ApoE Lipidation as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Scope of This Review
2. Introduction
3. Structures and Functions of apoE Isoforms
4. CNS apoE Protein
5. Effects of apoE Isoforms on Cholesterol Synthesis and Transport/Efflux
6. Effects of apoE Isoforms on Lipid Homeostasis
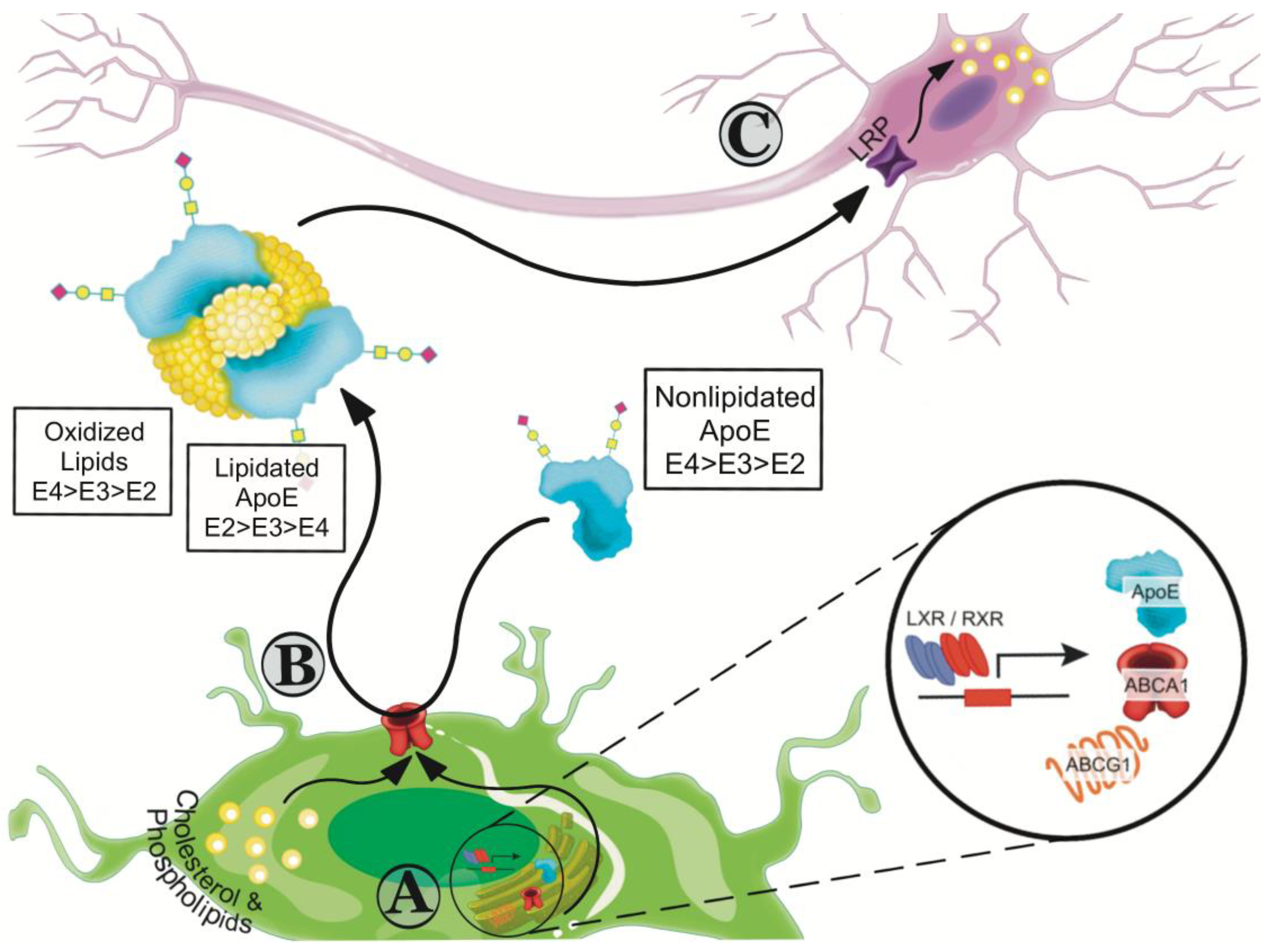
7. Effects of apoE Isoforms on Lipidation
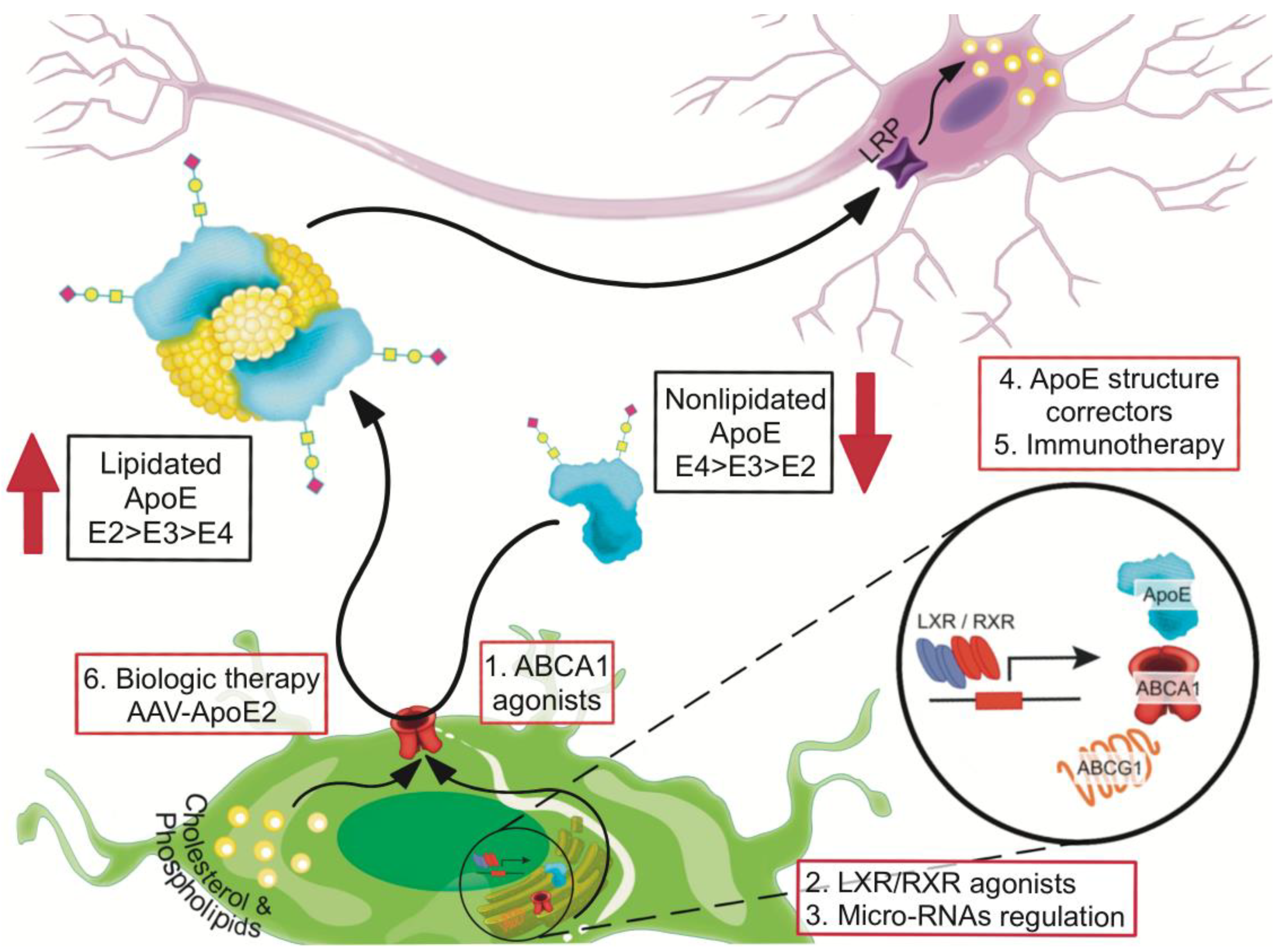
8. Recalibrating apoE Functions by Increasing Lipidation
8.1. Small Molecules that Enhance ABCA1-Mediated apoE4 Lipidation
8.2. Liver X Receptor (LXR) and Retinoid X Receptor (RXR) Agonists
8.3. Small Molecules as apoE4 Structure Correctors
8.4. Anti-apoE4 Immunotherapy
8.5. Recalibrating apoE Function by Using AAV-APOE2 Biologic Therapy
9. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ABCA1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 |
| ABCG1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 |
| apoE | Apolipoprotein E protein |
| APOE | Apolipoprotein E gene |
| APP | Amyloid precursor protein |
| ARF6 | ADP-ribosylation factor 6 |
| Aβ | Amyloid β |
| BBB | Blood-brain barrier |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| CYP46A1 | Cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase |
| FRET | Fluorescence resonance energy transfer |
| HD | Huntington’s disease |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| LRP | LDL receptor-related protein |
| LXR | Liver X receptors |
| NCP | Niemann-Pick type C |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PPAR-γ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| RXR | Retinoid X receptor |
| SLOS | Smith-Lemli Opitz syndrome |
| SREBP-1 | Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins |
| VLDL | Very-low-density lipoprotein |
References
- Strittmatter, W.J.; Saunders, A.M.; Schmechel, D.; Pericak-Vance, M.; Enghild, J.; Salvesen, G.S.; Roses, A.D. Apolipoprotein E: High-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corder, E.H.; Saunders, A.M.; Strittmatter, W.J.; Schmechel, D.E.; Gaskell, P.C.; Small, G.W.; Roses, A.D.; Haines, J.L.; Pericak-Vance, M.A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 1993, 261, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, A.L.; Chidgey, C.; Peng, P.; Masters, C.L.; Roberts, B.R. The Neurobiology and Age-Related Prevalence of the epsilon4 Allele of Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s Disease Cohorts. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 60, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, C.G.; Hamby, M.E.; McReynolds, M.L.; Ray, W.J. The Role of APOE4 in Disrupting the Homeostatic Functions of Astrocytes and Microglia in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tensaouti, Y.; Yu, T.S.; Kernie, S.G. Apolipoprotein E regulates the maturation of injury-induced adult-born hippocampal neurons following traumatic brain injury. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadyen, C.A.; Zeiler, F.A.; Newcombe, V.; Synnot, A.; Steyerberg, E.; Gruen, R.L.; Rosand, J.; Palotie, A.; Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K. Apolipoprotein E4 Polymorphism and Outcomes from Traumatic Brain Injury: A Living Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Neurotrauma 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosta, F.; Vossel, K.A.; Miller, B.L.; Migliaccio, R.; Bonasera, S.J.; Filippi, M.; Boxer, A.L.; Karydas, A.; Possin, K.L.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L. Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 is associated with disease-specific effects on brain atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2018–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroni, B.; Perani, D.; Archetti, S.; Agosti, C.; Paghera, B.; Bellelli, G.; Di Luca, M.; Padovani, A. Functional correlates of Apolipoprotein E genotype in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. BMC Neurol. 2006, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha-Chowdhury, R.; Henderson, J.W.; Raha, A.A.; Vuono, R.; Bickerton, A.; Jones, E.; Fincham, R.; Allinson, K.; Holland, A.; Zaman, S.H. Choroid Plexus Acts as Gatekeeper for TREM2, Abnormal Accumulation of ApoE, and Fibrillary Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease and in Down Syndrome Dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 69, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopenko, I.; Miyakawa, G.; Zheng, B.; Heikkinen, J.; Petrova Quayle, D.; Udeh-Momoh, C.; Claringbould, A.; Neumann, J.; Haytural, H.; Kaakinen, M.A.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease pathology explains association between dementia with Lewy bodies and APOE-epsilon4/TOMM40 long poly-T repeat allele variants. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 5, 814–824. [Google Scholar]
- Mahley, R.W. Apolipoprotein E: Remarkable Protein Sheds Light on Cardiovascular and Neurological Diseases. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahley, R.W. Apolipoprotein E: From cardiovascular disease to neurodegenerative disorders. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahley, R.W.; Rall, S.C., Jr. Apolipoprotein E: Far more than a lipid transport protein. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2000, 1, 507–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannis, V.I.; Breslow, J.L.; Utermann, G.; Mahley, R.W.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Havel, R.J.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S.; Schonfeld, G.; Hazzard, W.R.; et al. Proposed nomenclature of apoE isoproteins, apoE genotypes, and phenotypes. J. Lipid Res. 1982, 23, 911–914. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Topology of human apolipoprotein E3 uniquely regulates its diverse biological functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14813–14818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, P.S.; Narayanaswami, V.; Ryan, R.O. Apolipoprotein E: From lipid transport to neurobiology. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, N.; Krammer, E.M.; Stengel, F.; Adams, Q.; Van Liefferinge, F.; Hubin, E.; Chaves, R.; Efremov, R.; Aebersold, R.; Vandenbussche, G.; et al. Lipidated apolipoprotein E4 structure and its receptor binding mechanism determined by a combined cross-linking coupled to mass spectrometry and molecular dynamics approach. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raussens, V.; Drury, J.; Forte, T.M.; Choy, N.; Goormaghtigh, E.; Ruysschaert, J.M.; Narayanaswami, V. Orientation and mode of lipid-binding interaction of human apolipoprotein E C-terminal domain. Biochem. J. 2005, 387, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswami, V.; Maiorano, J.N.; Dhanasekaran, P.; Ryan, R.O.; Phillips, M.C.; Lund-Katz, S.; Davidson, W.S. Helix orientation of the functional domains in apolipoprotein e in discoidal high density lipoprotein particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 14273–14279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Dhanasekaran, P.; Baldwin, F.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Lund-Katz, S.; Phillips, M.C. Lipid binding-induced conformational change in human apolipoprotein E. Evidence for two lipid-bound states on spherical particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 40949–40954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswami, V.; Ryan, R.O. Molecular basis of exchangeable apolipoprotein function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1483, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieden, C.; Wang, H.; Ho, C.M.W. A mechanism for lipid binding to apoE and the role of intrinsically disordered regions coupled to domain-domain interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6292–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Wardell, M.R.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Mahley, R.W.; Agard, D.A. Three-dimensional structure of the LDL receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Science 1991, 252, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Mau, T.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Wardell, M.R.; Mahley, R.W.; Agard, D.A. Salt bridge relay triggers defective LDL receptor binding by a mutant apolipoprotein. Structure 1994, 2, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polazzi, E.; Mengoni, I.; Pena-Altamira, E.; Massenzio, F.; Virgili, M.; Petralla, S.; Monti, B. Neuronal Regulation of Neuroprotective Microglial Apolipoprotein E Secretion in Rat In Vitro Models of Brain Pathophysiology. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 818–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Bernardo, A.; Walker, D.; Kanegawa, T.; Mahley, R.W.; Huang, Y. Profile and regulation of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) expression in the CNS in mice with targeting of green fluorescent protein gene to the ApoE locus. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4985–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Mucke, L.; Mahley, R.W. Apolipoprotein E: Diversity of cellular origins, structural and biophysical properties, and effects in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2004, 23, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, R.E.; LaDu, M.J.; Pan, J.B.; Getz, G.S.; Frail, D.E.; Falduto, M.T. Neurons of the human frontal cortex display apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1996, 55, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyles, J.K.; Pitas, R.E.; Wilson, E.; Mahley, R.W.; Taylor, J.M. Apolipoprotein E associated with astrocytic glia of the central nervous system and with nonmyelinating glia of the peripheral nervous system. J. Clin. Investig. 1985, 76, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achariyar, T.M.; Li, B.; Peng, W.; Verghese, P.B.; Shi, Y.; McConnell, E.; Benraiss, A.; Kasper, T.; Song, W.; Takano, T.; et al. Glymphatic distribution of CSF-derived apoE into brain is isoform specific and suppressed during sleep deprivation. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, S.A.; Grant, O.C.; Woods, R.J.; Rebeck, G.W. O-glycosylation on cerebrospinal fluid and plasma apolipoprotein E differs in the lipid-binding domain. Glycobiology 2019, 30, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowers, S.A.; Rebeck, G.W. APOE in the normal brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 136, 104724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Meuret, C.; Go, S.; Yassine, H.N.; Nedelkov, D. Simple and Fast Assay for Apolipoprotein E Phenotyping and Glycotyping: Discovering Isoform-Specific Glycosylation in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kockx, M.; Traini, M.; Kritharides, L. Cell-specific production, secretion, and function of apolipoprotein E. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 96, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitas, R.E.; Boyles, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Foss, D.; Mahley, R.W. Astrocytes synthesize apolipoprotein E and metabolize apolipoprotein E-containing lipoproteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 917, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailly, F.; Davignon, J.; Nestruck, A.C. Analytical isoelectric focusing with immobilized pH gradients of human apolipoprotein E from very low density lipoproteins and total plasma. J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- DiBattista, A.M.; Dumanis, S.B.; Newman, J.; Rebeck, G.W. Identification and modification of amyloid-independent phenotypes of APOE4 mice. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 280, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruchaga, C.; Kauwe, J.S.; Nowotny, P.; Bales, K.; Pickering, E.H.; Mayo, K.; Bertelsen, S.; Hinrichs, A.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; Fagan, A.M.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid APOE levels: An endophenotype for genetic studies for Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 4558–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, D.R.; Zhou, H.; Atchison, K.; Warwick, H.K.; Atkinson, P.J.; Jefferson, J.; Xu, L.; Aschmies, S.; Kirksey, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. Impact of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) polymorphism on brain ApoE levels. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11445–11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.M.; Han, B.; Liu, F.; Mace, B.E.; Ervin, J.F.; Wu, S.; Koger, D.; Paul, S.; Bales, K.R. Reduced levels of human apoE4 protein in an animal model of cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Morillo, E.; Hansson, O.; Atagi, Y.; Bu, G.; Minthon, L.; Diamandis, E.P.; Nielsen, H.M. Total apolipoprotein E levels and specific isoform composition in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma from Alzheimer’s disease patients and controls. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, C.; Adorni, M.P.; Caffarra, P.; Ronda, N.; Spallazzi, M.; Barocco, F.; Galimberti, D.; Bernini, F.; Zimetti, F. ABCA1-and ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux capacity of cerebrospinal fluid is impaired in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, M.; Bellosta, S. Cholesterol: Its regulation and role in central nervous system disorders. Cholest. 2012, 2012, 292598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sloan, S.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Caneda, C.; Plaza, C.A.; Blumenthal, P.D.; Vogel, H.; Steinberg, G.K.; Edwards, M.S.; Li, G.; et al. Purification and Characterization of Progenitor and Mature Human Astrocytes Reveals Transcriptional and Functional Differences with Mouse. Neuron 2016, 89, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieweg, K.; Schaller, H.; Pfrieger, F.W. Marked differences in cholesterol synthesis between neurons and glial cells from postnatal rats. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrieger, F.W.; Ungerer, N. Cholesterol metabolism in neurons and astrocytes. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, C.N.; Raben, D.M. Lipid Metabolism Crosstalk in the Brain: Glia and Neurons. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, M.; Landreth, G.E. Therapeutic potential of nuclear receptor agonists in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lin, S.; Beyer, T.P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Bales, K.R.; DeMattos, R.B.; May, P.C.; Li, S.D.; Jiang, X.C.; et al. A liver X receptor and retinoid X receptor heterodimer mediates apolipoprotein E expression, secretion and cholesterol homeostasis in astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2004, 88, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, Y.; Ohkawa, R.; Lai, S.J.; Yamazaki, A.; Ikoma, H.; Yano, K.; Kameda, T.; Tozuka, M. Characterization of the cholesterol efflux of apolipoprotein E-containing high-density lipoprotein in THP-1 cells. Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarr, P.T.; Edwards, P.A. ABCG1 and ABCG4 are coexpressed in neurons and astrocytes of the CNS and regulate cholesterol homeostasis through SREBP-2. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, B.L.; Parkinson, P.F.; Racke, M.M.; Hirsch-Reinshagen, V.; Fan, J.; Wong, C.; Stukas, S.; Theroux, L.; Chan, J.Y.; Donkin, J.; et al. ABCG1 influences the brain cholesterol biosynthetic pathway but does not affect amyloid precursor protein or apolipoprotein E metabolism in vivo. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, E.G.; Guileyardo, J.M.; Russell, D.W. cDNA cloning of cholesterol 24-hydroxylase, a mediator of cholesterol homeostasis in the brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7238–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, J.E. Dysregulation of cholesterol balance in the brain: Contribution to neurodegenerative diseases. Dis. Model. Mech. 2012, 5, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, M.B.; Mukhopadhyay, D. Possible role of apolipoprotein A1 in healing and cell death after neuronal injury. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2016, 8, 460–477. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, B.P.; Jiang, Y.; Wong, G.K.; Shen, F.; Brewer, G.J.; Struble, R.G. Apolipoprotein E4 inhibits, and apolipoprotein E3 promotes neurite outgrowth in cultured adult mouse cortical neurons through the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. Brain Res. 2002, 928, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitas, R.E.; Ji, Z.S.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Mahley, R.W. Role of apolipoprotein E in modulating neurite outgrowth: Potential effect of intracellular apolipoprotein E. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1998, 26, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bellosta, S.; Langer, C.; Bernini, F.; Pitas, R.E.; Mahley, R.W.; Assmann, G.; von Eckardstein, A. Low-dose expression of a human apolipoprotein E transgene in macrophages restores cholesterol efflux capacity of apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7585–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Fitzner, D.; Bosch-Queralt, M.; Weil, M.T.; Su, M.; Sen, P.; Ruhwedel, T.; Mitkovski, M.; Trendelenburg, G.; Lutjohann, D.; et al. Defective cholesterol clearance limits remyelination in the aged central nervous system. Science 2018, 359, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Zhao, N.; Caulfield, T.R.; Liu, C.C.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Pathobiology and targeting strategies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, M.; Sato, N. The Roles of Apolipoprotein E, Lipids, and Glucose in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1128, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roda, A.R.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Villegas, S. The Role of Apolipoprotein E Isoforms in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 68, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, J.D.; Burchett, J.M.; Restivo, J.L.; Schuler, D.R.; Verghese, P.B.; Mahan, T.E.; Landreth, G.E.; Castellano, J.M.; Jiang, H.; Cirrito, J.R.; et al. In vivo measurement of apolipoprotein E from the brain interstitial fluid using microdialysis. Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenza, M.; Rigamonti, D.; Goffredo, D.; Zuccato, C.; Fenu, S.; Jamot, L.; Strand, A.; Tarditi, A.; Woodman, B.; Racchi, M.; et al. Dysfunction of the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway in Huntington’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 9932–9939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minagawa, H.; Gong, J.S.; Jung, C.G.; Watanabe, A.; Lund-Katz, S.; Phillips, M.C.; Saito, H.; Michikawa, M. Mechanism underlying apolipoprotein E (ApoE) isoform-dependent lipid efflux from neural cells in culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2498–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.S.; Morita, S.Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Handa, T.; Fujita, S.C.; Yanagisawa, K.; Michikawa, M. Novel action of apolipoprotein E (ApoE): ApoE isoform specifically inhibits lipid-particle-mediated cholesterol release from neurons. Mol. Neurodegener. 2007, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Matsushima, T.; Satoh, H.; Iso-o, N.; Noto, H.; Togo, M.; Kimura, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Tsukamoto, K. Isoform-dependent cholesterol efflux from macrophages by apolipoprotein E is modulated by cell surface proteoglycans. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Seo, J.; Gao, F.; Feldman, H.M.; Wen, H.L.; Penney, J.; Cam, H.P.; Gjoneska, E.; Raja, W.K.; Cheng, J.; et al. APOE4 Causes Widespread Molecular and Cellular Alterations Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease Phenotypes in Human iPSC-Derived Brain Cell Types. Neuron 2018, 98, 1141–1154.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia, T.C.W.; Liang, S.A.; Qian, L.; Pipalia, N.H.; Chao, M.J.; Shi, Y.; Bertelsen, S.E.; Kapoor, M.; Marcora, E.; Sikora, E.; et al. Cholesterol and matrisome pathways dysregulated in human APOE ε4 glia. BioRxiv 2019, 99, 713362. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, W.; Lee, H.; Cho, S.; Seo, J. ApoE4-Induced Cholesterol Dysregulation and Its Brain Cell Type-Specific Implications in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 739–746. [Google Scholar]
- de Chaves, E.P.; Narayanaswami, V. Apolipoprotein E and cholesterol in aging and disease in the brain. Future Lipidol. 2008, 3, 505–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papassotiropoulos, A.; Lutjohann, D.; Bagli, M.; Locatelli, S.; Jessen, F.; Buschfort, R.; Ptok, U.; Bjorkhem, I.; von Bergmann, K.; Heun, R. 24S-hydroxycholesterol in cerebrospinal fluid is elevated in early stages of dementia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2002, 36, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm-Cagan, A.; Bar, R.; Harats, D.; Shaish, A.; Levkovitz, H.; Bielicki, J.K.; Johansson, J.O.; Michaelson, D.M. Differential Effects of apoE4 and Activation of ABCA1 on Brain and Plasma Lipoproteins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, M.O.W.; Michaelson, D.M.; Hartmann, T. Omega-3 fatty acids, lipids, and apoE lipidation in Alzheimer’s disease: A rationale for multi-nutrient dementia prevention. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 2083–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samieri, C.; Lorrain, S.; Buaud, B.; Vaysse, C.; Berr, C.; Peuchant, E.; Cunnane, S.C.; Barberger-Gateau, P. Relationship between diet and plasma long-chain n-3 PUFAs in older people: Impact of apolipoprotein E genotype. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2559–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, B.C.; Kluemper, J.; Johnson, L.A. Apolipoprotein E4 Alters Astrocyte Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Droplet Formation. Cells 2019, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, M.; Choi, J.; Magnusson, K.; Truong, L.; Tanguay, R.; Traber, M.G. Chronic vitamin E deficiency impairs cognitive function in adult zebrafish via dysregulation of brain lipids and energy metabolism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 112, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Johnson, L.A. APOE in Alzheimer’s disease and neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 139, 104847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Mattson, M.P. Apolipoprotein E and oxidative stress in brain with relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 138, 104795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramassamy, C.; Averill, D.; Beffert, U.; Theroux, L.; Lussier-Cacan, S.; Cohn, J.S.; Christen, Y.; Schoofs, A.; Davignon, J.; Poirier, J. Oxidative insults are associated with apolipoprotein E genotype in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2000, 7, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauderback, C.M.; Kanski, J.; Hackett, J.M.; Maeda, N.; Kindy, M.S.; Butterfield, D.A. Apolipoprotein E modulates Alzheimer’s Abeta(1-42)-induced oxidative damage to synaptosomes in an allele-specific manner. Brain Res. 2002, 924, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, W.A.; Chan, S.L.; Mattson, M.P. A mechanism for the neuroprotective effect of apolipoprotein E: Isoform-specific modification by the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. ApoE and Abeta in Alzheimer’s disease: Accidental encounters or partners? Neuron 2014, 81, 740–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Liu, C.C.; Chen, X.F.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Opposing effects of viral mediated brain expression of apolipoprotein E2 (apoE2) and apoE4 on apoE lipidation and Abeta metabolism in apoE4-targeted replacement mice. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, A.J.; Bayer-Carter, J.L.; Green, P.S.; Montine, T.J.; Wilkinson, C.W.; Baker, L.D.; Watson, G.S.; Bonner, L.M.; Callaghan, M.; Leverenz, J.B.; et al. Effect of apolipoprotein E genotype and diet on apolipoprotein E lipidation and amyloid peptides: Randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinsinger, N.M.; Gachechiladze, M.A.; Rebeck, G.W. Apolipoprotein E Genotype Affects Size of ApoE Complexes in Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 75, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, C.S.; Atagi, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Tachibana, M.; Fu, Y.; Bu, G.; Kanekiyo, T. Apolipoprotein E Inhibits Cerebrovascular Pericyte Mobility through a RhoA Protein-mediated Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14208–14217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koldamova, R.; Fitz, N.F.; Lefterov, I. ATP-binding cassette transporter A1: From metabolism to neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 72, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubin, E.; Verghese, P.B.; van Nuland, N.; Broersen, K. Apolipoprotein E associated with reconstituted high-density lipoprotein-like particles is protected from aggregation. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Huang, Y.C.; Sheu, S.Y.; Lin, T.H.; Tsay, H.J.; Chang, G.G.; Shiao, M.S. Structural variation in human apolipoprotein E3 and E4: Secondary structure, tertiary structure, and size distribution. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugini, M.A.; Schuck, P.; Howlett, G.J. Self-association of human apolipoprotein E3 and E4 in the presence and absence of phospholipid. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36758–36765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garai, K.; Frieden, C. The association-dissociation behavior of the ApoE proteins: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9533–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, M.; Fryer, J.D.; Sullivan, P.M.; Christopher, E.A.; Wahrle, S.E.; DeMattos, R.B.; O’Dell, M.A.; Fagan, A.M.; Lashuel, H.A.; Walz, T.; et al. Production and characterization of astrocyte-derived human apolipoprotein E isoforms from immortalized astrocytes and their interactions with amyloid-beta. Neurobiol. Dis. 2005, 19, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Atagi, Y.; Nielsen, H.M.; Liu, C.C.; Zheng, H.; Shinohara, M.; Kanekiyo, T.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E lipoprotein particles inhibit amyloid-beta uptake through cell surface heparan sulphate proteoglycan. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodart, J.C.; Marr, R.A.; Koistinaho, M.; Gregersen, B.M.; Malkani, S.; Verma, I.M.; Paul, S.M. Gene delivery of human apolipoprotein E alters brain Abeta burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Davis, M.D.; Martens, Y.A.; Shinohara, M.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Younkin, S.G.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Kanekiyo, T.; Bu, G. APOE epsilon4/epsilon4 diminishes neurotrophic function of human iPSC-derived astrocytes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2690–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Song, C.; Reardon, C.A.; Liao, S.; Getz, G.S. Lipoproteins produced by ApoE-/- astrocytes infected with adenovirus expressing human ApoE. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potier, M.-C.; Hanbouch, L.; Marquer, C. Cholesterol and ApoE in Alzheimer’s disease. Oilseeds Fats Crop. Lipids 2018, 25, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Marquer, C.; Laine, J.; Dauphinot, L.; Hanbouch, L.; Lemercier-Neuillet, C.; Pierrot, N.; Bossers, K.; Le, M.; Corlier, F.; Benstaali, C.; et al. Increasing membrane cholesterol of neurons in culture recapitulates Alzheimer’s disease early phenotypes. Mol. Neurodegener. 2014, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, V.K.; Grimm, H.S.; Rothhaar, T.L.; Grosgen, S.; Hundsdorfer, B.; Haupenthal, V.J.; Zimmer, V.C.; Mett, J.; Weingartner, O.; Laufs, U.; et al. Plant sterols the better cholesterol in Alzheimer’s disease? A mechanistical study. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 16072–16087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima-Kawashima, M.; Han, X.; Tanimura, Y.; Hamanaka, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Sakurai, T.; Yokoyama, M.; Wada, K.; Nukina, N.; Fujita, S.C.; et al. Effects of human apolipoprotein E isoforms on the amyloid beta-protein concentration and lipid composition in brain low-density membrane domains. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitz, N.F.; Cronican, A.A.; Lefterov, I.; Koldamova, R. Comment on “ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models”. Science 2013, 340, 924-c. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, P.E.; Cirrito, J.R.; Wesson, D.W.; Lee, C.Y.; Karlo, J.C.; Zinn, A.E.; Casali, B.T.; Restivo, J.L.; Goebel, W.D.; James, M.J.; et al. ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models. Science 2012, 335, 1503–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, H.; Horie, T.; Burchett, J.M.; Restivo, J.L.; Rotllan, N.; Ramirez, C.M.; Verghese, P.B.; Ihara, M.; Hoe, H.S.; et al. microRNA-33 Regulates ApoE Lipidation and Amyloid-beta Metabolism in the Brain. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 14717–14726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, V.; Wang, S.; Sima, J.; Bar, R.; Liraz, O.; Gundimeda, U.; Parekh, T.; Chan, J.; Johansson, J.O.; Tang, C.; et al. ApoE4 Alters ABCA1 Membrane Trafficking in Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9611–9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiane, A.; Johansson, J.O.; Genest, J. ABCA1 Agonist Mimetic Peptide CS-6253 Induces Microparticles Release From Different Cell Types by ABCA1-Efflux-Dependent Mechanism. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm-Cagan, A.; Bar, R.; Liraz, O.; Bielicki, J.K.; Johansson, J.O.; Michaelson, D.M. ABCA1 Agonist Reverses the ApoE4-Driven Cognitive and Brain Pathologies. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 54, 1219–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handattu, S.P.; Monroe, C.E.; Nayyar, G.; Palgunachari, M.N.; Kadish, I.; van Groen, T.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Garber, D.W. In vivo and in vitro effects of an apolipoprotein e mimetic peptide on amyloid-beta pathology. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 36, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernick, D.; Ortiz-Valle, S.; Jeong, A.; Swaminathan, S.K.; Kandimalla, K.K.; Rebeck, G.W.; Li, L. High-density lipoprotein mimetic peptide 4F mitigates amyloid-beta-induced inhibition of apolipoprotein E secretion and lipidation in primary astrocytes and microglia. J. Neurochem. 2018, 147, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, R.L.; Movva, R.; Bloedon, L.T.; Duffy, D.; Norris, R.B.; Navab, M.; Fogelman, A.M.; Rader, D.J. Oral Apolipoprotein A-I Mimetic D-4F Lowers HDL-Inflammatory Index in High-Risk Patients: A First-in-Human Multiple-Dose, Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 10, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloedon, L.T.; Dunbar, R.; Duffy, D.; Pinell-Salles, P.; Norris, R.; DeGroot, B.J.; Movva, R.; Navab, M.; Fogelman, A.M.; Rader, D.J. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of oral apoA-I mimetic peptide D-4F in high-risk cardiovascular patients. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Lee, C.Y.; Mandrekar, S.; Wilkinson, B.; Cramer, P.; Zelcer, N.; Mann, K.; Lamb, B.; Willson, T.M.; Collins, J.L.; et al. ApoE promotes the proteolytic degradation of Abeta. Neuron 2008, 58, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddell, D.R.; Zhou, H.; Comery, T.A.; Kouranova, E.; Lo, C.F.; Warwick, H.K.; Ring, R.H.; Kirksey, Y.; Aschmies, S.; Xu, J.; et al. The LXR agonist TO901317 selectively lowers hippocampal Abeta42 and improves memory in the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2007, 34, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koldamova, R.P.; Lefterov, I.M.; Staufenbiel, M.; Wolfe, D.; Huang, S.; Glorioso, J.C.; Walter, M.; Roth, M.G.; Lazo, J.S. The liver X receptor ligand T0901317 decreases amyloid beta production in vitro and in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 4079–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, A.W.; Kodoma, N.; Casali, B.T.; Landreth, G.E. ABCA1 is Necessary for Bexarotene-Mediated Clearance of Soluble Amyloid Beta from the Hippocampus of APP/PS1 Mice. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm-Cagan, A.; Michaelson, D.M. Reversal of apoE4-driven brain pathology and behavioral deficits by bexarotene. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 7293–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, L.M.; Koster, K.P.; Luo, J.; Lee, S.H.; Wang, Y.T.; Collins, N.C.; Ben Aissa, M.; Thatcher, G.R.; LaDu, M.J. Amyloid-beta pathology and APOE genotype modulate retinoid X receptor agonist activity in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 30538–30555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M.; Malm, T.; Lamb, R.; Jay, T.R.; Neilson, L.; Casali, B.; Medarametla, L.; Landreth, G.E. Neuronally-directed effects of RXR activation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounier, A.; Georgiev, D.; Nam, K.N.; Fitz, N.F.; Castranio, E.L.; Wolfe, C.M.; Cronican, A.A.; Schug, J.; Lefterov, I.; Koldamova, R. Bexarotene-Activated Retinoid X Receptors Regulate Neuronal Differentiation and Dendritic Complexity. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 11862–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Nakashima, K.I.; Hirai, T.; Inoue, M. Neuroprotective effect of naturally occurring RXR agonists isolated from Sophora tonkinensis Gagnep. on amyloid-beta-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 73, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Nakashima, K.I.; Hirai, T.; Inoue, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of naturally occurring retinoid X receptor agonists isolated from Sophora tonkinensis Gagnep. via retinoid X receptor/liver X receptor heterodimers. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 73, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Najm, R.; Xu, Q.; Jeong, D.E.; Walker, D.; Balestra, M.E.; Yoon, S.Y.; Yuan, H.; Li, G.; Miller, Z.A.; et al. Gain of toxic apolipoprotein E4 effects in human iPSC-derived neurons is ameliorated by a small-molecule structure corrector. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.K.; Ji, Z.S.; Dodson, S.E.; Miranda, R.D.; Rosenblum, C.I.; Reynolds, I.J.; Freedman, S.B.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Huang, Y.; Mahley, R.W. Apolipoprotein E4 domain interaction mediates detrimental effects on mitochondria and is a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5215–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.K.; Liu, Z.; Meyer-Franke, A.; Brodbeck, J.; Miranda, R.D.; McGuire, J.G.; Pleiss, M.A.; Ji, Z.S.; Balestra, M.E.; Walker, D.W.; et al. Small molecule structure correctors abolish detrimental effects of apolipoprotein E4 in cultured neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 5253–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodbeck, J.; McGuire, J.; Liu, Z.; Meyer-Franke, A.; Balestra, M.E.; Jeong, D.E.; Pleiss, M.; McComas, C.; Hess, F.; Witter, D.; et al. Structure-dependent impairment of intracellular apolipoprotein E4 trafficking and its detrimental effects are rescued by small-molecule structure correctors. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17217–17226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raulin, A.C.; Kraft, L.; Al-Hilaly, Y.K.; Xue, W.F.; McGeehan, J.E.; Atack, J.R.; Serpell, L. The Molecular Basis for Apolipoprotein E4 as the Major Risk Factor for Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Mol. Biol 2019, 431, 2248–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, F.; Li, A.; Xiong, M.; Bien-Ly, N.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Finn, M.B.; Hoyle, R.; Keyser, J.; Lefton, K.B.; et al. Targeting of nonlipidated, aggregated apoE with antibodies inhibits amyloid accumulation. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.B.; Kaplitt, M.G.; De, B.P.; Chen, A.; Flagiello, T.; Salami, C.; Pey, E.; Zhao, L.; Ricart Arbona, R.J.; Monette, S.; et al. AAVrh.10-Mediated APOE2 Central Nervous System Gene Therapy for APOE4-Associated Alzheimer’s Disease. Hum. Gene. Ther. Clin. Dev. 2018, 29, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudry, E.; Dashkoff, J.; Roe, A.D.; Takeda, S.; Koffie, R.M.; Hashimoto, T.; Scheel, M.; Spires-Jones, T.; Arbel-Ornath, M.; Betensky, R.; et al. Gene transfer of human Apoe isoforms results in differential modulation of amyloid deposition and neurotoxicity in mouse brain. Sci Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 212ra161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gottesdiener, A.J.; Parmar, M.; Li, M.; Kaminsky, S.M.; Chiuchiolo, M.J.; Sondhi, D.; Sullivan, P.M.; Holtzman, D.M.; Crystal, R.G.; et al. Intracerebral adeno-associated virus gene delivery of apolipoprotein E2 markedly reduces brain amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 44, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMattos, R.B.; Brendza, R.P.; Heuser, J.E.; Kierson, M.; Cirrito, J.R.; Fryer, J.; Sullivan, P.M.; Fagan, A.M.; Han, X.; Holtzman, D.M. Purification and characterization of astrocyte-secreted apolipoprotein E and J-containing lipoproteins from wild-type and human apoE transgenic mice. Neurochem. Int. 2001, 39, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahrle, S.E.; Jiang, H.; Parsadanian, M.; Legleiter, J.; Han, X.; Fryer, J.D.; Kowalewski, T.; Holtzman, D.M. ABCA1 is required for normal central nervous system ApoE levels and for lipidation of astrocyte-secreted apoE. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40987–40993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahrle, S.E.; Jiang, H.; Parsadanian, M.; Kim, J.; Li, A.; Knoten, A.; Jain, S.; Hirsch-Reinshagen, V.; Wellington, C.L.; Bales, K.R.; et al. Overexpression of ABCA1 reduces amyloid deposition in the PDAPP mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch-Reinshagen, V.; Zhou, S.; Burgess, B.L.; Bernier, L.; McIsaac, S.A.; Chan, J.Y.; Tansley, G.H.; Cohn, J.S.; Hayden, M.R.; Wellington, C.L. Deficiency of ABCA1 impairs apolipoprotein E metabolism in brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41197–41207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahrle, S.E.; Jiang, H.; Parsadanian, M.; Hartman, R.E.; Bales, K.R.; Paul, S.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Deletion of Abca1 increases Abeta deposition in the PDAPP transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 43236–43242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koldamova, R.; Staufenbiel, M.; Lefterov, I. Lack of ABCA1 considerably decreases brain ApoE level and increases amyloid deposition in APP23 mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 43224–43235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koldamova, R.; Lefterov, I. Role of LXR and ABCA1 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease—implications for a new therapeutic approach. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2007, 4, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordestgaard, L.T.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Loss-of-function mutation in ABCA1 and risk of Alzheimer’s disease and cerebrovascular disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassine, H.N.; Feng, Q.; Chiang, J.; Petrosspour, L.M.; Fonteh, A.N.; Chui, H.C.; Harrington, M.G. ABCA1-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux Capacity to Cerebrospinal Fluid Is Reduced in Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, L.M.; Thomas, R.; Marottoli, F.M.; Koster, K.P.; Kanekiyo, T.; Morris, A.W.; Bu, G. The role of APOE in cerebrovascular dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namjoshi, D.R.; Martin, G.; Donkin, J.; Wilkinson, A.; Stukas, S.; Fan, J.; Carr, M.; Tabarestani, S.; Wuerth, K.; Hancock, R.E.; et al. The liver X receptor agonist GW3965 improves recovery from mild repetitive traumatic brain injury in mice partly through apolipoprotein E. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.L.; Zhong, K.; Kinney, J.W.; Heaney, C.; Moll-Tudla, J.; Joshi, A.; Pontecorvo, M.; Devous, M.; Tang, A.; Bena, J. Double-blind, placebo-controlled, proof-of-concept trial of bexarotene Xin moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2016, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.R.; Tu, H.; Luk, A.; Repa, J.J.; Medina, J.C.; Li, L.; Schwendner, S.; Wang, S.; Thoolen, M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; et al. Role of LXRs in control of lipogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.; Bourgeois, T.; Menegaut, L.; Lagrost, L.; Thomas, C.; Masson, D. Revisiting the Role of LXRs in PUFA Metabolism and Phospholipid Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brecht, W.J.; Harris, F.M.; Chang, S.; Tesseur, I.; Yu, G.Q.; Xu, Q.; Dee Fish, J.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Buttini, M.; Mucke, L.; et al. Neuron-specific apolipoprotein e4 proteolysis is associated with increased tau phosphorylation in brains of transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahley, R.W.; Huang, Y. Small-molecule structure correctors target abnormal protein structure and function: Structure corrector rescue of apolipoprotein E4-associated neuropathology. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8997–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Donarski, N.; Goetze, K.; Kreckel, M.; Stuerenburg, H.J.; Buhmann, C.; Beisiegel, U. Characterization of four lipoprotein classes in human cerebrospinal fluid. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar]
| Isoform | Amino Acids (112, 158) | Structural Description |
|---|---|---|
| ApoE2 | Cys, Cys |
|
| ApoE3 | Cys, Arg |
|
| ApoE4 | Arg, Arg |
|
| Class | Description | Example | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABCA1 agonist | Antisense oligonucleotides | miR-33 ARF6 | [104] [105] |
| Small peptides | CS-6253 Ac-hE18A-NH2 4F | [73], [106,107] [108] [73], [109,110,111] | |
| Nuclear Receptor agonist | LXR agonist | TO901317 GW3965 | [112,113,114] [112,113,114] |
| RXR agonist | Bexarotene LG100268 SPF1 and SPF2 | [115,116,117,118,119] [115,116,117] [120,121] | |
| Structure corrector | Small molecule that corrects apoE4 structure | PH002 GIND105 and GIND-25 | [122] [123,124,125] |
| Immunotherapy | Targets non-lipidated apoE4 | HAE-1 and HAE-4 | [126,127] |
| Biologics | AAV-directed therapy | AAV-expressing human APOE2 gene | [84], [128,129,130,131] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lanfranco, M.F.; Ng, C.A.; Rebeck, G.W. ApoE Lipidation as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176336
Lanfranco MF, Ng CA, Rebeck GW. ApoE Lipidation as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):6336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176336
Chicago/Turabian StyleLanfranco, Maria Fe, Christi Anne Ng, and G. William Rebeck. 2020. "ApoE Lipidation as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 6336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176336
APA StyleLanfranco, M. F., Ng, C. A., & Rebeck, G. W. (2020). ApoE Lipidation as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176336





