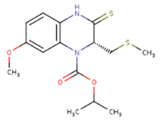 | 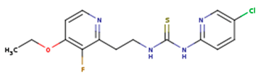 |
| KBT | HBY | FTC |
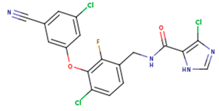 | 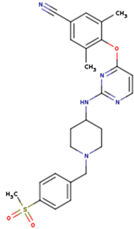 | 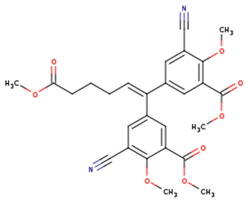 |
| CXD | DJZ | AC7 |
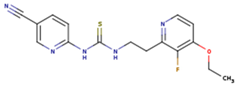 | 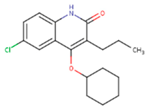 | 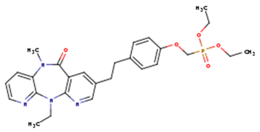 |
| FPT | H12 | NVE |
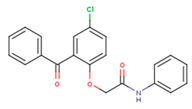 | 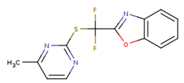 | 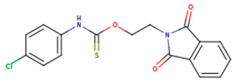 |
| GFA | YKN | NNC |
 | 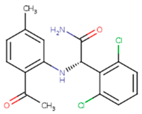 | 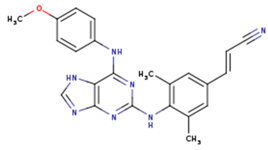 |
| H20 | AAP | G73 |
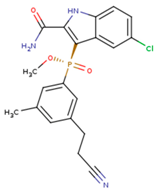 | 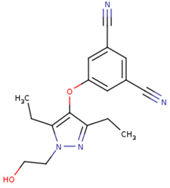 | 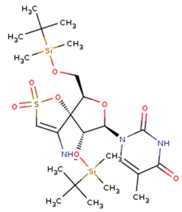 |
| 5DV | ZZE | QO9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paneth, A.; Płonka, W.; Paneth, P. Assessment of Nonnucleoside Inhibitors Binding to HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Using HYDE Scoring. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020064
Paneth A, Płonka W, Paneth P. Assessment of Nonnucleoside Inhibitors Binding to HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Using HYDE Scoring. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(2):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020064
Chicago/Turabian StylePaneth, Agata, Wojciech Płonka, and Piotr Paneth. 2019. "Assessment of Nonnucleoside Inhibitors Binding to HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Using HYDE Scoring" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 2: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020064
APA StylePaneth, A., Płonka, W., & Paneth, P. (2019). Assessment of Nonnucleoside Inhibitors Binding to HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Using HYDE Scoring. Pharmaceuticals, 12(2), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020064






