Volatile Flavoromics of Four Mesona chinensis Benth Cultivars: Metabolomic Basis for the Superior Aroma of the Zengcheng Elite Cultivar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Volatile Metabolite Profiling of Four M. chinensis Benth Cultivars
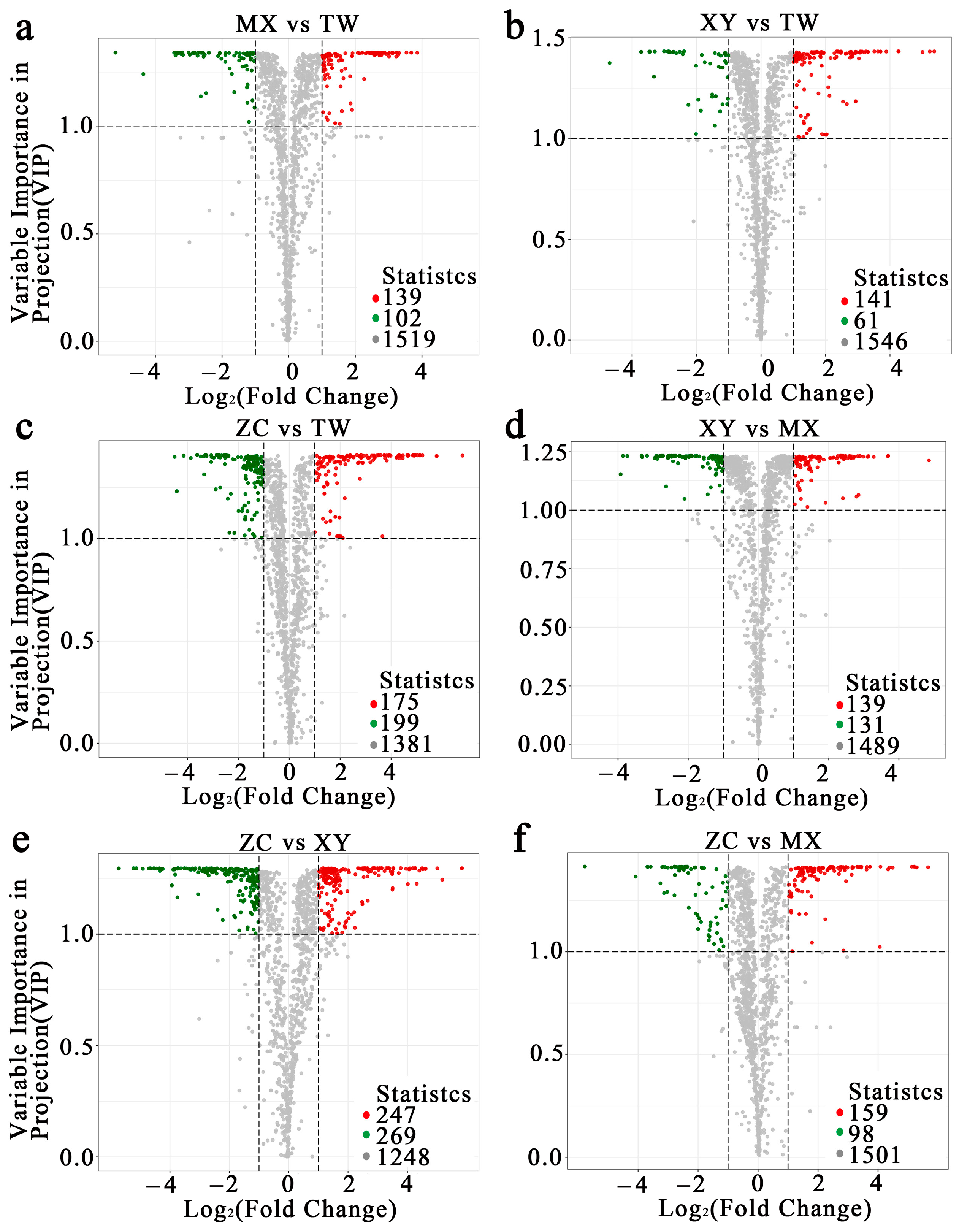
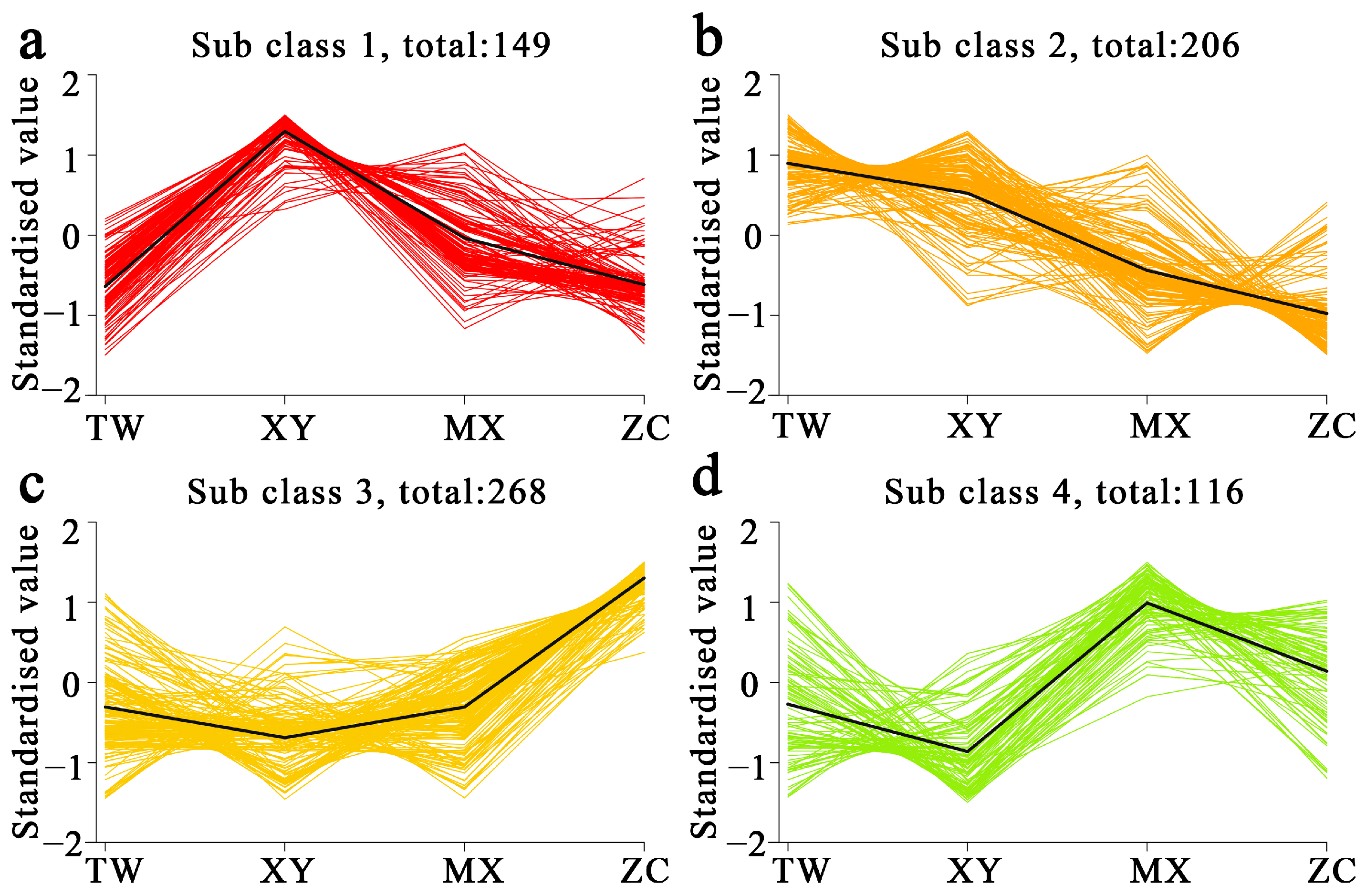
2.2. OPLS-DA and K-Means Reveal ZC-Specific Volatile Metabolome
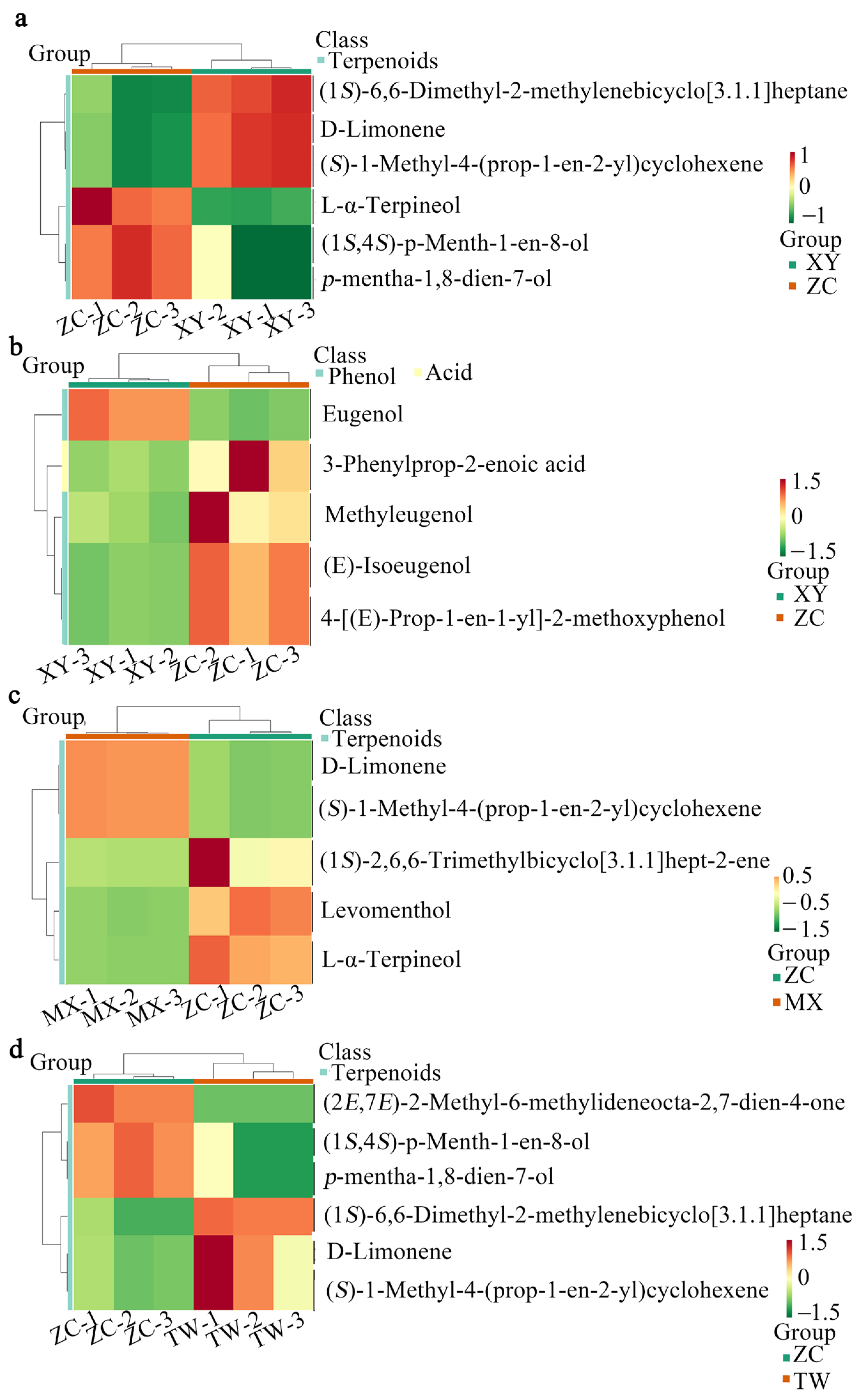
2.3. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Implicates Monoterpenoid Biosynthesis in the Distinctive Volatile Signature of ZC
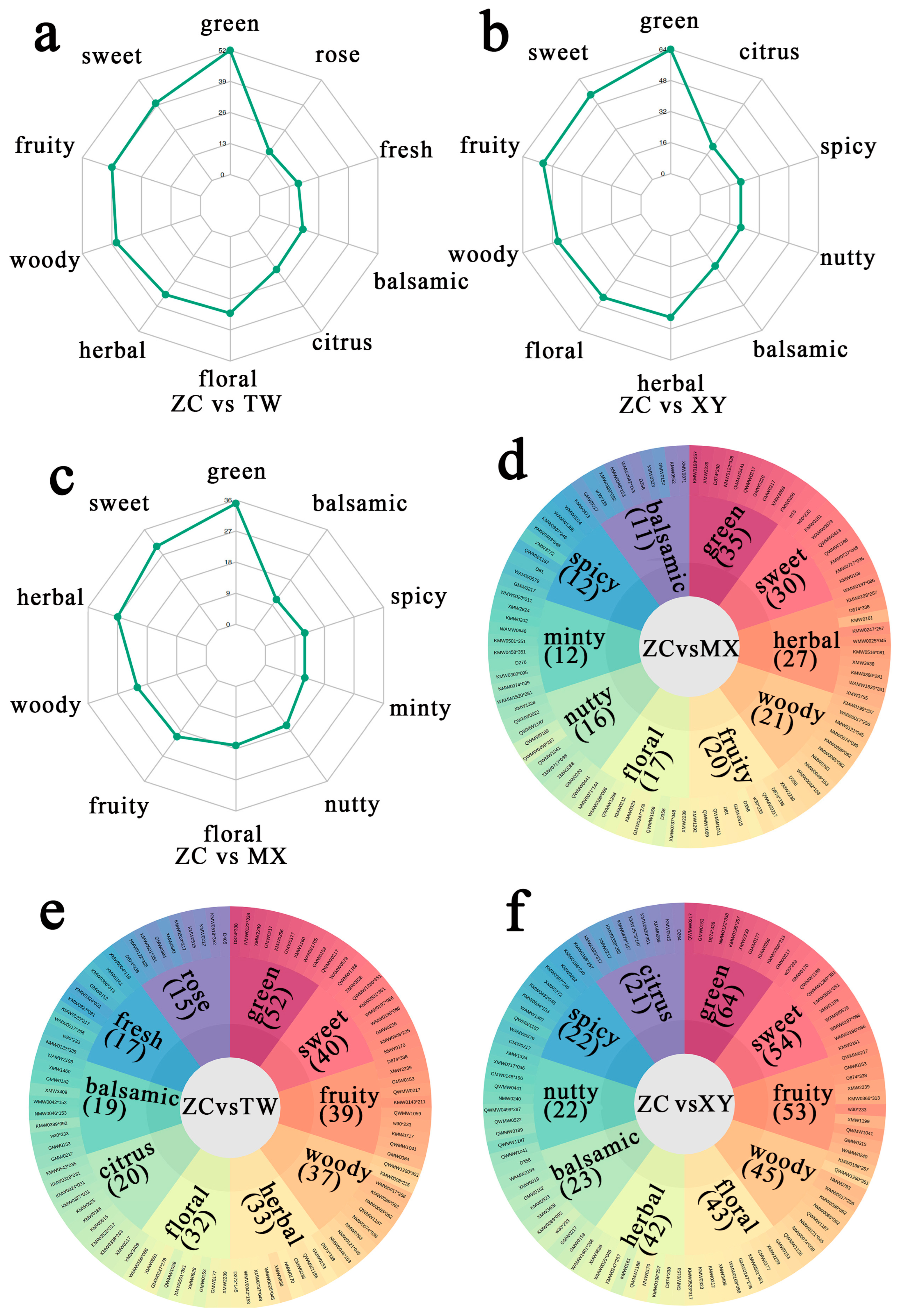
2.4. Sensory-Omics Atlas: Metabolite Drivers of ZC’s Distinctive Flavor Signature
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Sample Preparation and Extraction
4.3. Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Acquisition Conditions
4.4. OPLS-DA and PCA Analysis
4.5. Differential Metabolite Screening
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sytar, O.; Hajihashemi, S. Specific secondary metabolites of medicinal plants and their role in stress adaptation. In Plant Secondary Metabolites and Abiotic Stress; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, M.; Whitney, K. Examination of primary and secondary metabolites associated with a plant-based diet and their impact on human health. Foods 2024, 13, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbouzidi, A.; Haddou, M.; Baraich, A.; Taibi, M.; El Hachlafi, N.; Pareek, A.; Mesnard, F.; Addi, M. Biochemical insights into specialized plant metabolites: Advancing cosmeceutical applications for skin benefits. J. Agr. Food Res. 2025, 19, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Shi, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhang, X.; Xin, B.; Zhai, B.; Guo, D.; Sun, J.; Luan, F. Preparation technologies, structural features, and biological activities of polysaccharides from Mesona chinensis Benth.: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 326, 117979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Lu, X.; Yang, H.; Lin, C.; Li, L.; Ni, C.; Fang, Y.; Mo, S.; Zhan, R.; Yan, P. The Antioxidant and Hypolipidemic Effects of Mesona chinensis Benth Extracts. Molecules 2022, 27, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Shen, M.; Wu, T.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J. Mesona chinensis Benth polysaccharides protect against oxidative stress and immunosuppression in cyclophosphamide-treated mice via MAPKs signal transduction pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.X.; Huang, M.; Shen, M.Y.; Wen, P.W.; Wu, T.; Hong, Y.Z.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.H. Sulfated modification enhanced the antioxidant activity of Mesona chinensis Benth polysaccharide and its protective effect on cellular oxidative stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chusak, C.; Thilavech, T.; Adisakwattana, S. Consumption of Mesona chinensis attenuates postprandial glucose and improves antioxidant status induced by a high carbohydrate meal in overweight subjects. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 315–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.L.; Wang, P.; Xu, H.H.; Gan, X.L.; Zhang, H.S.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.P.; Wang, F.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.P. Metabolic profile and bioactivity of the peel of Zhoupigan (Citrus reticulata cv. Manau Gan), a special citrus variety in China, based on GC-MS, UPLC-ESI-MS/MS analysis, and in vitro assay. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Jiang, L.J.; Wen, L.L.; Tian, X.L.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, J.Z. Metabolomic profiles and differential metabolites of volatile components in Citrus aurantium Changshan-huyou pericarp during different growth and development stages. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.X.; Zhang, K.C.; Lu, Y.P.; Wu, W.Q.; Wan, R.F.; Shi, X.L.; Liu, H.; Sun, Z.W.; Zhao, X.S. Analysis of non-volatile and volatile metabolites during Ziziphus jujube leaf black tea processing via widely targeted metabolomics. LWT 2024, 205, 116507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Quan, C.; Huang, S.; Wei, F. Integrating LC-MS and HS-GC-MS for the metabolite characterization of the Chinese medicinal plant Platostoma palustre under different processing methods. Front Nutr. 2023, 19, 1181942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zang, E.H.; Sun, S.Y.; Li, M.H. Main flavor compounds and molecular regulation mechanisms in fruits and vegetables. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 11859–11879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.B.; Tian, Y.F.; Jiang, P.Y.Z.; Liu, X.L.; Yang, H.S. Recent advances in the application of metabolomics for food safety control and food quality analyses. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1448–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Xu, Z.; Sun, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. Advances in Food Aroma Analysis: Extraction, Separation, and Quantification Techniques. Foods 2025, 14, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.L.; Jiangfang, Y.D.; Liu, Z.H.; Su, R.X.; Li, Q.; Fang, C.Y.; Huang, S.S.; Liu, X.Q.; Fernie, A.R.; Luo, J. WTV2.0: A high-coverage plant volatilomics method with a comprehensive selectiveion monitoring acquisition mode. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 972–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.L.; Cao, G.P.; Hou, X.D.; Huang, M.L.; Du, P.M.; Tan, T.T.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhou, H.H.; Liu, X.Q.; Liu, L.; et al. Development of a widely targeted volatilomics method for profiling volatilomes in plants. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.X.; Wu, M.F.; Lin, R.M.; Li, X.; Ding, H.; Han, L.F.; Yang, W.Z.; Song, X.B.; Li, W.L.; Qu, H.B.; et al. Application and development trends of gas chromatography–ion mobility spectrometry for traditional Chinese medicine, clinical, food and environmental analysis. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, D.; Fu, X.; Xiong, C.; Nie, Q. Peel Essential Oil Composition and Antibacterial Activities of Citrus x sinensis L. Osbeck ‘Tarocco’ and Citrus reticulata Blanco. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.X.; Luo, L.B.; Zhao, J.M.; Wang, Y.T.; Luo, H. Biological potential and mechanisms of Tea’s bioactive compounds: An Updated review. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 65, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, S. The volatile composition, biosynthesis pathways, breeding strategies, and regulation measures of apple aroma: A review. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.C.; Niu, Y.W.; Xiao, Z.B. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in Laoshan green teas by application of odour activity value (OAV), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-olfactometry (GC-MS-O) and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC×GC-qMS). Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Q.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liang, H.; Ma, X.Q. Bioproduction of Geranyl Esters by Integrating Microbial Biosynthesis and Enzymatic Conversion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 24677–24686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.A.D.A.; Santos, J.V.D.O.; Cavalcanti, I.D.L.; Neto, A.F.S.; Nogueira, M.C.D.B.L.; Santos-Magalhães, N.S.; Cavalcanti, I.M.F. Natural products and combination therapy as strategies against bacterial biofilm. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2023, 77, 163–186. [Google Scholar]
- Omari, N.; Balahbib, A.; Bakrim, S.; Benali, T.; Ullah, R.; Alotaibi, A.; Mrabti, H.N.E.; Goh, B.H.; Ong, S.K.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Fenchone and camphor: Main natural compounds from Lavandula stoechas L.; expediting multiple in vitro biological activities. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chai, M.-F.; Shabala, S.; Wang, K.-H.; Zhang, J.-L. Editorial: Adaptation mechanisms of grass and forage plants to stressful environments. Plant J. 2023, 114, 567–569. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Cai, Q.; Yu, T.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Li, Y. ZmG6PDH1 in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase family enhances cold stress tolerance in maize. Front Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1116237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 23200.8-2016; Food Safety National Standard—Determination of 500 Pesticides and Related Chemical Residues in Fruits and Vegetables—Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Wang, D.D.; Zhang, L.X.; Huang, X.R.; Wang, X.; Yang, R.N.; Mao, J.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, X.P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P.W. Identiffcation of nutritional components in black sesame determined by widely targeted metabolomics and Traditional Chinese Medicines. Molecules 2018, 23, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.C.; Wu, J.C.; Shahid, M.Q.; He, Y.H.; Lin, S.Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Yang, X.H. Identiffcation of key taste components in loquat using widely targeted metabolomics. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, D.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y. Identification and inhibition of the key off-odorants in duck broth by means of the sensomics approach and binary odor mixture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13367–13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Cao, B.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Meng, R.; Chen, J.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y. Decoding of the enhancement of saltiness perception by aroma-active compounds during Hunan Larou (smoke-cured bacon) oral processing. Food Chem. 2025, 15, 141029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Tian, D.; Su, H. Volatile Flavoromics of Four Mesona chinensis Benth Cultivars: Metabolomic Basis for the Superior Aroma of the Zengcheng Elite Cultivar. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178713
Niu Y, Zhu Y, Zheng M, Zhu Y, Chen H, Tian D, Su H. Volatile Flavoromics of Four Mesona chinensis Benth Cultivars: Metabolomic Basis for the Superior Aroma of the Zengcheng Elite Cultivar. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178713
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Yuqing, Yujing Zhu, Meixia Zheng, Yanming Zhu, Hong Chen, Dagang Tian, and Hailan Su. 2025. "Volatile Flavoromics of Four Mesona chinensis Benth Cultivars: Metabolomic Basis for the Superior Aroma of the Zengcheng Elite Cultivar" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178713
APA StyleNiu, Y., Zhu, Y., Zheng, M., Zhu, Y., Chen, H., Tian, D., & Su, H. (2025). Volatile Flavoromics of Four Mesona chinensis Benth Cultivars: Metabolomic Basis for the Superior Aroma of the Zengcheng Elite Cultivar. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178713





