Agave Fructans as a Carbon Source to Develop a Postbiotic-Based Strategy for the Prophylaxis and Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
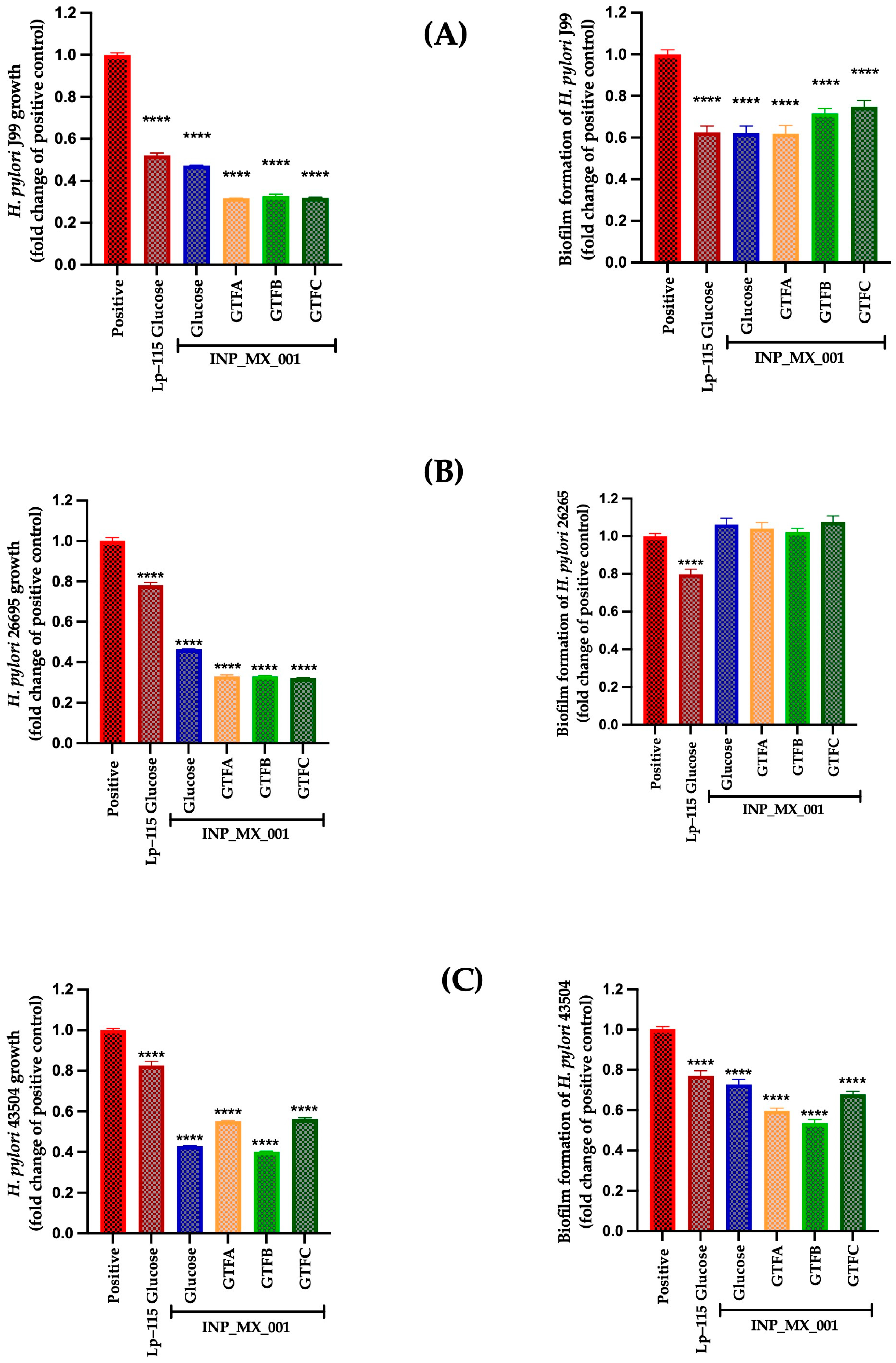
2.1. Prophylactic and Therapeutic Effects of LAB Strain E/S Products Against H. pylori
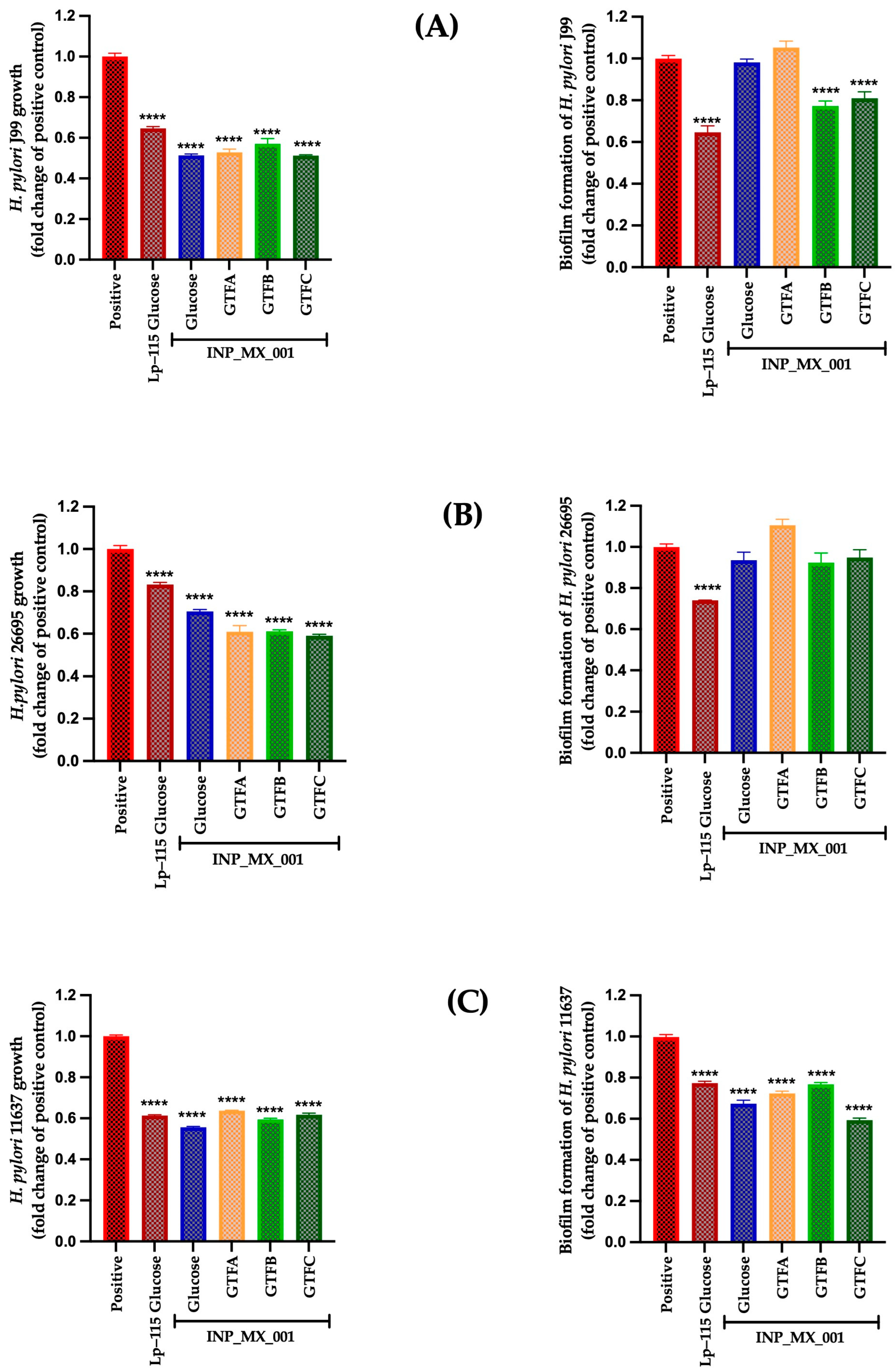
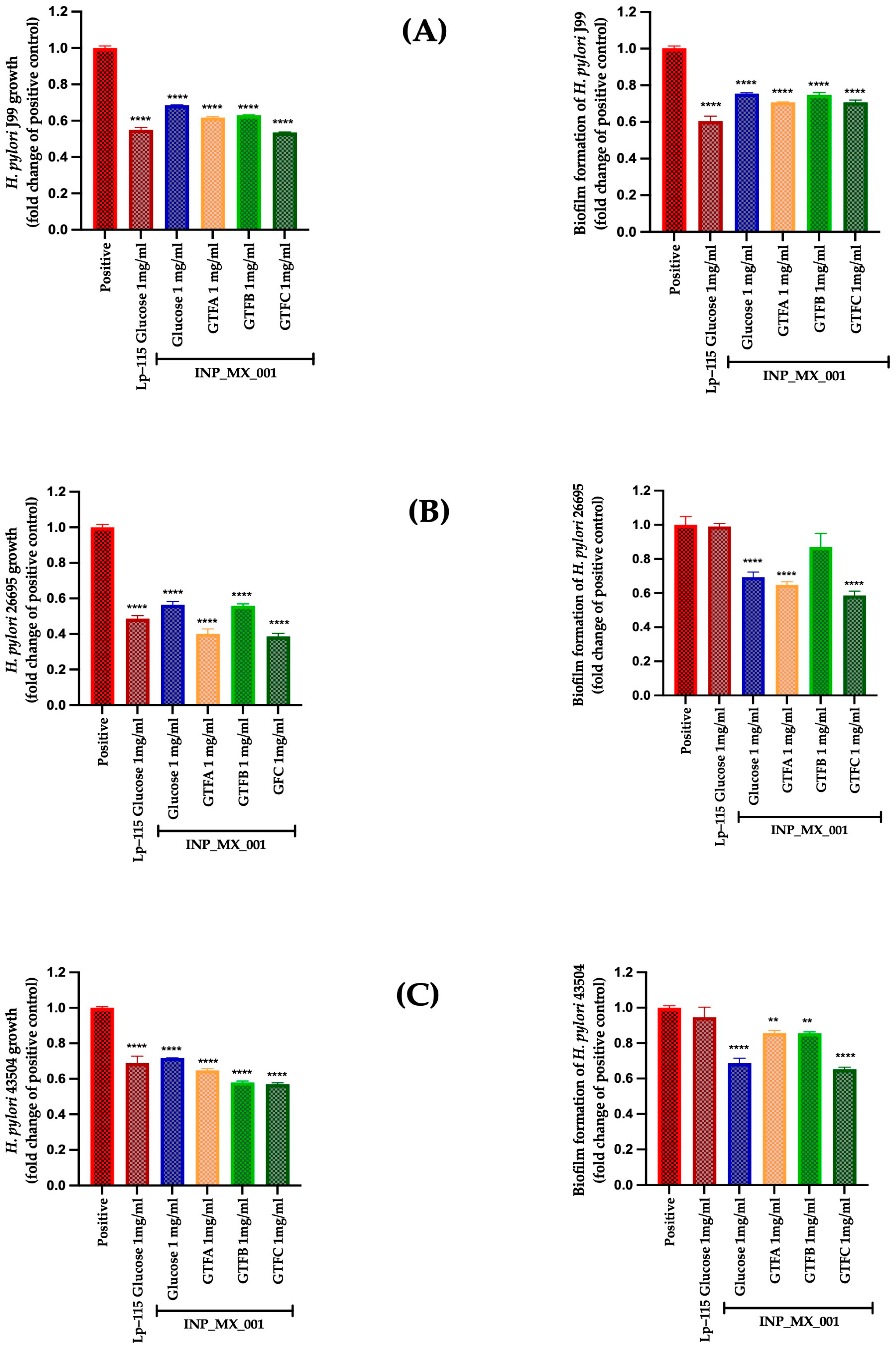
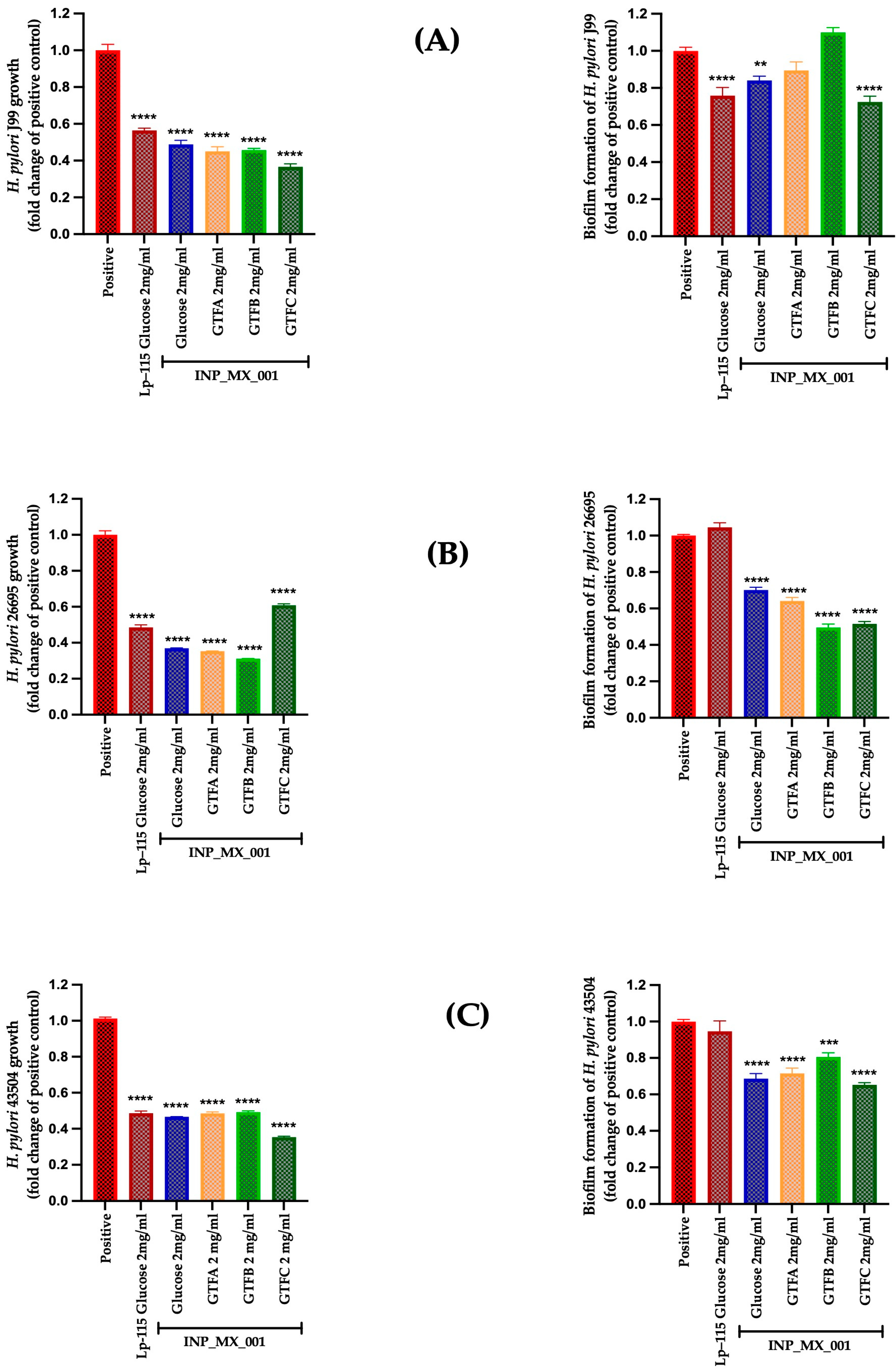
2.2. Prophylactic Effects Against H. pylori of EPSs Extracted from the INP_MX_001 LAB Strain Using the Different GTFs as Carbon Sources
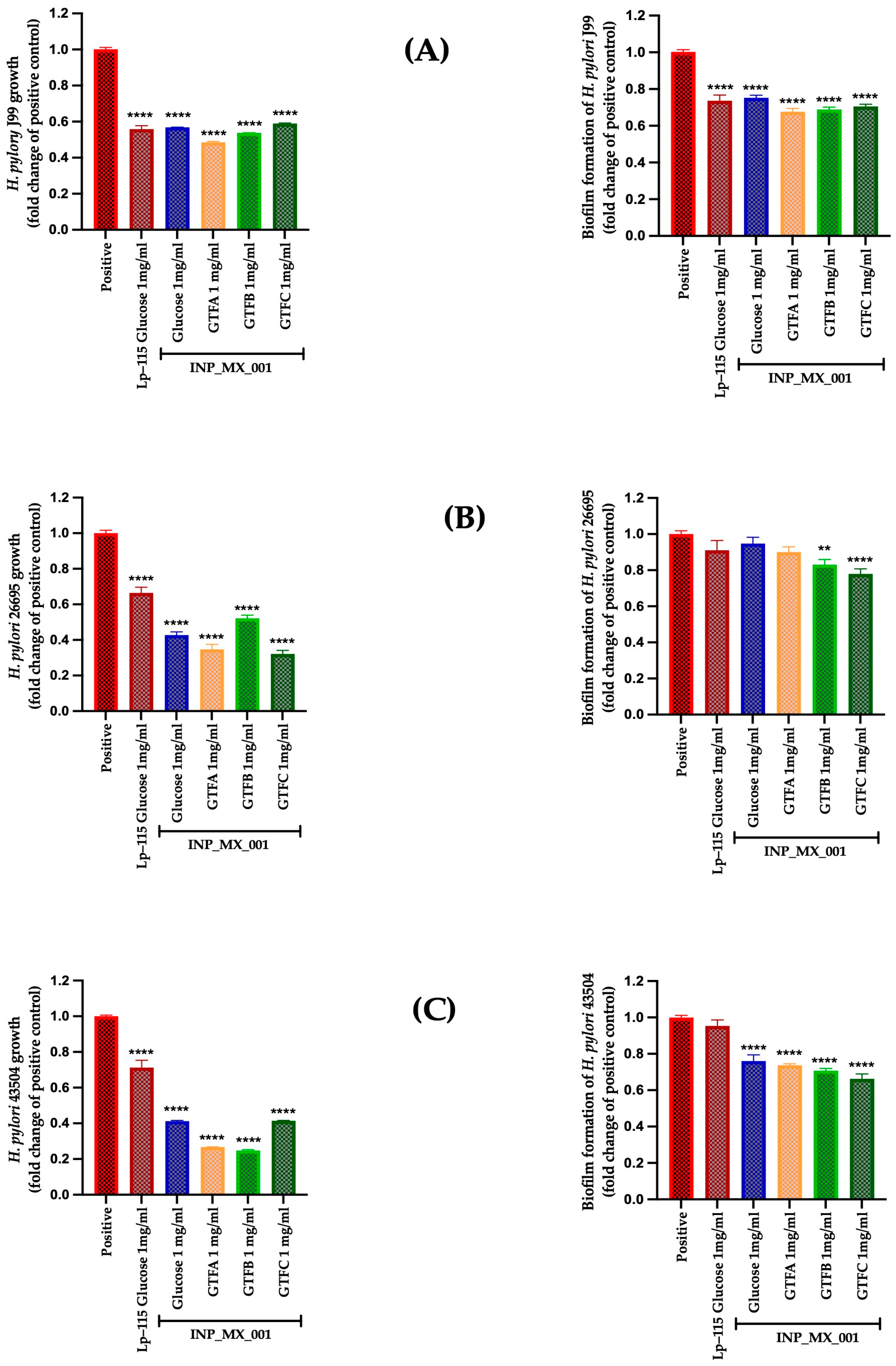
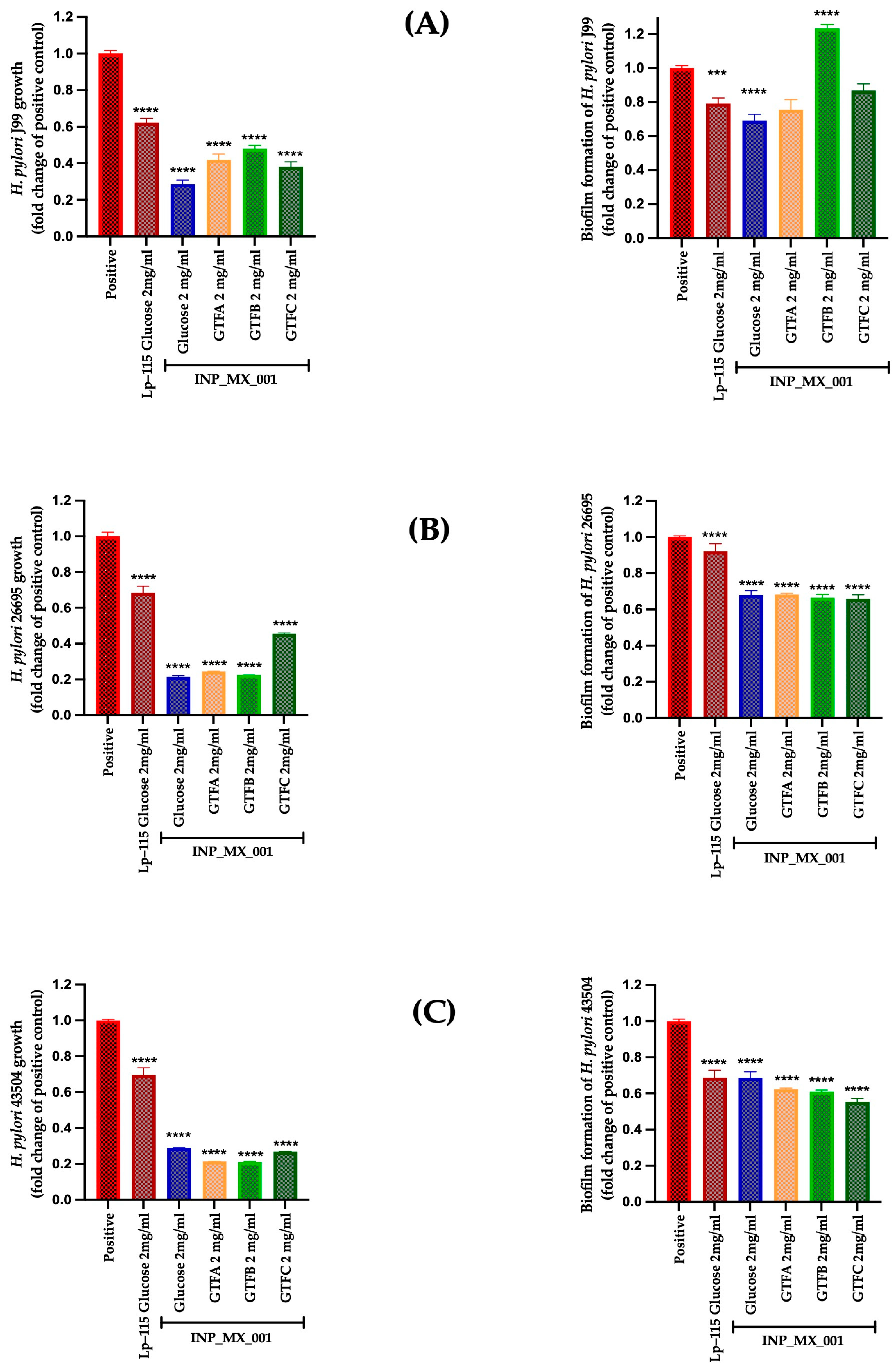
2.3. Therapeutic Effects of 1 and 2 mg/mL of EPSs Extracted from the INP_MX_001 LAB Strain Using the Different GTFs as Carbon Sources Against H. pylori
3. Discussion
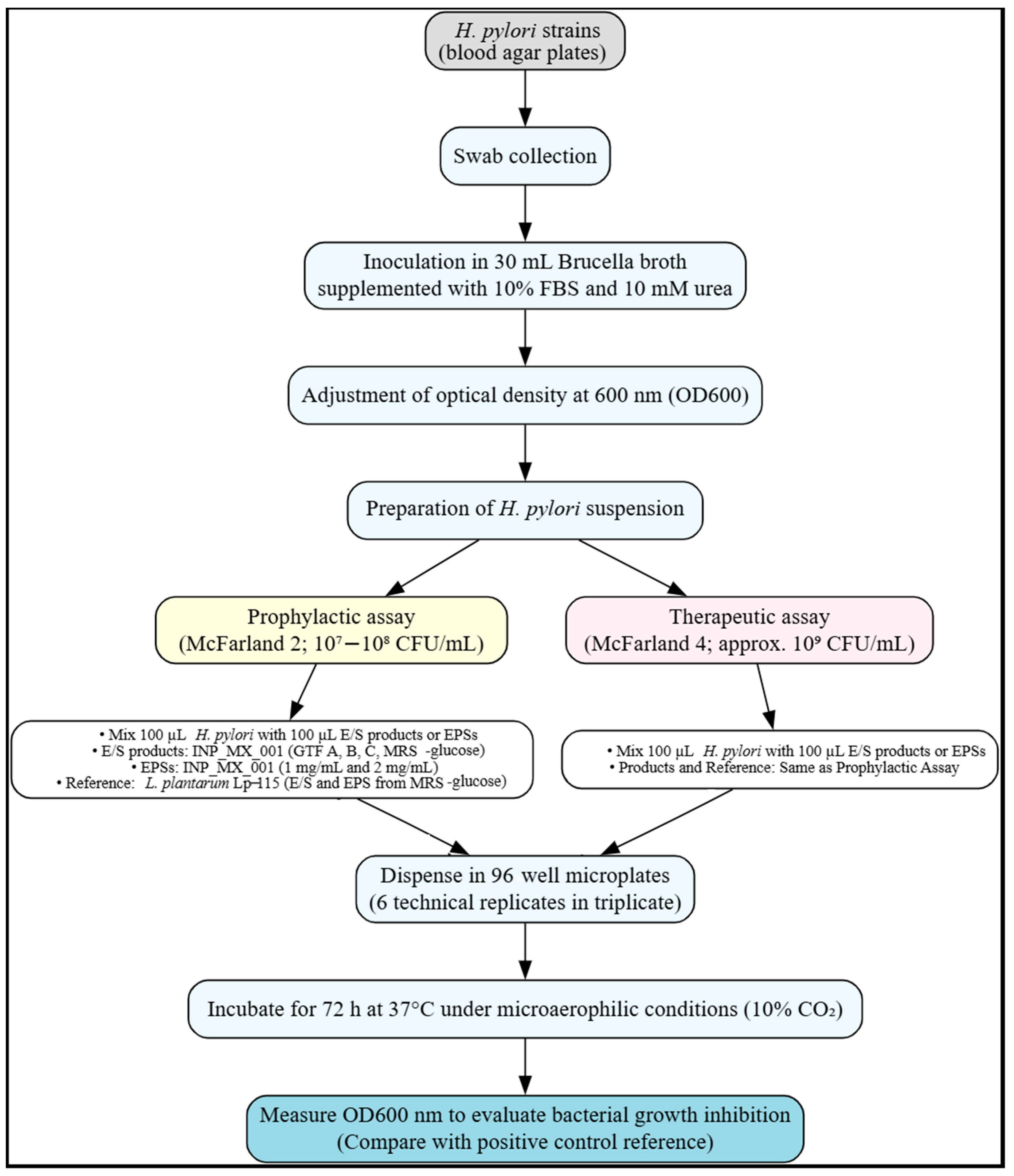
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. LAB Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. H. pylori Strains and Culture Conditions
4.3. Graminan-Type Fructans
4.4. Cultures of LAB in MRS–Graminan-Type Fructans Modified Media
4.5. Extraction and Quantification of EPSs from LAB Pellets Under Study
4.6. In Vitro Inhibition of H. pylori Strains by EPSs and E/S Products of LAB
4.7. In Vitro Inhibition of H. pylori Strains’ Biofilm Formation by EPSs and E/S Products of the INP_MX_001 LAB Strain
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chitas, R.; Fonseca, D.R.; Parreira, P.; Martins, M.C.L. Targeted Nanotherapeutics for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miqueleiz-Zapatero, A.; Alba-Rubio, C.; Domingo-García, D.; Cantón, R.; Gómez-García de la Pedrosa, E.; Aznar-Cano, E.; Leiva, J.; Montes, M.; Sánchez-Romero, I.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.C.; et al. Primera Encuesta Nacional Sobre El Diagnóstico de La Infección Por Helicobacter pylori En Los Laboratorios de Microbiología Clínica En España. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2020, 38, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Malfertheiner, P.; Yu, H.-T.; Kuo, C.-L.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Meng, F.-T.; Wu, Y.-X.; Hsiao, J.-L.; Chen, M.-J.; Lin, K.-P.; et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Incidence of Gastric Cancer Between 1980 and 2022. Gastroenterology 2024, 166, 605–619, Erratum in Gastroenterology 2025, 168, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelsberger, V.; Gerhard, M.; Mejías-Luque, R. Effects of Helicobacter pylori Infection on Intestinal Microbiota, Immunity and Colorectal Cancer Risk. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1339750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Tian, X.; Wei, T.; Wu, H.; Lu, J.; Lyu, M.; Wang, S. Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity of a Lactobacillus sp. Pw-7 Exopolysaccharide. Foods 2021, 10, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtare, M.; Ebrahimian, M.; Namazi, A.; Sadeghian, A.M.; Talaee, H.; Masoodi, M. The Efficacy of Paraprobiotic, Probiotic, and Mineral Supplementation on the Eradication Rate of Helicobacter pylori in Patients with Dyspepsia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Adv. Gut Microbiome Res. 2024, 2024, 9936691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daelemans, S.; Deseck, V.; Ingrid, E.; Vandenplas, Y. Are pro- and/or Synbiotics Beneficial in Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy in Children? A Narrative Review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 3225–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Sepúlveda, C.; Sánchez-Alonzo, K.; Olivares-Muñoz, J.; Gutiérrez-Zamorano, C.; Smith, C.T.; Carvajal, R.I.; Sáez-Carrillo, K.; González, C.; García-Cancino, A. Consumption of a Gelatin Supplemented with the Probiotic Strain Limosilactobacillus fermentum UCO-979C Prevents Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Young Adult Population Achieved. Foods 2022, 11, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M. Epidemiology of Gastric Cancer—Changing Trends and Global Disparities. Cancers 2024, 16, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.I.; Nawawi, K.N.M.; Hsin, D.C.C.; Hao, K.W.; Mahmood, N.R.K.N.; Chearn, G.L.C.; Wong, Z.; Tamil, A.M.; Joseph, H.; Raja Ali, R.A. Probiotic Containing Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17648 as an Adjunct Treatment for Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Helicobacter 2023, 28, e13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Ren, F.; Qin, H.; Bukhari, I.; Yang, J.; Gao, D.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Zheng, P.; Mi, Y. Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Lp-115 Inhibit Helicobacter pylori Colonization and Gastric Inflammation in a Murine Model. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1196084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorakkattu, P.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Shah, K.; Babu, K.S.; Mundanat, A.S.; Deliephan, A.; Deokar, G.S.; Santivarangkna, C.; Nirmal, N.P. Postbiotics: Current Trends in Food and Pharmaceutical Industry. Foods 2022, 11, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P.; Wu, S.; Zhou, T.; Gu, Q. Exopolysaccharide from Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Alleviates Gastritis in Helicobacter pylori Infected Mice by Regulating Gastric Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1426358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanhueza-Carrera, E.A.; Fernández-Lainez, C.; Castro-De la Mora, C.; Ortega-Álvarez, D.; Mendoza-Camacho, C.; Cortéz-Sánchez, J.M.; Pérez-Guillé, B.; de Vos, P.; López-Velázquez, G. Swine Gut Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Exopolysaccharides Differentially Modulate Toll-like Receptor Signaling Depending on the Agave Fructans Used as a Carbon Source. Animals 2025, 15, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, X.; Jin, H.; Man, C.; Jiang, Y. The Effect of Optimized Carbon Source on the Synthesis and Composition of Exopolysaccharides Produced by Lactobacillus paracasei. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 4023–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Lainez, C.; López-Velázquez, G.; de Vos, P. Health Benefits of Inulin and Agavin-Type Fructans in Food: Impact on Microbiota, Immune and Gut Barrier Function. In The Book of Fructans; Van Den Ende, W., Öner, E.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 211–234. ISBN 978-0-323-85410-8. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Lainez, C.; aan de Stegge, M.; Silva-Lagos, L.A.; López-Velázquez, G.; de Vos, P. β(2 → 1)-β(2 → 6) and β(2 → 1) Fructans Protect from Impairment of Intestinal Tight Junction’s Gene Expression and Attenuate Human Dendritic Cell Responses in a Fructan-Dependent Fashion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino, Y.N.V.; de Araújo Domingues, K.C.; Mathur, H.; Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Drouin, G.; Martínez-Abad, A.; Tótola, M.R.; Abreu, L.M.; Cotter, P.D.; Mantovani, H.C. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Bacillus spp. Inhibit Biofilm Formation by Staphylococcus aureus Strains Associated with Bovine Mastitis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astúa, A.; Estevez, M.C.; Ramírez-Lázaro, M.J.; Calvet, X.; Lario, S.; Lechuga, L.M. Identification and Ultrasensitive Quantification of H. pylori Infections on Gastric and Stool Human Samples with a Photonic Label-Free Nanobiosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 281, 117459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, A.L.; Boyte, M.E.; Elkins, C.A.; Goldman, V.S.; Heimbach, J.; Madden, E.; Oketch-Rabah, H.; Sanders, M.E.; Sirois, J.; Smith, A. Considerations for Determining Safety of Probiotics: A USP Perspective. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 136, 105266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y. Challenge Model for Helicobacter pylori Infection in Human Volunteers. Gut 2004, 53, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) Consensus Statement on the Definition and Scope of Postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 671, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, W. Postbiotics and Parabiotics Derived from Bacteria and Yeast: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. CyTA—J. Food 2024, 22, 2425838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayamohan, P.; Joseph, D.; Viju, L.S.; Baskaran, S.A.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Efficacy of Probiotics in Reducing Pathogenic Potential of Infectious Agents. Fermentation 2024, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.; Liang, L.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S. Modulatory Effects of Probiotics During Pathogenic Infections With Emphasis on Immune Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 1616713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corr, S.C.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G.M. Chapter 1 Understanding the Mechanisms by Which Probiotics Inhibit Gastrointestinal Pathogens. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 56, pp. 1–15. ISBN 9780123744395. [Google Scholar]
- Sanhueza, E.; Paredes-Osses, E.; González, C.L.; García, A. Effect of pH in the Survival of Lactobacillus salivarius Strain UCO_979C Wild Type and the pH Acid Acclimated Variant. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 18, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj, J.; Forma, A.; Sitarz, M.; Portincasa, P.; Garruti, G.; Krasowska, D.; Maciejewski, R. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors—Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogenicity in the Gastric Microenvironment. Cells 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesler, B.M.; Rabelo-Gonçalves, E.M.A.; Zeitune, J.M.R. Virulence Factors of Helicobacter pylori: A Review. Clin. Med. Insights Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, CGast.S13760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Peek, R.M.; Wilson, K.T. Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer: Factors That Modulate Disease Risk. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 713–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, J.; Su, Z.; Zhu, C. Strategies to Prevent, Curb and Eliminate Biofilm Formation Based on the Characteristics of Various Periods in One Biofilm Life Cycle. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1003033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Tian, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Antagonistic Activities of Lactobacilli against Helicobacter pylori Growth and Infection in Human Gastric Epithelial Cells. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Yang, H. In Vitro Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Ln66 and Antibiotics Used Alone or in Combination on Helicobacter pylori Mature Biofilm. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coconnier, M.-H.; Lievin, V.; Hemery, E.; Servin, A.L. Antagonistic Activity against Helicobacter Infection In Vitro and In Vivo by the Human Lactobacillus acidophilus Strain LB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 4573–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunanliganon, C.; Thong-Ngam, D.; Tumwasorn, S.; Klaikeaw, N. Lactobacillus plantarum B7 Inhibits Helicobacter pylori Growth and Attenuates Gastric Inflammation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2472–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.-R.; Ghim, S.-Y.; Hong, I.-H.; Park, J.-K.; Hong, K.-S.; Ji, A.-R.; Jeong, K.-S. In Vitro Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori Growth and of Adherence of cagA-Positive Strains to Gastric Epithelial Cells by Lactobacillus paraplantarum KNUC25 Isolated from Kimchi. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.A.; O’Hara, A.M.; van Pijkeren, J.-P.; Douillard, F.P.; O’Toole, P.W. Lactobacillus salivarius Modulates Cytokine Induction and Virulence Factor Gene Expression in Helicobacter pylori. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, E.L.; Guy-Von Stieglitz, S.; Zavan, L.; Cross, J.; Greening, D.W.; Hill, A.F.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M. The Effect of Altered pH Growth Conditions on the Production, Composition, and Proteomes of Helicobacter pylori Outer Membrane Vesicles. Proteomics 2024, 24, 2300269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Qureshi, N.; Xue, B.; Xie, Z.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Preventive and Therapeutic Effect of Lactobacillus paracasei ZFM54 on Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastritis by Ameliorating Inflammation and Restoring Gastric Microbiota in Mice Model. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 972569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Huo, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhang, C. Screening Probiotics for Anti-Helicobacter pylori and Investigating the Effect of Probiotics on Patients with Helicobacter pylori Infection. Foods 2024, 13, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivash, M.; Krishnamoorthi, R.; Mahalingam, P.U.; Malaikozhundan, B. Exopolysaccharide from Lactococcus hircilactis CH4 and Lactobacillus delbrueckii GRIPUMSK as New Therapeutics to Treat Biofilm Pathogens, Oxidative Stress and Human Colon Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamisi, O.E.; Ogidi, C.O.; Akinyele, B.J. Antimicrobial Metabolites from Probiotics, Pleurotus ostreatus and Their Co-Cultures against Foodborne Pathogens Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Foods. Ann. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcial, G.; Villena, J.; Faller, G.; Hensel, A.; de Valdéz, G.F. Exopolysaccharide-Producing Streptococcus thermophilus CRL1190 Reduces the Inflammatory Response Caused by Helicobacter pylori. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Castillo, V.; Marcial, G.; Albarracín, L.; Tomokiyo, M.; Clua, P.; Takahashi, H.; Kitazawa, H.; Garcia-Cancino, A.; Villena, J. The Exopolysaccharide of Lactobacillus fermentum UCO-979C Is Partially Involved in Its Immunomodulatory Effect and Its Ability to Improve the Resistance against Helicobacter pylori Infection. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathroubi, S.; Servetas, S.L.; Windham, I.; Merrell, D.S.; Ottemann, K.M. Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Formation and Its Potential Role in Pathogenesis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2018, 82, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Shi, J.; Fang, C.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Du, Q.; Tu, M.; Pan, D. Elimination of Pathogen Biofilms via Postbiotics from Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Promising Method in Food and Biomedicine. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toushik, S.H.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, K.; Ashrafudoulla, M.; Senakpon Isaie Ulrich, M.; Mizan, M.F.R.; Roy, P.K.; Shim, W.-B.; Kim, Y.-M.; Park, S.H.; et al. Antibiofilm Efficacy of Leuconostoc mesenteroides J.27-Derived Postbiotic and Food-Grade Essential Oils against Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli Alone and in Combination, and Their Application as a Green Preservative I. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Huang, W.; Shu, X.; Ma, S.; Yang, C.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, X.; Wu, Y. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Postbiotics Suppress Salmonella Infection via Modulating Bacterial Pathogenicity, Autophagy and Inflammasome in Mice. Animals 2023, 13, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.M.; Walker, J.M.; Beld, J.; Yin, K. Lactobacillus acidophilus (Strain Scav) Postbiotic Metabolites Reduce Infection and Modulate Inflammation in an In Vivo Model of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Wound Infection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 136, lxaf061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Mardani, K.; Tajik, H. Characterization and Application of Postbiotics of Lactobacillus spp. on Listeria monocytogenes in Vitro and in Food Models. LWT 2019, 111, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Yang, H. Effects of Lactobacillus salivarius LN12 in Combination with Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin on Helicobacter pylori Biofilm In Vitro. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Barreira, D.; Laurent, J.; Lourenço, J.; Novion Ducassou, J.; Couté, Y.; Guzzo, J.; Rieu, A. Membrane Vesicles Released by Lacticaseibacillus casei BL23 Inhibit the Biofilm Formation of Salmonella enteritidis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, G.B.; Quelemes, P.V.; da Silva Neta, E.R.; de Lima, S.G.; Vale, G.C. Chemical Characterization and Effect of a Lactobacilli-Postbiotic on Streptococcus mutans Biofilm In Vitro. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevin, S.; Karaca, B.; Haliscelik, O.; Kibar, H.; OmerOglou, E.; Kiran, F. Postbiotics Secreted by Lactobacillus sakei EIR/CM-1 Isolated from Cow Milk Microbiota, Display Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity against Ruminant Mastitis-Causing Pathogens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, N.; Abedi Soleimani, R.; Chadorshabi, S.; Moutab, B.P.; Milani, P.G.; Rad, A.H. Postbiotics as Candidates in Biofilm Inhibition in Food Industries. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 77, ovad069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, B.; Naldi, M.; Croatti, V.; Parolin, C.; Erdoğan, Ü.; Bartolini, M.; Vitali, B. Exopolysaccharides from Vaginal Lactobacilli Modulate Microbial Biofilms. Microb. Cell Fact. 2023, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, N.C.; Ramiro, J.M.P.; Quecan, B.X.V.; de Melo Franco, B.D.G. Use of Potential Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) Biofilms for the Control of Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Escherichia coli O157:H7 Biofilms Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, Z.; Khanzadi, S.; Salari, A. Biofilm Formation and Antagonistic Activity of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus (PTCC1712) and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (PTCC1745). AMB Express 2021, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Niu, M.; Song, D.; Song, X.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Lu, B.; Niu, G. Preparation, Partial Characterization and Biological Activity of Exopolysaccharides Produced from Lactobacillus fermentum S1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 129, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Sun, M.; Feng, L.; Liang, X.; Song, X.; Mu, G.; Tuo, Y.; Jiang, S.; Qian, F. Antibiofilm Activity of Lactobacillus plantarum 12 Exopolysaccharides against Shigella flexneri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00694-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, N.; Patel, J.; Singh, S.; Yadav, V.K.; Joshi, C.; Patani, A.; Prajapati, D.; Sahoo, D.K.; Patel, A. Postbiotic Production: Harnessing the Power of Microbial Metabolites for Health Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1306192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wu, M.S.; Tao, G.; Lu, M.W.; Lin, J.; Huang, J. qing Feruloylated Oligosaccharides and Ferulic Acid Alter Gut Microbiome to Alleviate Diabetic Syndrome. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Garcia-Varela, R.; Garcia, H.S.; Mata-Haro, V.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Hernández-Mendoza, A. Postbiotics: An Evolving Term within the Functional Foods Field. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilingiri, K.; Rescigno, M. Postbiotics: What Else? Benef. Microbes 2013, 4, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomb, J.-F.; White, O.; Kerlavage, A.R.; Clayton, R.A.; Sutton, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.D.; Ketchum, K.A.; Klenk, H.P.; Gill, S.; Dougherty, B.A.; et al. The Complete Genome Sequence of the Gastric Pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 1997, 388, 539–547, Erratum in Nature 1997, 389, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauser, F.; Hussain, M.A.; Ahmed, I.; Srinivas, S.; Devi, S.M.; Majeed, A.A.; Rao, K.R.; Khan, A.A.; Sechi, L.A.; Ahmed, N. Comparative Genomics of Helicobacter pylori Isolates Recovered from Ulcer Disease Patients in England. BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y.; Shiotani, A. New Concepts of Resistance in the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infections. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 5, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bang, C.S.; Gong, E.J. Antibiotic Resistance of Helicobacter pylori: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2024, 39, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita-Daitoku, R.; Ogura, Y.; Kiga, K.; Maruyama, F.; Kondo, T.; Nakagawa, I.; Hayashi, T.; Mimuro, H. Complete Genome Sequence of Helicobacter pylori Strain ATCC 43504, a Type Strain That Can Infect Gerbils. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, W.; Püls, J.; Buhrdorf, R.; Gebert, B.; Odenbreit, S.; Haas, R. Systematic Mutagenesis of the Helicobacter pylori Cag Pathogenicity Island: Essential Genes for CagA Translocation in Host Cells and Induction of Interleukin-8. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 42, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, M. Structure and Function of Helicobacter pylori CagA, the First-Identified Bacterial Protein Involved in Human Cancer. Proc. Japan Acad. Ser. B 2017, 93, 196–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; El–Zimaity, H.M.T.; Gutierrez, O.; Osato, M.S.; Graham, D.Y. Importance of Helicobacter pylori OipA in Clinical Presentation, Gastric Inflammation, and Mucosal Interleukin 8 Production. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backert, S.; Tegtmeyer, N. Type IV Secretion and Signal Transduction of Helicobacter pylori CagA through Interactions with Host Cell Receptors. Toxins 2017, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šterbenc, A.; Jarc, E.; Poljak, M.; Homan, M. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Genes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4870–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégraud, F.; Lehours, P. Helicobacter pylori Detection and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 280–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhialini, A.; Urdaci, M.; Doucet-Populaire, F.; Bébéar, C.M.; Lamouliatte, H.; Mégraud, F. Macrolide Resistance in Helicobacter pylori: Rapid Detection of Point Mutations and Assays of Macrolide Binding to Ribosomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 2724–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Hameleers, L.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Oerlemans, M.M.P.; de Vos, P.; Jurak, E.; Walvoort, M.T.C. Efficient Isolation of Membrane-Associated Exopolysaccharides of Four Commercial Bifidobacterial Strains. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. A Colorimetric Method for the Determination of Sugars. Nature 1951, 168, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanhueza-Carrera, E.A.; Hernández-Delgado, N.C.; Romo-González, C.; Castro-De la Mora, C.; Mendoza-Camacho, C.; Fernández-Lainez, C.; López-Velázquez, G. Agave Fructans as a Carbon Source to Develop a Postbiotic-Based Strategy for the Prophylaxis and Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211119
Sanhueza-Carrera EA, Hernández-Delgado NC, Romo-González C, Castro-De la Mora C, Mendoza-Camacho C, Fernández-Lainez C, López-Velázquez G. Agave Fructans as a Carbon Source to Develop a Postbiotic-Based Strategy for the Prophylaxis and Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211119
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanhueza-Carrera, Enrique A., Natalia C. Hernández-Delgado, Carolina Romo-González, César Castro-De la Mora, Claudia Mendoza-Camacho, Cynthia Fernández-Lainez, and Gabriel López-Velázquez. 2025. "Agave Fructans as a Carbon Source to Develop a Postbiotic-Based Strategy for the Prophylaxis and Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211119
APA StyleSanhueza-Carrera, E. A., Hernández-Delgado, N. C., Romo-González, C., Castro-De la Mora, C., Mendoza-Camacho, C., Fernández-Lainez, C., & López-Velázquez, G. (2025). Agave Fructans as a Carbon Source to Develop a Postbiotic-Based Strategy for the Prophylaxis and Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211119









